5dd0aaf78aaef558680681a13f4b93f8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 8
 Assessment of dietary compliance among patients with type ii diabetes mellitus receiving text message (sms) reminder: a randomized control trial Gulshan Bano Ali Senior Instructor (Research) Surgery, Aga Khan University Supervisor: Dr. Romaina Iqbal Committee Members: Mr. Iqbal Azam Dr. Shariq Khoja Dr. Javed Akhtar
Assessment of dietary compliance among patients with type ii diabetes mellitus receiving text message (sms) reminder: a randomized control trial Gulshan Bano Ali Senior Instructor (Research) Surgery, Aga Khan University Supervisor: Dr. Romaina Iqbal Committee Members: Mr. Iqbal Azam Dr. Shariq Khoja Dr. Javed Akhtar
 Background, Rationale, Objective • According to WHO estimates 285 million individuals are suffering from Diabetes Mellitus (DM) (WHO. 2011) • 2010 to 2030, there would be 69% and 20% increase in the number Physical of cases of DM in developing and developed countries respectively activity (Shaw JE. et al. 2009) • Prevalence in Pakistan is 7. 6% (IDF, Diabetes Atlas Fifth Edition. 2010) Objectives: Diet 1. To assess the difference in dietary compliance in patients with type 2 DM, who were reminded through text messages (SMS) vs. those Oral Insulin not reminded” Medication 2. To assess dietary compliance by using responses to fortnightly two -item questionnaire for the intake of fruits and vegetables in the last 24 hours 3. To assess the change in Hb. A 1 c level of participants in both the groups. 2
Background, Rationale, Objective • According to WHO estimates 285 million individuals are suffering from Diabetes Mellitus (DM) (WHO. 2011) • 2010 to 2030, there would be 69% and 20% increase in the number Physical of cases of DM in developing and developed countries respectively activity (Shaw JE. et al. 2009) • Prevalence in Pakistan is 7. 6% (IDF, Diabetes Atlas Fifth Edition. 2010) Objectives: Diet 1. To assess the difference in dietary compliance in patients with type 2 DM, who were reminded through text messages (SMS) vs. those Oral Insulin not reminded” Medication 2. To assess dietary compliance by using responses to fortnightly two -item questionnaire for the intake of fruits and vegetables in the last 24 hours 3. To assess the change in Hb. A 1 c level of participants in both the groups. 2
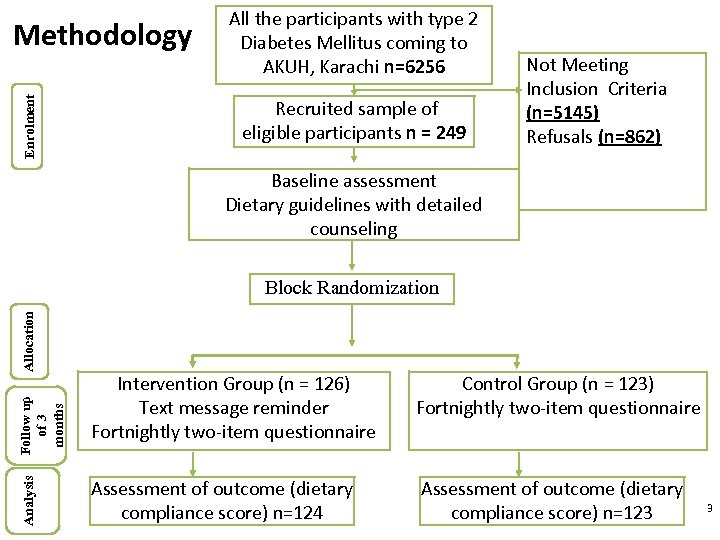 Enrolment Methodology All the participants with type 2 Diabetes Mellitus coming to AKUH, Karachi n=6256 Recruited sample of eligible participants n = 249 Not Meeting Inclusion Criteria (n=5145) Refusals (n=862) Baseline assessment Dietary guidelines with detailed counseling Analysis Follow up of 3 months Allocation Block Randomization Intervention Group (n = 126) Text message reminder Fortnightly two-item questionnaire Control Group (n = 123) Fortnightly two-item questionnaire Assessment of outcome (dietary compliance score) n=124 Assessment of outcome (dietary compliance score) n=123 3
Enrolment Methodology All the participants with type 2 Diabetes Mellitus coming to AKUH, Karachi n=6256 Recruited sample of eligible participants n = 249 Not Meeting Inclusion Criteria (n=5145) Refusals (n=862) Baseline assessment Dietary guidelines with detailed counseling Analysis Follow up of 3 months Allocation Block Randomization Intervention Group (n = 126) Text message reminder Fortnightly two-item questionnaire Control Group (n = 123) Fortnightly two-item questionnaire Assessment of outcome (dietary compliance score) n=124 Assessment of outcome (dietary compliance score) n=123 3
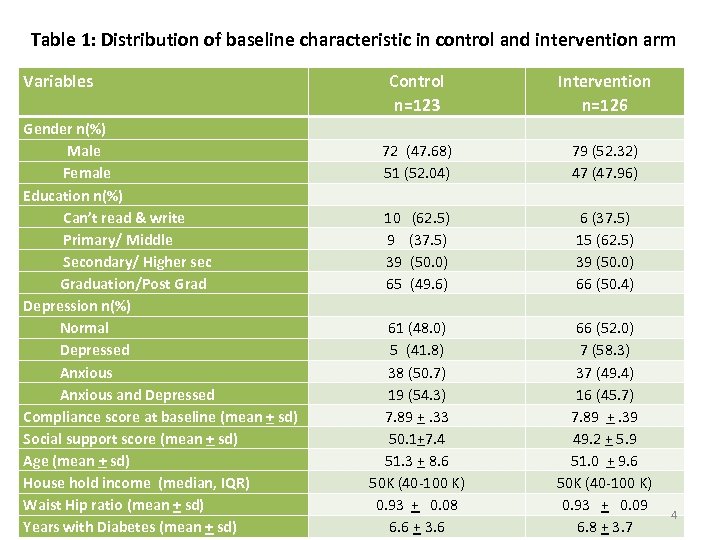 Table 1: Distribution of baseline characteristic in control and intervention arm Variables Gender n(%) Male Female Education n(%) Can’t read & write Primary/ Middle Secondary/ Higher sec Graduation/Post Grad Depression n(%) Normal Depressed Anxious and Depressed Compliance score at baseline (mean + sd) Social support score (mean + sd) Age (mean + sd) House hold income (median, IQR) Waist Hip ratio (mean + sd) Years with Diabetes (mean + sd) Control n=123 Intervention n=126 72 (47. 68) 51 (52. 04) 10 (62. 5) 9 (37. 5) 39 (50. 0) 65 (49. 6) 61 (48. 0) 5 (41. 8) 38 (50. 7) 19 (54. 3) 7. 89 +. 33 50. 1+7. 4 51. 3 + 8. 6 50 K (40 -100 K) 0. 93 + 0. 08 6. 6 + 3. 6 79 (52. 32) 47 (47. 96) 6 (37. 5) 15 (62. 5) 39 (50. 0) 66 (50. 4) 66 (52. 0) 7 (58. 3) 37 (49. 4) 16 (45. 7) 7. 89 +. 39 49. 2 + 5. 9 51. 0 + 9. 6 50 K (40 -100 K) 0. 93 + 0. 09 6. 8 + 3. 7 4
Table 1: Distribution of baseline characteristic in control and intervention arm Variables Gender n(%) Male Female Education n(%) Can’t read & write Primary/ Middle Secondary/ Higher sec Graduation/Post Grad Depression n(%) Normal Depressed Anxious and Depressed Compliance score at baseline (mean + sd) Social support score (mean + sd) Age (mean + sd) House hold income (median, IQR) Waist Hip ratio (mean + sd) Years with Diabetes (mean + sd) Control n=123 Intervention n=126 72 (47. 68) 51 (52. 04) 10 (62. 5) 9 (37. 5) 39 (50. 0) 65 (49. 6) 61 (48. 0) 5 (41. 8) 38 (50. 7) 19 (54. 3) 7. 89 +. 33 50. 1+7. 4 51. 3 + 8. 6 50 K (40 -100 K) 0. 93 + 0. 08 6. 6 + 3. 6 79 (52. 32) 47 (47. 96) 6 (37. 5) 15 (62. 5) 39 (50. 0) 66 (50. 4) 66 (52. 0) 7 (58. 3) 37 (49. 4) 16 (45. 7) 7. 89 +. 39 49. 2 + 5. 9 51. 0 + 9. 6 50 K (40 -100 K) 0. 93 + 0. 09 6. 8 + 3. 7 4
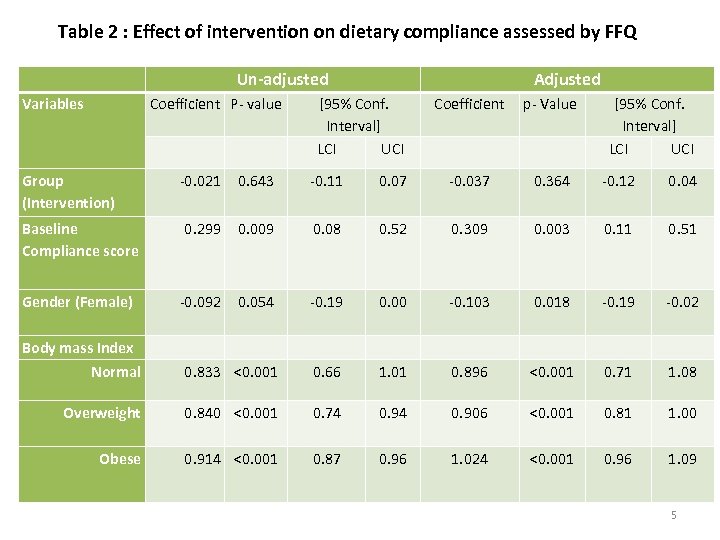 Table 2 : Effect of intervention on dietary compliance assessed by FFQ Un-adjusted Variables Coefficient P- value Group (Intervention) Adjusted [95% Conf. Interval] LCI UCI Coefficient p- Value [95% Conf. Interval] LCI UCI -0. 021 0. 643 -0. 11 0. 07 -0. 037 0. 364 -0. 12 0. 04 Baseline Compliance score 0. 299 0. 009 0. 08 0. 52 0. 309 0. 003 0. 11 0. 51 Gender (Female) -0. 092 0. 054 -0. 19 0. 00 -0. 103 0. 018 -0. 19 -0. 02 Body mass Index Normal 0. 833 <0. 001 0. 66 1. 01 0. 896 <0. 001 0. 71 1. 08 Overweight 0. 840 <0. 001 0. 74 0. 906 <0. 001 0. 81 1. 00 Obese 0. 914 <0. 001 0. 87 0. 96 1. 024 <0. 001 0. 96 1. 09 5
Table 2 : Effect of intervention on dietary compliance assessed by FFQ Un-adjusted Variables Coefficient P- value Group (Intervention) Adjusted [95% Conf. Interval] LCI UCI Coefficient p- Value [95% Conf. Interval] LCI UCI -0. 021 0. 643 -0. 11 0. 07 -0. 037 0. 364 -0. 12 0. 04 Baseline Compliance score 0. 299 0. 009 0. 08 0. 52 0. 309 0. 003 0. 11 0. 51 Gender (Female) -0. 092 0. 054 -0. 19 0. 00 -0. 103 0. 018 -0. 19 -0. 02 Body mass Index Normal 0. 833 <0. 001 0. 66 1. 01 0. 896 <0. 001 0. 71 1. 08 Overweight 0. 840 <0. 001 0. 74 0. 906 <0. 001 0. 81 1. 00 Obese 0. 914 <0. 001 0. 87 0. 96 1. 024 <0. 001 0. 96 1. 09 5
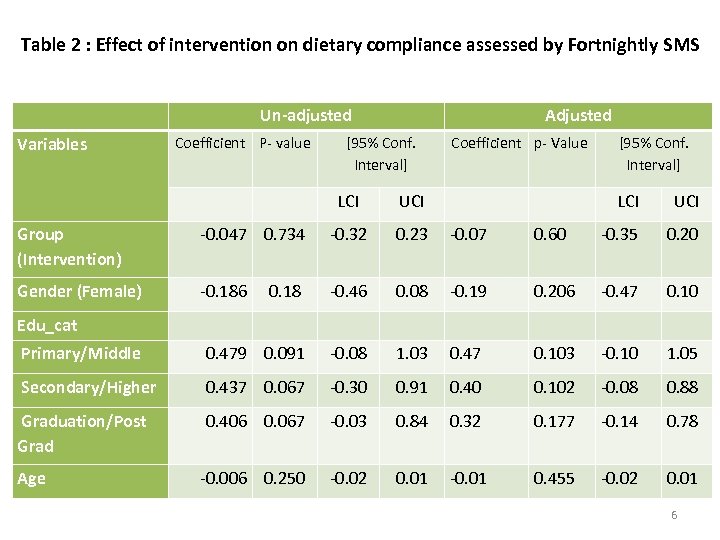 Table 2 : Effect of intervention on dietary compliance assessed by Fortnightly SMS Variables Un-adjusted Coefficient P- value Adjusted [95% Conf. Interval] Coefficient p- Value LCI UCI [95% Conf. Interval] LCI UCI Group (Intervention) -0. 047 0. 734 -0. 32 0. 23 -0. 07 0. 60 -0. 35 0. 20 Gender (Female) -0. 186 0. 18 -0. 46 0. 08 -0. 19 0. 206 -0. 47 0. 10 Edu_cat Primary/Middle 0. 479 0. 091 -0. 08 1. 03 0. 47 0. 103 -0. 10 1. 05 Secondary/Higher 0. 437 0. 067 -0. 30 0. 91 0. 40 0. 102 -0. 08 0. 88 Graduation/Post Grad 0. 406 0. 067 -0. 03 0. 84 0. 32 0. 177 -0. 14 0. 78 -0. 006 0. 250 -0. 02 0. 01 -0. 01 0. 455 -0. 02 0. 01 Age 6
Table 2 : Effect of intervention on dietary compliance assessed by Fortnightly SMS Variables Un-adjusted Coefficient P- value Adjusted [95% Conf. Interval] Coefficient p- Value LCI UCI [95% Conf. Interval] LCI UCI Group (Intervention) -0. 047 0. 734 -0. 32 0. 23 -0. 07 0. 60 -0. 35 0. 20 Gender (Female) -0. 186 0. 18 -0. 46 0. 08 -0. 19 0. 206 -0. 47 0. 10 Edu_cat Primary/Middle 0. 479 0. 091 -0. 08 1. 03 0. 47 0. 103 -0. 10 1. 05 Secondary/Higher 0. 437 0. 067 -0. 30 0. 91 0. 40 0. 102 -0. 08 0. 88 Graduation/Post Grad 0. 406 0. 067 -0. 03 0. 84 0. 32 0. 177 -0. 14 0. 78 -0. 006 0. 250 -0. 02 0. 01 -0. 01 0. 455 -0. 02 0. 01 Age 6
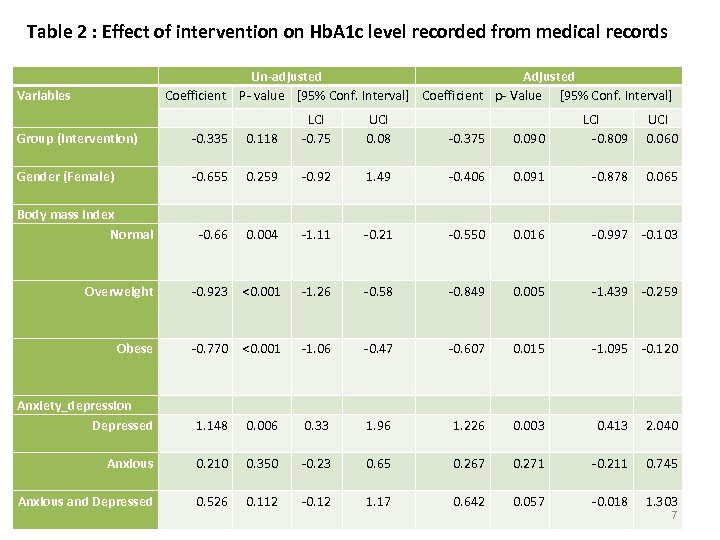 Table 2 : Effect of intervention on Hb. A 1 c level recorded from medical records Variables Un-adjusted Adjusted Coefficient P- value [95% Conf. Interval] Coefficient p- Value [95% Conf. Interval] Group (Intervention) -0. 335 0. 118 Gender (Female) -0. 655 0. 259 -0. 92 1. 49 -0. 406 0. 091 -0. 878 Body mass Index Normal -0. 66 0. 004 -1. 11 -0. 21 -0. 550 0. 016 -0. 997 -0. 103 Overweight -0. 923 <0. 001 -1. 26 -0. 58 -0. 849 0. 005 -1. 439 -0. 259 Obese -0. 770 <0. 001 -1. 06 -0. 47 -0. 607 0. 015 -1. 095 -0. 120 0. 003 0. 413 2. 040 Anxiety_depression Depressed LCI -0. 75 UCI 0. 08 -0. 375 0. 090 LCI -0. 809 UCI 0. 060 0. 065 1. 148 0. 006 0. 33 1. 96 1. 226 Anxious 0. 210 0. 350 -0. 23 0. 65 0. 267 0. 271 -0. 211 0. 745 Anxious and Depressed 0. 526 0. 112 -0. 12 1. 17 0. 642 0. 057 -0. 018 1. 303 7
Table 2 : Effect of intervention on Hb. A 1 c level recorded from medical records Variables Un-adjusted Adjusted Coefficient P- value [95% Conf. Interval] Coefficient p- Value [95% Conf. Interval] Group (Intervention) -0. 335 0. 118 Gender (Female) -0. 655 0. 259 -0. 92 1. 49 -0. 406 0. 091 -0. 878 Body mass Index Normal -0. 66 0. 004 -1. 11 -0. 21 -0. 550 0. 016 -0. 997 -0. 103 Overweight -0. 923 <0. 001 -1. 26 -0. 58 -0. 849 0. 005 -1. 439 -0. 259 Obese -0. 770 <0. 001 -1. 06 -0. 47 -0. 607 0. 015 -1. 095 -0. 120 0. 003 0. 413 2. 040 Anxiety_depression Depressed LCI -0. 75 UCI 0. 08 -0. 375 0. 090 LCI -0. 809 UCI 0. 060 0. 065 1. 148 0. 006 0. 33 1. 96 1. 226 Anxious 0. 210 0. 350 -0. 23 0. 65 0. 267 0. 271 -0. 211 0. 745 Anxious and Depressed 0. 526 0. 112 -0. 12 1. 17 0. 642 0. 057 -0. 018 1. 303 7
 Conclusion We are unable to find any significant difference in the dietary compliance in type 2 diabetic patients in two study arms • These findings suggest that there is no effect of text messages on dietary compliance of type 2 diabetic patients • The reasons might be short follow up time for a behavioral change intervention, or it could be because of ignorance of the patients. •
Conclusion We are unable to find any significant difference in the dietary compliance in type 2 diabetic patients in two study arms • These findings suggest that there is no effect of text messages on dietary compliance of type 2 diabetic patients • The reasons might be short follow up time for a behavioral change intervention, or it could be because of ignorance of the patients. •


