80ffb3402ff3ec1e04e925f61e6d2c5f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Assessment of carbon sequestration potential in soil and in belowground biomass of six perennial bioenergy crops Carlo Chimento, Stefano Amaducci Department of Sustainable Vegetable Productions Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore di Piacenza 18 December 2014 – Wageningen

Contents • Research context • Experimental field lay out • Objectives • Results • Conclusions

Research context Agronomical aspect: Biomass production Environmental aspect: C sequestration ….

Field layout Rhizomatous grasses Arundo donax L. (Giant reed) Miscanthus x giganteus (Miscanthus) Panicum virgatum (Switchgrass) Trees SRF Populus spp (Poplar) Robinia pseudoacacia (Black locust) Salix (Willow)
Field layout Transplant spring 2006

Field layout Rhizomatous grasses Arundo donax L. (Giant reed) Miscanthus x giganteus (Miscanthus) Panicum virgatum (Switchgrass) Trees SRF Populus spp (Poplar) Robinia pseudoacacia (Black locust) Salix (Willow)

Field layout Rhizomatous grasses Arundo donax L. (Giant reed) Miscanthus x giganteus (Miscanthus) Panicum virgatum (Switchgrass) Trees SRF Populus spp (Poplar) Robinia pseudoacacia (Black locust) Salix (Willow) Surface area: 8100 m-2

Objectives Main objective: identify which crop has the highest soil C sequestration potential Root biomass production and distribution along the soil profile Assessment of SOC stock variation and its degree of stabilization
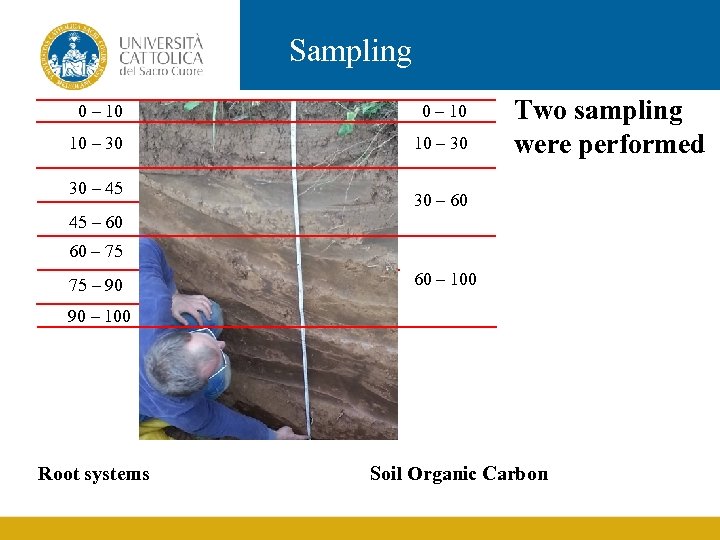
Sampling 0 – 10 10 – 30 30 – 45 Two sampling were performed 30 – 60 45 – 60 60 – 75 75 – 90 60 – 100 90 – 100 Root systems Soil Organic Carbon
Analysis Root systems Soil Organic Carbon

Analysis Root systems Root Biomass Weight RBW (t ha-1) Soil Organic Carbon

Analysis Root systems Root Biomass Weight RBW (t ha-1) Soil Organic Carbon Total Soil Organic Carbon (g Kg-1) Soil Organic Carbon stock (g m-2)

SOC fractions and stabilization mechanisms Wet sieving, density and …… - c. POM (2000 – 250 µm) and f. POM (250 – 53 m), unprotected SOC fractions - i. POM (250 – 53 µm), physically protected SOC fraction ……… chemical fractionation - HC ds+c chemically protected SOC fraction - HC µs+c chemically protected SOC fraction - NHC ds+c biochemically protected SOC fraction - NHC µs+c biochemically protected SOC fraction
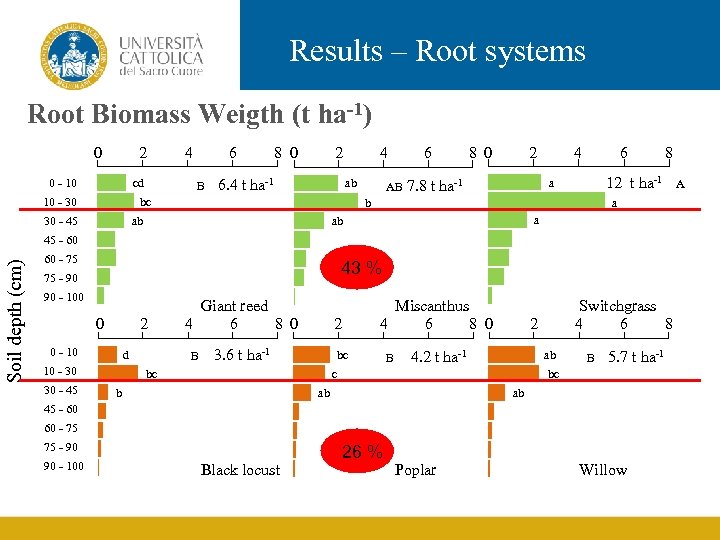
Results – Root systems Root Biomass Weigth (t ha-1) 0 2 0 - 10 cd 4 6 B 8 0 2 6. 4 t ha-1 4 ab bc 10 - 30 AB 8 0 2 4 6 8 12 t ha-1 a 7. 8 t ha-1 a b ab 30 - 45 6 a ab Soil depth (cm) 45 - 60 60 - 75 43 % 75 - 90 90 - 100 0 2 0 - 10 d 10 - 30 30 - 45 Giant reed 4 6 8 0 B 2 3. 6 t ha-1 Miscanthus 4 6 8 0 bc bc B 2 4. 2 t ha-1 ab c b Switchgrass 4 6 8 B 5. 7 t ha-1 bc ab ab 45 - 60 60 - 75 75 - 90 90 - 100 Black locust 26 % Poplar Willow A
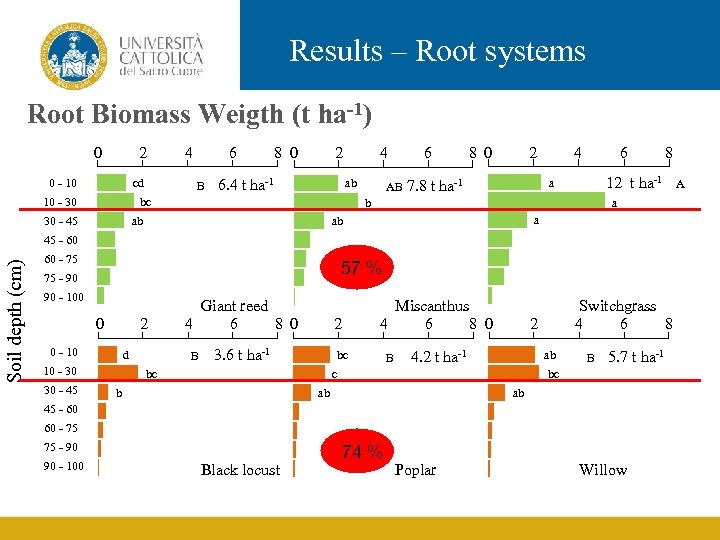
Results – Root systems Root Biomass Weigth (t ha-1) 0 2 0 - 10 cd 4 6 B 8 0 2 6. 4 t ha-1 4 ab bc 10 - 30 AB 8 0 2 4 6 8 12 t ha-1 a 7. 8 t ha-1 a b ab 30 - 45 6 a ab Soil depth (cm) 45 - 60 60 - 75 57 % 75 - 90 90 - 100 0 2 0 - 10 d 10 - 30 30 - 45 Giant reed 4 6 8 0 B 2 3. 6 t ha-1 Miscanthus 4 6 8 0 bc bc B 2 4. 2 t ha-1 ab c b Switchgrass 4 6 8 B 5. 7 t ha-1 bc ab ab 45 - 60 60 - 75 75 - 90 90 - 100 Black locust 74 % Poplar Willow A
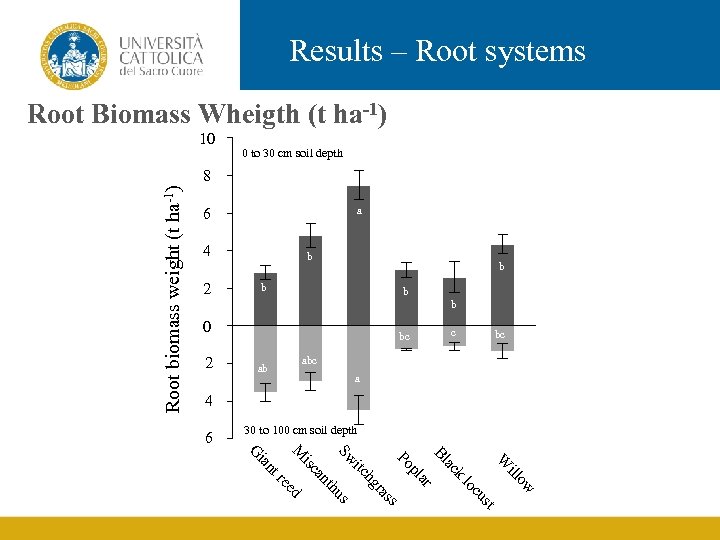
Results – Root systems Root Biomass Wheigth (t ha-1) 10 0 to 30 cm soil depth Root biomass weight (t ha-1) 8 a 6 4 2 b b b 0 2 c bc bc ab a 4 6 30 to 100 cm soil depth k st cu lo ow ill W ac Bl ar pl ss ra us th hg itc Po Sw ed re an isc nt ia M G
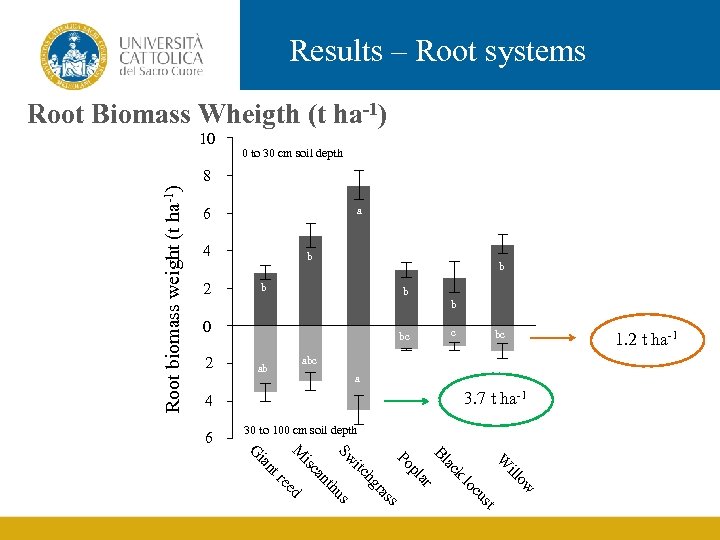
Results – Root systems Root Biomass Wheigth (t ha-1) 10 0 to 30 cm soil depth Root biomass weight (t ha-1) 8 a 6 4 2 b b b 0 2 c bc bc ab a 3. 7 t ha-1 4 6 30 to 100 cm soil depth 1. 2 t ha-1 k st cu lo ow ill W ac Bl ar pl ss ra us th hg itc Po Sw ed re an isc nt ia M G
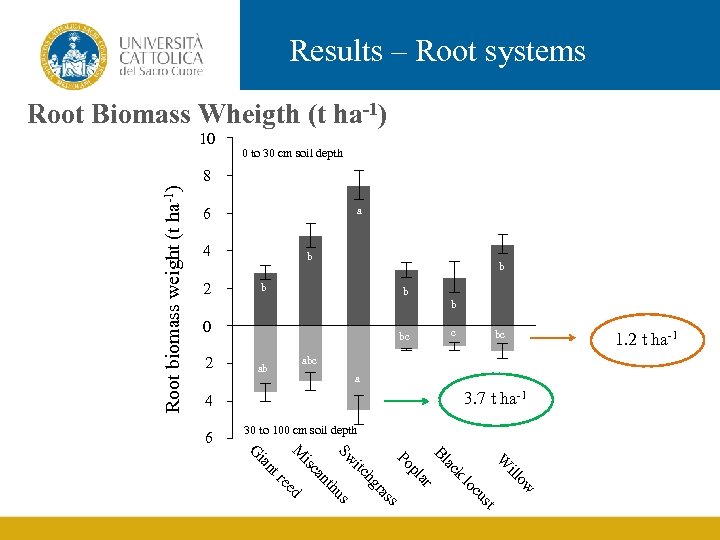
Results – Root systems Root Biomass Wheigth (t ha-1) 10 0 to 30 cm soil depth Root biomass weight (t ha-1) 8 a 6 4 2 b b b 0 2 c bc bc ab a 3. 7 t ha-1 4 6 30 to 100 cm soil depth 1. 2 t ha-1 k st cu lo ow ill W ac Bl ar pl ss ra us th hg itc Po Sw ed re an isc nt ia M G
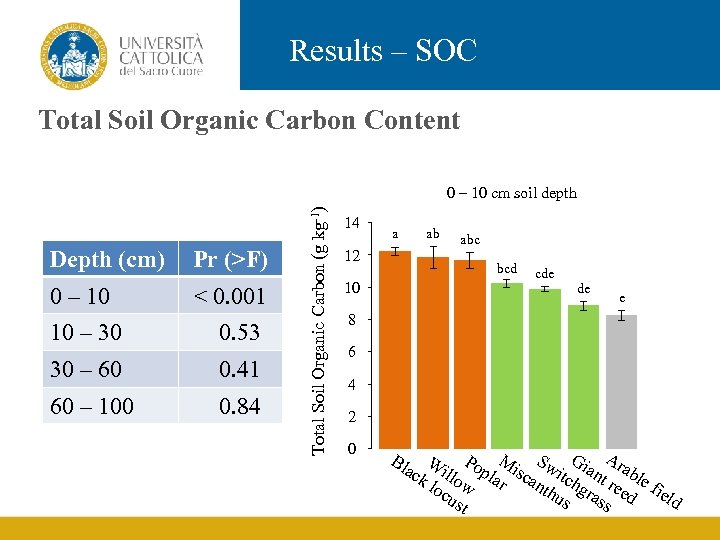
Results – SOC Total Soil Organic Carbon Content Depth (cm) Pr (>F) 0 – 10 < 0. 001 10 – 30 0. 53 30 – 60 0. 41 60 – 100 0. 84 Total Soil Organic Carbon (g kg-1) 0 – 10 cm soil depth 14 a 12 ab abc bcd 10 cde de e 8 6 4 2 0 P M S G A ack Will opl isc witc iant rabl loc ow ar anth hgr ree e fie us ass d ld ust Bl
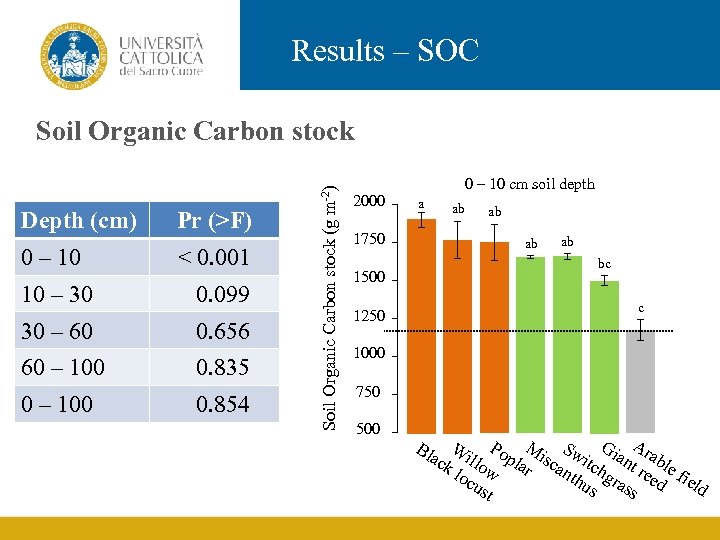
Results – SOC Depth (cm) 0 – 10 Pr (>F) < 0. 001 10 – 30 0. 099 30 – 60 0. 656 60 – 100 0. 835 0. 854 Soil Organic Carbon stock (g m-2) Soil Organic Carbon stock 2000 0 – 10 cm soil depth a 1750 ab ab bc 1500 c 1250 1000 750 500 G A W P M S ack illo opla isc witc iant rabl r ant hg re e fi loc w hu ras ed eld ust s s Bl
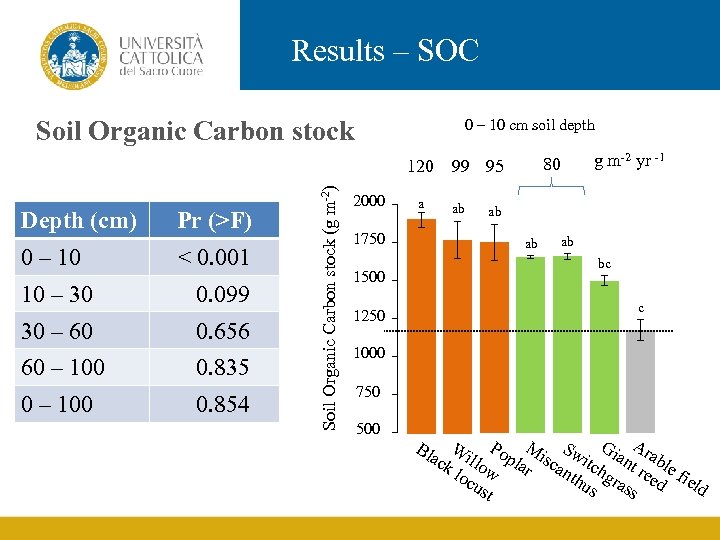
Results – SOC Soil Organic Carbon stock 0 – 10 cm soil depth Depth (cm) 0 – 10 Pr (>F) < 0. 001 10 – 30 0. 099 30 – 60 0. 656 60 – 100 0. 835 0. 854 Soil Organic Carbon stock (g m-2) 120 2000 a 1750 ab g m-2 yr -1 80 99 95 ab ab ab bc 1500 c 1250 1000 750 500 G A W P M S ack illo opla isc witc iant rabl r ant hg re e fi loc w hu ras ed eld ust s s Bl
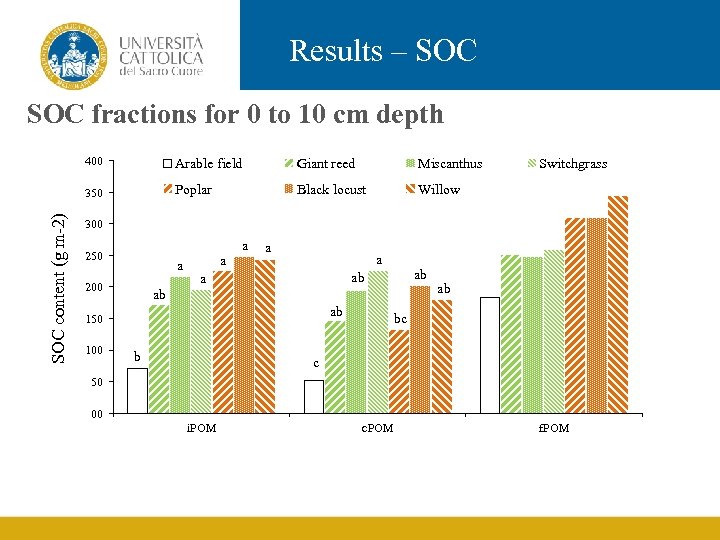
Results – SOC fractions for 0 to 10 cm depth Arable field Giant reed Miscanthus 350 SOC content (g m-2) 400 Poplar Black locust Willow Switchgrass 300 250 a 200 a a ab ab 150 100 ab ab a b ab bc c 50 00 i. POM c. POM f. POM
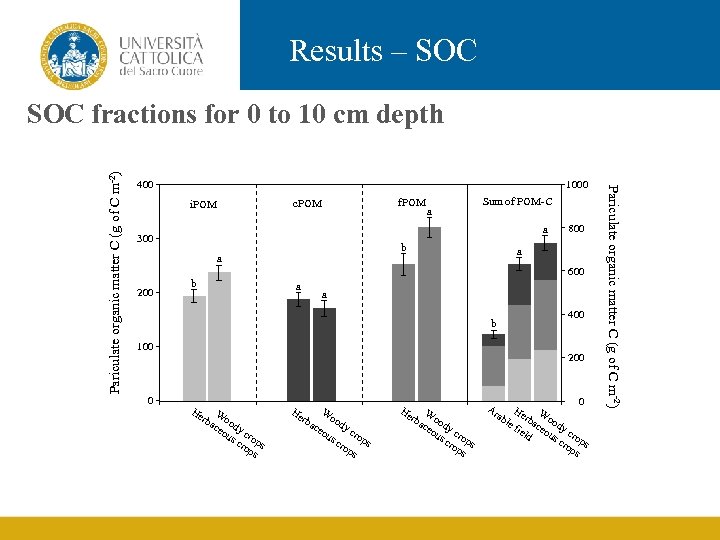
Results – SOC 400 1000 f. POM c. POM i. POM Sum of POM-C a 300 b a 200 a a 600 b a a b 100 0 800 400 200 He rba Woo ce dy ou cr s c op rop s s He He rba W ce oo ou dy sc cro rop s ps rba Woo ce dy ou cr s c op rop s s 0 Ar ab Herb Wo o le fie aceo dy c ld us ro cro ps ps Pariculate organic matter C (g of C m-2) SOC fractions for 0 to 10 cm depth

Results - summarizing After six years …… SOC stock increased only in the first soil layer, and the increase of the SOC stock has been faster in woody than herbaceous species Leaf litter seems to play a major role in SOC accumulation and stabilization Root biomass could play an important role in the long term especially if the bioenergy crop will be reconverted in arable land

Conclusions After six years …… - woody species showed the greatest SOC sequestration potential in the first soil layer, but their ability to allocate root biomass in the deeper soil layers was limited. - herbaceous species allocated a high amount of root biomass in the deeper soil layers, but only switchgrass and miscanthus sequester C in the first soil layer.

Thank you for your attention. . .
80ffb3402ff3ec1e04e925f61e6d2c5f.ppt