3d434d25e749c6d1a9602a8b19690d9e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Assessing Reading with Reading 3 D Implementing a State-wide Assessment to Show Reading Growth
Assessing Reading with Reading 3 D Implementing a State-wide Assessment to Show Reading Growth
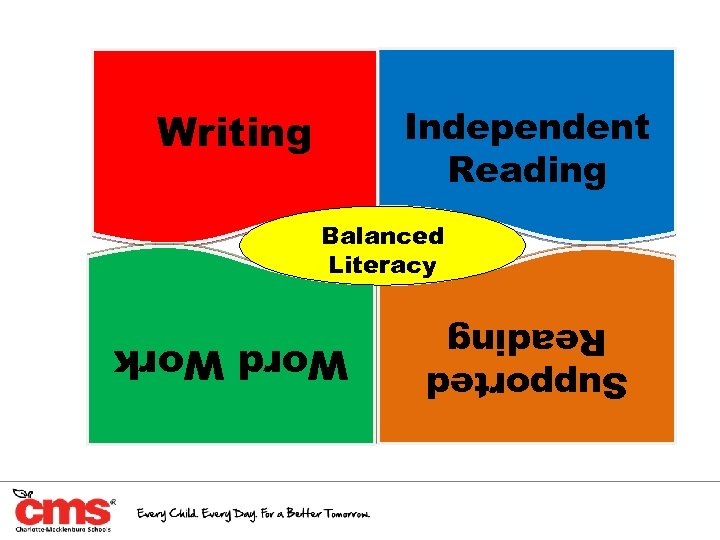 Independent Reading Writing Balanced Literacy Supported Reading Word Work
Independent Reading Writing Balanced Literacy Supported Reading Word Work
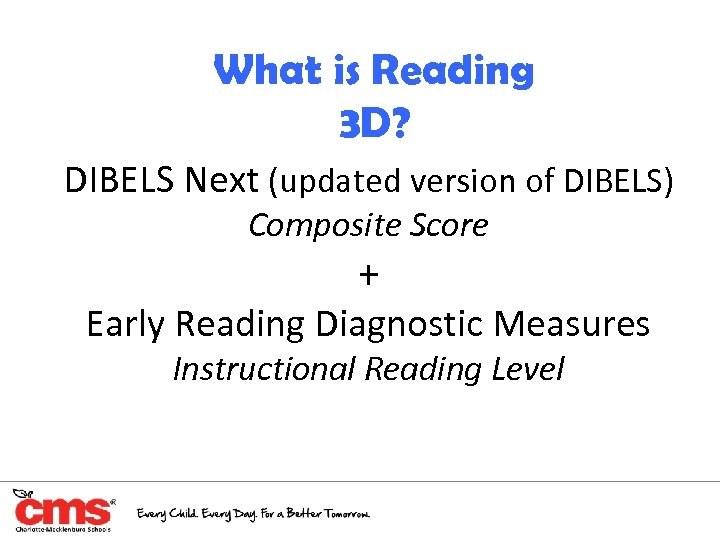 What is Reading 3 D? DIBELS Next (updated version of DIBELS) Composite Score + Early Reading Diagnostic Measures Instructional Reading Level
What is Reading 3 D? DIBELS Next (updated version of DIBELS) Composite Score + Early Reading Diagnostic Measures Instructional Reading Level
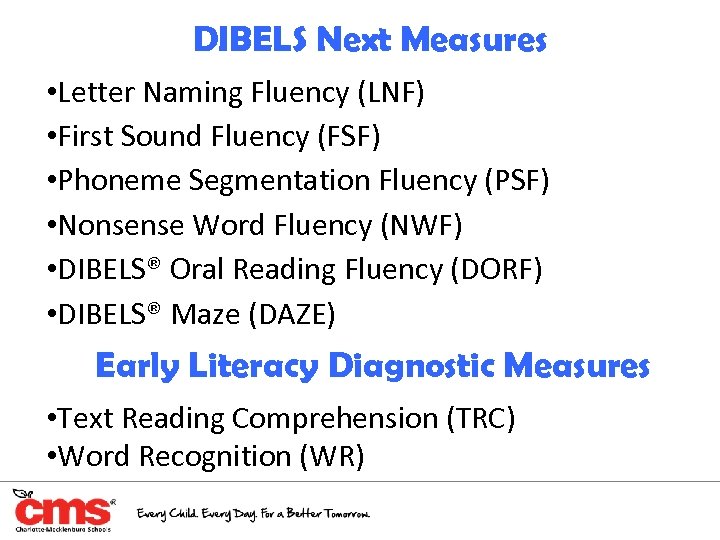 DIBELS Next Measures • Letter Naming Fluency (LNF) • First Sound Fluency (FSF) • Phoneme Segmentation Fluency (PSF) • Nonsense Word Fluency (NWF) • DIBELS® Oral Reading Fluency (DORF) • DIBELS® Maze (DAZE) Early Literacy Diagnostic Measures • Text Reading Comprehension (TRC) • Word Recognition (WR)
DIBELS Next Measures • Letter Naming Fluency (LNF) • First Sound Fluency (FSF) • Phoneme Segmentation Fluency (PSF) • Nonsense Word Fluency (NWF) • DIBELS® Oral Reading Fluency (DORF) • DIBELS® Maze (DAZE) Early Literacy Diagnostic Measures • Text Reading Comprehension (TRC) • Word Recognition (WR)
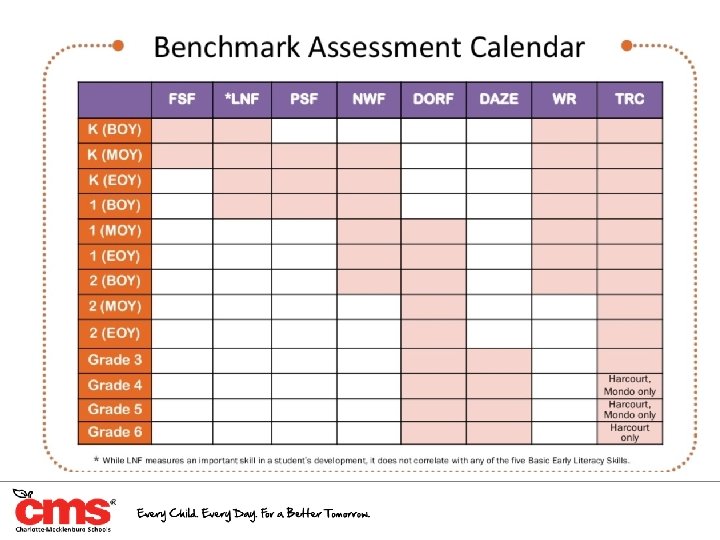
 CMS Reading 3 D Benchmark Windows For Traditional Calendar schools BOY: September 9 -October 1 (Testing may not occur on Sept. 25 & 26) MOY: January 7 - January 30 EOY: April 27 - May 15 For Continuous Learning Calendars (Bruns, Druid Hills, Thomasboro, and Byers only) BOY: July 21 -August 8 (Testing may not occur on July 29) MOY: January 7 - January 30 EOY: Bruns and Byers: April 27 -May 15; Druid Hills and Thomasboro May 4 -May 22
CMS Reading 3 D Benchmark Windows For Traditional Calendar schools BOY: September 9 -October 1 (Testing may not occur on Sept. 25 & 26) MOY: January 7 - January 30 EOY: April 27 - May 15 For Continuous Learning Calendars (Bruns, Druid Hills, Thomasboro, and Byers only) BOY: July 21 -August 8 (Testing may not occur on July 29) MOY: January 7 - January 30 EOY: Bruns and Byers: April 27 -May 15; Druid Hills and Thomasboro May 4 -May 22
 Tools and Resources • mclasshome. com • http: //www. ncpublicschools. org/k 3 literacy/resources/ • Amplify. net • Scott Miller (Amplify Rep) • Amplify Customer Care • Phone: (800) 823 -1969, option 3 • mclasshome. com/assessment
Tools and Resources • mclasshome. com • http: //www. ncpublicschools. org/k 3 literacy/resources/ • Amplify. net • Scott Miller (Amplify Rep) • Amplify Customer Care • Phone: (800) 823 -1969, option 3 • mclasshome. com/assessment
 i. Pad App for Assessment
i. Pad App for Assessment
 Let’s Practice with DIBELS® Next Where would you like to start?
Let’s Practice with DIBELS® Next Where would you like to start?
 Text Reading Comprehension Components -Print Concepts -Reading Behaviors -Reading Records
Text Reading Comprehension Components -Print Concepts -Reading Behaviors -Reading Records
 Text Reading Comprehension Let’s watch an assessment
Text Reading Comprehension Let’s watch an assessment
 Reading Level Cutpoints Please visit the Humanities Page on the CMS Intranet. Click on the Literacy tab and then click on the Elementary Literacy Curriculum 2013 -2014 tab to access this document (link at the top of the page)
Reading Level Cutpoints Please visit the Humanities Page on the CMS Intranet. Click on the Literacy tab and then click on the Elementary Literacy Curriculum 2013 -2014 tab to access this document (link at the top of the page)
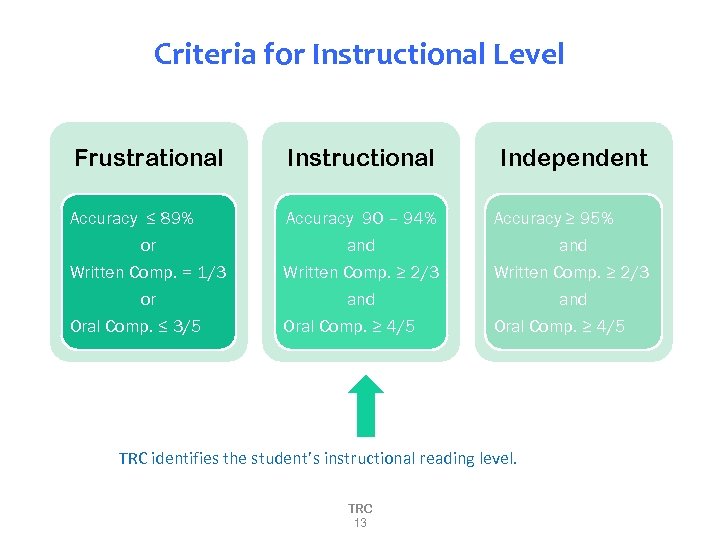 Criteria for Instructional Level Frustrational Instructional Independent Accuracy ≤ 89% Accuracy 90 – 94% Accuracy ≥ 95% or Written Comp. = 1/3 or Oral Comp. ≤ 3/5 and Written Comp. ≥ 2/3 and Oral Comp. ≥ 4/5 TRC identifies the student’s instructional reading level. TRC 13
Criteria for Instructional Level Frustrational Instructional Independent Accuracy ≤ 89% Accuracy 90 – 94% Accuracy ≥ 95% or Written Comp. = 1/3 or Oral Comp. ≤ 3/5 and Written Comp. ≥ 2/3 and Oral Comp. ≥ 4/5 TRC identifies the student’s instructional reading level. TRC 13
 Jake’s Plan Let’s say Jake scores Frustrational at Level N and Instructional at Level M. 1. Which book level would you use for small-group instruction? 2. Which book level would you suggest he check out of the library for reading at home? 3. Which levels would you guide him away from when reading independently? TRC 14
Jake’s Plan Let’s say Jake scores Frustrational at Level N and Instructional at Level M. 1. Which book level would you use for small-group instruction? 2. Which book level would you suggest he check out of the library for reading at home? 3. Which levels would you guide him away from when reading independently? TRC 14
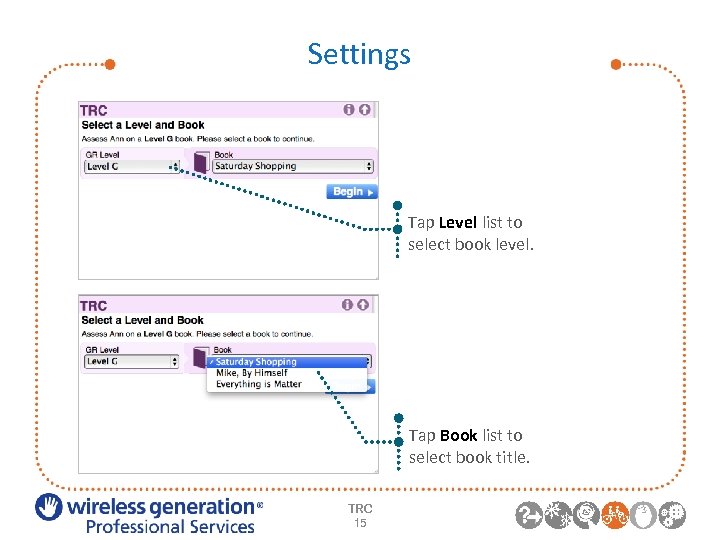 Settings Tap Level list to select book level. Tap Book list to select book title. TRC 15
Settings Tap Level list to select book level. Tap Book list to select book title. TRC 15
 Record Errors • Self Correction (SC) • Substitution (sub) • Insertion (^) • Omission (omit) • Told (told) TRC 16
Record Errors • Self Correction (SC) • Substitution (sub) • Insertion (^) • Omission (omit) • Told (told) TRC 16
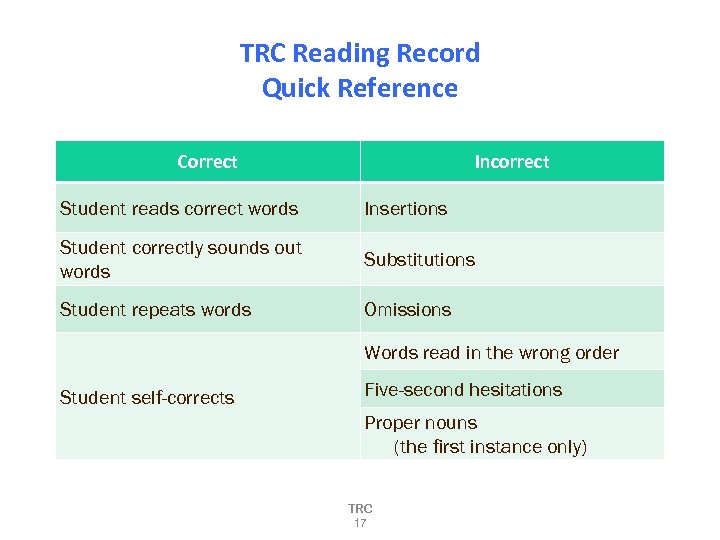 TRC Reading Record Quick Reference Correct Incorrect Student reads correct words Insertions Student correctly sounds out words Substitutions Student repeats words Omissions Words read in the wrong order Student self-corrects Five-second hesitations Proper nouns (the first instance only) TRC 17
TRC Reading Record Quick Reference Correct Incorrect Student reads correct words Insertions Student correctly sounds out words Substitutions Student repeats words Omissions Words read in the wrong order Student self-corrects Five-second hesitations Proper nouns (the first instance only) TRC 17
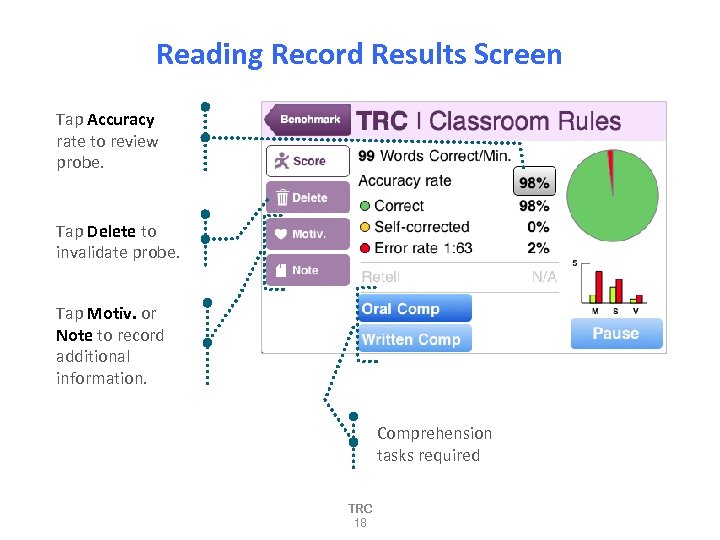 Reading Record Results Screen Tap Accuracy rate to review probe. Tap Delete to invalidate probe. Tap Motiv. or Note to record additional information. Comprehension tasks required TRC 18
Reading Record Results Screen Tap Accuracy rate to review probe. Tap Delete to invalidate probe. Tap Motiv. or Note to record additional information. Comprehension tasks required TRC 18
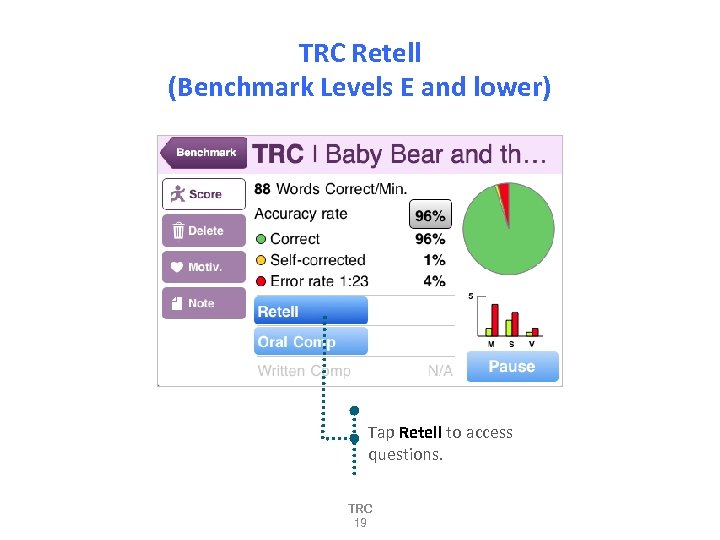 TRC Retell (Benchmark Levels E and lower) Tap Retell to access questions. TRC 19
TRC Retell (Benchmark Levels E and lower) Tap Retell to access questions. TRC 19
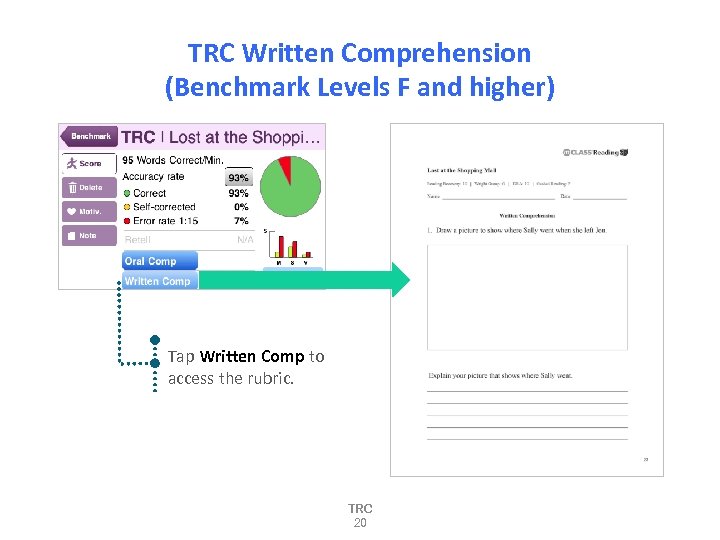 TRC Written Comprehension (Benchmark Levels F and higher) Tap Written Comp to access the rubric. TRC 20
TRC Written Comprehension (Benchmark Levels F and higher) Tap Written Comp to access the rubric. TRC 20
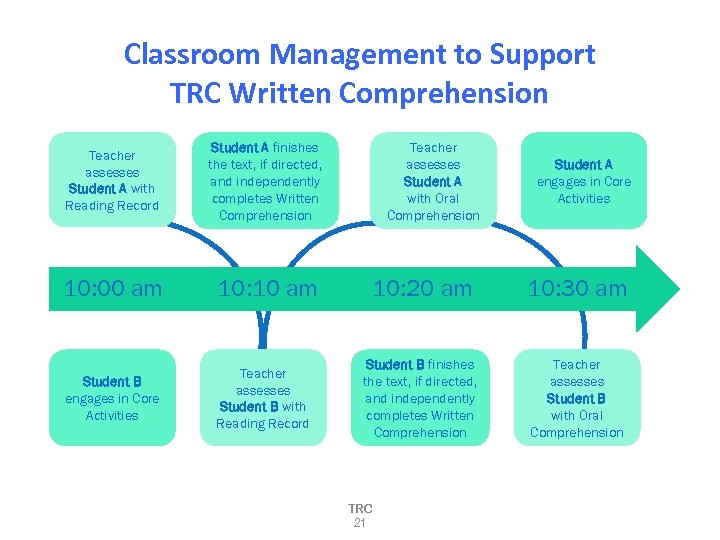 Classroom Management to Support TRC Written Comprehension Teacher assesses Student A with Reading Record Student A finishes the text, if directed, and independently completes Written Comprehension 10: 00 am 10: 10 am Student B engages in Core Activities Teacher assesses Student B with Reading Record Teacher assesses Student A with Oral Comprehension Student A engages in Core Activities 10: 20 am 10: 30 am Student B finishes the text, if directed, and independently completes Written Comprehension Teacher assesses Student B with Oral Comprehension TRC 21
Classroom Management to Support TRC Written Comprehension Teacher assesses Student A with Reading Record Student A finishes the text, if directed, and independently completes Written Comprehension 10: 00 am 10: 10 am Student B engages in Core Activities Teacher assesses Student B with Reading Record Teacher assesses Student A with Oral Comprehension Student A engages in Core Activities 10: 20 am 10: 30 am Student B finishes the text, if directed, and independently completes Written Comprehension Teacher assesses Student B with Oral Comprehension TRC 21
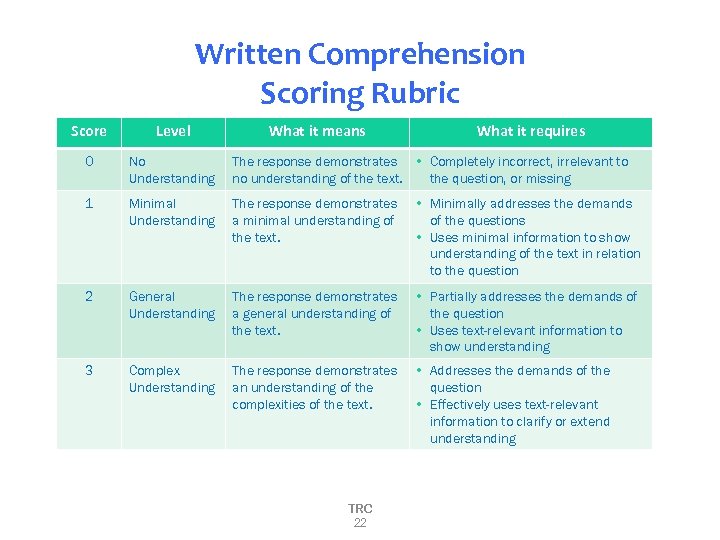 Written Comprehension Scoring Rubric Score Level What it means 0 No Understanding The response demonstrates no understanding of the text. • Completely incorrect, irrelevant to the question, or missing 1 Minimal Understanding The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of the text. • Minimally addresses the demands of the questions • Uses minimal information to show understanding of the text in relation to the question 2 General Understanding The response demonstrates a general understanding of the text. • Partially addresses the demands of the question • Uses text-relevant information to show understanding 3 Complex Understanding The response demonstrates an understanding of the complexities of the text. • Addresses the demands of the question • Effectively uses text-relevant information to clarify or extend understanding TRC 22 What it requires
Written Comprehension Scoring Rubric Score Level What it means 0 No Understanding The response demonstrates no understanding of the text. • Completely incorrect, irrelevant to the question, or missing 1 Minimal Understanding The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of the text. • Minimally addresses the demands of the questions • Uses minimal information to show understanding of the text in relation to the question 2 General Understanding The response demonstrates a general understanding of the text. • Partially addresses the demands of the question • Uses text-relevant information to show understanding 3 Complex Understanding The response demonstrates an understanding of the complexities of the text. • Addresses the demands of the question • Effectively uses text-relevant information to clarify or extend understanding TRC 22 What it requires
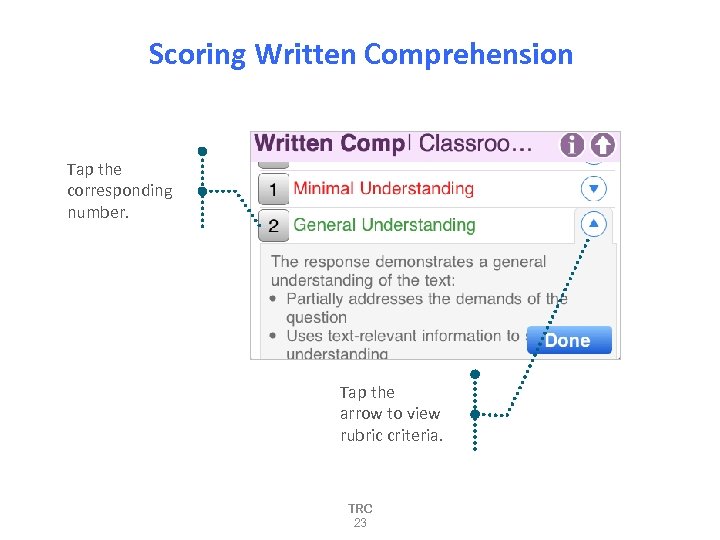 Scoring Written Comprehension Tap the corresponding number. Tap the arrow to view rubric criteria. TRC 23
Scoring Written Comprehension Tap the corresponding number. Tap the arrow to view rubric criteria. TRC 23
 Practice Scoring TRC Written Comprehension Harry the Tow Truck, Level J 1. What problem does Harry need to solve to help the car drivers get home? 2. Describe the events at the end of the story that solved Harry’s problem. A 1. 2. C 1. 2. Student Sample B He needs to get the orange van onto it’s wheels and get the van out of the way. Harry has to get ther fast and get the gob[job] done fast so the drivers can get home. Harry’s problem was Harry tought he can’t pulled the red truck pass the big tree. Student Sample 1. He had to hurry getting the orange truck on the road. 2. He got a strong rope and tied it to the truck and move the truck on the road. Student Sample D 1. Harry and Bod had to solve the probrem of the orig [orange] mooveing truk. What solved Bob’s and Harry’s probrem was the strog rope that Bob tied aroend the van and then the van came back on it’s willis [wheels]. 2. Student Sample He can go faster or tell them to go the other way. He was happy because that job was not hard at all. * All grammar and spelling in these samples are true to students’ original responses. TRC 24
Practice Scoring TRC Written Comprehension Harry the Tow Truck, Level J 1. What problem does Harry need to solve to help the car drivers get home? 2. Describe the events at the end of the story that solved Harry’s problem. A 1. 2. C 1. 2. Student Sample B He needs to get the orange van onto it’s wheels and get the van out of the way. Harry has to get ther fast and get the gob[job] done fast so the drivers can get home. Harry’s problem was Harry tought he can’t pulled the red truck pass the big tree. Student Sample 1. He had to hurry getting the orange truck on the road. 2. He got a strong rope and tied it to the truck and move the truck on the road. Student Sample D 1. Harry and Bod had to solve the probrem of the orig [orange] mooveing truk. What solved Bob’s and Harry’s probrem was the strog rope that Bob tied aroend the van and then the van came back on it’s willis [wheels]. 2. Student Sample He can go faster or tell them to go the other way. He was happy because that job was not hard at all. * All grammar and spelling in these samples are true to students’ original responses. TRC 24
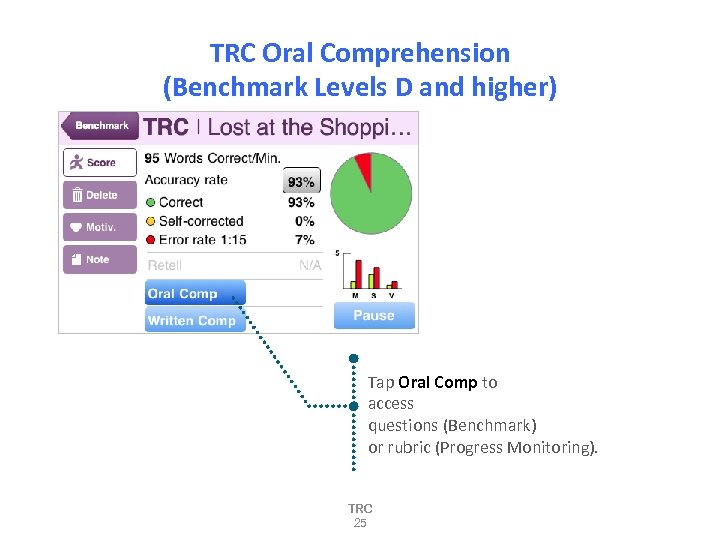 TRC Oral Comprehension (Benchmark Levels D and higher) Tap Oral Comp to access questions (Benchmark) or rubric (Progress Monitoring). TRC 25
TRC Oral Comprehension (Benchmark Levels D and higher) Tap Oral Comp to access questions (Benchmark) or rubric (Progress Monitoring). TRC 25
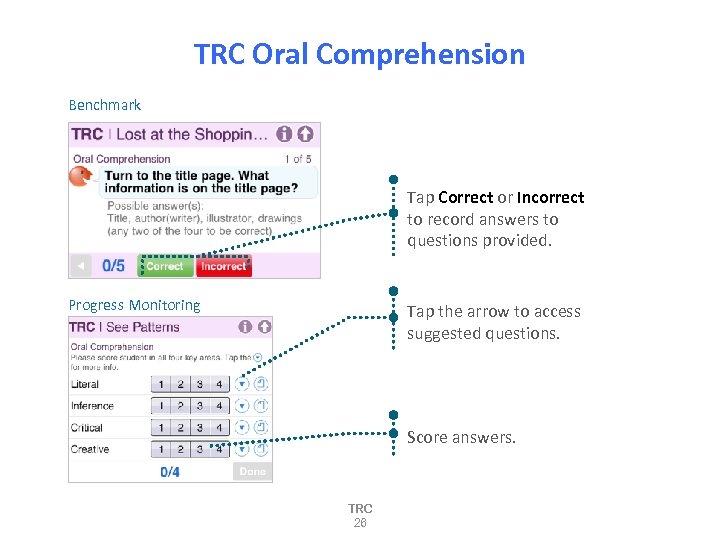 TRC Oral Comprehension Benchmark Tap Correct or Incorrect to record answers to questions provided. Progress Monitoring Tap the arrow to access suggested questions. Score answers. TRC 26
TRC Oral Comprehension Benchmark Tap Correct or Incorrect to record answers to questions provided. Progress Monitoring Tap the arrow to access suggested questions. Score answers. TRC 26
 Reading Record (MSV) Analysis • Helps teachers better understand students’ instructional needs. • Based on Marie Clay’s running records. • Identifies the reader’s sources of information. • Meaning, Structure, and/or Visual represent the way information is processed. TRC 27
Reading Record (MSV) Analysis • Helps teachers better understand students’ instructional needs. • Based on Marie Clay’s running records. • Identifies the reader’s sources of information. • Meaning, Structure, and/or Visual represent the way information is processed. TRC 27
 MSV Analysis Meaning • Does the word the student used make sense? • Did the student preserve meaning? Syntax/Structure • Does the word the student used sound right? • Did the student preserve language structure? Visual • Does the word the student used match the print? • Did the student preserve the visual appearance of the word? TRC 28
MSV Analysis Meaning • Does the word the student used make sense? • Did the student preserve meaning? Syntax/Structure • Does the word the student used sound right? • Did the student preserve language structure? Visual • Does the word the student used match the print? • Did the student preserve the visual appearance of the word? TRC 28
 MSV Practice Which strategies did this student use to substitute while reading? 1. We live in a home at the lake. house M 2. Billy and the girl playing ball until dark. 2. played • We are going to ride he bus to he beach. the TRC 29 V S V M • I got a new pair of shoes. 1. have S M 3. Our family had a ran cat. pet V M 2. We walked to a store. the S S V M S V
MSV Practice Which strategies did this student use to substitute while reading? 1. We live in a home at the lake. house M 2. Billy and the girl playing ball until dark. 2. played • We are going to ride he bus to he beach. the TRC 29 V S V M • I got a new pair of shoes. 1. have S M 3. Our family had a ran cat. pet V M 2. We walked to a store. the S S V M S V
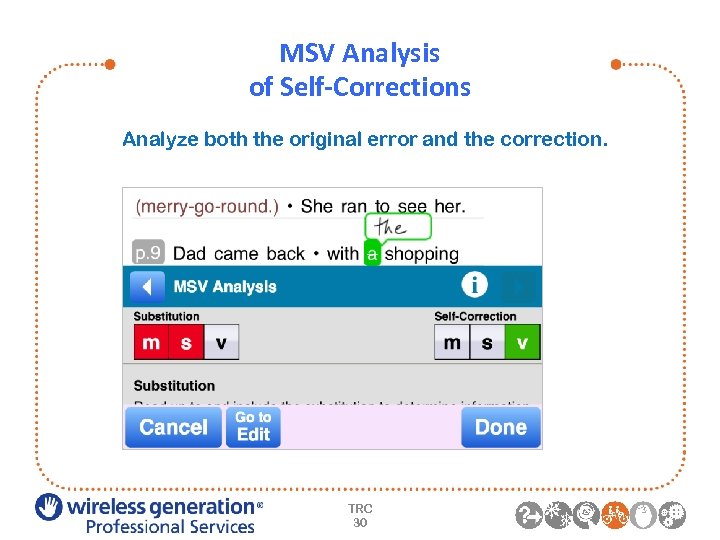 MSV Analysis of Self-Corrections Analyze both the original error and the correction. TRC 30
MSV Analysis of Self-Corrections Analyze both the original error and the correction. TRC 30
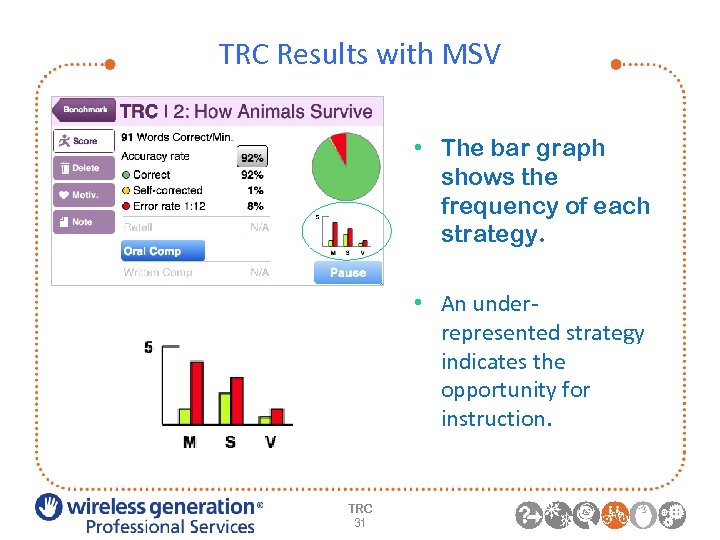 TRC Results with MSV • The bar graph shows the frequency of each strategy. • An underrepresented strategy indicates the opportunity for instruction. TRC 31
TRC Results with MSV • The bar graph shows the frequency of each strategy. • An underrepresented strategy indicates the opportunity for instruction. TRC 31
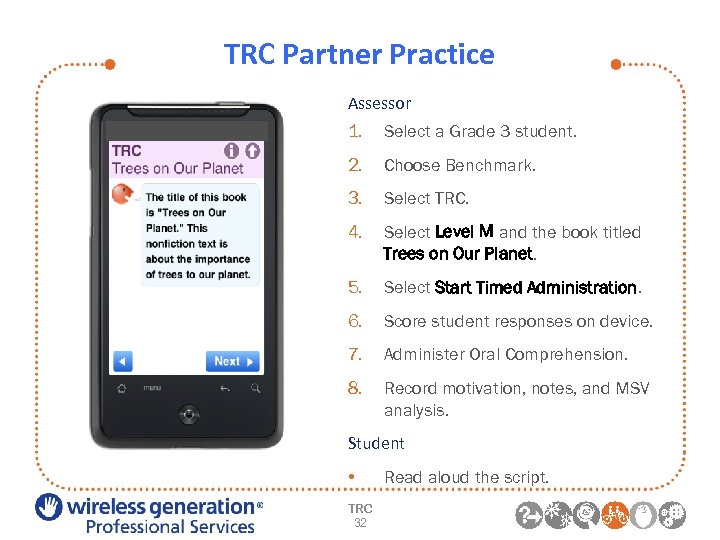 TRC Partner Practice Assessor 1. Select a Grade 3 student. 2. Choose Benchmark. 3. Select TRC. 4. Select Level M and the book titled Trees on Our Planet. 5. Select Start Timed Administration. 6. Score student responses on device. 7. Administer Oral Comprehension. 8. Record motivation, notes, and MSV analysis. Student • TRC 32 Read aloud the script.
TRC Partner Practice Assessor 1. Select a Grade 3 student. 2. Choose Benchmark. 3. Select TRC. 4. Select Level M and the book titled Trees on Our Planet. 5. Select Start Timed Administration. 6. Score student responses on device. 7. Administer Oral Comprehension. 8. Record motivation, notes, and MSV analysis. Student • TRC 32 Read aloud the script.
 TRC Partner Practice Script An ellipsis (…) indicates a five-second hesitation. An asterisk (*) indicates an omission. Key: A bold word indicates a mistake. A comma (, ) indicates a self‑correction. People have been cutting down trees for thousand of years. The wood from trees is very useful. It can be used to build houses. It can be used to make tables and chair and other furniture. Wood can be made into paper, too. But, all around the world, too much, many trees have been cut down. More and more houses have been built. Large cities has been built. In the past, people decide to turn huge areas of forest into farm land. They cut down millions of trees. They clear the land quickly. But then some heavy rain came, and good soil on top of the ground washed away. Nothing much would grow there. Today, people realized how important trees are. Their wide branches help to stop the rain * washing the topsoil away. Their strong roots hold the soil in place, even on … mountains. And forest provide a home for many different kinds of nice animals. So people are now growing trees to replace * ones that have been cut down. When the young trees are strong … , they are planted where they are need most. But they take a long time to grow tall. We must all help to put trees back on our plant. TRC 33
TRC Partner Practice Script An ellipsis (…) indicates a five-second hesitation. An asterisk (*) indicates an omission. Key: A bold word indicates a mistake. A comma (, ) indicates a self‑correction. People have been cutting down trees for thousand of years. The wood from trees is very useful. It can be used to build houses. It can be used to make tables and chair and other furniture. Wood can be made into paper, too. But, all around the world, too much, many trees have been cut down. More and more houses have been built. Large cities has been built. In the past, people decide to turn huge areas of forest into farm land. They cut down millions of trees. They clear the land quickly. But then some heavy rain came, and good soil on top of the ground washed away. Nothing much would grow there. Today, people realized how important trees are. Their wide branches help to stop the rain * washing the topsoil away. Their strong roots hold the soil in place, even on … mountains. And forest provide a home for many different kinds of nice animals. So people are now growing trees to replace * ones that have been cut down. When the young trees are strong … , they are planted where they are need most. But they take a long time to grow tall. We must all help to put trees back on our plant. TRC 33
 Don’t forget to visit mclasshome. com for more information, resources, tutorials, and support. Make the most of Reading 3 D to indentify the strengths of your students and show great growth this year!
Don’t forget to visit mclasshome. com for more information, resources, tutorials, and support. Make the most of Reading 3 D to indentify the strengths of your students and show great growth this year!


