f32435f3cca1334a661ea81254f5e959.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING

Course Objectives • Identify the major component of a PC-based system, describe the steps involving in assembling, linking, and executing a program • Write/Debug programs in assembly language to perform the given task and run them

Textbook/Technology requirement Textbook: IBM PC Assembly Language and Programming. Peter Abel. 2001. Fifth Edition. Prentice Hall. ISBN: 0 -13 -030655 -X Software: Emu 8086 microprocessor assembler and emulator software. Available at www. emu 8086. com

Introduction Tell me about yourself and what you expect to get out from this course
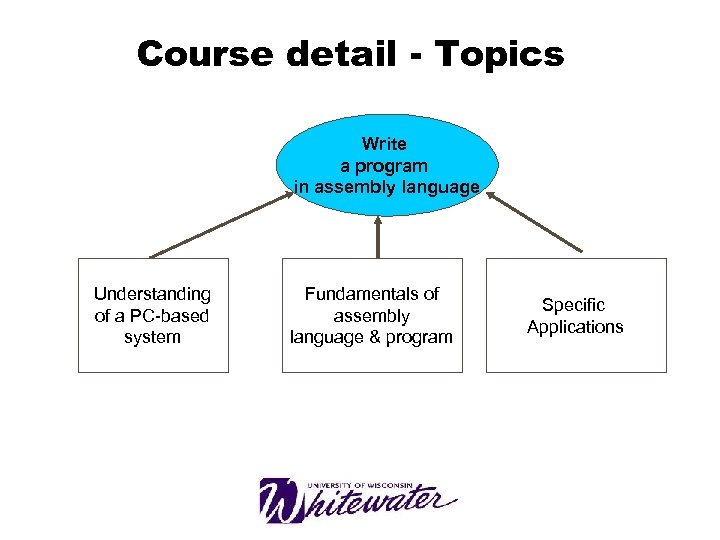
Course detail - Topics Write a program in assembly language Understanding of a PC-based system Fundamentals of assembly language & program Specific Applications

What does it take to success -Attend the class regularly and actively participate in the class discussion (ask questions, answer questions, etc. . ) -Don’t give up on programming assignments. Pay attention to detail -Try many options when doing programming assignments

Questions?

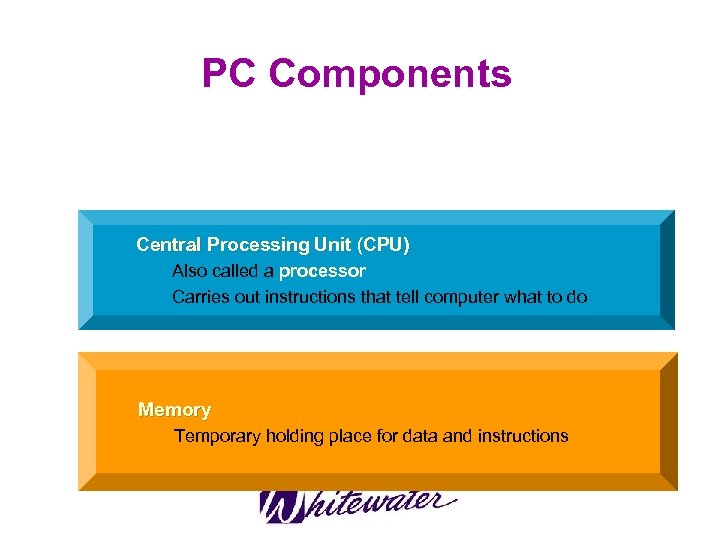
Overview Fundamental of PC Hardware and Software

Basic features of PC Hardware • Binary and Hexadecimal Number Systems – Bits/bytes – Binary number systems – Hexadecimal – ASCII • PC Components – Processor – Memory
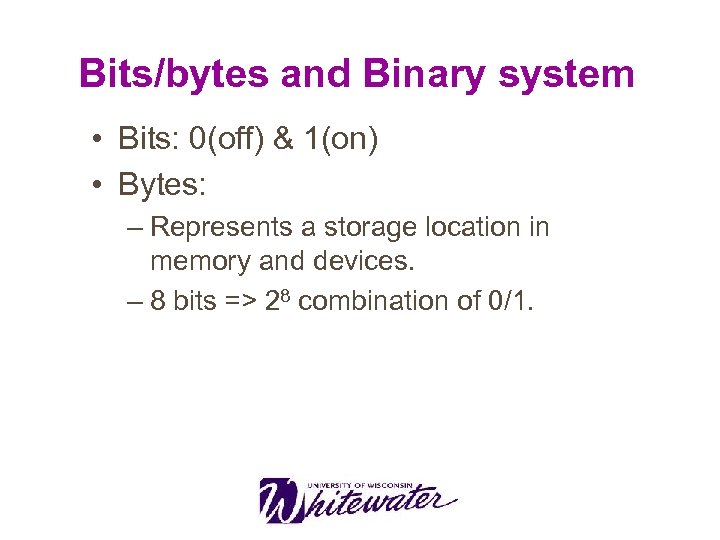
Bits/bytes and Binary system • Bits: 0(off) & 1(on) • Bytes: – Represents a storage location in memory and devices. – 8 bits => 28 combination of 0/1.
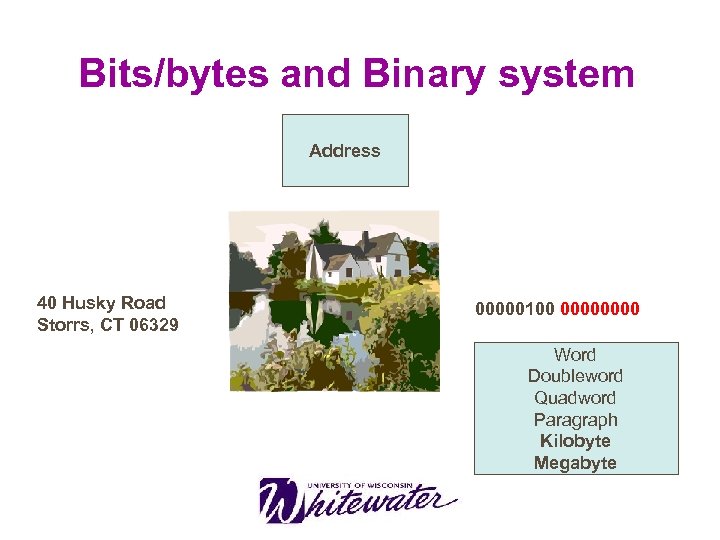
Bits/bytes and Binary system Address 40 Husky Road Storrs, CT 06329 00000100 0000 Word Doubleword Quadword Paragraph Kilobyte Megabyte
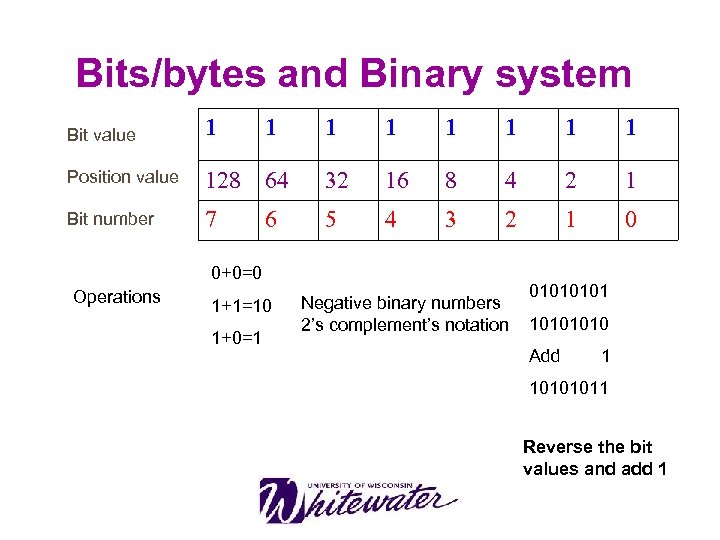
Bits/bytes and Binary system Bit value 1 Position value Bit number 1 1 1 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 7 5 4 3 2 1 0 6 0+0=0 Operations 1+1=10 1+0=1 Negative binary numbers 2’s complement’s notation 0101 1010 Add 1 10101011 Reverse the bit values and add 1

1. What is the value of 0101? 2. How to represent -25 in 2’s complement notation?
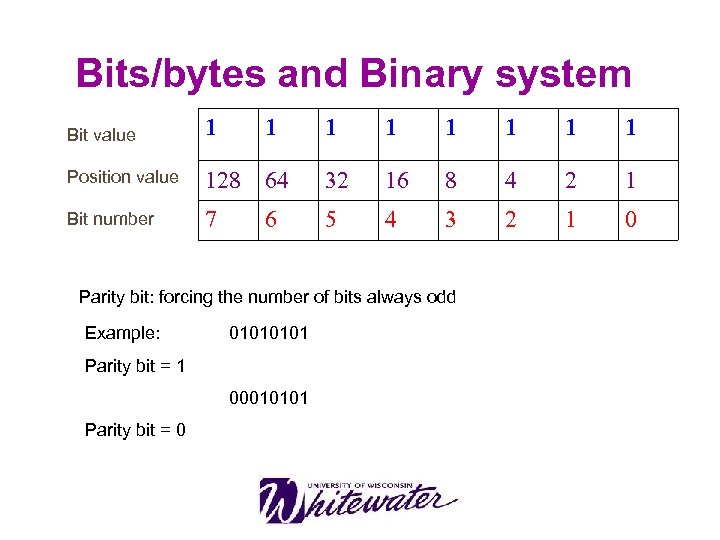
Bits/bytes and Binary system Bit value 1 Position value Bit number 1 1 1 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 7 5 4 3 2 1 0 6 Parity bit: forcing the number of bits always odd Example: 0101 Parity bit = 1 00010101 Parity bit = 0
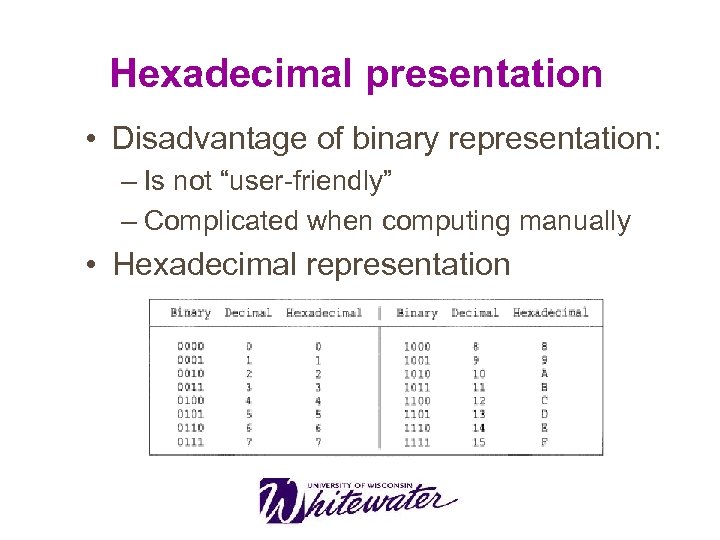
Hexadecimal presentation • Disadvantage of binary representation: – Is not “user-friendly” – Complicated when computing manually • Hexadecimal representation

Hexadecimal presentation Hexadecimal arithmetic 7+1=8 7+2=9 7+3=A 7+4=B 7+8=F 7+9=?

Practice • Convert from decimal to hexadecimal 23 = ? ? 254 = ? ? • Adding hexadecimal value 13 B 4 H + 0033 H = ? ? DCBEH + 35 B 5 H = ? ?

Popular coding systems to represent data Ø ASCII—American Standard Code for Information Interchange Ø EBCDIC—Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code Ø Unicode—coding scheme capable of representing all world’s languages

Conversion from letter to binary format and back Step 1. Step 2. The user presses the capital letter D (shift+D key) on the keyboard. Step 4. After processing, the binary code for the capital letter D is converted to an image, and displayed on the output device. An electronic signal for the capital letter D is sent to the system unit. Step 3. The signal for the capital letter D is converted to its ASCII binary code (0100) and is stored in memory for processing.

Question?

PC Components speaker PC camera system unit printer speaker monitor keyboard modem scanner mouse microphone digital camera
PC Components Central Processing Unit (CPU) Also called a processor Carries out instructions that tell computer what to do Memory Temporary holding place for data and instructions
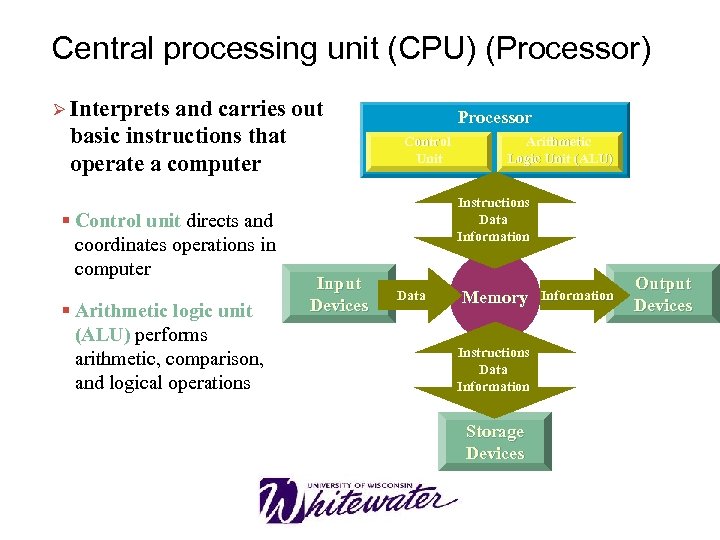
Central processing unit (CPU) (Processor) Ø Interprets and carries out basic instructions that operate a computer § Control unit directs and coordinates operations in computer § Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) performs arithmetic, comparison, and logical operations Processor Control Unit Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Instructions Data Information Input Devices Data Memory Instructions Data Information Storage Devices Information Output Devices
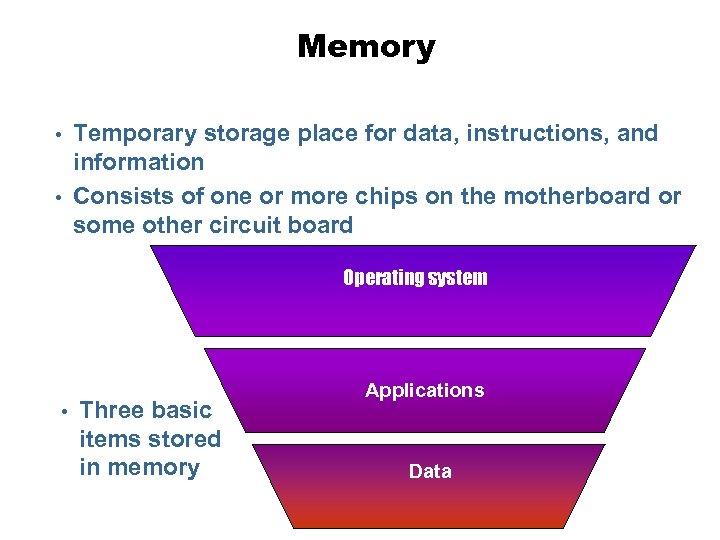
Memory • • Temporary storage place for data, instructions, and information Consists of one or more chips on the motherboard or some other circuit board Operating system • Three basic items stored in memory Applications Data
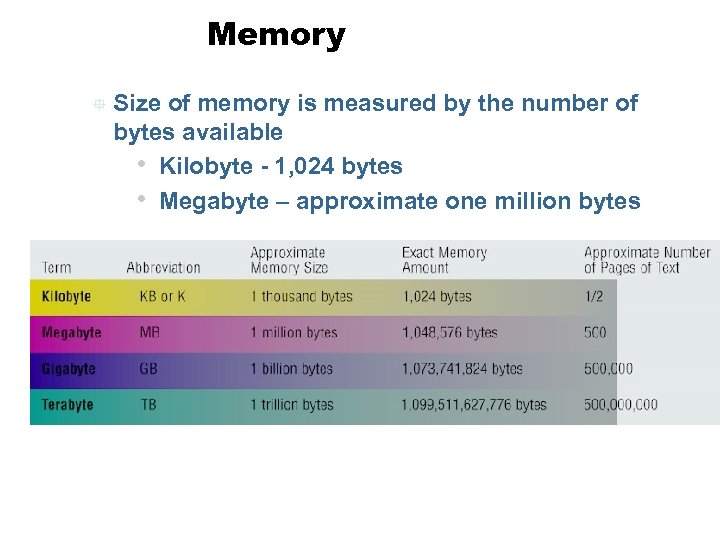
Memory ° Size of memory is measured by the number of bytes available • Kilobyte - 1, 024 bytes • Megabyte – approximate one million bytes
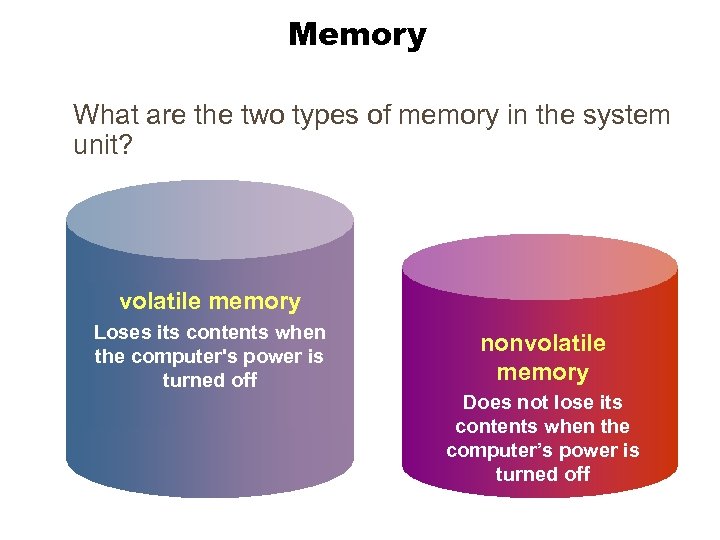
Memory What are the two types of memory in the system unit? volatile memory Volatile Memory Loses its contents when the computer's power off computer's power is turned off nonvolatile memory Does not lose its contents when the computer’s power is turned off
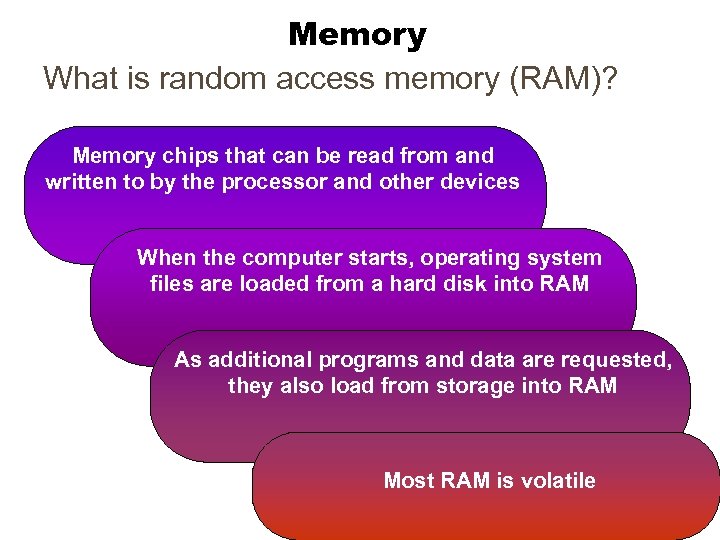
Memory What is random access memory (RAM)? Memory chips that can be read from and written to by the processor and other devices When the computer starts, operating system files are loaded from a hard disk into RAM As additional programs and data are requested, they also load from storage into RAM Most RAM is volatile

Addressing data in Memory • Difference between address of a memory Location and its content • Processor stores the data in memory in reverse by sequence • Two types of addressing schemes absolute address segment-offset address

Segment • • • Code segment (CS) Data segment (DS) Stack segment (SS) Extra segment (ES) Actual address = segment address + offset

Registers • Segment register – CS, DS, SS, ES, FS and GS • Pointer register – IP, SP, BP • General purpose register – AX, BX, CX, DX • Index register – SI, DI

Flags OF, DF, IF, SF, ZF, AF, PF, CF If cleared: NV, UP, EI, PL, NZ, NA, PO, NC If set: OV, DN, EI, NG, ZR, AC, PE, CY
f32435f3cca1334a661ea81254f5e959.ppt