db167f389e0462a4255c3214a76cfb09.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Assembly Language • Advantages • 1. It reveals the secret of your computer’s hardware and software. • 2. Speed. • 3. Some special applications and occasions. • Disadvantages • 1. Not as easy to do the programming. • 2. Debug is not as easy compared with highlevel language. • 3. Not transferable between different CPUs.
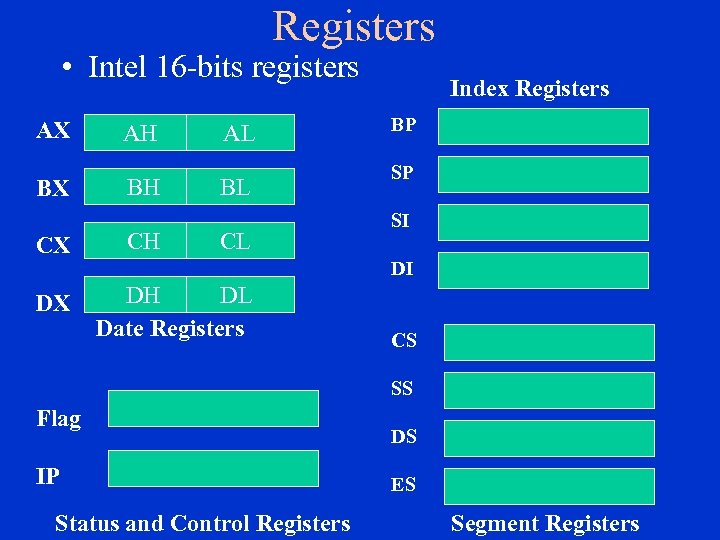
Registers • Intel 16 -bits registers AX BX AH AL BH BL CX CH CL DX DH DL Date Registers Index Registers BP SP SI DI CS SS Flag IP Status and Control Registers DS ES Segment Registers
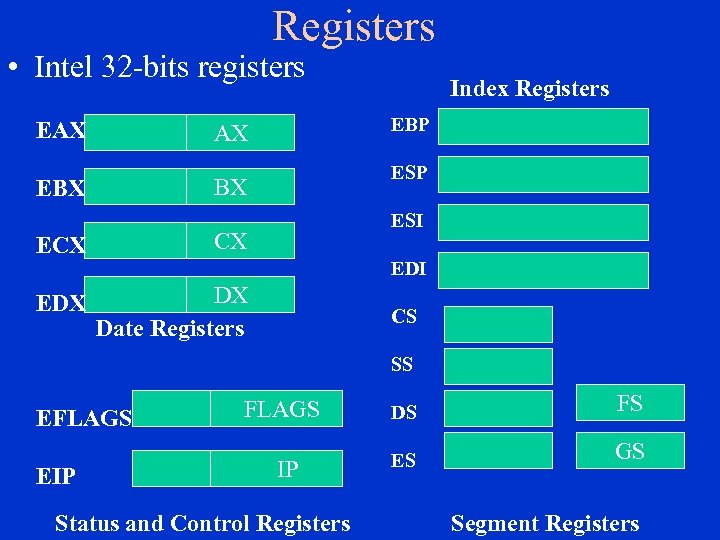
Registers • Intel 32 -bits registers EAX EBX AX BX ECX CX EDX DX Date Registers Index Registers EBP ESI EDI CS SS EFLAGS FLAGS DS FS EIP IP ES GS Status and Control Registers Segment Registers

Flag Register • 16 -bits Flag Register x x O D I T S Z x A x P x C • The most common used flag bits O D I S Z A P C O—Overflow D--- Direction I-----Interrupt S----Sign Z---Zero A---Auxiliary Carry P----Parity C----Carry

General Rules about Flags • • • “ 1”---Set the flag. “ 0”---Clear the flag. “? ”---May change the flag to an undetermined value (Blank)---The flag is not changed * ----Change the flag to specific rules associated with the flag
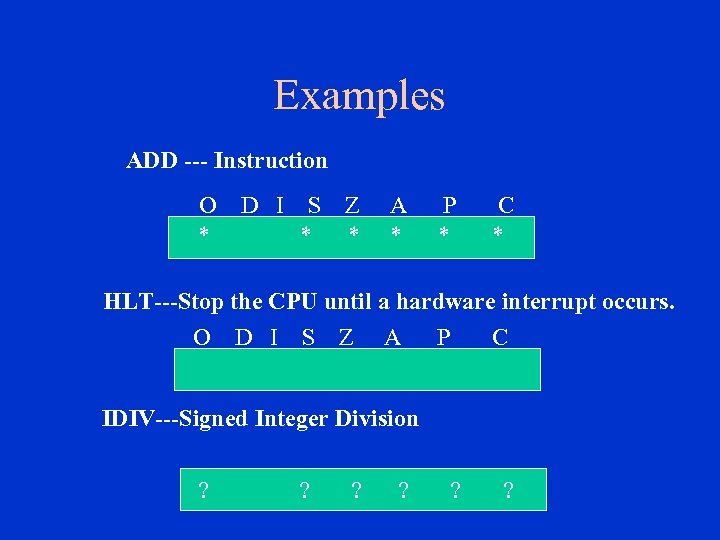
Examples ADD --- Instruction O D I S Z A P C * * * * HLT---Stop the CPU until a hardware interrupt occurs. O D I S Z A P C IDIV---Signed Integer Division ? ? ?

The Hello World Program • • • • • title Hello World Program (hello. asm) ; This program displays "Hello, world!". model small. stack 100 h. data message db "Hello, world!", 0 dh, 0 ah, '$'. code main proc mov ax, @data mov ds, ax mov ah, 9 mov dx, offset message int 21 h mov ax, 4 C 00 h int 21 h main endp end main

Arithmetic Instructions • • ADD and SUB instructions ADD reg, reg ADD mem, reg ADD reg, mem ADD reg, immed ADD mem, immed ADD accum, immed Flag O D I S Z A P C * * * * * • SUB has the similar instruction format

MS -Debug • Debug is a MS-DOS command which can be used to enter machine language into the computer either to create programs or test computer peripherals by receiving back various computer machine code.

ABOUT DEBUG • Debug is a method of looking at portions of your computer and writing assembly code to perform certain tasks on your computer. • MS-DOS 2. x - 4. x uses debug. com MS-DOS 5. x and above uses debug. exe

A History of MS-DEBUG • In 1980, Tim Paterson began working on a 16 -bit OS for the 8086 S-100 Bus card he had designed for SCP (Seattle Computer Products) the previous year. To help in getting QDOS (later called 86 -DOS) to work correctly, Tim created a debugger in a ROM chip; the code for that ROM version was released into the Public Domain. Later, Tim adapted the code to run as a. COM program under QDOS, and also added the ability to disassemble 8086 machine code.

• In the meantime, Microsoft® had been busy purchasing the rights to sell Tim's QDOS to IBM® for their 'secret' PC project. Tim was hired by Microsoft as the primary author of their first OS. When he completed his work on IBM's Personal Computer™ DOS 1. 00 in 1981, his DEBUG. COM utility was included with it. All the functionality that Tim put into DEBUG is still there and little has been added to it (the major exception being the Assemble command; added under DOS 2. 0).

Debug Availability • AVAILABILITYThe debug command is an external command is available in the below Microsoft Operating Systems. • All Versions of MS-DOS Windows 95 Windows 98 Windows ME Windows NT Windows 2000 Windows XP
![Debug Commands • • • • • ? assemble A [address] Compare C range Debug Commands • • • • • ? assemble A [address] Compare C range](https://present5.com/presentation/db167f389e0462a4255c3214a76cfb09/image-14.jpg)
Debug Commands • • • • • ? assemble A [address] Compare C range address dump D [range] enter E address [list] fill F range list go G [=address] [addresses] hex H value 1 value 2 (Learn 2's Complement!) input I port load L [address] [drive] [firstsector] [number] move M range address name N [pathname] [arglist] output O port byte Proceed P [=address] [number] quit Q. . (Learn this first!) Register R [register] search S range list trace T [=address] [number] unassemble U [range] write W [address] [drive] [firstsector] [number]

Debug • • • -F -D -E -T----Make sure you check the IP to see if its counts is pointing the right location. -R IP to change it -A 100 Mov dl, [0200] Mov [0201], dl Mov ax, 4 c 00(h) Int 21

Example • • Under Windows XP: 1. Click run and type cmd 2. type debug 3. type D 40: 0 and you will get a display screen with the first line looks as: • 0040: 0000 F 8 03 F 8 02 E 8 03 E 8 02 - 78 03 78 02 BC 03

The meaning of the line • F 8 03 F 8 02 E 8 03 E 8 02 78 03 7802 BC 03 • COM 1 COM 2 COM 3 COM 4 LPT 1 LPT 2 LPT 3 The above graph shows you what the feed back means as far as port, so if you see F 8 03, this would be an indication that COM 1 is being detected; if you see 00 00, this is an indication that it is not being detected, which could mean that hardware is bad or that it is disabled in CMOS.

Some Debug Routine Applications • TESTING PORTS CLEAR CMOS PRINTER TEST JOYSTICK TEST ERASE SECTOR 2 ERASE ALL HDD INFORMATION ERASE HDD AND CLEAR CMOS DISCHARGE OLD LAPTOP BATTERIES REBOOT YOUR COMPUTER CREATE A SLEEP FILE FOR DOS CHECK BIOS DATE VIDEO CARD TYPE

CHECK BIOS DATE • The below debug routine is to check the date of your BIOS. All BIOS dates on PC compatible computers is stored at memory address FFFF 5 h. To display the date of your BIOS do the following: • At the C: > type debug • - d FFFF: 5 L 8 • After typing the above command you should receive a string similar to: • FFFF: 0000 30 34 2 F-33 30 2 F 39 38 4/30/98 • The 4/30/98 would be the date of your computer BIOS.

Check Your Computer’s Video • -d c 000: 0040
![Debug • • Mov si, 0200 Mov ax, [si] Mov [0270], ax Mov ax, Debug • • Mov si, 0200 Mov ax, [si] Mov [0270], ax Mov ax,](https://present5.com/presentation/db167f389e0462a4255c3214a76cfb09/image-21.jpg)
Debug • • Mov si, 0200 Mov ax, [si] Mov [0270], ax Mov ax, 4 c 00 Int 21 -T -T -T
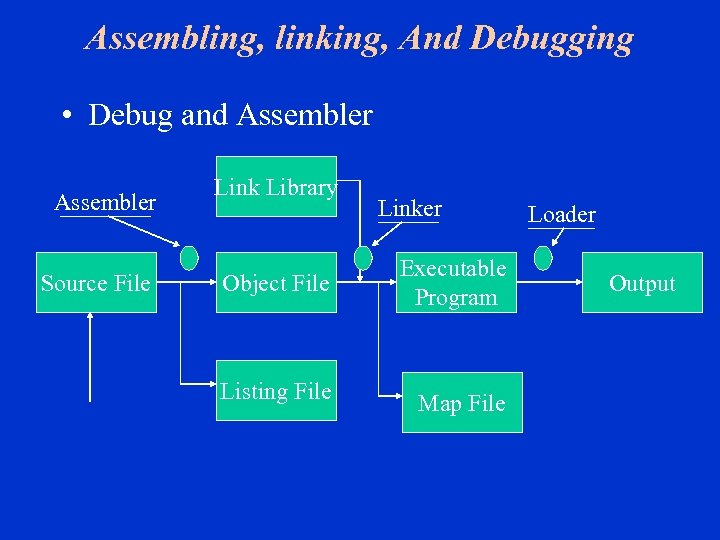
Assembling, linking, And Debugging • Debug and Assembler Source File Link Library Linker Object File Executable Program Listing File Map File Loader Output
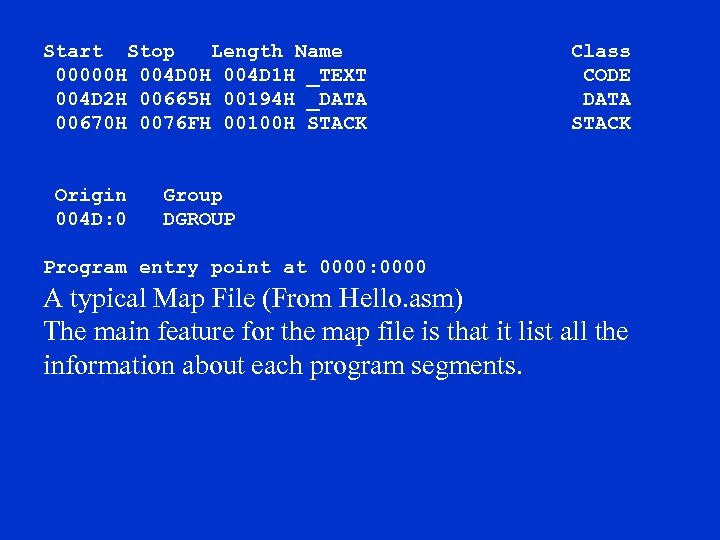
Start Stop Length Name Class 00000 H 004 D 1 H _TEXT CODE 004 D 2 H 00665 H 00194 H _DATA DATA 00670 H 0076 FH 00100 H STACK Origin Group 004 D: 0 DGROUP Program entry point at 0000: 0000 A typical Map File (From Hello. asm) The main feature for the map file is that it list all the information about each program segments.
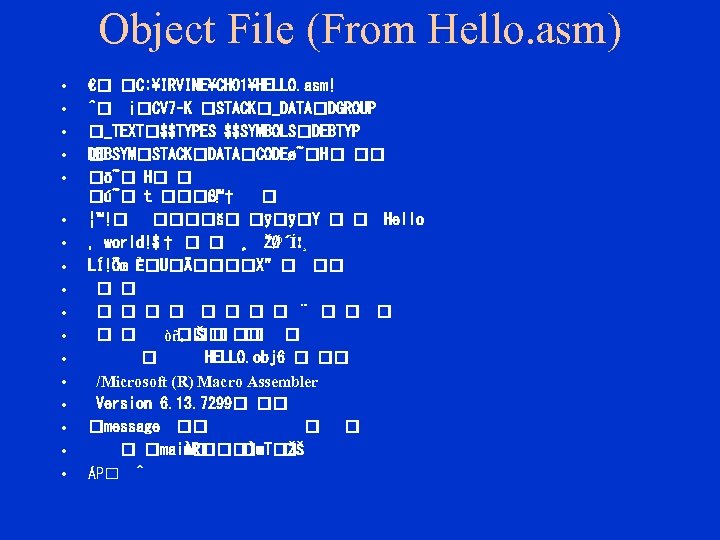
Object File (From Hello. asm) • • • • • € C: IRVINECH 01HELLO. asm! ˆ ¡ CV 7–K STACK _DATA DGROUP _TEXT $$TYPES $$SYMBOLS DEBTYP DEBSYM STACK DATA CODEø˜ H ö˜ H ú˜ t ß™ !† ¦™! š ÿ ÿ Y Hello , world!$† ¸ ŽØ´ º Í!¸ LÍ!Õœ È U Ä X” ¨ òñ, Š HELLO. obj 6 /Microsoft (R) Macro Assembler Version 6. 13. 7299 message main œ ÌR Ìv. T ŽŠ ÁP ^

Target Processor Directives • • • . 8086 ----8086, 8088. 186 --. 286 --. 386. 486. 586. 287. 387 When using. 386, the program can only run on 386 and above processors.
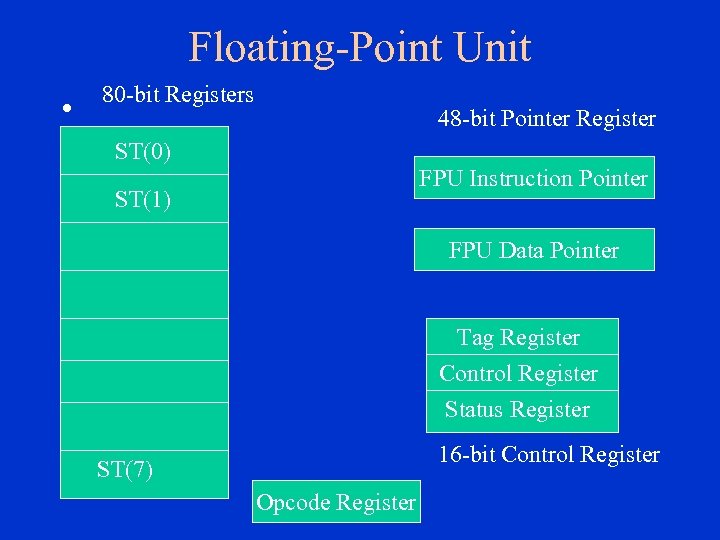
Floating-Point Unit • 80 -bit Registers 48 -bit Pointer Register ST(0) FPU Instruction Pointer ST(1) FPU Data Pointer Tag Register Control Register Status Register 16 -bit Control Register ST(7) Opcode Register

Debug and Debugger • MASM supplies a good 16 -bit debugger named Code View. • TASM supplies one named Turbo Debugger. • For 32 -bit Windows Console programs, the preferred debugger is Microsoft Visual Studio (msdev. exe), part of Microsoft Visual C++.
db167f389e0462a4255c3214a76cfb09.ppt