0ee2d953fe55dcc999caa1c6d7507dad.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Assembling the “Heart team” : Dynamics , Decision making and Collaboration During Procedures Alec Vahanian, FESC, FRCP Pr Alec Vahanian, FESC, FRCP (Edin. ) Bichat Hospital, Paris, France

Alec Vahanian, MD § Honoraria: § Valtech § Edwards Lifesciences § Medtronic § Abbott
(EACTS/ESC/EAPCI Position Statement, Eur Heart J, 2008; 29: 1463 -1470, Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 34 (2008) 1 -8, Eurointerv. 2008; 4: 193 -199)

The “Heart Team” Ø A group of valve specialists who collaborate to: ü Select the most appropriate procedure ü Perform the procedures ü Evaluate the results (EACTS/ESC/EAPCI Position Statement, Eur Heart J, 2008; 29: 1463 -1470, Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 34 (2008) 1 -8, Eurointerv. 2008; 4: 193 -199)
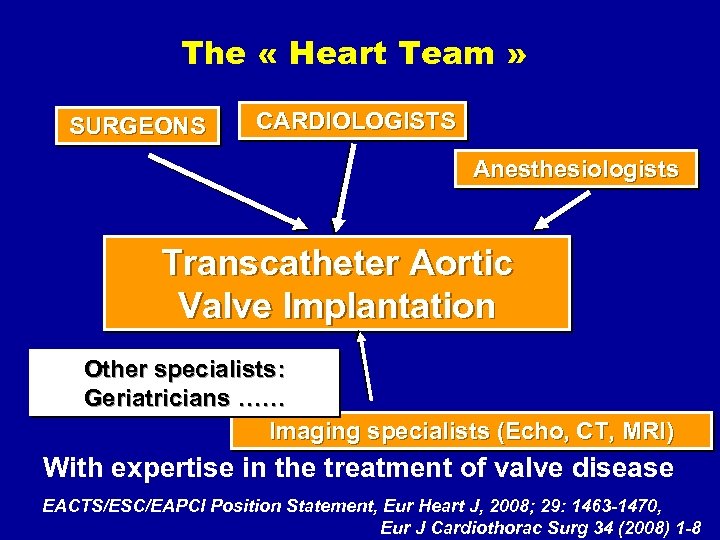
The « Heart Team » SURGEONS CARDIOLOGISTS Anesthesiologists Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Other specialists: Geriatricians …… Imaging specialists (Echo, CT, MRI) With expertise in the treatment of valve disease EACTS/ESC/EAPCI Position Statement, Eur Heart J, 2008; 29: 1463 -1470, Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 34 (2008) 1 -8

Risk-Benefit Assessment Ø Decision-making for intervention is multifactorial: ü Prognosis according to severity and consequences of valvular disease ü Risks and late consequences of intervention ü Patient life expectancy and quality of life ü Patient wishes after information ü Local resources, in particular results of surgery
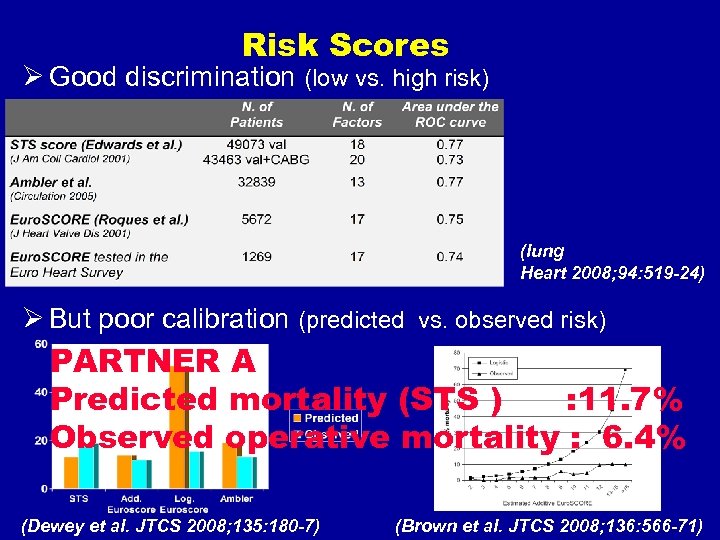
Risk Scores Ø Good discrimination (low vs. high risk) (Iung Heart 2008; 94: 519 -24) Ø But poor calibration (predicted vs. observed risk) PARTNER A Predicted mortality (STS ) : 11. 7% Observed operative mortality : 6. 4% (Dewey et al. JTCS 2008; 135: 180 -7) (Brown et al. JTCS 2008; 136: 566 -71)
Assessment of Frailty Surgeon’s eye-ball test and beyond !!!!
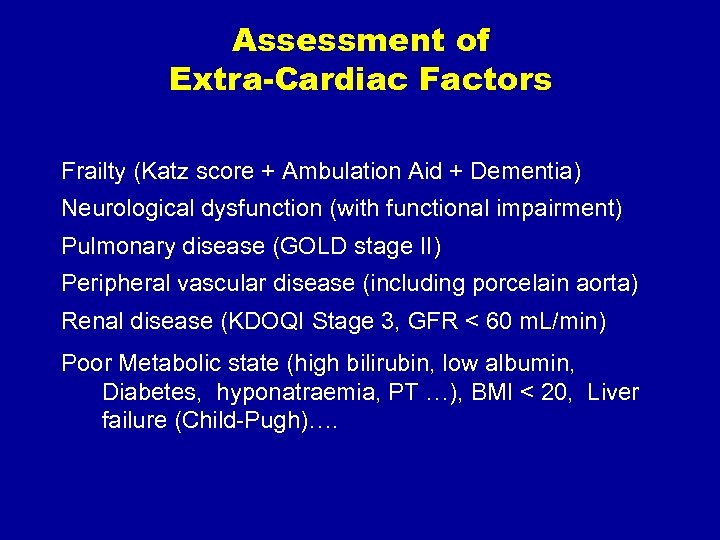
Assessment of Extra-Cardiac Factors Frailty (Katz score + Ambulation Aid + Dementia) Neurological dysfunction (with functional impairment) Pulmonary disease (GOLD stage II) Peripheral vascular disease (including porcelain aorta) Renal disease (KDOQI Stage 3, GFR < 60 m. L/min) Poor Metabolic state (high bilirubin, low albumin, Diabetes, hyponatraemia, PT …), BMI < 20, Liver failure (Child-Pugh)….
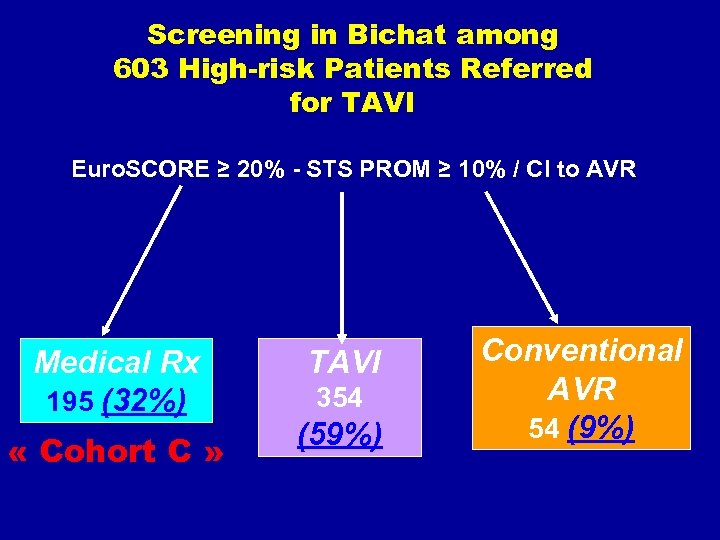
Screening in Bichat among 603 High-risk Patients Referred for TAVI Euro. SCORE ≥ 20% - STS PROM ≥ 10% / CI to AVR Medical Rx 195 (32%) « Cohort C » TAVI 354 (59%) Conventional AVR 54 (9%)

Needs Who Skills Ø Cardiologists/ Surgeons/ Anesthesiologists/ Geriatricians Ø Clinical/ echocardiography Ø Clinical

Risk-Benefit Assessment Ø Decision-making for intervention is multifactorial: ü Prognosis according to the severity and consequences of valvular disease ü Risks and late consequences of intervention ü Patient life expectancy and quality of life ü Patient wishes after information ü Local resources, in particular results of surgery ü Feasibility of transcatheter intervention
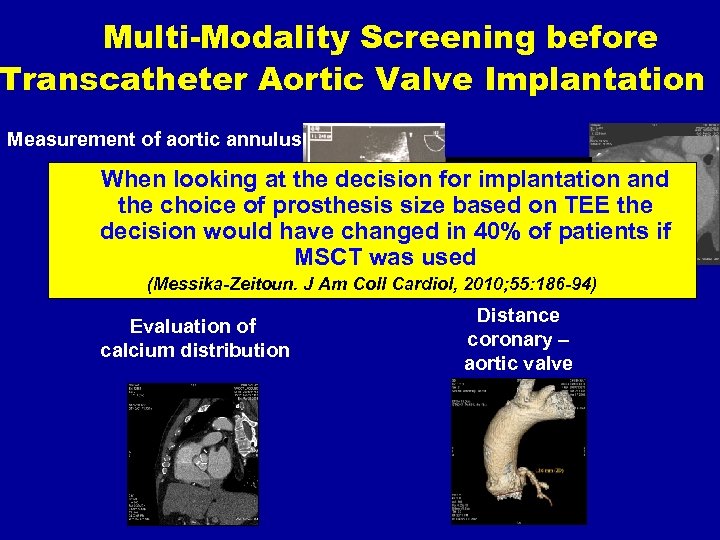
Multi-Modality Screening before Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Measurement of aortic annulus When looking at the decision for implantation and the choice of prosthesis size based on TEE the decision would have changed in 40% of patients if MSCT was used (Messika-Zeitoun. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2010; 55: 186 -94) Evaluation of calcium distribution Distance coronary – aortic valve
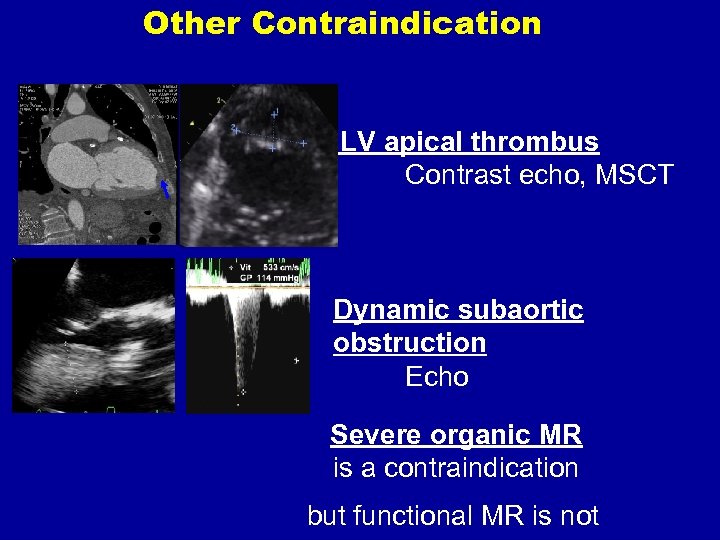
Other Contraindication LV apical thrombus Contrast echo, MSCT Dynamic subaortic obstruction Echo Severe organic MR is a contraindication but functional MR is not
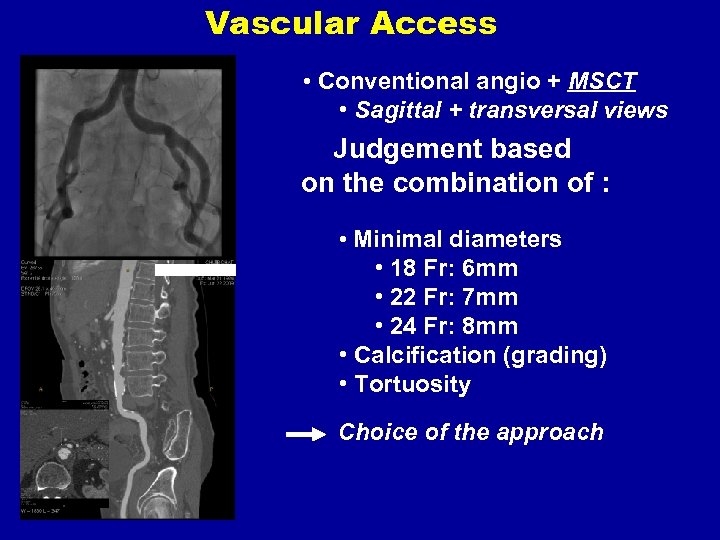
Vascular Access • Conventional angio + MSCT • Sagittal + transversal views Judgement based on the combination of : • Minimal diameters • 18 Fr: 6 mm • 22 Fr: 7 mm • 24 Fr: 8 mm • Calcification (grading) • Tortuosity Choice of the approach

Needs Who Skills Ø Cardiologists/ Surgeons Ø Cadiologists/ Surgeons/ Geriatricians Ø Cardiologists/ Radiologists/Surgeons Ø Clinical/ echocardiography Ø Clinical Ø Echocardiography / CT/ MRI

The “Heart Team” Ø A group of valve specialists who collaborate to: ü Select the most appropriate procedure ü Perform the procedures ü Evaluate the results (EACTS/ESC/EAPCI Position Statement, Eur Heart J, 2008; 29: 1463 -1470, Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 34 (2008) 1 -8, Eurointerv. 2008; 4: 193 -199)

Where Should we Perform? In cardiology and cardiac surgery centers
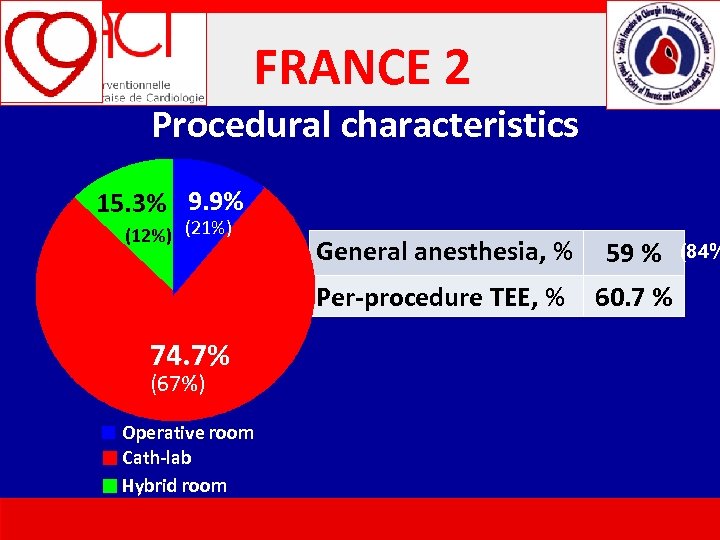
FRANCE 2 Procedural characteristics 15. 3% 9. 9% (12%) (21%) (67%) Operative room Cath-lab Hybrid room 59 % Per-procedure TEE, % 74. 7% General anesthesia, % 60. 7 % (84%
Echocardiography is Helpful in Monitoring the Procedure
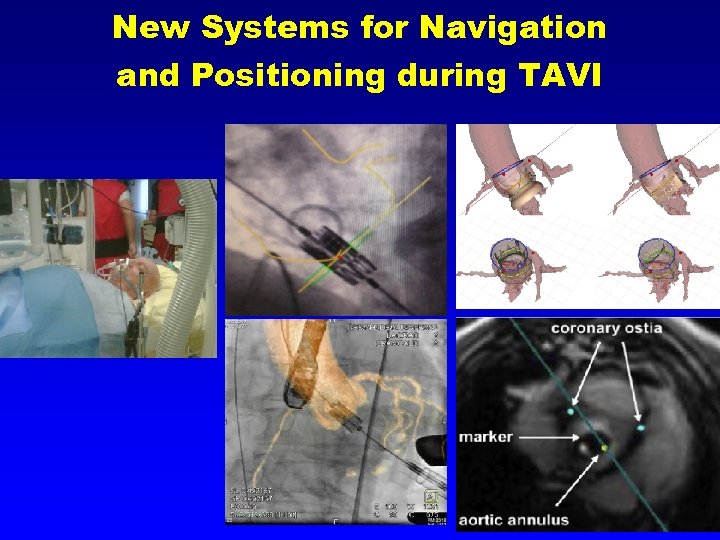
New Systems for Navigation and Positioning during TAVI
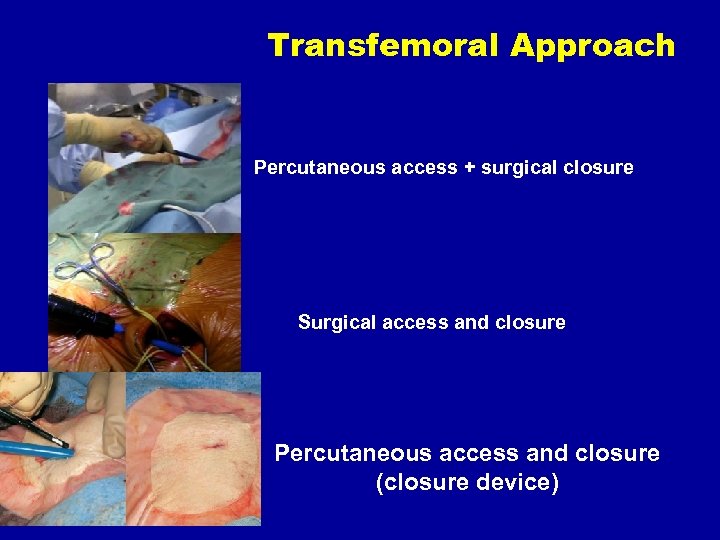
Transfemoral Approach Percutaneous access + surgical closure Surgical access and closure Percutaneous access and closure (closure device)
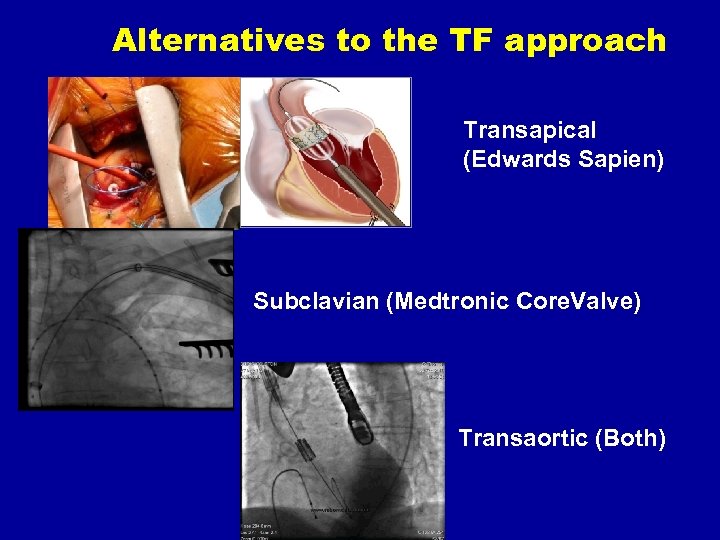
Alternatives to the TF approach Transapical (Edwards Sapien) Subclavian (Medtronic Core. Valve) Transaortic (Both)
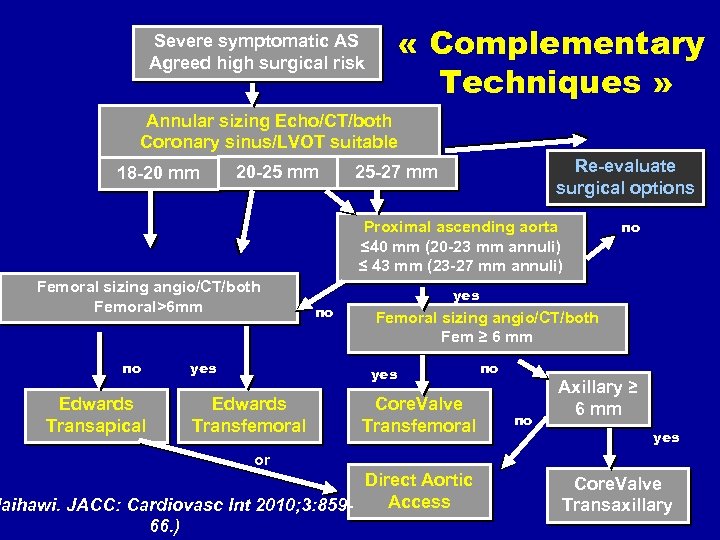
« Complementary Techniques » Severe symptomatic AS Agreed high surgical risk Annular sizing Echo/CT/both Coronary sinus/LVOT suitable 18 -20 mm 20 -25 mm Re-evaluate surgical options 25 -27 mm Proximal ascending aorta ≤ 40 mm (20 -23 mm annuli) ≤ 43 mm (23 -27 mm annuli) Femoral sizing angio/CT/both Femoral>6 mm no Edwards Transapical yes no yes Femoral sizing angio/CT/both Fem ≥ 6 mm yes Edwards Transfemoral no Core. Valve Transfemoral no no Axillary ≥ 6 mm yes or Direct Aortic Access laihawi. JACC: Cardiovasc Int 2010; 3: 85966. ) Core. Valve Transaxillary
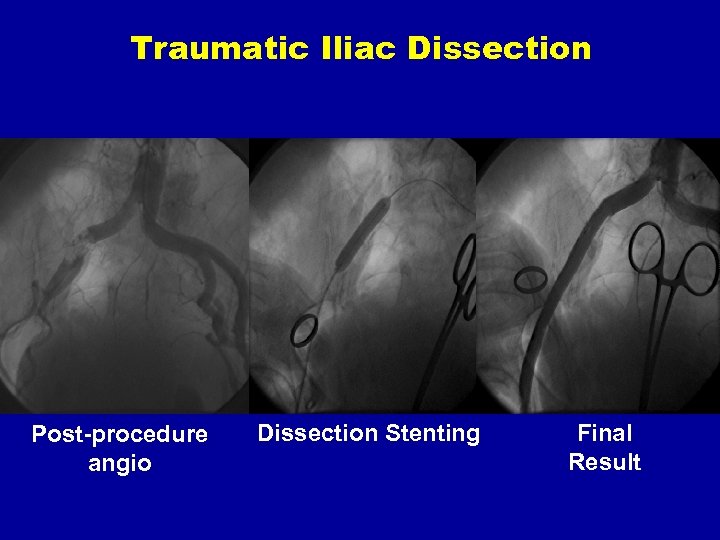
Traumatic Iliac Dissection Post-procedure angio Dissection Stenting Final Result
Rescue Surgery « Be prepared »

Needs Who Skills Ø Cardiologists/surgeons/ Geriatricians Ø Cardiologists/surgeons/ radiologists Ø Interventionists/ echocardiographists/ anesthesiologists/ surgeons/paramedical staff of cath lab Ø Clinical /echocardiography Ø Clinical Ø Echocardiography/CT Ø Working in a sterile environment/valvular catheterization/balloon valvuloplasty/vascular access/peripheral intervention /valve surgery/cardiac assistance

Needs Who Ø Interventionists/ anesthesiologists/ surgeons/ paramedical staff of cath lab and/or Ø Cardiologists/surgeons/ anesthesists/intensive care/EP specialists Skills Ø Working in a sterile environment/Valvular catheterization/balloon valvuloplasty/vascular access/peripheral intervention/monitoring/valve surgery/Cardiac assistance Ø Post operative care
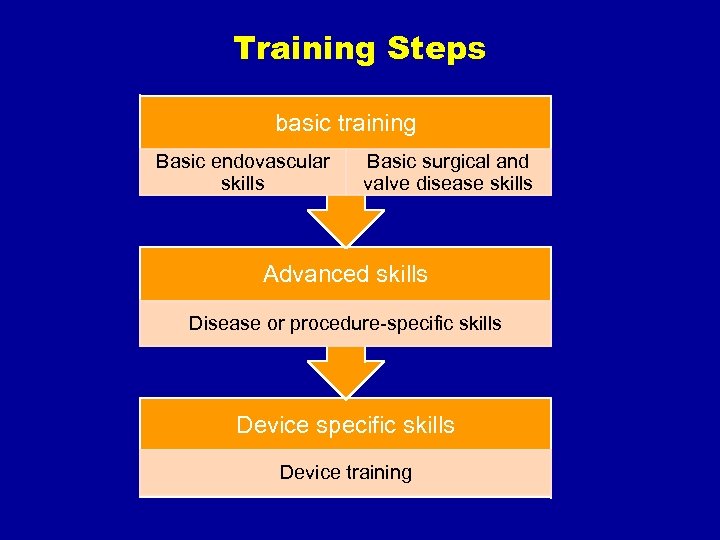
Training Steps basic training Basic endovascular skills Basic surgical and valve disease skills Advanced skills Disease or procedure-specific skills Device training

Accredited Programs vs Alternative Training Ø Current pathway ü Cross training ü Bench training and Simulators ü Animal lab ü PCR / TCT / CRT /JIM / ICI. . . ü Industry sponsored postgraduate courses ü Scientific Societies sponsored postgraduate courses Ø Accredited postgraduate residency or fellowship training program

The “Heart Team” Ø A group of valve specialists who collaborate to: ü Select most appropriate procedure ü Perform it ü Evaluate the results

Evaluation of TAVI Ø As well as enrolment in randomized clinical trials, data should be accumulated in registries with F. U. Ø In centres performing TAVI, multidisciplinary meetings should be held to discuss indications, procedural techniques, and case outcomes. Hospitals should keep proof of close medico-surgical collaboration and maintain a log of all patients referred to TAVI for continuous evaluation of the programme (EACTS/ESC/EAPCI Position Statement, Eur Heart J, 2008; 29: 1463 -1470, Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 34 (2008) 1 -8, Eurointerv. 2008; 4: 193 -199)

Conclusions Ø Team members must learn to collaborate, select the best candidates, perform the procedure and evaluate the results Ø Institutional and individual training is necessary Ø The appropriate environment must be available in terms of sterility, imaging, access to surgery and cardiac support

“We may have all come in different ships, but we’re in the same boat now” Martin Luther King, Jr.
0ee2d953fe55dcc999caa1c6d7507dad.ppt