820ff6e47c38473c58c20868fb72d4f8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Aspen Technology, Inc. : Currency Hedging Review
Aspen Technology, Inc. : Currency Hedging Review
 History and Overview • Specialized in the development of simulation software for customer in process manufacturing industries • Advanced System for Process Engineering (ASPEN) project conducted at the Massachusetts Intitutes of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge Massachusetts, from 1976 to 1981 • Founded in 1981 by Dr. Larry Evans, a professor of chemical engineering at MIT • Larry Evans"leadership in the development and application of integrated systems for modeling, simulation and optimization of industrial chemical process
History and Overview • Specialized in the development of simulation software for customer in process manufacturing industries • Advanced System for Process Engineering (ASPEN) project conducted at the Massachusetts Intitutes of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge Massachusetts, from 1976 to 1981 • Founded in 1981 by Dr. Larry Evans, a professor of chemical engineering at MIT • Larry Evans"leadership in the development and application of integrated systems for modeling, simulation and optimization of industrial chemical process
 History and Overview • In 1982 its first year of operations, Aspen. Tech lost USD 565, 000 on sales of USD 182, 000 • Over next 13 years Aspen. Tech’s sales grew rapidly as it became a major payer in the process simulation segment of the software industry. • 1995 company earned net income $5. 4 million on sales $57. 5 million. Aspen. Tech estimated that it commanded 50% of the simulation market for chemical sector. • 1995, it employed 417 people of which 265 ware based in the US and the remainder in office in 5 countries.
History and Overview • In 1982 its first year of operations, Aspen. Tech lost USD 565, 000 on sales of USD 182, 000 • Over next 13 years Aspen. Tech’s sales grew rapidly as it became a major payer in the process simulation segment of the software industry. • 1995 company earned net income $5. 4 million on sales $57. 5 million. Aspen. Tech estimated that it commanded 50% of the simulation market for chemical sector. • 1995, it employed 417 people of which 265 ware based in the US and the remainder in office in 5 countries.
 History and Overview • Aspen. Tech went public in USDD 31 million IPO which included a USD 18 Million primary offering and USD 13 Million secondary offering : – to finance further R&D – to acquire externally developed technologies – to allow early investors to monetize their holdings in the company, • Feb 1995, Aspentech conducted a $23 million public offering, which included a USD 1 million primary offering and USD 22 million secondary offering. • 1995, Aspen. Tech was the only one of the firms that specialized in simulation programs for chemical petroleum, and petrochemicals industries that was publicly traded.
History and Overview • Aspen. Tech went public in USDD 31 million IPO which included a USD 18 Million primary offering and USD 13 Million secondary offering : – to finance further R&D – to acquire externally developed technologies – to allow early investors to monetize their holdings in the company, • Feb 1995, Aspentech conducted a $23 million public offering, which included a USD 1 million primary offering and USD 22 million secondary offering. • 1995, Aspen. Tech was the only one of the firms that specialized in simulation programs for chemical petroleum, and petrochemicals industries that was publicly traded.
 Products (versi makalah) • Aspen Plus is the most popular product a steady state modeling system built around the core technology This product accounted 48% of sales in 1995 • Speed UP It was Aspen. Tech’s dynamic process modeling product commercialized in 1986 by Prosys Tecknology that Aspen. Tech purchased in 1991 • Max It is a less powerful version of Aspen Plus • Advent A software to optimize the tradeoff between capital expenditures for energy saving heat exchangers and the energy saving realized
Products (versi makalah) • Aspen Plus is the most popular product a steady state modeling system built around the core technology This product accounted 48% of sales in 1995 • Speed UP It was Aspen. Tech’s dynamic process modeling product commercialized in 1986 by Prosys Tecknology that Aspen. Tech purchased in 1991 • Max It is a less powerful version of Aspen Plus • Advent A software to optimize the tradeoff between capital expenditures for energy saving heat exchangers and the energy saving realized
 Product Portfolio (versi makalah) • Properties PLUS It is a database of chemicals properties underlying its other products, popular with customers ~ developed in-house modeling software • Other modules – offers to the customers ~ license separately – use with its other products to model subsystems used in highly specialized chemicals processing application.
Product Portfolio (versi makalah) • Properties PLUS It is a database of chemicals properties underlying its other products, popular with customers ~ developed in-house modeling software • Other modules – offers to the customers ~ license separately – use with its other products to model subsystems used in highly specialized chemicals processing application.
 Product Portfolio (versi web) • Process Engineering – – – – Process simulation Chemicals (10 products : Aspen. Plus) Process simulation Oil&Gas (8 products : Aspen. HYSYS) Process simulation Refining (11 products : Aspenadsim+) Process simulation Batch/Pharma (8 products : Aspenproperties) Model Deployment (3 products : Aspen. Modelrunner) Equipment modeling (8 products : Aspen. Acol+) Basic Engineering (2 products : Aspen. Kbase) Economic Evaluation (3 products : Aspn Icarus Project Manager) • Advance Process Control (14 products : Aspen Apollo, Aspen IQ) • Planning & Scheduling (10 products : Aspen Advisor, Aspen MBO) • Supply & Distribution (3 products : Aspen Retail) • Production Management & Execution (16 products : Aspen 0 server)
Product Portfolio (versi web) • Process Engineering – – – – Process simulation Chemicals (10 products : Aspen. Plus) Process simulation Oil&Gas (8 products : Aspen. HYSYS) Process simulation Refining (11 products : Aspenadsim+) Process simulation Batch/Pharma (8 products : Aspenproperties) Model Deployment (3 products : Aspen. Modelrunner) Equipment modeling (8 products : Aspen. Acol+) Basic Engineering (2 products : Aspen. Kbase) Economic Evaluation (3 products : Aspn Icarus Project Manager) • Advance Process Control (14 products : Aspen Apollo, Aspen IQ) • Planning & Scheduling (10 products : Aspen Advisor, Aspen MBO) • Supply & Distribution (3 products : Aspen Retail) • Production Management & Execution (16 products : Aspen 0 server)
 Sales & Marketing • 1995, licensed to more than 450 companies ~ chemical industry and 350 univerities • The selling cycle for process modelling software was long (6 -12 months) • Aspen. Tech charged a premium over competitors products, raise licensing fees three times (1998 -1995)~10% • Customer loyalty – Over 90% renewed their software – 1994 : 34% revenue from software renewal; 34% from expansion from existing customer
Sales & Marketing • 1995, licensed to more than 450 companies ~ chemical industry and 350 univerities • The selling cycle for process modelling software was long (6 -12 months) • Aspen. Tech charged a premium over competitors products, raise licensing fees three times (1998 -1995)~10% • Customer loyalty – Over 90% renewed their software – 1994 : 34% revenue from software renewal; 34% from expansion from existing customer
 Sales & Marketing • United States : – Directs sales force – Earned combination of salary & commission • Sales subsidiaries : UK, Japan, Hong. Kong, Brussels – Serve local & regional markets via directs sales forces • Licensed software for a non-cancelable term ~ 3 or 5 years • Charge : – annual fee x license term (year) – Interest rate 9. 5% - 11% currently 12% • Customer were more likely to buy software priced in local currency
Sales & Marketing • United States : – Directs sales force – Earned combination of salary & commission • Sales subsidiaries : UK, Japan, Hong. Kong, Brussels – Serve local & regional markets via directs sales forces • Licensed software for a non-cancelable term ~ 3 or 5 years • Charge : – annual fee x license term (year) – Interest rate 9. 5% - 11% currently 12% • Customer were more likely to buy software priced in local currency
 Risk Exposure 1. Foreign Exchange Risk – – sell software in local currencies installment from three-to-five years creates foreign exchange exposure exchange rate fluctuations 52% revenue generated from foreign company with following revenues figures: • • Europe 31% Asia 12% Other countries 9% In United State 48%. Risk exposure are might be applicable : – – Transaction Exposure (High) most the costumer operated outside of US Translation Exposure (Low) convert foreign currency financial statements into a single currency (USD).
Risk Exposure 1. Foreign Exchange Risk – – sell software in local currencies installment from three-to-five years creates foreign exchange exposure exchange rate fluctuations 52% revenue generated from foreign company with following revenues figures: • • Europe 31% Asia 12% Other countries 9% In United State 48%. Risk exposure are might be applicable : – – Transaction Exposure (High) most the costumer operated outside of US Translation Exposure (Low) convert foreign currency financial statements into a single currency (USD).
 Risk Exposure 2. Interest Rate Risk (low) – Aspen. Tech debt using US dollar currency fix interest rate and mid term (3 years) – place a seasonal line-of-credit facility with a New England Bank
Risk Exposure 2. Interest Rate Risk (low) – Aspen. Tech debt using US dollar currency fix interest rate and mid term (3 years) – place a seasonal line-of-credit facility with a New England Bank
 Risk Exposure 3. Credit Risk – Credit risk (default risk) in high exposure level • • • – 2 sources probability trigger this risk: • • 4. growing rapidly customer choose to defer payment of their license over the life of the contract Ex: Aspen. Tech was liable for $ 4, 6 million of this amount under limited recourse agreement Unwilling (Low) most of the customers are a loyal customer Unable (High) depend on the type of business of customer Liquidity Risk • • • many of its customers chose to defer payment of their licenses over the life of the contract the company usually experienced an operating cash shortfall Ex: the firm booked revenue of USD 57. 5 million, yet receive cash payments directly from customers of only $38. 5 million (66. 96%).
Risk Exposure 3. Credit Risk – Credit risk (default risk) in high exposure level • • • – 2 sources probability trigger this risk: • • 4. growing rapidly customer choose to defer payment of their license over the life of the contract Ex: Aspen. Tech was liable for $ 4, 6 million of this amount under limited recourse agreement Unwilling (Low) most of the customers are a loyal customer Unable (High) depend on the type of business of customer Liquidity Risk • • • many of its customers chose to defer payment of their licenses over the life of the contract the company usually experienced an operating cash shortfall Ex: the firm booked revenue of USD 57. 5 million, yet receive cash payments directly from customers of only $38. 5 million (66. 96%).
 Management Risk Perform by Aspen. Tech • Foreign Exchange Risk eliminated all sales transaction exposure arising from foreign currency denominated license contract inline with its risk management policy by doing hedging : – Sale non USD installment receivable for USD – forward currency agreement • Credit Risk – Aspen. Tech has not managed the risk of the uncollectible installment – The contract with GE and Sanwa in selling the account receivable has limited recourse agreement • Liquidity Risk – To manage its liquidity risk in order to cover their day to day operation, Aspen. Tech sell its receivable to GE and Sanwa and other financial institution. –Aspen. Tech also has debt to Massachusetts Capital Resources – placed a seasonal line of credit facility with New England bank.
Management Risk Perform by Aspen. Tech • Foreign Exchange Risk eliminated all sales transaction exposure arising from foreign currency denominated license contract inline with its risk management policy by doing hedging : – Sale non USD installment receivable for USD – forward currency agreement • Credit Risk – Aspen. Tech has not managed the risk of the uncollectible installment – The contract with GE and Sanwa in selling the account receivable has limited recourse agreement • Liquidity Risk – To manage its liquidity risk in order to cover their day to day operation, Aspen. Tech sell its receivable to GE and Sanwa and other financial institution. –Aspen. Tech also has debt to Massachusetts Capital Resources – placed a seasonal line of credit facility with New England bank.
 Recommendation • Aspen. Tech’s should reexamine the firm risk management policies and practices in light of the changes : – – – • over the past year Aspen. Tech’s international sales had remained a substantial portion of its revenues the firm international expenses had increase a slightly faster rate than its international revenue Aspen. Tech had gone from private company into a publicly traded company Aspen. Tech’s should review and determine an acceptable level of risk. It involves determining reasonable level of risk in-line with appropriate opportunity to gain
Recommendation • Aspen. Tech’s should reexamine the firm risk management policies and practices in light of the changes : – – – • over the past year Aspen. Tech’s international sales had remained a substantial portion of its revenues the firm international expenses had increase a slightly faster rate than its international revenue Aspen. Tech had gone from private company into a publicly traded company Aspen. Tech’s should review and determine an acceptable level of risk. It involves determining reasonable level of risk in-line with appropriate opportunity to gain
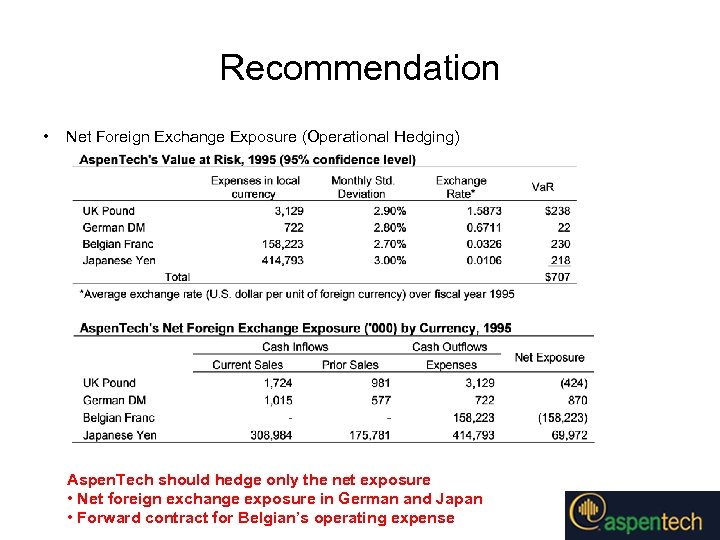 Recommendation • Net Foreign Exchange Exposure (Operational Hedging) Aspen. Tech should hedge only the net exposure • Net foreign exchange exposure in German and Japan • Forward contract for Belgian’s operating expense
Recommendation • Net Foreign Exchange Exposure (Operational Hedging) Aspen. Tech should hedge only the net exposure • Net foreign exchange exposure in German and Japan • Forward contract for Belgian’s operating expense
 Recommendation • Liquidity & Credit Risk – Aspen. Tech should look other possibility to deal with other financial institution to increase their bargaining position to GE and Sanwa With higher bargaining position, Aspen. Tech can get lower cost and better position in managing their credit risk – Maximize in selling long term receivable first
Recommendation • Liquidity & Credit Risk – Aspen. Tech should look other possibility to deal with other financial institution to increase their bargaining position to GE and Sanwa With higher bargaining position, Aspen. Tech can get lower cost and better position in managing their credit risk – Maximize in selling long term receivable first
 Recommendation • Others Hedging Instrument : – Plain-Vanilla Options • give the buyer of the option the right but not the obligation to buy (call) or sell (put) a specific amount of currency at a predetermined strike price (exchange rate • High cost – Average-Rate Options • Spot rate are calculated as an average over a period • Transaction possible during the expiry period at several predetermined dates • Strike rate can be fixed or floating – Knock-in/knock-out Options • Does not provide full protection • The key is in determining the barrier rate • Low cost – Cross-currency transactions – Foreign currency money-market borrowing
Recommendation • Others Hedging Instrument : – Plain-Vanilla Options • give the buyer of the option the right but not the obligation to buy (call) or sell (put) a specific amount of currency at a predetermined strike price (exchange rate • High cost – Average-Rate Options • Spot rate are calculated as an average over a period • Transaction possible during the expiry period at several predetermined dates • Strike rate can be fixed or floating – Knock-in/knock-out Options • Does not provide full protection • The key is in determining the barrier rate • Low cost – Cross-currency transactions – Foreign currency money-market borrowing
 Recommendation • Others Hedging Instrument : – Cross-currency transactions • transaction basically does not provide ability to hedge or secure any risk • provide probability of arbitrage if there is a difference between cross rate and indirect rate. – Foreign currency money-market borrowing • Borrowing in the money market, rather difficult to use since the company need to determine level of debt that matched with its cash inflow from other matched currency
Recommendation • Others Hedging Instrument : – Cross-currency transactions • transaction basically does not provide ability to hedge or secure any risk • provide probability of arbitrage if there is a difference between cross rate and indirect rate. – Foreign currency money-market borrowing • Borrowing in the money market, rather difficult to use since the company need to determine level of debt that matched with its cash inflow from other matched currency


