d6febf307b8ba03483f4fefe82a13a32.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Asian Development Bank Statistical Capacity Building 21 July 2008 21/07/2008

Outline Introduction Need for statistical capacity building Shortfalls Revised strategy for sustainability Sustainability of SCB in recipient countries Inter agency collaboration 21/07/2008 2

Introduction • ADB has history of technical assistance (TA) in statistical capacity building (SCB) since 1974 • Only development agency in region with a SCB TA program • Assist in SCB activities through country specific TA programs or regional technical assistance (RETA) programs – Country specific TA (21 developing member countries have benefited) – Regional technical TA (all 44 developing member countries have benefited) 21/07/2008 3

Within ADB, the Economics and Research Dept. has been the prime mover of statistical capacity building • Areas of SCB focused on: – developing skills on national accounts, price statistics, services sector statistics, poverty statistics, developing statistical plans, statistics act etc – resource transfer to underwrite statistical operation (surveys – household and establishment) – procurement of equipment • Significant strides have been made, but need for SCB TA still remains 21/07/2008 4
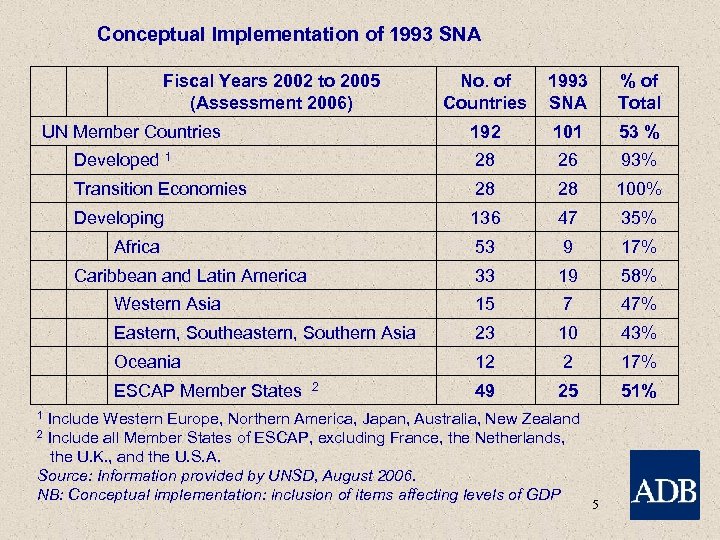
Conceptual Implementation of 1993 SNA No. of Countries 1993 SNA % of Total UN Member Countries 192 101 53 % Developed 1 28 26 93% Transition Economies 28 28 100% Developing 136 47 35% 53 9 17% 33 19 58% Fiscal Years 2002 to 2005 (Assessment 2006) Africa Caribbean and Latin America Western Asia 15 7 47% Eastern, Southern Asia 23 10 43% Oceania 12 2 17% ESCAP Member States 2 49 25 51% 1 Include Western Europe, Northern America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand 2 Include all Member States of ESCAP, excluding France, the Netherlands, the U. K. , and the U. S. A. Source: Information provided by UNSD, August 2006. NB: Conceptual implementation: inclusion of items affecting levels of GDP 5
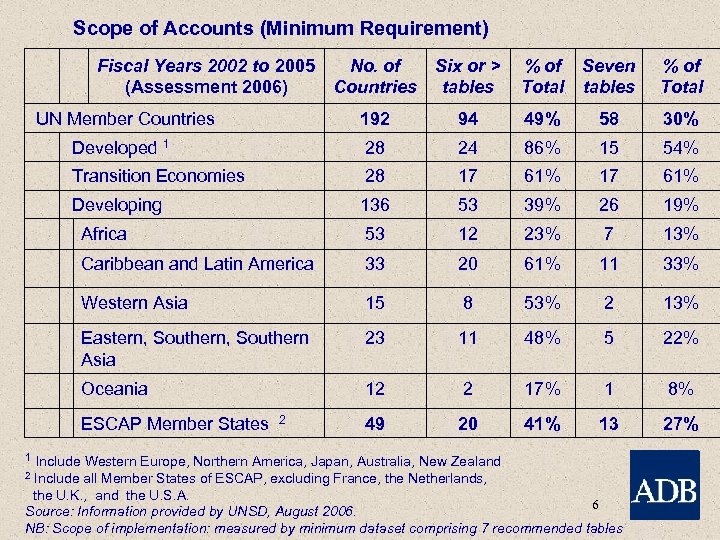
Scope of Accounts (Minimum Requirement) Fiscal Years 2002 to 2005 No. of (Assessment 2006) Countries UN Member Countries Six or > tables % of Total Seven tables % of Total 192 94 49% 58 30% Developed 1 28 24 86% 15 54% Transition Economies 28 17 61% Developing 136 53 39% 26 19% Africa 53 12 23% 7 13% Caribbean and Latin America 33 20 61% 11 33% Western Asia 15 8 53% 2 13% Eastern, Southern Asia 23 11 48% 5 22% Oceania 12 2 17% 1 8% ESCAP Member States 2 49 20 41% 13 27% 1 Include Western Europe, Northern America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand 2 Include all Member States of ESCAP, excluding France, the Netherlands, the U. K. , and the U. S. A. 6 Source: Information provided by UNSD, August 2006. NB: Scope of implementation: measured by minimum dataset comprising 7 recommended tables

Need for SCB assistance Strengthen national statistical system: – Generate timely, reliable and quality statistics for efficient administration, management and evidence-based policy making – Ability to collect primary data – Generate internationally comparable statistics • Assisting countries with weak statistical systems to build statistical infrastructure 21/07/2008 7

Shortfalls • Gap filling: – substantial funding shortfall in NSO – satisfy an immediate demand of key users • Based on ad hoc requests by countries • SCB done on a piecemeal basis - devoid of any sustainability • Did not involve a systematic assessment of needs and relevance from: – standpoint of client county’s medium and long term statistical development strategy – in context of ADB’s own priority goals for statistical development in the region 21/07/2008 8

Revised strategy for sustainability 1. Systematic – conduct diagnostic studies with direct country involvement • Examine statistical strength and weaknesses • Identify obstacles and positive factors for the development of statistics • Access availability of budgets for: – – 21/07/2008 Statistical development Human resources Information technology Field operation (surveys) 9

2. Long-term SCB programs drawn factoring in • Institutional environment – – Availability of statistical legislative framework Management and organization of statistical system Level of budgetary resources for statistical activities Reflect national priorities • Stakeholder consultations – NSOs; line ministries 3. SCB to be results oriented • Clear and measurable targets – Design and monitoring framework drawn up with clearly stated outcomes and outputs 21/07/2008 10

• Appropriate conditionalities included – Country consent – Memorandum of Agreement - to promote and ensure government ownership and buy-in – Milestones to achieve outputs are set – Workshops to present results and assess results – Release of funds upon satisfactory attainment of predetermined and agreed milestones 4. Integrate SCB programs into the Country Partnership Strategy (CPS) for long-term commitment 5. Promoting use administrative data sources – Improve administrative data (AD) sources – Country assessment studies of AD system – Manual on Use of AD sources 21/07/2008 11

Sustainability of SCB in recipient country • Improved legal framework (statistics act) – NSOs mandated as primary source of official statistics • Statistical master plan (or a national statistics development strategy) with buy-in from government/Central Bank • programmed/structured implementation of statistical activities • set priorities based on budget allocation • secure government commitment to invest in SCB 21/07/2008 12

• NSOs must remain relevant - conduct regular dialogue with users • produce timely, reliable and relevant statistics • understand priorities of users and developments in the economic world • ability to respond in a timely manner • Human resource issues • In developing countries staff costs typically represent more than 75% of budget (Source: WB) • Chronic budgetary shortfall for routine statistical activities • High staff turnover undermine the effectiveness of training • Need to develop skills and keep up with technical developments • Limited supply of skills • Limited flexibilities • Small staff size • Limited training opportunities 21/07/2008 13

Inter agency collaboration in SCB • Training • Organizing training seminars and workshops – make it relevant to regional circumstances – immediate relevance to countries in the region • Targeted technical assistance, advisory missions and consultancies • Advocacy workshops on need for statistics for policy making 21/07/2008 14

Technical cooperation The 2005 ICP modal Governance structure premised on • Regional coordinating agencies working closely with beneficiary countries at regional level • World Bank working with regional coordinating agencies at global level The IMF-WB modal in Anglophone Africa Formal separation of responsibilities • the IMF covers macroeconomic and financial statistics • World Bank covers socio-demographic statistics 21/07/2008 15

Thank you 21/07/2008 16
d6febf307b8ba03483f4fefe82a13a32.ppt