0ed684e28d617958c684572c318e99aa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

Asian Banker Research Regulators coming with a vengeance Following the mis-selling incidents, banks must improve sales processes and customer protection March 2010 Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 1

Agenda § Impact of mis-selling incidents on Asian customers § Analysis of pre-crisis regulatory guidelines that led to the misselling incidents § Asian regulators’ responses Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 2
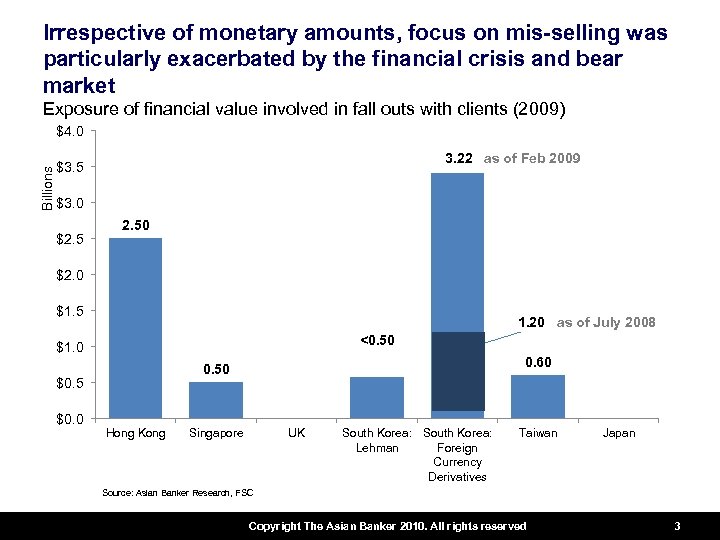
Irrespective of monetary amounts, focus on mis-selling was particularly exacerbated by the financial crisis and bear market Exposure of financial value involved in fall outs with clients (2009) Billions $4. 0 3. 22 3. 40 as of Feb 2009 $3. 5 $3. 0 $2. 50 $2. 0 $1. 5 1. 20 as of July 2008 <0. 50 $1. 0 $0. 5 $0. 0 0. 60 0. 50 Hong Kong Singapore UK South Korea: Lehman Foreign Currency Derivatives Taiwan Japan Source: Asian Banker Research, FSC Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 3
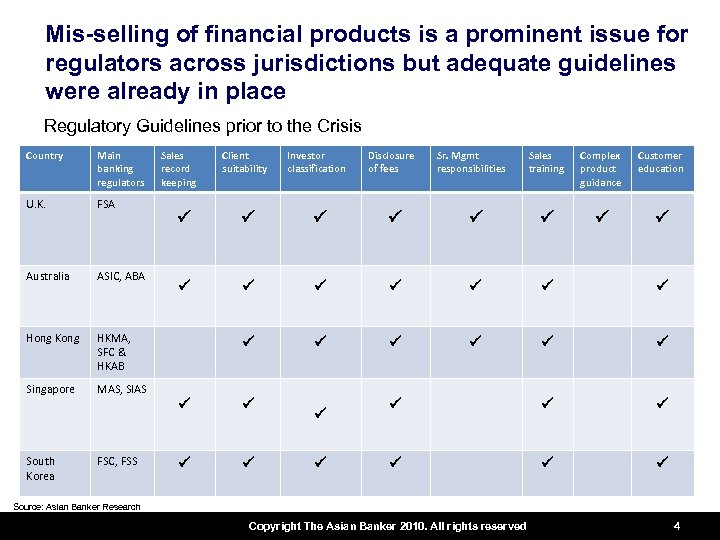
Mis-selling of financial products is a prominent issue for regulators across jurisdictions but adequate guidelines were already in place Regulatory Guidelines prior to the Crisis Country Main banking regulators U. K. FSA Australia ASIC, ABA Hong Kong HKMA, SFC & HKAB Singapore Sales record keeping Client suitability MAS, SIAS FSC, FSS Disclosure of fees Sr. Mgmt responsibilities Sales training Complex product guidance Customer education P P P P P P P South Korea Investor classification P P P Source: Asian Banker Research Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 4

Principle based recommendations by the FSA Authority in the UK will come along with larger and heavier fines § Performance related pay to be based on long term performance, and to be calculated on profits, not revenues § Inform customers in a sufficient, appropriate and comprehensible manner § Customer service must remain prompt, efficient and fair § Distributors should identify the target market and customer suitability § Products should be stress tested prior to being sold § Firms must establish, implement and maintain effective, transparent customer complaint-handling systems § Larger and heavier fines proposed for misconduct § FSA refused to regulate performance based payment at the senior executive and RM level Source: FSA U. K. Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 5 5
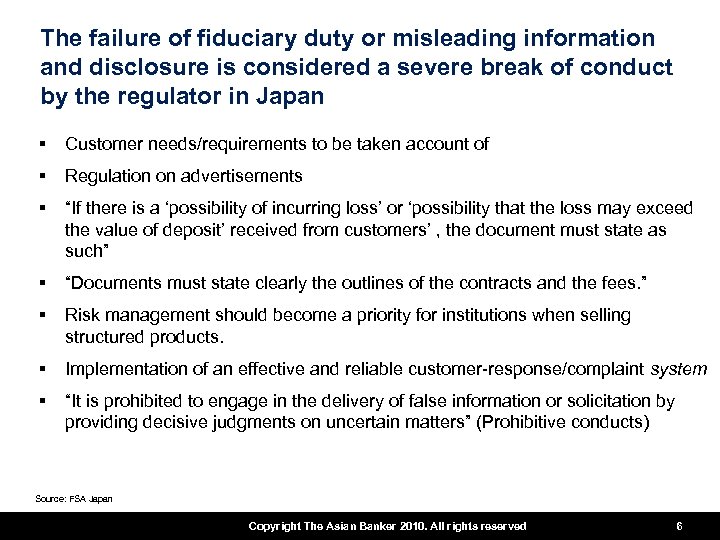
The failure of fiduciary duty or misleading information and disclosure is considered a severe break of conduct by the regulator in Japan § Customer needs/requirements to be taken account of § Regulation on advertisements § “If there is a ‘possibility of incurring loss’ or ‘possibility that the loss may exceed the value of deposit’ received from customers’ , the document must state as such” § “Documents must state clearly the outlines of the contracts and the fees. ” § Risk management should become a priority for institutions when selling structured products. § Implementation of an effective and reliable customer-response/complaint system § “It is prohibited to engage in the delivery of false information or solicitation by providing decisive judgments on uncertain matters” (Prohibitive conducts) Source: FSA Japan Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 6 6

The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) highlighted a variety of reasons that led to the mis-selling incidences among several banks § § Risk ratings assigned to notes were inconsistent with risk warnings § § § Incompliance with regulation § § Notes sold on an “execution-only” basis § § Relationship Managers not trained before marketing and selling the products Warnings on risk were not prominently presented and clearly explained to the client Products often marketed as structured deposits, yet greatly differed to deposits. Miss-selling of notes with a high risk-rating to clients with a low or normal risk profile Relationship Managers not equipped with complete information about the products. Relationship Managers did miss or skip required training Source: Monetary Authority of Singapore Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 7
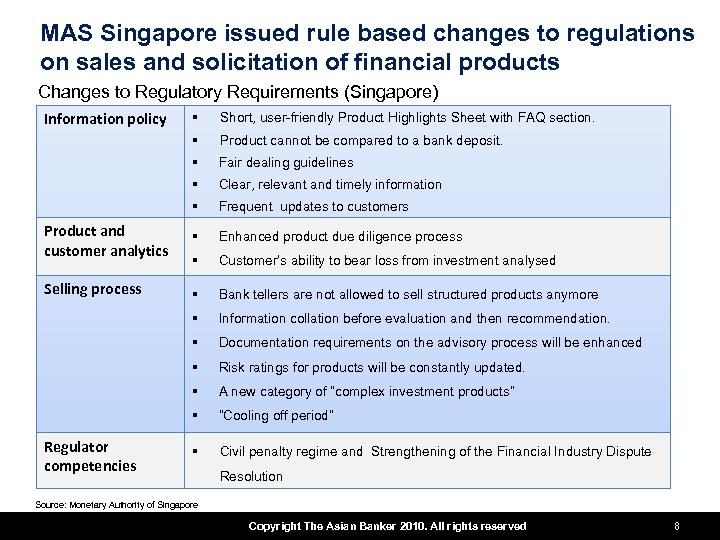
MAS Singapore issued rule based changes to regulations on sales and solicitation of financial products Changes to Regulatory Requirements (Singapore) Information policy § Short, user-friendly Product Highlights Sheet with FAQ section. § Product cannot be compared to a bank deposit. § Fair dealing guidelines § Clear, relevant and timely information § Frequent updates to customers Product and customer analytics § Enhanced product due diligence process § Customer’s ability to bear loss from investment analysed Selling process § Bank tellers are not allowed to sell structured products anymore § Information collation before evaluation and then recommendation. § Documentation requirements on the advisory process will be enhanced § Risk ratings for products will be constantly updated. § A new category of “complex investment products” § “Cooling off period” § Civil penalty regime and Strengthening of the Financial Industry Dispute Regulator competencies Resolution Source: Monetary Authority of Singapore Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 8

HKMA in Hong Kong highlighted also structural reasons for the escalation of mis-selling products § § Structured investment products were targeted at retail banking customers § § § High pressure, aggressive sales tactics § No clear differentiation between traditional deposit banking and retail securities business Often, substantially the same product, with slight variance in structure, was distributed by different banks Customer complaints were often given low priority Lack of accountability Distributors selling the products did not have full knowledge about products Poor, outdated risk profiling for customers and products A mismatch between the customers’ risk profiles and the products’ risk rating Source: Monetary Authority of Singapore Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 9
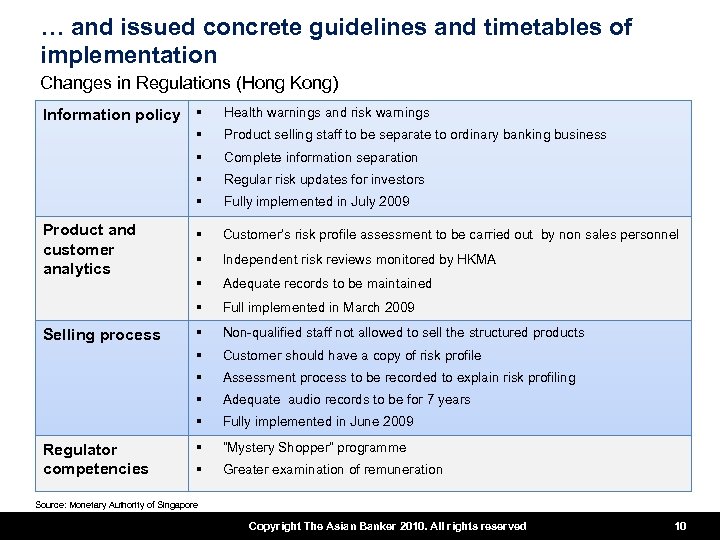
… and issued concrete guidelines and timetables of implementation Changes in Regulations (Hong Kong) Information policy § Health warnings and risk warnings § § Fully implemented in July 2009 § Customer’s risk profile assessment to be carried out by non sales personnel § Independent risk reviews monitored by HKMA § Adequate records to be maintained § Full implemented in March 2009 § Non-qualified staff not allowed to sell the structured products § Customer should have a copy of risk profile § Assessment process to be recorded to explain risk profiling § Adequate audio records to be for 7 years § Regulator competencies Regular risk updates for investors § Selling process Complete information separation § Product and customer analytics Product selling staff to be separate to ordinary banking business Fully implemented in June 2009 § “Mystery Shopper” programme § Greater examination of remuneration Source: Monetary Authority of Singapore Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 10
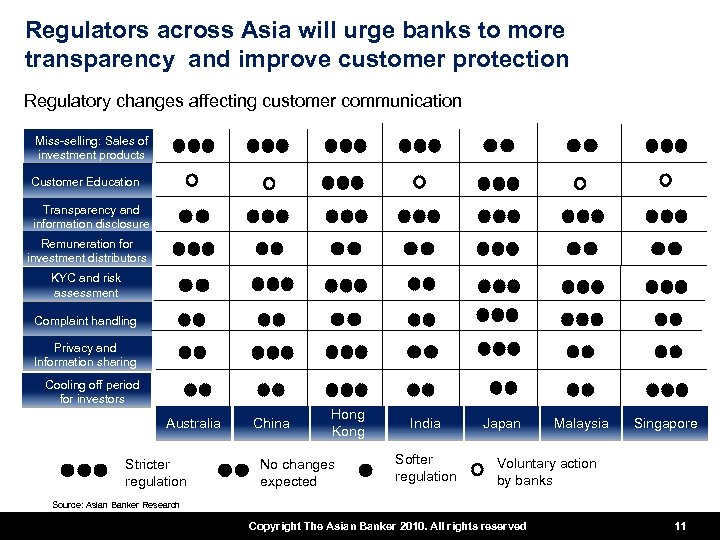
Regulators across Asia will urge banks to more transparency and improve customer protection Regulatory changes affecting customer communication Miss-selling: Sales of investment products Customer Education Transparency and information disclosure Remuneration for investment distributors KYC and risk assessment Complaint handling Privacy and Information sharing Cooling off period for investors Australia Stricter regulation China Hong Kong No changes expected India Softer regulation Japan Malaysia Singapore Voluntary action by banks Source: Asian Banker Research Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 11

In addition to existing compliance procedures, banks acknowledge that much needs to be done to restore customer confidence “Indicate your personal opinion on the party(s) most responsible” Source: Asian Banker Research Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 12

“The banks we like” HSBC grants a 30 days service pledge, which allows customers to cancel the purchase of investment and insurance products. HSBC was the first bank in Hong Kong to adopt physical segregation and fully implemented all new regulatory requirements for investor protection measures. OCBC for its stringent due diligence and family focussed sales and advisory process, not pushing customers for sophisticated and risky investment products. The banks quickly adjusted its remuneration scheme, reduced sales incentives and introduced claw- back mechanisms. Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 13 13

The Questions We Ask • What measures to take to assure customer protection and responsible sales due diligence. • How to manage sales incentives against over-selling and misselling? Does your bank proceed regulatory changes or react on them? How to optimise employee training and minimise attrition while revisiting remuneration? How to align product development, marketing, sales to satisfy what the customer needs. • • • Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 14

For further information § Members and subscribers to this programme may request further explanations and consult with Asian Banker Research analysts on additional information and specific needs. § If the additional information you require can be repackaged from primary data we have already collected previously, the analyst will send it to you as part of your subscription or membership. § If the additional information you request requires new primary work that is unique to your organisation, then a small fee may be applicable. § For more information about this article and Project Bank. Metrics please contact us at analyst@theasianbanker. com. Copyright The Asian Banker 2010. All rights reserved 15 15
0ed684e28d617958c684572c318e99aa.ppt