c2b9f73a44ea1613f20b576474e11371.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
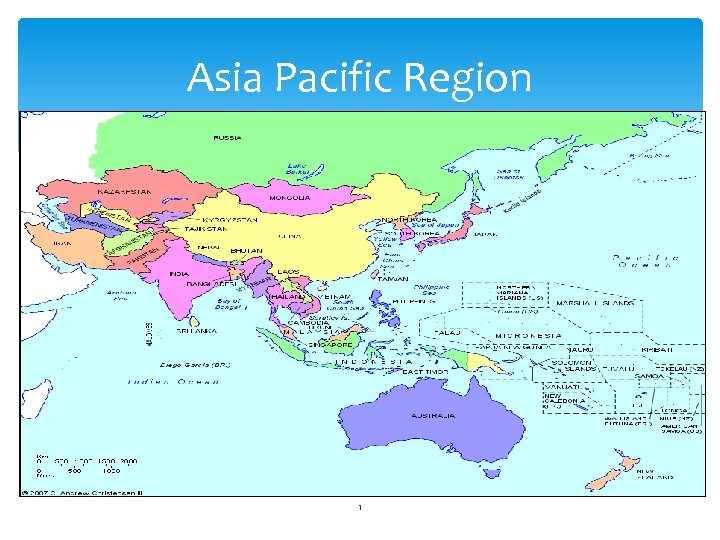
Asia Pacific Region 1
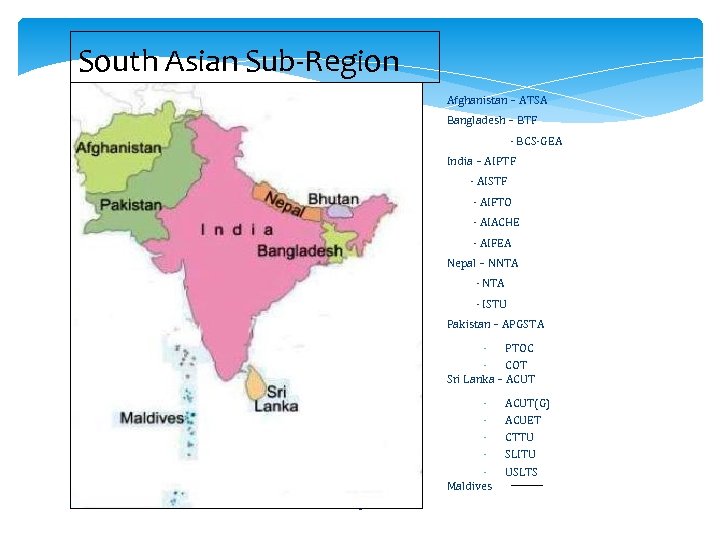
South Asian Sub-Region Afghanistan – ATSA Bangladesh – BTF - BCS-GEA India – AIPTF - AISTF - AIFTO - AIACHE - AIFEA Nepal – NNTA - ISTU Pakistan – APGSTA - PTOC - COT Sri Lanka – ACUT Maldives 2 ACUT(G) ACUET CTTU SLITU USLTS
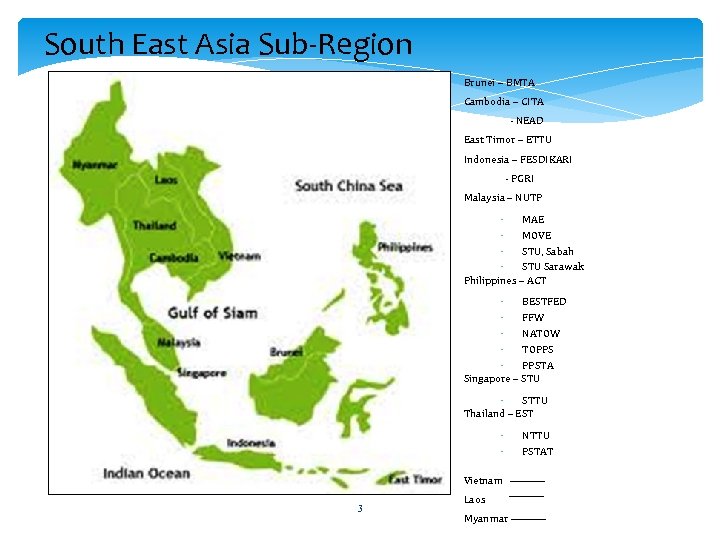
South East Asia Sub-Region Brunei – BMTA Cambodia – CITA - NEAD East Timor – ETTU Indonesia – FESDIKARI - PGRI Malaysia – NUTP MAE MOVE STU, Sabah STU Sarawak Philippines – ACT BESTFED FFW NATOW TOPPS PPSTA Singapore – STU STTU Thailand – EST Vietnam 3 Laos Myanmar NTTU PSTAT
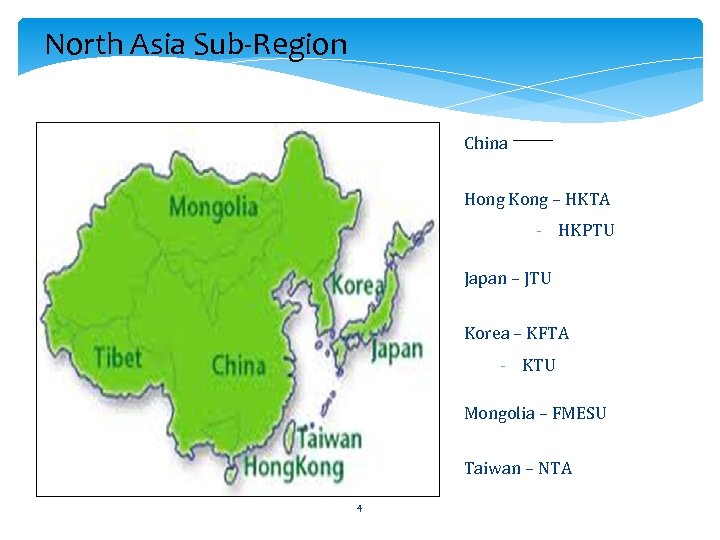
North Asia Sub-Region China Hong Kong – HKTA North Asia Sub. Region - HKPTU Japan – JTU Korea – KFTA - KTU Mongolia – FMESU Taiwan – NTA 4
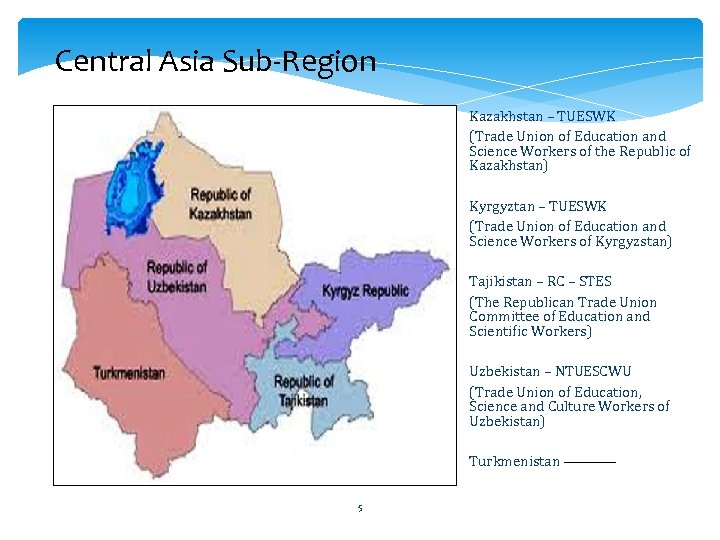
Central Asia Sub-Region Kazakhstan – TUESWK (Trade Union of Education and Science Workers of the Republic of Kazakhstan) Kyrgyztan – TUESWK (Trade Union of Education and Science Workers of Kyrgyzstan) Tajikistan – RC – STES (The Republican Trade Union Committee of Education and Scientific Workers) Uzbekistan – NTUESCWU (Trade Union of Education, Science and Culture Workers of Uzbekistan) Turkmenistan 5
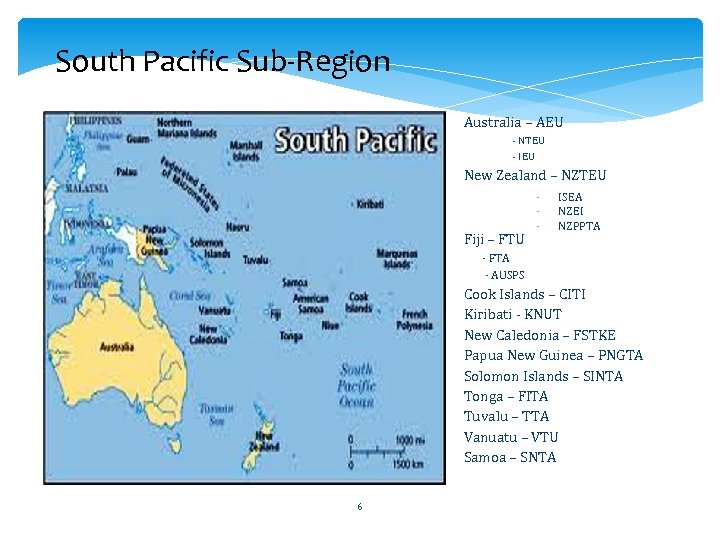
South Pacific Sub-Region Australia – AEU - NTEU - IEU New Zealand – NZTEU South Pacific Sub. Region Fiji – FTU - ISEA NZEI NZPPTA - FTA - AUSPS Cook Islands – CITI Kiribati - KNUT New Caledonia – FSTKE Papua New Guinea – PNGTA Solomon Islands – SINTA Tonga – FITA Tuvalu – TTA Vanuatu – VTU Samoa – SNTA 6

New Entry to Asia Pacific Region Iraq – Kurdistan Teachers’ Union, KTU - Iraqi Teachers’ Union, ITU Jordan – General Union of Workers in Teaching, GWTU Kuwait - 7
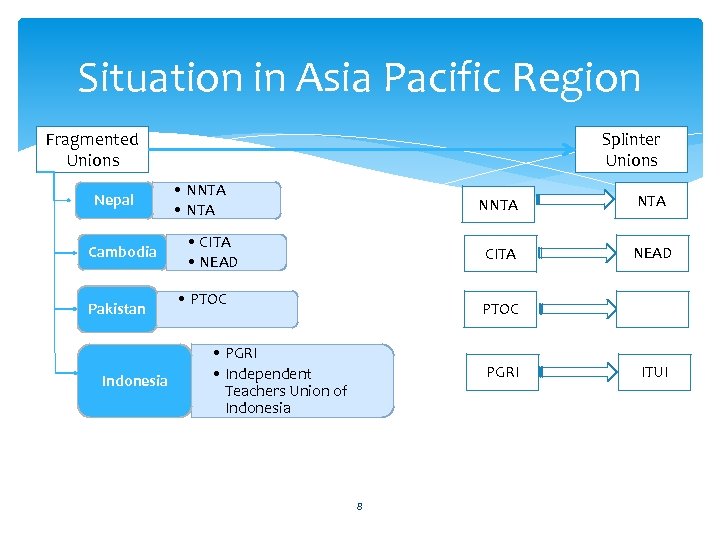
Situation in Asia Pacific Region Fragmented Unions Nepal Cambodia Pakistan Indonesia Splinter Unions • NNTA • NTA NNTA CITA • CITA • NEAD • PTOC NTA NEAD PTOC • PGRI • Independent Teachers Union of Indonesia PGRI 8 ITUI
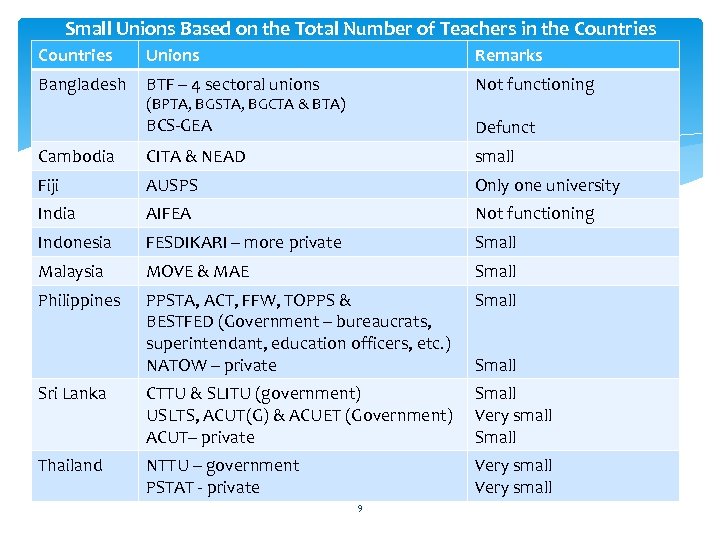
Small Unions Based on the Total Number of Teachers in the Countries Unions Remarks Bangladesh BTF – 4 sectoral unions Not functioning BCS-GEA Defunct Cambodia CITA & NEAD small Fiji AUSPS Only one university India AIFEA Not functioning Indonesia FESDIKARI – more private Small Malaysia MOVE & MAE Small Philippines PPSTA, ACT, FFW, TOPPS & BESTFED (Government – bureaucrats, superintendant, education officers, etc. ) NATOW – private Small Sri Lanka CTTU & SLITU (government) USLTS, ACUT(G) & ACUET (Government) ACUT– private Small Very small Small Thailand NTTU – government PSTAT - private Very small (BPTA, BGSTA, BGCTA & BTA) 9 Small

Reasons for the situation: Fragmentation, Splinters and Small Unions v backed by the government e. g. SLITU, Sri Lanka. v Based on language (ACUET, USLTS) v Based on language and ethnicity (CTTU) v Concentrating in some regions, sub-regions and provinces e. g. APGSTA – Karachi, PTOC – Balochstan, COT – Chatta, Punjab, CTTU – North and North East Sri Lanka. v Based on strong political ideology e. g. NNTA and NTA, Nepal v Constitution allows retired teachers including bureaucrats in leadership, hindering growth of the union e. g. PGRI. v Lack of young teachers both in leadership and membership. v Undemocratic leaders not following the constitution 10

v Not effectively representing the cause of education and teachers v Poor governance and lack of transparency v Autocratic leaders, personal ego / prestige issue of the leadership v Fear of loosing the benefits being enjoyed by leaders without paying proper dues to EI e. g. participation in the EI Congress, Conference, etc. v Acceptance of nominal dues by EI v Fear of loosing DC activities v Contract teachers v Privatisation v Removal of protection and subsidies v Political developments in the region 11
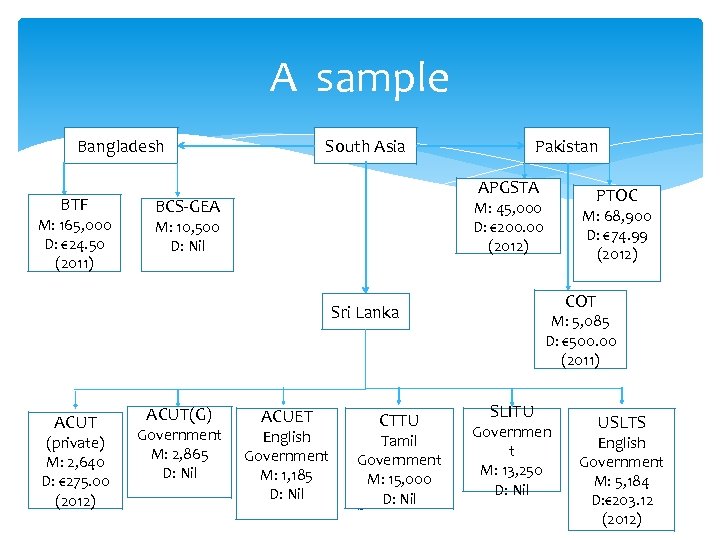
A sample Bangladesh BTF M: 165, 000 D: € 24. 50 (2011) South Asia Pakistan APGSTA BCS-GEA M: 10, 500 D: Nil (private) M: 2, 640 D: € 275. 00 (2012) ACUT(G) Government M: 2, 865 D: Nil ACUET English Government M: 1, 185 D: Nil CTTU Tamil Government M: 15, 000 D: Nil 12 M: 68, 900 D: € 74. 99 (2012) COT Sri Lanka ACUT PTOC M: 45, 000 D: € 200. 00 (2012) M: 5, 085 D: € 500. 00 (2011) SLITU Governmen t M: 13, 250 D: Nil USLTS English Government M: 5, 184 D: € 203. 12 (2012)

How to fight with the Situation: Possible Solutions q Assist member organisations in making the members aware about the risks and dangers of the government run organisation e. g. yellow unions. q Assist member organisations in transforming them as trade unions and service providers to the members. q Encourage member organisations in getting recognition certificate by the provincial / national governments through capacity building of the leaders. q Provide systematic training on trade unions rights and develop skills to fight for these rights to the focus groups. q Education: joint activities at micro level and organise membership campaigns. q Organise joint programmes and activities at various levels. 13

Use joint forum in holding discussion on unity. Hold dialogue with the leaders of the unions Encourage national unions to form joint action committees / forum to address the problems and issues concerning education and teachers. Motivate women and youth to leadership role. Look into the possibility of reducing some benefits to small organisations. Encourage member organisations to form federations where merger is not practical or possible. 14
c2b9f73a44ea1613f20b576474e11371.ppt