68b4fb6fe914df06887274255ab7d69c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
 Asia Climate Security : Perception and Reality – A China Energy perspective A presentation at the Royal United Services Institute for Defence and Security Studies, Whitehall, London, 24 April 2007 Andrew K. P. Leung, SBS, FRSA Founder and Chairman Andrew Leung International Consultants Limited
Asia Climate Security : Perception and Reality – A China Energy perspective A presentation at the Royal United Services Institute for Defence and Security Studies, Whitehall, London, 24 April 2007 Andrew K. P. Leung, SBS, FRSA Founder and Chairman Andrew Leung International Consultants Limited
 Hunger for Energy • Global Industrial Revolution 21 st C • History’s largest and fastest urbanisation and industrialisation • Already 41% urbanised, to increase to 60% by 2020 • 85, 000 km expressway in 30 years > US Interstate by 10, 000 km • 7 arteries radiating from Beijing; 9 N/S; 18 E/W • 19 m cars (2005) = 8@1000 ~ 500@1000 US – to jump to 130 m by 2020 (Goldman Sachs) • 24 m jobs p. a. need ‘to stay even’ • The looming approach of China’s ‘greying period’ • China 94% energy self-sufficient but 77% from coal • 40% crude oil imported (target 12 -15%) (Japan, almost all; India 60 -70%)
Hunger for Energy • Global Industrial Revolution 21 st C • History’s largest and fastest urbanisation and industrialisation • Already 41% urbanised, to increase to 60% by 2020 • 85, 000 km expressway in 30 years > US Interstate by 10, 000 km • 7 arteries radiating from Beijing; 9 N/S; 18 E/W • 19 m cars (2005) = 8@1000 ~ 500@1000 US – to jump to 130 m by 2020 (Goldman Sachs) • 24 m jobs p. a. need ‘to stay even’ • The looming approach of China’s ‘greying period’ • China 94% energy self-sufficient but 77% from coal • 40% crude oil imported (target 12 -15%) (Japan, almost all; India 60 -70%)
 Scramble for Oil • Saudi Arabia (17% supply; 90 day strategic oil reserve: 100, 000 cu m at Zhenhai; 2 nd in Qingdao, both completed) • Iran – Yadavaran US 20 b • Kazakhstan – 1200 km pipeline completed for 10 mb to N Xinjiang • SCO (+ Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrjystan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan + observers: India, Pakistan, Iran, Afghanistan, and Turkey) • Africa (1/3 supply) ~ Sudan and Angola • South America – Venezuela as key supplier; as Brazil’s 3 rd largest oil export destination – US backyard with centre-left tendencies • Russia – modified eastward pipeline but increasing cooperation • Australia upbeat with China but Osaka Gas won 25 -yr deal for 1. 5 m tonnes (cheaper and cleaner) LNG p. a. from Gorgon field (NW) (2. 5 m tonnes for US W Coast for 20 yrs) • Japan – dispute over fields in East China Sea (7 trillion cu ft of natural gas and 100 b barrels of oil)
Scramble for Oil • Saudi Arabia (17% supply; 90 day strategic oil reserve: 100, 000 cu m at Zhenhai; 2 nd in Qingdao, both completed) • Iran – Yadavaran US 20 b • Kazakhstan – 1200 km pipeline completed for 10 mb to N Xinjiang • SCO (+ Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrjystan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan + observers: India, Pakistan, Iran, Afghanistan, and Turkey) • Africa (1/3 supply) ~ Sudan and Angola • South America – Venezuela as key supplier; as Brazil’s 3 rd largest oil export destination – US backyard with centre-left tendencies • Russia – modified eastward pipeline but increasing cooperation • Australia upbeat with China but Osaka Gas won 25 -yr deal for 1. 5 m tonnes (cheaper and cleaner) LNG p. a. from Gorgon field (NW) (2. 5 m tonnes for US W Coast for 20 yrs) • Japan – dispute over fields in East China Sea (7 trillion cu ft of natural gas and 100 b barrels of oil)
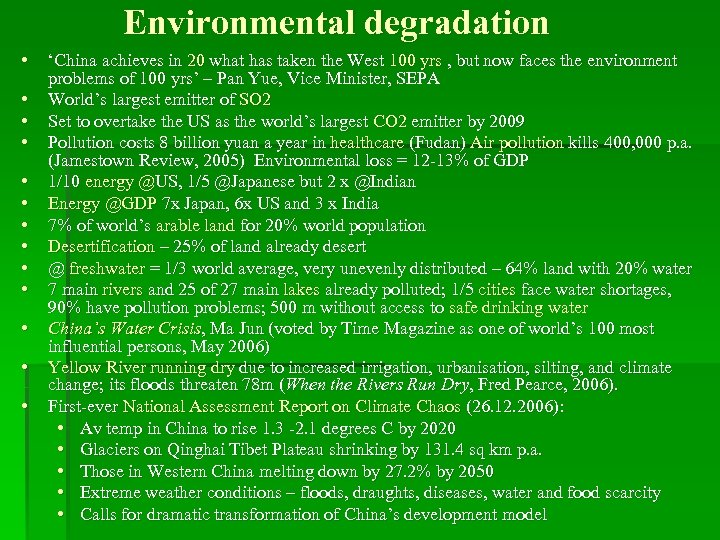 Environmental degradation • • • • ‘China achieves in 20 what has taken the West 100 yrs , but now faces the environment problems of 100 yrs’ – Pan Yue, Vice Minister, SEPA World’s largest emitter of SO 2 Set to overtake the US as the world’s largest CO 2 emitter by 2009 Pollution costs 8 billion yuan a year in healthcare (Fudan) Air pollution kills 400, 000 p. a. (Jamestown Review, 2005) Environmental loss = 12 -13% of GDP 1/10 energy @US, 1/5 @Japanese but 2 x @Indian Energy @GDP 7 x Japan, 6 x US and 3 x India 7% of world’s arable land for 20% world population Desertification – 25% of land already desert @ freshwater = 1/3 world average, very unevenly distributed – 64% land with 20% water 7 main rivers and 25 of 27 main lakes already polluted; 1/5 cities face water shortages, 90% have pollution problems; 500 m without access to safe drinking water China’s Water Crisis, Ma Jun (voted by Time Magazine as one of world’s 100 most influential persons, May 2006) Yellow River running dry due to increased irrigation, urbanisation, silting, and climate change; its floods threaten 78 m (When the Rivers Run Dry, Fred Pearce, 2006). First-ever National Assessment Report on Climate Chaos (26. 12. 2006): • Av temp in China to rise 1. 3 -2. 1 degrees C by 2020 • Glaciers on Qinghai Tibet Plateau shrinking by 131. 4 sq km p. a. • Those in Western China melting down by 27. 2% by 2050 • Extreme weather conditions – floods, draughts, diseases, water and food scarcity • Calls for dramatic transformation of China’s development model
Environmental degradation • • • • ‘China achieves in 20 what has taken the West 100 yrs , but now faces the environment problems of 100 yrs’ – Pan Yue, Vice Minister, SEPA World’s largest emitter of SO 2 Set to overtake the US as the world’s largest CO 2 emitter by 2009 Pollution costs 8 billion yuan a year in healthcare (Fudan) Air pollution kills 400, 000 p. a. (Jamestown Review, 2005) Environmental loss = 12 -13% of GDP 1/10 energy @US, 1/5 @Japanese but 2 x @Indian Energy @GDP 7 x Japan, 6 x US and 3 x India 7% of world’s arable land for 20% world population Desertification – 25% of land already desert @ freshwater = 1/3 world average, very unevenly distributed – 64% land with 20% water 7 main rivers and 25 of 27 main lakes already polluted; 1/5 cities face water shortages, 90% have pollution problems; 500 m without access to safe drinking water China’s Water Crisis, Ma Jun (voted by Time Magazine as one of world’s 100 most influential persons, May 2006) Yellow River running dry due to increased irrigation, urbanisation, silting, and climate change; its floods threaten 78 m (When the Rivers Run Dry, Fred Pearce, 2006). First-ever National Assessment Report on Climate Chaos (26. 12. 2006): • Av temp in China to rise 1. 3 -2. 1 degrees C by 2020 • Glaciers on Qinghai Tibet Plateau shrinking by 131. 4 sq km p. a. • Those in Western China melting down by 27. 2% by 2050 • Extreme weather conditions – floods, draughts, diseases, water and food scarcity • Calls for dramatic transformation of China’s development model
 Energy security and geopolitics • Supply – • By 2020 ME will account for 83% of global oil reserves (up from 2/3 at present), • Debate notwithstanding, the topping point is in sight (now ~ 3 decades? ) – Half Gone, Jeremy Leggett, 2005 • Not how much is left but how soon can it be got out? • Transportation – • Much passing through Iran-controlled Strait of Hortmuz and Strait of Malacca (controlled by US with naval base at Changi, Singapore) • Hence alternative land supply routes e. g Central Asia, Russia, Gwadar Port • Geopolitics – • • Scramble for Oil politik – Russia and Iran Territorial disputes 1996 Iran and Libya Sanctions Act • Economics – cost (2004 price rise decreased China’s GDP by 0. 8%) and volatility, industrialisation, urbanisation, income, employment, overall development • Environment
Energy security and geopolitics • Supply – • By 2020 ME will account for 83% of global oil reserves (up from 2/3 at present), • Debate notwithstanding, the topping point is in sight (now ~ 3 decades? ) – Half Gone, Jeremy Leggett, 2005 • Not how much is left but how soon can it be got out? • Transportation – • Much passing through Iran-controlled Strait of Hortmuz and Strait of Malacca (controlled by US with naval base at Changi, Singapore) • Hence alternative land supply routes e. g Central Asia, Russia, Gwadar Port • Geopolitics – • • Scramble for Oil politik – Russia and Iran Territorial disputes 1996 Iran and Libya Sanctions Act • Economics – cost (2004 price rise decreased China’s GDP by 0. 8%) and volatility, industrialisation, urbanisation, income, employment, overall development • Environment
 Drive for Sustainable Development • • • • The impossible American Dream 11 th Five Year Plan (2006 -10): 4% saving + 2% reduction p. a. China to invest US 2. 3 trillion in energy development 2001 -30 (IEA) US 200 b on renewable energy next 15 yrs (^ 7 -10% p. a. by 2010 and 20% p. a. by 2020) 2 nuclear power stations p. a. for next 15 years S/N Water Diversion Project (US 60 billion) Three Gorges Dam to increase hydroelectric power from 108 GW to 290 GW by 2020 – China’s full potential at 400 GW Wind power (~ Inner Mongolia) to grow from 1 GW to 30 GW by 2020, for 13 -30 million households by 2020 30 m solar households e. g Tibet (60% of world); photovoltaic energy = 65 MW, to increase to 300 m sq meters for 2 GW by 2020 (= 40 million tonnes of coal p. a. ) NYSElisted Suntech, within world’s top ten SASOL to build CTL plant in Ningxia and Shaanxi at total cost of US 10 b (10 m tonnes of crude oil by 2010; 30 m tonnes by 2020 = 16 % of China’s crude output) Attractive current cost US 15 per barrel 3 rd largest ethanol producer ~ 1 b gallons p. a. in Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Anhui and Henan - Mandated use of gasohol Incentives for energy crops (+GM) e. g. corn, sugar cane, sweet sorghum, and sweet potato (corn= 20% grain production so drive for rapeseed, waste and biomass) US 8 b plant-oil plantation project in Kalimantan, Indonesia, threatens 1. 8 m hectares of virgin forest (2/3 size of Belgium) World’s first Eco-city at Dongtan on Chiongming Island, to open in time for Shanghai Expo 2010
Drive for Sustainable Development • • • • The impossible American Dream 11 th Five Year Plan (2006 -10): 4% saving + 2% reduction p. a. China to invest US 2. 3 trillion in energy development 2001 -30 (IEA) US 200 b on renewable energy next 15 yrs (^ 7 -10% p. a. by 2010 and 20% p. a. by 2020) 2 nuclear power stations p. a. for next 15 years S/N Water Diversion Project (US 60 billion) Three Gorges Dam to increase hydroelectric power from 108 GW to 290 GW by 2020 – China’s full potential at 400 GW Wind power (~ Inner Mongolia) to grow from 1 GW to 30 GW by 2020, for 13 -30 million households by 2020 30 m solar households e. g Tibet (60% of world); photovoltaic energy = 65 MW, to increase to 300 m sq meters for 2 GW by 2020 (= 40 million tonnes of coal p. a. ) NYSElisted Suntech, within world’s top ten SASOL to build CTL plant in Ningxia and Shaanxi at total cost of US 10 b (10 m tonnes of crude oil by 2010; 30 m tonnes by 2020 = 16 % of China’s crude output) Attractive current cost US 15 per barrel 3 rd largest ethanol producer ~ 1 b gallons p. a. in Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Anhui and Henan - Mandated use of gasohol Incentives for energy crops (+GM) e. g. corn, sugar cane, sweet sorghum, and sweet potato (corn= 20% grain production so drive for rapeseed, waste and biomass) US 8 b plant-oil plantation project in Kalimantan, Indonesia, threatens 1. 8 m hectares of virgin forest (2/3 size of Belgium) World’s first Eco-city at Dongtan on Chiongming Island, to open in time for Shanghai Expo 2010
 Energy Cooperation • Priorities: Energy Supply & Security, Exploration, Coordination, Efficiency, Safety, Clean and Sustainable Energy R & D and Technologies • New Dehli initiative (Mani Shankar Aiyar, Indian’s Oil Minister, 11. 2005) – 20, 000 km oil and gas pipelines linking Russia, Japan, S Korea, China, India, Thailand, Myanmar, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Iran and Central Asia. (Iran-Pakistan. India pipeline could extend to Yunnan, China) • Yadavaran: China (50%) India (20%); Sudan’s Greater Nile Project: China (40%) India (25%) • Pakistan’s Gwadar Port offers alternative route overland for ME and Africa oil • Five-country Energy Ministers Meeting, Beijing, 16. 12. 2006 (China, India, Japan, S Korea, and US) • Asian Energy Agency? (AEA~ IEA) • China exploiting only 40 m of 7. 3 billion tonnes standard coal equivalent of renewal energy resources • Cost reduction technology for renewables: large-scale power 20% > expensive if produced in small hydropower stations, 70% > biomass or wind and 10 -17 times > with solar cells.
Energy Cooperation • Priorities: Energy Supply & Security, Exploration, Coordination, Efficiency, Safety, Clean and Sustainable Energy R & D and Technologies • New Dehli initiative (Mani Shankar Aiyar, Indian’s Oil Minister, 11. 2005) – 20, 000 km oil and gas pipelines linking Russia, Japan, S Korea, China, India, Thailand, Myanmar, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Iran and Central Asia. (Iran-Pakistan. India pipeline could extend to Yunnan, China) • Yadavaran: China (50%) India (20%); Sudan’s Greater Nile Project: China (40%) India (25%) • Pakistan’s Gwadar Port offers alternative route overland for ME and Africa oil • Five-country Energy Ministers Meeting, Beijing, 16. 12. 2006 (China, India, Japan, S Korea, and US) • Asian Energy Agency? (AEA~ IEA) • China exploiting only 40 m of 7. 3 billion tonnes standard coal equivalent of renewal energy resources • Cost reduction technology for renewables: large-scale power 20% > expensive if produced in small hydropower stations, 70% > biomass or wind and 10 -17 times > with solar cells.
 China’s energy agenda • Five challenges: • • • (a) Supply shortfall (b) Production capacity (c) Coal pollution (d) Obsolete technology (e) Supply and price volatility • President Hu at G 8 Dialogue at St Petersburg (17. 7. 2006): • • • (a) cooperation, coordination and diversification (b) promotion of R & D in clean, safe, economic, and sustainable energies (c) geopolitical environment conducive to global energy security and stability • International Thermo-nuclear Energy Reactor (ITER) 35 yr project for inexhaustible, clean and safe fusion energy – EU, Japan, China, India, Korea, Russia and US
China’s energy agenda • Five challenges: • • • (a) Supply shortfall (b) Production capacity (c) Coal pollution (d) Obsolete technology (e) Supply and price volatility • President Hu at G 8 Dialogue at St Petersburg (17. 7. 2006): • • • (a) cooperation, coordination and diversification (b) promotion of R & D in clean, safe, economic, and sustainable energies (c) geopolitical environment conducive to global energy security and stability • International Thermo-nuclear Energy Reactor (ITER) 35 yr project for inexhaustible, clean and safe fusion energy – EU, Japan, China, India, Korea, Russia and US
 • Climate Security Climate Change (IPCC) • • • Whole forest types disappearing Gulf Stream disrupted Biodiversity loss Sea-level rise Global insurance industry threatened Food and water supplies at risk Human health at risk Consequential local, regional, and international conflicts Threat to societal stability Amplifying feedbacks e. g melting permafrost (methane=24 CO 2)), dying forests, receding glaciers and icefields Possible Tipping Point of Runaway Effect (Half Gone – Jeremy Leggett, 2005) (Half • Water Crises • • Melting glaciers deplete sources for the Ganges, Indus, Brahmaputra, Salween, Irradwaddy, Mekong, Yangtze Brahmaputra, Salween, Irradwaddy, Ever deeper boreholes drying up irreplaceable aquifers (some arsenic) Dams threaten ecosystems and fisheries in river basins (e. g. Mekong) and caused floods during extreme rainfalls Rotten vegetation in reservoirs - 1/5 man-made methane (7% man-made greenhouse effect) > aircraft emissions – most needed for electricity and irrigation for water and energy-intensive industries e. g. textiles By 2025, water demand for domestic and industrial use to increase by 2/3; scarcity expected to reduce global food production > US grain harvest Water at heart of regional conflicts inc the West Bank and Golan heights, and Kashmir Water-related catastrophes wiped out ancient civilizations of Angkor Wat and the Mayans? (When the Rivers Run Dry – Fred Pearce, 2006) (When • Balance between Industry and Agriculture? – Also China’s • New global lifestyle needed? 1 st 1988 Conference, 75 Nobel Prize Laureates concluded ‘If mankind is to survive 21 st • ‘The Stone Age came to an end not for a lack of stones. So will the Age of Oil. ’ (Retired Saudi Oil Minister Sheik. Yamani, 2000) 11 th FYP Century, the ancient wisdom of Confucianism (harmony with Nature) must be revisited. ’ cf Environmentalism, Renewable Energies, rain, fog and dew harvesting (<1/3 consumption); flood plains restoration, ‘porous’ and eco-cities, non-profligacy, Water as restoration, ‘porous’ a sacred part of Nature
• Climate Security Climate Change (IPCC) • • • Whole forest types disappearing Gulf Stream disrupted Biodiversity loss Sea-level rise Global insurance industry threatened Food and water supplies at risk Human health at risk Consequential local, regional, and international conflicts Threat to societal stability Amplifying feedbacks e. g melting permafrost (methane=24 CO 2)), dying forests, receding glaciers and icefields Possible Tipping Point of Runaway Effect (Half Gone – Jeremy Leggett, 2005) (Half • Water Crises • • Melting glaciers deplete sources for the Ganges, Indus, Brahmaputra, Salween, Irradwaddy, Mekong, Yangtze Brahmaputra, Salween, Irradwaddy, Ever deeper boreholes drying up irreplaceable aquifers (some arsenic) Dams threaten ecosystems and fisheries in river basins (e. g. Mekong) and caused floods during extreme rainfalls Rotten vegetation in reservoirs - 1/5 man-made methane (7% man-made greenhouse effect) > aircraft emissions – most needed for electricity and irrigation for water and energy-intensive industries e. g. textiles By 2025, water demand for domestic and industrial use to increase by 2/3; scarcity expected to reduce global food production > US grain harvest Water at heart of regional conflicts inc the West Bank and Golan heights, and Kashmir Water-related catastrophes wiped out ancient civilizations of Angkor Wat and the Mayans? (When the Rivers Run Dry – Fred Pearce, 2006) (When • Balance between Industry and Agriculture? – Also China’s • New global lifestyle needed? 1 st 1988 Conference, 75 Nobel Prize Laureates concluded ‘If mankind is to survive 21 st • ‘The Stone Age came to an end not for a lack of stones. So will the Age of Oil. ’ (Retired Saudi Oil Minister Sheik. Yamani, 2000) 11 th FYP Century, the ancient wisdom of Confucianism (harmony with Nature) must be revisited. ’ cf Environmentalism, Renewable Energies, rain, fog and dew harvesting (<1/3 consumption); flood plains restoration, ‘porous’ and eco-cities, non-profligacy, Water as restoration, ‘porous’ a sacred part of Nature
 A Green Bonanza? • Surge in green investments worldwide (Economist, 18 November 2006): Aggregate US 63 b (2006) >US 49 b (2005), US 30 b (2004), growing 20 -30% p. a. (biggest job and wealth creation opportunity in 21 st C? ) • UN set up carbon trading exchange in Beijing (FT, 5 Feb, 2007) • Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) 2007 Report echoed by Bush (State of Union Address), UK and rest of world • Toyota developing new generation of Prius: BMW pioneering with hydrogen fuel cars; GM announced plan to sell hydrogen-cell vehicles by 2010; Japan plans 50, 000 fuel-cell vehicles by 2010; China R & D at US 200 m p. a. for past few years to be world leader in hydrogen-fuel-cell cars; 172 prototypes and 87 hydrogen filling stations already created worldwide • New urban planning and transport systems • Possible new 21 st C lifestyle to drive Eco-Industrial Revolution (21 st C Management, Matthew Kiernan, 1996) or Ecological Civilisation (Pan Yue, Vice Minister, China’s State Environmental Protection Administration, February 2007) • China sets up new State Foreign Exchange Investment Corporation to invest growth (US 210 b p. a. ) of China’s huge foreign currency reserve – an opportunity to kill many birds with one stone? • Partnership with Petrodollars?
A Green Bonanza? • Surge in green investments worldwide (Economist, 18 November 2006): Aggregate US 63 b (2006) >US 49 b (2005), US 30 b (2004), growing 20 -30% p. a. (biggest job and wealth creation opportunity in 21 st C? ) • UN set up carbon trading exchange in Beijing (FT, 5 Feb, 2007) • Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) 2007 Report echoed by Bush (State of Union Address), UK and rest of world • Toyota developing new generation of Prius: BMW pioneering with hydrogen fuel cars; GM announced plan to sell hydrogen-cell vehicles by 2010; Japan plans 50, 000 fuel-cell vehicles by 2010; China R & D at US 200 m p. a. for past few years to be world leader in hydrogen-fuel-cell cars; 172 prototypes and 87 hydrogen filling stations already created worldwide • New urban planning and transport systems • Possible new 21 st C lifestyle to drive Eco-Industrial Revolution (21 st C Management, Matthew Kiernan, 1996) or Ecological Civilisation (Pan Yue, Vice Minister, China’s State Environmental Protection Administration, February 2007) • China sets up new State Foreign Exchange Investment Corporation to invest growth (US 210 b p. a. ) of China’s huge foreign currency reserve – an opportunity to kill many birds with one stone? • Partnership with Petrodollars?
 Thank you Andrew K. P. Leung, SBS, FRSA www. andrewleunginternationalconsultants. com Founder and Chairman, Andrew Leung International Consultants Limited Chairman, China Group, Institute of Directors City Branch, London Chairman, China Group, Royal Society of Arts, London Region Senior Consultant, MEC International Member, Executive Committee, 48 Group Club Member, Governing Council, King’s College London Member, Advisory Board, China Policy Institute, Nottingham University Invited Member, ATCA (Asymmetric Threats Contingency Alliance) - elite global think-tank Visiting Professor, NIMBAS Graduate School of Management, Holland Visiting Professor, Business School, Sun Yat-sen University, China Visiting Professor, Business School, Lingnan University, China Global Business Agent, Changsha City, China
Thank you Andrew K. P. Leung, SBS, FRSA www. andrewleunginternationalconsultants. com Founder and Chairman, Andrew Leung International Consultants Limited Chairman, China Group, Institute of Directors City Branch, London Chairman, China Group, Royal Society of Arts, London Region Senior Consultant, MEC International Member, Executive Committee, 48 Group Club Member, Governing Council, King’s College London Member, Advisory Board, China Policy Institute, Nottingham University Invited Member, ATCA (Asymmetric Threats Contingency Alliance) - elite global think-tank Visiting Professor, NIMBAS Graduate School of Management, Holland Visiting Professor, Business School, Sun Yat-sen University, China Visiting Professor, Business School, Lingnan University, China Global Business Agent, Changsha City, China


