ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Boarding Schools of Tatarstan R. F.


ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Boarding Schools of Tatarstan R.F.

Reproduction is the process by which an organism produces others of its same kind.

ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Asexual reproduction is the production of offspring from a single parent by simple division.

ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION

PROPERTIES OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1. There is the less variation among of offspring. 2. It is rapid and many offspring are formed. 3. All cells contain same hereditary information as the parent cell. 4. Asexual reproduction occurs by means of mitotic cell division. 5. There is only one parent organism

Asexual reproduction is seen in unicellular organisms, some plants and simple animals.

TYPES OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1. Binary fission 2. Budding 3. Sporulation 4. Vegetative propagation 5. Regeneration 6. Tissue culture 7. Parthenogenesis
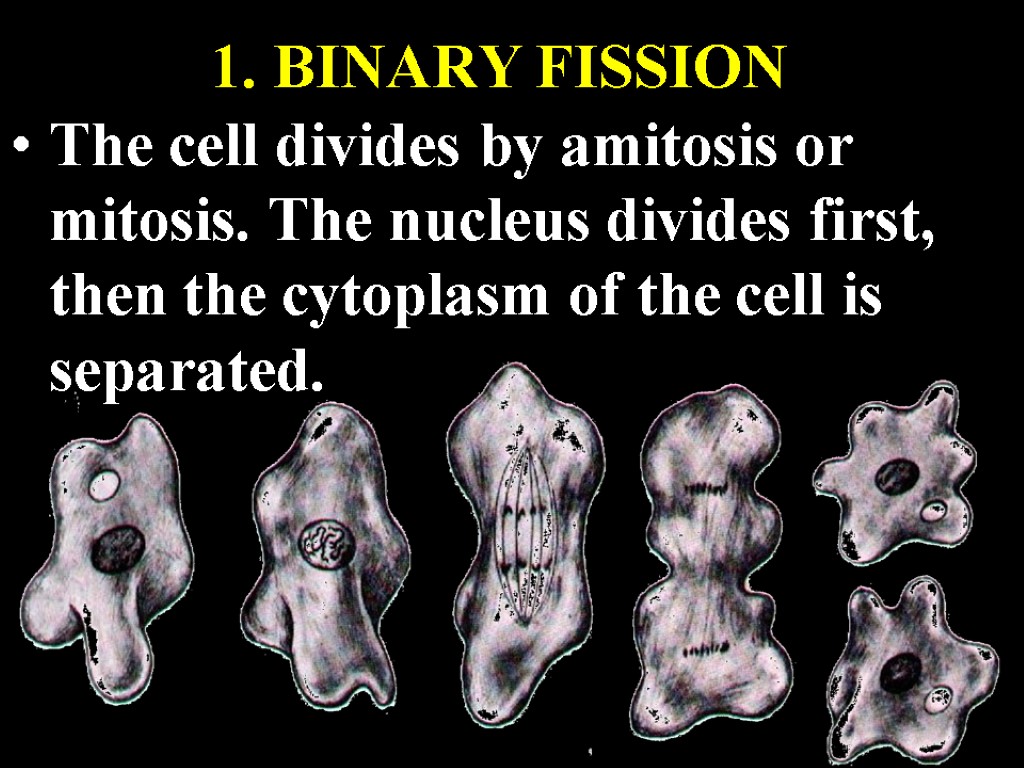
1. BINARY FISSION The cell divides by amitosis or mitosis. The nucleus divides first, then the cytoplasm of the cell is separated.


Binary fission is seen in bacteria, amoeba, paramecium and other unicellular organisms.
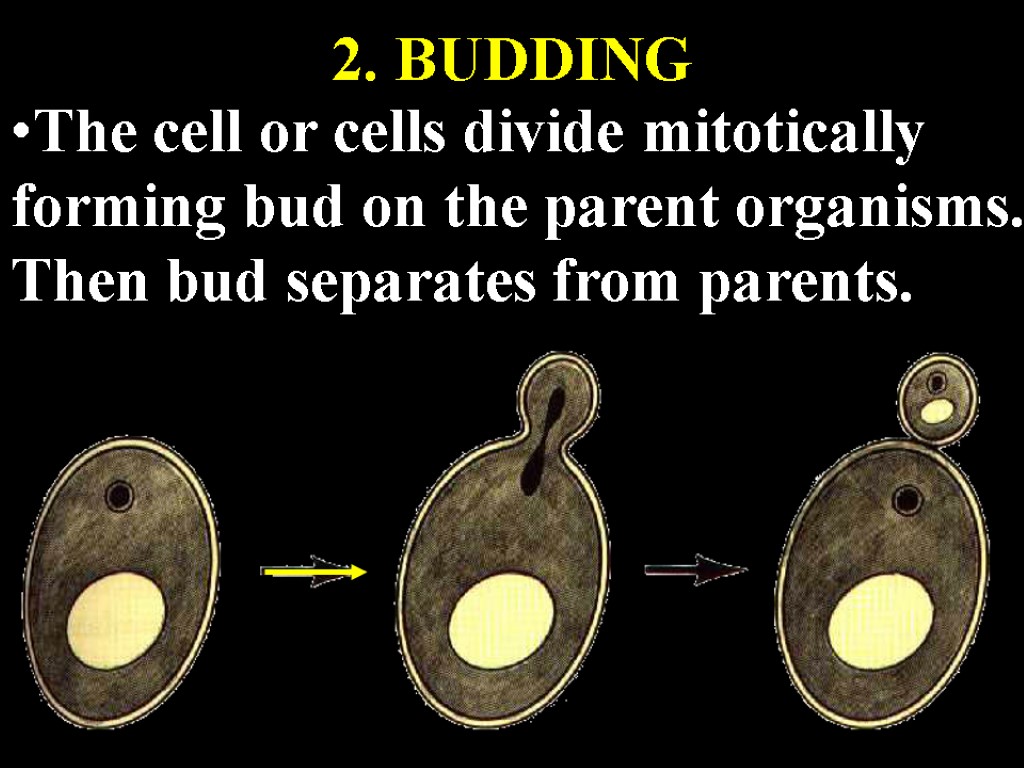
2. BUDDING The cell or cells divide mitotically forming bud on the parent organisms. Then bud separates from parents.
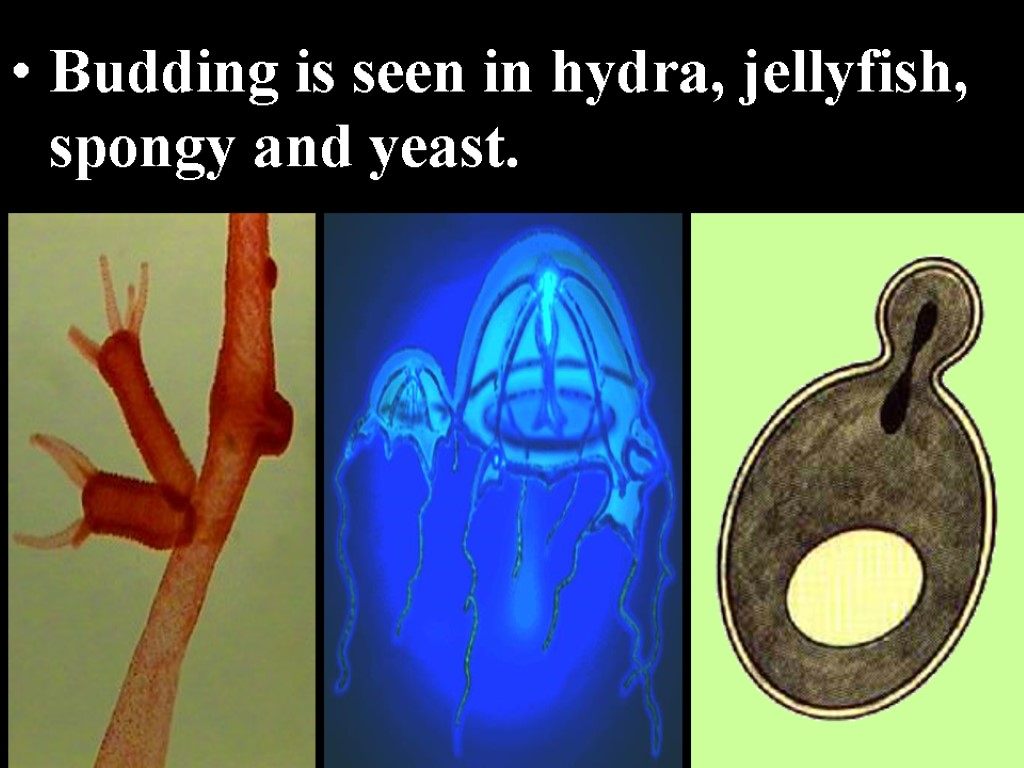
Budding is seen in hydra, jellyfish, spongy and yeast.


3. SPORULATION Many plant produce specialized cells called spores. Each spore can produce new organisms. Spore is surrounded by special thick, hard cell wall.

Spore formation is seen in some fungi, algae and protozoa. ULVA CHARA DINOFLAGELLATE

VEGETATIVE PROPOGATION Root, stem and leaves are called vegetative organs in plants. When they give rise to new plants this process is called vegetative reproduction.

1. Tuber 2. Stolons and runners 3. Rhizome 4. Cutting 5. Stem grafting TYPES OF VEGETATIVE PROPOGATION

TUBER

RUNNER STOLEN
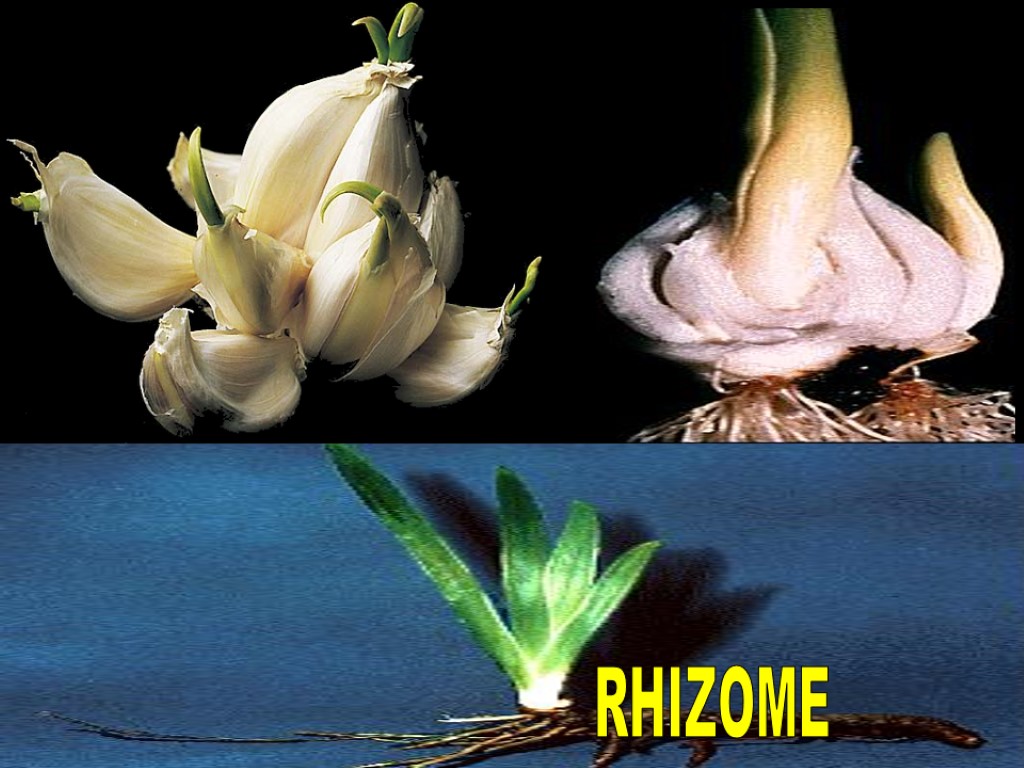

RHIZOME
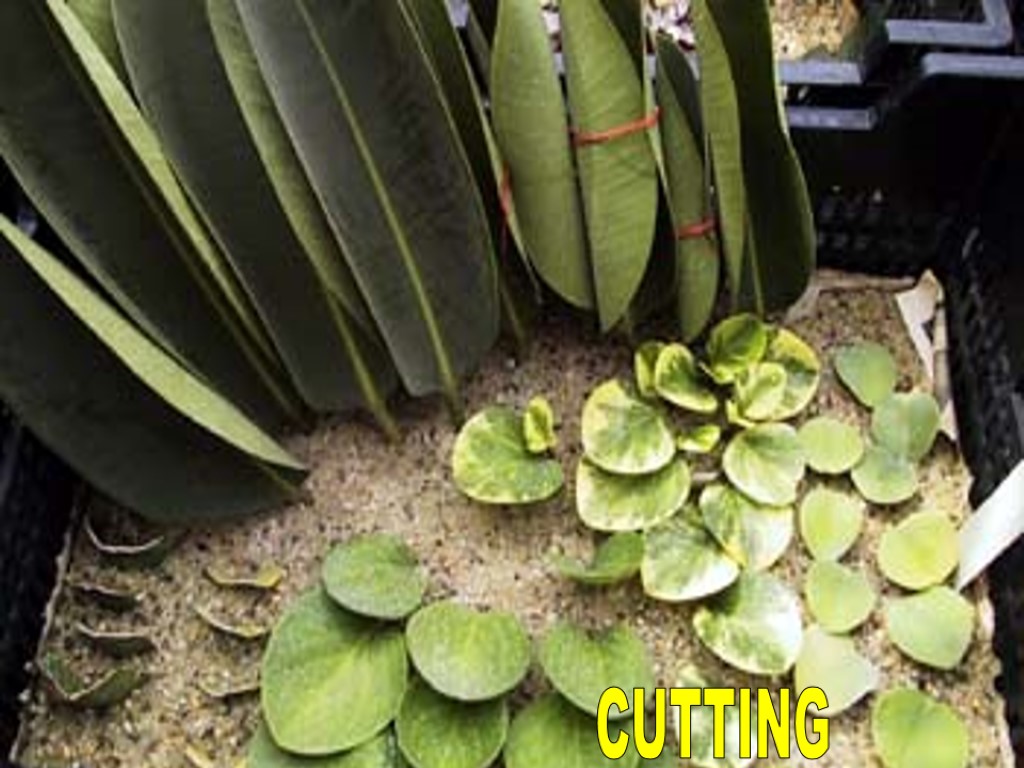

CUTTING
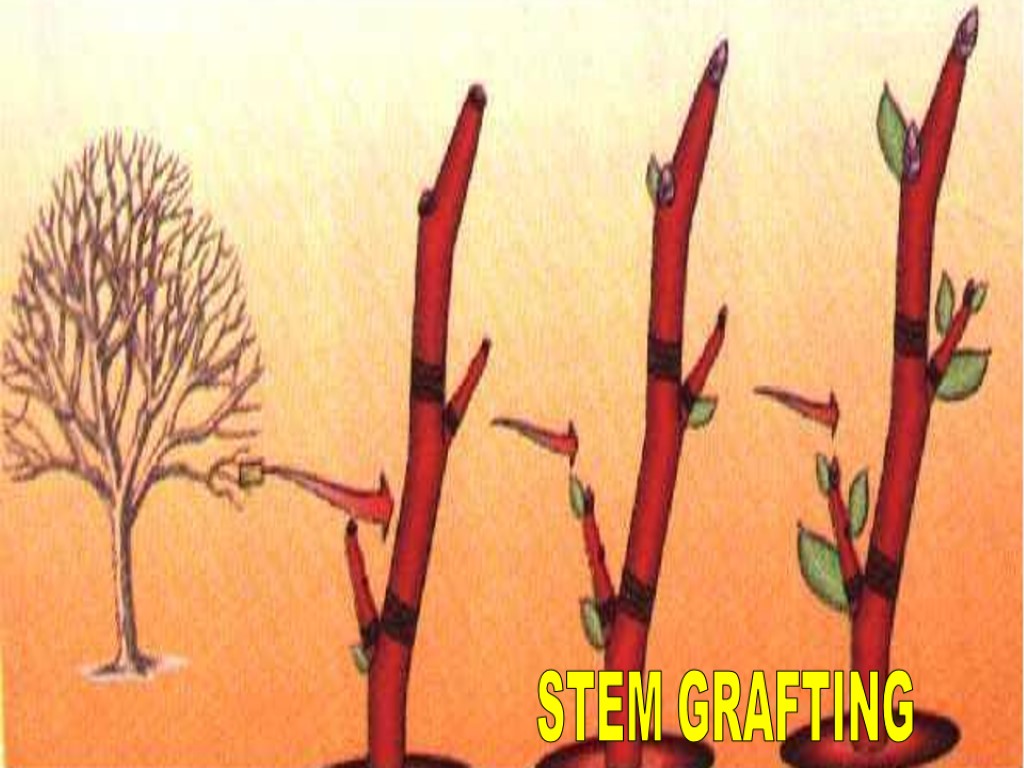

STEM GRAFTING

5. REGENERATION Regeneration is the ability to regenerate a missing part is possible to varying extents in all organisms. Some organisms regenerate lost body part. EX:Crab, lizard and earthworm

Planaria, hydra and starfish can reproduce by regeneration.

6. TISSUE CULTURE (Cloning) Tissue culture enables the propagation of a new organism from a small amount of the parent tissue.

In 1996 a sheep named Dolly was successfully cloned from a cell of an adult female sheep. This advance proved that adult cells could provide the cloning potential of embryonic cells.

7. PARTHENOGENESIS In rotifers, as well as some insects, fish, amphibians and reptiles the eggs produced by females develop directly into adults without being fertilized by sperm. This process is called parthenogenesis

Baby aphid
asexual_reproduction.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

