ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 90
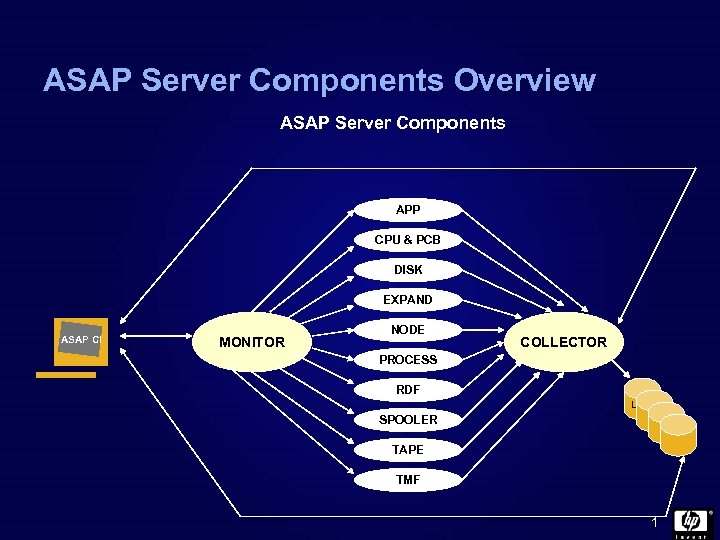 ASAP Server Components Overview ASAP Server Components APP CPU & PCB DISK EXPAND ASAP CI MONITOR NODE COLLECTOR PROCESS RDF LOG SPOOLER TAPE TMF 1
ASAP Server Components Overview ASAP Server Components APP CPU & PCB DISK EXPAND ASAP CI MONITOR NODE COLLECTOR PROCESS RDF LOG SPOOLER TAPE TMF 1
 ASAP - Command, Control, & Diagnosis ASAP command interpreter provides: • Command, control, status, and reporting for ASAP. • ASAP database configuration. • ASAP CI is also used to view ASAP exception log. This section covers: • ASAP CI control commands. • ASAP CI control example. • ASAP CI status and log commands. • ASAP CI database configuration commands. • ASAP CI database maintenance commands. • ASAP CI server time synchronization. • ASAP CI entity display commands. • ASAP CI basic commands. 2
ASAP - Command, Control, & Diagnosis ASAP command interpreter provides: • Command, control, status, and reporting for ASAP. • ASAP database configuration. • ASAP CI is also used to view ASAP exception log. This section covers: • ASAP CI control commands. • ASAP CI control example. • ASAP CI status and log commands. • ASAP CI database configuration commands. • ASAP CI database maintenance commands. • ASAP CI server time synchronization. • ASAP CI entity display commands. • ASAP CI basic commands. 2
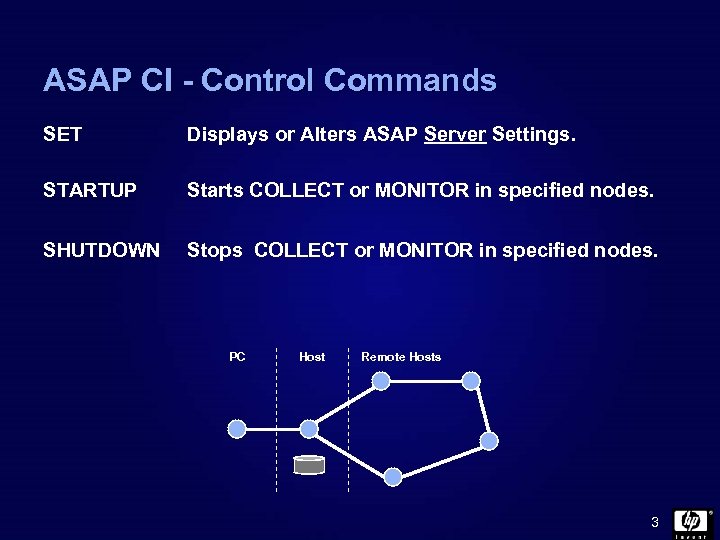 ASAP CI - Control Commands SET Displays or Alters ASAP Server Settings. STARTUP Starts COLLECT or MONITOR in specified nodes. SHUTDOWN Stops COLLECT or MONITOR in specified nodes. PC Host Remote Hosts 3
ASAP CI - Control Commands SET Displays or Alters ASAP Server Settings. STARTUP Starts COLLECT or MONITOR in specified nodes. SHUTDOWN Stops COLLECT or MONITOR in specified nodes. PC Host Remote Hosts 3
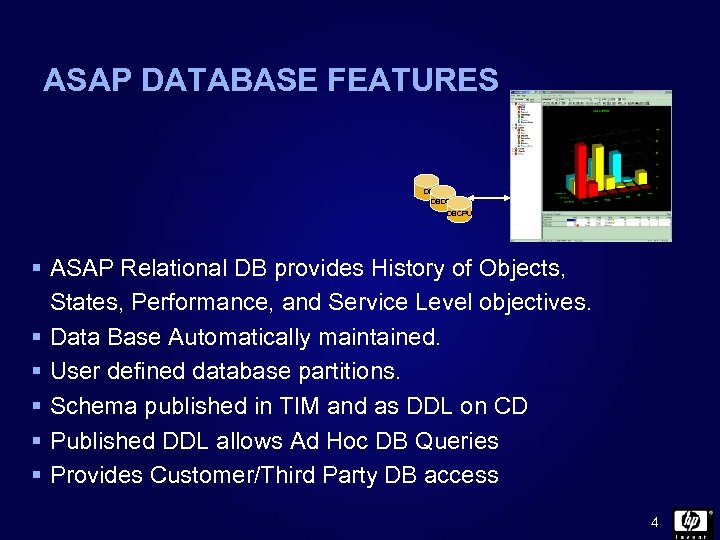 ASAP DATABASE FEATURES DBAPP DBDSK DBCPU § ASAP Relational DB provides History of Objects, States, Performance, and Service Level objectives. § Data Base Automatically maintained. § User defined database partitions. § Schema published in TIM and as DDL on CD § Published DDL allows Ad Hoc DB Queries § Provides Customer/Third Party DB access 4
ASAP DATABASE FEATURES DBAPP DBDSK DBCPU § ASAP Relational DB provides History of Objects, States, Performance, and Service Level objectives. § Data Base Automatically maintained. § User defined database partitions. § Schema published in TIM and as DDL on CD § Published DDL allows Ad Hoc DB Queries § Provides Customer/Third Party DB access 4
 ASAP Database Configuration ASAP Database configuration allows: § Default Database support. § User defined Database location. § Defined partition support for any ASAP entity. § User defined default partitioning rules. Database configuration commands: § SET Collect command. § SET DB command. § SET SLEEPTIME command. § SET Partition command. Note: Asap Version 1 records can be written to the ASAP Version 2 collector. 5
ASAP Database Configuration ASAP Database configuration allows: § Default Database support. § User defined Database location. § Defined partition support for any ASAP entity. § User defined default partitioning rules. Database configuration commands: § SET Collect command. § SET DB command. § SET SLEEPTIME command. § SET Partition command. Note: Asap Version 1 records can be written to the ASAP Version 2 collector. 5
 Database Commands § SET COLLECT defines the Node were the ASAP Database resides. SET COLLECT DBNODE § SET DB defines the location ($Volume. subvol) for the ASAP database files SET DB $DATA. ASAPDB. DB § SET SLEEPTIME defines the time range (hhmm, hhmm) that statistics collection does not occur. Although statistics collection ceases, the ASAP system remains active. SET SLEEPTIME 00: 00, 03: 30 6
Database Commands § SET COLLECT defines the Node were the ASAP Database resides. SET COLLECT DBNODE § SET DB defines the location ($Volume. subvol) for the ASAP database files SET DB $DATA. ASAPDB. DB § SET SLEEPTIME defines the time range (hhmm, hhmm) that statistics collection does not occur. Although statistics collection ceases, the ASAP system remains active. SET SLEEPTIME 00: 00, 03: 30 6
 Partition Command § SET PARTITION displays and defines partitioning parameters for the ASAP database. Asap partitioning uses standard NSK partitioning rules. The parameters can be set individually for each entity, globally for all entities, or may utilize a combination of the two approaches. To display the current partitioning settings, enter SET PARTITION without any additional parameters. $Data 00 $Data 01 $Data 02 DBCPU Part 0 DBCPU Part 1 DBCPU Part 2 7
Partition Command § SET PARTITION displays and defines partitioning parameters for the ASAP database. Asap partitioning uses standard NSK partitioning rules. The parameters can be set individually for each entity, globally for all entities, or may utilize a combination of the two approaches. To display the current partitioning settings, enter SET PARTITION without any additional parameters. $Data 00 $Data 01 $Data 02 DBCPU Part 0 DBCPU Part 1 DBCPU Part 2 7
 SET PARTITION Continued § SET PARTITION [
SET PARTITION Continued § SET PARTITION [
 SET PARTITION Continued
SET PARTITION Continued
 SET PARTITION Notes NOTES: § A VOLUME cannot be specified for a base partition (i. e. partition number = 0), since this is controlled by the SET DB command. § Volume, Sys. No, and Key values cannot be specified if the partition number is all. § A KEY and/or SYSNO value must be given for all secondary partitions. § Partitioning keys (made up of a combination of the SYSNO and KEY values) must be defined in ascending order for each partition. § A VOLUME must be given for all secondary partitions. 10
SET PARTITION Notes NOTES: § A VOLUME cannot be specified for a base partition (i. e. partition number = 0), since this is controlled by the SET DB command. § Volume, Sys. No, and Key values cannot be specified if the partition number is all. § A KEY and/or SYSNO value must be given for all secondary partitions. § Partitioning keys (made up of a combination of the SYSNO and KEY values) must be defined in ascending order for each partition. § A VOLUME must be given for all secondary partitions. 10
 Notes Continued § MAXEXTENTS values cannot be specified for secondary partitions if Format 2 is ON. PRIEXT, SECEXT, and MAXEXTS values specified for partitions of the DEFAULT entity are used when creating partitions of all other entities. The collector automatically adjusts the length of the partitioning keys. SET DB command will reset all partitioning attributes. The Collector utilizes only valid partition descriptions when creating the database. When partitioning is enabled for a given entity, the "Valid" column of the SET PARTITION output will indicate the status of each configured partition. The column contains one of the following values: § § § • • • YES No-Vol No-Sys/Key No-Vol, Sys/Key No-Prior Inv ? ? -Key Seq ? ? -Dup Vol ? ? -Vol Un. Known ? ? -Vol Down ? ? -Partn Size Max. Ext n/a 11
Notes Continued § MAXEXTENTS values cannot be specified for secondary partitions if Format 2 is ON. PRIEXT, SECEXT, and MAXEXTS values specified for partitions of the DEFAULT entity are used when creating partitions of all other entities. The collector automatically adjusts the length of the partitioning keys. SET DB command will reset all partitioning attributes. The Collector utilizes only valid partition descriptions when creating the database. When partitioning is enabled for a given entity, the "Valid" column of the SET PARTITION output will indicate the status of each configured partition. The column contains one of the following values: § § § • • • YES No-Vol No-Sys/Key No-Vol, Sys/Key No-Prior Inv ? ? -Key Seq ? ? -Dup Vol ? ? -Vol Un. Known ? ? -Vol Down ? ? -Partn Size Max. Ext n/a 11
 SET PARTITION Examples § SET PARTITION DEFAULT ALL PRIEXT 256, SECEXT 512, MAXEXTENTS 300 § SET PARTITION PROCESS 1 SYSNO 53 § SET PARTITION PROCESS 1 SYSNO 11, VOLUME $DATA 1 § SET PARTITION PROCESS 2 SYSNO 21, VOLUME $DATA 2 § SET PARTITION APP 1 SYSNO 120, KEY “FUNDSTRANSFER”, VOLUME $DATA § SET PARTITION APP 0 SYSNO 120 12
SET PARTITION Examples § SET PARTITION DEFAULT ALL PRIEXT 256, SECEXT 512, MAXEXTENTS 300 § SET PARTITION PROCESS 1 SYSNO 53 § SET PARTITION PROCESS 1 SYSNO 11, VOLUME $DATA 1 § SET PARTITION PROCESS 2 SYSNO 21, VOLUME $DATA 2 § SET PARTITION APP 1 SYSNO 120, KEY “FUNDSTRANSFER”, VOLUME $DATA § SET PARTITION APP 0 SYSNO 120 12
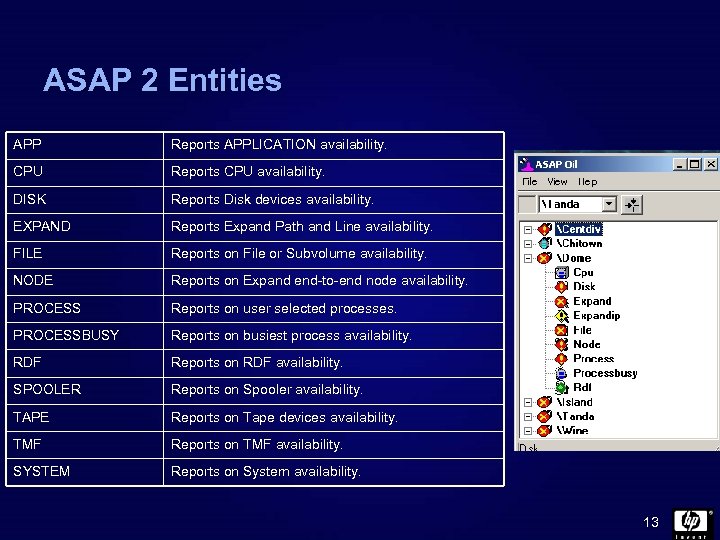 ASAP 2 Entities APP Reports APPLICATION availability. CPU Reports CPU availability. DISK Reports Disk devices availability. EXPAND Reports Expand Path and Line availability. FILE Reports on File or Subvolume availability. NODE Reports on Expand end-to-end node availability. PROCESS Reports on user selected processes. PROCESSBUSY Reports on busiest process availability. RDF Reports on RDF availability. SPOOLER Reports on Spooler availability. TAPE Reports on Tape devices availability. TMF Reports on TMF availability. SYSTEM Reports on System availability. 13
ASAP 2 Entities APP Reports APPLICATION availability. CPU Reports CPU availability. DISK Reports Disk devices availability. EXPAND Reports Expand Path and Line availability. FILE Reports on File or Subvolume availability. NODE Reports on Expand end-to-end node availability. PROCESS Reports on user selected processes. PROCESSBUSY Reports on busiest process availability. RDF Reports on RDF availability. SPOOLER Reports on Spooler availability. TAPE Reports on Tape devices availability. TMF Reports on TMF availability. SYSTEM Reports on System availability. 13
 ASAP 2. 0 ENTITIES ASAP Entities Characteristics: § Default Entity support. § User defined Entity configurations. § Entities can report on availability of user specified objects. § User defined threshold settings of specified objects and attributes using the operators >, <, =, <>, <= and >=. Entity configuration commands: § SET
ASAP 2. 0 ENTITIES ASAP Entities Characteristics: § Default Entity support. § User defined Entity configurations. § Entities can report on availability of user specified objects. § User defined threshold settings of specified objects and attributes using the operators >, <, =, <>, <= and >=. Entity configuration commands: § SET
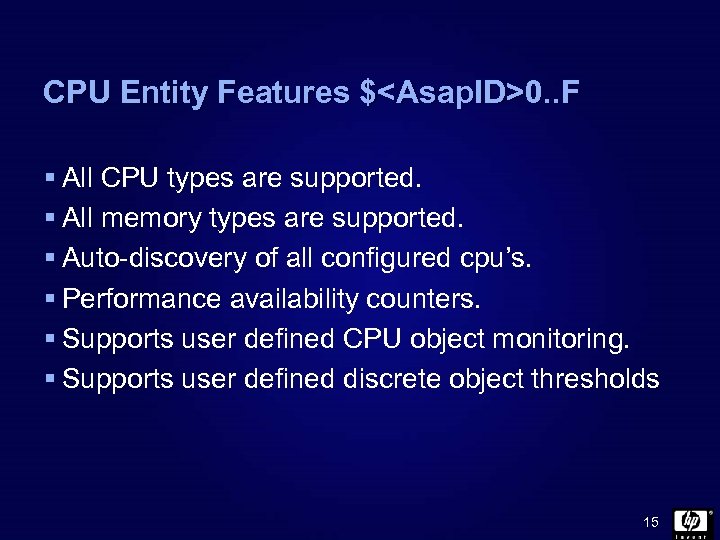 CPU Entity Features $
CPU Entity Features $
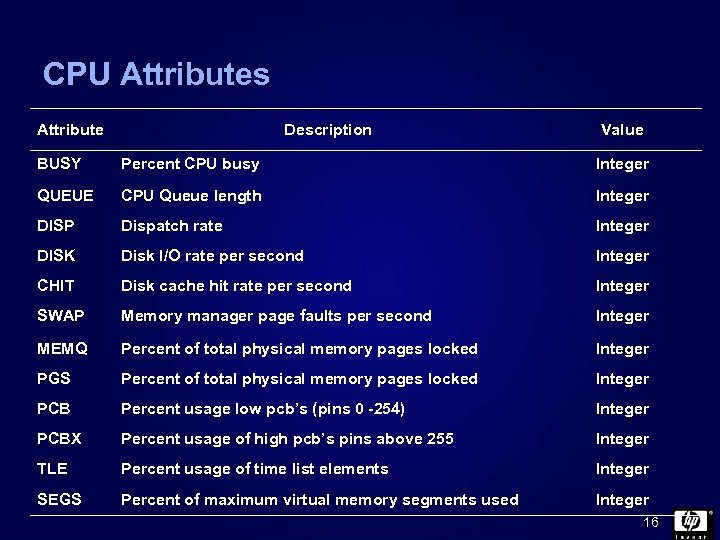 CPU Attributes Attribute Description Value BUSY Percent CPU busy Integer QUEUE CPU Queue length Integer DISP Dispatch rate Integer DISK Disk I/O rate per second Integer CHIT Disk cache hit rate per second Integer SWAP Memory manager page faults per second Integer MEMQ Percent of total physical memory pages locked Integer PGS Percent of total physical memory pages locked Integer PCB Percent usage low pcb’s (pins 0 -254) Integer PCBX Percent usage of high pcb’s pins above 255 Integer TLE Percent usage of time list elements Integer SEGS Percent of maximum virtual memory segments used Integer 16
CPU Attributes Attribute Description Value BUSY Percent CPU busy Integer QUEUE CPU Queue length Integer DISP Dispatch rate Integer DISK Disk I/O rate per second Integer CHIT Disk cache hit rate per second Integer SWAP Memory manager page faults per second Integer MEMQ Percent of total physical memory pages locked Integer PGS Percent of total physical memory pages locked Integer PCB Percent usage low pcb’s (pins 0 -254) Integer PCBX Percent usage of high pcb’s pins above 255 Integer TLE Percent usage of time list elements Integer SEGS Percent of maximum virtual memory segments used Integer 16
 DISK Entity Features $
DISK Entity Features $
 DISK SET Command § SET Disk ON|OFF Enables/Disables disk availability information. Default OFF § Set Disk object $System. system. asapdsk defines the Disk program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPDSK § Set Disk Param “Param, param 1…” Disk params: CPU
DISK SET Command § SET Disk ON|OFF Enables/Disables disk availability information. Default OFF § Set Disk object $System. system. asapdsk defines the Disk program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPDSK § Set Disk Param “Param, param 1…” Disk params: CPU
![DISK SET Command Continued Disk Params Cont: VOLUME [<$volume>][. ][<subvolume>] specifies the location of DISK SET Command Continued Disk Params Cont: VOLUME [<$volume>][. ][<subvolume>] specifies the location of](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-19.jpg) DISK SET Command Continued Disk Params Cont: VOLUME [<$volume>][. ][
DISK SET Command Continued Disk Params Cont: VOLUME [<$volume>][. ][
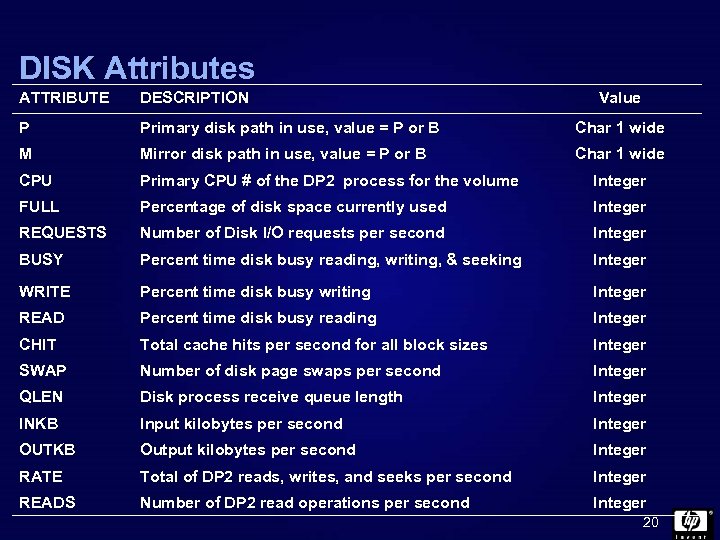 DISK Attributes ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION Value P Primary disk path in use, value = P or B Char 1 wide M Mirror disk path in use, value = P or B Char 1 wide CPU Primary CPU # of the DP 2 process for the volume Integer FULL Percentage of disk space currently used Integer REQUESTS Number of Disk I/O requests per second Integer BUSY Percent time disk busy reading, writing, & seeking Integer WRITE Percent time disk busy writing Integer READ Percent time disk busy reading Integer CHIT Total cache hits per second for all block sizes Integer SWAP Number of disk page swaps per second Integer QLEN Disk process receive queue length Integer INKB Input kilobytes per second Integer OUTKB Output kilobytes per second Integer RATE Total of DP 2 reads, writes, and seeks per second Integer READS Number of DP 2 read operations per second Integer 20
DISK Attributes ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION Value P Primary disk path in use, value = P or B Char 1 wide M Mirror disk path in use, value = P or B Char 1 wide CPU Primary CPU # of the DP 2 process for the volume Integer FULL Percentage of disk space currently used Integer REQUESTS Number of Disk I/O requests per second Integer BUSY Percent time disk busy reading, writing, & seeking Integer WRITE Percent time disk busy writing Integer READ Percent time disk busy reading Integer CHIT Total cache hits per second for all block sizes Integer SWAP Number of disk page swaps per second Integer QLEN Disk process receive queue length Integer INKB Input kilobytes per second Integer OUTKB Output kilobytes per second Integer RATE Total of DP 2 reads, writes, and seeks per second Integer READS Number of DP 2 read operations per second Integer 20
 DISK – Troubleshooting tips § DISK SGP uses measure API interface for collecting raw DP 2 counters. – Use the commands in MEASCOM for determining if it is a measure problem or disk entity problem § ADD MEASUREMENT $VOL. SUBVOL. ZASP
DISK – Troubleshooting tips § DISK SGP uses measure API interface for collecting raw DP 2 counters. – Use the commands in MEASCOM for determining if it is a measure problem or disk entity problem § ADD MEASUREMENT $VOL. SUBVOL. ZASP
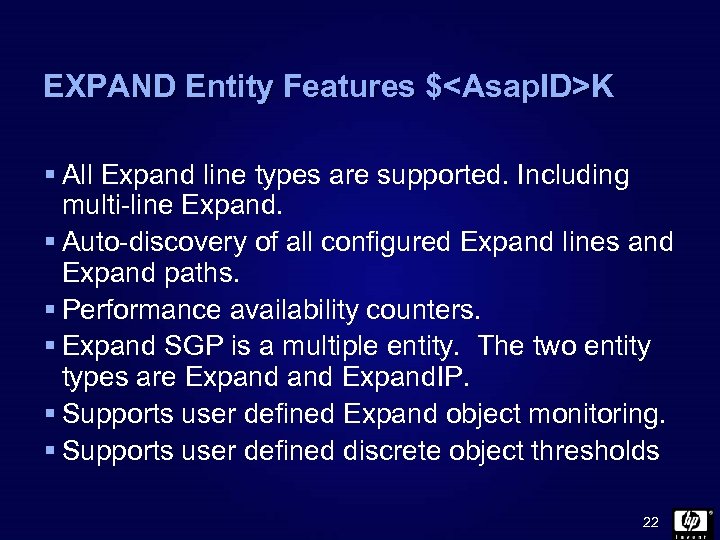 EXPAND Entity Features $
EXPAND Entity Features $
 EXPAND Set Command § Set Expand ON|OFF Enables/Disables Expand availability information. Default OFF § Set Expand object $System. system. asapdsk defines the Expand program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPEXP § Set Expand Param “Param” Expand params: RATE
EXPAND Set Command § Set Expand ON|OFF Enables/Disables Expand availability information. Default OFF § Set Expand object $System. system. asapdsk defines the Expand program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPEXP § Set Expand Param “Param” Expand params: RATE
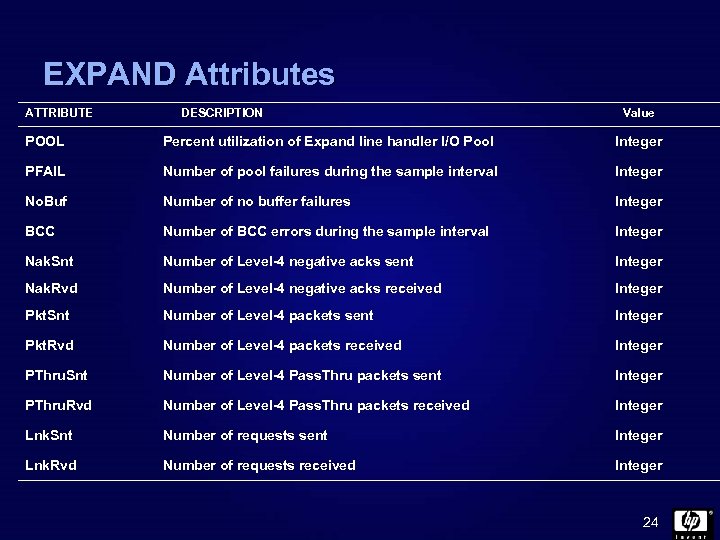 EXPAND Attributes ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION Value POOL Percent utilization of Expand line handler I/O Pool Integer PFAIL Number of pool failures during the sample interval Integer No. Buf Number of no buffer failures Integer BCC Number of BCC errors during the sample interval Integer Nak. Snt Number of Level-4 negative acks sent Integer Nak. Rvd Number of Level-4 negative acks received Integer Pkt. Snt Number of Level-4 packets sent Integer Pkt. Rvd Number of Level-4 packets received Integer PThru. Snt Number of Level-4 Pass. Thru packets sent Integer PThru. Rvd Number of Level-4 Pass. Thru packets received Integer Lnk. Snt Number of requests sent Integer Lnk. Rvd Number of requests received Integer 24
EXPAND Attributes ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION Value POOL Percent utilization of Expand line handler I/O Pool Integer PFAIL Number of pool failures during the sample interval Integer No. Buf Number of no buffer failures Integer BCC Number of BCC errors during the sample interval Integer Nak. Snt Number of Level-4 negative acks sent Integer Nak. Rvd Number of Level-4 negative acks received Integer Pkt. Snt Number of Level-4 packets sent Integer Pkt. Rvd Number of Level-4 packets received Integer PThru. Snt Number of Level-4 Pass. Thru packets sent Integer PThru. Rvd Number of Level-4 Pass. Thru packets received Integer Lnk. Snt Number of requests sent Integer Lnk. Rvd Number of requests received Integer 24
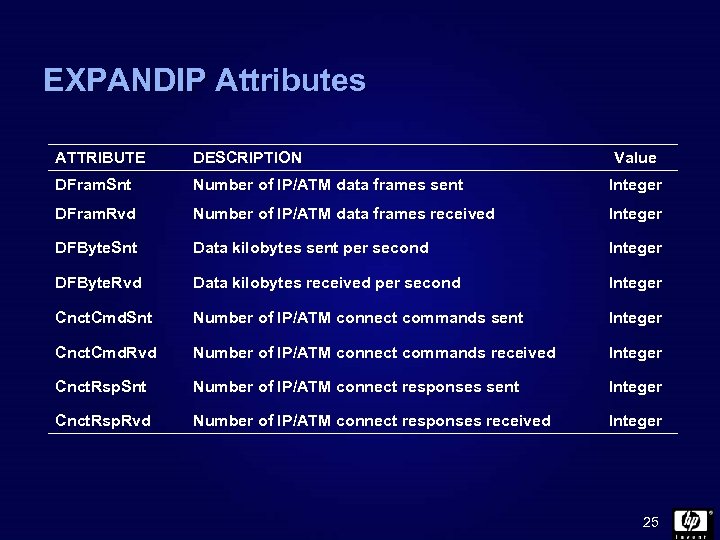 EXPANDIP Attributes ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION Value DFram. Snt Number of IP/ATM data frames sent Integer DFram. Rvd Number of IP/ATM data frames received Integer DFByte. Snt Data kilobytes sent per second Integer DFByte. Rvd Data kilobytes received per second Integer Cnct. Cmd. Snt Number of IP/ATM connect commands sent Integer Cnct. Cmd. Rvd Number of IP/ATM connect commands received Integer Cnct. Rsp. Snt Number of IP/ATM connect responses sent Integer Cnct. Rsp. Rvd Number of IP/ATM connect responses received Integer 25
EXPANDIP Attributes ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION Value DFram. Snt Number of IP/ATM data frames sent Integer DFram. Rvd Number of IP/ATM data frames received Integer DFByte. Snt Data kilobytes sent per second Integer DFByte. Rvd Data kilobytes received per second Integer Cnct. Cmd. Snt Number of IP/ATM connect commands sent Integer Cnct. Cmd. Rvd Number of IP/ATM connect commands received Integer Cnct. Rsp. Snt Number of IP/ATM connect responses sent Integer Cnct. Rsp. Rvd Number of IP/ATM connect responses received Integer 25
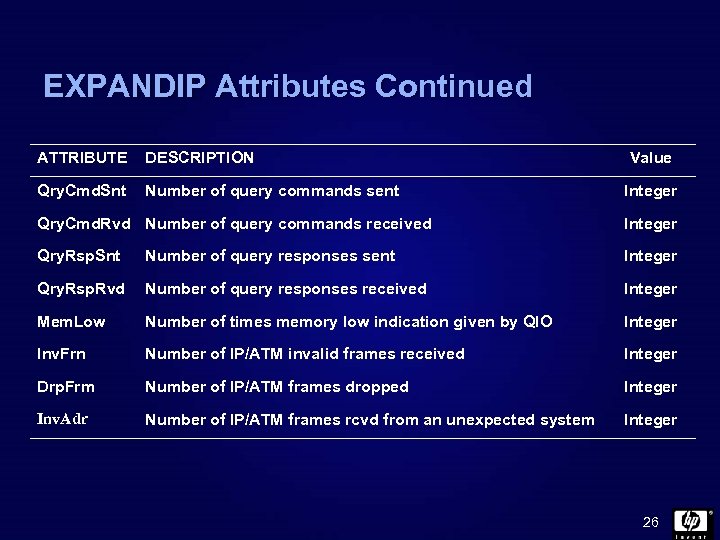 EXPANDIP Attributes Continued ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION Qry. Cmd. Snt Number of query commands sent Value Integer Qry. Cmd. Rvd Number of query commands received Integer Qry. Rsp. Snt Number of query responses sent Integer Qry. Rsp. Rvd Number of query responses received Integer Mem. Low Number of times memory low indication given by QIO Integer Inv. Frn Number of IP/ATM invalid frames received Integer Drp. Frm Number of IP/ATM frames dropped Integer Inv. Adr Number of IP/ATM frames rcvd from an unexpected system Integer 26
EXPANDIP Attributes Continued ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION Qry. Cmd. Snt Number of query commands sent Value Integer Qry. Cmd. Rvd Number of query commands received Integer Qry. Rsp. Snt Number of query responses sent Integer Qry. Rsp. Rvd Number of query responses received Integer Mem. Low Number of times memory low indication given by QIO Integer Inv. Frn Number of IP/ATM invalid frames received Integer Drp. Frm Number of IP/ATM frames dropped Integer Inv. Adr Number of IP/ATM frames rcvd from an unexpected system Integer 26
 EXPAND – Troubleshooting tips § Expand SGP uses SPI interface for communicating with the Expand manager process $Zexp. – Use the commands in SCF for determining if it is a Expand manager problem or Expand entity problem § Assume line $
EXPAND – Troubleshooting tips § Expand SGP uses SPI interface for communicating with the Expand manager process $Zexp. – Use the commands in SCF for determining if it is a Expand manager problem or Expand entity problem § Assume line $
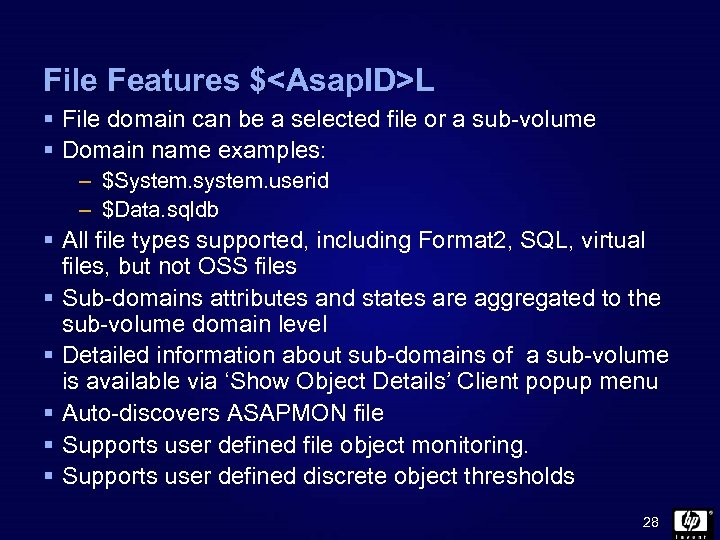 File Features $
File Features $
 FILE Set Command § Set File ON|OFF Enables/Disables file availability information. Default ON § Set File object $System. Asapfil defines the File program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPFIL § Set File Param “Param” File params: RATE
FILE Set Command § Set File ON|OFF Enables/Disables file availability information. Default ON § Set File object $System. Asapfil defines the File program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPFIL § Set File Param “Param” File params: RATE
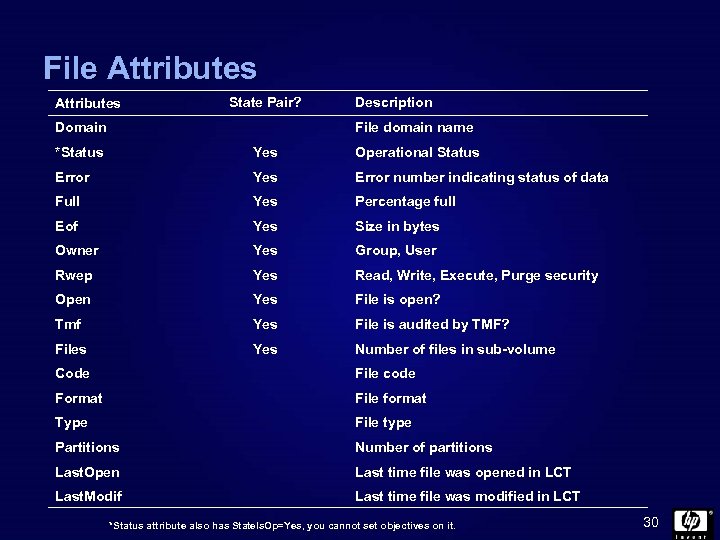 File Attributes State Pair? Domain Description File domain name *Status Yes Operational Status Error Yes Error number indicating status of data Full Yes Percentage full Eof Yes Size in bytes Owner Yes Group, User Rwep Yes Read, Write, Execute, Purge security Open Yes File is open? Tmf Yes File is audited by TMF? Files Yes Number of files in sub-volume Code File code Format File format Type File type Partitions Number of partitions Last. Open Last time file was opened in LCT Last. Modif Last time file was modified in LCT *Status attribute also has State. Is. Op=Yes, you cannot set objectives on it. 30
File Attributes State Pair? Domain Description File domain name *Status Yes Operational Status Error Yes Error number indicating status of data Full Yes Percentage full Eof Yes Size in bytes Owner Yes Group, User Rwep Yes Read, Write, Execute, Purge security Open Yes File is open? Tmf Yes File is audited by TMF? Files Yes Number of files in sub-volume Code File code Format File format Type File type Partitions Number of partitions Last. Open Last time file was opened in LCT Last. Modif Last time file was modified in LCT *Status attribute also has State. Is. Op=Yes, you cannot set objectives on it. 30
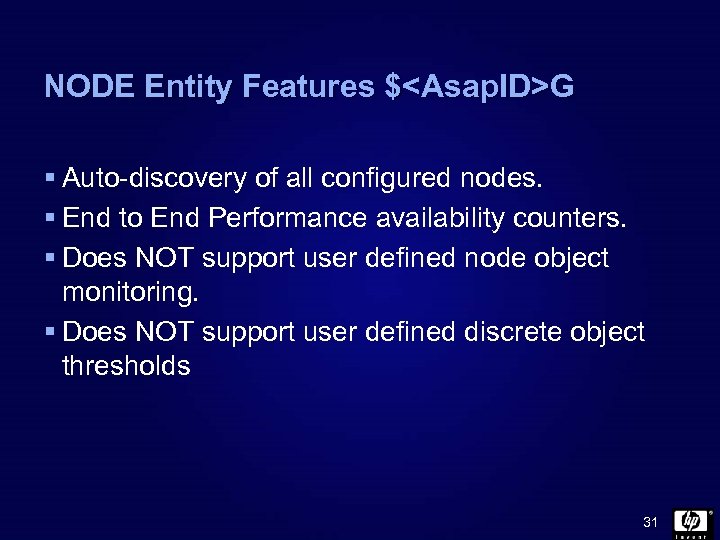 NODE Entity Features $
NODE Entity Features $
 NODE Set Command § Set Node ON|OFF Enables/Disables Node availability information. Default OFF § Set File object $System. Asapncp defines the node program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPNCP § Set Node Param “Param” Node params: RATE
NODE Set Command § Set Node ON|OFF Enables/Disables Node availability information. Default OFF § Set File object $System. Asapncp defines the node program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPNCP § Set Node Param “Param” Node params: RATE
 PROCESS Entity Features $
PROCESS Entity Features $
 PROCESS Set Command § Set Process ON|OFF Enables/Disables Process availability information. Default ON. § Set Process object $System. Asappro defines the Process program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPPRO § Set Process Param “Param, Param 1” Process params: RATE
PROCESS Set Command § Set Process ON|OFF Enables/Disables Process availability information. Default ON. § Set Process object $System. Asappro defines the Process program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPPRO § Set Process Param “Param, Param 1” Process params: RATE
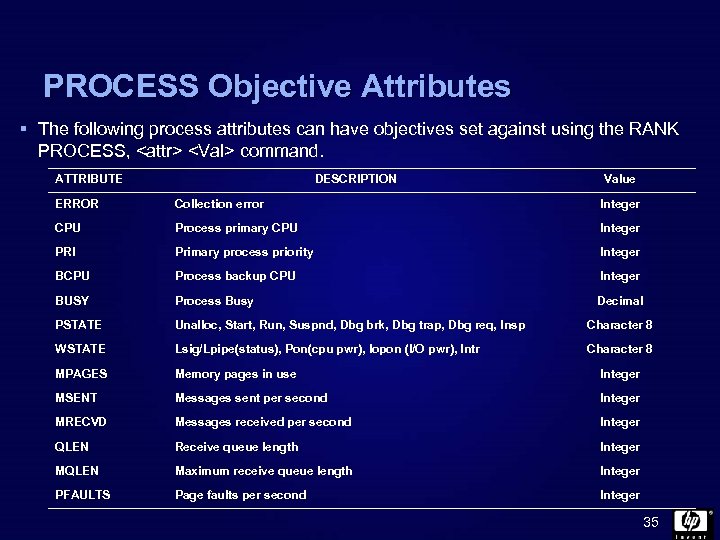 PROCESS Objective Attributes § The following process attributes can have objectives set against using the RANK PROCESS,
PROCESS Objective Attributes § The following process attributes can have objectives set against using the RANK PROCESS,
 PROCESSBUSY Features $
PROCESSBUSY Features $
 PROCESSBUSY Attributes ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION Value BUSY Average Cpu Busy Integer RCVQ Process receive queue length integrated Integer RCVMSG Messages received per second Integer SNDMSG Messages sent per second Integer PAGES Number of memory manager pages allocated to process Integer LCB Number of LCBs in use by the process Integer 37
PROCESSBUSY Attributes ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION Value BUSY Average Cpu Busy Integer RCVQ Process receive queue length integrated Integer RCVMSG Messages received per second Integer SNDMSG Messages sent per second Integer PAGES Number of memory manager pages allocated to process Integer LCB Number of LCBs in use by the process Integer 37
 PROCESSBUSY Set Command § Processbusy is not an Extended SGP it is part of the CPUSGP ($ZOO 0. . $ZOOF) § To set Processbusy availability information off use the Monitor Processbusy 0. . F, OFF. Default ON § Set Processbusy Param “Param, Param 1” Processbusy params ENTRIES
PROCESSBUSY Set Command § Processbusy is not an Extended SGP it is part of the CPUSGP ($ZOO 0. . $ZOOF) § To set Processbusy availability information off use the Monitor Processbusy 0. . F, OFF. Default ON § Set Processbusy Param “Param, Param 1” Processbusy params ENTRIES
 RDF Features $
RDF Features $
 RDF Set Command § Set RDF ON|OFF Enables/Disables RDF availability information. Default OFF § Set RDF object $System. Asaprdf defines the RDF program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPRDF § Set RDF Param “Param, Param 1” RDF params: RATE
RDF Set Command § Set RDF ON|OFF Enables/Disables RDF availability information. Default OFF § Set RDF object $System. Asaprdf defines the RDF program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPRDF § Set RDF Param “Param, Param 1” RDF params: RATE
 MONITOR RDF command § The alternative to autodiscovery is to monitor specific RDF environments. MONITOR RDF CHI->NYC (note no backslashes on node names) § Limited validation, errors will be reported by RDF SGP to event log every poll interval 41
MONITOR RDF command § The alternative to autodiscovery is to monitor specific RDF environments. MONITOR RDF CHI->NYC (note no backslashes on node names) § Limited validation, errors will be reported by RDF SGP to event log every poll interval 41
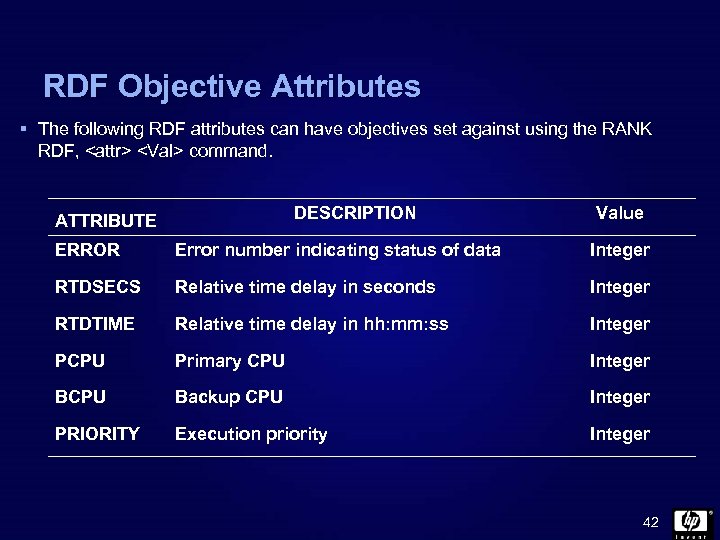 RDF Objective Attributes § The following RDF attributes can have objectives set against using the RANK RDF,
RDF Objective Attributes § The following RDF attributes can have objectives set against using the RANK RDF,
![RDF Command RDF [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>] RDF Command RDF [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>]](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-43.jpg) RDF Command RDF [/out
RDF Command RDF [/out
 RDF Troubleshooting § Check RDF SGP is actually running on both the RDF primary and backup nodes § If no stats are being reported, check RDF status with RDFCOM from the RDF primary system using STATUS RDF § If autodiscovery is being used find all the code 721 RDF CONFIG files FILEINFO $SYSTEM. *. CONFIG This will show the environments that should be reporting stats § If using MONITOR RDF for specific RDF environments check what is being monitored with MONITOR RDF, LIST § Manually stopping the $
RDF Troubleshooting § Check RDF SGP is actually running on both the RDF primary and backup nodes § If no stats are being reported, check RDF status with RDFCOM from the RDF primary system using STATUS RDF § If autodiscovery is being used find all the code 721 RDF CONFIG files FILEINFO $SYSTEM. *. CONFIG This will show the environments that should be reporting stats § If using MONITOR RDF for specific RDF environments check what is being monitored with MONITOR RDF, LIST § Manually stopping the $
 Spooler Features $
Spooler Features $
 Spooler Features (cont. ) § Information available in 2 modes: aggregation and detail – $SPLSDev is the aggregate for the print devices – $SPLSDev$LP is a specific device available in detail mode § SGP default mode is aggregation – Use SGP startup parameter DETAIL to have SGP work in detail mode 46
Spooler Features (cont. ) § Information available in 2 modes: aggregation and detail – $SPLSDev is the aggregate for the print devices – $SPLSDev$LP is a specific device available in detail mode § SGP default mode is aggregation – Use SGP startup parameter DETAIL to have SGP work in detail mode 46
 SPOOLER Set Command § Set Spooler ON|OFF Enables/Disables Spooler availability information. Default OFF § Set Spooler object $System. Asapspl defines the node program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPSPL § Set SPL Param “Param, Param 1” SPL params: DETAIL returns individual records for the spooler collector, processes and devices. RATE
SPOOLER Set Command § Set Spooler ON|OFF Enables/Disables Spooler availability information. Default OFF § Set Spooler object $System. Asapspl defines the node program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPSPL § Set SPL Param “Param, Param 1” SPL params: DETAIL returns individual records for the spooler collector, processes and devices. RATE
 SPOOLER Set Command Continued TRACE turns on $RECEIVE trace to the EMS and ASAP log files. Here is an example of the SET SPOOLER command: +SET SPOOLER ON, OBJECT $SYSTEM. ASAPSPL, PARAMETERS “RATE 10 TRACE" 48
SPOOLER Set Command Continued TRACE turns on $RECEIVE trace to the EMS and ASAP log files. Here is an example of the SET SPOOLER command: +SET SPOOLER ON, OBJECT $SYSTEM. ASAPSPL, PARAMETERS “RATE 10 TRACE" 48
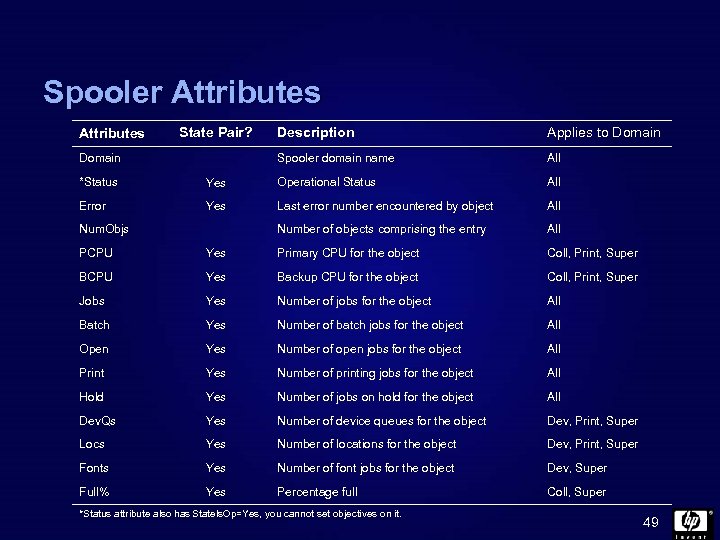 Spooler Attributes State Pair? Applies to Domain Spooler domain name Domain Description All *Status Yes Operational Status All Error Yes Last error number encountered by object All Number of objects comprising the entry All Num. Objs PCPU Yes Primary CPU for the object Coll, Print, Super BCPU Yes Backup CPU for the object Coll, Print, Super Jobs Yes Number of jobs for the object All Batch Yes Number of batch jobs for the object All Open Yes Number of open jobs for the object All Print Yes Number of printing jobs for the object All Hold Yes Number of jobs on hold for the object All Dev. Qs Yes Number of device queues for the object Dev, Print, Super Locs Yes Number of locations for the object Dev, Print, Super Fonts Yes Number of font jobs for the object Dev, Super Full% Yes Percentage full Coll, Super *Status attribute also has State. Is. Op=Yes, you cannot set objectives on it. 49
Spooler Attributes State Pair? Applies to Domain Spooler domain name Domain Description All *Status Yes Operational Status All Error Yes Last error number encountered by object All Number of objects comprising the entry All Num. Objs PCPU Yes Primary CPU for the object Coll, Print, Super BCPU Yes Backup CPU for the object Coll, Print, Super Jobs Yes Number of jobs for the object All Batch Yes Number of batch jobs for the object All Open Yes Number of open jobs for the object All Print Yes Number of printing jobs for the object All Hold Yes Number of jobs on hold for the object All Dev. Qs Yes Number of device queues for the object Dev, Print, Super Locs Yes Number of locations for the object Dev, Print, Super Fonts Yes Number of font jobs for the object Dev, Super Full% Yes Percentage full Coll, Super *Status attribute also has State. Is. Op=Yes, you cannot set objectives on it. 49
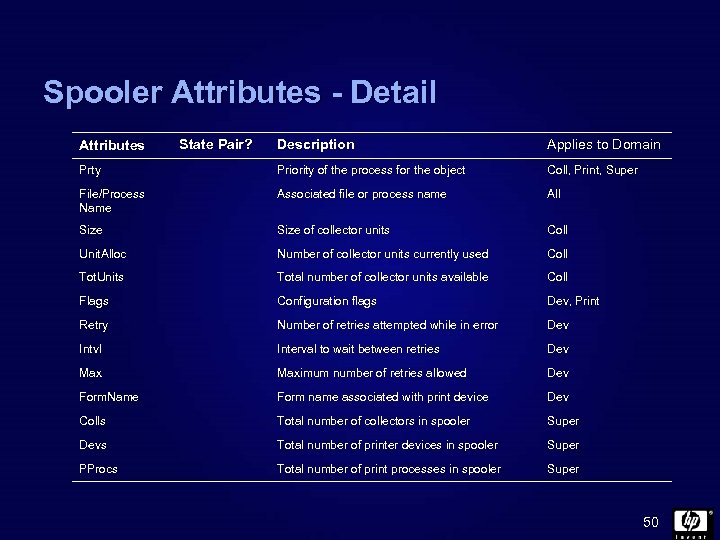 Spooler Attributes - Detail Description Applies to Domain Prty Priority of the process for the object Coll, Print, Super File/Process Name Associated file or process name All Size of collector units Coll Unit. Alloc Number of collector units currently used Coll Tot. Units Total number of collector units available Coll Flags Configuration flags Dev, Print Retry Number of retries attempted while in error Dev Intvl Interval to wait between retries Dev Maximum number of retries allowed Dev Form. Name Form name associated with print device Dev Colls Total number of collectors in spooler Super Devs Total number of printer devices in spooler Super PProcs Total number of print processes in spooler Super Attributes State Pair? 50
Spooler Attributes - Detail Description Applies to Domain Prty Priority of the process for the object Coll, Print, Super File/Process Name Associated file or process name All Size of collector units Coll Unit. Alloc Number of collector units currently used Coll Tot. Units Total number of collector units available Coll Flags Configuration flags Dev, Print Retry Number of retries attempted while in error Dev Intvl Interval to wait between retries Dev Maximum number of retries allowed Dev Form. Name Form name associated with print device Dev Colls Total number of collectors in spooler Super Devs Total number of printer devices in spooler Super PProcs Total number of print processes in spooler Super Attributes State Pair? 50
 Spooler – Troubleshooting Tips § Autoconfiguration is $SPLS only. § Spooler SGP uses the SPOOLER Procedures Calls SPOOLERSTATUS or SPOOLERSTATUS 2 to get the state and status information § Aggregation vs Detail – Default SGP behavior is aggregation – SPOOLER, DETAIL or SHOW DETAIL INFO can be used to get detail – Use SGP STARTUP PARAM DETAIL to have Spooler SGP collect data in detail mode 51
Spooler – Troubleshooting Tips § Autoconfiguration is $SPLS only. § Spooler SGP uses the SPOOLER Procedures Calls SPOOLERSTATUS or SPOOLERSTATUS 2 to get the state and status information § Aggregation vs Detail – Default SGP behavior is aggregation – SPOOLER, DETAIL or SHOW DETAIL INFO can be used to get detail – Use SGP STARTUP PARAM DETAIL to have Spooler SGP collect data in detail mode 51
 SYSTEM Entity Features $
SYSTEM Entity Features $
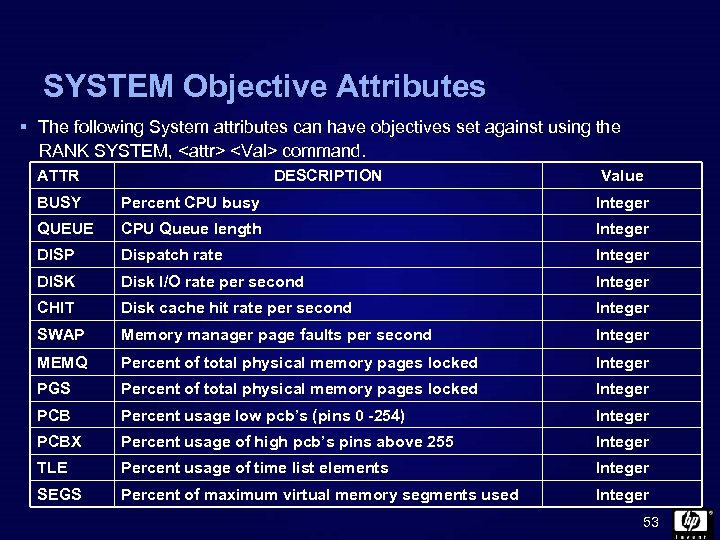 SYSTEM Objective Attributes § The following System attributes can have objectives set against using the RANK SYSTEM,
SYSTEM Objective Attributes § The following System attributes can have objectives set against using the RANK SYSTEM,
 Tape Features $
Tape Features $
 TAPE Set Command § Set Tape ON|OFF Enables/Disables Tape availability information. Default OFF § Set Tape object $System. Asaptap defines the Tape program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPTAP § Set TAPE Param “Param, Param 1” Tape params: RATE
TAPE Set Command § Set Tape ON|OFF Enables/Disables Tape availability information. Default OFF § Set Tape object $System. Asaptap defines the Tape program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPTAP § Set TAPE Param “Param, Param 1” Tape params: RATE
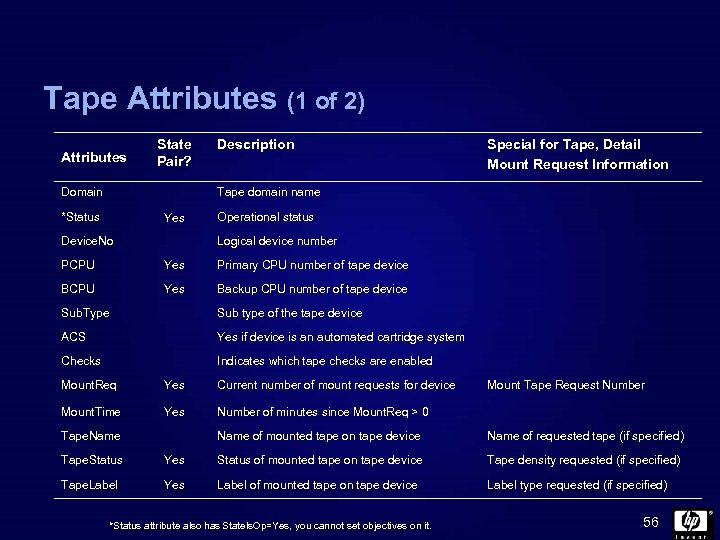 Tape Attributes (1 of 2) Attributes State Pair? Domain Description Special for Tape, Detail Mount Request Information Tape domain name *Status Yes Device. No Operational status Logical device number PCPU Yes Primary CPU number of tape device BCPU Yes Backup CPU number of tape device Sub. Type Sub type of the tape device ACS Yes if device is an automated cartridge system Checks Indicates which tape checks are enabled Mount. Req Yes Current number of mount requests for device Mount. Time Yes Number of minutes since Mount. Req > 0 Tape. Name Mount Tape Request Number Name of mounted tape on tape device Name of requested tape (if specified) Tape. Status Yes Status of mounted tape on tape device Tape density requested (if specified) Tape. Label Yes Label of mounted tape on tape device Label type requested (if specified) *Status attribute also has State. Is. Op=Yes, you cannot set objectives on it. 56
Tape Attributes (1 of 2) Attributes State Pair? Domain Description Special for Tape, Detail Mount Request Information Tape domain name *Status Yes Device. No Operational status Logical device number PCPU Yes Primary CPU number of tape device BCPU Yes Backup CPU number of tape device Sub. Type Sub type of the tape device ACS Yes if device is an automated cartridge system Checks Indicates which tape checks are enabled Mount. Req Yes Current number of mount requests for device Mount. Time Yes Number of minutes since Mount. Req > 0 Tape. Name Mount Tape Request Number Name of mounted tape on tape device Name of requested tape (if specified) Tape. Status Yes Status of mounted tape on tape device Tape density requested (if specified) Tape. Label Yes Label of mounted tape on tape device Label type requested (if specified) *Status attribute also has State. Is. Op=Yes, you cannot set objectives on it. 56
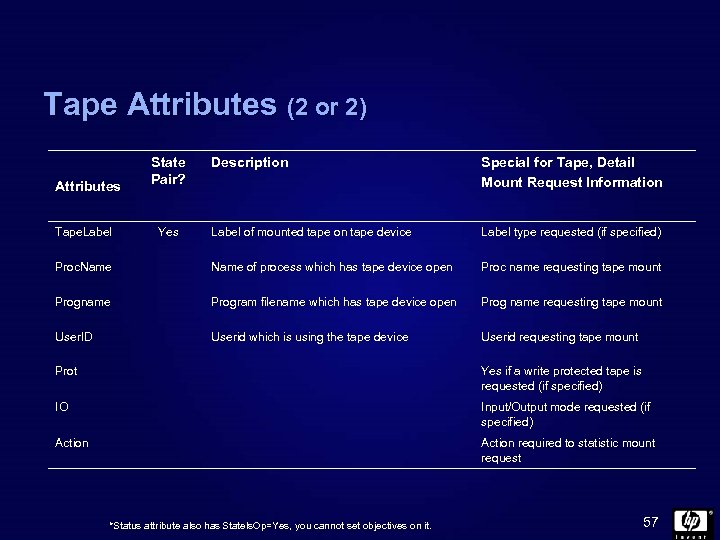 Tape Attributes (2 or 2) Description Special for Tape, Detail Mount Request Information Label of mounted tape on tape device Label type requested (if specified) Proc. Name of process which has tape device open Proc name requesting tape mount Progname Program filename which has tape device open Prog name requesting tape mount User. ID Userid which is using the tape device Userid requesting tape mount Attributes Tape. Label State Pair? Yes Prot Yes if a write protected tape is requested (if specified) IO Input/Output mode requested (if specified) Action required to statistic mount request *Status attribute also has State. Is. Op=Yes, you cannot set objectives on it. 57
Tape Attributes (2 or 2) Description Special for Tape, Detail Mount Request Information Label of mounted tape on tape device Label type requested (if specified) Proc. Name of process which has tape device open Proc name requesting tape mount Progname Program filename which has tape device open Prog name requesting tape mount User. ID Userid which is using the tape device Userid requesting tape mount Attributes Tape. Label State Pair? Yes Prot Yes if a write protected tape is requested (if specified) IO Input/Output mode requested (if specified) Action required to statistic mount request *Status attribute also has State. Is. Op=Yes, you cannot set objectives on it. 57
 Tape – Troubleshooting tips § TAPE SGP uses SPI interface to talk to MEDIASRV server – MEDIASRV server must at least be D 42 AAT or newer – MEDIASRV is part of the DSM/Tape Catalog Product and must installed properly – MEDIASRV uses the tape server ZSERVER ($ZSVR) SCF; STOP TAPE $*; ALTER $ZZSTO, LABELTAPE ON; START TAPE $* ZSERVER /NAME $ZSVR, NOWAIT, cpu 0, pri 160, term $ymiop. #clci/1 MEDIACOM; ALTER TAPEDRIVE *, NLCHECK OFF 58
Tape – Troubleshooting tips § TAPE SGP uses SPI interface to talk to MEDIASRV server – MEDIASRV server must at least be D 42 AAT or newer – MEDIASRV is part of the DSM/Tape Catalog Product and must installed properly – MEDIASRV uses the tape server ZSERVER ($ZSVR) SCF; STOP TAPE $*; ALTER $ZZSTO, LABELTAPE ON; START TAPE $* ZSERVER /NAME $ZSVR, NOWAIT, cpu 0, pri 160, term $ymiop. #clci/1 MEDIACOM; ALTER TAPEDRIVE *, NLCHECK OFF 58
 TMF Features $
TMF Features $
 TMF Set Command § Set TMF ON|OFF Enables/Disables Tape availability information. Default OFF § Set TMF object $System. Asaptmf defines the TMF program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPTMF § Set TMF Param “Param, Param 1” Tape params: RATE
TMF Set Command § Set TMF ON|OFF Enables/Disables Tape availability information. Default OFF § Set TMF object $System. Asaptmf defines the TMF program object filename. Default $SYSTEM. ASAPTMF § Set TMF Param “Param, Param 1” Tape params: RATE
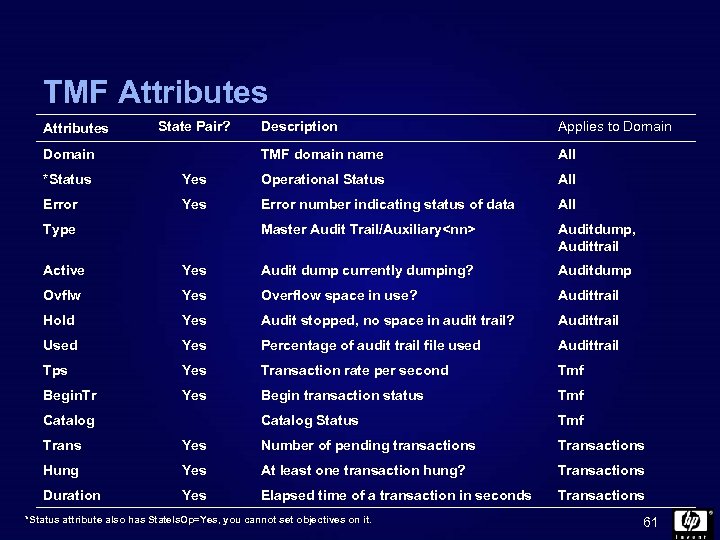 TMF Attributes State Pair? Applies to Domain TMF domain name Domain Description All *Status Yes Operational Status All Error Yes Error number indicating status of data All Master Audit Trail/Auxiliary
TMF Attributes State Pair? Applies to Domain TMF domain name Domain Description All *Status Yes Operational Status All Error Yes Error number indicating status of data All Master Audit Trail/Auxiliary
 TMF – Troubleshooting tips § TMF SGP uses SPI interface to talk to TMFCOM server – Use those commands in TMFCOM to get the information displayed by the TMF SGP: § status tmf § status transactions § status audittrail § info audittrail § status auditdump 62
TMF – Troubleshooting tips § TMF SGP uses SPI interface to talk to TMFCOM server – Use those commands in TMFCOM to get the information displayed by the TMF SGP: § status tmf § status transactions § status audittrail § info audittrail § status auditdump 62
 ASAP SET Control Command § ASAP control and node configurations settings are performed by using the ASAP SET command. SET APP
ASAP SET Control Command § ASAP control and node configurations settings are performed by using the ASAP SET command. SET APP
 SET Control Command Continued SET ID $
SET Control Command Continued SET ID $
 SET Command Continued SET IOCONTROL
SET Command Continued SET IOCONTROL
 SET Commands Continued SET LOGGING ON | OFF Logging on captures all ASAP CI input/output to be written to the file set by LOGFILE. SET ASAPLOG
SET Commands Continued SET LOGGING ON | OFF Logging on captures all ASAP CI input/output to be written to the file set by LOGFILE. SET ASAPLOG
 SET Command Continued SET SET SET OBJECTIVESEVENTUP ON | OFF OBJECTIVESEVENTCONSOLEUP ON | OFF OBJECTIVESEVENTSTATE
SET Command Continued SET SET SET OBJECTIVESEVENTUP ON | OFF OBJECTIVESEVENTCONSOLEUP ON | OFF OBJECTIVESEVENTSTATE
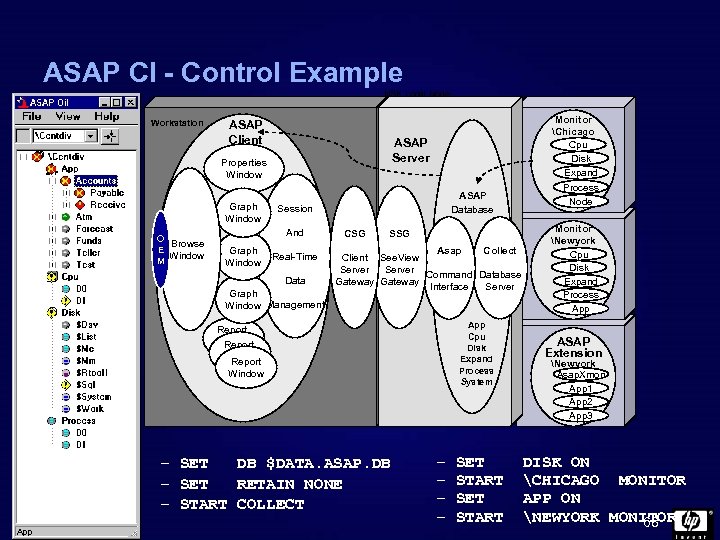 ASAP CI - Control Example NSK Local Node Workstation ASAP Client ASAP Server Properties Window Graph Window O Browse E Window M Session And Graph Window ASAP Database Real-Time Data Graph Window Management CSG SSG Collect Asap Client See. View Server Command Database Gateway Interface Server App Cpu Disk Expand Process System Report Window – SET DB $DATA. ASAP. DB – SET RETAIN NONE – START COLLECT – – SET START Monitor Chicago Cpu Disk Expand Process Node Monitor Newyork Cpu Disk Expand Process App ASAP Extension Newyork Asap. Xmon App 1 App 2 App 3 DISK ON CHICAGO MONITOR APP ON NEWYORK MONITOR 68
ASAP CI - Control Example NSK Local Node Workstation ASAP Client ASAP Server Properties Window Graph Window O Browse E Window M Session And Graph Window ASAP Database Real-Time Data Graph Window Management CSG SSG Collect Asap Client See. View Server Command Database Gateway Interface Server App Cpu Disk Expand Process System Report Window – SET DB $DATA. ASAP. DB – SET RETAIN NONE – START COLLECT – – SET START Monitor Chicago Cpu Disk Expand Process Node Monitor Newyork Cpu Disk Expand Process App ASAP Extension Newyork Asap. Xmon App 1 App 2 App 3 DISK ON CHICAGO MONITOR APP ON NEWYORK MONITOR 68
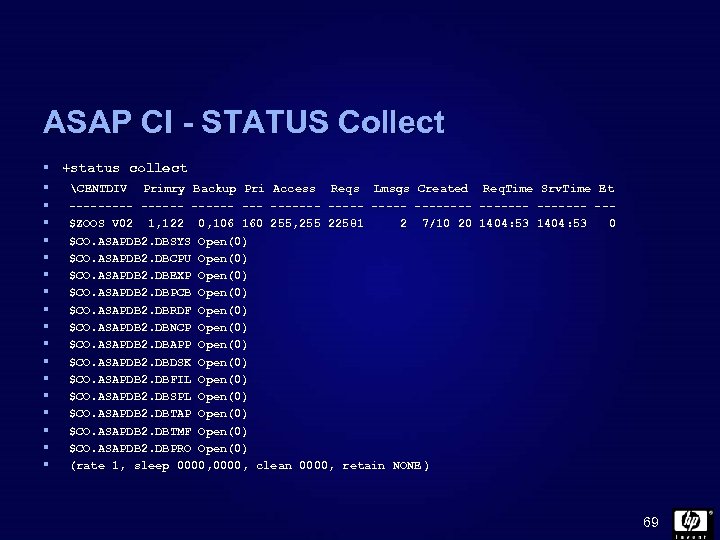 ASAP CI - STATUS Collect § +status collect § CENTDIV Primry Backup Pri Access § § § § Reqs Lmsgs Created Req. Time Srv. Time Et ------ ------- ------- --$ZOOS V 02 1, 122 0, 106 160 255, 255 22581 2 7/10 20 1404: 53 0 $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBSYS Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBCPU Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBEXP Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBPCB Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBRDF Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBNCP Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBAPP Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBDSK Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBFIL Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBSPL Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBTAP Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBTMF Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBPRO Open(0) (rate 1, sleep 0000, clean 0000, retain NONE ) 69
ASAP CI - STATUS Collect § +status collect § CENTDIV Primry Backup Pri Access § § § § Reqs Lmsgs Created Req. Time Srv. Time Et ------ ------- ------- --$ZOOS V 02 1, 122 0, 106 160 255, 255 22581 2 7/10 20 1404: 53 0 $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBSYS Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBCPU Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBEXP Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBPCB Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBRDF Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBNCP Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBAPP Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBDSK Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBFIL Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBSPL Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBTAP Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBTMF Open(0) $CO. ASAPDB 2. DBPRO Open(0) (rate 1, sleep 0000, clean 0000, retain NONE ) 69
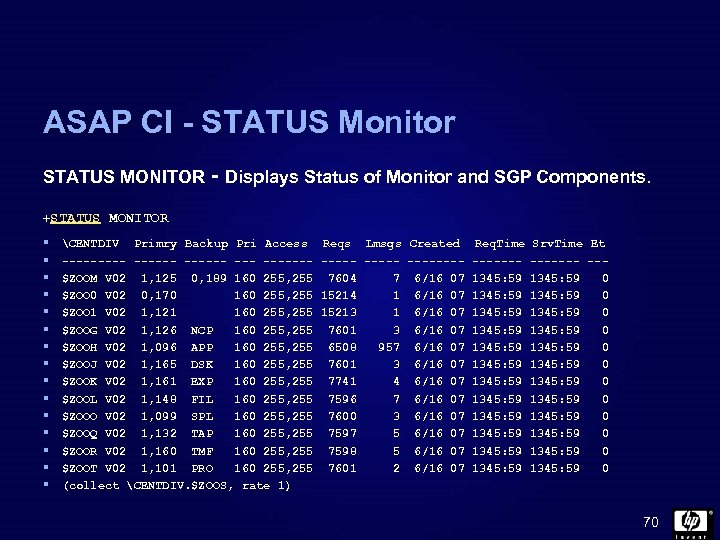 ASAP CI - STATUS Monitor STATUS MONITOR - Displays Status of Monitor and SGP Components. +STATUS MONITOR § § § § CENTDIV Primry Backup Pri Access ------ ------$ZOOM V 02 1, 125 0, 189 160 255, 255 $ZOO 0 V 02 0, 170 160 255, 255 $ZOO 1 V 02 1, 121 160 255, 255 $ZOOG V 02 1, 126 NCP 160 255, 255 $ZOOH V 02 1, 096 APP 160 255, 255 $ZOOJ V 02 1, 165 DSK 160 255, 255 $ZOOK V 02 1, 161 EXP 160 255, 255 $ZOOL V 02 1, 148 FIL 160 255, 255 $ZOOO V 02 1, 099 SPL 160 255, 255 $ZOOQ V 02 1, 132 TAP 160 255, 255 $ZOOR V 02 1, 160 TMF 160 255, 255 $ZOOT V 02 1, 101 PRO 160 255, 255 (collect CENTDIV. $ZOOS, rate 1) Reqs Lmsgs Created Req. Time Srv. Time Et ----- ------- --7604 7 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 15214 1 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 15213 1 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7601 3 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 6508 957 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7601 3 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7741 4 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7596 7 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7600 3 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7597 5 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7598 5 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7601 2 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 70
ASAP CI - STATUS Monitor STATUS MONITOR - Displays Status of Monitor and SGP Components. +STATUS MONITOR § § § § CENTDIV Primry Backup Pri Access ------ ------$ZOOM V 02 1, 125 0, 189 160 255, 255 $ZOO 0 V 02 0, 170 160 255, 255 $ZOO 1 V 02 1, 121 160 255, 255 $ZOOG V 02 1, 126 NCP 160 255, 255 $ZOOH V 02 1, 096 APP 160 255, 255 $ZOOJ V 02 1, 165 DSK 160 255, 255 $ZOOK V 02 1, 161 EXP 160 255, 255 $ZOOL V 02 1, 148 FIL 160 255, 255 $ZOOO V 02 1, 099 SPL 160 255, 255 $ZOOQ V 02 1, 132 TAP 160 255, 255 $ZOOR V 02 1, 160 TMF 160 255, 255 $ZOOT V 02 1, 101 PRO 160 255, 255 (collect CENTDIV. $ZOOS, rate 1) Reqs Lmsgs Created Req. Time Srv. Time Et ----- ------- --7604 7 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 15214 1 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 15213 1 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7601 3 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 6508 957 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7601 3 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7741 4 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7596 7 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7600 3 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7597 5 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7598 5 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 7601 2 6/16 07 1345: 59 0 70
 ASAP CI - LOG Command § § § § 01/06/16 01/06/16 01/06/16 01/06/16 0701: 57 0702: 03 0702: 04 0702: 05 0702: 06 0702: 08 0702: 09 0702: 10 0702: 12 0702: 13 0702: 15 0702: 39 0702: 53 3001 1022 1023 1023 1023 1881 1720 ZOOM INFO ZOO 0 INFO ZOO 1 INFO ZOOG INFO ZOOH INFO ZOOJ INFO ZOOK INFO ZOOL INFO ZOOO INFO ZOOQ INFO ZOOR INFO ZOOT INFO ZOOH 0 INFO ZOOH 1 INFO ZOOJ INFO Non. Stop Backup Created. Cpu: MONITOR V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP NCP V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP APP V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP DSK V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP EXP V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP FIL V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP SPL V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP TAP V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP TMF V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP PRO V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started APP V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started ASAPDSK ZASPZOO started. Notes: 1. All ASAP Exceptions are logged in Tandem EMS Event log. 2. Asap Messages can be found in the Asap Messages Manual 71
ASAP CI - LOG Command § § § § 01/06/16 01/06/16 01/06/16 01/06/16 0701: 57 0702: 03 0702: 04 0702: 05 0702: 06 0702: 08 0702: 09 0702: 10 0702: 12 0702: 13 0702: 15 0702: 39 0702: 53 3001 1022 1023 1023 1023 1881 1720 ZOOM INFO ZOO 0 INFO ZOO 1 INFO ZOOG INFO ZOOH INFO ZOOJ INFO ZOOK INFO ZOOL INFO ZOOO INFO ZOOQ INFO ZOOR INFO ZOOT INFO ZOOH 0 INFO ZOOH 1 INFO ZOOJ INFO Non. Stop Backup Created. Cpu: MONITOR V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP NCP V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP APP V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP DSK V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP EXP V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP FIL V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP SPL V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP TAP V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP TMF V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started SGP PRO V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started APP V 02. 00 (29 JUN 2001) started ASAPDSK ZASPZOO started. Notes: 1. All ASAP Exceptions are logged in Tandem EMS Event log. 2. Asap Messages can be found in the Asap Messages Manual 71
 ASAP CI - Database Maintenance Commands § SET RETAIN – Controls what the ASAP Server does at “Cleantime”. SET RETAIN ALL NONE ROLLOVER
ASAP CI - Database Maintenance Commands § SET RETAIN – Controls what the ASAP Server does at “Cleantime”. SET RETAIN ALL NONE ROLLOVER
 ASAP CI - Time Synchronization Commands PC Host Remote Hosts • SET SYNC
ASAP CI - Time Synchronization Commands PC Host Remote Hosts • SET SYNC
 ASAP CI - Entity Commands • Entity Commands provide reporting of availability. • Used for batch reporting & trouble-shooting of statistic values. APP Reports APPLICATION availability. CPU Reports CPU availability. DISK Reports DISK availability. FILE Reports File availability LH Reports Expand Line Handler availability. NODE Reports Expand end-to-end availability. PROCESS Reports User selected Process availability. PROCESSBUSY Reports Busiest Process. RDF Reports RDF subsystem availability. SPOOLER Reports Spooler subsystem availability. TAPE Reports Tape subsystem availability. TMF Reports TMF subsystem availability. 74
ASAP CI - Entity Commands • Entity Commands provide reporting of availability. • Used for batch reporting & trouble-shooting of statistic values. APP Reports APPLICATION availability. CPU Reports CPU availability. DISK Reports DISK availability. FILE Reports File availability LH Reports Expand Line Handler availability. NODE Reports Expand end-to-end availability. PROCESS Reports User selected Process availability. PROCESSBUSY Reports Busiest Process. RDF Reports RDF subsystem availability. SPOOLER Reports Spooler subsystem availability. TAPE Reports Tape subsystem availability. TMF Reports TMF subsystem availability. 74
![CPU Command CPU [/out <file>/] [* ] [<node>] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] CPU Command CPU [/out <file>/] [* ] [<node>] [[. ] * ] [, <options>]](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-75.jpg) CPU Command CPU [/out
CPU Command CPU [/out
 CPU Command Continued AVG TYPE TIME STATE Displays the statistical averages across all running CPUs for the specified system during each sample period. Displays CPU types. hh[: mm [m/d/y]] Shows all attributes that have an associated state. 76
CPU Command Continued AVG TYPE TIME STATE Displays the statistical averages across all running CPUs for the specified system during each sample period. Displays CPU types. hh[: mm [m/d/y]] Shows all attributes that have an associated state. 76
![DISK Command DISK [/out <file>/] [* ] [<node>] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] DISK Command DISK [/out <file>/] [* ] [<node>] [[. ] * ] [, <options>]](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-77.jpg) DISK Command DISK [/out
DISK Command DISK [/out
![FILE Command FILE [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>] FILE Command FILE [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>]](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-78.jpg) FILE Command FILE [/out
FILE Command FILE [/out
![LH Command LH [/out <file>/] [* ] [<node>] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] LH Command LH [/out <file>/] [* ] [<node>] [[. ] * ] [, <options>]](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-79.jpg) LH Command LH [/out
LH Command LH [/out
 LH Command Continued STATE TIME USE Show all attributes that have an associated state. Works with the options, rate, queue. Show stats starting at a time other than the current time. Displays statistics about current pool usage. 80
LH Command Continued STATE TIME USE Show all attributes that have an associated state. Works with the options, rate, queue. Show stats starting at a time other than the current time. Displays statistics about current pool usage. 80
![NODE Command NODE [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>] NODE Command NODE [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>]](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-81.jpg) NODE Command NODE [/out
NODE Command NODE [/out
![PROCESS Command PROCESS [/out <file>/] [* [<node>] ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] PROCESS Command PROCESS [/out <file>/] [* [<node>] ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>]](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-82.jpg) PROCESS Command PROCESS [/out
PROCESS Command PROCESS [/out
![PROCESSBUSY / PB Command PROCESSBUSY | PB [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * PROCESSBUSY / PB Command PROCESSBUSY | PB [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] *](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-83.jpg) PROCESSBUSY / PB Command PROCESSBUSY | PB [/out
PROCESSBUSY / PB Command PROCESSBUSY | PB [/out
![RDF Command RDF [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>] RDF Command RDF [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>]](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-84.jpg) RDF Command RDF [/out
RDF Command RDF [/out
![Spooler Command SPOOLER [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>] Spooler Command SPOOLER [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>]](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-85.jpg) Spooler Command SPOOLER [/out
Spooler Command SPOOLER [/out
 Spooler Command Continued TIME Show stats starting at a time other than the current time. § To get spooler detail information in the ASAP client, use SHOW DETAIL INFORMATION 86
Spooler Command Continued TIME Show stats starting at a time other than the current time. § To get spooler detail information in the ASAP client, use SHOW DETAIL INFORMATION 86
![Tape Command TAPE [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>] Tape Command TAPE [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>]](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-87.jpg) Tape Command TAPE [/out
Tape Command TAPE [/out
![TMF Command TMF [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>] TMF Command TMF [/out <file>/] [* ] [[. ] * ] [, <options>] [<node>]](https://present5.com/presentation/ca97bbfd4fa9df3b3b6fb337d06ccfee/image-88.jpg) TMF Command TMF [/out
TMF Command TMF [/out
 ASAP CI - Basic Commands EXIT Stops the ASAP command interpreter. FC Standard Tandem Fix Command. HELP Displays explanation of specified ASAP command. NEW FEATURES Enter HELP NEW FEATURES for new features NEW USER Enter HELP NEW USER for getting started. OBEY Causes commands in OBEY file to be executed. PAUSE Suspends program until stop/abend/brk msg. SYSTEM Specifies default system name. VOLUME Changes and/or Displays default volume name. ! Exclamation Mark is End-of-line Comment Delimeter. 89
ASAP CI - Basic Commands EXIT Stops the ASAP command interpreter. FC Standard Tandem Fix Command. HELP Displays explanation of specified ASAP command. NEW FEATURES Enter HELP NEW FEATURES for new features NEW USER Enter HELP NEW USER for getting started. OBEY Causes commands in OBEY file to be executed. PAUSE Suspends program until stop/abend/brk msg. SYSTEM Specifies default system name. VOLUME Changes and/or Displays default volume name. ! Exclamation Mark is End-of-line Comment Delimeter. 89
 90
90


