4b9a8ad4cc0b0d896f1edfa13611b0f0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 AS Multi choice practice Complete your answers on BACK of sheet. Choose option & explain (define, formula / calculate, explain) Return
AS Multi choice practice Complete your answers on BACK of sheet. Choose option & explain (define, formula / calculate, explain) Return
 1.
1.
 Answer: B (1) • Explanation of how prices ration scarce goods – interaction of supply and demand (2) – Supply and demand diagram to show equilibrium price (1) plus – a further mark (1) for showing a change in equilibrium price (2) – Correct identification of other features of free market economy, e. g. , private ownership of resources - up to 2 marks (2) – Also allow credit for: – Definition of price mechanism (1) – Definition of scarcity (1)
Answer: B (1) • Explanation of how prices ration scarce goods – interaction of supply and demand (2) – Supply and demand diagram to show equilibrium price (1) plus – a further mark (1) for showing a change in equilibrium price (2) – Correct identification of other features of free market economy, e. g. , private ownership of resources - up to 2 marks (2) – Also allow credit for: – Definition of price mechanism (1) – Definition of scarcity (1)
 2.
2.
 Answer: A (1) – Definition of income elasticity of demand (1) – Correct numerical calculation (1) – Potatoes are an inferior good (1) – A rise in incomes will cause a fall in demand (1)
Answer: A (1) – Definition of income elasticity of demand (1) – Correct numerical calculation (1) – Potatoes are an inferior good (1) – A rise in incomes will cause a fall in demand (1)
 3.
3.
 Answer: C (1) • Define consumer surplus (2 marks) or description of the area between demand curve and price (1 mark). • Maximum of 2 marks can be awarded here. • Diagram or written explanation that consumer surplus falls when the supply curve shifts to the left – caused by a rise in the costs of production (2 marks).
Answer: C (1) • Define consumer surplus (2 marks) or description of the area between demand curve and price (1 mark). • Maximum of 2 marks can be awarded here. • Diagram or written explanation that consumer surplus falls when the supply curve shifts to the left – caused by a rise in the costs of production (2 marks).
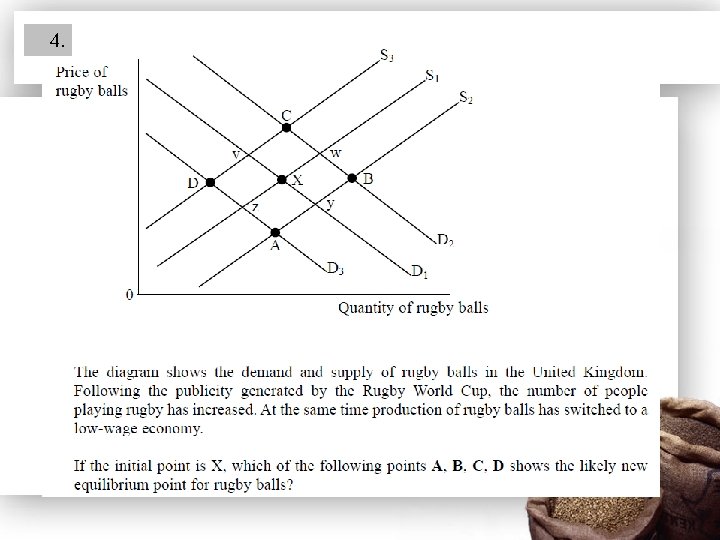 4.
4.
 Answer: B (1) • Explanation that increase in demand for rugby balls causes publicity & participation generates a shift in demand from D 1 to D 2 (1 mark). • Explanation that fall in costs will result in shift of the supply curve from S 1 to S 2 (1 mark) • With signals to generate more profit (1 mark). • Annotation of diagram (1 mark)
Answer: B (1) • Explanation that increase in demand for rugby balls causes publicity & participation generates a shift in demand from D 1 to D 2 (1 mark). • Explanation that fall in costs will result in shift of the supply curve from S 1 to S 2 (1 mark) • With signals to generate more profit (1 mark). • Annotation of diagram (1 mark)
 Economics of Buffer Stock Schemes AS Economics
Economics of Buffer Stock Schemes AS Economics
 Syllabus Requirements • Buffer Stocks • Students should be able to apply the concept of government intervention in the form of buffer stocks that seeks to stabilise prices and incomes in agricultural markets Any exam Q on price stability requires this theory
Syllabus Requirements • Buffer Stocks • Students should be able to apply the concept of government intervention in the form of buffer stocks that seeks to stabilise prices and incomes in agricultural markets Any exam Q on price stability requires this theory
 What is a buffer stock? • Many farmers of primary commodities face the problems of volatile prices and incomes • Buffer stock schemes seek to stabilise the market price of agricultural products by buying up supplies of the product when harvests are plentiful and selling stocks of the product onto the market when supplies are low
What is a buffer stock? • Many farmers of primary commodities face the problems of volatile prices and incomes • Buffer stock schemes seek to stabilise the market price of agricultural products by buying up supplies of the product when harvests are plentiful and selling stocks of the product onto the market when supplies are low
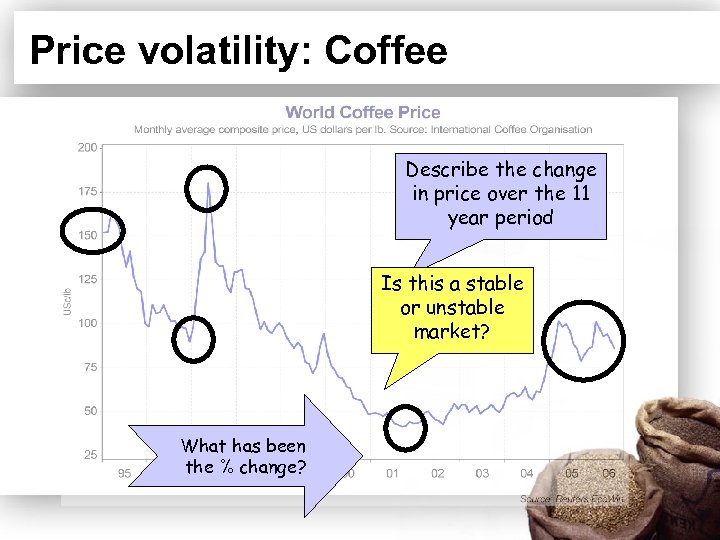 Price volatility: Coffee Describe the change in price over the 11 year period Is this a stable or unstable market? What has been the % change?
Price volatility: Coffee Describe the change in price over the 11 year period Is this a stable or unstable market? What has been the % change?
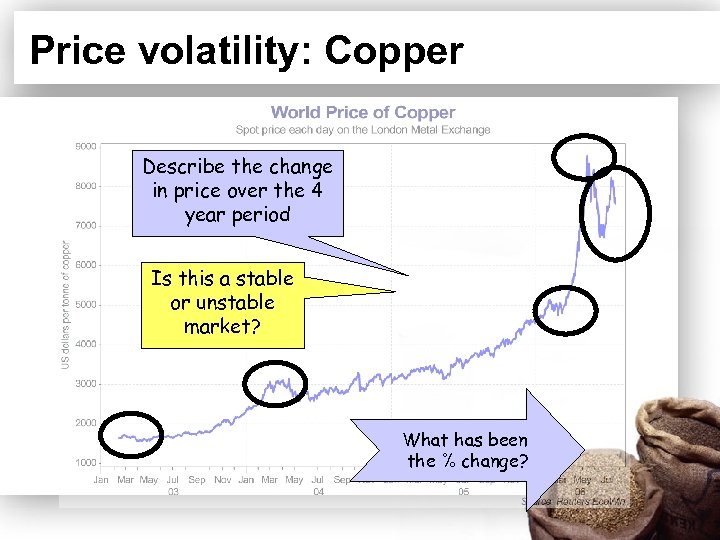 Price volatility: Copper Describe the change in price over the 4 year period Is this a stable or unstable market? What has been the % change?
Price volatility: Copper Describe the change in price over the 4 year period Is this a stable or unstable market? What has been the % change?
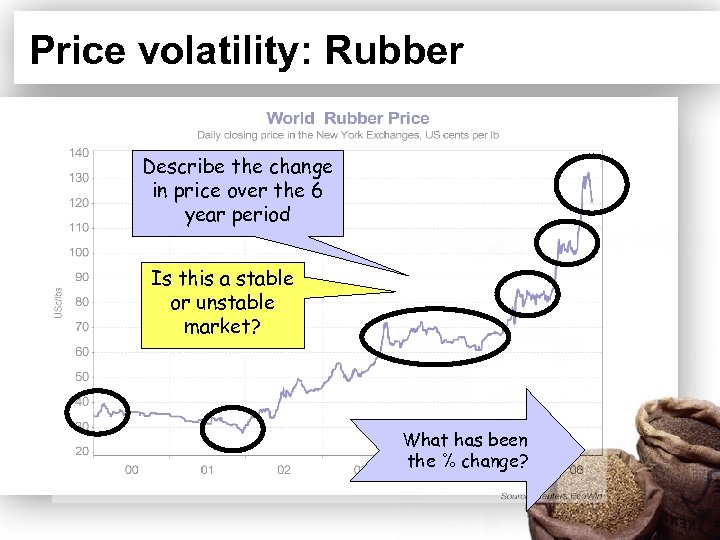 Price volatility: Rubber Describe the change in price over the 6 year period Is this a stable or unstable market? What has been the % change?
Price volatility: Rubber Describe the change in price over the 6 year period Is this a stable or unstable market? What has been the % change?
 Rubber plantations • 90% of rubber production comes from plantations of rubber trees in Southeast Asia!
Rubber plantations • 90% of rubber production comes from plantations of rubber trees in Southeast Asia!
 Commodities prices… • Producing commodities such as coffee, cotton or tobacco for the international markets is a hazardous business. • Commodity markets are characterised by instability and uncertainty. • This uncertainty may arise due to ¶ fluctuations in the market prices due to market conditions changing ¶ changes in prices due to changes in exchange rates ¶ changes in foreign government protectionist measures
Commodities prices… • Producing commodities such as coffee, cotton or tobacco for the international markets is a hazardous business. • Commodity markets are characterised by instability and uncertainty. • This uncertainty may arise due to ¶ fluctuations in the market prices due to market conditions changing ¶ changes in prices due to changes in exchange rates ¶ changes in foreign government protectionist measures
 Maximum Prices
Maximum Prices
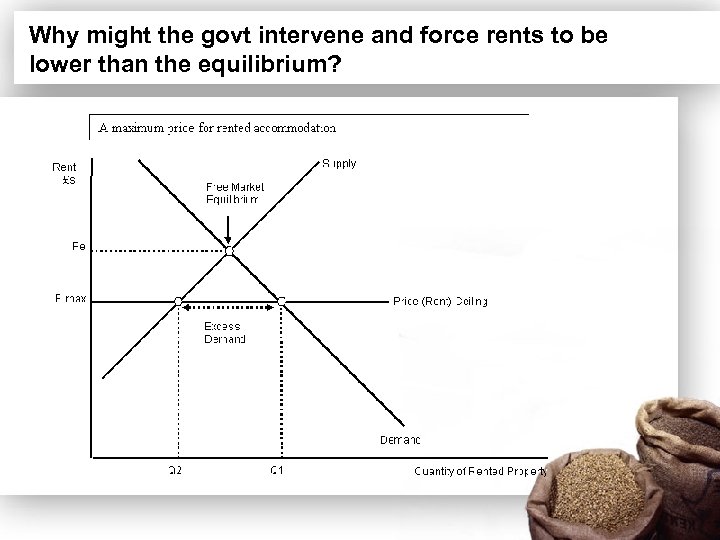 Why might the govt intervene and force rents to be lower than the equilibrium?
Why might the govt intervene and force rents to be lower than the equilibrium?
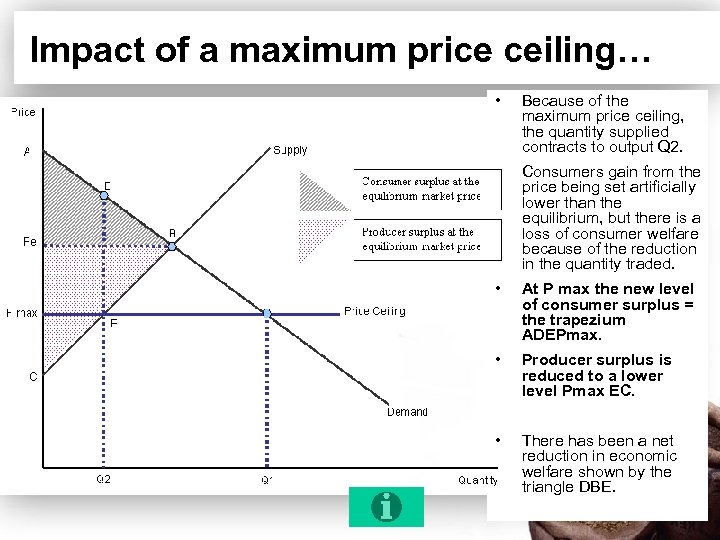 Impact of a maximum price ceiling… • Because of the maximum price ceiling, the quantity supplied contracts to output Q 2. • Consumers gain from the price being set artificially lower than the equilibrium, but there is a loss of consumer welfare because of the reduction in the quantity traded. • At P max the new level of consumer surplus = the trapezium ADEPmax. • Producer surplus is reduced to a lower level Pmax EC. • There has been a net reduction in economic welfare shown by the triangle DBE.
Impact of a maximum price ceiling… • Because of the maximum price ceiling, the quantity supplied contracts to output Q 2. • Consumers gain from the price being set artificially lower than the equilibrium, but there is a loss of consumer welfare because of the reduction in the quantity traded. • At P max the new level of consumer surplus = the trapezium ADEPmax. • Producer surplus is reduced to a lower level Pmax EC. • There has been a net reduction in economic welfare shown by the triangle DBE.
 Minimum prices
Minimum prices
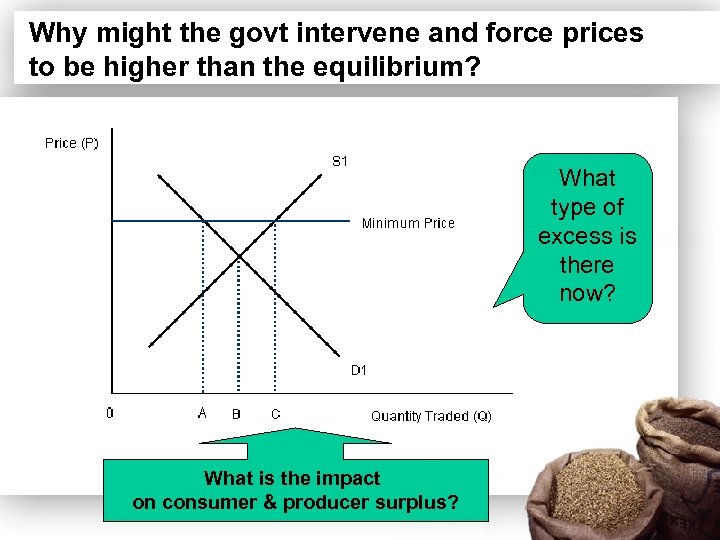 Why might the govt intervene and force prices to be higher than the equilibrium? What type of excess is there now? What is the impact on consumer & producer surplus?
Why might the govt intervene and force prices to be higher than the equilibrium? What type of excess is there now? What is the impact on consumer & producer surplus?
 Buffer Stocks
Buffer Stocks
 Examples of buffer stock schemes • Cotton Price Stabilization Board • International Coffee Agreement • International Tin Council Coffee beans!
Examples of buffer stock schemes • Cotton Price Stabilization Board • International Coffee Agreement • International Tin Council Coffee beans!
 Draw a Demand Supply diagram for coffee commodity rather than starbucks! • Show a ‘shock’ to the market – what would happen if there was a coffee ‘mite’? • Show the immediate reaction? • How would ‘business’ consumers react? • How would the supplier react to this? • So what do you think might happen in the next season?
Draw a Demand Supply diagram for coffee commodity rather than starbucks! • Show a ‘shock’ to the market – what would happen if there was a coffee ‘mite’? • Show the immediate reaction? • How would ‘business’ consumers react? • How would the supplier react to this? • So what do you think might happen in the next season?
 Buffer Zone in diagrams
Buffer Zone in diagrams
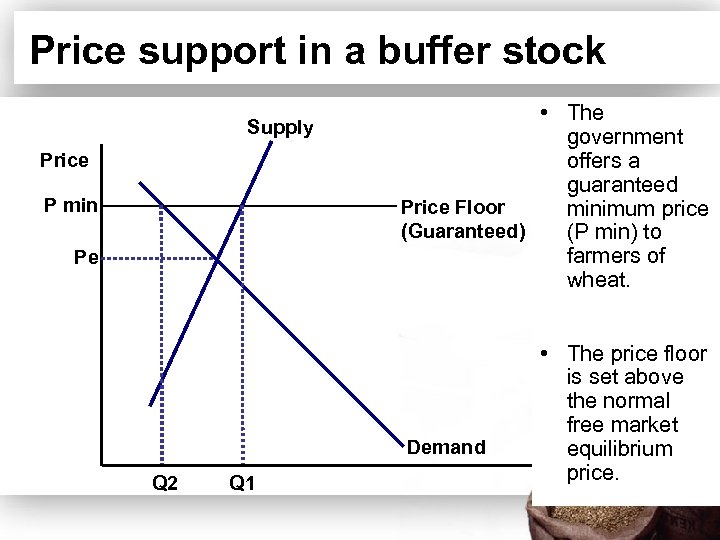 Price support in a buffer stock Supply Price P min Pe • The government offers a guaranteed Price Floor minimum price (Guaranteed) (P min) to farmers of wheat. Demand Q 2 Q 1 • The price floor is set above the normal free market equilibrium price. Quantity
Price support in a buffer stock Supply Price P min Pe • The government offers a guaranteed Price Floor minimum price (Guaranteed) (P min) to farmers of wheat. Demand Q 2 Q 1 • The price floor is set above the normal free market equilibrium price. Quantity
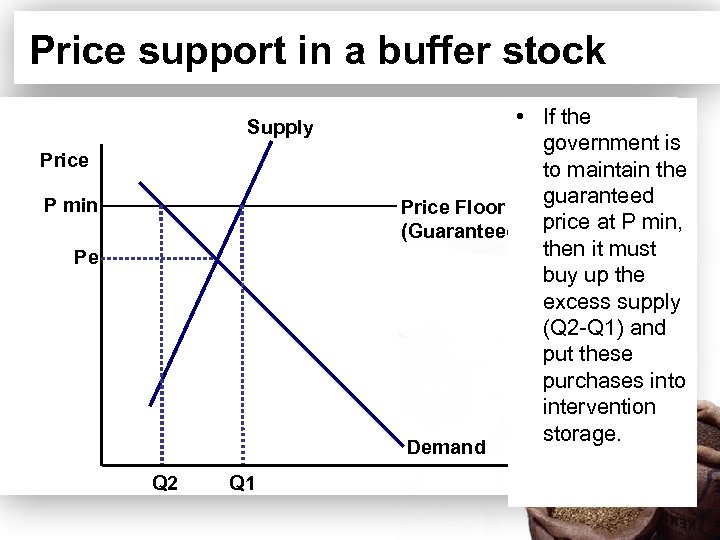 Price support in a buffer stock Supply Price P min Pe • If the government is to maintain the guaranteed Price Floor (Guaranteed) price at P min, then it must buy up the excess supply (Q 2 -Q 1) and put these purchases into intervention storage. Demand Q 2 Q 1 Quantity
Price support in a buffer stock Supply Price P min Pe • If the government is to maintain the guaranteed Price Floor (Guaranteed) price at P min, then it must buy up the excess supply (Q 2 -Q 1) and put these purchases into intervention storage. Demand Q 2 Q 1 Quantity
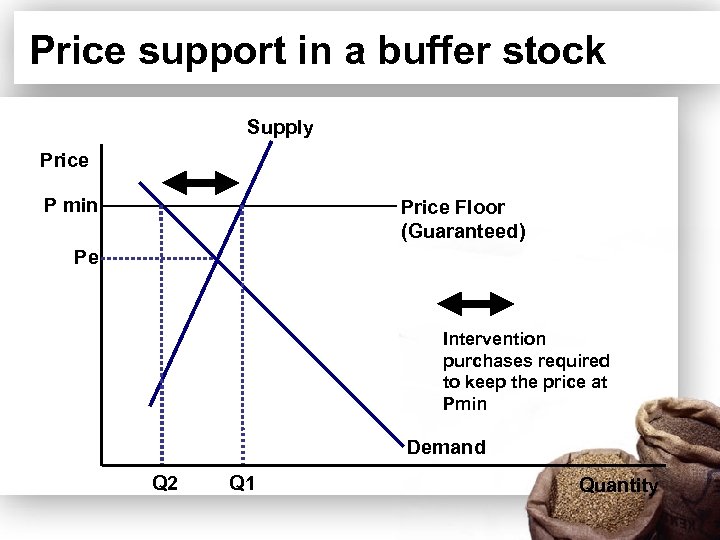 Price support in a buffer stock Supply Price P min Price Floor (Guaranteed) Pe Intervention purchases required to keep the price at Pmin Demand Q 2 Q 1 Quantity
Price support in a buffer stock Supply Price P min Price Floor (Guaranteed) Pe Intervention purchases required to keep the price at Pmin Demand Q 2 Q 1 Quantity
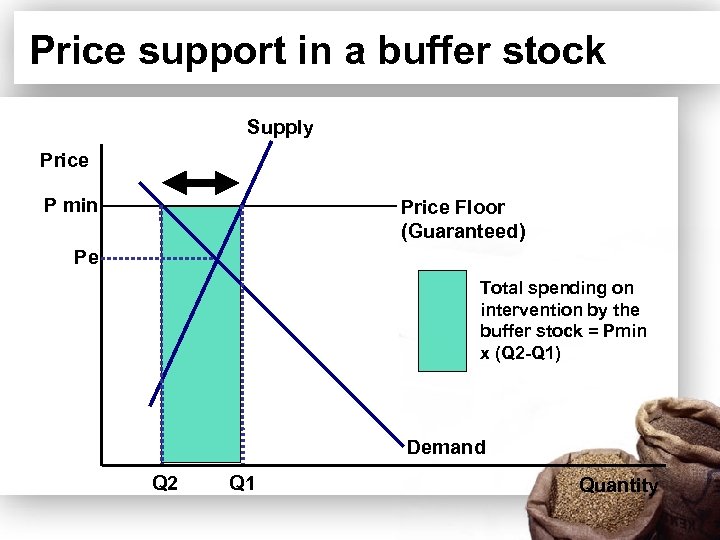 Price support in a buffer stock Supply Price P min Price Floor (Guaranteed) Pe Total spending on intervention by the buffer stock = Pmin x (Q 2 -Q 1) Demand Q 2 Q 1 Quantity
Price support in a buffer stock Supply Price P min Price Floor (Guaranteed) Pe Total spending on intervention by the buffer stock = Pmin x (Q 2 -Q 1) Demand Q 2 Q 1 Quantity
 The effects of a rise in supply • Should there be a large rise in supply due to better than expected yields of wheat at harvest time, the market supply of wheat will shift out putting downward pressure on the free market equilibrium price • In this situation, the government will have to intervene once more in the market and buy up the surplus stock of wheat to prevent the price from falling.
The effects of a rise in supply • Should there be a large rise in supply due to better than expected yields of wheat at harvest time, the market supply of wheat will shift out putting downward pressure on the free market equilibrium price • In this situation, the government will have to intervene once more in the market and buy up the surplus stock of wheat to prevent the price from falling.
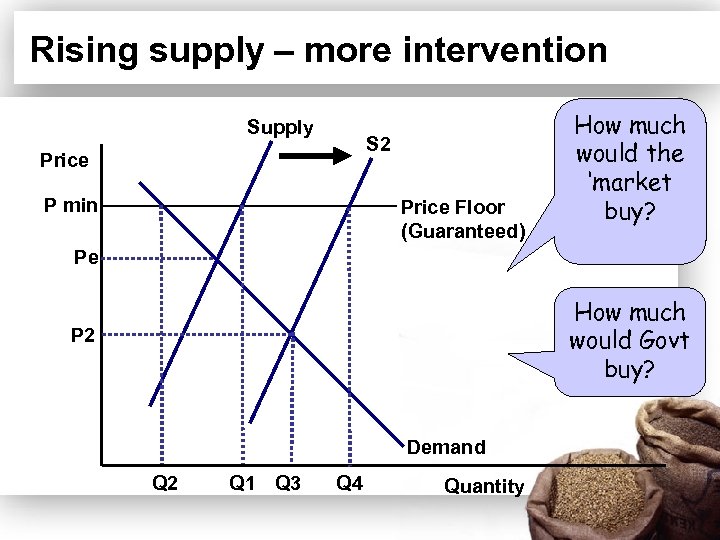 Rising supply – more intervention Supply S 2 Price P min Price Floor (Guaranteed) How much would the ‘market buy? Pe How much would Govt buy? P 2 Demand Q 2 Q 1 Q 3 Q 4 Quantity
Rising supply – more intervention Supply S 2 Price P min Price Floor (Guaranteed) How much would the ‘market buy? Pe How much would Govt buy? P 2 Demand Q 2 Q 1 Q 3 Q 4 Quantity
 Does it really work?
Does it really work?
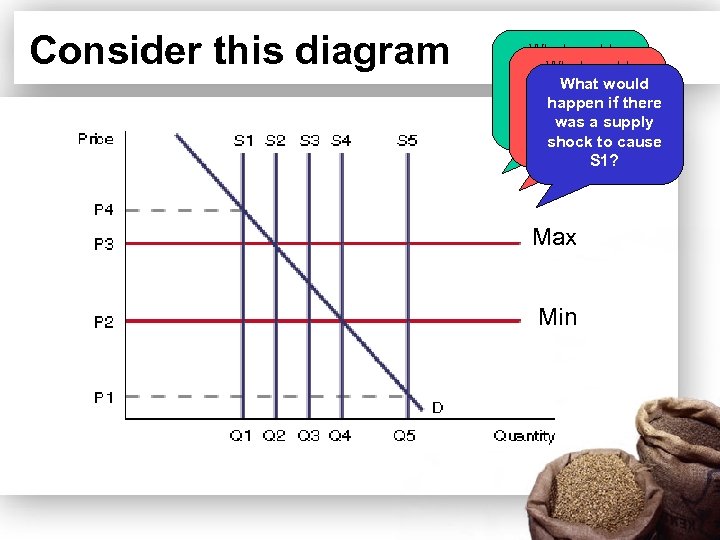 Consider this diagram What would happen is supply What there happen if would curve shifts happen if there was S 2, S 3 betweena supply was a shock to cause and S 4? supply shock to cause S 5? S 1? Max Min
Consider this diagram What would happen is supply What there happen if would curve shifts happen if there was S 2, S 3 betweena supply was a shock to cause and S 4? supply shock to cause S 5? S 1? Max Min
 The answers! • In the diagram shifts in the supply curve between S 2, S 3 and S 4 will only result in the price changing between the acceptable price band. • If a supply shock causes the supply curve to shift to the right to S 5 then the buffer stock authority will intervene and purchase the surplus Q 4 -Q 5 thus preventing the market clearing by itself through a lowering of the equilibrium market price to P 1. • If the supply curve shifted to the left then the buffer stock authority would release stocks equal to Q 1 Q 2 on to the market thus preventing the price rising to P 4.
The answers! • In the diagram shifts in the supply curve between S 2, S 3 and S 4 will only result in the price changing between the acceptable price band. • If a supply shock causes the supply curve to shift to the right to S 5 then the buffer stock authority will intervene and purchase the surplus Q 4 -Q 5 thus preventing the market clearing by itself through a lowering of the equilibrium market price to P 1. • If the supply curve shifted to the left then the buffer stock authority would release stocks equal to Q 1 Q 2 on to the market thus preventing the price rising to P 4.
 What can you do with surplus stock? • In the case where the surplus is bought there are number of options that can happen to the stock • It can be stored • It can be destroyed What are the implications of each of these? • It can be sold to other countries • It can be given as overseas assistance.
What can you do with surplus stock? • In the case where the surplus is bought there are number of options that can happen to the stock • It can be stored • It can be destroyed What are the implications of each of these? • It can be sold to other countries • It can be given as overseas assistance.
 Implications of stock surplus… • Storage is expensive and involves an opportunity costs of the storage facilities. • Destroying surpluses especially if the surplus is a food is morally questionable in a world devastated by poverty and hunger. • Selling to other countries at low prices or dumping can undermine domestic producers in the countries where the goods are sold. • Giving the food as aid could, it is argued, lead to a dependency culture.
Implications of stock surplus… • Storage is expensive and involves an opportunity costs of the storage facilities. • Destroying surpluses especially if the surplus is a food is morally questionable in a world devastated by poverty and hunger. • Selling to other countries at low prices or dumping can undermine domestic producers in the countries where the goods are sold. • Giving the food as aid could, it is argued, lead to a dependency culture.
 Problems with buffer stocks • Setting up a buffer stock scheme requires a significant amount of start up capital, since money is needed to buy up the product when prices are low. There also high administrative and storage costs to be considered. • The success of a buffer stock scheme however ultimately depends on the ability of those managing a scheme to correctly estimate the average price of the product over a period of time
Problems with buffer stocks • Setting up a buffer stock scheme requires a significant amount of start up capital, since money is needed to buy up the product when prices are low. There also high administrative and storage costs to be considered. • The success of a buffer stock scheme however ultimately depends on the ability of those managing a scheme to correctly estimate the average price of the product over a period of time
 Problems with buffer stocks • If the target price is significantly above the correct average price then the organization will find itself buying more produce than it is selling and it will eventually run out of money • Conversely if the target price is too low then the organization will often find the price rising above the boundary, it will end up selling more than it is buying and will eventually run out of stocks
Problems with buffer stocks • If the target price is significantly above the correct average price then the organization will find itself buying more produce than it is selling and it will eventually run out of money • Conversely if the target price is too low then the organization will often find the price rising above the boundary, it will end up selling more than it is buying and will eventually run out of stocks
 Exam skills • Using at least one demand supply diagram and the information in Extract B, explain how ? ? might try to stabilise the world price of ? ? ? between $55 and $65? Any exam Q on price stability requires Buffer stock diagrams!
Exam skills • Using at least one demand supply diagram and the information in Extract B, explain how ? ? might try to stabilise the world price of ? ? ? between $55 and $65? Any exam Q on price stability requires Buffer stock diagrams!


