 Архитектура модульной системы хранения данных Front-End, SCSI Target
Архитектура модульной системы хранения данных Front-End, SCSI Target
 Contents • Configurations • SCSI Model – – – Architecture Model Standards Family Standards Architecture Distributed Service Model Client-Server Model • SCSI Commands – – – Command Descriptor Block Primary Commands Block Commands Task Management Functions Persistent Reservations
Contents • Configurations • SCSI Model – – – Architecture Model Standards Family Standards Architecture Distributed Service Model Client-Server Model • SCSI Commands – – – Command Descriptor Block Primary Commands Block Commands Task Management Functions Persistent Reservations
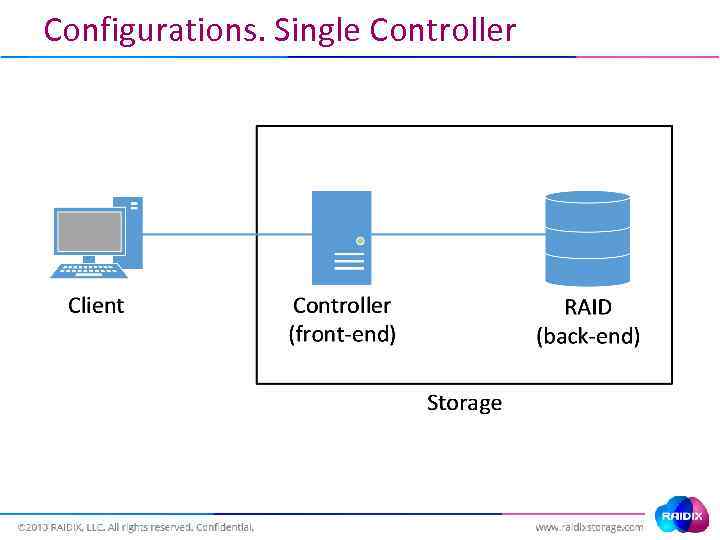 Configurations. Single Controller
Configurations. Single Controller
 Configurations • Single Controller • Dual Controller (DC) Active-Passive* Active-Active • • Symmetric Active-Active Asymmetric Active-Active** *RAIDIX AAP - Asymmetric Active Passive **ALUA - Asymmetric Logical Unit Access
Configurations • Single Controller • Dual Controller (DC) Active-Passive* Active-Active • • Symmetric Active-Active Asymmetric Active-Active** *RAIDIX AAP - Asymmetric Active Passive **ALUA - Asymmetric Logical Unit Access
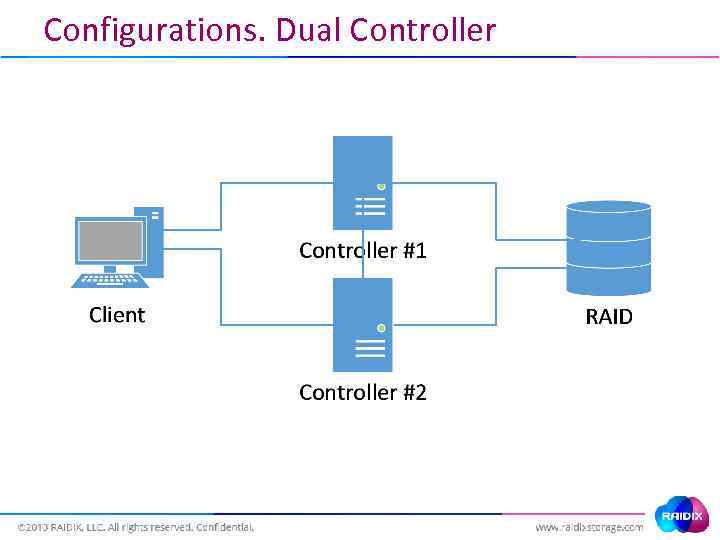 Configurations. Dual Controller
Configurations. Dual Controller
 Configurations. Dual Controller Target port access states: • Active/optimized • Active/non-optimized • Standby • Unavailable • Offline (AA, AP) (AA, AP)
Configurations. Dual Controller Target port access states: • Active/optimized • Active/non-optimized • Standby • Unavailable • Offline (AA, AP) (AA, AP)
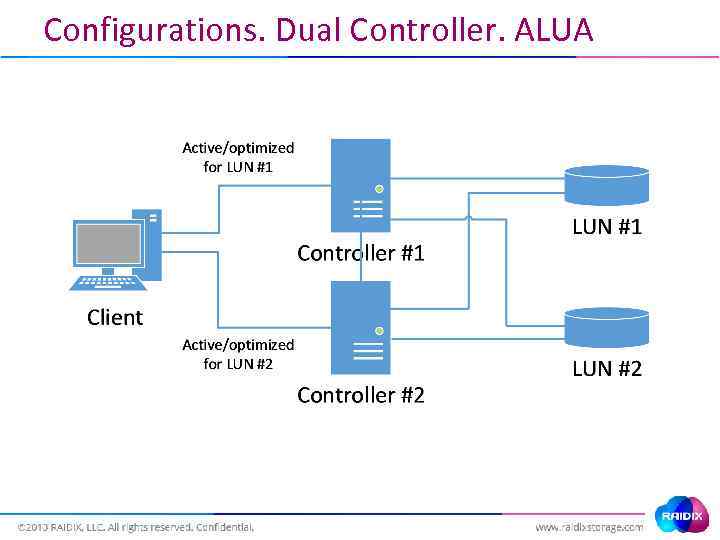 Configurations. Dual Controller. ALUA
Configurations. Dual Controller. ALUA
 SCSI Architecture Model • Client-server model. • SCSI-based protocols. • Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. • The set of SCSI standards specifies the interfaces, functions, and operations necessary to ensure interoperability between conforming SCSI implementations.
SCSI Architecture Model • Client-server model. • SCSI-based protocols. • Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. • The set of SCSI standards specifies the interfaces, functions, and operations necessary to ensure interoperability between conforming SCSI implementations.
 SCSI Standards Family
SCSI Standards Family
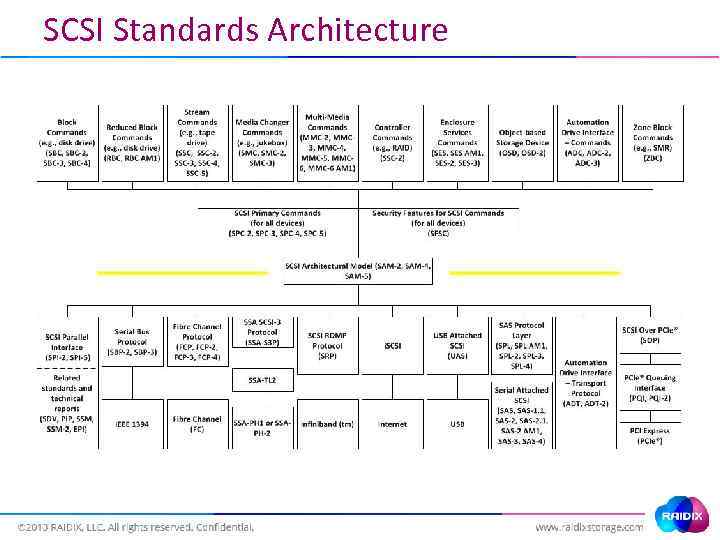 SCSI Standards Architecture
SCSI Standards Architecture
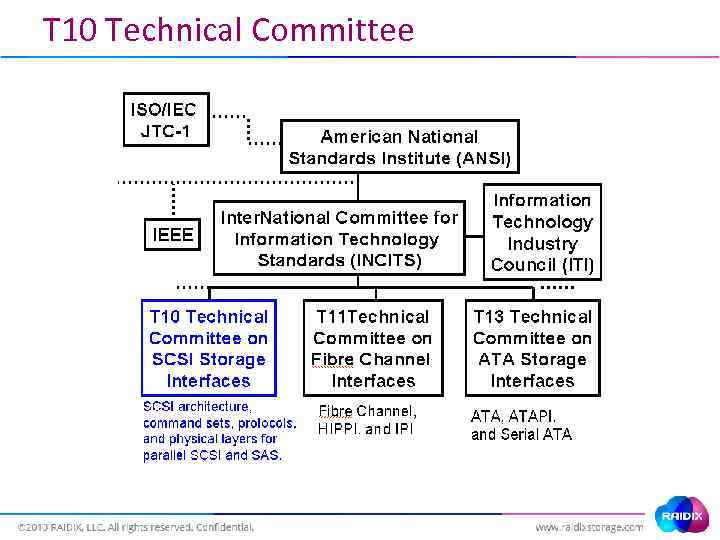 T 10 Technical Committee
T 10 Technical Committee
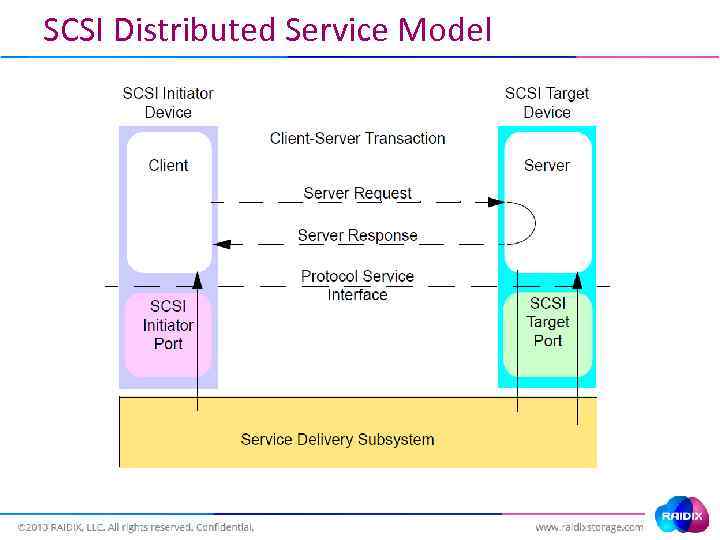 SCSI Distributed Service Model
SCSI Distributed Service Model
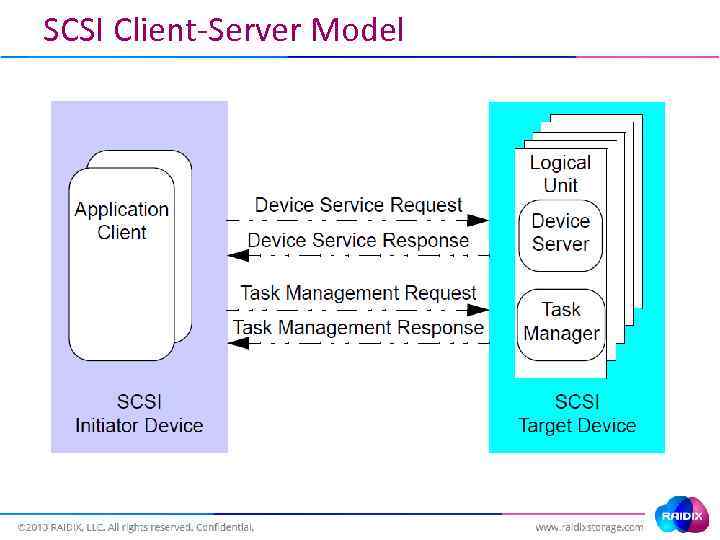 SCSI Client-Server Model
SCSI Client-Server Model
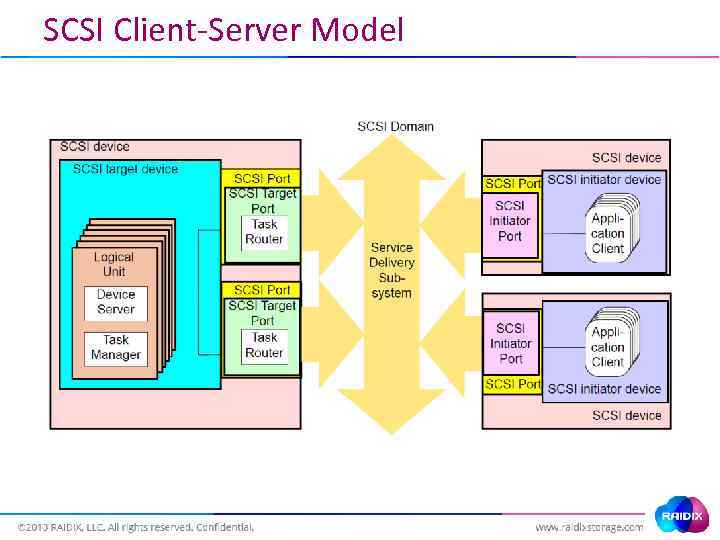 SCSI Client-Server Model
SCSI Client-Server Model
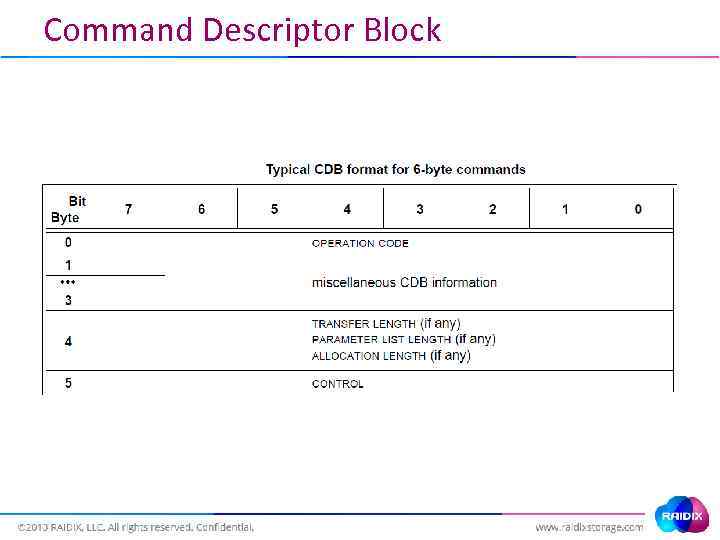 Command Descriptor Block
Command Descriptor Block
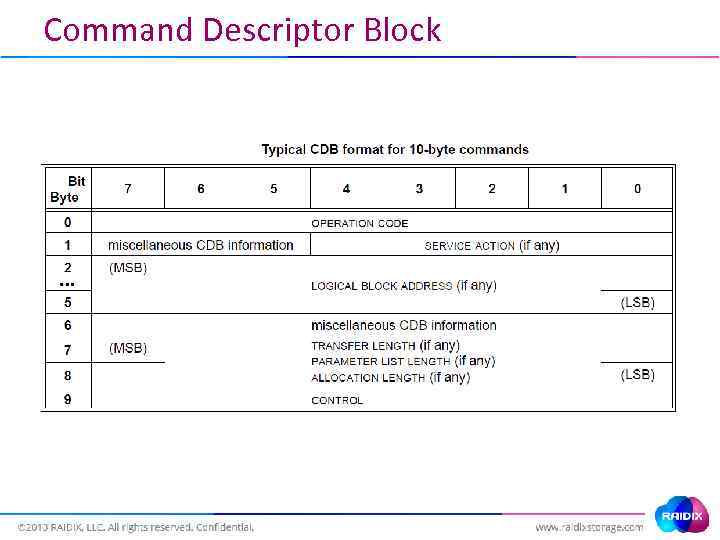 Command Descriptor Block
Command Descriptor Block
 SCSI Primary Commands Mandatory commands: • INQUIRY – determines the configuration of a logical unit (device type, vendor’s name, model number). • REPORT LUNS – reports of the logical units that are accessible to the host. • TEST UNIT READY – checks a logical unit if it is ready.
SCSI Primary Commands Mandatory commands: • INQUIRY – determines the configuration of a logical unit (device type, vendor’s name, model number). • REPORT LUNS – reports of the logical units that are accessible to the host. • TEST UNIT READY – checks a logical unit if it is ready.
 SCSI Block Commands Mandatory commands: • READ CAPACITY – describes the capacity and medium format of the direct access block device. • READ • WRITE
SCSI Block Commands Mandatory commands: • READ CAPACITY – describes the capacity and medium format of the direct access block device. • READ • WRITE
 Task Management Functions • • • ABORT TASK SET CLEAR TASK SET I_T NEXUS RESET LOGICAL UNIT RESET
Task Management Functions • • • ABORT TASK SET CLEAR TASK SET I_T NEXUS RESET LOGICAL UNIT RESET
 SCSI Persistent Reservations • Reservations may be used to allow a device server to process commands from a selected set of I_T nexuses and reject commands from I_T nexuses outside the selected set. • The device server uniquely identifies I_T nexuses using protocol specific mechanisms. • SCSI commands: – PERSISTENT RESERVE IN – identify which I_T nexuses are registered. – PERSISTENT RESERVE OUT – register an I_T nexus.
SCSI Persistent Reservations • Reservations may be used to allow a device server to process commands from a selected set of I_T nexuses and reject commands from I_T nexuses outside the selected set. • The device server uniquely identifies I_T nexuses using protocol specific mechanisms. • SCSI commands: – PERSISTENT RESERVE IN – identify which I_T nexuses are registered. – PERSISTENT RESERVE OUT – register an I_T nexus.