a1e568c42b5288618eaebf593210883f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Arts Col 753, Animation Production with CSE 682, Computer Animation Winter 2010 Professors: Maria Palazzi and Rick Parent Technical Group Reports --- Rendering and project management Group Members: Jane Drozd, Adam Kane, Kang-che Lee, Shengying Shen, Ross Wang
Arts Col 753, Animation Production with CSE 682, Computer Animation Winter 2010 Professors: Maria Palazzi and Rick Parent Technical Group Reports --- Rendering and project management Group Members: Jane Drozd, Adam Kane, Kang-che Lee, Shengying Shen, Ross Wang
 Outline Rendering: playblast controlling rendering quality software v. hardware rendering render output: image formats, channels, etc. batch rendering the ACCAD render-farm render layers Project management groups sets and partitions making an object unselectable (template) display layers copies v. instances file referencing proxy references 2
Outline Rendering: playblast controlling rendering quality software v. hardware rendering render output: image formats, channels, etc. batch rendering the ACCAD render-farm render layers Project management groups sets and partitions making an object unselectable (template) display layers copies v. instances file referencing proxy references 2
 Rendering 3
Rendering 3
 Playblast A fast way to render in Maya Use screen capture to make animation Make sure the area to be displayed is not obstructed 4
Playblast A fast way to render in Maya Use screen capture to make animation Make sure the area to be displayed is not obstructed 4
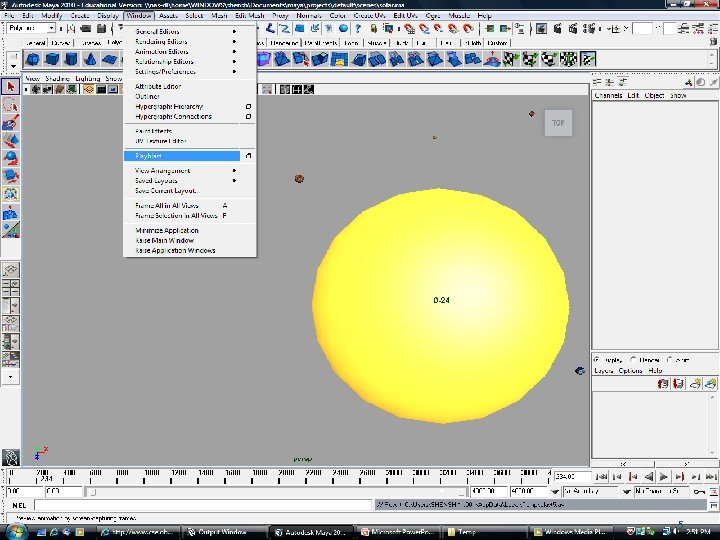 Playblast Steps Window -> Playblast 5
Playblast Steps Window -> Playblast 5
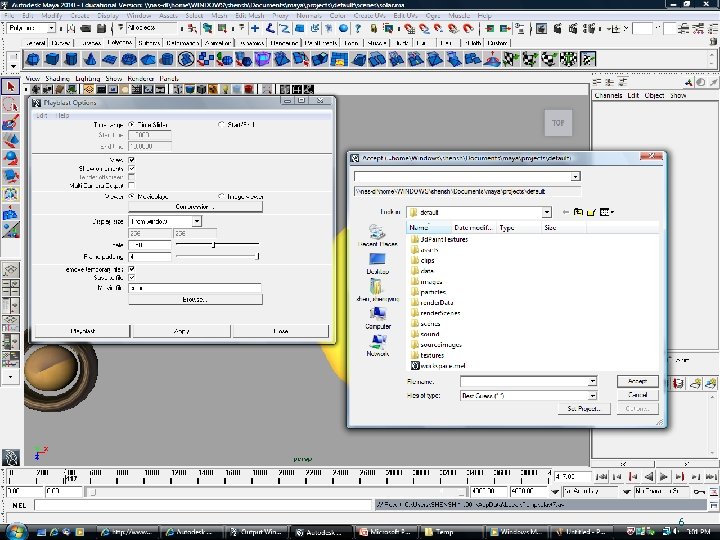 Playblast Steps 6
Playblast Steps 6
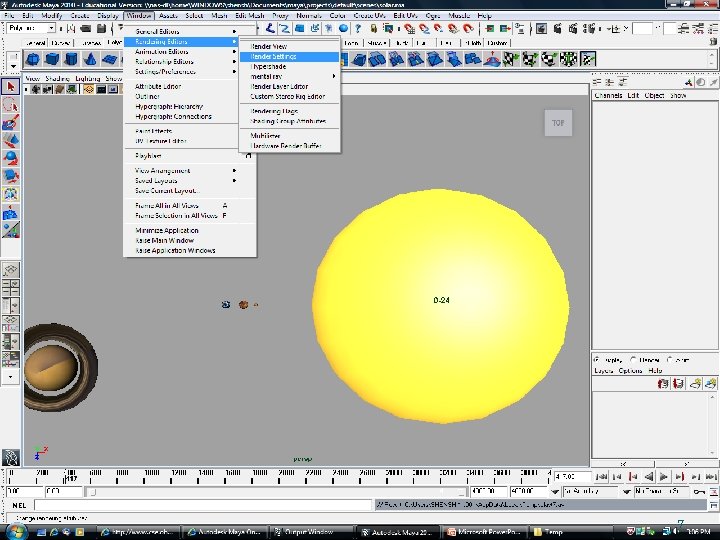 Rendering Quality Window -> Rendering Editors -> Render Settings 7
Rendering Quality Window -> Rendering Editors -> Render Settings 7
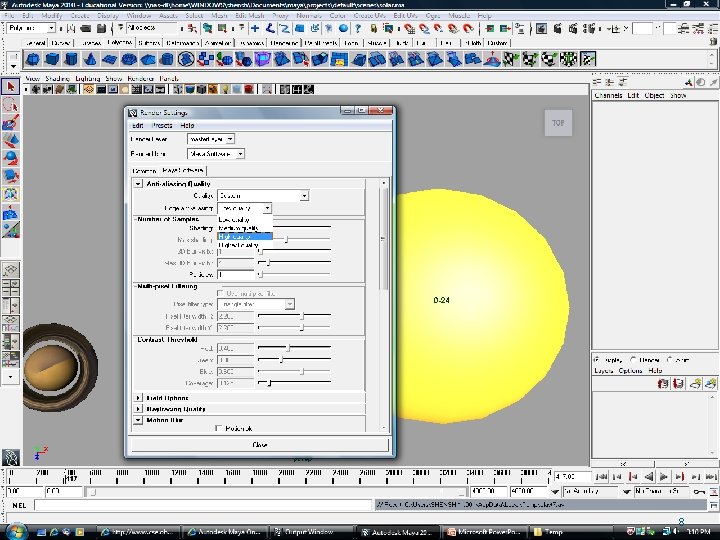 Rendering Quality 8
Rendering Quality 8
 Software VS Hardware Rendering Software Computation done by the computer instead of special hardware It is flexible programming Slower than hardware since it needs more time for calculation Hardware Computation done through video card and drivers It is faster than software rendering Usually it produce a lower quality than software rendering 9
Software VS Hardware Rendering Software Computation done by the computer instead of special hardware It is flexible programming Slower than hardware since it needs more time for calculation Hardware Computation done through video card and drivers It is faster than software rendering Usually it produce a lower quality than software rendering 9
 Render Output Formats Default: Maya Image File Format (IFF) Two main types: Raster: pixel based format TIFF, BMP, JPG… Vector: line/curve based format AI, SWF, SVG… 10
Render Output Formats Default: Maya Image File Format (IFF) Two main types: Raster: pixel based format TIFF, BMP, JPG… Vector: line/curve based format AI, SWF, SVG… 10
 Render Output Channels: Four main channels per pixel 3 color channels Red Green Blue Alpha channel, used for transparency. Depth channel may be used to record how far away a given pixel is. 11
Render Output Channels: Four main channels per pixel 3 color channels Red Green Blue Alpha channel, used for transparency. Depth channel may be used to record how far away a given pixel is. 11
 Channels 12
Channels 12
 Batch Rendering Allows rendering of multiple images at once Rendering an animation: Configure options Check Script Editor 13
Batch Rendering Allows rendering of multiple images at once Rendering an animation: Configure options Check Script Editor 13
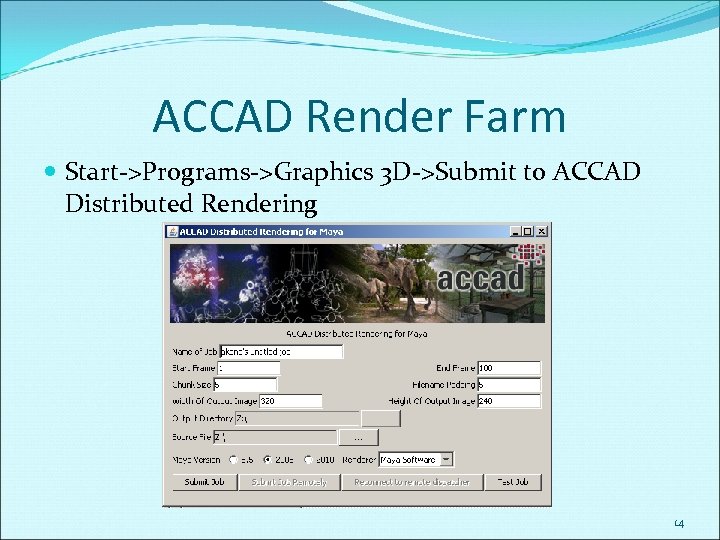 ACCAD Render Farm Start->Programs->Graphics 3 D->Submit to ACCAD Distributed Rendering 14
ACCAD Render Farm Start->Programs->Graphics 3 D->Submit to ACCAD Distributed Rendering 14
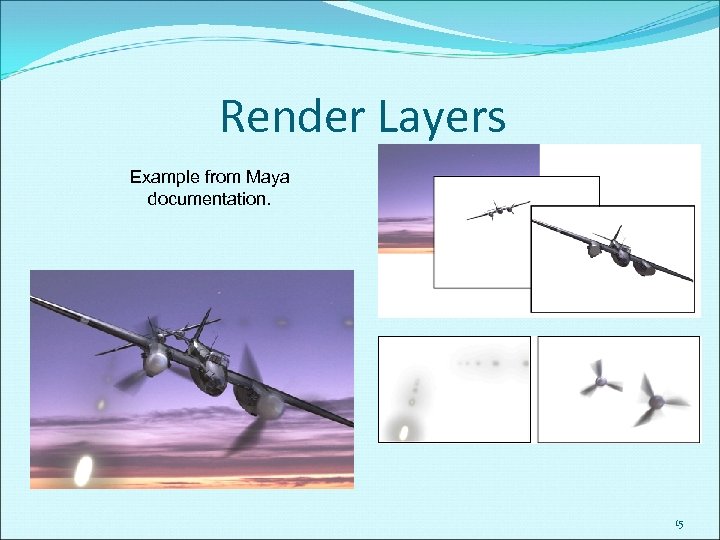 Render Layers Example from Maya documentation. 15
Render Layers Example from Maya documentation. 15
 Reasons to Composite Creativity Modifiability Efficiency 16
Reasons to Composite Creativity Modifiability Efficiency 16
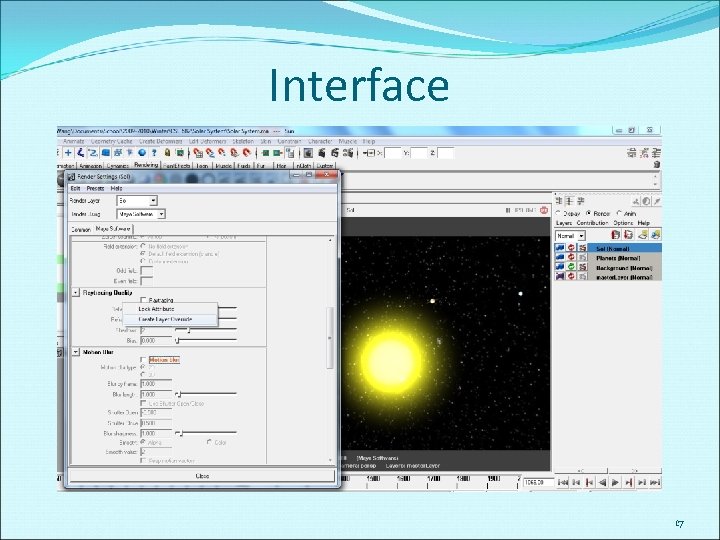 Interface 17
Interface 17
 Caveats Be mindful of compositor expectations Color and channel interpretation 18
Caveats Be mindful of compositor expectations Color and channel interpretation 18
 Project Management
Project Management
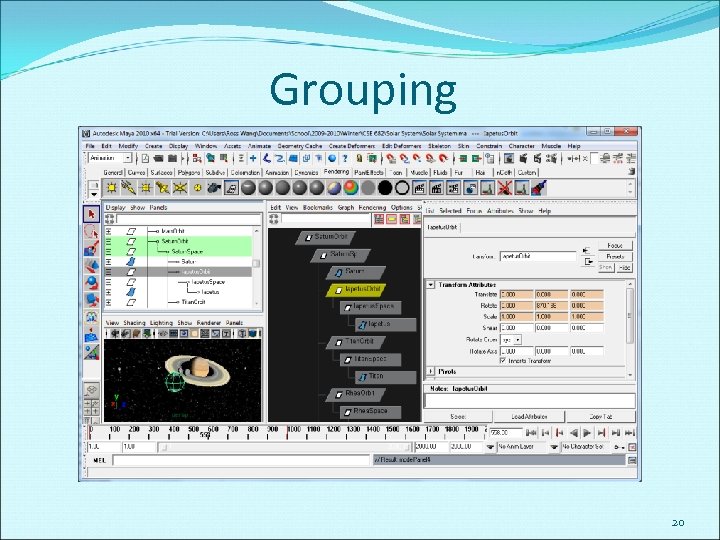 Grouping 20
Grouping 20
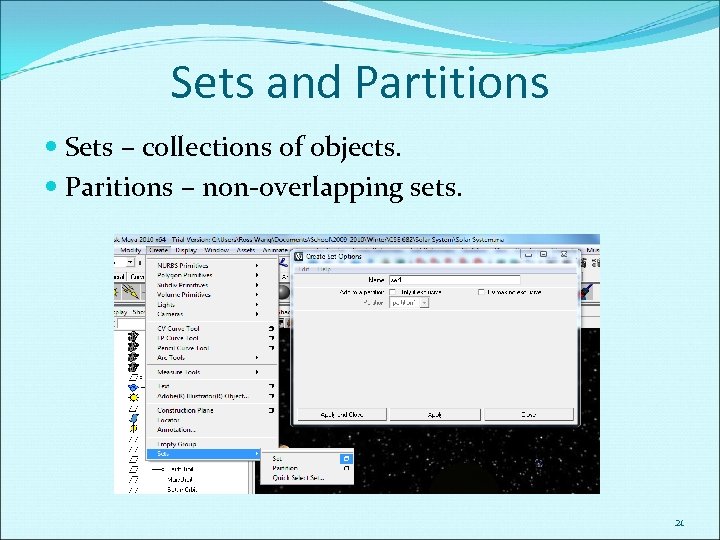 Sets and Partitions Sets – collections of objects. Paritions – non-overlapping sets. 21
Sets and Partitions Sets – collections of objects. Paritions – non-overlapping sets. 21
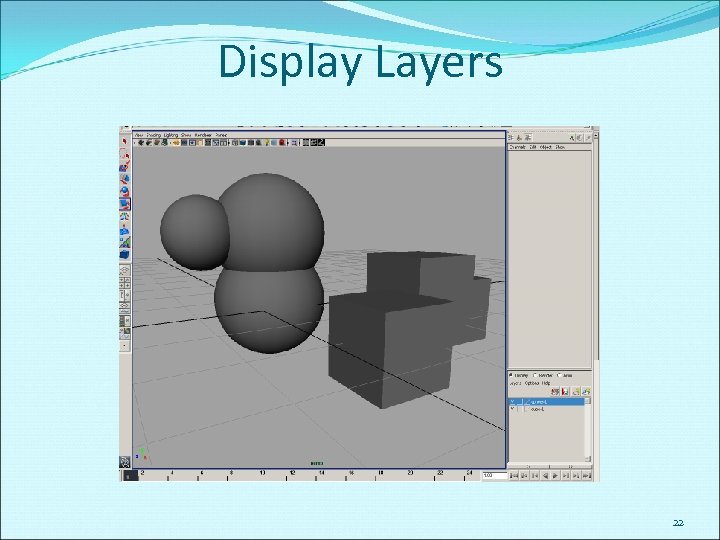 Display Layers 22
Display Layers 22
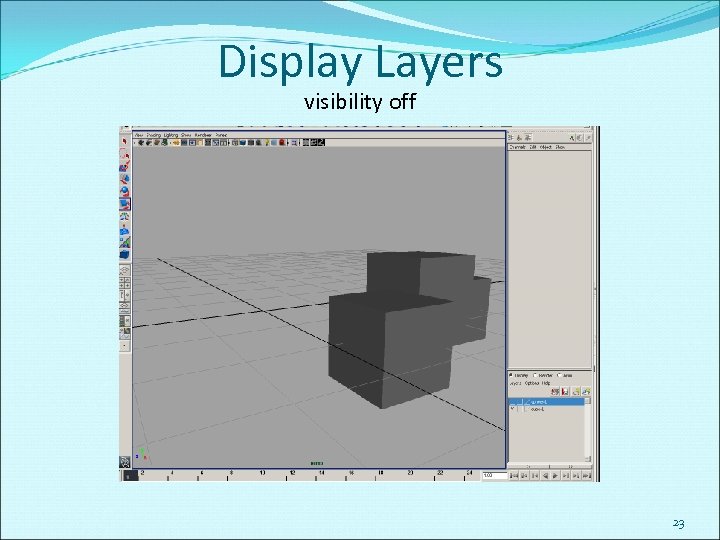 Display Layers visibility off 23
Display Layers visibility off 23
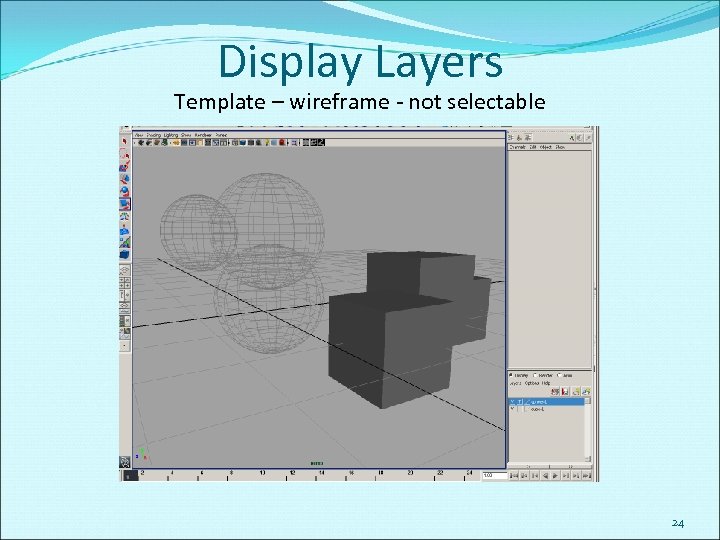 Display Layers Template – wireframe - not selectable 24
Display Layers Template – wireframe - not selectable 24
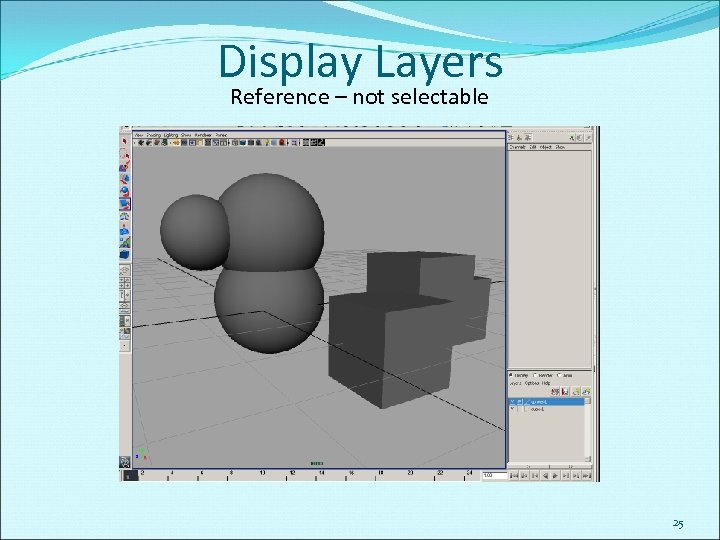 Display Layers Reference – not selectable 25
Display Layers Reference – not selectable 25
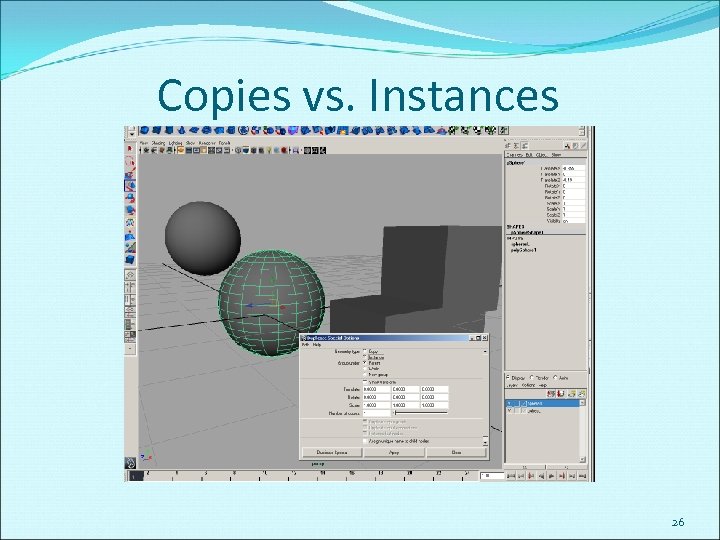 Copies vs. Instances 26
Copies vs. Instances 26
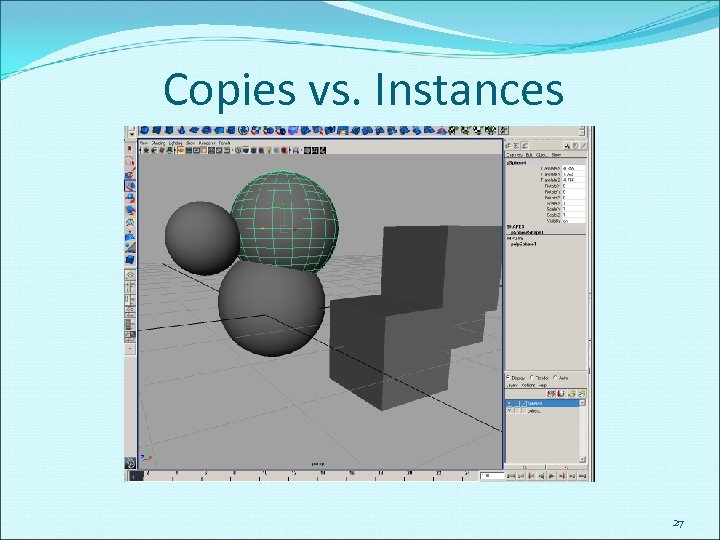 Copies vs. Instances 27
Copies vs. Instances 27
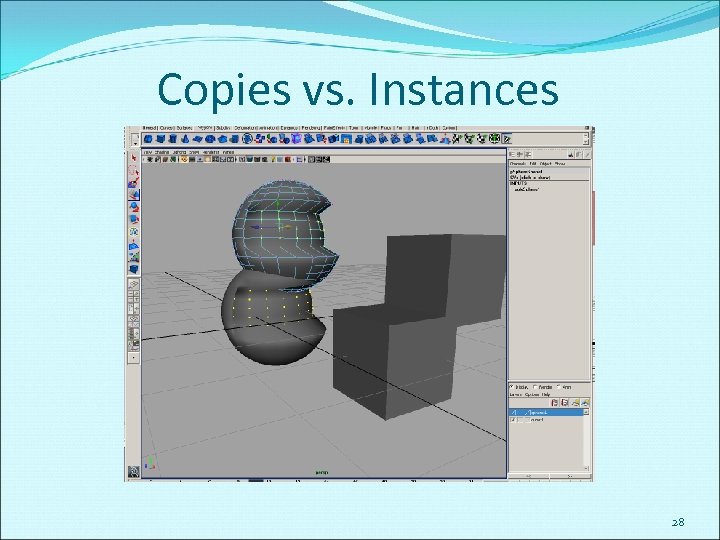 Copies vs. Instances 28
Copies vs. Instances 28
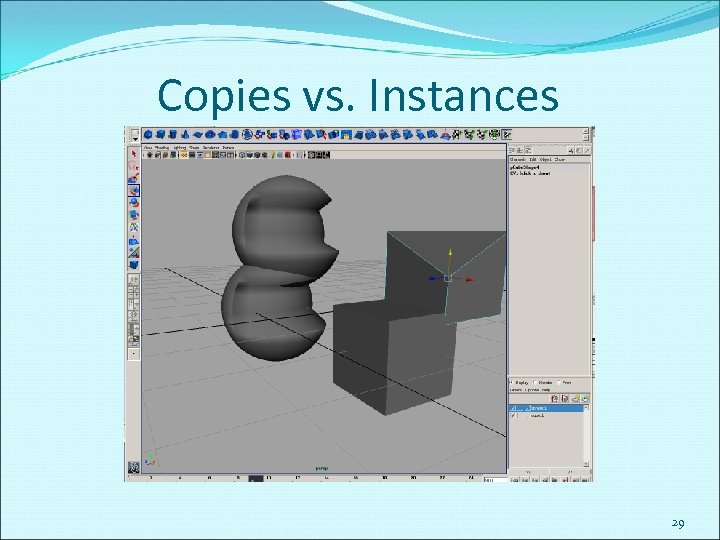 Copies vs. Instances 29
Copies vs. Instances 29
 File Referencing allows you to assemble multiple objects, shading materials, animation, and so on, into a scene without importing the files into the scene. allows users to segment scenes as required to suit the production workflow. not like Importing where the objects get copied over. Referencing needs an active link. reduces file size of the composited scene. 30
File Referencing allows you to assemble multiple objects, shading materials, animation, and so on, into a scene without importing the files into the scene. allows users to segment scenes as required to suit the production workflow. not like Importing where the objects get copied over. Referencing needs an active link. reduces file size of the composited scene. 30
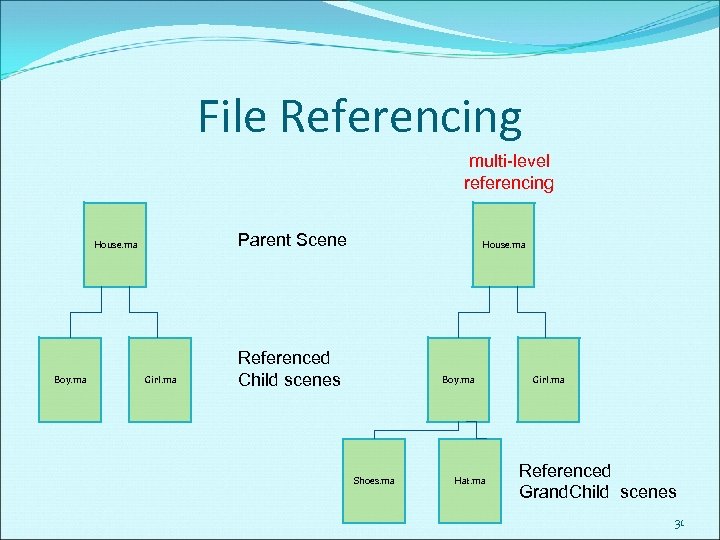 File Referencing multi-level referencing Parent Scene House. ma Boy. ma Girl. ma House. ma Referenced Child scenes Boy. ma Shoes. ma Hat. ma Girl. ma Referenced Grand. Child scenes 31
File Referencing multi-level referencing Parent Scene House. ma Boy. ma Girl. ma House. ma Referenced Child scenes Boy. ma Shoes. ma Hat. ma Girl. ma Referenced Grand. Child scenes 31
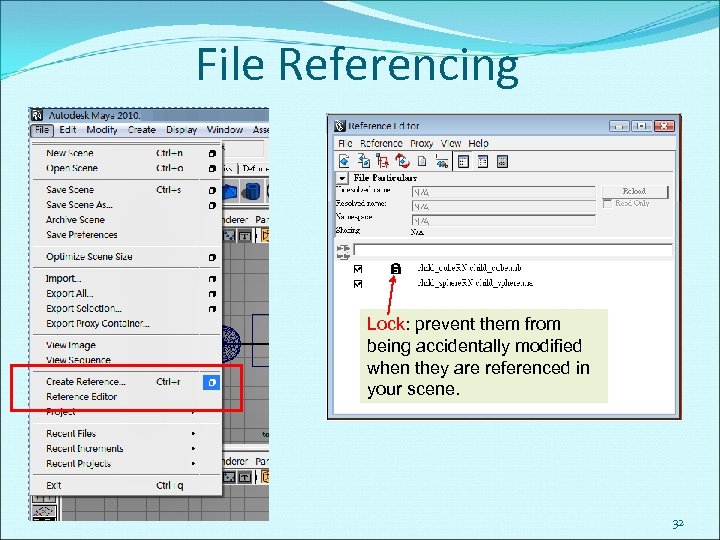 File Referencing Lock: prevent them from being accidentally modified when they are referenced in your scene. 32
File Referencing Lock: prevent them from being accidentally modified when they are referenced in your scene. 32
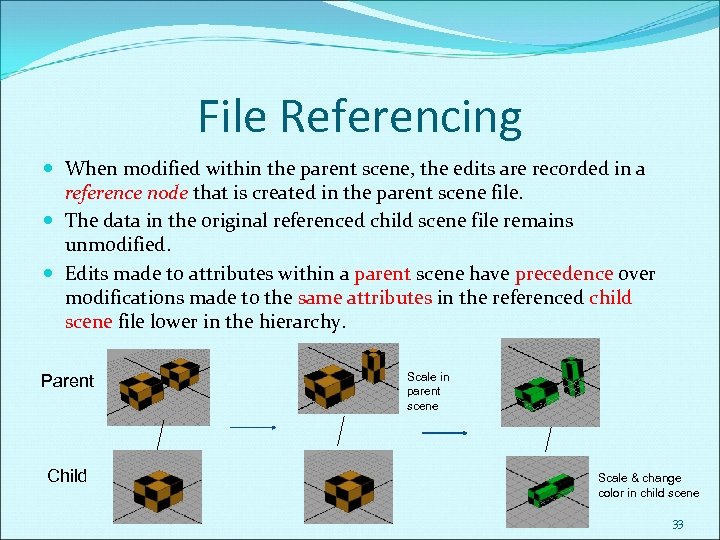 File Referencing When modified within the parent scene, the edits are recorded in a reference node that is created in the parent scene file. The data in the original referenced child scene file remains unmodified. Edits made to attributes within a parent scene have precedence over modifications made to the same attributes in the referenced child scene file lower in the hierarchy. Parent Child Scale in parent scene Scale & change color in child scene 33
File Referencing When modified within the parent scene, the edits are recorded in a reference node that is created in the parent scene file. The data in the original referenced child scene file remains unmodified. Edits made to attributes within a parent scene have precedence over modifications made to the same attributes in the referenced child scene file lower in the hierarchy. Parent Child Scale in parent scene Scale & change color in child scene 33
 Proxy References substitute one or more file references by creating a set of possible substitute references, known as proxies, for a given file reference. are used to temporarily simplify complex scenes by substituting simpler versions of the objects into the scene. allowing you to focus on the elements you need to work on while still maintaining a spatial context of the scene’s elements. A proxy reference can only be created for an existing file reference. http: //download. autodesk. com/us/ma ya/2009 help/index. html? url=File_refe rencing_About_proxy_references. ht m, topic. Number=d 0 e 117929 34
Proxy References substitute one or more file references by creating a set of possible substitute references, known as proxies, for a given file reference. are used to temporarily simplify complex scenes by substituting simpler versions of the objects into the scene. allowing you to focus on the elements you need to work on while still maintaining a spatial context of the scene’s elements. A proxy reference can only be created for an existing file reference. http: //download. autodesk. com/us/ma ya/2009 help/index. html? url=File_refe rencing_About_proxy_references. ht m, topic. Number=d 0 e 117929 34
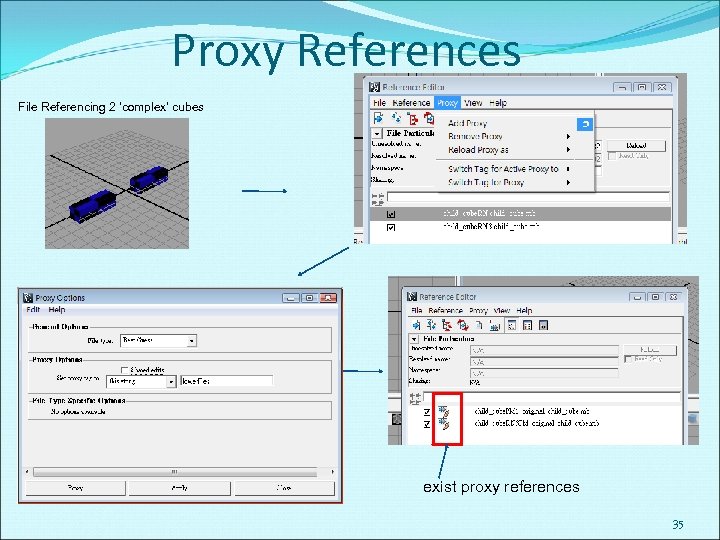 Proxy References File Referencing 2 ‘complex’ cubes exist proxy references 35
Proxy References File Referencing 2 ‘complex’ cubes exist proxy references 35
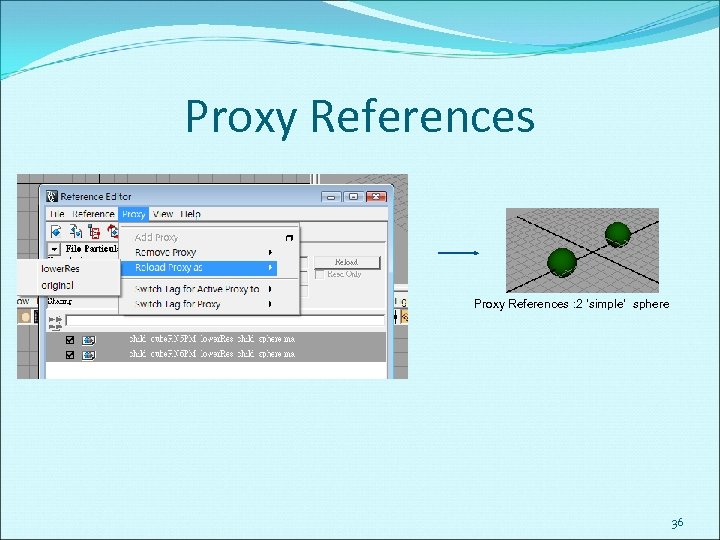 Proxy References : 2 ‘simple’ sphere 36
Proxy References : 2 ‘simple’ sphere 36
 Thank you ! 37
Thank you ! 37


