03c670118f4d614590630707df36535d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Artificial Intelligence 2. Intelligent Agents Dr. M. Tounsi CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
Artificial Intelligence 2. Intelligent Agents Dr. M. Tounsi CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 Definition n Is anything: ð ð n perceiving its environment through sensors acting upon its environment through effectors Example: With Robotic agent ü Sensors: Cameras and infrared ü Effectors: various motors CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
Definition n Is anything: ð ð n perceiving its environment through sensors acting upon its environment through effectors Example: With Robotic agent ü Sensors: Cameras and infrared ü Effectors: various motors CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
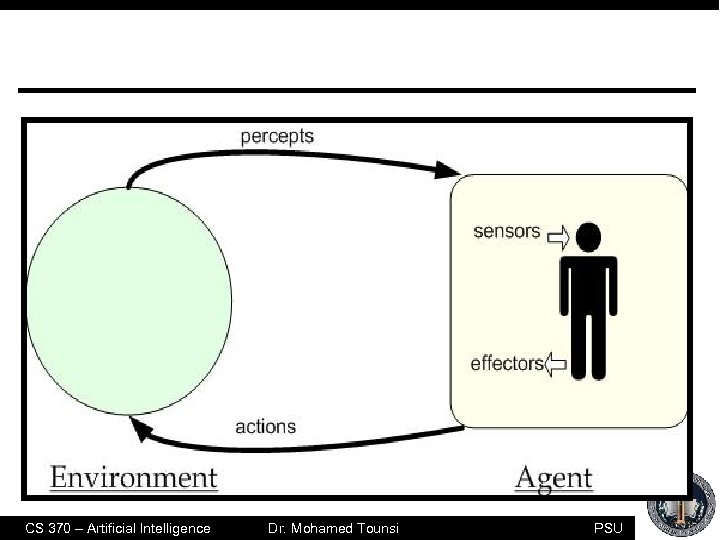 CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 Definitions and Concepts n Rational Agent l ð n Performance Measure Ø n Criteria that determines how successful an agent is Percept Sequence Ø E One that does the right thing (most successful!) Issue: how and when to evaluate the agent’s success ? Everything that the agent has perceived so far Ideal Rational Agent Ø Should do whatever action is expected to maximize its performance measure based on percept sequence and whatever build-in knowledge the agent has CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
Definitions and Concepts n Rational Agent l ð n Performance Measure Ø n Criteria that determines how successful an agent is Percept Sequence Ø E One that does the right thing (most successful!) Issue: how and when to evaluate the agent’s success ? Everything that the agent has perceived so far Ideal Rational Agent Ø Should do whatever action is expected to maximize its performance measure based on percept sequence and whatever build-in knowledge the agent has CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 Rational agents n An agent should strive to "do the right thing", based on what it can perceive and the actions it can perform. The right action is the one that will cause the agent to be most successful n Performance measure: An objective criterion for success of an agent's behavior n E. g. , performance measure of a vacuum-cleaner agent could be amount of dirt cleaned up, amount of time taken, amount of electricity consumed, amount of noise generated, etc. CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
Rational agents n An agent should strive to "do the right thing", based on what it can perceive and the actions it can perform. The right action is the one that will cause the agent to be most successful n Performance measure: An objective criterion for success of an agent's behavior n E. g. , performance measure of a vacuum-cleaner agent could be amount of dirt cleaned up, amount of time taken, amount of electricity consumed, amount of noise generated, etc. CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 PEAS n n n PEAS: Performance measure, Environment, Actuators, Sensors Definition: Actuator = Effector Must first specify the setting for intelligent agent design Example: the task of designing an automated taxi driver: l l Performance measure: Safe, fast, legal, comfortable trip, maximize profits Environment: Roads, other traffic, pedestrians, customers Actuators: Steering wheel, accelerator, brake, signal, horn Sensors: Cameras, sonar, speedometer, GPS, odometer, engine sensors, keyboard CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
PEAS n n n PEAS: Performance measure, Environment, Actuators, Sensors Definition: Actuator = Effector Must first specify the setting for intelligent agent design Example: the task of designing an automated taxi driver: l l Performance measure: Safe, fast, legal, comfortable trip, maximize profits Environment: Roads, other traffic, pedestrians, customers Actuators: Steering wheel, accelerator, brake, signal, horn Sensors: Cameras, sonar, speedometer, GPS, odometer, engine sensors, keyboard CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 PEAS n n n Agent: Medical diagnosis system Performance measure: Healthy patient, minimize costs, … Environment: Patient, hospital, staff Actuators: Screen display (questions, tests, diagnoses, treatments, referrals) Sensors: Keyboard (entry of symptoms, findings, patient's answers) CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
PEAS n n n Agent: Medical diagnosis system Performance measure: Healthy patient, minimize costs, … Environment: Patient, hospital, staff Actuators: Screen display (questions, tests, diagnoses, treatments, referrals) Sensors: Keyboard (entry of symptoms, findings, patient's answers) CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 PEAS n n n Agent: Part-picking robot Performance measure: Percentage of parts in correct bins Environment: Conveyor belt with parts, bins Actuators: Jointed arm and hand Sensors: Camera, joint angle sensors CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
PEAS n n n Agent: Part-picking robot Performance measure: Percentage of parts in correct bins Environment: Conveyor belt with parts, bins Actuators: Jointed arm and hand Sensors: Camera, joint angle sensors CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 PEAS n n n Agent: Interactive English tutor Performance measure: Maximize student's score on test Environment: Set of students Actuators: Screen display (exercises, suggestions, corrections) Sensors: Keyboard CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
PEAS n n n Agent: Interactive English tutor Performance measure: Maximize student's score on test Environment: Set of students Actuators: Screen display (exercises, suggestions, corrections) Sensors: Keyboard CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 Agent functions and programs n An agent is represented by the agent function which maps percept sequences to actions n Aim: find a way to implement the rational agent function concisely CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
Agent functions and programs n An agent is represented by the agent function which maps percept sequences to actions n Aim: find a way to implement the rational agent function concisely CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 Table-lookup agent Function Table-Agent(percept) returns an Action Static: percepts // sequence, initially empty Table // table of actions, indexed by percept, initially fully specified Begin Append perept to the end of the percepts Action : = LOOKUP(percepts, Table) return Action End Drawbacks: l Huge table l Take a long time to build the table l No autonomy l Even with learning, need a long time to learn the table entries CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
Table-lookup agent Function Table-Agent(percept) returns an Action Static: percepts // sequence, initially empty Table // table of actions, indexed by percept, initially fully specified Begin Append perept to the end of the percepts Action : = LOOKUP(percepts, Table) return Action End Drawbacks: l Huge table l Take a long time to build the table l No autonomy l Even with learning, need a long time to learn the table entries CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 Program Agent The design of the agent depends on the percepts, actions, goals and environment Function SKELETON-AGENT (percept) Static: memory; memory <- Update-Mem (memory, percept) action <- Choose-Best-Action (Memory) Memory <- Update-Memory(memory, action) Return action CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
Program Agent The design of the agent depends on the percepts, actions, goals and environment Function SKELETON-AGENT (percept) Static: memory; memory <- Update-Mem (memory, percept) action <- Choose-Best-Action (Memory) Memory <- Update-Memory(memory, action) Return action CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 Agent types Four basic types in order of increasing generality: 1. Simple reflex agents respond immediately to percepts (i. e. : rules) 2. 3. Model-based reflex agents Goal-based agents act so that they will achieve their goal(s) 4. Utility-based agents try to maximize their own happiness CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
Agent types Four basic types in order of increasing generality: 1. Simple reflex agents respond immediately to percepts (i. e. : rules) 2. 3. Model-based reflex agents Goal-based agents act so that they will achieve their goal(s) 4. Utility-based agents try to maximize their own happiness CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 Example: Simplex reflex agent Function Reflex-Vacum_agent(location, status) return actions { If status = dirty then action= Clean_ON; else { if location = A then action=right; else action = left; } } CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
Example: Simplex reflex agent Function Reflex-Vacum_agent(location, status) return actions { If status = dirty then action= Clean_ON; else { if location = A then action=right; else action = left; } } CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
 Autonomy n n If the agent is based completely on the “built-in knowledge” part, such that it pays no attention to its percepts, then we say that the agent lacks autonomy If the behavior of the agent is determined by only its own experience the system is autonomous AI Agent should have initial knowledge as well as an ability to learn CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU
Autonomy n n If the agent is based completely on the “built-in knowledge” part, such that it pays no attention to its percepts, then we say that the agent lacks autonomy If the behavior of the agent is determined by only its own experience the system is autonomous AI Agent should have initial knowledge as well as an ability to learn CS 370 – Artificial Intelligence Dr. Mohamed Tounsi PSU


