3a96892f2f2b5787ff64cbb80d8dd0b2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52

Artifact为中心的业务过程建模方法 Artifact-Centric Approach to Business Process Modeling Jianwen Su University of California, Santa Barbara CBPM '11 2011/08/25

Outline n Challenges in Business Process Management n Artifact-centric n. A Modeling Approach Design Methodology n Conclusions CBPM '11 2011/08/25 2
Business (Biz) Processes n. A set of one or more linked activities (automated or manual) that collectively realize a business objective or policy goal, normally within the context of an organizational structure defining functional roles and relationships Obtaining a Permit CBPM '11 2011/08/25 3
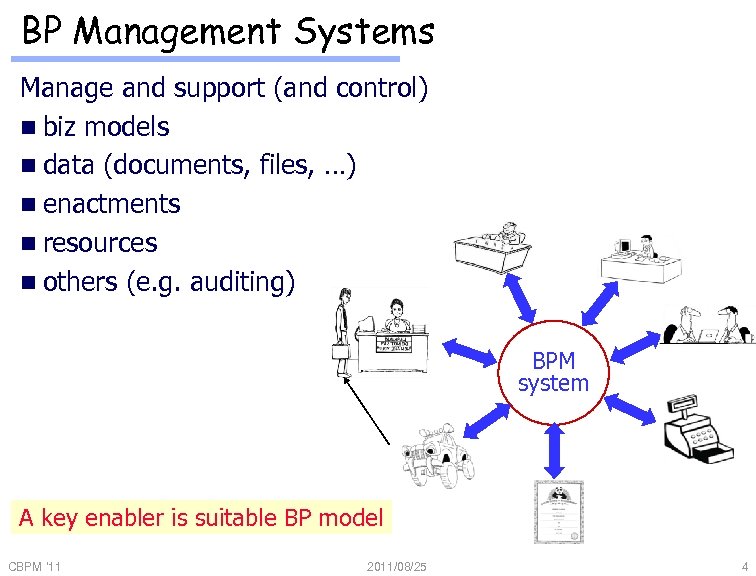
BP Management Systems Manage and support (and control) n biz models n data (documents, files, …) n enactments n resources n others (e. g. auditing) BPM system A key enabler is suitable BP model CBPM '11 2011/08/25 4

Major Obstacles in BPM n Hard to design, ad hoc solutions Lack of hierarchical approach with good disciplines n Hard to modify (evolution) E. g. , go back to the original contractor (if lucky) n Hard to analyze Biz intelligence is a growing research area n Hard to interoperate E. g. , hard to get data out in Cottage Hospital at Santa Barbara, CA n. A key factor for many problems: insufficient conceptual modeling CBPM '11 2011/08/25 5
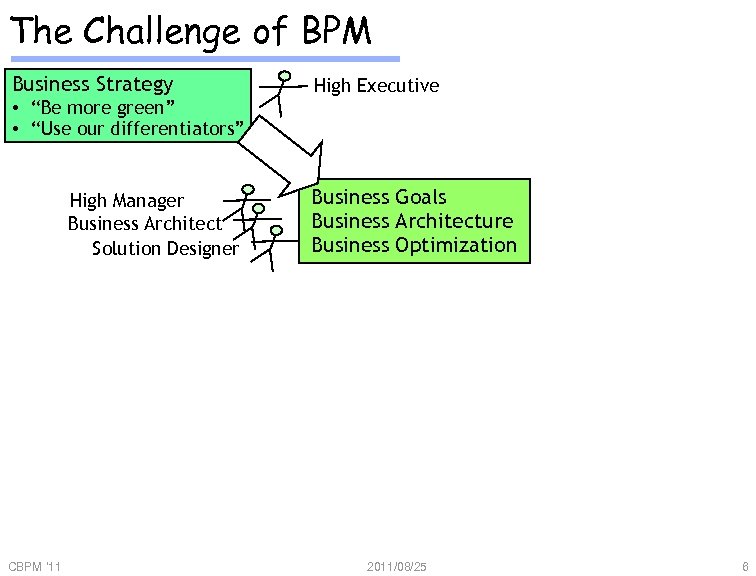
The Challenge of BPM Business Strategy • “Be more green” • “Use our differentiators” High Manager Business Architect Solution Designer CBPM '11 High Executive Business Goals Business Architecture Business Optimization 2011/08/25 6
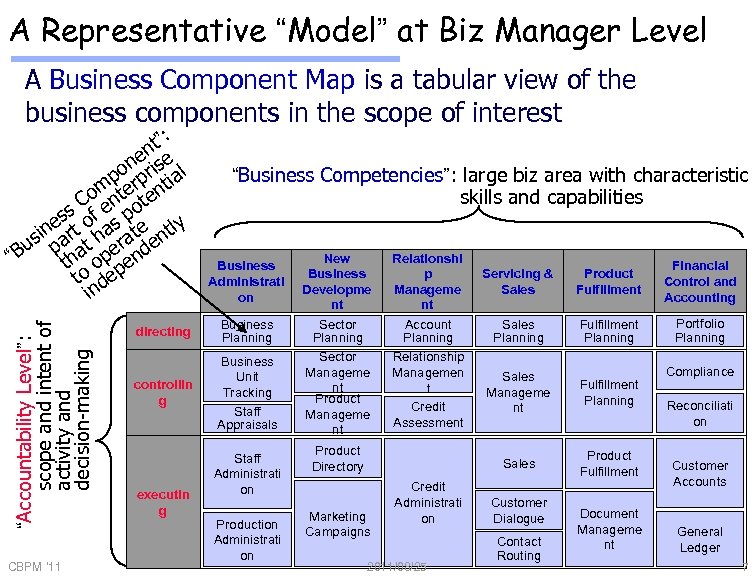
A Representative “Model” at Biz Manager Level A Business Component Map is a tabular view of the business components in the scope of interest “Accountability Level”: scope and intent of activity and decision-making t ”: n ne rise l po rp tia om nte ten C ss of e s po ineart ha ate ntly s Bu p hat per nde “ t o pe to de in CBPM '11 “Business Competencies”: large biz area with characteristic skills and capabilities Business Administrati on directing Business Planning controllin g Business Unit Tracking Staff Appraisals executin g Staff Administrati on Production Administrati on New Business Developme nt Sector Planning Sector Manageme nt Product Manageme nt Relationshi p Manageme nt Account Planning Relationship Managemen t Credit Assessment Servicing & Sales Product Fulfillment Financial Control and Accounting Sales Planning Fulfillment Planning Portfolio Planning Marketing Campaigns Credit Administrati on 2011/08/25 Fulfillment Planning Sales Product Directory Sales Manageme nt Product Fulfillment Customer Dialogue Contact Routing Document Manageme nt Compliance Reconciliati on Customer Accounts General Ledger 7
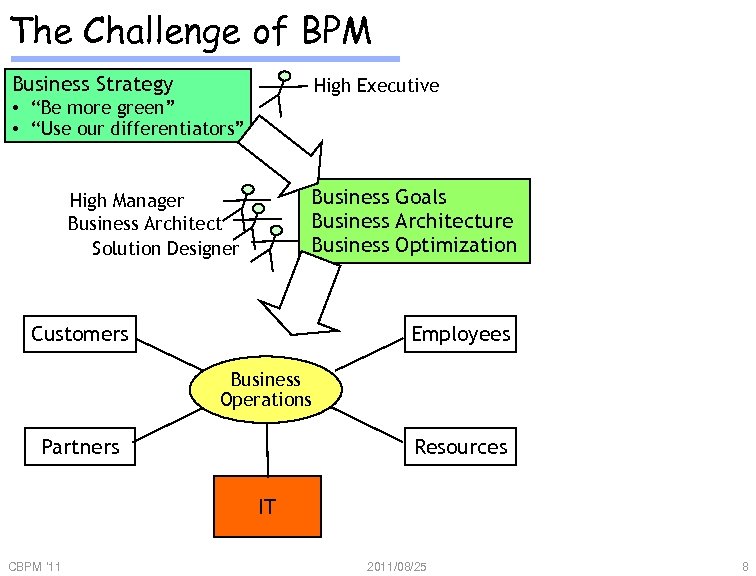
The Challenge of BPM Business Strategy High Executive • “Be more green” • “Use our differentiators” Business Goals Business Architecture Business Optimization High Manager Business Architect Solution Designer Customers Employees Business Operations Partners Resources IT CBPM '11 2011/08/25 8
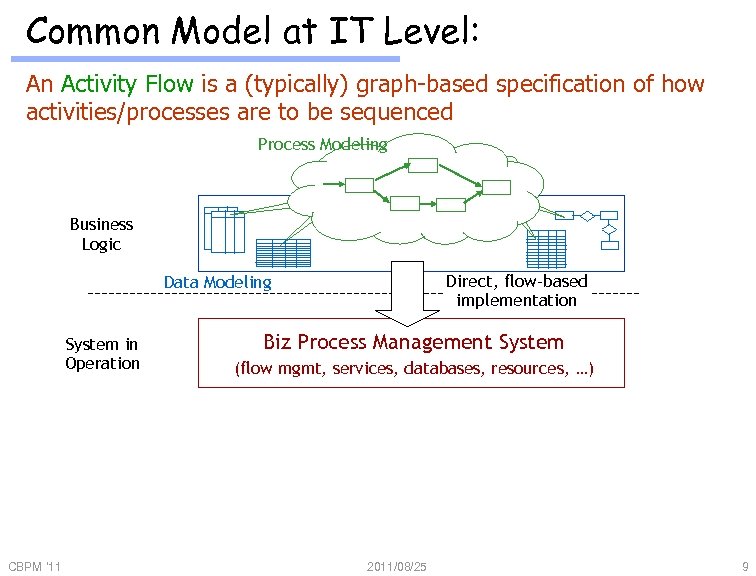
Common Model at IT Level: An Activity Flow is a (typically) graph-based specification of how activities/processes are to be sequenced Process Modeling Business Logic Direct, flow-based implementation Data Modeling System in Operation CBPM '11 Biz Process Management System (flow mgmt, services, databases, resources, …) 2011/08/25 9
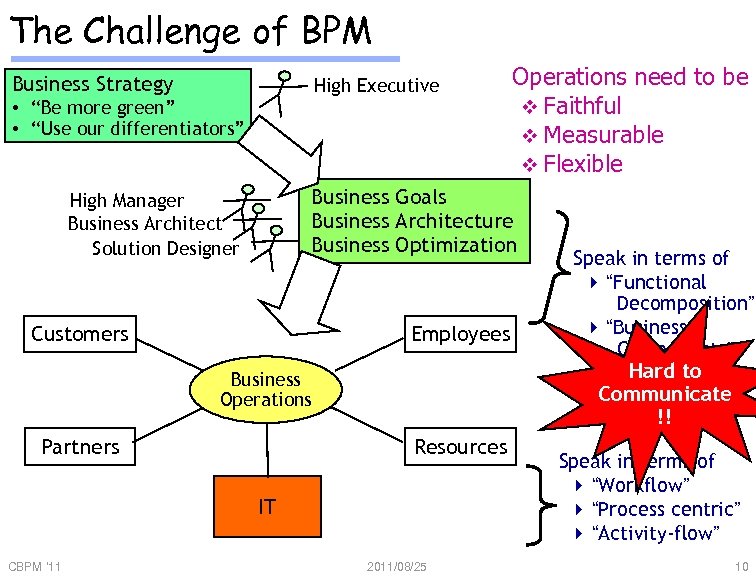
The Challenge of BPM Business Strategy High Executive • “Be more green” • “Use our differentiators” Business Goals Business Architecture Business Optimization High Manager Business Architect Solution Designer Customers Employees Partners Speak in terms of 4 “Functional Decomposition” 4 “Business Components” Hard to Communicate !! Business Operations Resources IT CBPM '11 Operations need to be v Faithful v Measurable v Flexible 2011/08/25 Speak in terms of 4 “Workflow” 4 “Process centric” 4 “Activity-flow” 10
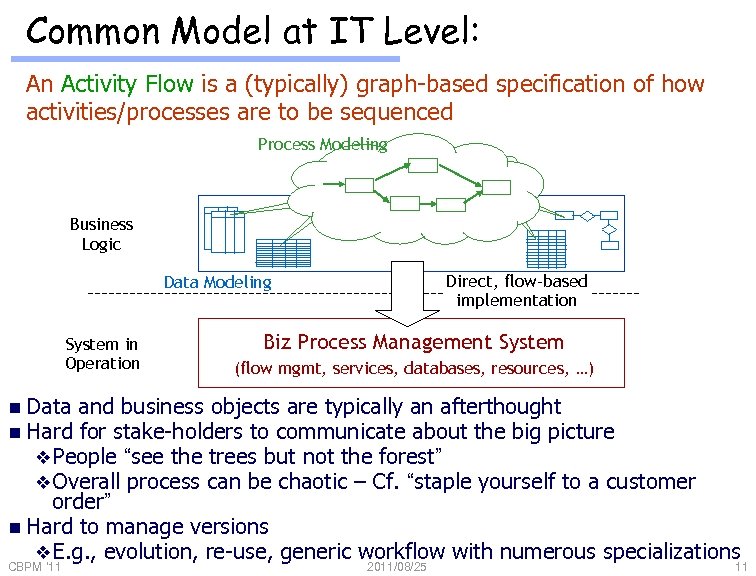
Common Model at IT Level: An Activity Flow is a (typically) graph-based specification of how activities/processes are to be sequenced Process Modeling Business Logic Direct, flow-based implementation Data Modeling System in Operation Biz Process Management System (flow mgmt, services, databases, resources, …) n Data and business objects are typically an afterthought n Hard for stake-holders to communicate about the big picture v People “see the trees but not the forest” v Overall process can be chaotic – Cf. “staple yourself to a customer order” n Hard to manage versions v E. g. , evolution, re-use, generic workflow with numerous specializations CBPM '11 2011/08/25 11
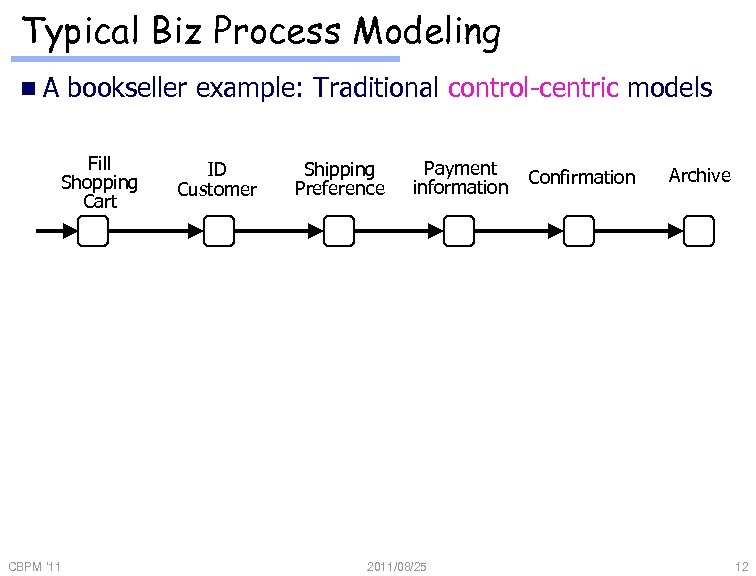
Typical Biz Process Modeling n. A bookseller example: Traditional control-centric models Fill Shopping Cart CBPM '11 ID Customer Shipping Preference Payment information 2011/08/25 Confirmation Archive 12
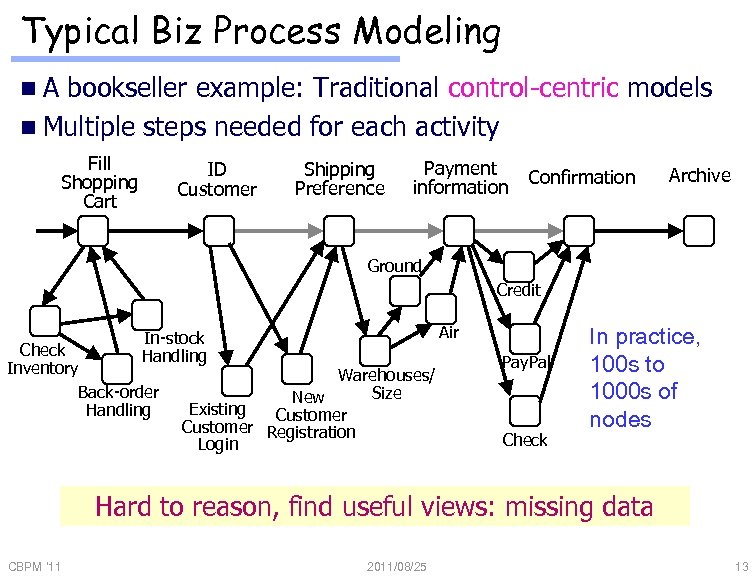
Typical Biz Process Modeling n. A bookseller example: Traditional control-centric models n Multiple steps needed for each activity Fill Shopping Cart ID Customer Shipping Preference Payment information Confirmation Archive Ground Credit Air In-stock Handling Check Inventory Back-order Handling Warehouses/ Size New Existing Customer Registration Login Pay. Pal Check In practice, 100 s to 1000 s of nodes Hard to reason, find useful views: missing data CBPM '11 2011/08/25 13
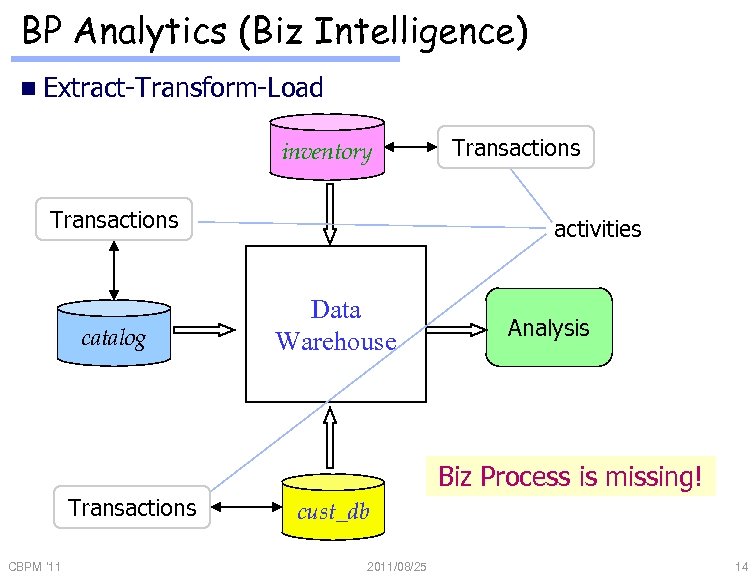
BP Analytics (Biz Intelligence) n Extract-Transform-Load inventory Transactions catalog Transactions activities Data Warehouse Analysis Biz Process is missing! Transactions CBPM '11 cust_db 2011/08/25 14
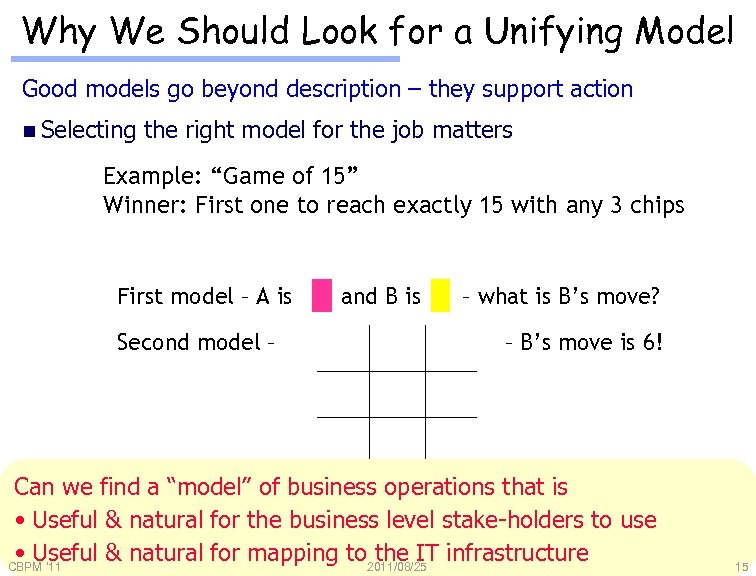
Why We Should Look for a Unifying Model Good models go beyond description – they support action n Selecting the right model for the job matters Example: “Game of 15” Winner: First one to reach exactly 15 with any 3 chips 1 2 3 First model – A is 4 5 and B is Second model – 6 7 8 9 – what is B’s move? – B’s move is 6! Example due to a “model”(IBM) Can we find David Cohn of business operations that is • Useful & natural for the business level stake-holders to use • Useful & natural for mapping to 2011/08/25 infrastructure the IT CBPM '11 15
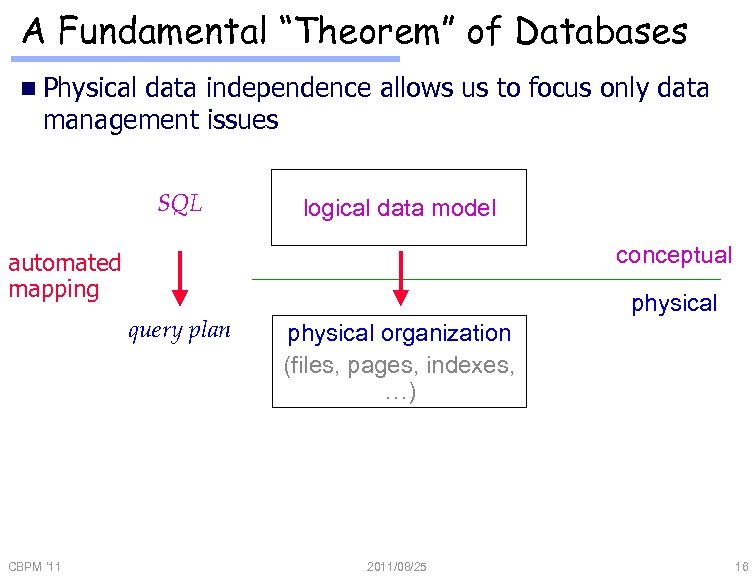
A Fundamental “Theorem” of Databases n Physical data independence allows us to focus only data management issues SQL logical data model conceptual automated mapping query plan CBPM '11 physical organization (files, pages, indexes, …) 2011/08/25 16
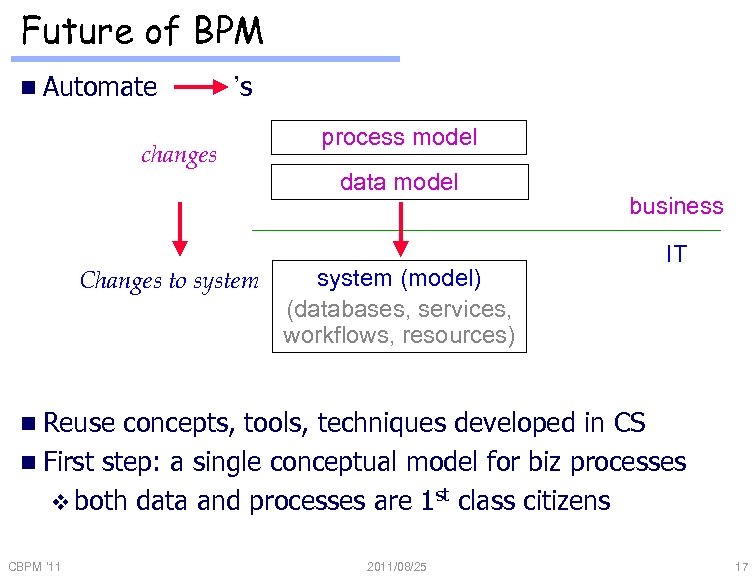
Future of BPM n Automate ’s changes Changes to system process model data model system (model) (databases, services, workflows, resources) business IT n Reuse concepts, tools, techniques developed in CS n First step: a single conceptual model for biz processes v both data and processes are 1 st class citizens CBPM '11 2011/08/25 17

Outline n Challenges in Business Process Management n Artifact-centric n. A Modeling Approach Design Methodology n Conclusions CBPM '11 2011/08/25 18
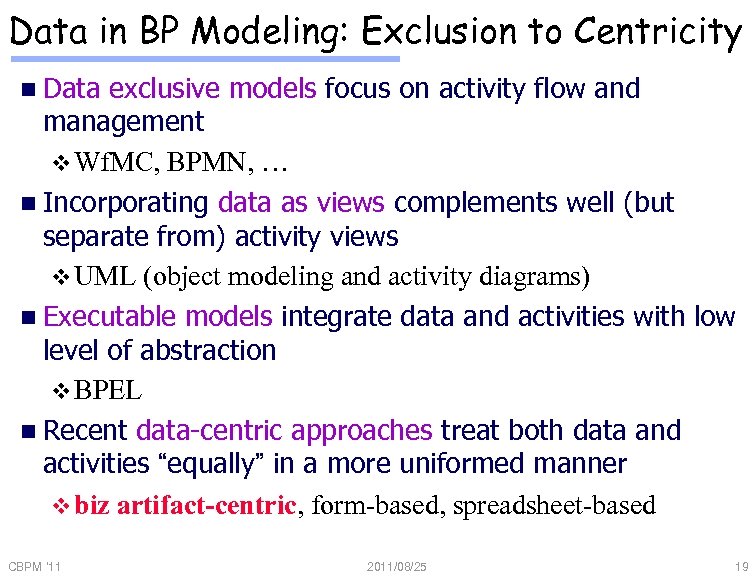
Data in BP Modeling: Exclusion to Centricity n Data exclusive models focus on activity flow and management v Wf. MC, BPMN, … n Incorporating data as views complements well (but separate from) activity views v UML (object modeling and activity diagrams) n Executable models integrate data and activities with low level of abstraction v BPEL n Recent data-centric approaches treat both data and activities “equally” in a more uniformed manner v biz artifact-centric, form-based, spreadsheet-based CBPM '11 2011/08/25 19
![Business Artifacts [Nigam-Caswell 03] n. A business artifact is a key conceptual business entity Business Artifacts [Nigam-Caswell 03] n. A business artifact is a key conceptual business entity](https://present5.com/presentation/3a96892f2f2b5787ff64cbb80d8dd0b2/image-20.jpg)
Business Artifacts [Nigam-Caswell 03] n. A business artifact is a key conceptual business entity that is used in guiding the operation of the business v fedex package delivery, patient visit, application form, insurance claim, order, financial deal, registration, … v both “information carrier” and “road-maps” n Very natural to business managers and BP modelers n Includes two parts: v Information model: data needed to move through workflow v Lifecycle: possible ways to evolve CBPM '11 2011/08/25 20
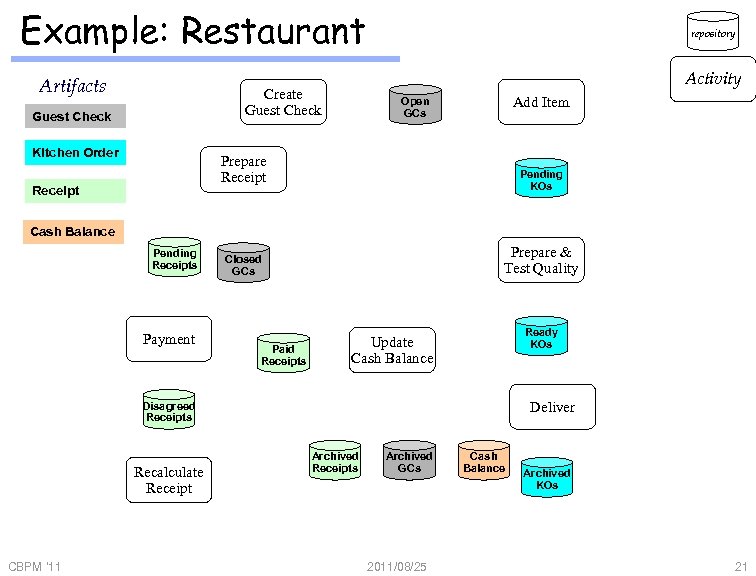
Example: Restaurant Artifacts Activity Create Guest Check Kitchen Order repository Add Item Open GCs Prepare Receipt Pending KOs Cash Balance Pending Receipts Payment Prepare & Test Quality Closed GCs Paid Receipts Ready KOs Update Cash Balance Deliver Disagreed Receipts Recalculate Receipt CBPM '11 Archived Receipts Archived GCs 2011/08/25 Cash Balance Archived KOs 21
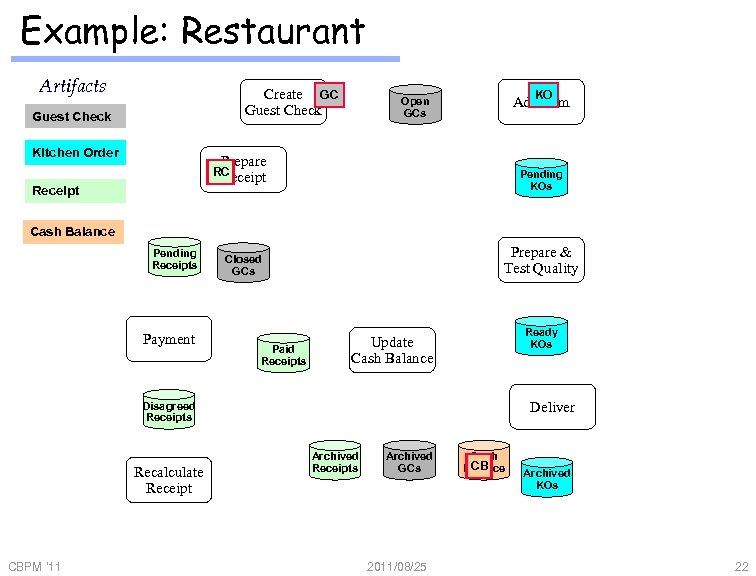
Example: Restaurant Artifacts Create GC Guest Check Kitchen Order KO Add Item Open GCs Prepare Receipt RC Receipt Pending KOs Cash Balance Pending Receipts Payment Prepare & Test Quality Closed GCs Paid Receipts Ready KOs Update Cash Balance Deliver Disagreed Receipts Recalculate Receipt CBPM '11 Archived Receipts Archived GCs 2011/08/25 Cash CB Balance Archived KOs 22
![Artifact Life Cycle [Nigam-Caswell 03] n An artifact life cycle captures the end-to-end processing Artifact Life Cycle [Nigam-Caswell 03] n An artifact life cycle captures the end-to-end processing](https://present5.com/presentation/3a96892f2f2b5787ff64cbb80d8dd0b2/image-23.jpg)
Artifact Life Cycle [Nigam-Caswell 03] n An artifact life cycle captures the end-to-end processing of a specific artifact, from creation to completion and archiving n Artifact processing is a way to describe the operations of a business Described by v Repositories, a means for archiving artifacts v Tasks (activity), a localization of function n Biz operations are described by IFF (Information, Function, and Flow) CBPM '11 2011/08/25 23
![Properties on Tasks [Nigam-Caswell 03] n. A task performs an action and records the Properties on Tasks [Nigam-Caswell 03] n. A task performs an action and records the](https://present5.com/presentation/3a96892f2f2b5787ff64cbb80d8dd0b2/image-24.jpg)
Properties on Tasks [Nigam-Caswell 03] n. A task performs an action and records the outcome on artifacts in its possession n A task transforms artifacts in its possession by adding/modifying content of an artifact using information in the other artifacts v multiple artifacts can reside in a task, and their content can be arbitrarily exchanged n After a task completes, it ejects all artifacts within it v no residual information: all artifacts are either sent out or discarded CBPM '11 2011/08/25 24
![Flows [Nigam-Caswell 03] n Tasks and repositories can be connected through flow connectors which Flows [Nigam-Caswell 03] n Tasks and repositories can be connected through flow connectors which](https://present5.com/presentation/3a96892f2f2b5787ff64cbb80d8dd0b2/image-25.jpg)
Flows [Nigam-Caswell 03] n Tasks and repositories can be connected through flow connectors which may be viewed as transport pipes v Through these pipes, artifacts or artifact content can be transmitted from one place (task/repository) to another Properties on flow: n A flow connector is a directed connector between a from. Place and a to. Place n A flow connector ensures reliable transmission of artifacts n A flow connector, when connecting a task to a repository, provides a reliable request-response style of communication va task that sends a request to a repository is ensured to receive one or more artifacts (or artifact content) or a NONE FOUND indication CBPM '11 2011/08/25 25
![Life Cycle of Guest Check Artifact [Nigam-Caswell 03] Daily Specials Manu Cash Balance CREATE Life Cycle of Guest Check Artifact [Nigam-Caswell 03] Daily Specials Manu Cash Balance CREATE](https://present5.com/presentation/3a96892f2f2b5787ff64cbb80d8dd0b2/image-26.jpg)
Life Cycle of Guest Check Artifact [Nigam-Caswell 03] Daily Specials Manu Cash Balance CREATE GUEST CHECK CUSTOMER Service Request Active Guest Checks Guest Check Paid Guest Checks External agent ADD ITEMS TO GUEST CHECK Waiter Manu Daily Active Special Guest Check TENDER GUEST CHECK Active Guest Check Complete Guest Check Account Paid Guest Check Kitchen Order Triggers task when artifact or content is received PREPARE ITEMS Emits artifact or content when task is finished Kitchen Order Complete Kitchen Order Human-initiated task Artifact is requested, updated, and returned to the source repository Requests and receives artifact content Requests and receives artifact CBPM '11 Repository 2011/08/25 Task 26
Data (Biz Objects, Documents, …) vs Artifacts n They all contain data needed for business logic, e. g. , customer info, shopping cart, product catalog, … n Biz objects are not artifacts: artifacts are uniquely identified with biz process instances, biz objects are just data objects needed for biz process n Biz artifacts also contain: v (Schema) Lifecycle, i. e. , process (or workflow) to evolve an artifact from creation to archive v (Enactment) Runtime states of instances (cases), i. e. , containing a part of the system snapshot concerning this artifact/enactment CBPM '11 2011/08/25 27
![Case Study : IBM Global Financing [Chao, Cohn, et al BPM 2009] n Finance Case Study : IBM Global Financing [Chao, Cohn, et al BPM 2009] n Finance](https://present5.com/presentation/3a96892f2f2b5787ff64cbb80d8dd0b2/image-28.jpg)
Case Study : IBM Global Financing [Chao, Cohn, et al BPM 2009] n Finance HW, SW & services from IBM & others for clients n IBM internal financing business w/ global reach v World’s largest IT financier w/ $38 B asset base v Financing >$40 B IT assets / year for last 3 years v 125 K clients across >50 countries (9% of IBM profit) n Business challenges v Operations tailored to mega-deals becoming too costly v Efficiency & cost control required global performance metrics v Country “silos” inhibited integration & annoyed clients v Current methods failed to produce end-to-end “tangible model” v Needed globally standard process w/ local variations CBPM '11 2011/08/25 28

How the Artifact-Centric Approach Helped n In a 3 -day workshop with 15 business SMEs from IGF, a preliminary artifact design was created v Already useful to stakeholders from different regions as a common vocabulary n 6 weeks of design refinements lead to final design v Enabled visibility into the global process and the regional variations: not possible before v A blueprint for transformation of IGF operations l VP roles assigned to pieces of top-level artifact model n Current plan: automate the global-level artifact model v Anticipate significant improvement in efficiency v Plan to substantially augment the sales staff CBPM '11 2011/08/25 29

Outline n Challenges in Business Process Management n Artifact-centric n. A Modeling Approach Design Methodology n Conclusions CBPM '11 2011/08/25 30
![A Data-Centric Design Methodology n. A [Bhattacharya-Hull-S. 09] three-level framework Specification Business Operations Model A Data-Centric Design Methodology n. A [Bhattacharya-Hull-S. 09] three-level framework Specification Business Operations Model](https://present5.com/presentation/3a96892f2f2b5787ff64cbb80d8dd0b2/image-31.jpg)
A Data-Centric Design Methodology n. A [Bhattacharya-Hull-S. 09] three-level framework Specification Business Operations Model (BOM) Optimization Conceptual Flow Execution CBPM '11 (artifacts, activities, flow) (artifacts, services, choreography/orchestration) Workflow (artifacts, executable services, messages) 2011/08/25 31
Key Elements in BOMs n Artifact information model v Represent all information needed for the biz process n Artifact (macro-level) lifecycle v Specify how an artifact evolves using e. g. , state machines n Services v Represent activities n Associations v Define how and when artifacts are changed by services CBPM '11 2011/08/25 32
Artifact-Centric Design Methodology Step 1: Business Artifacts Discovery a) Identify critical artifacts for the business process b) Discover key stages of artifacts’ life cycles from the scenario -based requirements Step 2: Design of Business Operations Model (BOM) a) Logical design of artifact schemas b) Specify services for artifacts needed for moving artifacts through the life-cycles c) Develop ECA rules that enable artifacts progress in their life cycles Step 3: Design of Conceptual Flow Diagram Step 4: Workflow Realization CBPM '11 2011/08/25 33
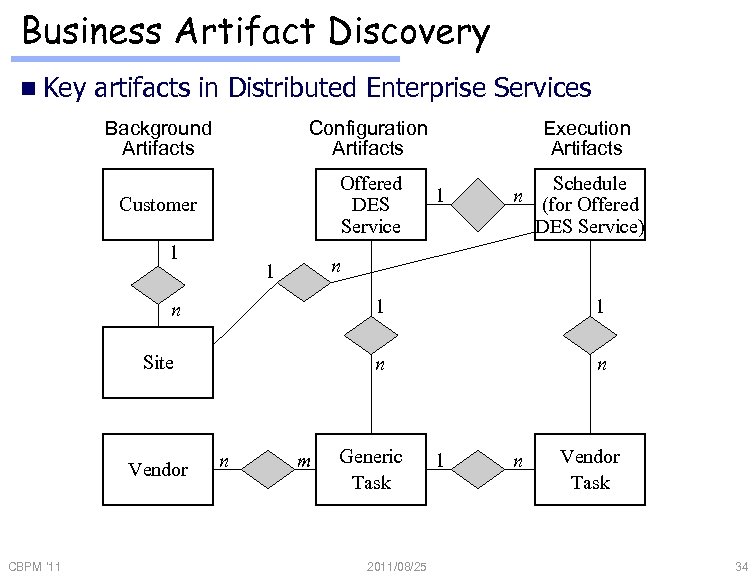
Business Artifact Discovery n Key artifacts in Distributed Enterprise Services Background Artifacts Configuration Artifacts Customer Offered DES Service 1 Schedule n (for Offered DES Service) 1 n m 1 n Site CBPM '11 1 n Vendor Execution Artifacts n Generic Task 2011/08/25 1 n Vendor Task 34
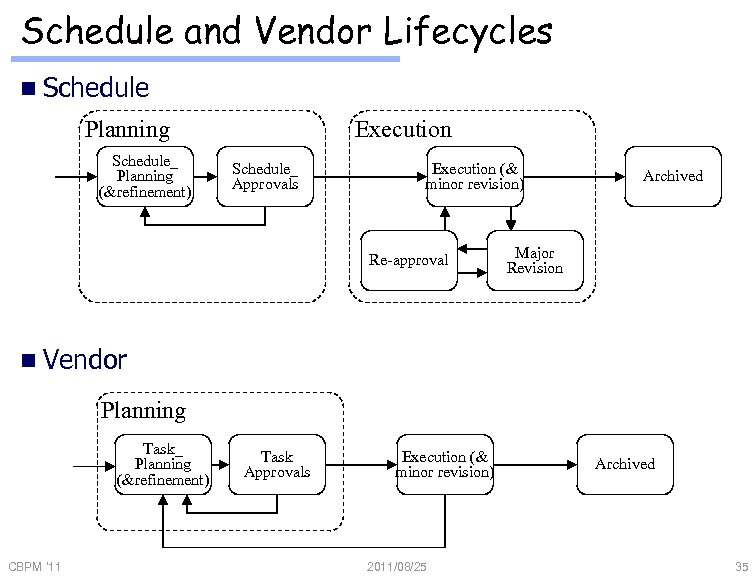
Schedule and Vendor Lifecycles n Schedule Planning Schedule_ Planning (&refinement) Execution Schedule_ Approvals Execution (& minor revision) Re-approval Archived Major Revision n Vendor Planning Task_ Planning (&refinement) CBPM '11 Task Approvals Execution (& minor revision) 2011/08/25 Archived 35
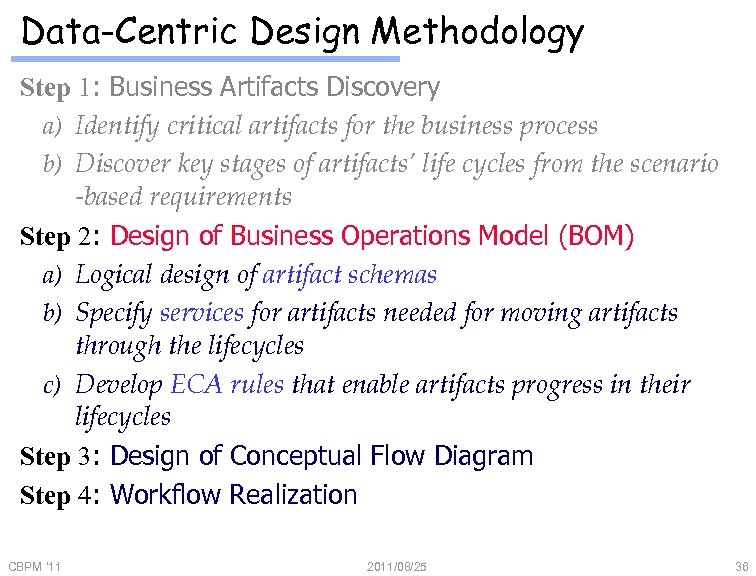
Data-Centric Design Methodology Step 1: Business Artifacts Discovery a) Identify critical artifacts for the business process b) Discover key stages of artifacts’ life cycles from the scenario -based requirements Step 2: Design of Business Operations Model (BOM) a) Logical design of artifact schemas b) Specify services for artifacts needed for moving artifacts through the lifecycles c) Develop ECA rules that enable artifacts progress in their lifecycles Step 3: Design of Conceptual Flow Diagram Step 4: Workflow Realization CBPM '11 2011/08/25 36
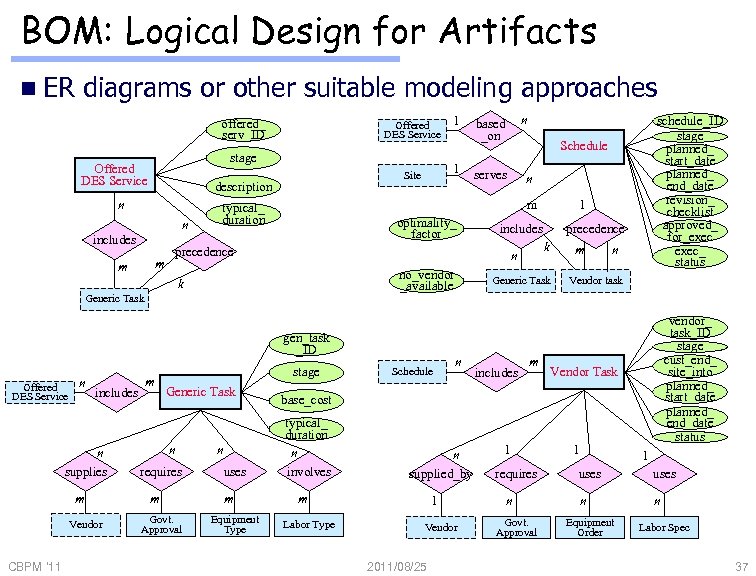
BOM: Logical Design for Artifacts n ER diagrams or other suitable modeling approaches offered_ serv_ID stage Offered DES Service n includes m optimality_ factor gen_task _ID Offered DES Service includes n supplies m Vendor CBPM '11 serves stage Generic Task n requires m Govt. Approval n uses m Equipment Type n 1 includes Schedule precedence k n no_vendor _available m Generic Task n schedule_ID stage planned_ start_date planned_ end_date revision_ checklist approved_ for_exec_ status Schedule precedence Generic Task m n based _on m typical_ duration k n 1 1 Site description n m Offered DES Service includes m n Vendor task vendor_ task_ID stage cust_end_ site_into planned_ start_date planned_ end_date status Vendor Task base_cost typical_ duration n involves n supplied_by m Labor Type 1 Vendor 2011/08/25 1 requires n Govt. Approval 1 1 uses n n Equipment Order Labor Spec 37
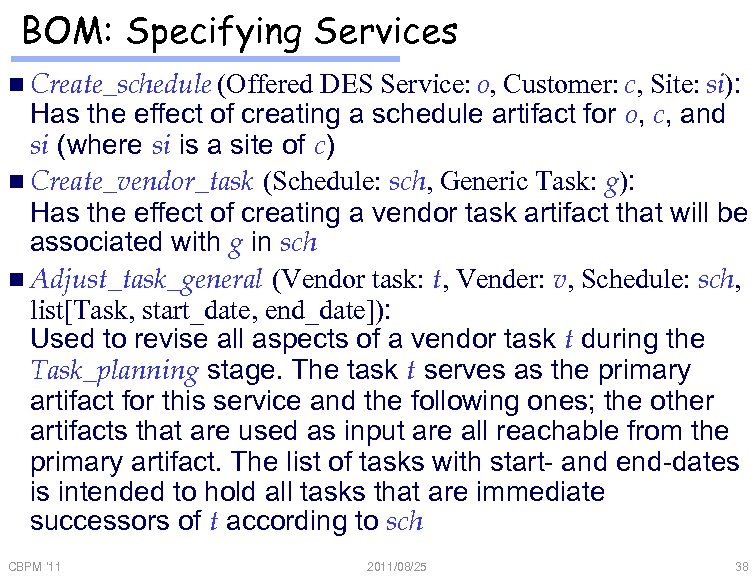
BOM: Specifying Services n Create_schedule (Offered DES Service: o, Customer: c, Site: si): Has the effect of creating a schedule artifact for o, c, and si (where si is a site of c) n Create_vendor_task (Schedule: sch, Generic Task: g): Has the effect of creating a vendor task artifact that will be associated with g in sch n Adjust_task_general (Vendor task: t, Vender: v, Schedule: sch, list[Task, start_date, end_date]): Used to revise all aspects of a vendor task t during the Task_planning stage. The task t serves as the primary artifact for this service and the following ones; the other artifacts that are used as input are all reachable from the primary artifact. The list of tasks with start- and end-dates is intended to hold all tasks that are immediate successors of t according to sch CBPM '11 2011/08/25 38
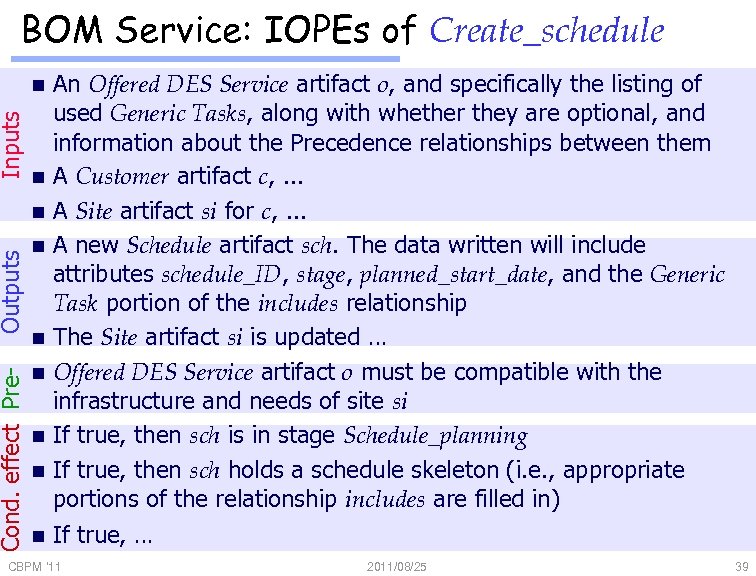
BOM Service: IOPEs of Create_schedule Inputs n n Cond. effect Pre- Outputs n n n n An Offered DES Service artifact o, and specifically the listing of used Generic Tasks, along with whether they are optional, and information about the Precedence relationships between them A Customer artifact c, . . . A Site artifact si for c, . . . A new Schedule artifact sch. The data written will include attributes schedule_ID, stage, planned_start_date, and the Generic Task portion of the includes relationship The Site artifact si is updated … Offered DES Service artifact o must be compatible with the infrastructure and needs of site si If true, then sch is in stage Schedule_planning If true, then sch holds a schedule skeleton (i. e. , appropriate portions of the relationship includes are filled in) If true, … CBPM '11 2011/08/25 39
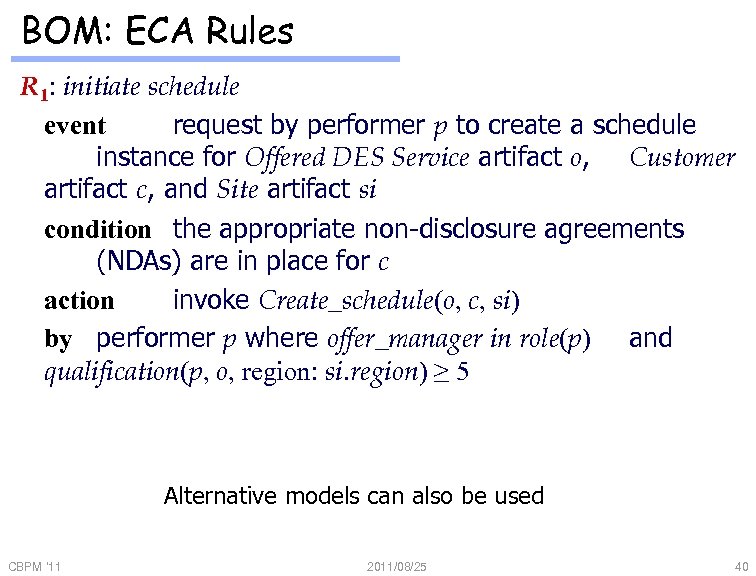
BOM: ECA Rules R 1: initiate schedule event request by performer p to create a schedule instance for Offered DES Service artifact o, Customer artifact c, and Site artifact si condition the appropriate non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are in place for c action invoke Create_schedule(o, c, si) by performer p where offer_manager in role(p) and qualification(p, o, region: si. region) ≥ 5 Alternative models can also be used CBPM '11 2011/08/25 40
Data-Centric Design Methodology Step 1: Business Artifacts Discovery a) Identify critical artifacts for the business process b) Discover key stages of artifacts’ life cycles from the scenario -based requirements Step 2: Design of Business Operations Model (BOM) a) Logical design of artifact schemas b) Specify services for artifacts needed for moving artifacts through the life-cycles c) Develop ECA rules that enable artifacts progress in their life cycles Step 3: Design of Conceptual Flow Diagram Step 4: Workflow Realization CBPM '11 2011/08/25 41
![Conceptual Flow Diagram (EZ-Flows) [Arti. Flow/EZ-Flow, 2009, 2010] CBPM '11 2011/08/25 42 Conceptual Flow Diagram (EZ-Flows) [Arti. Flow/EZ-Flow, 2009, 2010] CBPM '11 2011/08/25 42](https://present5.com/presentation/3a96892f2f2b5787ff64cbb80d8dd0b2/image-42.jpg)
Conceptual Flow Diagram (EZ-Flows) [Arti. Flow/EZ-Flow, 2009, 2010] CBPM '11 2011/08/25 42
![Interpreting EZ-Flows Alternative: Mapping to BPEL [Liu-Qin-S. -Yan-Zhang 2009] CBPM '11 2011/08/25 43 Interpreting EZ-Flows Alternative: Mapping to BPEL [Liu-Qin-S. -Yan-Zhang 2009] CBPM '11 2011/08/25 43](https://present5.com/presentation/3a96892f2f2b5787ff64cbb80d8dd0b2/image-43.jpg)
Interpreting EZ-Flows Alternative: Mapping to BPEL [Liu-Qin-S. -Yan-Zhang 2009] CBPM '11 2011/08/25 43
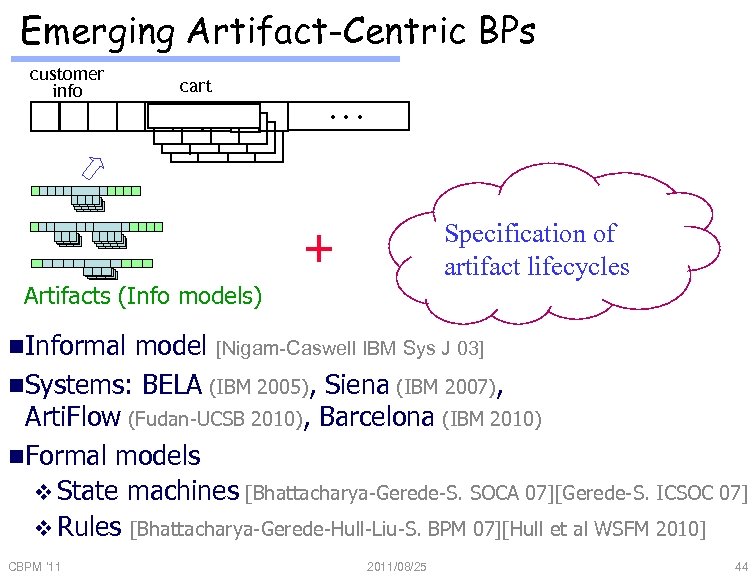
Emerging Artifact-Centric BPs customer info cart . . . + Specification of artifact lifecycles Artifacts (Info models) n Informal model [Nigam-Caswell IBM Sys J 03] n Systems: BELA (IBM 2005), Siena (IBM 2007), Arti. Flow (Fudan-UCSB 2010), Barcelona (IBM 2010) n Formal models v State machines [Bhattacharya-Gerede-S. SOCA 07][Gerede-S. ICSOC 07] v Rules [Bhattacharya-Gerede-Hull-Liu-S. BPM 07][Hull et al WSFM 2010] CBPM '11 2011/08/25 44
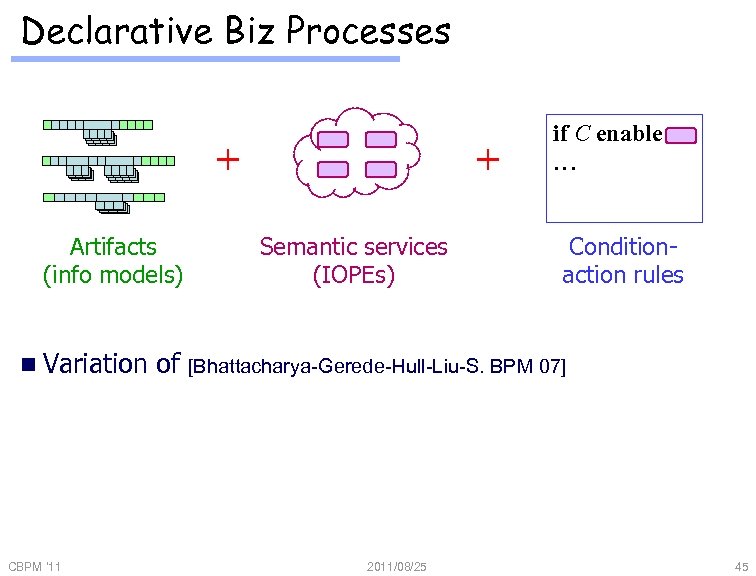
Declarative Biz Processes + Artifacts (info models) n Variation CBPM '11 of + Semantic services (IOPEs) if C enable … Conditionaction rules [Bhattacharya-Gerede-Hull-Liu-S. BPM 07] 2011/08/25 45
![GSM: Requisition Order Lifecycle [Hull et al 2010] Creating Proc. Orders Initiate Req. Order GSM: Requisition Order Lifecycle [Hull et al 2010] Creating Proc. Orders Initiate Req. Order](https://present5.com/presentation/3a96892f2f2b5787ff64cbb80d8dd0b2/image-46.jpg)
GSM: Requisition Order Lifecycle [Hull et al 2010] Creating Proc. Orders Initiate Req. Order Assembling All Line Items ordered Req. Order cancelled some Proc. Order Rejected & affected Line Items researched Request to begin assembling & enough Line Items to start Assembly finished Assembly cancelled Generating Report requested Report generated Top of each hour t e n g in rtitio l en Milestone: l a s w r tin m a e Stage: s em r Guard: toperational s p ur er t n rde lloc ms tim • Business-relevant. I e e p m oc rd es. O e a Ite O ite u • Cluster of activities n e • Has the effect of objective stom Lin Pr O eq eq o in intended to achieve L R R D ID Cu opening the stage • Expressed as event and/or condition • Has effect of closing the stage CBPM '11 Data attributes one (of perhaps … several) milestones • May be nested … • Expressed as event and/or condition Event (occurrence) attributes 2011/08/25 46
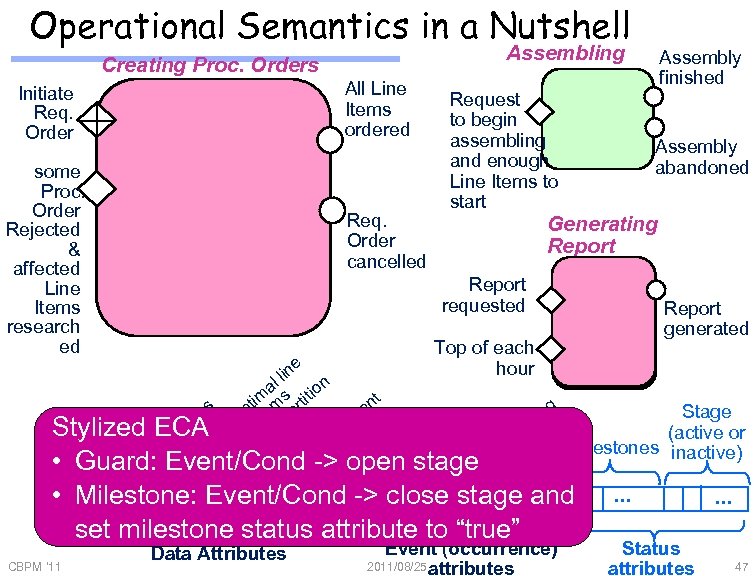
Operational Semantics in a Nutshell Assembling Creating Proc. Orders All Line Items ordered Initiate Req. Order some Proc. Order Rejected & affected Line Items research ed Req. Order cancelled Request to begin assembling and enough Line Items to start Assembly finished Assembly abandoned Generating Report requested Report generated Top of each hour e lin al s tion t im ti g s en pt item par Stage m w r tin O e e a s emrs te I r c n Stylizedr ECA (active or e e cu rde st Ord allo tem milestones n m o e o • Li inactive) Pr O open stage ne e I st qu eq. Guard: Event/Cond -> u n Re R • ID • C Do Li • • … … • Milestone: Event/Cond • -> close stage and set milestone status attribute to “true” CBPM '11 Data Attributes Event (occurrence) 2011/08/25 attributes • … Status attributes • … 47
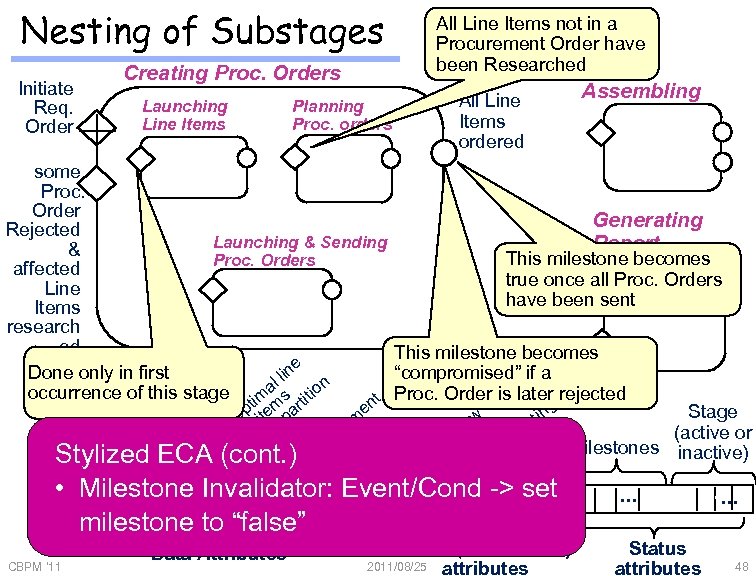
Nesting of Substages Creating Proc. Orders Initiate Req. Order Launching Line Items All Line Items not in a Procurement Order have been Researched All Line Items ordered Planning Proc. orders Assembling some Proc. Order Generating Rejected Launching & Sending Report & This milestone becomes Proc. Orders affected true once all Proc. Orders Line have been sent Items research ed This milestone becomes e n Done only in first “compromised” if a l li n occurrence of this stage ima s titio t Proc. Order is later rejected g s en pt item par Stage m w r tin O e e a s emrs te r c n (active or er e I cu rde st Ord allo tem milestones n m e o inactive) e e. I Stylized • Li ECA (cont. ) Pro O st qu q. u e Re R • ID • C n n Do Li • Milestone Invalidator: Event/Cond ->… • set • … milestone to “false” CBPM '11 Data Attributes Event (occurrence) 2011/08/25 attributes • … Status attributes • … 48
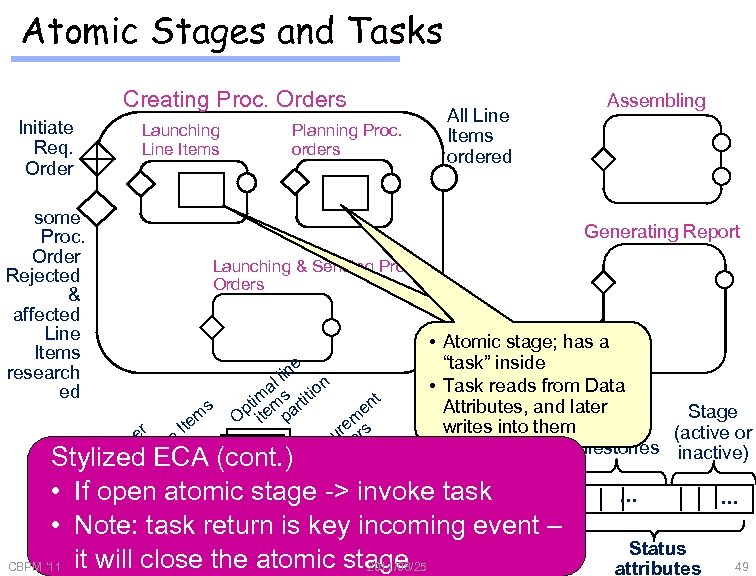
Atomic Stages and Tasks Creating Proc. Orders Initiate Req. Order some Proc. Order Rejected & affected Line Items research ed Launching Line Items All Line Items ordered Planning Proc. orders Assembling Generating Report Launching & Sending Proc. Orders e lin al s tion t im ti s en pt item par m O m Ite r re rs e u e m in oc rde L to Stylized • ECA (cont. ) Pr O us • ID • C • Atomic stage; has a “task” inside • Task reads from Data g Attributes, and later Stage w r tin e e into athem writes oc s n (active or st Ord all tem milestones e inactive) e e. I qu q. e Re R n n Do Li • If open atomic stage -> • … invoke task • … • Note: task return is key incoming event – Event (occurrence) Data Attributes it will close the atomic stage attributes CBPM '11 2011/08/25 • … Status attributes • … 49

Outline n Challenges in Business Process Management n Artifact-centric n. A Modeling Approach Design Methodology n Conclusions CBPM '11 2011/08/25 50

Brief Summary of Research Problems n Verification v Temporal properties of transition systems [Gerede-S. ICSOC 07] [Bhattacharya-Gerede-Hull-Liu-S. BPM 07] [Deutch-Vianu et al ICDT 09, 11]… n Interoperation [Hull-Narendra-Nigam ICSOC 09] n Automated construction [Frits-Hull-S. ICDT 09] n Dominance [Calvanese-De Giacomo-Hull-S. ICSOC 09] n Modeling: Declarative, semantics, execution [Cangialosi-De Giacomo-De Masellis-Rosati ICSOC 10] n Flexible execution [Xu-S. -Yang-Zhang Coop. IS 11] n Preserving Data ICs [Liu-S. -Yang Coop. IS 2011] CBPM '11 2011/08/25 51

Conclusions n Biz process modeling: a foundation for many BPM issues v Many challenges: “old” and new v Data-centric or data aware approaches promising n Business artifacts as the modeling foundation: v Extension of business objects with lifecycle/enactments v Many styles of modeling approaches: declarative, procedural, combinations n Modeling is/need be explored in conjunction with various technical issues in BP management n. A CBPM '11 longer tutorial is at BPM 2011 (next week) 2011/08/25 52
3a96892f2f2b5787ff64cbb80d8dd0b2.ppt