 Articles of Confederation- 1 st govt. Weak and Afraid of strong government • • Weaknesses One Branch = Congress No President or Court Cannot tax No power to enforce laws Strengths • Northwest Ordinance • Land Ordinance system that divided up western land allowed it to become a state
Articles of Confederation- 1 st govt. Weak and Afraid of strong government • • Weaknesses One Branch = Congress No President or Court Cannot tax No power to enforce laws Strengths • Northwest Ordinance • Land Ordinance system that divided up western land allowed it to become a state
 Constitutional Convention and the Great Compromise • Settled the dispute over representation • Bicameral Legislature = Senate and House or Representatives • Senate= 2 senators. • House of Representatives is determined by state’s population.
Constitutional Convention and the Great Compromise • Settled the dispute over representation • Bicameral Legislature = Senate and House or Representatives • Senate= 2 senators. • House of Representatives is determined by state’s population.
 Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution • • • Articles One Branch = Congress Unicameral Each state has one vote in Congress Cannot tax All 13 states must agree to amend • • • Constitution Strong Central Government Three Branches Bicameral- Senate and House of Representatives Power to tax ¾ states agree to amend
Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution • • • Articles One Branch = Congress Unicameral Each state has one vote in Congress Cannot tax All 13 states must agree to amend • • • Constitution Strong Central Government Three Branches Bicameral- Senate and House of Representatives Power to tax ¾ states agree to amend
 Federalist Papers Articles written to convince states to ratify the Constitution Anti-Federalists demanded a Bill of Rights
Federalist Papers Articles written to convince states to ratify the Constitution Anti-Federalists demanded a Bill of Rights
 3/5’s Compromise Used to determine representation Why was representation so important? More Representatives = More votes in congress = more influence in the creation of laws
3/5’s Compromise Used to determine representation Why was representation so important? More Representatives = More votes in congress = more influence in the creation of laws
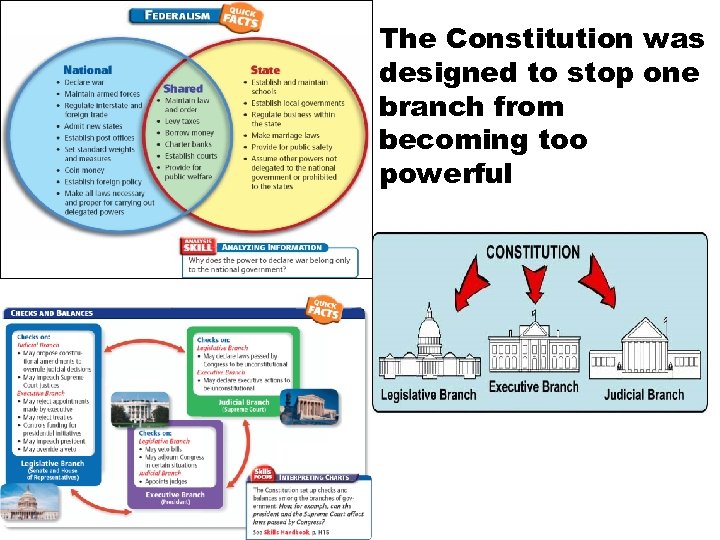 The Constitution was designed to stop one branch from becoming too powerful
The Constitution was designed to stop one branch from becoming too powerful
 A Republic or Republican form of government! • R for Representatives • Different from the Political Party
A Republic or Republican form of government! • R for Representatives • Different from the Political Party
 Constitutional Principles Popular Sovereignty Belief that government’s power comes from the consent of the governed. Power comes from the people Federalism Power is dived between Federal and State governments. Delegated Powers- Federal, Reserved Powers- State, Concurrent- shared Separation of Powers Power is divided between Three Branches. Legislative, Executive, Judicial Influenced by Montesquieu (Enlightenment) Checks and Balances Ability for one branch to limit the power of the other two branches. Stops one branch from becoming too powerful Limited Government Belief that governments power should be limited. Examples- Federalism, Bill of Rights, Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances
Constitutional Principles Popular Sovereignty Belief that government’s power comes from the consent of the governed. Power comes from the people Federalism Power is dived between Federal and State governments. Delegated Powers- Federal, Reserved Powers- State, Concurrent- shared Separation of Powers Power is divided between Three Branches. Legislative, Executive, Judicial Influenced by Montesquieu (Enlightenment) Checks and Balances Ability for one branch to limit the power of the other two branches. Stops one branch from becoming too powerful Limited Government Belief that governments power should be limited. Examples- Federalism, Bill of Rights, Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances
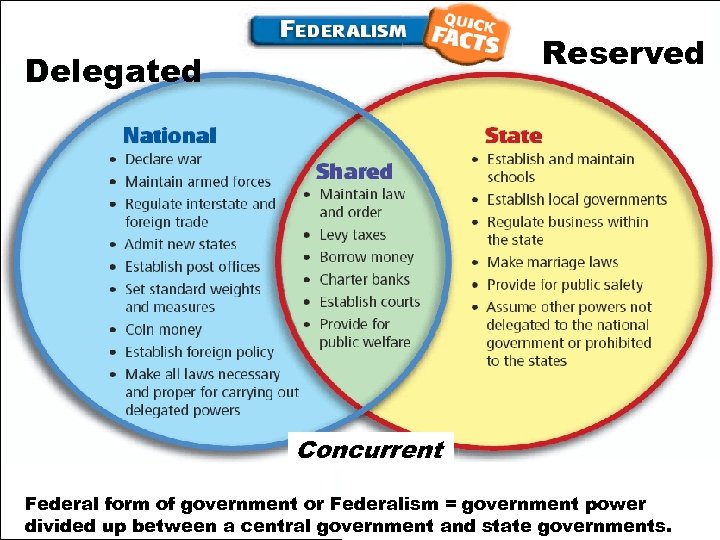 Reserved Delegated Concurrent Federal form of government or Federalism = government power divided up between a central government and state governments.
Reserved Delegated Concurrent Federal form of government or Federalism = government power divided up between a central government and state governments.
 Elastic Clause Make all laws “Necessary and Proper” Gives Congress the ability to increase its power by creating laws not specifically mentioned in the Constitution.
Elastic Clause Make all laws “Necessary and Proper” Gives Congress the ability to increase its power by creating laws not specifically mentioned in the Constitution.
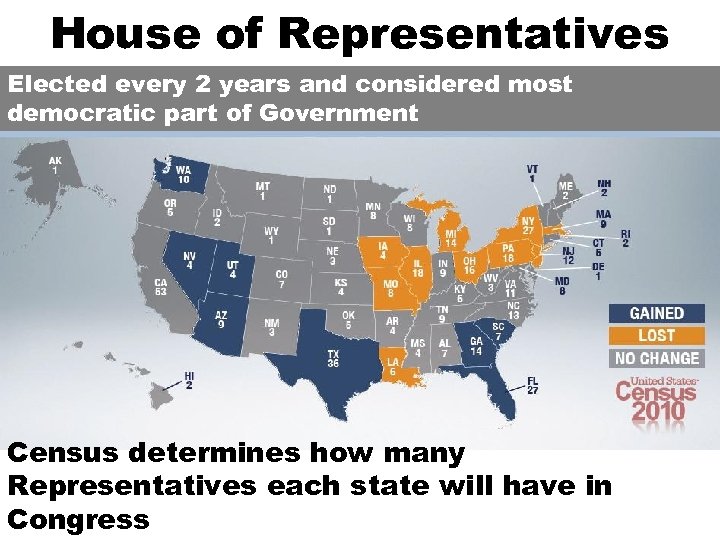 House of Representatives Elected every 2 years and considered most democratic part of Government Census determines how many Representatives each state will have in Congress
House of Representatives Elected every 2 years and considered most democratic part of Government Census determines how many Representatives each state will have in Congress
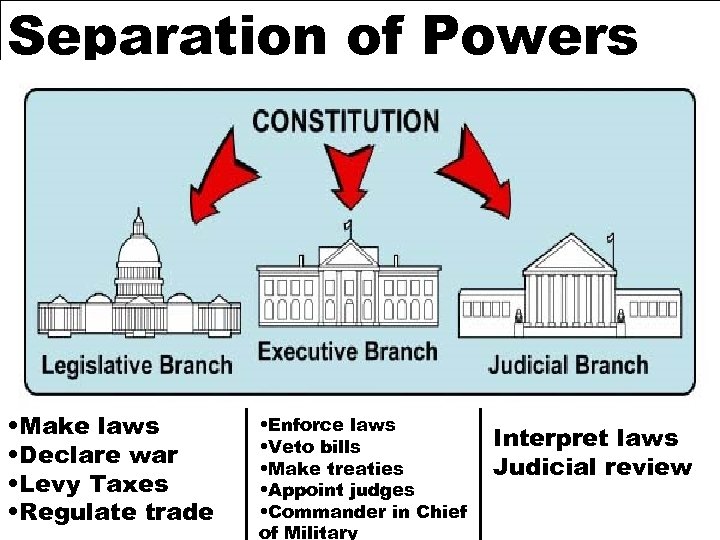 Separation of Powers • Make laws • Declare war • Levy Taxes • Regulate trade • Enforce laws • Veto bills • Make treaties • Appoint judges • Commander in Chief of Military Interpret laws Judicial review
Separation of Powers • Make laws • Declare war • Levy Taxes • Regulate trade • Enforce laws • Veto bills • Make treaties • Appoint judges • Commander in Chief of Military Interpret laws Judicial review
 The Constitution is a Limited, Flexible and Living Document Flexible and Limited Living Government Document • Federalism • Checks and Balances • Separation of Powers • Bill of Rights • Amendments • Elastic Clause
The Constitution is a Limited, Flexible and Living Document Flexible and Limited Living Government Document • Federalism • Checks and Balances • Separation of Powers • Bill of Rights • Amendments • Elastic Clause