проект Мотевич ARTICLES.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 27
 ARTICLES
ARTICLES
 Article…what is it?
Article…what is it?
 It is a word that combines with a noun to indicate the type of reference being made by the noun
It is a word that combines with a noun to indicate the type of reference being made by the noun
 There are only three a articles in English: a, an and the There are two types of articles indefinite 'a' and 'an' or definite 'the'.
There are only three a articles in English: a, an and the There are two types of articles indefinite 'a' and 'an' or definite 'the'.
 Indefinite article A/An
Indefinite article A/An
 We use it: in the meaning “one of”, “some” (=“какой-то”), “any” (= “любой”): ex. There is a wardrobe in the room. in the meaning “one”, “one more”: ex. Wait a minute, please. with price, distance and frequency: ex. 50 p a kilo, 100 km an hour, once a week etc. with adjectives followed by nouns: ex. This is a beautiful lake.
We use it: in the meaning “one of”, “some” (=“какой-то”), “any” (= “любой”): ex. There is a wardrobe in the room. in the meaning “one”, “one more”: ex. Wait a minute, please. with price, distance and frequency: ex. 50 p a kilo, 100 km an hour, once a week etc. with adjectives followed by nouns: ex. This is a beautiful lake.
 when we refer to an unknown person: ex. A Mr Brown called you yesterday. before words meaning profession or occupation: ex. My father is an engineer. with the verbs be and have to got: ex. I’ve got a dog.
when we refer to an unknown person: ex. A Mr Brown called you yesterday. before words meaning profession or occupation: ex. My father is an engineer. with the verbs be and have to got: ex. I’ve got a dog.
 with the words expressing emotions and mental activity (understanding, distrust, education, relief, pity, shame, wonder, knowledge and so on) when the meaning of these words is limited or defined more exactly: ex. What a shame!
with the words expressing emotions and mental activity (understanding, distrust, education, relief, pity, shame, wonder, knowledge and so on) when the meaning of these words is limited or defined more exactly: ex. What a shame!
 with illnesses: 1. a/an witha cold, a headache, a sore throat; 2. use or omit withcatch (a) cold, have (a) stomachache; 3. no article withmeasles, mumps, shingles; 4. no article with(high) blood pressure, gout, hepatitis.
with illnesses: 1. a/an witha cold, a headache, a sore throat; 2. use or omit withcatch (a) cold, have (a) stomachache; 3. no article withmeasles, mumps, shingles; 4. no article with(high) blood pressure, gout, hepatitis.
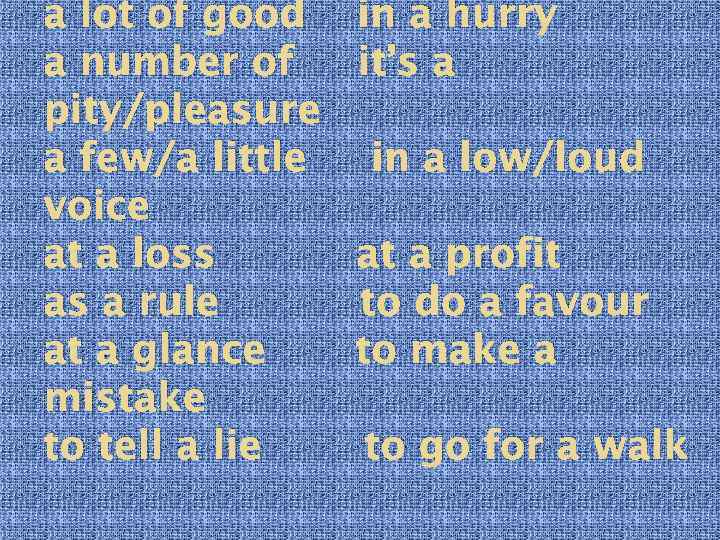 a lot of good a number of pity/pleasure a few/a little voice at a loss as a rule at a glance mistake to tell a lie in a hurry it’s a in a low/loud at a profit to do a favour to make a to go for a walk
a lot of good a number of pity/pleasure a few/a little voice at a loss as a rule at a glance mistake to tell a lie in a hurry it’s a in a low/loud at a profit to do a favour to make a to go for a walk
 Definite article The:
Definite article The:
 We use it: when the speaker and the listener know what particular object is meant: ex. Where is the car? NB! There is a difference between knowing what object is spoken about and knowing the object itself: ex. I can’t speak to the man. I haven’t seen him before.
We use it: when the speaker and the listener know what particular object is meant: ex. Where is the car? NB! There is a difference between knowing what object is spoken about and knowing the object itself: ex. I can’t speak to the man. I haven’t seen him before.
 when the speaker uses an attribute pointing out a particular object – a particularising attribute: ex. The houses they built last year are painted pink. NB! A particularising attribute should not be confused with a descriptive attribute, which is used to describe an object or to give some additional information about it. A descriptive attribute does not affect the use of the article: ex. We went to the lake which was stormy that day.
when the speaker uses an attribute pointing out a particular object – a particularising attribute: ex. The houses they built last year are painted pink. NB! A particularising attribute should not be confused with a descriptive attribute, which is used to describe an object or to give some additional information about it. A descriptive attribute does not affect the use of the article: ex. We went to the lake which was stormy that day.
 when the situation (context) itself makes the object definite: ex. The wedding was rather sad. The bride was too old and the bridegroom was too young. when the noun denotes a thing unique: ex. The Sun, the Solar system, etc. NB! The indefinite article can be used when we mean a certain state or aspect of the sun, the moon, the sky: ex. A pearl-white moon smiles through the green trees.
when the situation (context) itself makes the object definite: ex. The wedding was rather sad. The bride was too old and the bridegroom was too young. when the noun denotes a thing unique: ex. The Sun, the Solar system, etc. NB! The indefinite article can be used when we mean a certain state or aspect of the sun, the moon, the sky: ex. A pearl-white moon smiles through the green trees.
 with nouns used in a generic sense (as a type or a genre): ex. The tragedy and the comedy appeared in Greece. NB! In a generic sense: - with the noun man no article is used: ex. His trust in man has been destroyed. - with the noun woman the definite or no article is used: ex. He had always been interested in that mysterious being – the woman.
with nouns used in a generic sense (as a type or a genre): ex. The tragedy and the comedy appeared in Greece. NB! In a generic sense: - with the noun man no article is used: ex. His trust in man has been destroyed. - with the noun woman the definite or no article is used: ex. He had always been interested in that mysterious being – the woman.
 with the nouns modified by: a) adjectives in the superlative degree: ex. The best, the highest, etc. b) the pronouns same, all and the adjectives wrong, right, very, next, following, last, only, whole: ex. You are the very person I need. NB! “next” meaning future and “last” meaning pastare used without articles: ex. next month, last week c) the ordinal numerals: ex. first, second, etc.
with the nouns modified by: a) adjectives in the superlative degree: ex. The best, the highest, etc. b) the pronouns same, all and the adjectives wrong, right, very, next, following, last, only, whole: ex. You are the very person I need. NB! “next” meaning future and “last” meaning pastare used without articles: ex. next month, last week c) the ordinal numerals: ex. first, second, etc.
 with substantivized adjectives and participles: the old, the dead, the rich, the poor, the blind, the sick, etc. ex. There are special schools for the blind and the deaf. with the words school, college, university, class, court, prison, church, hospital , etc. if we go there as a visitor: ex. Yesterday I went to the hospital to visit my colleague. for musical instruments: ex. The piano was her favourite instrument. He could play the guitar perfectly well.
with substantivized adjectives and participles: the old, the dead, the rich, the poor, the blind, the sick, etc. ex. There are special schools for the blind and the deaf. with the words school, college, university, class, court, prison, church, hospital , etc. if we go there as a visitor: ex. Yesterday I went to the hospital to visit my colleague. for musical instruments: ex. The piano was her favourite instrument. He could play the guitar perfectly well.
 in front of the nationality nouns (in general): a) the + -ese/ss: the Chinese, the Swiss; b) the + plural ending: -ians: the Austrians, the Russians; -ans: the Americans, the Mexicans; -s: the Arabs, the Scots. c) the Danes/ the Danish, the Spaniards/ the Spanish, the Swedes/ the Swedish. d) the + ch/sh: the British, the French
in front of the nationality nouns (in general): a) the + -ese/ss: the Chinese, the Swiss; b) the + plural ending: -ians: the Austrians, the Russians; -ans: the Americans, the Mexicans; -s: the Arabs, the Scots. c) the Danes/ the Danish, the Spaniards/ the Spanish, the Swedes/ the Swedish. d) the + ch/sh: the British, the French
 In such expressions as: in the morning/ afternoon/ evening; in the past/future; the other day; at the moment; by the way; on the whole; in the original; in the sun/ shade/ rain; on the one/ other hand;
In such expressions as: in the morning/ afternoon/ evening; in the past/future; the other day; at the moment; by the way; on the whole; in the original; in the sun/ shade/ rain; on the one/ other hand;
 under the impression; at the top/ bottom; on the left/ right; in the middle; to lay the table; to tell the truth/ the time; to do the cleaning/ washing.
under the impression; at the top/ bottom; on the left/ right; in the middle; to lay the table; to tell the truth/ the time; to do the cleaning/ washing.
 No article is used:
No article is used:
 before nouns in plural: ex. Women are expected to like babies. before abstract nouns: ex. Business is going well at the moment. before cardinal numerals: ex. They met in 2011. before names of sciences and subjects: ex. We are studying linguistics.
before nouns in plural: ex. Women are expected to like babies. before abstract nouns: ex. Business is going well at the moment. before cardinal numerals: ex. They met in 2011. before names of sciences and subjects: ex. We are studying linguistics.
 before names of languages: ex. I like French. BUT: the French language. before kinds of sport: ex. He plays football nearly every day. before seasons, months, days of the week and parts of the day: ex. I like summer. I have birthday in September. Monday is the most difficult day of the week.
before names of languages: ex. I like French. BUT: the French language. before kinds of sport: ex. He plays football nearly every day. before seasons, months, days of the week and parts of the day: ex. I like summer. I have birthday in September. Monday is the most difficult day of the week.
 before the nouns breakfast, lunch, dinner, supper in the meaning “to have a meal, to eat”: ex. She usually has breakfast at 7. when we address to somebody: ex. Ladies and gentleman!
before the nouns breakfast, lunch, dinner, supper in the meaning “to have a meal, to eat”: ex. She usually has breakfast at 7. when we address to somebody: ex. Ladies and gentleman!
 In the following expressions: at present for ages on second thoughts in charge at first sight by heart in detail at night
In the following expressions: at present for ages on second thoughts in charge at first sight by heart in detail at night
 by mistake on average from beginning to end by chance to tell lies to pay attention to shake hands to be on fire
by mistake on average from beginning to end by chance to tell lies to pay attention to shake hands to be on fire
 Thank you for attention! I hope this information will help you prepared by Motevich Irina th the 9 group
Thank you for attention! I hope this information will help you prepared by Motevich Irina th the 9 group


