0dd095ec1cf858853dba4ae774ff70a4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Article I: The Legislature
Article I: The Legislature
 Article I – Section I “All legislative Powers herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States, which shall consist of a Senate and House of Representatives. ” n Framers intended for this to be most powerful branch Most “familiar” n Set up similar to parliament with some improvements n n Use of Senate and House creates a “bicameral” legislature
Article I – Section I “All legislative Powers herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States, which shall consist of a Senate and House of Representatives. ” n Framers intended for this to be most powerful branch Most “familiar” n Set up similar to parliament with some improvements n n Use of Senate and House creates a “bicameral” legislature
 Section II - House n Clause 1: Members of the House will be elected every 2 years n Clause 2: Qualifications to be a member of the House of Reps 25 years old n Live in the state you represent n Citizen for 7 years n Aaron Schock, 30
Section II - House n Clause 1: Members of the House will be elected every 2 years n Clause 2: Qualifications to be a member of the House of Reps 25 years old n Live in the state you represent n Citizen for 7 years n Aaron Schock, 30
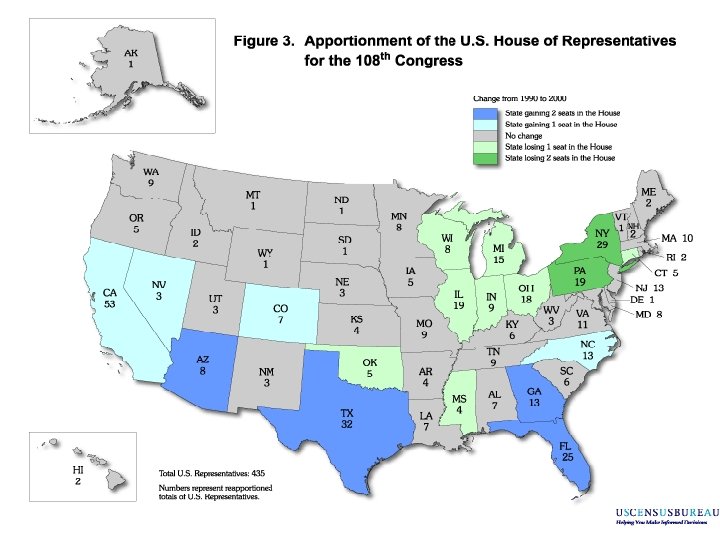
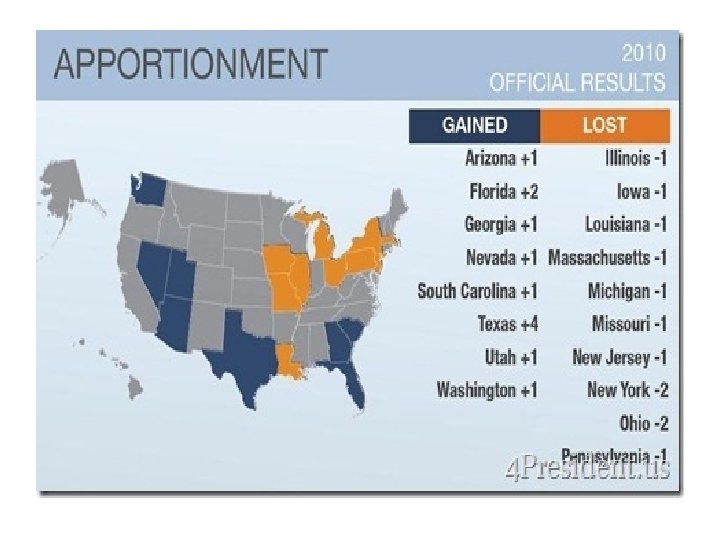
 Section II – (Continued) n Clause 3: Apportionment of representatives n Each state will have at least 1 rep n Must count population every 10 years (census) n Originally included 3/5 compromise (removed by 14 th amendment) n Originally allowed for 1 rep / 30, 000 people n Current number is about 1 rep / 700, 000 § Roughly 1/435 of the population § Wyoming, Vermont, Alaska, and ND don’t even have 1/435 of the population!
Section II – (Continued) n Clause 3: Apportionment of representatives n Each state will have at least 1 rep n Must count population every 10 years (census) n Originally included 3/5 compromise (removed by 14 th amendment) n Originally allowed for 1 rep / 30, 000 people n Current number is about 1 rep / 700, 000 § Roughly 1/435 of the population § Wyoming, Vermont, Alaska, and ND don’t even have 1/435 of the population!
 Section II - Continued n Clauses 4 and 5 n How to fill vacancies and choose the speaker/officers n Gives sole power of impeachment (5)
Section II - Continued n Clauses 4 and 5 n How to fill vacancies and choose the speaker/officers n Gives sole power of impeachment (5)
 Section III - Senate n Clause 1: 2 Senators from each state for 6 years Originally chosen by state legislatures n 17 th amendment allows for elections n Designed to be the higher esteemed house n n Clause 2: Divides senate in 3 rds for reelection n How to deal with vacancies (superseded by 17 th am)
Section III - Senate n Clause 1: 2 Senators from each state for 6 years Originally chosen by state legislatures n 17 th amendment allows for elections n Designed to be the higher esteemed house n n Clause 2: Divides senate in 3 rds for reelection n How to deal with vacancies (superseded by 17 th am)
 Section III - continued n Clause 3: Qualifications to be Senator n 30 years old n Citizen for 9 years n Reside in state at time of election John Henry Eaton n. Clauses 4 – 5: Vice President Daniel Inouye will preside over senate and when he is out, the Senate will choose a President Pro Tempore
Section III - continued n Clause 3: Qualifications to be Senator n 30 years old n Citizen for 9 years n Reside in state at time of election John Henry Eaton n. Clauses 4 – 5: Vice President Daniel Inouye will preside over senate and when he is out, the Senate will choose a President Pro Tempore
 Section III – continued n Clauses 6 – 7: Impeachment trials n Requires 2/3 of members present n Requires Chief Justice to preside for President n If convicted, person can only be removed from Office by Senate, no other punishment by the Senate n Person can still face criminal/civil trial
Section III – continued n Clauses 6 – 7: Impeachment trials n Requires 2/3 of members present n Requires Chief Justice to preside for President n If convicted, person can only be removed from Office by Senate, no other punishment by the Senate n Person can still face criminal/civil trial
 Section IV – Elections/Meeting n Clause 1: “The Times, Places and Manner of holding Elections for Senators and Representatives, shall be prescribed in each State by the Legislature thereof…” n Congress can tamper with this some (National elections on same day, etc) n Clause 2: Congress must meet once a year n 20 th amendment makes date Jan. 3 rd
Section IV – Elections/Meeting n Clause 1: “The Times, Places and Manner of holding Elections for Senators and Representatives, shall be prescribed in each State by the Legislature thereof…” n Congress can tamper with this some (National elections on same day, etc) n Clause 2: Congress must meet once a year n 20 th amendment makes date Jan. 3 rd
 Section V – Procedures n Each house decides if members are qualified and properly elected n A quorum is required to do business Simple majority = quorum n In practice, this is largely ignored n n Rules are decided by each house n Constitution requires 2/3 to expel a member n Requires a record of proceedings to be kept and published n Neither house can move or adjourn without the other’s permission
Section V – Procedures n Each house decides if members are qualified and properly elected n A quorum is required to do business Simple majority = quorum n In practice, this is largely ignored n n Rules are decided by each house n Constitution requires 2/3 to expel a member n Requires a record of proceedings to be kept and published n Neither house can move or adjourn without the other’s permission
 Section VI – Compensation/Priveleges n “The Senators and Representatives shall receive a Compensation for their Services, to be ascertained by Law, and paid out of the Treasury of the United States” n 27 th amendment: A change in compensation can’t go into place until after the next election n n Privilege from arrest during session n n Proposed 1789, Ratified 1992 (202 years!) Does not apply to major crimes “Speech and Debate Clause” n n Can not be sued for slander during debates Must be part of the legislative process!
Section VI – Compensation/Priveleges n “The Senators and Representatives shall receive a Compensation for their Services, to be ascertained by Law, and paid out of the Treasury of the United States” n 27 th amendment: A change in compensation can’t go into place until after the next election n n Privilege from arrest during session n n Proposed 1789, Ratified 1992 (202 years!) Does not apply to major crimes “Speech and Debate Clause” n n Can not be sued for slander during debates Must be part of the legislative process!
 Section VI – Compensation/Privileges (cont’d) n Senators/Representatives may NOT serve in any other government role n Different than Parliament! n Cabinet members required to be in Parliament n May not resign for a government job that is higher paying
Section VI – Compensation/Privileges (cont’d) n Senators/Representatives may NOT serve in any other government role n Different than Parliament! n Cabinet members required to be in Parliament n May not resign for a government job that is higher paying
 Section VII – Legislative Process n All bills related to revenue must start in the House n Not always done in practice n Clause 2 describes the legislative process n Veto process also described n Takes 2/3 of BOTH houses to override a veto
Section VII – Legislative Process n All bills related to revenue must start in the House n Not always done in practice n Clause 2 describes the legislative process n Veto process also described n Takes 2/3 of BOTH houses to override a veto
 Section VIII – Enumerated Powers n Lay and collect taxes n Borrow money n Establish naturalization procedures n Coin Money (and punish counterfeiters) n Establish weights and measures n Establish post office/roads n Provide for copyrights, patents n Punish pirates!
Section VIII – Enumerated Powers n Lay and collect taxes n Borrow money n Establish naturalization procedures n Coin Money (and punish counterfeiters) n Establish weights and measures n Establish post office/roads n Provide for copyrights, patents n Punish pirates!
 Section VIII – Enumerated Powers “Commerce Clause” n Regulate commerce n What can congress do with it? w/ nations and n Tell a state what it can/can’t “among the several do with transportation states” systems that connect to other states (Gibbons v. n AKA: Interstate Ogden) commerce clause n Make federal laws regulating n Has greatly local businesses if those expanded businesses might ship items congress’s power of somewhere interfering with free§ “Stream of commerce” market transactions n Make federal laws that affect businesses that deal with people from different states n Basically, what it wants!
Section VIII – Enumerated Powers “Commerce Clause” n Regulate commerce n What can congress do with it? w/ nations and n Tell a state what it can/can’t “among the several do with transportation states” systems that connect to other states (Gibbons v. n AKA: Interstate Ogden) commerce clause n Make federal laws regulating n Has greatly local businesses if those expanded businesses might ship items congress’s power of somewhere interfering with free§ “Stream of commerce” market transactions n Make federal laws that affect businesses that deal with people from different states n Basically, what it wants!
 Section VIII – Enumerated Powers War/Military Powers n Declare War n Checks and balances n Madison “thwart the tyranny of kings” n Issue “letters of marque and reprisal” n Authorize “privateers” n Raise and support an army n Maintain a navy n Regulate the land naval forces n Court martials, etc n Call the militia to “repel invasions” and “supress insurrectons n “Staff” the military (Draft)
Section VIII – Enumerated Powers War/Military Powers n Declare War n Checks and balances n Madison “thwart the tyranny of kings” n Issue “letters of marque and reprisal” n Authorize “privateers” n Raise and support an army n Maintain a navy n Regulate the land naval forces n Court martials, etc n Call the militia to “repel invasions” and “supress insurrectons n “Staff” the military (Draft)
 Section VIII – Enumerated Powers “Necessary and Proper” Clause n “To make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers” AKA the “elastic” clause n HIGHLY controversial early on n Federalists: in favor, how could the Constitution function without it? Anti-Federalists: opposed, allows congress to justify nearly anything
Section VIII – Enumerated Powers “Necessary and Proper” Clause n “To make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers” AKA the “elastic” clause n HIGHLY controversial early on n Federalists: in favor, how could the Constitution function without it? Anti-Federalists: opposed, allows congress to justify nearly anything
 Section VIII – Enumerated Powers “Necessary and Proper” Clause (cont’d) n Mc. Culloch v. Maryland (1821) n Maryland was taxing a branch of the 2 nd national bank n Congress not given power to make banks in the Constitution n SC said Maryland could NOT tax bank and the bank was necessary and proper n Other uses: n Commerce clause, Federal Kidnapping law, laws against harming government employees
Section VIII – Enumerated Powers “Necessary and Proper” Clause (cont’d) n Mc. Culloch v. Maryland (1821) n Maryland was taxing a branch of the 2 nd national bank n Congress not given power to make banks in the Constitution n SC said Maryland could NOT tax bank and the bank was necessary and proper n Other uses: n Commerce clause, Federal Kidnapping law, laws against harming government employees
 Section IX – Limits on Powers n Can not ban slavery until 1808 n n Can not suspend the writ of Habeas Corpus n Exceptions: rebellion, public safety Compromise to get Southern states on board
Section IX – Limits on Powers n Can not ban slavery until 1808 n n Can not suspend the writ of Habeas Corpus n Exceptions: rebellion, public safety Compromise to get Southern states on board
 Section IX – Limits on Powers Continued n No bill of attainder n Laws that specifically target one person or group n n n Specifically identifies group Imposes punishment Does not allow for a trial n No Ex Post Facto Laws n Laws that go into effect retroactively or punish people retroactively n Example: Convicted sex offenders have to register when they move or join certain groups (Smith vs. Doe)
Section IX – Limits on Powers Continued n No bill of attainder n Laws that specifically target one person or group n n n Specifically identifies group Imposes punishment Does not allow for a trial n No Ex Post Facto Laws n Laws that go into effect retroactively or punish people retroactively n Example: Convicted sex offenders have to register when they move or join certain groups (Smith vs. Doe)
 Section IX – Limits on Powers Continued n No taxes on state exports n No laws that “prefer” one state over another n No money can be spent without Appropriations n No laws can grant nobility titles n No sitting government official can accept monetary gifts or titles from foreign governments
Section IX – Limits on Powers Continued n No taxes on state exports n No laws that “prefer” one state over another n No money can be spent without Appropriations n No laws can grant nobility titles n No sitting government official can accept monetary gifts or titles from foreign governments
 Section 10 – Limits on states n Clause 1 = states can’t do most of what Congress can’t do n Contract Clause n State’s can’t write laws that interfere with contracts n States can’t tax exports/imports n They CAN charge inspection fees, but any profits go to the treasury department n States can’t keep standing militaries during peace time
Section 10 – Limits on states n Clause 1 = states can’t do most of what Congress can’t do n Contract Clause n State’s can’t write laws that interfere with contracts n States can’t tax exports/imports n They CAN charge inspection fees, but any profits go to the treasury department n States can’t keep standing militaries during peace time


