0fa2fde53be2e2da1b8d8cb3c00c4177.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 105
 ART products and usage TOTAL CYCLE CONTROL Leong Ka Hong MDCM DSc Adjunct Professor Dept of Obs/Gyn Mc. Gill University Montreal Canada Specialist Reproductive Medicine Hong Kong Shanghai 14 May 2004
ART products and usage TOTAL CYCLE CONTROL Leong Ka Hong MDCM DSc Adjunct Professor Dept of Obs/Gyn Mc. Gill University Montreal Canada Specialist Reproductive Medicine Hong Kong Shanghai 14 May 2004
 BRAVELLETM Highly purified urofollitropin Ferring Pharmaceuticals
BRAVELLETM Highly purified urofollitropin Ferring Pharmaceuticals
 BRAVELLE • • Highly purified urinary FSH NOT a generic Metrodin-HP NDA in USFDA Indications – Ovulation induction – IVF
BRAVELLE • • Highly purified urinary FSH NOT a generic Metrodin-HP NDA in USFDA Indications – Ovulation induction – IVF
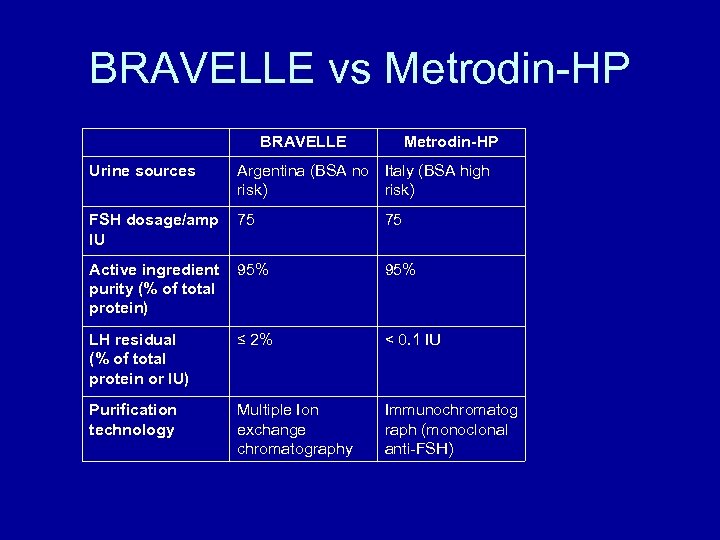 BRAVELLE vs Metrodin-HP BRAVELLE Metrodin-HP Urine sources Argentina (BSA no Italy (BSA high risk) FSH dosage/amp IU 75 75 Active ingredient purity (% of total protein) 95% LH residual (% of total protein or IU) ≤ 2% < 0. 1 IU Purification technology Multiple Ion exchange chromatography Immunochromatog raph (monoclonal anti-FSH)
BRAVELLE vs Metrodin-HP BRAVELLE Metrodin-HP Urine sources Argentina (BSA no Italy (BSA high risk) FSH dosage/amp IU 75 75 Active ingredient purity (% of total protein) 95% LH residual (% of total protein or IU) ≤ 2% < 0. 1 IU Purification technology Multiple Ion exchange chromatography Immunochromatog raph (monoclonal anti-FSH)
 BRAVELLE vs r. FSH • Sources – Bravelle: pooled human urine – r. FSH: r. FSH containing culture media with Fetal Bovine serum • Purification steps – Bravelle: ion exchange chromatography – r. FSH: immuno-chromatography • Other industrial steps – More or less the same
BRAVELLE vs r. FSH • Sources – Bravelle: pooled human urine – r. FSH: r. FSH containing culture media with Fetal Bovine serum • Purification steps – Bravelle: ion exchange chromatography – r. FSH: immuno-chromatography • Other industrial steps – More or less the same
 Risks of Prion Contamination • Bravelle: – Low possibility, from pooled human urine – Urine from Argentina (CJD low risk) • r. FSH – Possibility 1, Fetal Bovine Serum used in culturing CHO cells (FBS were from US or Canadian sources in which BSE cases found recently) – Possibility 2, immunopurification step which employed monoclonal FSH antibody. Mab was also made from cultured cells which grown in media with FBS
Risks of Prion Contamination • Bravelle: – Low possibility, from pooled human urine – Urine from Argentina (CJD low risk) • r. FSH – Possibility 1, Fetal Bovine Serum used in culturing CHO cells (FBS were from US or Canadian sources in which BSE cases found recently) – Possibility 2, immunopurification step which employed monoclonal FSH antibody. Mab was also made from cultured cells which grown in media with FBS
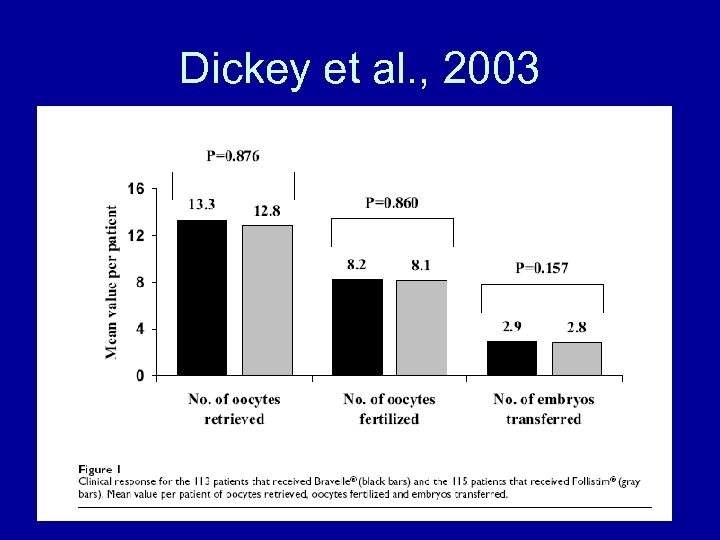 Dickey et al. , 2003
Dickey et al. , 2003
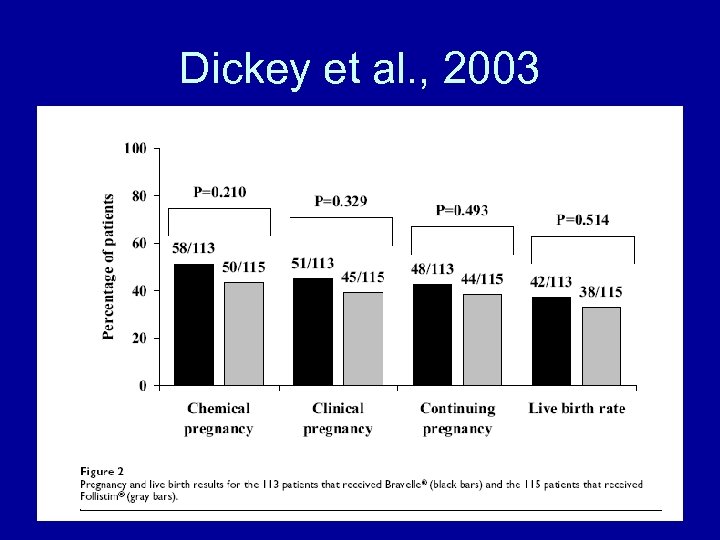 Dickey et al. , 2003
Dickey et al. , 2003
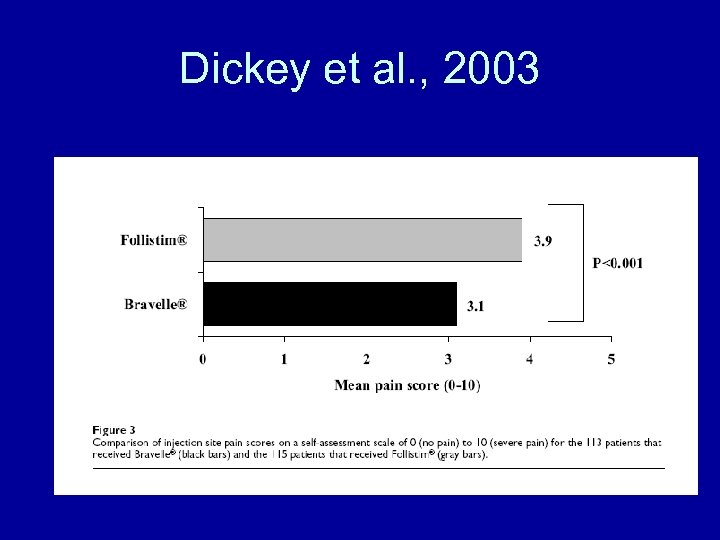 Dickey et al. , 2003
Dickey et al. , 2003
 Dickey et al. , 2003 • Conclusions – Bravelle(R) and Follistim(R) had comparable efficacy in controlled ovarian hyperstimulation in women undergoing IVF-ET. There were no differences in the nature or number of adverse events between the treatment groups although Bravelle(R) injections were reported to be significantly less painful.
Dickey et al. , 2003 • Conclusions – Bravelle(R) and Follistim(R) had comparable efficacy in controlled ovarian hyperstimulation in women undergoing IVF-ET. There were no differences in the nature or number of adverse events between the treatment groups although Bravelle(R) injections were reported to be significantly less painful.
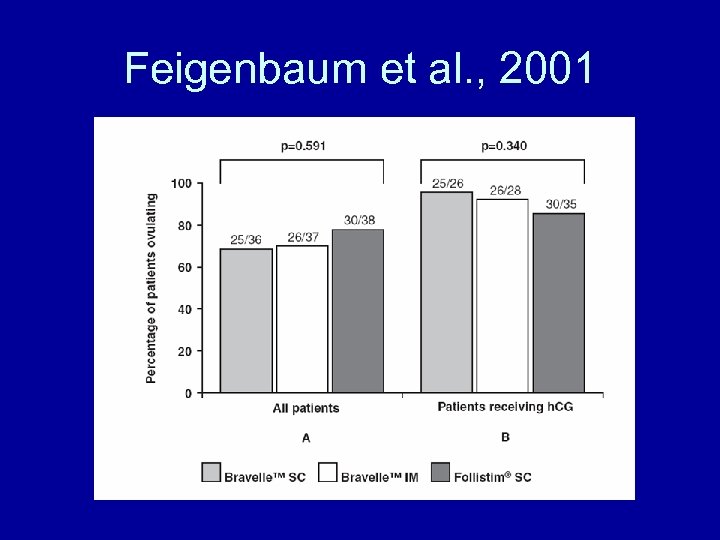 Feigenbaum et al. , 2001
Feigenbaum et al. , 2001
 Feigenbaum et al. , 2001
Feigenbaum et al. , 2001
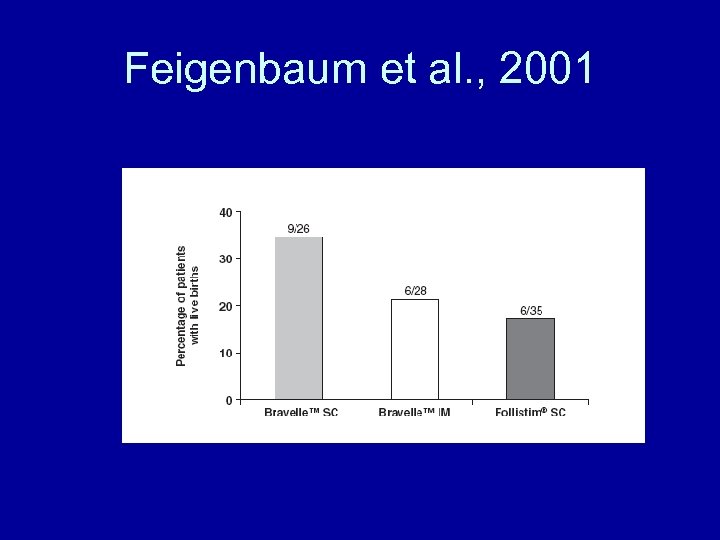 Feigenbaum et al. , 2001
Feigenbaum et al. , 2001
 Feigenbaum et al. , 2001 • Conclusion • The efficacy and treatment toleration of Bravelle™, a new, highly purified, humanderived FSH, is comparable to that of recombinant follitropin beta in patients undergoing ovulation induction.
Feigenbaum et al. , 2001 • Conclusion • The efficacy and treatment toleration of Bravelle™, a new, highly purified, humanderived FSH, is comparable to that of recombinant follitropin beta in patients undergoing ovulation induction.
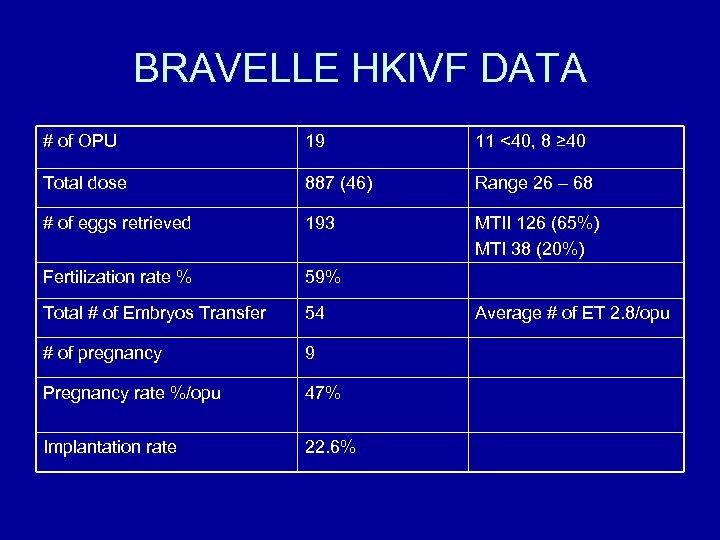 BRAVELLE HKIVF DATA # of OPU 19 11 <40, 8 ≥ 40 Total dose 887 (46) Range 26 – 68 # of eggs retrieved 193 MTII 126 (65%) MTI 38 (20%) Fertilization rate % 59% Total # of Embryos Transfer 54 # of pregnancy 9 Pregnancy rate %/opu 47% Implantation rate 22. 6% Average # of ET 2. 8/opu
BRAVELLE HKIVF DATA # of OPU 19 11 <40, 8 ≥ 40 Total dose 887 (46) Range 26 – 68 # of eggs retrieved 193 MTII 126 (65%) MTI 38 (20%) Fertilization rate % 59% Total # of Embryos Transfer 54 # of pregnancy 9 Pregnancy rate %/opu 47% Implantation rate 22. 6% Average # of ET 2. 8/opu
 Progesterone Sites of production • Corpus luteum • Placenta Functions • Increase endometrial receptivity • Maintain pregnancy
Progesterone Sites of production • Corpus luteum • Placenta Functions • Increase endometrial receptivity • Maintain pregnancy
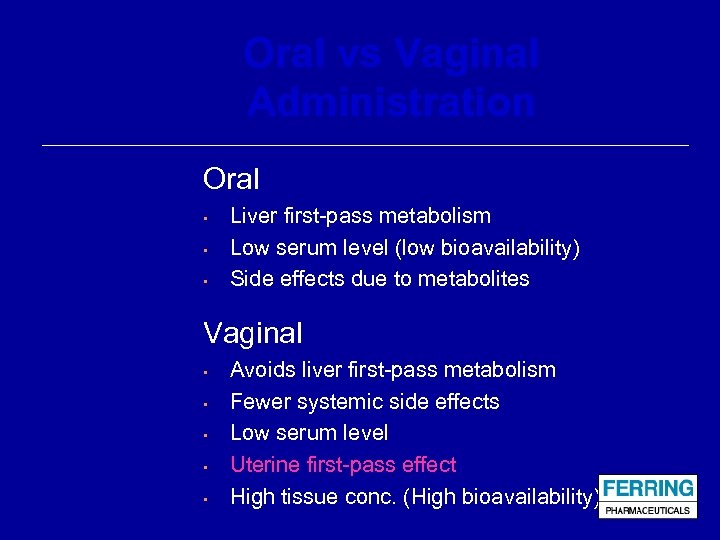 Oral vs Vaginal Administration Oral • • • Liver first-pass metabolism Low serum level (low bioavailability) Side effects due to metabolites Vaginal • • • Avoids liver first-pass metabolism Fewer systemic side effects Low serum level Uterine first-pass effect High tissue conc. (High bioavailability)
Oral vs Vaginal Administration Oral • • • Liver first-pass metabolism Low serum level (low bioavailability) Side effects due to metabolites Vaginal • • • Avoids liver first-pass metabolism Fewer systemic side effects Low serum level Uterine first-pass effect High tissue conc. (High bioavailability)
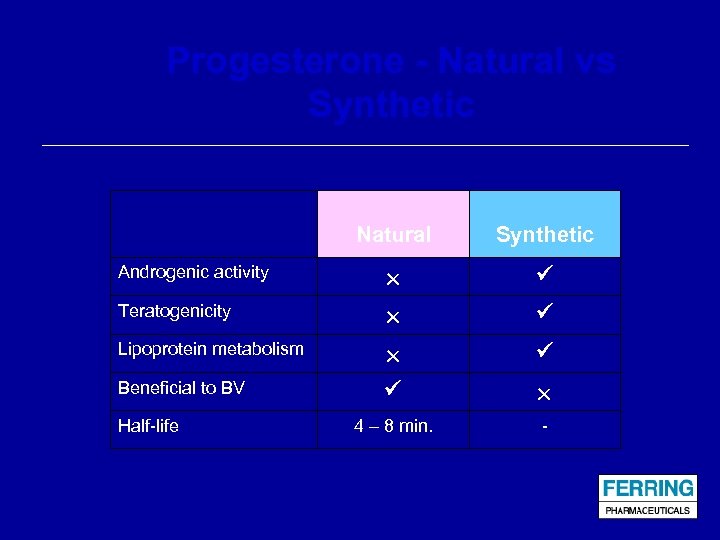 Progesterone - Natural vs Synthetic Natural Androgenic activity Teratogenicity Lipoprotein metabolism Beneficial to BV Half-life Synthetic 4 – 8 min. -
Progesterone - Natural vs Synthetic Natural Androgenic activity Teratogenicity Lipoprotein metabolism Beneficial to BV Half-life Synthetic 4 – 8 min. -
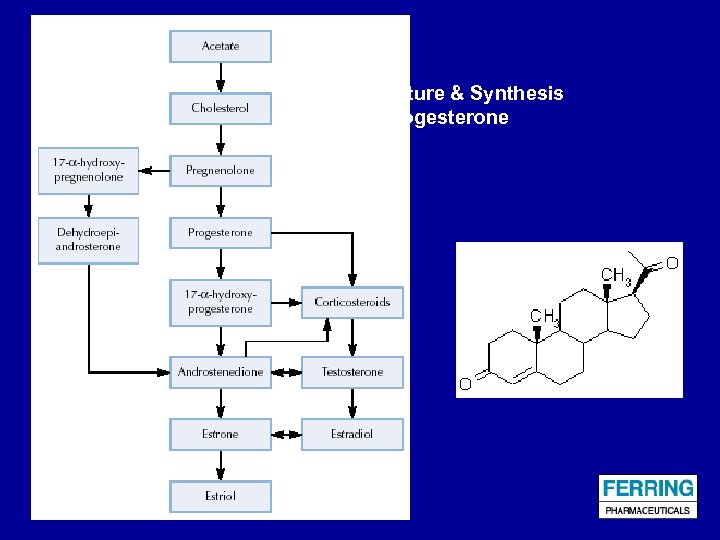 Structure & Synthesis of Progesterone
Structure & Synthesis of Progesterone
 Plasma Progesterone Levels • Follicular phase: <2 ng/ml • Luteal phase: 2 - 20 ng/ml • • • 1 st trimester of pregnancy: ~10 - 40 ng/ml Near term: ~ 100 - 200 ng/ml 15% drop: 1 hr after a meal & in the early morning
Plasma Progesterone Levels • Follicular phase: <2 ng/ml • Luteal phase: 2 - 20 ng/ml • • • 1 st trimester of pregnancy: ~10 - 40 ng/ml Near term: ~ 100 - 200 ng/ml 15% drop: 1 hr after a meal & in the early morning
 Endometrin® Product Description • Progesterone vaginal tablet (with applicator) • Developed in Israel • Micronized progesterone (100 mg) Indication • Progesterone supplementation or replacement in cases such as treatment of infertile women and IVF
Endometrin® Product Description • Progesterone vaginal tablet (with applicator) • Developed in Israel • Micronized progesterone (100 mg) Indication • Progesterone supplementation or replacement in cases such as treatment of infertile women and IVF
 Endometrin Characteristics • Prolong release for 12 hours (100 mg) – Bid • Uterine 1 st pass effects – Ensures maximal uterine/endometrial exposure • Advanced formulation – Easy administration with specific applicator – Without messy discharge – Unaltered vaginal p. H – minimized risks of infection
Endometrin Characteristics • Prolong release for 12 hours (100 mg) – Bid • Uterine 1 st pass effects – Ensures maximal uterine/endometrial exposure • Advanced formulation – Easy administration with specific applicator – Without messy discharge – Unaltered vaginal p. H – minimized risks of infection
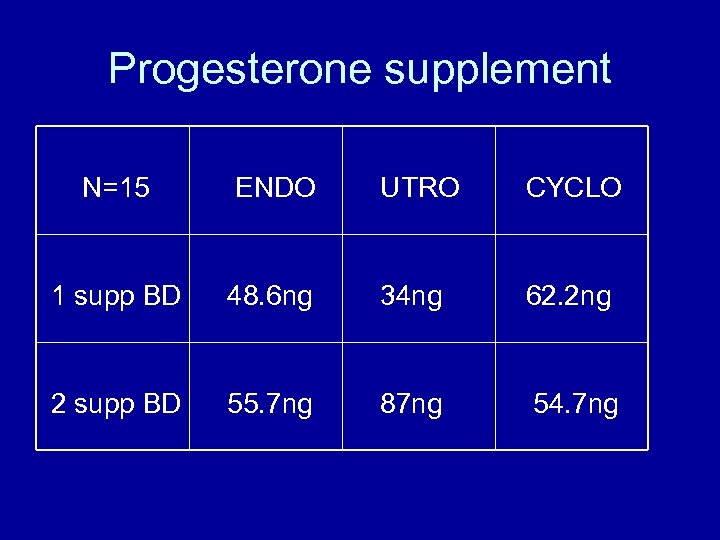 Progesterone supplement N=15 ENDO UTRO CYCLO 1 supp BD 48. 6 ng 34 ng 62. 2 ng 2 supp BD 55. 7 ng 87 ng 54. 7 ng
Progesterone supplement N=15 ENDO UTRO CYCLO 1 supp BD 48. 6 ng 34 ng 62. 2 ng 2 supp BD 55. 7 ng 87 ng 54. 7 ng
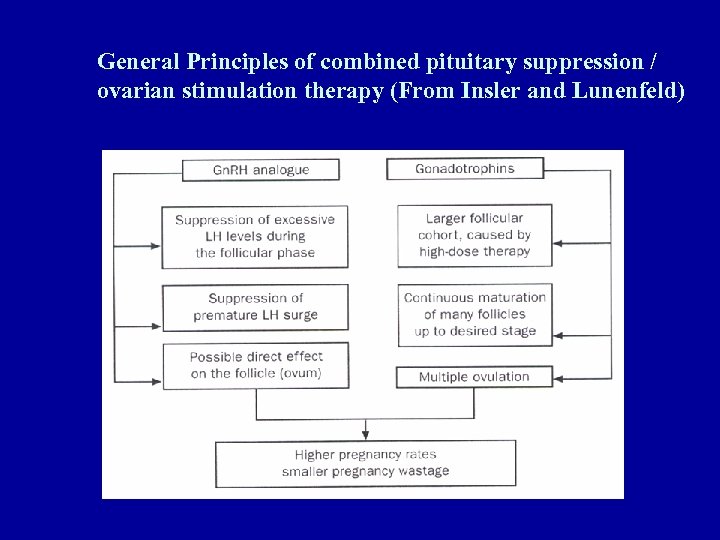 General Principles of combined pituitary suppression / ovarian stimulation therapy (From Insler and Lunenfeld)
General Principles of combined pituitary suppression / ovarian stimulation therapy (From Insler and Lunenfeld)
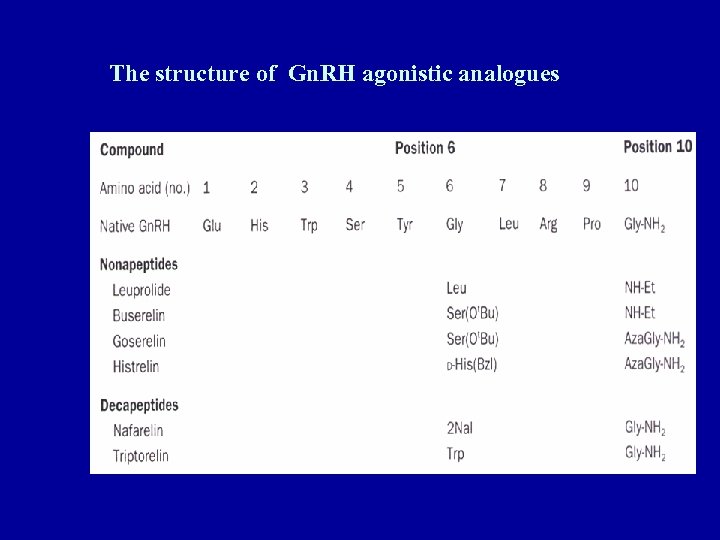 The structure of Gn. RH agonistic analogues
The structure of Gn. RH agonistic analogues
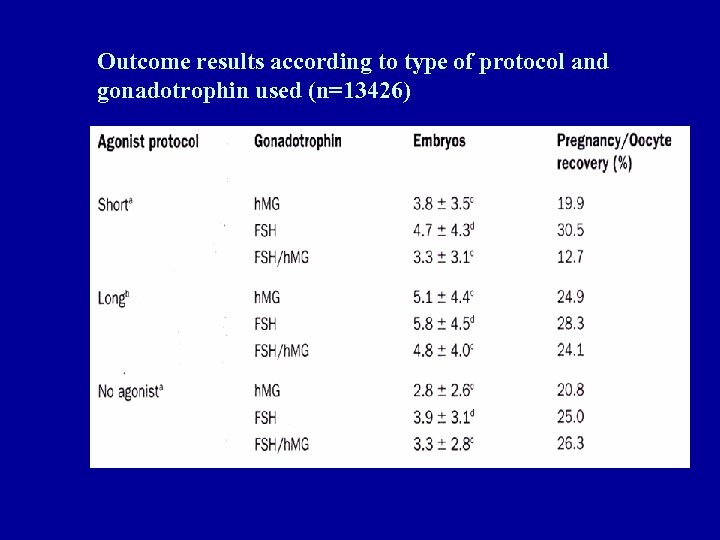 Outcome results according to type of protocol and gonadotrophin used (n=13426)
Outcome results according to type of protocol and gonadotrophin used (n=13426)
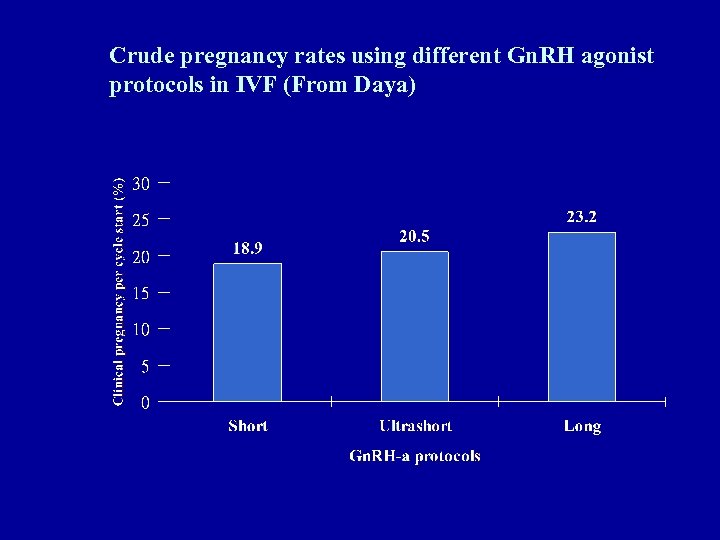 Crude pregnancy rates using different Gn. RH agonist protocols in IVF (From Daya)
Crude pregnancy rates using different Gn. RH agonist protocols in IVF (From Daya)
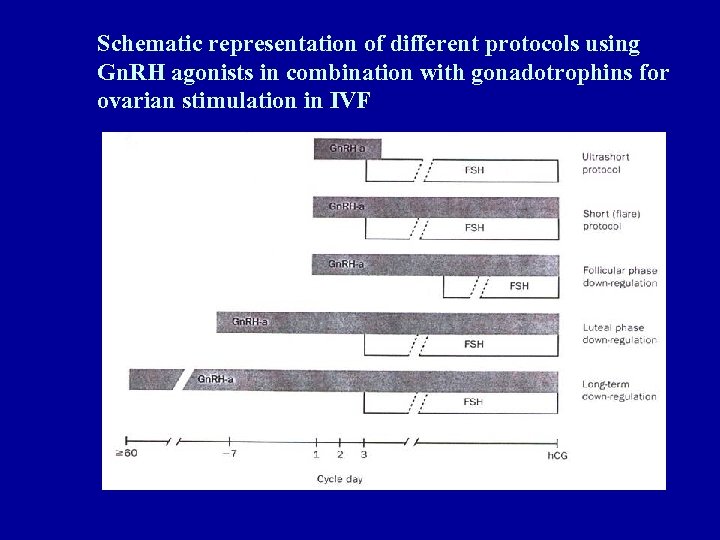 Schematic representation of different protocols using Gn. RH agonists in combination with gonadotrophins for ovarian stimulation in IVF
Schematic representation of different protocols using Gn. RH agonists in combination with gonadotrophins for ovarian stimulation in IVF
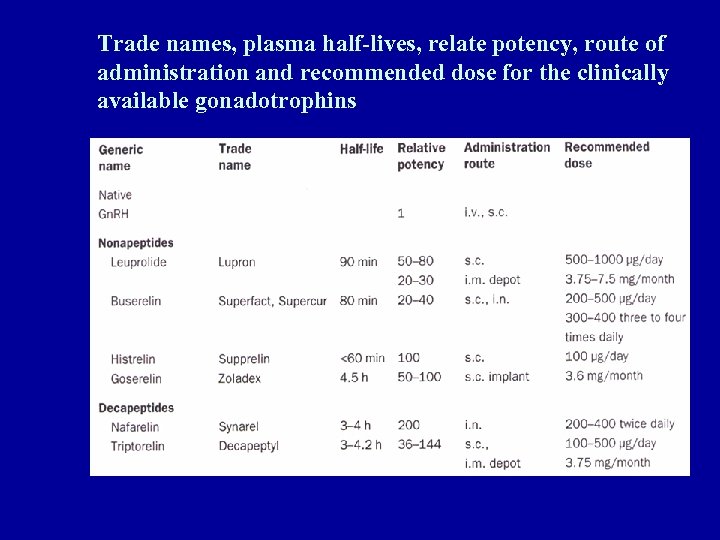 Trade names, plasma half-lives, relate potency, route of administration and recommended dose for the clinically available gonadotrophins
Trade names, plasma half-lives, relate potency, route of administration and recommended dose for the clinically available gonadotrophins
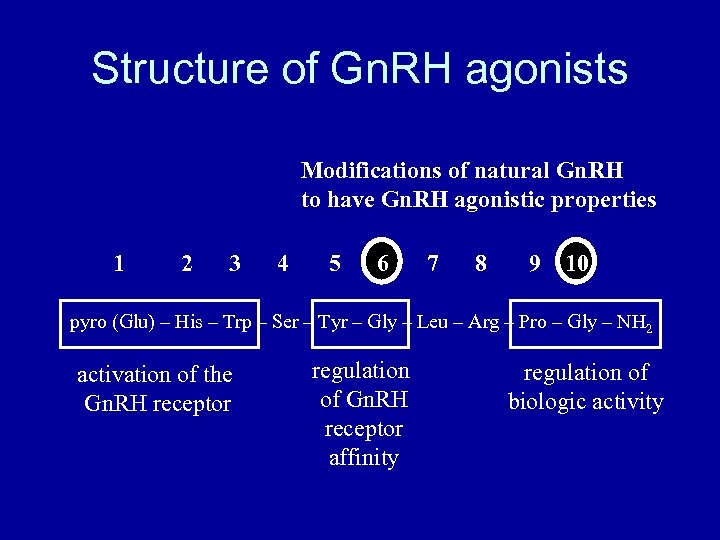 Structure of Gn. RH agonists Modifications of natural Gn. RH to have Gn. RH agonistic properties 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 pyro (Glu) – His – Trp – Ser – Tyr – Gly – Leu – Arg – Pro – Gly – NH 2 activation of the Gn. RH receptor regulation of Gn. RH receptor affinity regulation of biologic activity
Structure of Gn. RH agonists Modifications of natural Gn. RH to have Gn. RH agonistic properties 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 pyro (Glu) – His – Trp – Ser – Tyr – Gly – Leu – Arg – Pro – Gly – NH 2 activation of the Gn. RH receptor regulation of Gn. RH receptor affinity regulation of biologic activity
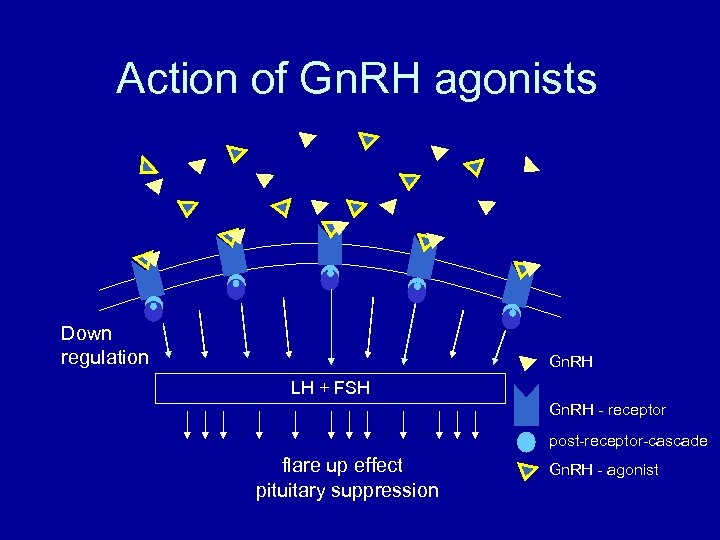 Action of Gn. RH agonists Down regulation Gn. RH LH + FSH Gn. RH - receptor post-receptor-cascade flare up effect pituitary suppression Gn. RH - agonist
Action of Gn. RH agonists Down regulation Gn. RH LH + FSH Gn. RH - receptor post-receptor-cascade flare up effect pituitary suppression Gn. RH - agonist
 Premature LH surge • Poor quality • No fertilization or very poor pregnancy rate • Cancel egg retrieval 5 -20% All cycles treated in 1980’s
Premature LH surge • Poor quality • No fertilization or very poor pregnancy rate • Cancel egg retrieval 5 -20% All cycles treated in 1980’s
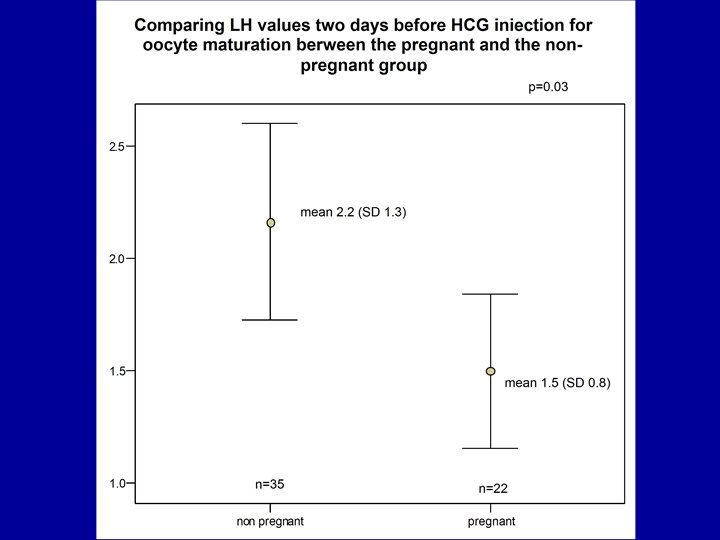
 Results of first application of Gn. RH-agonists in the long protocol • 11 patients eligible for IVF • Gn. RH agonist s. c. (buserelin) started at day of menstruation or one day before • ovarian stimulation started with HMG or purified FSH when all ovarian follicles and the endometrial lining has disappeared on ultrasound (average: 15 days) • one ongoing pregnancy achieved Porter et al. , 1984
Results of first application of Gn. RH-agonists in the long protocol • 11 patients eligible for IVF • Gn. RH agonist s. c. (buserelin) started at day of menstruation or one day before • ovarian stimulation started with HMG or purified FSH when all ovarian follicles and the endometrial lining has disappeared on ultrasound (average: 15 days) • one ongoing pregnancy achieved Porter et al. , 1984
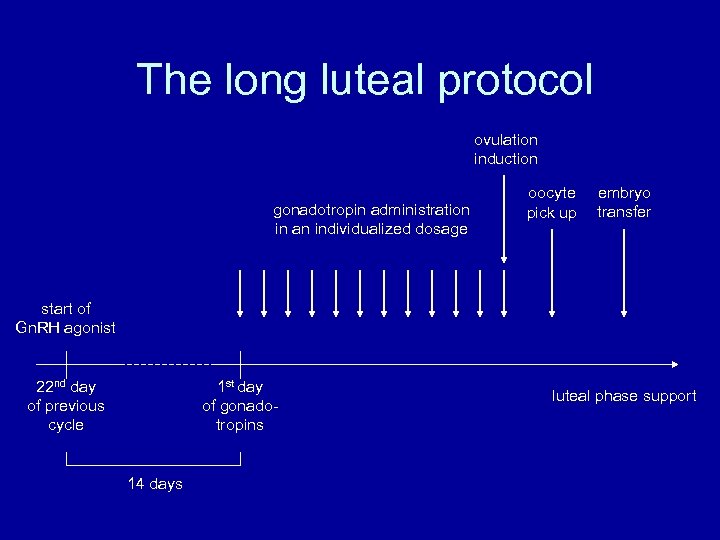 The long luteal protocol ovulation induction gonadotropin administration in an individualized dosage oocyte pick up embryo transfer start of Gn. RH agonist 22 nd day of previous cycle 1 st day of gonadotropins 14 days luteal phase support
The long luteal protocol ovulation induction gonadotropin administration in an individualized dosage oocyte pick up embryo transfer start of Gn. RH agonist 22 nd day of previous cycle 1 st day of gonadotropins 14 days luteal phase support
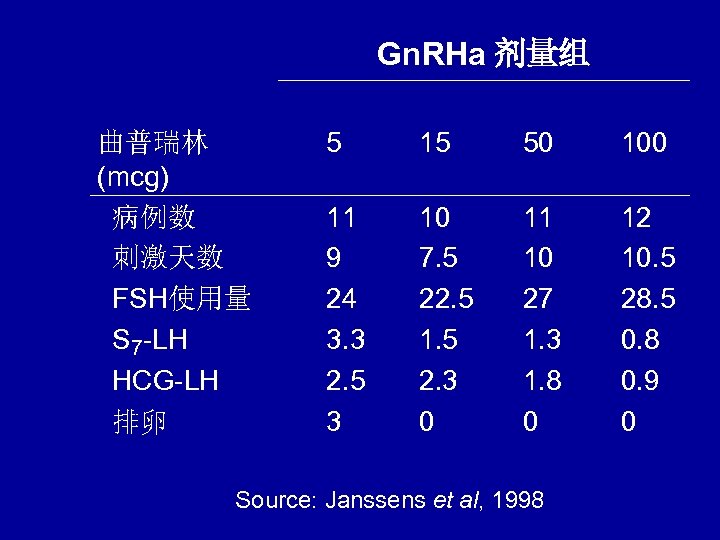 Gn. RHa 剂量组 曲普瑞林 (mcg) 病例数 刺激天数 FSH使用量 S 7 -LH HCG-LH 排卵 5 15 50 100 11 9 24 3. 3 2. 5 3 10 7. 5 22. 5 1. 5 2. 3 0 11 10 27 1. 3 1. 8 0 12 10. 5 28. 5 0. 8 0. 9 0 Source: Janssens et al, 1998
Gn. RHa 剂量组 曲普瑞林 (mcg) 病例数 刺激天数 FSH使用量 S 7 -LH HCG-LH 排卵 5 15 50 100 11 9 24 3. 3 2. 5 3 10 7. 5 22. 5 1. 5 2. 3 0 11 10 27 1. 3 1. 8 0 12 10. 5 28. 5 0. 8 0. 9 0 Source: Janssens et al, 1998
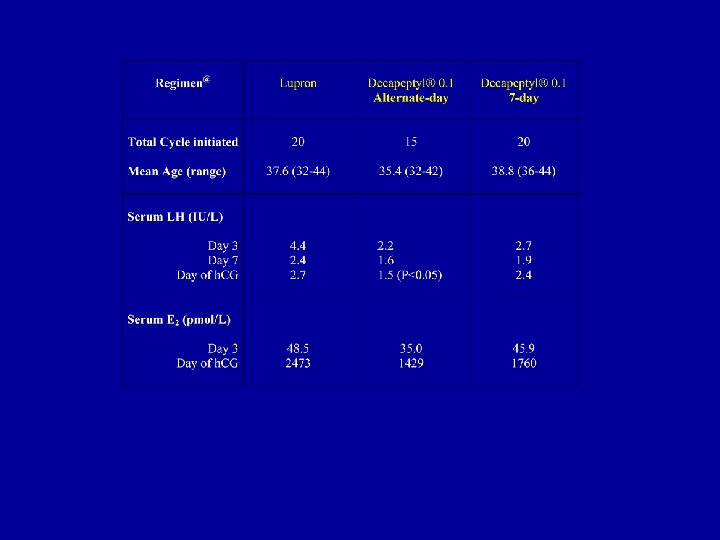
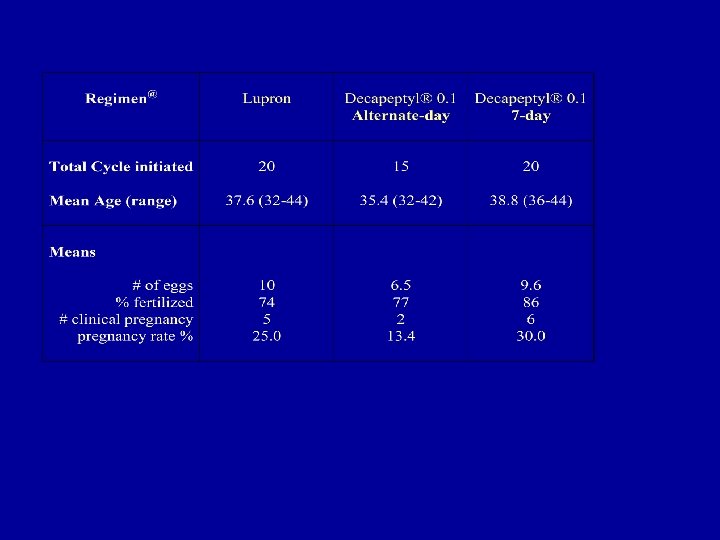
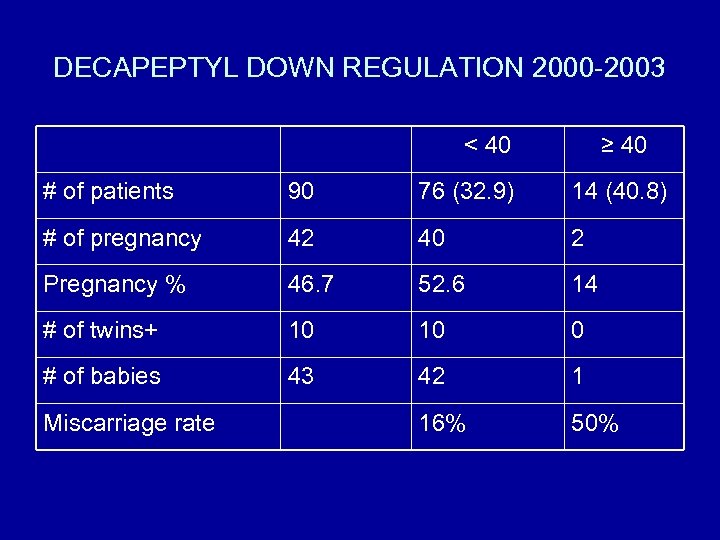 DECAPEPTYL DOWN REGULATION 2000 -2003 < 40 ≥ 40 # of patients 90 76 (32. 9) 14 (40. 8) # of pregnancy 42 40 2 Pregnancy % 46. 7 52. 6 14 # of twins+ 10 10 0 # of babies 43 42 1 16% 50% Miscarriage rate
DECAPEPTYL DOWN REGULATION 2000 -2003 < 40 ≥ 40 # of patients 90 76 (32. 9) 14 (40. 8) # of pregnancy 42 40 2 Pregnancy % 46. 7 52. 6 14 # of twins+ 10 10 0 # of babies 43 42 1 16% 50% Miscarriage rate
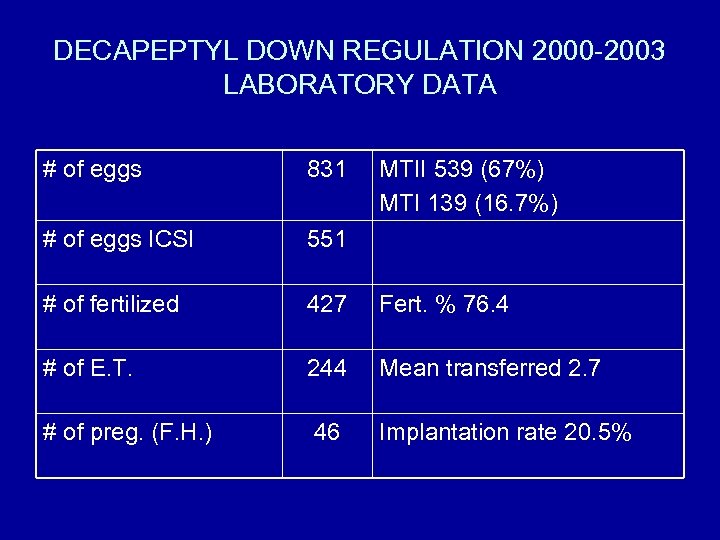 DECAPEPTYL DOWN REGULATION 2000 -2003 LABORATORY DATA # of eggs 831 MTII 539 (67%) MTI 139 (16. 7%) # of eggs ICSI 551 # of fertilized 427 Fert. % 76. 4 # of E. T. 244 Mean transferred 2. 7 # of preg. (F. H. ) 46 Implantation rate 20. 5%
DECAPEPTYL DOWN REGULATION 2000 -2003 LABORATORY DATA # of eggs 831 MTII 539 (67%) MTI 139 (16. 7%) # of eggs ICSI 551 # of fertilized 427 Fert. % 76. 4 # of E. T. 244 Mean transferred 2. 7 # of preg. (F. H. ) 46 Implantation rate 20. 5%
 Gn. RH agonists Over-suppression: • LH becomes so low that it affects the production of estrogen, and possibly progesterone in the luteal phase • Leads to poor response, poor pregnancy outcome due to early abortion Also it is: • Too long and too much drug use, cost, cancelled cycles and it is unnatural.
Gn. RH agonists Over-suppression: • LH becomes so low that it affects the production of estrogen, and possibly progesterone in the luteal phase • Leads to poor response, poor pregnancy outcome due to early abortion Also it is: • Too long and too much drug use, cost, cancelled cycles and it is unnatural.
 Ovulation Stimulation Scheme • • BCP to control cycle (or ovulation monitor) BCP D 16/ovulation +7 day DECAPEPTYL Decapepyl 100 mcg/day x 7 days D 2 FSH, LH, E D 3 Bravelle 225 -300 IU/day with monitor Choragon 10000 IU for induction Endometrin BD (+ Progesterone)
Ovulation Stimulation Scheme • • BCP to control cycle (or ovulation monitor) BCP D 16/ovulation +7 day DECAPEPTYL Decapepyl 100 mcg/day x 7 days D 2 FSH, LH, E D 3 Bravelle 225 -300 IU/day with monitor Choragon 10000 IU for induction Endometrin BD (+ Progesterone)
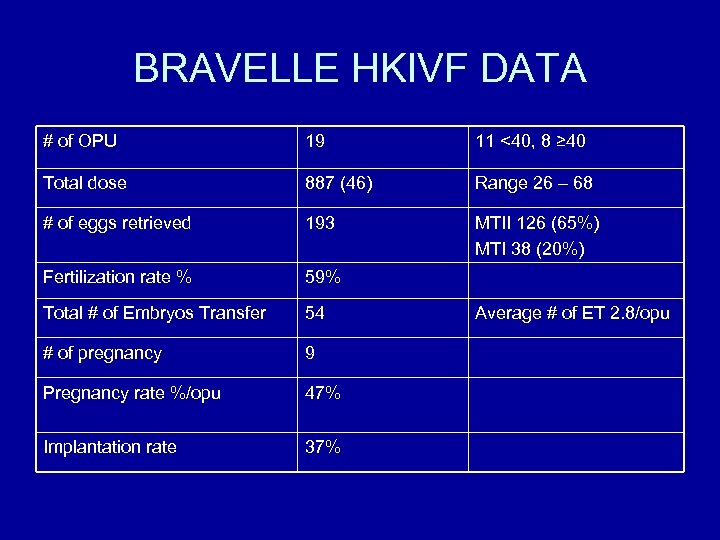 BRAVELLE HKIVF DATA # of OPU 19 11 <40, 8 ≥ 40 Total dose 887 (46) Range 26 – 68 # of eggs retrieved 193 MTII 126 (65%) MTI 38 (20%) Fertilization rate % 59% Total # of Embryos Transfer 54 # of pregnancy 9 Pregnancy rate %/opu 47% Implantation rate 37% Average # of ET 2. 8/opu
BRAVELLE HKIVF DATA # of OPU 19 11 <40, 8 ≥ 40 Total dose 887 (46) Range 26 – 68 # of eggs retrieved 193 MTII 126 (65%) MTI 38 (20%) Fertilization rate % 59% Total # of Embryos Transfer 54 # of pregnancy 9 Pregnancy rate %/opu 47% Implantation rate 37% Average # of ET 2. 8/opu
 OVULATION STIMULATION Comparison of protocols: 1. Decapeptyl Down Regulation 2. Long Lucrin Down Regulation 3. Antagonist, no down regulation
OVULATION STIMULATION Comparison of protocols: 1. Decapeptyl Down Regulation 2. Long Lucrin Down Regulation 3. Antagonist, no down regulation
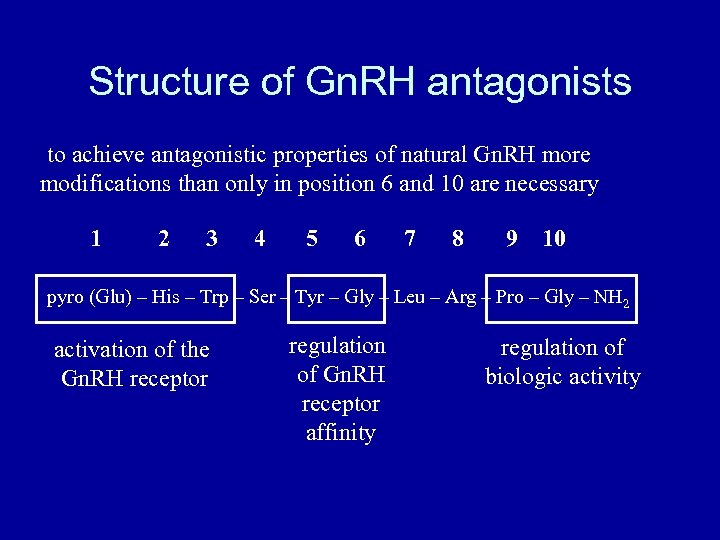 Structure of Gn. RH antagonists to achieve antagonistic properties of natural Gn. RH more modifications than only in position 6 and 10 are necessary 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 pyro (Glu) – His – Trp – Ser – Tyr – Gly – Leu – Arg – Pro – Gly – NH 2 activation of the Gn. RH receptor regulation of Gn. RH receptor affinity regulation of biologic activity
Structure of Gn. RH antagonists to achieve antagonistic properties of natural Gn. RH more modifications than only in position 6 and 10 are necessary 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 pyro (Glu) – His – Trp – Ser – Tyr – Gly – Leu – Arg – Pro – Gly – NH 2 activation of the Gn. RH receptor regulation of Gn. RH receptor affinity regulation of biologic activity
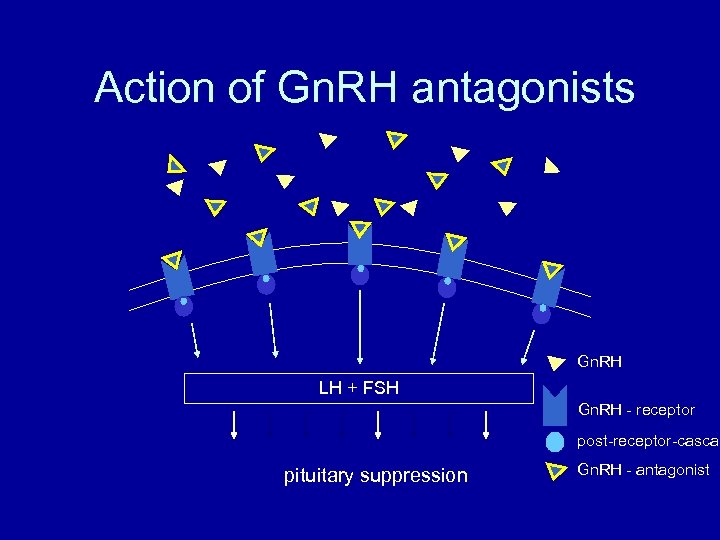 Action of Gn. RH antagonists Gn. RH LH + FSH Gn. RH - receptor post-receptor-cascad pituitary suppression Gn. RH - antagonist
Action of Gn. RH antagonists Gn. RH LH + FSH Gn. RH - receptor post-receptor-cascad pituitary suppression Gn. RH - antagonist
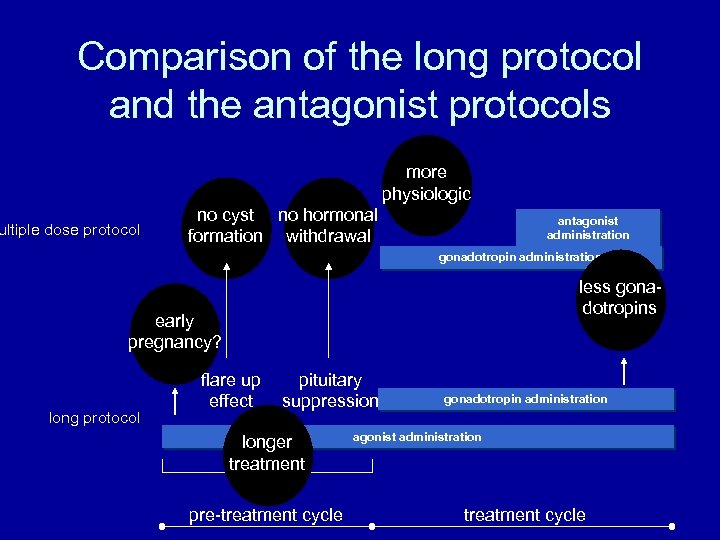 Comparison of the long protocol and the antagonist protocols more physiologic ultiple dose protocol no cyst no hormonal formation withdrawal antagonist administration gonadotropin administration less gonadotropins early pregnancy? long protocol flare up effect pituitary suppression longer treatment pre-treatment cycle gonadotropin administration agonist administration treatment cycle
Comparison of the long protocol and the antagonist protocols more physiologic ultiple dose protocol no cyst no hormonal formation withdrawal antagonist administration gonadotropin administration less gonadotropins early pregnancy? long protocol flare up effect pituitary suppression longer treatment pre-treatment cycle gonadotropin administration agonist administration treatment cycle
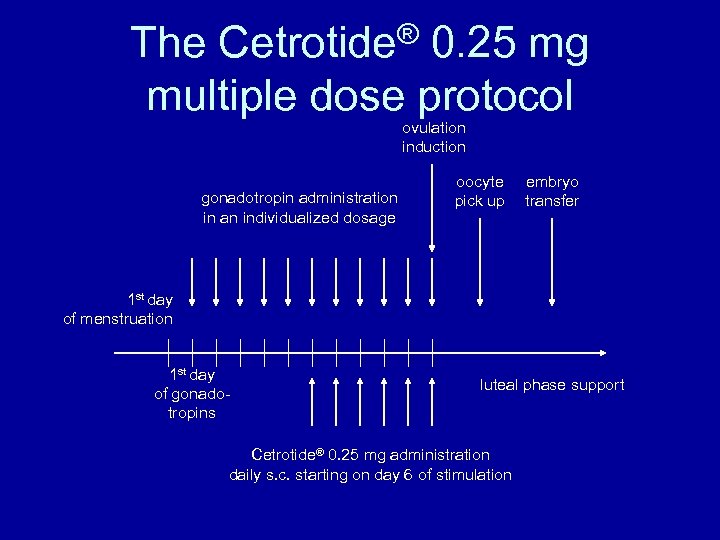 The Cetrotide® 0. 25 mg multiple dose protocol ovulation induction gonadotropin administration in an individualized dosage oocyte pick up embryo transfer 1 st day of menstruation 1 st day of gonadotropins luteal phase support Cetrotide® 0. 25 mg administration daily s. c. starting on day 6 of stimulation
The Cetrotide® 0. 25 mg multiple dose protocol ovulation induction gonadotropin administration in an individualized dosage oocyte pick up embryo transfer 1 st day of menstruation 1 st day of gonadotropins luteal phase support Cetrotide® 0. 25 mg administration daily s. c. starting on day 6 of stimulation
 Possibilities to individualize the multiple dose protocol • To avoid a premature LH rise the administration of cetrotide® 0. 25 mg on day 6 of stimulation should be the standard procedure • Using the standard procedure, a mean of 6. 3 injections are necessary • This is in accordance with the package size of 7 ampoules cetrotide® 0. 25 mg per patient
Possibilities to individualize the multiple dose protocol • To avoid a premature LH rise the administration of cetrotide® 0. 25 mg on day 6 of stimulation should be the standard procedure • Using the standard procedure, a mean of 6. 3 injections are necessary • This is in accordance with the package size of 7 ampoules cetrotide® 0. 25 mg per patient
 Possibilities to individualize the multiple dose protocol • Individualized administration of Cetrotide® 0. 25 mg can be done – According to follicle size: only if leading follicle is 14 mm • Thereby, the multiple dose protocol can also be adapted to patients with a lower response
Possibilities to individualize the multiple dose protocol • Individualized administration of Cetrotide® 0. 25 mg can be done – According to follicle size: only if leading follicle is 14 mm • Thereby, the multiple dose protocol can also be adapted to patients with a lower response
 Personal experience with multiple dose of Cetrorelix 0. 25 mg Patient group: • Over suppression with agonist long protocol (LH < 1 ml. U) • Patient over 40 • Poor response to agonists suppression
Personal experience with multiple dose of Cetrorelix 0. 25 mg Patient group: • Over suppression with agonist long protocol (LH < 1 ml. U) • Patient over 40 • Poor response to agonists suppression
 Cetrorelix 0. 125 mg Flexible Dose Trial Selection Criteria: 1. 2. 3. Previous over-suppression with agonist Previous poor response Previous LH surge if no agonist
Cetrorelix 0. 125 mg Flexible Dose Trial Selection Criteria: 1. 2. 3. Previous over-suppression with agonist Previous poor response Previous LH surge if no agonist
 Cetrorelix 0. 125 mg Flexible Dose Trial Methods: 1. FSH LH E 2 on day 2 2. U/S on day 3, start Gonal-F 225 IU/day 3. Stimulation day 4, check E 2 LH U/S
Cetrorelix 0. 125 mg Flexible Dose Trial Methods: 1. FSH LH E 2 on day 2 2. U/S on day 3, start Gonal-F 225 IU/day 3. Stimulation day 4, check E 2 LH U/S
 Cetrorelix 0. 125 mg Flexible Dose Trial Treatment Criteria 1. LH > 1. 5 IU/L 2. Leading follicle = 15 mm diameter • Cetrorelix 0. 125 mg/day given until day of HCG injection • Monitor by E 2 LH U/S everyday
Cetrorelix 0. 125 mg Flexible Dose Trial Treatment Criteria 1. LH > 1. 5 IU/L 2. Leading follicle = 15 mm diameter • Cetrorelix 0. 125 mg/day given until day of HCG injection • Monitor by E 2 LH U/S everyday
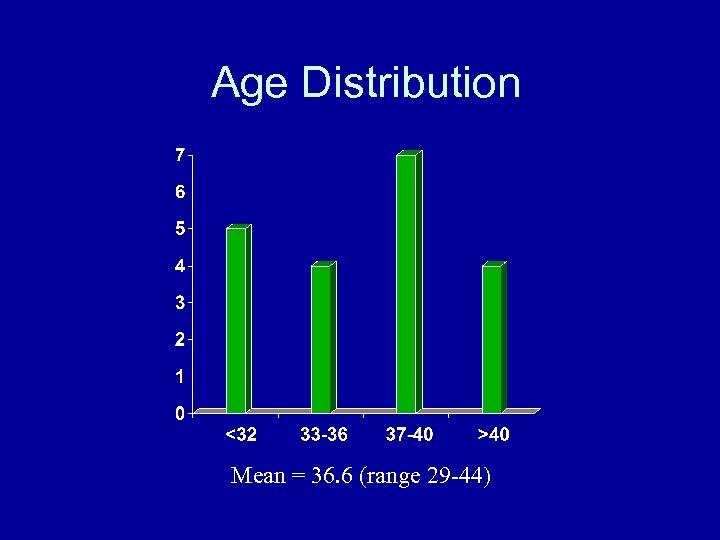 Age Distribution Mean = 36. 6 (range 29 -44)
Age Distribution Mean = 36. 6 (range 29 -44)
 Cetrorelix 0. 125 mg Flexible Dose Trial RESULTS
Cetrorelix 0. 125 mg Flexible Dose Trial RESULTS
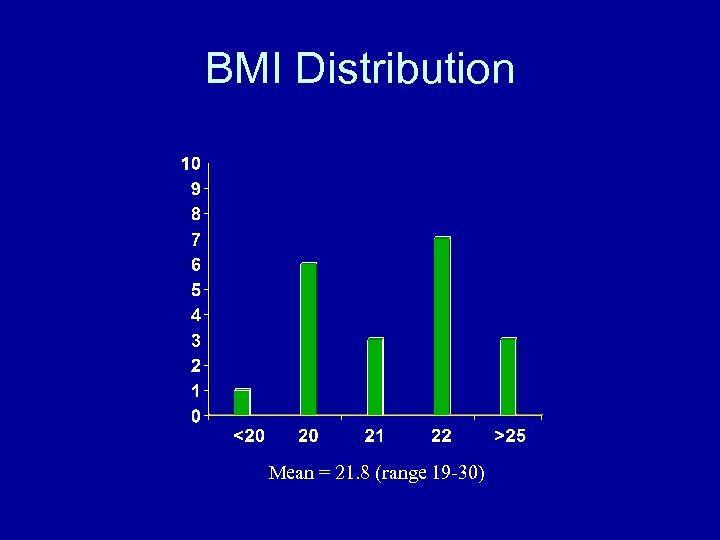 BMI Distribution Mean = 21. 8 (range 19 -30)
BMI Distribution Mean = 21. 8 (range 19 -30)
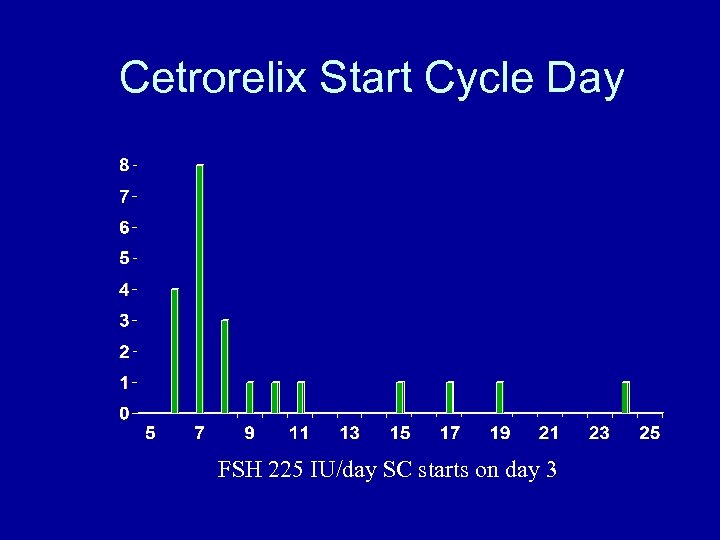 Cetrorelix Start Cycle Day FSH 225 IU/day SC starts on day 3
Cetrorelix Start Cycle Day FSH 225 IU/day SC starts on day 3
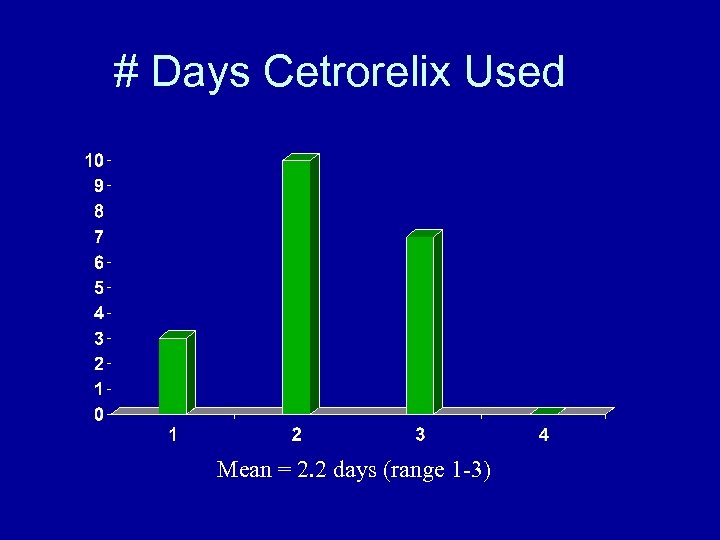 # Days Cetrorelix Used Mean = 2. 2 days (range 1 -3)
# Days Cetrorelix Used Mean = 2. 2 days (range 1 -3)
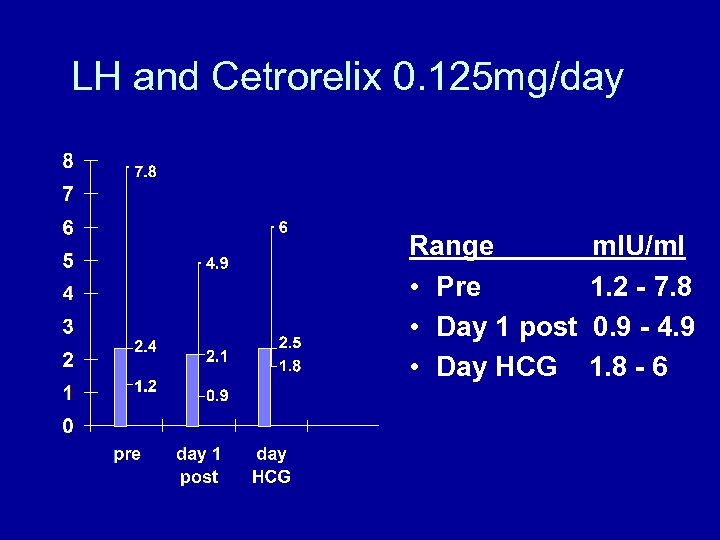 LH and Cetrorelix 0. 125 mg/day Range • Pre • Day 1 post • Day HCG m. IU/ml 1. 2 - 7. 8 0. 9 - 4. 9 1. 8 - 6
LH and Cetrorelix 0. 125 mg/day Range • Pre • Day 1 post • Day HCG m. IU/ml 1. 2 - 7. 8 0. 9 - 4. 9 1. 8 - 6
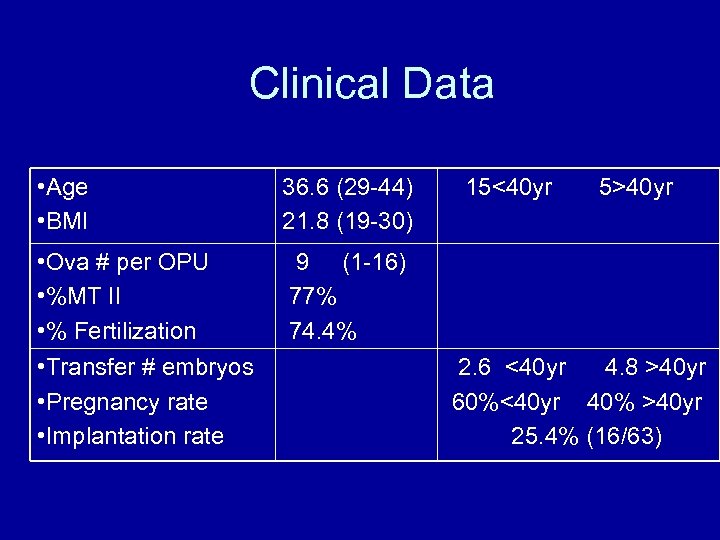 Clinical Data • Age • BMI 36. 6 (29 -44) 21. 8 (19 -30) • Ova # per OPU • %MT II • % Fertilization • Transfer # embryos • Pregnancy rate • Implantation rate 9 (1 -16) 77% 74. 4% 15<40 yr 5>40 yr 2. 6 <40 yr 4. 8 >40 yr 60%<40 yr 40% >40 yr 25. 4% (16/63)
Clinical Data • Age • BMI 36. 6 (29 -44) 21. 8 (19 -30) • Ova # per OPU • %MT II • % Fertilization • Transfer # embryos • Pregnancy rate • Implantation rate 9 (1 -16) 77% 74. 4% 15<40 yr 5>40 yr 2. 6 <40 yr 4. 8 >40 yr 60%<40 yr 40% >40 yr 25. 4% (16/63)
 Experience with Cetrotide 0. 125 mg
Experience with Cetrotide 0. 125 mg
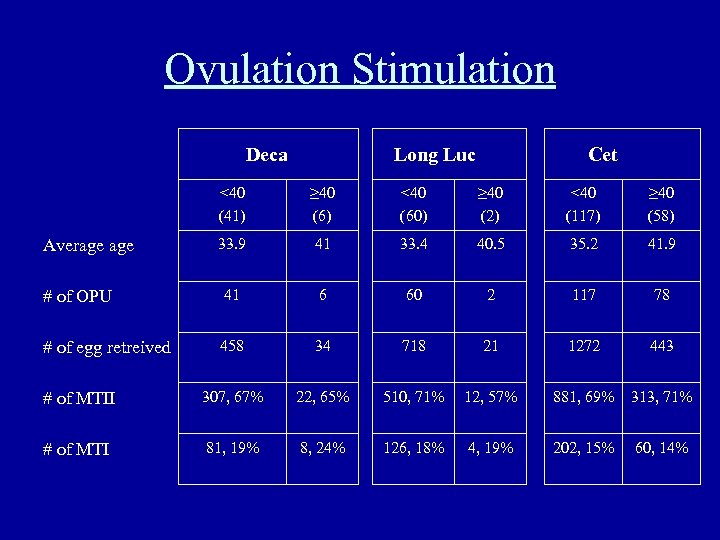 Ovulation Stimulation Deca Long Luc Cet <40 (41) ≥ 40 (6) <40 (60) ≥ 40 (2) <40 (117) ≥ 40 (58) 33. 9 41 33. 4 40. 5 35. 2 41. 9 # of OPU 41 6 60 2 117 78 # of egg retreived 458 34 718 21 1272 443 # of MTII 307, 67% 22, 65% 510, 71% 12, 57% 881, 69% 313, 71% # of MTI 81, 19% 8, 24% 126, 18% 4, 19% 202, 15% 60, 14% Average
Ovulation Stimulation Deca Long Luc Cet <40 (41) ≥ 40 (6) <40 (60) ≥ 40 (2) <40 (117) ≥ 40 (58) 33. 9 41 33. 4 40. 5 35. 2 41. 9 # of OPU 41 6 60 2 117 78 # of egg retreived 458 34 718 21 1272 443 # of MTII 307, 67% 22, 65% 510, 71% 12, 57% 881, 69% 313, 71% # of MTI 81, 19% 8, 24% 126, 18% 4, 19% 202, 15% 60, 14% Average
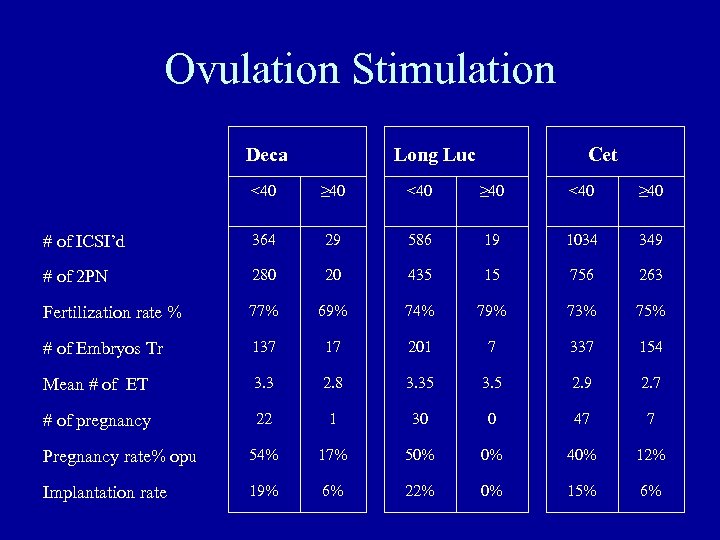 Ovulation Stimulation Deca Long Luc Cet <40 ≥ 40 # of ICSI’d 364 29 586 19 1034 349 # of 2 PN 280 20 435 15 756 263 Fertilization rate % 77% 69% 74% 79% 73% 75% # of Embryos Tr 137 17 201 7 337 154 Mean # of ET 3. 3 2. 8 3. 35 3. 5 2. 9 2. 7 # of pregnancy 22 1 30 0 47 7 Pregnancy rate% opu 54% 17% 50% 0% 40% 12% Implantation rate 19% 6% 22% 0% 15% 6%
Ovulation Stimulation Deca Long Luc Cet <40 ≥ 40 # of ICSI’d 364 29 586 19 1034 349 # of 2 PN 280 20 435 15 756 263 Fertilization rate % 77% 69% 74% 79% 73% 75% # of Embryos Tr 137 17 201 7 337 154 Mean # of ET 3. 3 2. 8 3. 35 3. 5 2. 9 2. 7 # of pregnancy 22 1 30 0 47 7 Pregnancy rate% opu 54% 17% 50% 0% 40% 12% Implantation rate 19% 6% 22% 0% 15% 6%
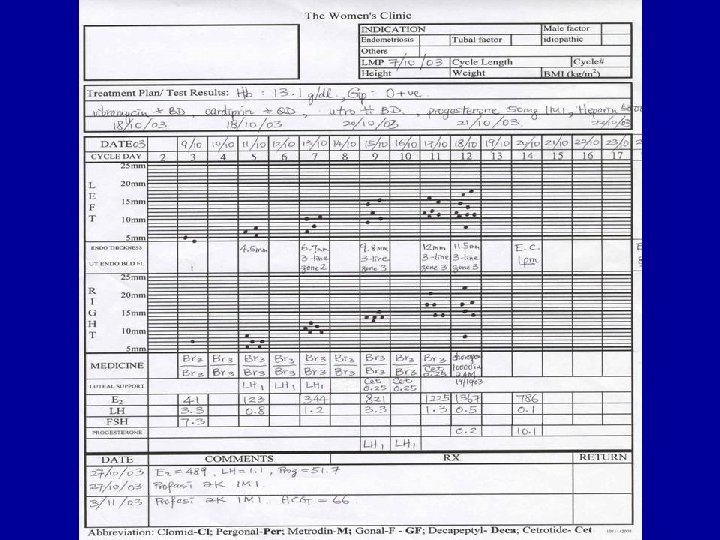
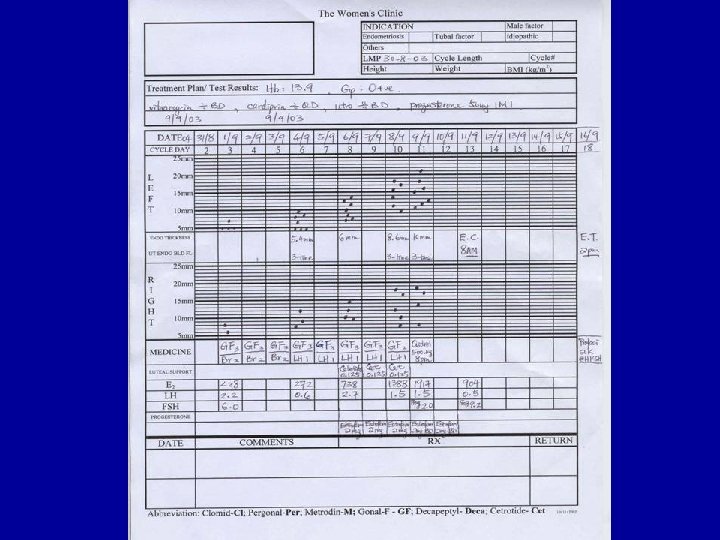
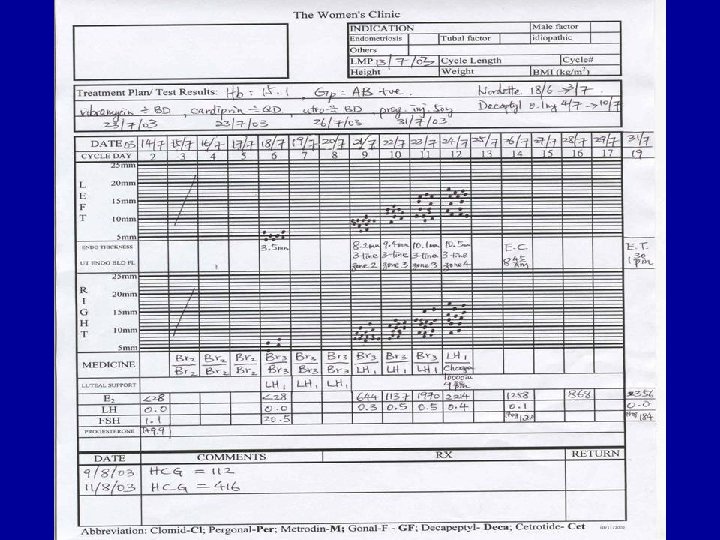
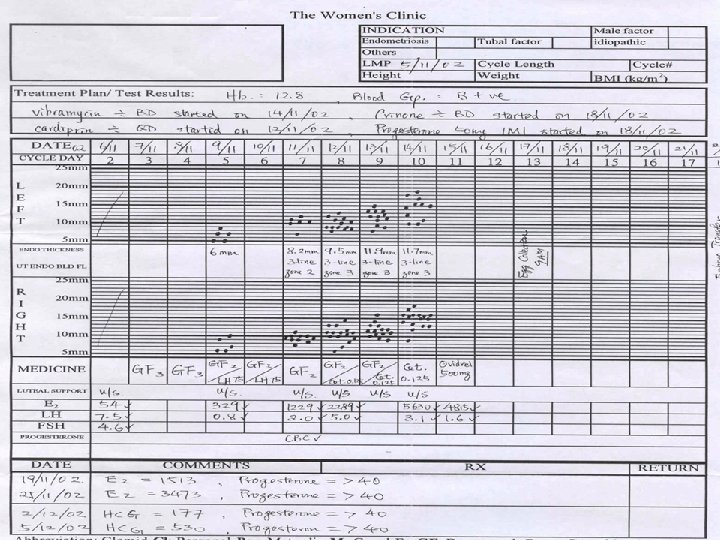
 Flexible Stimulation • • When dn reg showed over suppression Low E, LH, small follicles D 2 E=30. 7 pg LH=0. 54 IU/L D 6 E=214 pg LH=0. 7 IU/L r. LH added to Bravelle dosage D(HCG) E=1856. 5 pg LH 1. 45 IU/L 6/8 cases pregnant
Flexible Stimulation • • When dn reg showed over suppression Low E, LH, small follicles D 2 E=30. 7 pg LH=0. 54 IU/L D 6 E=214 pg LH=0. 7 IU/L r. LH added to Bravelle dosage D(HCG) E=1856. 5 pg LH 1. 45 IU/L 6/8 cases pregnant
 Infertility • 1/6 couples trying for pregnancy • Medical, social and psychological problems studied • Very few perception studies
Infertility • 1/6 couples trying for pregnancy • Medical, social and psychological problems studied • Very few perception studies
 Perception study in Infertility • Bertarelli Foundation Survey 2000 • 1 st published population perception survey • Polled 6 European Countries, USA and Australia 1998/1999 • Telephone survey: random selection households • 7036 polled, no mention of % completion
Perception study in Infertility • Bertarelli Foundation Survey 2000 • 1 st published population perception survey • Polled 6 European Countries, USA and Australia 1998/1999 • Telephone survey: random selection households • 7036 polled, no mention of % completion
 Perception Survey in Infertility • 6 questions • Asked You/your friend to avoid rejection • 52 % claimed personally know somebody who had infertility
Perception Survey in Infertility • 6 questions • Asked You/your friend to avoid rejection • 52 % claimed personally know somebody who had infertility
 Perception Study in Infertility • Is Infertility a disease? Mean 38% • Australia, UK, USA 20% • Germany, Italy 55% • Heard of IVF? • 77% (Germany) to 99% (Sweden)
Perception Study in Infertility • Is Infertility a disease? Mean 38% • Australia, UK, USA 20% • Germany, Italy 55% • Heard of IVF? • 77% (Germany) to 99% (Sweden)
 Perception study in infertility • Should IVF be reimbursed? • Told respondent cost 3 x IVF equals hip replacement • 60 -80% said to reimburse
Perception study in infertility • Should IVF be reimbursed? • Told respondent cost 3 x IVF equals hip replacement • 60 -80% said to reimburse
 Perception Study in Infertility • Although 97% of respondents heard of IVF and approved of IVF, only 16% answered correctly that IVF success is similar to that of natural pregnancy. • Most people guessed the success rate, and no correlation can be established
Perception Study in Infertility • Although 97% of respondents heard of IVF and approved of IVF, only 16% answered correctly that IVF success is similar to that of natural pregnancy. • Most people guessed the success rate, and no correlation can be established
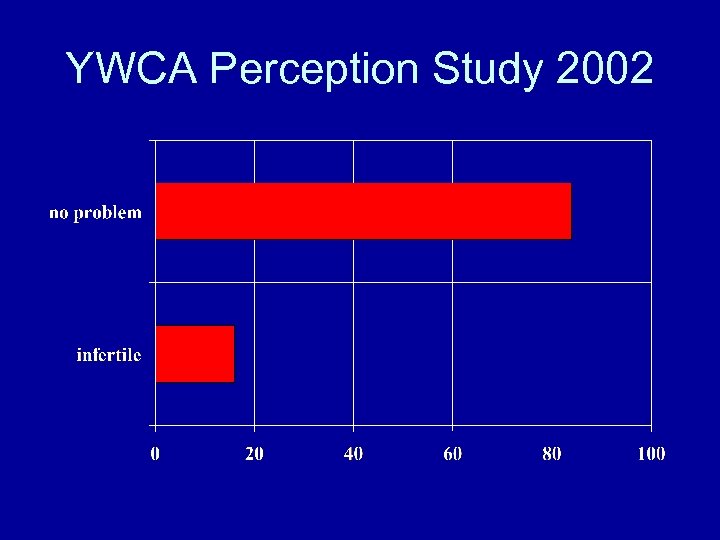
 YWCA Perception Study 2002 • • Aims: Infertility problem vs no problem psycho-social states medical aspects - treatment profiles
YWCA Perception Study 2002 • • Aims: Infertility problem vs no problem psycho-social states medical aspects - treatment profiles
 Bertarelli vs. Hong Kong Survey Bertarelli Hong Kong • • • 50% know infertility • 20%know success rate • 46% know IVF • 50% said infertility=disease 52% know infertility 16% know success rate 89% know IVF 38% said infertility = disease
Bertarelli vs. Hong Kong Survey Bertarelli Hong Kong • • • 50% know infertility • 20%know success rate • 46% know IVF • 50% said infertility=disease 52% know infertility 16% know success rate 89% know IVF 38% said infertility = disease
 YWCA Perception Study 2002 • • Methodology: Telephone survey Randomly called numbers No demographic questions to maximise response • Respondents answer 7, 15, or 16 questions
YWCA Perception Study 2002 • • Methodology: Telephone survey Randomly called numbers No demographic questions to maximise response • Respondents answer 7, 15, or 16 questions
 YWCA Perception Study 2002 • • • Randomly dialed Numbers Carried out July to October Successfully Connected: 147897 Valid Data: 7028 Success Rate: 5%
YWCA Perception Study 2002 • • • Randomly dialed Numbers Carried out July to October Successfully Connected: 147897 Valid Data: 7028 Success Rate: 5%
 YWCA Perception Study 2002
YWCA Perception Study 2002
 Why Reject IVF
Why Reject IVF
 Investigations on Treated Subjects
Investigations on Treated Subjects
 Investigations done Treated subjects
Investigations done Treated subjects
 Basic Investigations Made
Basic Investigations Made
 Summary of Results • 16% of polled has infertility problem • 45% view infertility as disease. For infertile couples 52% consider it a disease • 35% only has heard of IVF centers • 50% know the reason for their infertility • 30% know IVF success rate (20 -40%)
Summary of Results • 16% of polled has infertility problem • 45% view infertility as disease. For infertile couples 52% consider it a disease • 35% only has heard of IVF centers • 50% know the reason for their infertility • 30% know IVF success rate (20 -40%)
 Summary of Results • • • 1173/7208 polled claimed to be infertile only 265 (34%) have received or under treatment 50. 6% had ovulation induction 34% had intra-uterine insemination 24% had IVF/related treatment
Summary of Results • • • 1173/7208 polled claimed to be infertile only 265 (34%) have received or under treatment 50. 6% had ovulation induction 34% had intra-uterine insemination 24% had IVF/related treatment
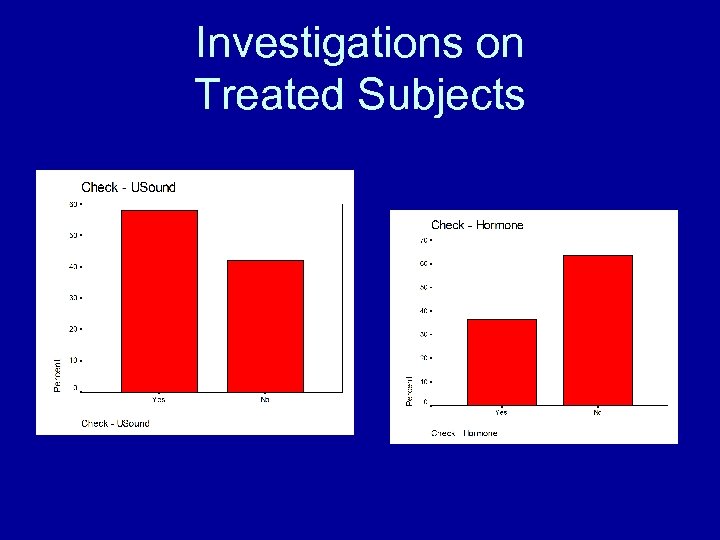
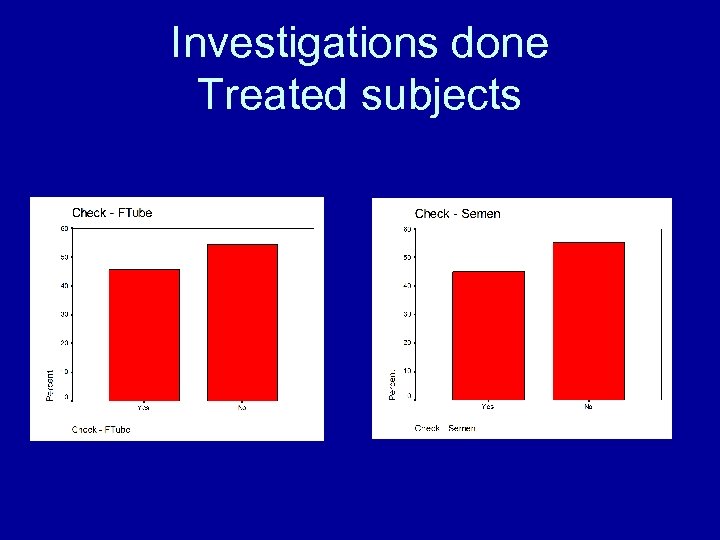
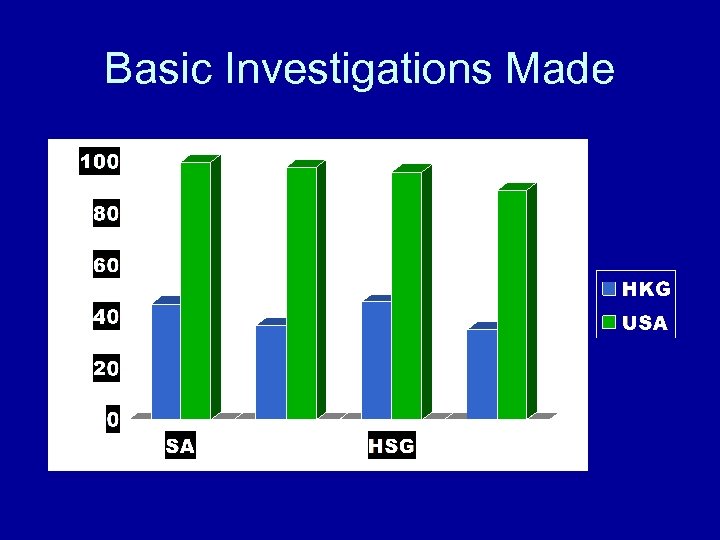
 Summary of Results • • • Diagnosis procedures reported Ovulation/hormone, laparoscopy 35% SA, HSG only 45% Ultrasound only test >50% (58%) 42% answered that none of the above tests were done
Summary of Results • • • Diagnosis procedures reported Ovulation/hormone, laparoscopy 35% SA, HSG only 45% Ultrasound only test >50% (58%) 42% answered that none of the above tests were done
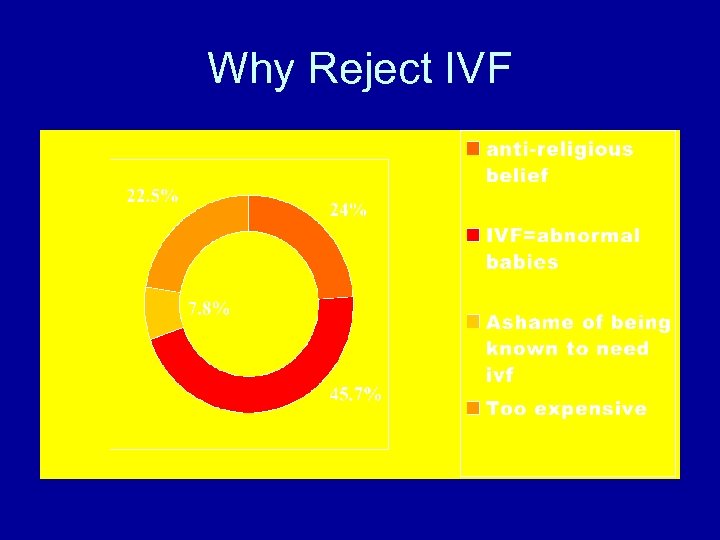
 Summary of Results • Although 50% of respondents who are under treatment accepts IVF • Only 30% actually received IVF treatment • This is 6. 5% of respondents who has infertility • Of those rejecting IVF, 45. 7% worry IVF begets abnormal babies. 22. 5% think too expensive
Summary of Results • Although 50% of respondents who are under treatment accepts IVF • Only 30% actually received IVF treatment • This is 6. 5% of respondents who has infertility • Of those rejecting IVF, 45. 7% worry IVF begets abnormal babies. 22. 5% think too expensive
 CONCLUSIONS • There is misconception about IVF mainly in the availability, success rate, and the technology itself • There is a problem of education, so that appropriate tests were not done • Funding is not enough, especially third party payment
CONCLUSIONS • There is misconception about IVF mainly in the availability, success rate, and the technology itself • There is a problem of education, so that appropriate tests were not done • Funding is not enough, especially third party payment
 CONCLUSIONS • Patients are not seeking treat-ment. Social factors and other psychological reasons may be present. • May also be that right treatment is not readily offered, so treat-ment abandoned after a while
CONCLUSIONS • Patients are not seeking treat-ment. Social factors and other psychological reasons may be present. • May also be that right treatment is not readily offered, so treat-ment abandoned after a while
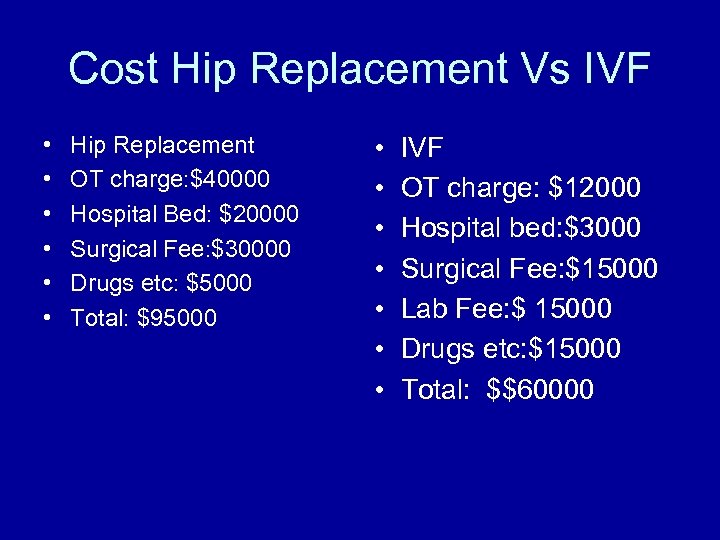 Cost Hip Replacement Vs IVF • • • Hip Replacement OT charge: $40000 Hospital Bed: $20000 Surgical Fee: $30000 Drugs etc: $5000 Total: $95000 • • IVF OT charge: $12000 Hospital bed: $3000 Surgical Fee: $15000 Lab Fee: $ 15000 Drugs etc: $15000 Total: $$60000
Cost Hip Replacement Vs IVF • • • Hip Replacement OT charge: $40000 Hospital Bed: $20000 Surgical Fee: $30000 Drugs etc: $5000 Total: $95000 • • IVF OT charge: $12000 Hospital bed: $3000 Surgical Fee: $15000 Lab Fee: $ 15000 Drugs etc: $15000 Total: $$60000
 ACTION, STRUCTURE AND USE OF Gn. RH AGONISTS AND ANTAGONIST
ACTION, STRUCTURE AND USE OF Gn. RH AGONISTS AND ANTAGONIST
 Structure of Gn. RH antagonists
Structure of Gn. RH antagonists
 Comparison: Mode of Actions Antagonists Agonists • Immediate onset of actions • long pre-treatment (shortens treatment durations) • Prevents hormonal withdrawal symptoms • No recovery time of the pituitary • Hormonal (estrogen) withdrawal symptoms through desensitization of pituitary • Recovery of the pituitary gonadotrophin secretion, after stopping the treatment takes about 2 weeks.
Comparison: Mode of Actions Antagonists Agonists • Immediate onset of actions • long pre-treatment (shortens treatment durations) • Prevents hormonal withdrawal symptoms • No recovery time of the pituitary • Hormonal (estrogen) withdrawal symptoms through desensitization of pituitary • Recovery of the pituitary gonadotrophin secretion, after stopping the treatment takes about 2 weeks.
 Characteristics of Gn. RH Ganirelix Cetrorelix • Fully effective within 4 hours, within 8 hours, with a half-life of about 13 hours 36 hours R. E. Felberbaum and K. Diedrich, 1999.
Characteristics of Gn. RH Ganirelix Cetrorelix • Fully effective within 4 hours, within 8 hours, with a half-life of about 13 hours 36 hours R. E. Felberbaum and K. Diedrich, 1999.
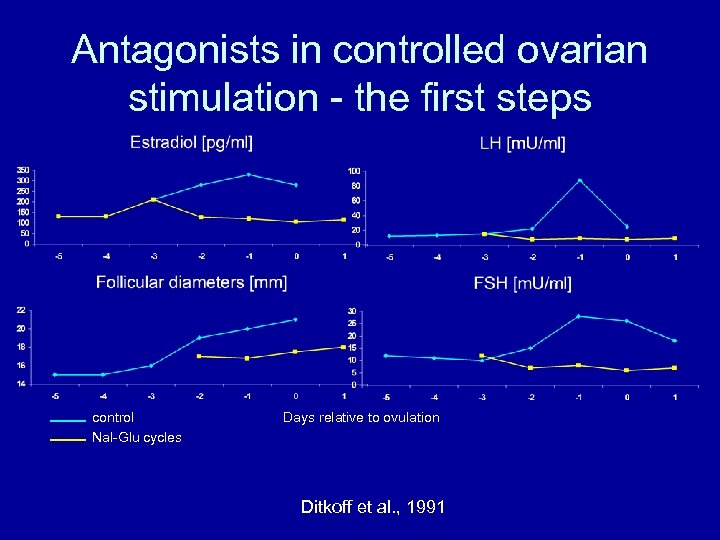 Antagonists in controlled ovarian stimulation - the first steps control Nal-Glu cycles Days relative to ovulation Ditkoff et al. , 1991
Antagonists in controlled ovarian stimulation - the first steps control Nal-Glu cycles Days relative to ovulation Ditkoff et al. , 1991
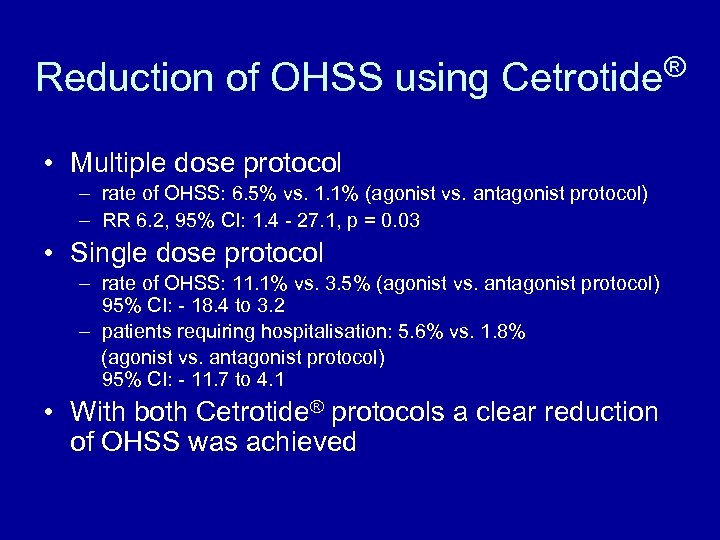 Reduction of OHSS using Cetrotide® • Multiple dose protocol – rate of OHSS: 6. 5% vs. 1. 1% (agonist vs. antagonist protocol) – RR 6. 2, 95% CI: 1. 4 - 27. 1, p = 0. 03 • Single dose protocol – rate of OHSS: 11. 1% vs. 3. 5% (agonist vs. antagonist protocol) 95% CI: - 18. 4 to 3. 2 – patients requiring hospitalisation: 5. 6% vs. 1. 8% (agonist vs. antagonist protocol) 95% CI: - 11. 7 to 4. 1 • With both Cetrotide® protocols a clear reduction of OHSS was achieved
Reduction of OHSS using Cetrotide® • Multiple dose protocol – rate of OHSS: 6. 5% vs. 1. 1% (agonist vs. antagonist protocol) – RR 6. 2, 95% CI: 1. 4 - 27. 1, p = 0. 03 • Single dose protocol – rate of OHSS: 11. 1% vs. 3. 5% (agonist vs. antagonist protocol) 95% CI: - 18. 4 to 3. 2 – patients requiring hospitalisation: 5. 6% vs. 1. 8% (agonist vs. antagonist protocol) 95% CI: - 11. 7 to 4. 1 • With both Cetrotide® protocols a clear reduction of OHSS was achieved
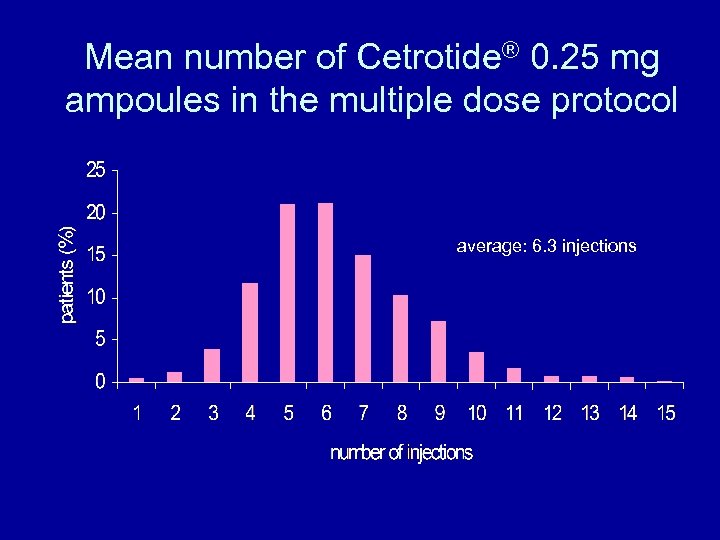 Mean number of Cetrotide® 0. 25 mg ampoules in the multiple dose protocol average: 6. 3 injections
Mean number of Cetrotide® 0. 25 mg ampoules in the multiple dose protocol average: 6. 3 injections
 The Gn. RH Antagonists Conclusions: 1. Why treat 100% of patients when we are trying to prevent 5 -10% LH surge 2. Avoid over-suppression and poor response 3. Effective in preventing LH surge 4. Reduction of hyper-stimulation 5. Lower costs
The Gn. RH Antagonists Conclusions: 1. Why treat 100% of patients when we are trying to prevent 5 -10% LH surge 2. Avoid over-suppression and poor response 3. Effective in preventing LH surge 4. Reduction of hyper-stimulation 5. Lower costs
 Safety Profile • Possible side effects headache, weakness, mild vaginitis & breast sensitivity etc • No known drug interaction • Overdose unlikely & no side effects
Safety Profile • Possible side effects headache, weakness, mild vaginitis & breast sensitivity etc • No known drug interaction • Overdose unlikely & no side effects
 Precautions • • History of depression, DM Not taken with other intravaginal products Not recommended during lactation Stored in a dry place, <25 o. C
Precautions • • History of depression, DM Not taken with other intravaginal products Not recommended during lactation Stored in a dry place, <25 o. C
 Progesterone Functions • Increase endometrial receptivity • Maintain pregnancy Routes of administration • Injection (IM / IV) • Oral • Rectal • Vaginal, etc
Progesterone Functions • Increase endometrial receptivity • Maintain pregnancy Routes of administration • Injection (IM / IV) • Oral • Rectal • Vaginal, etc
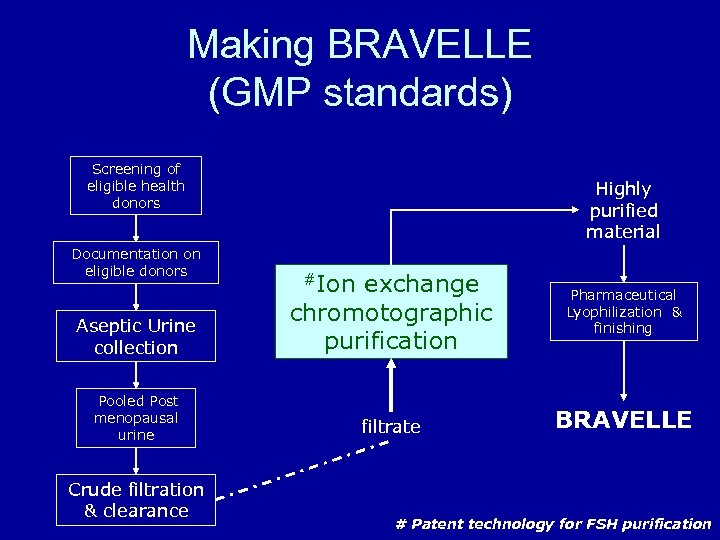 Making BRAVELLE (GMP standards) Screening of eligible health donors Documentation on eligible donors Highly purified material Aseptic Urine collection exchange chromotographic purification Pooled Post menopausal urine filtrate Crude filtration & clearance #Ion Pharmaceutical Lyophilization & finishing BRAVELLE # Patent technology for FSH purification
Making BRAVELLE (GMP standards) Screening of eligible health donors Documentation on eligible donors Highly purified material Aseptic Urine collection exchange chromotographic purification Pooled Post menopausal urine filtrate Crude filtration & clearance #Ion Pharmaceutical Lyophilization & finishing BRAVELLE # Patent technology for FSH purification
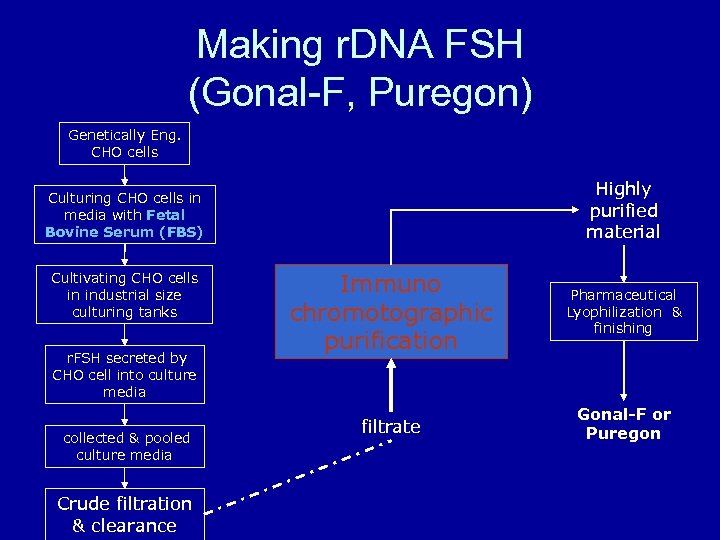 Making r. DNA FSH (Gonal-F, Puregon) Genetically Eng. CHO cells Highly purified material Culturing CHO cells in media with Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) Cultivating CHO cells in industrial size culturing tanks r. FSH secreted by CHO cell into culture media collected & pooled culture media Crude filtration & clearance Immuno chromotographic purification Pharmaceutical Lyophilization & finishing filtrate Gonal-F or Puregon
Making r. DNA FSH (Gonal-F, Puregon) Genetically Eng. CHO cells Highly purified material Culturing CHO cells in media with Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) Cultivating CHO cells in industrial size culturing tanks r. FSH secreted by CHO cell into culture media collected & pooled culture media Crude filtration & clearance Immuno chromotographic purification Pharmaceutical Lyophilization & finishing filtrate Gonal-F or Puregon


