Arrythmias and EKGs 2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Arrhythmias and EKGs Part 2
Arrhythmias and EKGs Part 2
 Outline 1. Sinus Arrhythmia and Sick Sinus 2. 3. 4. Syndrome Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Bigeminal Rhythms Preexcitation and AVRT
Outline 1. Sinus Arrhythmia and Sick Sinus 2. 3. 4. Syndrome Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Bigeminal Rhythms Preexcitation and AVRT
 Mechanisms of Arrhythmogenesis
Mechanisms of Arrhythmogenesis
 Sinus Arrhythmia Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine, 7 th ed. , 2005. EKG Characteristics: Presence of sinus P waves Variation of the PP interval which cannot be q attributed to either SA nodal block or PACs When the variations in PP interval occur in phase with respiration, this is considered to be a normal variant. When they are unrelated to respiration, they may be caused by the same etiologies leading to sinus bradycardia.
Sinus Arrhythmia Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine, 7 th ed. , 2005. EKG Characteristics: Presence of sinus P waves Variation of the PP interval which cannot be q attributed to either SA nodal block or PACs When the variations in PP interval occur in phase with respiration, this is considered to be a normal variant. When they are unrelated to respiration, they may be caused by the same etiologies leading to sinus bradycardia.
 Sick Sinus Syndrome Characterized by a collection of symptoms and ECG findings due to chronic dysfunction of the sinoatrial (SA) node: – Chronic and severe sinus bradycardia – Sinus pauses – Sinus arrhythmia – Complete sinus arrest – Progressive development of atrial arrhythmias (aflutter, a-fib, atrial tachycardia) Patients are usually elderly and present with lightheadedness and/or syncope, but it can also manifest as angina, dyspnea, and palpitations. About 50% of people with SSS also display some degree of dysfunction of the AV node
Sick Sinus Syndrome Characterized by a collection of symptoms and ECG findings due to chronic dysfunction of the sinoatrial (SA) node: – Chronic and severe sinus bradycardia – Sinus pauses – Sinus arrhythmia – Complete sinus arrest – Progressive development of atrial arrhythmias (aflutter, a-fib, atrial tachycardia) Patients are usually elderly and present with lightheadedness and/or syncope, but it can also manifest as angina, dyspnea, and palpitations. About 50% of people with SSS also display some degree of dysfunction of the AV node
 Sick Sinus Syndrome Sinus bradycardia (rate of ~43 bpm) with a sinus pause
Sick Sinus Syndrome Sinus bradycardia (rate of ~43 bpm) with a sinus pause
 Etiologies of Sick Sinus Syndrome More Common Sinus node firbosis Atherosclerosis of the SA artery Congenital heart disease Excessive vagal tone Drugs Less Common Familial SSS (due to mutations in SCN 5 A) Infiltrative diseases Pericarditis Lyme disease Hypothyroidism Rheumatic fever
Etiologies of Sick Sinus Syndrome More Common Sinus node firbosis Atherosclerosis of the SA artery Congenital heart disease Excessive vagal tone Drugs Less Common Familial SSS (due to mutations in SCN 5 A) Infiltrative diseases Pericarditis Lyme disease Hypothyroidism Rheumatic fever
 Tachycardia-Bradycardia Syndrome Common variant of sick sinus syndrome severe bradycardia alternates with paroxysmal tachycardias, most often atrial fibrillation. There is usually a prolonged pause in the cardiac rhythm following cessation of the tachyarrhythmia.
Tachycardia-Bradycardia Syndrome Common variant of sick sinus syndrome severe bradycardia alternates with paroxysmal tachycardias, most often atrial fibrillation. There is usually a prolonged pause in the cardiac rhythm following cessation of the tachyarrhythmia.
 Tachycardia-Bradycardia Syndrome Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine, 7 th ed. , 2005. Abrupt termination of atrial flutter with variable AV block, followed by sinus arrest with a junctional escape beat.
Tachycardia-Bradycardia Syndrome Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine, 7 th ed. , 2005. Abrupt termination of atrial flutter with variable AV block, followed by sinus arrest with a junctional escape beat.
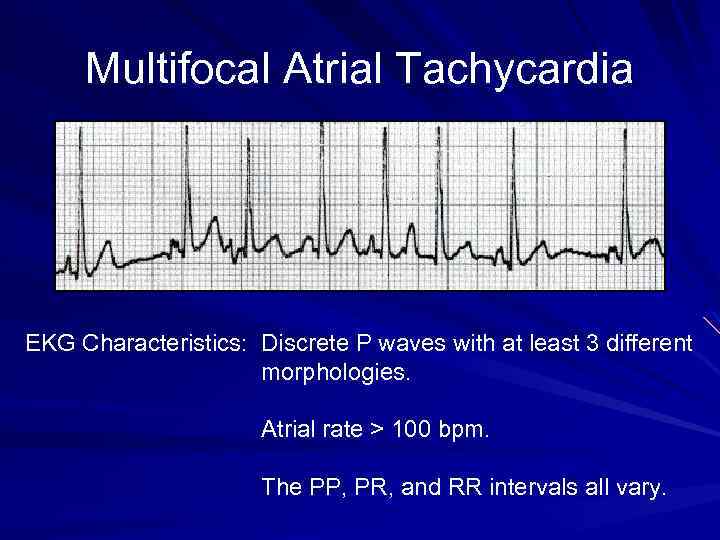 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia EKG Characteristics: Discrete P waves with at least 3 different morphologies. Atrial rate > 100 bpm. The PP, PR, and RR intervals all vary.
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia EKG Characteristics: Discrete P waves with at least 3 different morphologies. Atrial rate > 100 bpm. The PP, PR, and RR intervals all vary.
 Bigeminal Rhythms Arrhythmias in which each normal sinus beat is followed by a premature contraction (PAC, PJC, or PVC). Results in a couplet rhythm which can be detected by pulse or auscultation. Generally benign
Bigeminal Rhythms Arrhythmias in which each normal sinus beat is followed by a premature contraction (PAC, PJC, or PVC). Results in a couplet rhythm which can be detected by pulse or auscultation. Generally benign
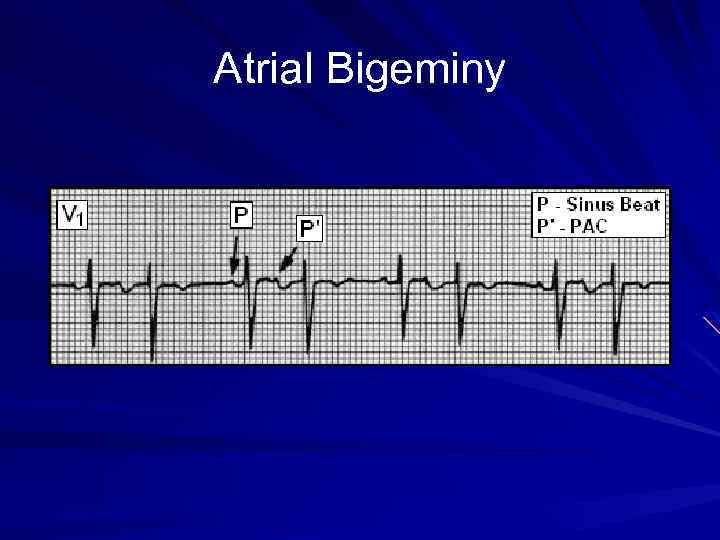 Atrial Bigeminy
Atrial Bigeminy
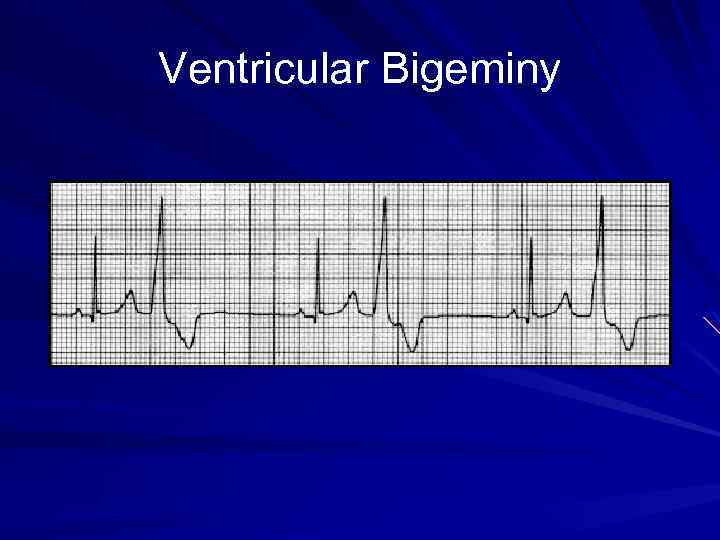 Ventricular Bigeminy
Ventricular Bigeminy
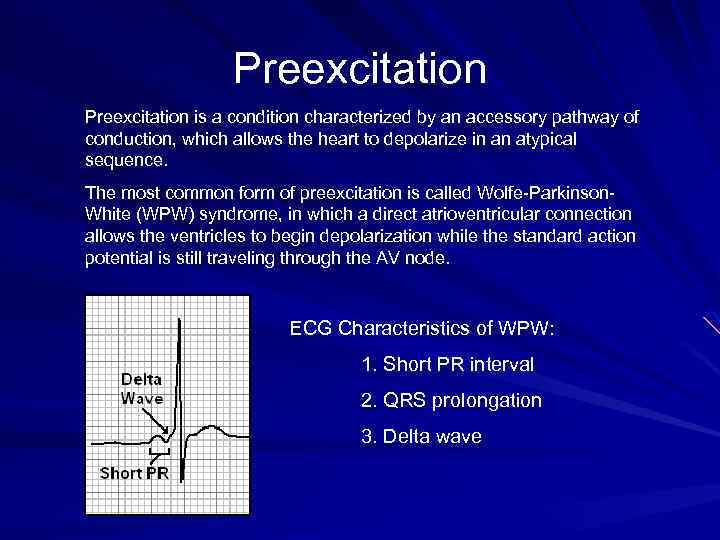 Preexcitation is a condition characterized by an accessory pathway of conduction, which allows the heart to depolarize in an atypical sequence. The most common form of preexcitation is called Wolfe-Parkinson. White (WPW) syndrome, in which a direct atrioventricular connection allows the ventricles to begin depolarization while the standard action potential is still traveling through the AV node. ECG Characteristics of WPW: 1. Short PR interval 2. QRS prolongation 3. Delta wave
Preexcitation is a condition characterized by an accessory pathway of conduction, which allows the heart to depolarize in an atypical sequence. The most common form of preexcitation is called Wolfe-Parkinson. White (WPW) syndrome, in which a direct atrioventricular connection allows the ventricles to begin depolarization while the standard action potential is still traveling through the AV node. ECG Characteristics of WPW: 1. Short PR interval 2. QRS prolongation 3. Delta wave
 AV Reentrant Tachycardia (AVRT) In patients with WPW, a reentrant rhythm can be generated where the AV node serves as one arm of the reentrant circuit, and the accessory pathway as the other.
AV Reentrant Tachycardia (AVRT) In patients with WPW, a reentrant rhythm can be generated where the AV node serves as one arm of the reentrant circuit, and the accessory pathway as the other.
 Types of AVRT Orthodromic AVRT (More common) – Narrow complex tachycardia in which the wave of depolarization travels down the AV node and retrograde up the accessory pathway. Antidromic AVRT (Less common) – Wide complex tachycardia in which the wave of depolarization travels down the accessory pathway and retrograde up the AV node.
Types of AVRT Orthodromic AVRT (More common) – Narrow complex tachycardia in which the wave of depolarization travels down the AV node and retrograde up the accessory pathway. Antidromic AVRT (Less common) – Wide complex tachycardia in which the wave of depolarization travels down the accessory pathway and retrograde up the AV node.
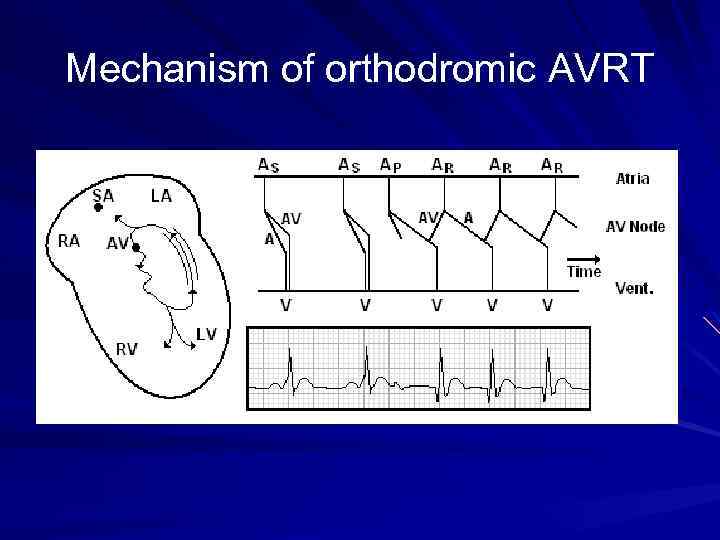 Mechanism of orthodromic AVRT
Mechanism of orthodromic AVRT
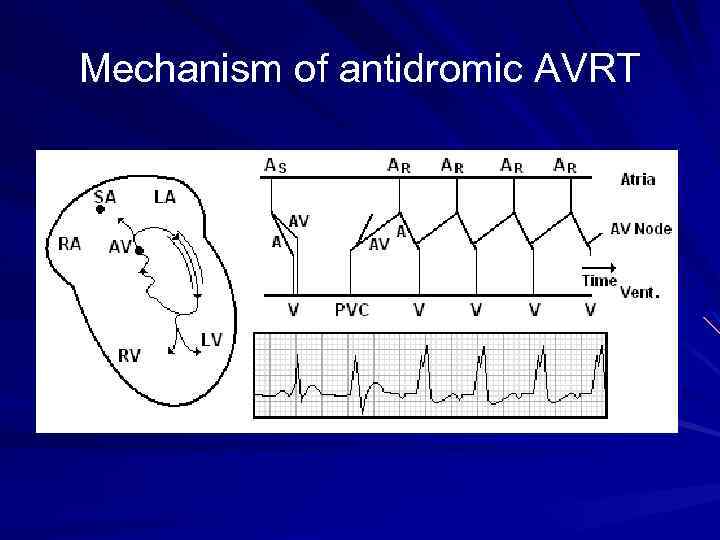 Mechanism of antidromic AVRT
Mechanism of antidromic AVRT
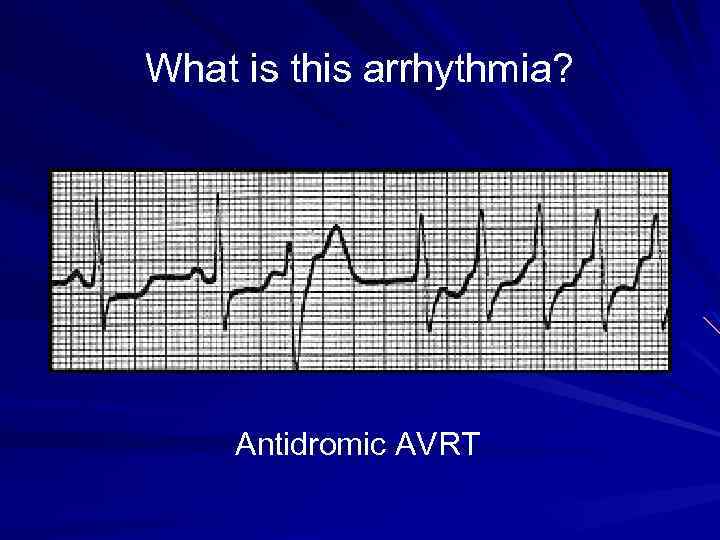 What is this arrhythmia? Antidromic AVRT
What is this arrhythmia? Antidromic AVRT
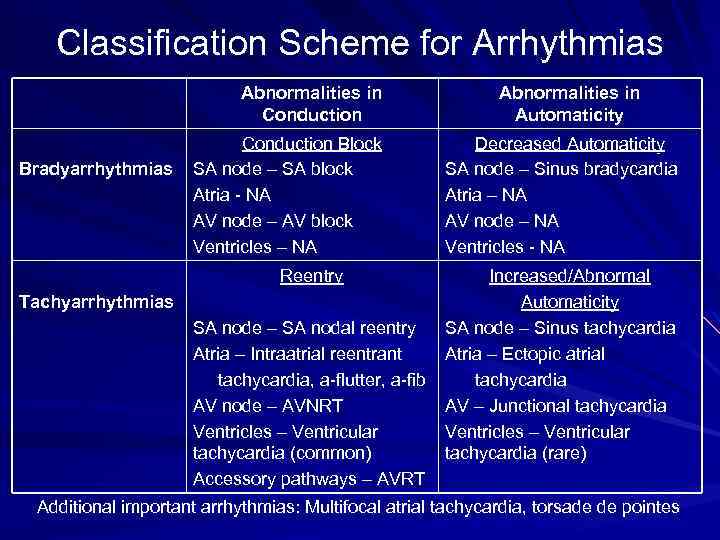 Classification Scheme for Arrhythmias Abnormalities in Conduction Bradyarrhythmias Conduction Block SA node – SA block Atria - NA AV node – AV block Ventricles – NA Reentry Tachyarrhythmias SA node – SA nodal reentry Atria – Intraatrial reentrant tachycardia, a-flutter, a-fib AV node – AVNRT Ventricles – Ventricular tachycardia (common) Accessory pathways – AVRT Abnormalities in Automaticity Decreased Automaticity SA node – Sinus bradycardia Atria – NA AV node – NA Ventricles - NA Increased/Abnormal Automaticity SA node – Sinus tachycardia Atria – Ectopic atrial tachycardia AV – Junctional tachycardia Ventricles – Ventricular tachycardia (rare) Additional important arrhythmias: Multifocal atrial tachycardia, torsade de pointes
Classification Scheme for Arrhythmias Abnormalities in Conduction Bradyarrhythmias Conduction Block SA node – SA block Atria - NA AV node – AV block Ventricles – NA Reentry Tachyarrhythmias SA node – SA nodal reentry Atria – Intraatrial reentrant tachycardia, a-flutter, a-fib AV node – AVNRT Ventricles – Ventricular tachycardia (common) Accessory pathways – AVRT Abnormalities in Automaticity Decreased Automaticity SA node – Sinus bradycardia Atria – NA AV node – NA Ventricles - NA Increased/Abnormal Automaticity SA node – Sinus tachycardia Atria – Ectopic atrial tachycardia AV – Junctional tachycardia Ventricles – Ventricular tachycardia (rare) Additional important arrhythmias: Multifocal atrial tachycardia, torsade de pointes


