c036b6e563c4926d53901e25c0321b55.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 ARL New Measures Initiative The E-Metrics Project Recommended Statistics and Measures for Library Networked Services ARL E-Metrics Phase II Report Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 1
ARL New Measures Initiative The E-Metrics Project Recommended Statistics and Measures for Library Networked Services ARL E-Metrics Phase II Report Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 1
 List of Project Participants Alberta Maryland USC Arizona State U. Mass Texas A & M Auburn Nebraska Virginia Tech Chicago Notre Dame W. Ontario Connecticut Pennsylvania Wisconsin Cornell Penn State Yale Illinois-Chicago Pittsburgh LC Manitoba Purdue NYPL Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 2
List of Project Participants Alberta Maryland USC Arizona State U. Mass Texas A & M Auburn Nebraska Virginia Tech Chicago Notre Dame W. Ontario Connecticut Pennsylvania Wisconsin Cornell Penn State Yale Illinois-Chicago Pittsburgh LC Manitoba Purdue NYPL Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 2
 Vendor Statistics Working Group Ø Invited 12 major ARL vendors to meet in Denver preceding 2000 ACRL Meeting Academic Press/IDEAL * Elsevier/Science Direct Lexis/Nexis Ovid Bell & Howell Gale Group ISI * † net. Library Silver Platter * EBSCO JSTOR OCLC/First Search * Unable to attend Denver Meeting † Nonparticipant in project. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 3
Vendor Statistics Working Group Ø Invited 12 major ARL vendors to meet in Denver preceding 2000 ACRL Meeting Academic Press/IDEAL * Elsevier/Science Direct Lexis/Nexis Ovid Bell & Howell Gale Group ISI * † net. Library Silver Platter * EBSCO JSTOR OCLC/First Search * Unable to attend Denver Meeting † Nonparticipant in project. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 3
 A Framework for Developing & Selecting Network Statistics & Measures Ø The Network Components Ø Technical Infrastructure Ø Information Content Ø Information Services Ø Support Ø Management Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 4
A Framework for Developing & Selecting Network Statistics & Measures Ø The Network Components Ø Technical Infrastructure Ø Information Content Ø Information Services Ø Support Ø Management Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 4
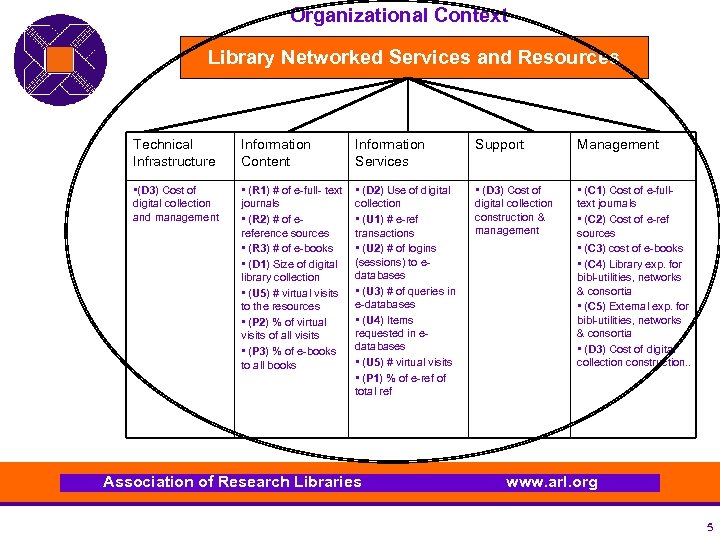 Organizational Context Library Networked Services and Resources Technical Infrastructure Information Content Information Services Support Management • (D 3) Cost of digital collection and management • (R 1) # of e-full- text journals • (R 2) # of ereference sources • (R 3) # of e-books • (D 1) Size of digital library collection • (U 5) # virtual visits to the resources • (P 2) % of virtual visits of all visits • (P 3) % of e-books to all books • (D 2) Use of digital collection • (U 1) # e-ref transactions • (U 2) # of logins (sessions) to edatabases • (U 3) # of queries in e-databases • (U 4) Items requested in edatabases • (U 5) # virtual visits • (P 1) % of e-ref of total ref • (D 3) Cost of digital collection construction & management • (C 1) Cost of e-fulltext journals • (C 2) Cost of e-ref sources • (C 3) cost of e-books • (C 4) Library exp. for bibl-utilities, networks & consortia • (C 5) External exp. for bibl-utilities, networks & consortia • (D 3) Cost of digital collection construction. . Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 5
Organizational Context Library Networked Services and Resources Technical Infrastructure Information Content Information Services Support Management • (D 3) Cost of digital collection and management • (R 1) # of e-full- text journals • (R 2) # of ereference sources • (R 3) # of e-books • (D 1) Size of digital library collection • (U 5) # virtual visits to the resources • (P 2) % of virtual visits of all visits • (P 3) % of e-books to all books • (D 2) Use of digital collection • (U 1) # e-ref transactions • (U 2) # of logins (sessions) to edatabases • (U 3) # of queries in e-databases • (U 4) Items requested in edatabases • (U 5) # virtual visits • (P 1) % of e-ref of total ref • (D 3) Cost of digital collection construction & management • (C 1) Cost of e-fulltext journals • (C 2) Cost of e-ref sources • (C 3) cost of e-books • (C 4) Library exp. for bibl-utilities, networks & consortia • (C 5) External exp. for bibl-utilities, networks & consortia • (D 3) Cost of digital collection construction. . Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 5
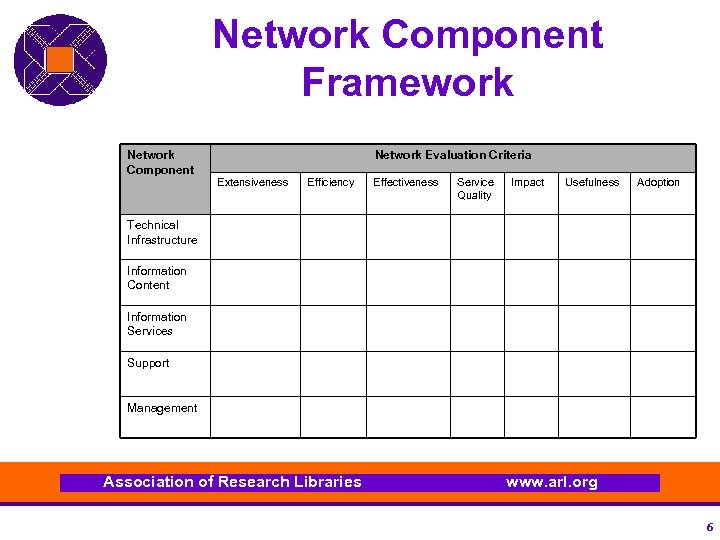 Network Component Framework Network Component Network Evaluation Criteria Extensiveness Efficiency Effectiveness Service Quality Impact Usefulness Adoption Technical Infrastructure Information Content Information Services Support Management Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 6
Network Component Framework Network Component Network Evaluation Criteria Extensiveness Efficiency Effectiveness Service Quality Impact Usefulness Adoption Technical Infrastructure Information Content Information Services Support Management Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 6
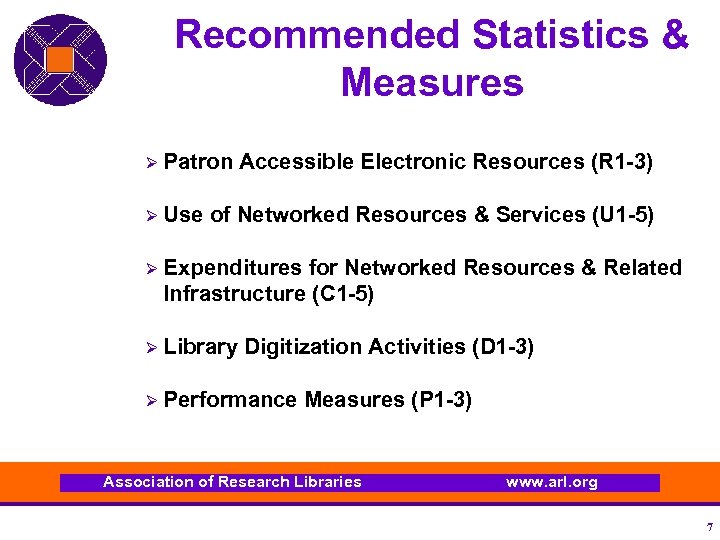 Recommended Statistics & Measures Ø Patron Ø Use Accessible Electronic Resources (R 1 -3) of Networked Resources & Services (U 1 -5) Ø Expenditures for Networked Resources & Related Infrastructure (C 1 -5) Ø Library Digitization Activities (D 1 -3) Ø Performance Measures (P 1 -3) Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 7
Recommended Statistics & Measures Ø Patron Ø Use Accessible Electronic Resources (R 1 -3) of Networked Resources & Services (U 1 -5) Ø Expenditures for Networked Resources & Related Infrastructure (C 1 -5) Ø Library Digitization Activities (D 1 -3) Ø Performance Measures (P 1 -3) Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 7
 Patron Accessible Electronic Resources Ø R 1 – Number of electronic full-text journals Ø R 2 – Number of electronic reference sources Ø R 3 – Number of electronic books Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 8
Patron Accessible Electronic Resources Ø R 1 – Number of electronic full-text journals Ø R 2 – Number of electronic reference sources Ø R 3 – Number of electronic books Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 8
 R 1 – Number of Electronic Full-text Journals Ø Definition - Number of electronic full-text journal subscriptions – by individual institution or consortia licensing. Ø Rationale – Documents degree of expansion of electronic subscriptions available. Can be used to show good coverage & need for more funding. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 9
R 1 – Number of Electronic Full-text Journals Ø Definition - Number of electronic full-text journal subscriptions – by individual institution or consortia licensing. Ø Rationale – Documents degree of expansion of electronic subscriptions available. Can be used to show good coverage & need for more funding. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 9
 R 1 – Number of Electronic Full-text Journals Ø Data source – local or vendors. Ø Frequency – annual, monthly, etc. Ø Process – parse into database or spreadsheet, update dynamically from local catalog or vendor record. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 10
R 1 – Number of Electronic Full-text Journals Ø Data source – local or vendors. Ø Frequency – annual, monthly, etc. Ø Process – parse into database or spreadsheet, update dynamically from local catalog or vendor record. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 10
 R 2 – Number of Electronic Reference Resources Ø Definition - number of electronic reference resources & aggregation services – by individual institution or consortia licensing. Ø Rationale – documents degree of expansion of electronic resources available. Can be used to show good coverage & need for more funding. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 11
R 2 – Number of Electronic Reference Resources Ø Definition - number of electronic reference resources & aggregation services – by individual institution or consortia licensing. Ø Rationale – documents degree of expansion of electronic resources available. Can be used to show good coverage & need for more funding. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 11
 R 2 – Number of Electronic Reference Resources Ø Unit of Measure – database - not the service. Ø Data source – local or vendors. Ø Frequency – annual, monthly, etc. Ø Process – parse into database or spreadsheet, update dynamically from local catalog or vendor record. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 12
R 2 – Number of Electronic Reference Resources Ø Unit of Measure – database - not the service. Ø Data source – local or vendors. Ø Frequency – annual, monthly, etc. Ø Process – parse into database or spreadsheet, update dynamically from local catalog or vendor record. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 12
 R 3 – Number of Electronic Books Ø Definition - # of full-text monographs – by individual institution or consortia licensing. Ø Rationale – documents degree of expansion of e-books – to be used with caution as tech & use evolves. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 13
R 3 – Number of Electronic Books Ø Definition - # of full-text monographs – by individual institution or consortia licensing. Ø Rationale – documents degree of expansion of e-books – to be used with caution as tech & use evolves. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 13
 R 3 – Number of Electronic Books Ø Unit of Measure – title count. Ø Data source – local or vendors. Ø Frequency – annual, monthly, etc. Ø Process – parse title into database or spreadsheet, update dynamically from local catalog or vendor record. Count duplicate titles. Ø Related Issues – evolving tech, location, access, use vs. circulation, etc. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 14
R 3 – Number of Electronic Books Ø Unit of Measure – title count. Ø Data source – local or vendors. Ø Frequency – annual, monthly, etc. Ø Process – parse title into database or spreadsheet, update dynamically from local catalog or vendor record. Count duplicate titles. Ø Related Issues – evolving tech, location, access, use vs. circulation, etc. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 14
 Use of Networked Resources & Related Infrastructure Ø U 1 – Number of electronic reference transactions Ø U 2 – Number of logins (sessions) to electronic databases Ø U 3 – Number of queries (searches) in electronic databases Ø U 4 – Items requested in electronic databases Ø U 5 – Virtual visits to library’s Web site and catalog Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 15
Use of Networked Resources & Related Infrastructure Ø U 1 – Number of electronic reference transactions Ø U 2 – Number of logins (sessions) to electronic databases Ø U 3 – Number of queries (searches) in electronic databases Ø U 4 – Items requested in electronic databases Ø U 5 – Virtual visits to library’s Web site and catalog Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 15
 U 1 – Number of Electronic Reference Transactions Ø Definition - number of electronic reference transactions – via e-mail, WWW form, etc. Ø Rationale – libraries are interested in tracking the development of new electronic services. Attempt to measure reference transactions through new electronic tools and services. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 16
U 1 – Number of Electronic Reference Transactions Ø Definition - number of electronic reference transactions – via e-mail, WWW form, etc. Ø Rationale – libraries are interested in tracking the development of new electronic services. Attempt to measure reference transactions through new electronic tools and services. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 16
 U 1 – Number of Electronic Reference Transactions Ø Unit of Measure – request count, time it took. Ø Data Source – local server, manual tally, e-mail count. Ø Frequency – daily, monthly, annually, etc. Ø Process – clarify process, identify activity points, identify collectors of data, consolidate data. Ø Related Issues –This measure may have to be broken down into additional data types – time, type of query, type of interaction, scheduling issues, measures of quality and reliability. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 17
U 1 – Number of Electronic Reference Transactions Ø Unit of Measure – request count, time it took. Ø Data Source – local server, manual tally, e-mail count. Ø Frequency – daily, monthly, annually, etc. Ø Process – clarify process, identify activity points, identify collectors of data, consolidate data. Ø Related Issues –This measure may have to be broken down into additional data types – time, type of query, type of interaction, scheduling issues, measures of quality and reliability. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 17
 U 2 – Number of Logins (Sessions) to Electronic Databases Ø Definition - number of user initiated sessions in licensed electronic resources. Starts at connection & ends with explicit termination (timeout or logout). Ø Rationale – will give data about relative use of each database. Will show use of networked resource. Ø Related Issues – need vendors to report by agreed standards. Need to understand why counts fluctuate, changes in the database itself, type of license, infrastructure stability. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 18
U 2 – Number of Logins (Sessions) to Electronic Databases Ø Definition - number of user initiated sessions in licensed electronic resources. Starts at connection & ends with explicit termination (timeout or logout). Ø Rationale – will give data about relative use of each database. Will show use of networked resource. Ø Related Issues – need vendors to report by agreed standards. Need to understand why counts fluctuate, changes in the database itself, type of license, infrastructure stability. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 18
 U 2 – Number of Logins (Sessions) to Electronic Databases Ø Unit of Measure – Logins or session counts. Ø Data Source – vendor report. Ø Frequency – daily, monthly, annually, etc. Ø Process – get monthly usage data from vendors, copy or parse data for each database to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Calculate totals if comparable. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 19
U 2 – Number of Logins (Sessions) to Electronic Databases Ø Unit of Measure – Logins or session counts. Ø Data Source – vendor report. Ø Frequency – daily, monthly, annually, etc. Ø Process – get monthly usage data from vendors, copy or parse data for each database to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Calculate totals if comparable. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 19
 U 3 – Number of Queries (Searches) in Electronic Databases Ø Definition - number of user initiated queries (searches) in licensed electronic resources. Usually a search is recorded each time a search request is submitted to the server. Ø Rationale – indicate use of databases, areas of interest to clients, level of use beyond individual session. Ø Related Issues – not all vendors provide this data, need standardization of what is counted here by different vendors, difficult to calculate an aggregate count. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 20
U 3 – Number of Queries (Searches) in Electronic Databases Ø Definition - number of user initiated queries (searches) in licensed electronic resources. Usually a search is recorded each time a search request is submitted to the server. Ø Rationale – indicate use of databases, areas of interest to clients, level of use beyond individual session. Ø Related Issues – not all vendors provide this data, need standardization of what is counted here by different vendors, difficult to calculate an aggregate count. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 20
 U 3 – Number of Queries (Searches) in Electronic Databases Ø Unit of Measure – count of search requests. Ø Data Source – vendor report. Ø Frequency – daily, monthly, annually, etc. Ø Process – get monthly data from vendors, copy or parse data for each database to an inhouse spreadsheet or database. Calculate totals if comparable. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 21
U 3 – Number of Queries (Searches) in Electronic Databases Ø Unit of Measure – count of search requests. Ø Data Source – vendor report. Ø Frequency – daily, monthly, annually, etc. Ø Process – get monthly data from vendors, copy or parse data for each database to an inhouse spreadsheet or database. Calculate totals if comparable. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 21
 U 4 – Number of Items Requested in Electronic Databases Ø Definition - number of items requested in all of the library’s electronic resources. Can include journal articles, e-books, and other type of materials – may be citation, abstract, TOC, full-text. Ø Rationale – circulation count for electronic content – equivalent to in-house counts. Ø Related Issues – not all vendors provide this data, need standardization of what is counted here by different vendors, difficult to calculate an aggregate count. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 22
U 4 – Number of Items Requested in Electronic Databases Ø Definition - number of items requested in all of the library’s electronic resources. Can include journal articles, e-books, and other type of materials – may be citation, abstract, TOC, full-text. Ø Rationale – circulation count for electronic content – equivalent to in-house counts. Ø Related Issues – not all vendors provide this data, need standardization of what is counted here by different vendors, difficult to calculate an aggregate count. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 22
 U 4 – Number of Items Requested in Electronic Databases Ø Unit of Measure – count of items requested. Ø Data Source – vendor report. Ø Frequency – daily, monthly, annually, etc. Ø Process – get monthly data from vendors, copy or parse data for each database to an inhouse spreadsheet or database. Calculate totals if comparable. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 23
U 4 – Number of Items Requested in Electronic Databases Ø Unit of Measure – count of items requested. Ø Data Source – vendor report. Ø Frequency – daily, monthly, annually, etc. Ø Process – get monthly data from vendors, copy or parse data for each database to an inhouse spreadsheet or database. Calculate totals if comparable. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 23
 U 5 – Virtual Visits to Library’s Website and Catalog Ø Definition - number of client visits to the library’s Web site or catalog from outside the physical library premises without regard to the number of pages viewed. As some may be misleading, this is an estimate only. Ø Rationale – reflects external interest in library services; show demand for library resources; can be used to justify investment in electronic resources. Ø Related Issues – need staff with systems skills. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 24
U 5 – Virtual Visits to Library’s Website and Catalog Ø Definition - number of client visits to the library’s Web site or catalog from outside the physical library premises without regard to the number of pages viewed. As some may be misleading, this is an estimate only. Ø Rationale – reflects external interest in library services; show demand for library resources; can be used to justify investment in electronic resources. Ø Related Issues – need staff with systems skills. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 24
 U 5 – Virtual Visits to Library’s Website and Catalog Ø Unit of Measure – count visits to the library’s Web site or catalog. Ø Data Source – local count of external access to library Web site, remote logins to non-Web based library databases & remotely accessible library OPAC. Ø Frequency – daily, monthly, annually, etc. Ø Process – identify all sources of visits and local servers; exclude internal use; use log analysis software – possibly parse data to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 25
U 5 – Virtual Visits to Library’s Website and Catalog Ø Unit of Measure – count visits to the library’s Web site or catalog. Ø Data Source – local count of external access to library Web site, remote logins to non-Web based library databases & remotely accessible library OPAC. Ø Frequency – daily, monthly, annually, etc. Ø Process – identify all sources of visits and local servers; exclude internal use; use log analysis software – possibly parse data to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 25
 Expenditures for Networked Resources & Related Infrastructure Ø C 1 Cost of electronic full-text journals Ø C 2 Cost of electronic reference sources Ø C 3 Cost of electronic books Ø C 4 Library expenditures for bibliographic utilities, networks & consortia Ø C 5 External expenditures for bibliographic utilities, networks & consortia Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 26
Expenditures for Networked Resources & Related Infrastructure Ø C 1 Cost of electronic full-text journals Ø C 2 Cost of electronic reference sources Ø C 3 Cost of electronic books Ø C 4 Library expenditures for bibliographic utilities, networks & consortia Ø C 5 External expenditures for bibliographic utilities, networks & consortia Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 26
 C 1 – Cost of Electronic Full-Text Journals Ø Definition – expenditures for electronic full-text journal subscriptions. Include initial purchase cost, membership fees, annual licenses paid directly or as part of consortia. Ø Rationale – indicates expenditures (costs) for ejournals; show increased demand for e-journals – which replace print; can calculate unit cost of e -journal by collecting C 1 & R 1 statistics – measure of effectiveness. Ø Related Issues – use to see expenditure trends; longitudinal analysis. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 27
C 1 – Cost of Electronic Full-Text Journals Ø Definition – expenditures for electronic full-text journal subscriptions. Include initial purchase cost, membership fees, annual licenses paid directly or as part of consortia. Ø Rationale – indicates expenditures (costs) for ejournals; show increased demand for e-journals – which replace print; can calculate unit cost of e -journal by collecting C 1 & R 1 statistics – measure of effectiveness. Ø Related Issues – use to see expenditure trends; longitudinal analysis. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 27
 C 1 – Cost of Electronic Full-Text Journals Ø Unit of Measure – cost in dollars. Ø Data Source – local data (acquisition report). Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – identify all expenditures to the lowest level – one item; can group by material type, vendor, publisher, subject, fund; parse data to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 28
C 1 – Cost of Electronic Full-Text Journals Ø Unit of Measure – cost in dollars. Ø Data Source – local data (acquisition report). Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – identify all expenditures to the lowest level – one item; can group by material type, vendor, publisher, subject, fund; parse data to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 28
 C 2 – Cost of Electronic Reference Sources Ø Definition – expenditures for electronic reference sources & aggregate services. Include annual access fees & other service costs paid directly to vendor or through consortia arrangements. Ø Rationale – indicates expenditures (costs) for ereference databases; shows shift of budget allocations to electronic databases; can calculate unit cost of database by collecting C 2 & R 2 statistics – measure of effectiveness. Ø Related Issues – use to see expenditure trends; longitudinal analysis. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 29
C 2 – Cost of Electronic Reference Sources Ø Definition – expenditures for electronic reference sources & aggregate services. Include annual access fees & other service costs paid directly to vendor or through consortia arrangements. Ø Rationale – indicates expenditures (costs) for ereference databases; shows shift of budget allocations to electronic databases; can calculate unit cost of database by collecting C 2 & R 2 statistics – measure of effectiveness. Ø Related Issues – use to see expenditure trends; longitudinal analysis. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 29
 C 2 – Cost of Electronic Reference Sources Ø Ø Unit of Measure – cost in dollars. Data Source – local data (acquisition report). Frequency – annually. Process – definition of electronic ref resource see R 2. Can group by individual title, vendor, publisher, subject, fund; parse data to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 30
C 2 – Cost of Electronic Reference Sources Ø Ø Unit of Measure – cost in dollars. Data Source – local data (acquisition report). Frequency – annually. Process – definition of electronic ref resource see R 2. Can group by individual title, vendor, publisher, subject, fund; parse data to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 30
 C 3 – Cost of Electronic Books Ø Definition – expenditures for electronic full-text monographs. Include annual purchase costs & membership fees, annual access & service fees paid directly to vendor or through consortia arrangements. Ø Rationale – indicates expenditures (costs) for e -books; show shift of budget allocations to electronic resources – which replace print; can calculate unit cost of e-book by collecting C 3 & R 3 statistics – measure of effectiveness. Ø Related Issues – still in flux; use to see expenditure trends; longitudinal analysis. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 31
C 3 – Cost of Electronic Books Ø Definition – expenditures for electronic full-text monographs. Include annual purchase costs & membership fees, annual access & service fees paid directly to vendor or through consortia arrangements. Ø Rationale – indicates expenditures (costs) for e -books; show shift of budget allocations to electronic resources – which replace print; can calculate unit cost of e-book by collecting C 3 & R 3 statistics – measure of effectiveness. Ø Related Issues – still in flux; use to see expenditure trends; longitudinal analysis. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 31
 C 3 – Cost of Electronic Books Ø Unit of Measure – cost in dollars. Ø Data Source – local data (acquisition report). Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – definition of electronic books see R 3. Can group by individual title, vendor, publisher, subject, fund; parse data to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 32
C 3 – Cost of Electronic Books Ø Unit of Measure – cost in dollars. Ø Data Source – local data (acquisition report). Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – definition of electronic books see R 3. Can group by individual title, vendor, publisher, subject, fund; parse data to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 32
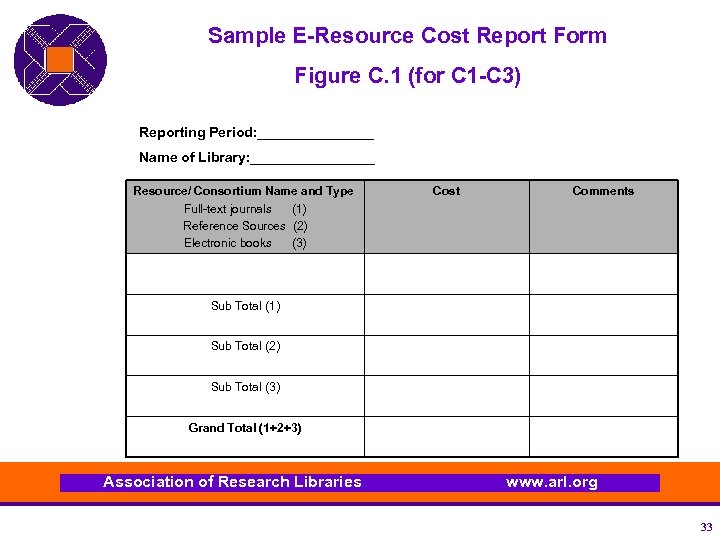 Sample E-Resource Cost Report Form Figure C. 1 (for C 1 -C 3) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Resource/ Consortium Name and Type Full-text journals (1) Reference Sources (2) Electronic books (3) Cost Comments Sub Total (1) Sub Total (2) Sub Total (3) Grand Total (1+2+3) Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 33
Sample E-Resource Cost Report Form Figure C. 1 (for C 1 -C 3) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Resource/ Consortium Name and Type Full-text journals (1) Reference Sources (2) Electronic books (3) Cost Comments Sub Total (1) Sub Total (2) Sub Total (3) Grand Total (1+2+3) Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 33
 C 4 – Library Expenditures for Bibliographic Utilities, Networks & Consortia Ø Definition – expenditures for services provided by national, regional & local bibliographic utilities, networks, & consortia (OCLC, RLG); exclude fees paid for client database access which should be reported in C 1 through C 3. Ø Rationale – opportunity for benchmarking by file size; shows in-house digitizing effort. Shows extent of digital library projects, resource & “virtual storage” requirements. Ø Related Issues – each digital collection is unique; important to use appropriate units of measure to describe overall size & extensiveness of collection. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 34
C 4 – Library Expenditures for Bibliographic Utilities, Networks & Consortia Ø Definition – expenditures for services provided by national, regional & local bibliographic utilities, networks, & consortia (OCLC, RLG); exclude fees paid for client database access which should be reported in C 1 through C 3. Ø Rationale – opportunity for benchmarking by file size; shows in-house digitizing effort. Shows extent of digital library projects, resource & “virtual storage” requirements. Ø Related Issues – each digital collection is unique; important to use appropriate units of measure to describe overall size & extensiveness of collection. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 34
 C 4 – Library Expenditures for Bibliographic Utilities, Networks & Consortia Ø Unit of Measure – cost in dollars. Ø Data Source – local data (acquisition report). Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – data from acquisitions system; parse data to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Sample; parse data to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 35
C 4 – Library Expenditures for Bibliographic Utilities, Networks & Consortia Ø Unit of Measure – cost in dollars. Ø Data Source – local data (acquisition report). Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – data from acquisitions system; parse data to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Sample; parse data to an in-house spreadsheet or database. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 35
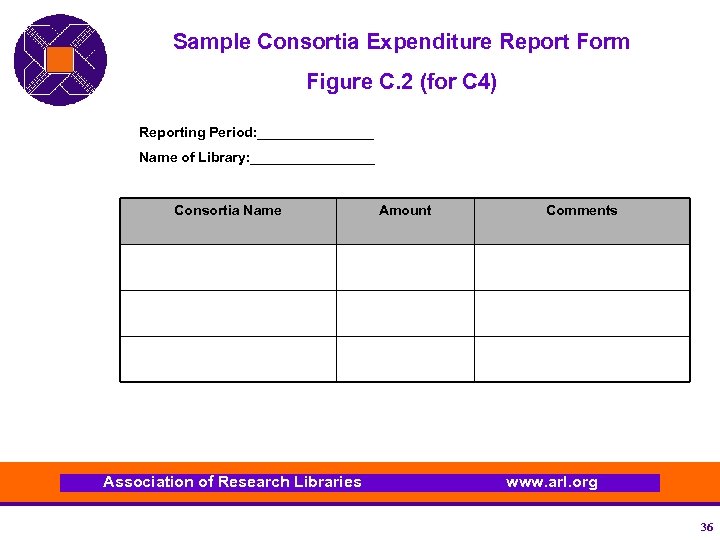 Sample Consortia Expenditure Report Form Figure C. 2 (for C 4) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Consortia Name Association of Research Libraries Amount Comments www. arl. org 36
Sample Consortia Expenditure Report Form Figure C. 2 (for C 4) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Consortia Name Association of Research Libraries Amount Comments www. arl. org 36
 C 5 – External Expenditures for Bibliographic Utilities, Networks & Consortia Ø Definition – expenditures paid by external agencies, on the library’s behalf, for access to computer files, e-journals or search services through a centrally funded system or consortia arrangements. (Examples – VIVA (Virginia), CNSLP (Canada), U-Cal California Digital Library Expenditures). Ø Rationale – based on the ARL Supplementary Statistics. Estimate of external costs that may become expenditures eventually when funds run out. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 37
C 5 – External Expenditures for Bibliographic Utilities, Networks & Consortia Ø Definition – expenditures paid by external agencies, on the library’s behalf, for access to computer files, e-journals or search services through a centrally funded system or consortia arrangements. (Examples – VIVA (Virginia), CNSLP (Canada), U-Cal California Digital Library Expenditures). Ø Rationale – based on the ARL Supplementary Statistics. Estimate of external costs that may become expenditures eventually when funds run out. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 37
 C 5 – External Expenditures for Bibliographic Utilities, Networks & Consortia Ø Unit of Measure – cost in dollars. Ø Data Source – local data (acquisition report). Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – data from acquisitions system or collections office or find out which part of the funding is attributed to local library; create an in-house spreadsheet or database. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 38
C 5 – External Expenditures for Bibliographic Utilities, Networks & Consortia Ø Unit of Measure – cost in dollars. Ø Data Source – local data (acquisition report). Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – data from acquisitions system or collections office or find out which part of the funding is attributed to local library; create an in-house spreadsheet or database. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 38
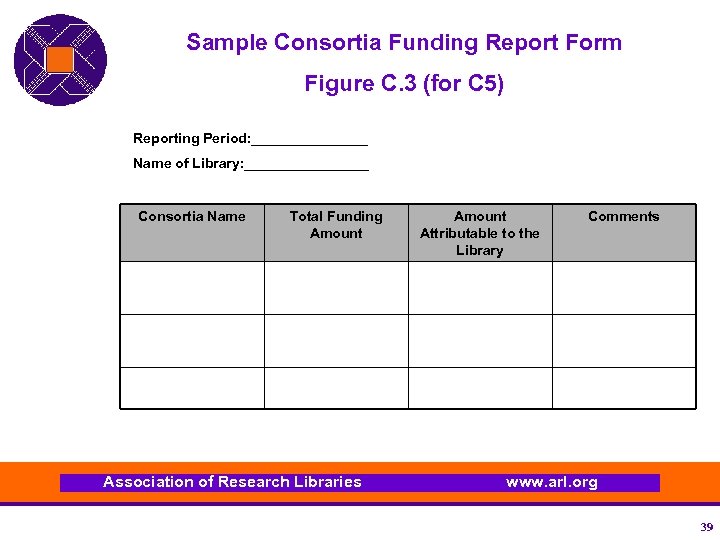 Sample Consortia Funding Report Form Figure C. 3 (for C 5) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Consortia Name Total Funding Amount Association of Research Libraries Amount Attributable to the Library Comments www. arl. org 39
Sample Consortia Funding Report Form Figure C. 3 (for C 5) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Consortia Name Total Funding Amount Association of Research Libraries Amount Attributable to the Library Comments www. arl. org 39
 Library Digitization Activities Ø D 1 – Size of library digital collection Ø D 2 – Use of library digital collection Ø D 3 – Cost of digital collection construction & management (Collecting these data requires staff familiar with the digital environment. ) Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 40
Library Digitization Activities Ø D 1 – Size of library digital collection Ø D 2 – Use of library digital collection Ø D 3 – Cost of digital collection construction & management (Collecting these data requires staff familiar with the digital environment. ) Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 40
 D 1 – Size of Library Digital Collection Ø Definition – digital materials created or converted by the library & made available electronically. Includes e-theses, special collections, maps, sound recordings, films – not purchased. Ø Rationale – Collecting library digitization measures may provide an opportunity for benchmarking in terms of file sizes for the resources that have been digitized. Moreover, the statistic can demonstrate that libraries are not merely brokers of external information resources, but also producers of information content and useful finding aids. This statistic provides information on the extent of digital library projects, the life cycle of such projects, and the "virtual space" requirements of such collections. Ø Related Issues – use to see expenditure trends; longitudinal analysis. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 41
D 1 – Size of Library Digital Collection Ø Definition – digital materials created or converted by the library & made available electronically. Includes e-theses, special collections, maps, sound recordings, films – not purchased. Ø Rationale – Collecting library digitization measures may provide an opportunity for benchmarking in terms of file sizes for the resources that have been digitized. Moreover, the statistic can demonstrate that libraries are not merely brokers of external information resources, but also producers of information content and useful finding aids. This statistic provides information on the extent of digital library projects, the life cycle of such projects, and the "virtual space" requirements of such collections. Ø Related Issues – use to see expenditure trends; longitudinal analysis. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 41
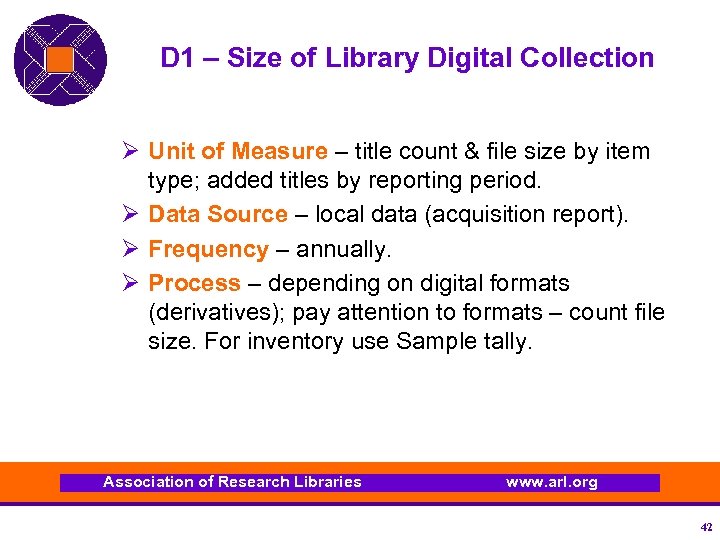 D 1 – Size of Library Digital Collection Ø Unit of Measure – title count & file size by item type; added titles by reporting period. Ø Data Source – local data (acquisition report). Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – depending on digital formats (derivatives); pay attention to formats – count file size. For inventory use Sample tally. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 42
D 1 – Size of Library Digital Collection Ø Unit of Measure – title count & file size by item type; added titles by reporting period. Ø Data Source – local data (acquisition report). Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – depending on digital formats (derivatives); pay attention to formats – count file size. For inventory use Sample tally. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 42
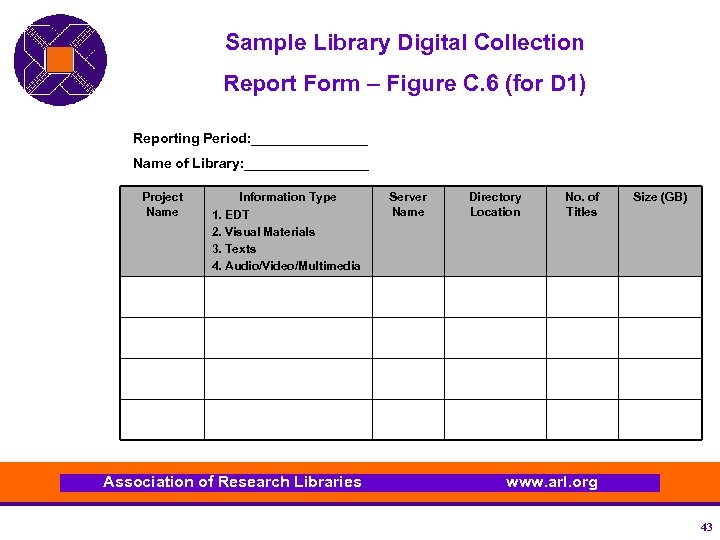 Sample Library Digital Collection Report Form – Figure C. 6 (for D 1) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Project Name Information Type 1. EDT 2. Visual Materials 3. Texts 4. Audio/Video/Multimedia Association of Research Libraries Server Name Directory Location No. of Titles Size (GB) www. arl. org 43
Sample Library Digital Collection Report Form – Figure C. 6 (for D 1) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Project Name Information Type 1. EDT 2. Visual Materials 3. Texts 4. Audio/Video/Multimedia Association of Research Libraries Server Name Directory Location No. of Titles Size (GB) www. arl. org 43
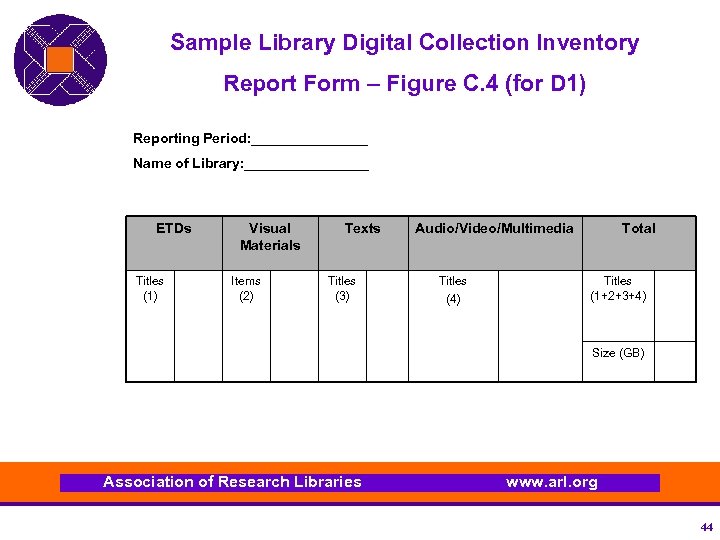 Sample Library Digital Collection Inventory Report Form – Figure C. 4 (for D 1) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ ETDs Titles (1) Visual Materials Items (2) Texts Titles (3) Audio/Video/Multimedia Titles (4) Total Titles (1+2+3+4) Size (GB) Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 44
Sample Library Digital Collection Inventory Report Form – Figure C. 4 (for D 1) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ ETDs Titles (1) Visual Materials Items (2) Texts Titles (3) Audio/Video/Multimedia Titles (4) Total Titles (1+2+3+4) Size (GB) Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 44
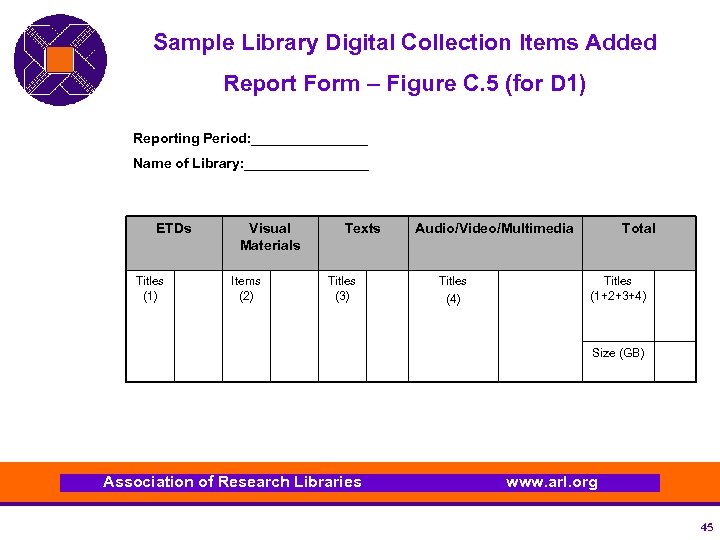 Sample Library Digital Collection Items Added Report Form – Figure C. 5 (for D 1) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ ETDs Titles (1) Visual Materials Items (2) Texts Titles (3) Audio/Video/Multimedia Titles (4) Total Titles (1+2+3+4) Size (GB) Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 45
Sample Library Digital Collection Items Added Report Form – Figure C. 5 (for D 1) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ ETDs Titles (1) Visual Materials Items (2) Texts Titles (3) Audio/Video/Multimedia Titles (4) Total Titles (1+2+3+4) Size (GB) Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 45
 D 2 – Use of Library Digital Collection Ø Definition – number of times digital collection titles and files are accessed; number of searches conducted during reporting period. Ø Rationale – as these collections are unique, the information is used locally. May show quality of local service. Ø Related Issues – exclude accesses by Web search spiders if possible. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 46
D 2 – Use of Library Digital Collection Ø Definition – number of times digital collection titles and files are accessed; number of searches conducted during reporting period. Ø Rationale – as these collections are unique, the information is used locally. May show quality of local service. Ø Related Issues – exclude accesses by Web search spiders if possible. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 46
 D 2 – Use of Library Digital Collection Ø Unit of Measure – title access count; search count. Ø Data Source – local data (OPAC or unique database). Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – analyze Web logs and data provided by the software. May need knowledge of SQL. May collect physical file access count only to save time. May install special Web traffic analysis software (Web. Trends). May collect only sample data & extrapolate. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 47
D 2 – Use of Library Digital Collection Ø Unit of Measure – title access count; search count. Ø Data Source – local data (OPAC or unique database). Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – analyze Web logs and data provided by the software. May need knowledge of SQL. May collect physical file access count only to save time. May install special Web traffic analysis software (Web. Trends). May collect only sample data & extrapolate. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 47
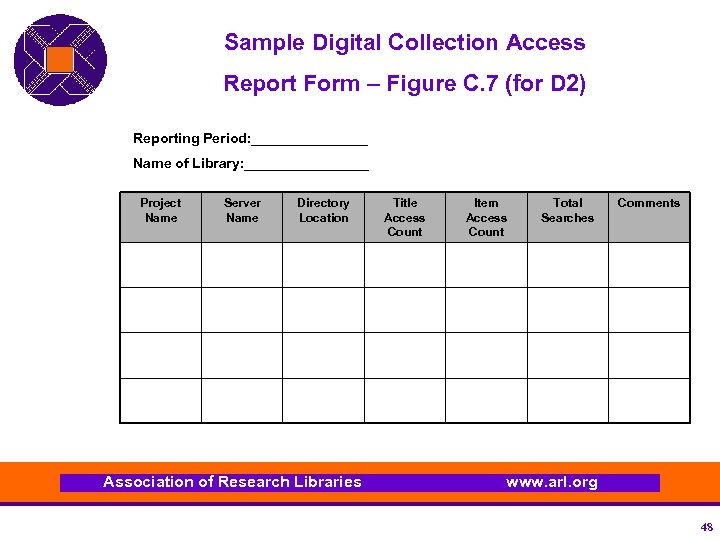 Sample Digital Collection Access Report Form – Figure C. 7 (for D 2) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Project Name Server Name Directory Location Association of Research Libraries Title Access Count Item Access Count Total Searches Comments www. arl. org 48
Sample Digital Collection Access Report Form – Figure C. 7 (for D 2) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Project Name Server Name Directory Location Association of Research Libraries Title Access Count Item Access Count Total Searches Comments www. arl. org 48
 D 3 – Cost of Digital Collection Construction and Management Ø Definition – direct costs (personnel, equipment, software, contracted services) to create digital materials or to convert; include expenditures related to digitization, OCR, any creation, preparation, data storage & copyright clearance; exclude costs for resources purchased externally. Ø Rationale – as these collections are unique, the information is used locally – may show quality of local service. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 49
D 3 – Cost of Digital Collection Construction and Management Ø Definition – direct costs (personnel, equipment, software, contracted services) to create digital materials or to convert; include expenditures related to digitization, OCR, any creation, preparation, data storage & copyright clearance; exclude costs for resources purchased externally. Ø Rationale – as these collections are unique, the information is used locally – may show quality of local service. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 49
 D 3 – Cost of Digital Collection Construction and Management Ø Unit of Measure – all costs – see above. Ø Data Source – local data (acquisition or project office); salaries – from accounting or personnel department. Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – all staff involved in the digital initiative fill out worksheet. For reporting period; estimate time spent doing work – capture as FTE. Breakdown of activity may be very detailed; salary information calculated & added; cost of equipment amortized. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 50
D 3 – Cost of Digital Collection Construction and Management Ø Unit of Measure – all costs – see above. Ø Data Source – local data (acquisition or project office); salaries – from accounting or personnel department. Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – all staff involved in the digital initiative fill out worksheet. For reporting period; estimate time spent doing work – capture as FTE. Breakdown of activity may be very detailed; salary information calculated & added; cost of equipment amortized. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 50
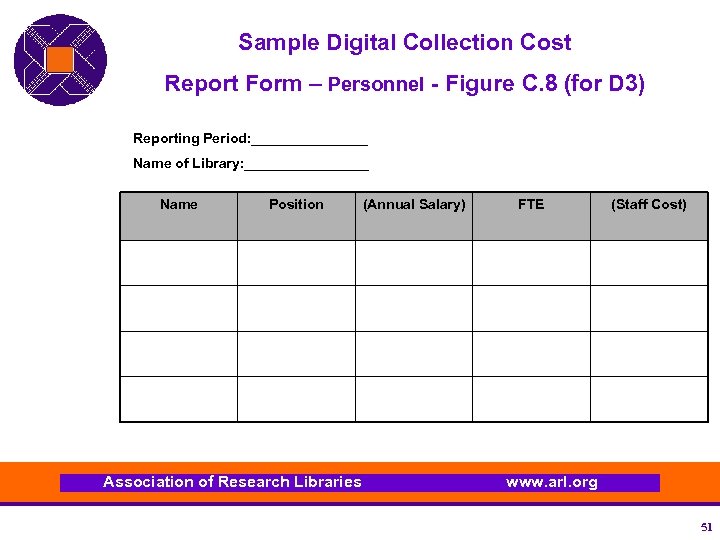 Sample Digital Collection Cost Report Form – Personnel - Figure C. 8 (for D 3) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Name Position Association of Research Libraries (Annual Salary) FTE (Staff Cost) www. arl. org 51
Sample Digital Collection Cost Report Form – Personnel - Figure C. 8 (for D 3) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Name Position Association of Research Libraries (Annual Salary) FTE (Staff Cost) www. arl. org 51
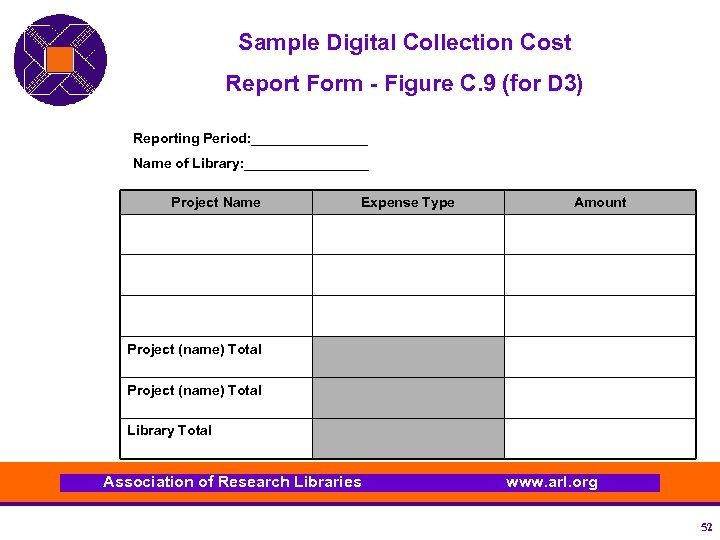 Sample Digital Collection Cost Report Form - Figure C. 9 (for D 3) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Project Name Expense Type Amount Project (name) Total Library Total Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 52
Sample Digital Collection Cost Report Form - Figure C. 9 (for D 3) Reporting Period: ________ Name of Library: ________ Project Name Expense Type Amount Project (name) Total Library Total Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 52
 Performance Measures Ø P 1 – Percentage of electronic reference transactions of total reference Ø P 2 – Percentage of virtual visits of all library visits Ø P 3 – Percentage of electronic books to all monographs Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 53
Performance Measures Ø P 1 – Percentage of electronic reference transactions of total reference Ø P 2 – Percentage of virtual visits of all library visits Ø P 3 – Percentage of electronic books to all monographs Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 53
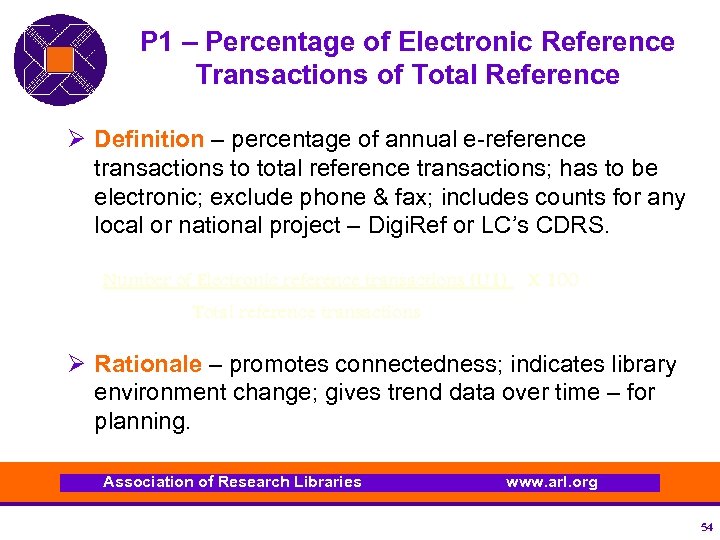 P 1 – Percentage of Electronic Reference Transactions of Total Reference Ø Definition – percentage of annual e-reference transactions to total reference transactions; has to be electronic; exclude phone & fax; includes counts for any local or national project – Digi. Ref or LC’s CDRS. Number of Electronic reference transactions (U 1) X 100 Total reference transactions Ø Rationale – promotes connectedness; indicates library environment change; gives trend data over time – for planning. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 54
P 1 – Percentage of Electronic Reference Transactions of Total Reference Ø Definition – percentage of annual e-reference transactions to total reference transactions; has to be electronic; exclude phone & fax; includes counts for any local or national project – Digi. Ref or LC’s CDRS. Number of Electronic reference transactions (U 1) X 100 Total reference transactions Ø Rationale – promotes connectedness; indicates library environment change; gives trend data over time – for planning. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 54
 P 1 – Percentage of Electronic Reference Transactions of Total Reference Ø Ø Unit of Measure – transaction counts. Data Source – local data. Frequency – annually. Process – can do sample counts & extrapolate. Use daily tally sheets. For electronic transactions, use counts for procedure U 1. Total all transactions; do the calculation. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 55
P 1 – Percentage of Electronic Reference Transactions of Total Reference Ø Ø Unit of Measure – transaction counts. Data Source – local data. Frequency – annually. Process – can do sample counts & extrapolate. Use daily tally sheets. For electronic transactions, use counts for procedure U 1. Total all transactions; do the calculation. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 55
 P 2 – Percentage of Virtual Visits of All Library Visits Ø Definition – number of virtual library visits out of all library visits. A virtual visit is when a client is visiting the library’s Web site or catalog from outside the physical plant of the library. Exclude use of electronic resources. This measure is an estimate due to management issues. # virtual library visits X 100 total library visits Ø Rationale – external visit shows interest in the library; outside regular hours; show use while physical attendance may decrease. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 56
P 2 – Percentage of Virtual Visits of All Library Visits Ø Definition – number of virtual library visits out of all library visits. A virtual visit is when a client is visiting the library’s Web site or catalog from outside the physical plant of the library. Exclude use of electronic resources. This measure is an estimate due to management issues. # virtual library visits X 100 total library visits Ø Rationale – external visit shows interest in the library; outside regular hours; show use while physical attendance may decrease. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 56
 P 2 – Percentage of Virtual Visits of All Library Visits Ø Unit of Measure – Web visit counts; turnstile counts. Ø Data Source – local data. Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – need Web log analysis software. Follow procedure for U 5; physical attendance count from turnstile counts. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 57
P 2 – Percentage of Virtual Visits of All Library Visits Ø Unit of Measure – Web visit counts; turnstile counts. Ø Data Source – local data. Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – need Web log analysis software. Follow procedure for U 5; physical attendance count from turnstile counts. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 57
 P 3 – Percentage of Electronic Books to All Monographs Ø Definition – percentage of the number of e-books available to all monographs available. Ø Rationale – the measure attempts to document the degree of expansion of e -books to all monographs. This whole area is in flux and will no doubt change. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 58
P 3 – Percentage of Electronic Books to All Monographs Ø Definition – percentage of the number of e-books available to all monographs available. Ø Rationale – the measure attempts to document the degree of expansion of e -books to all monographs. This whole area is in flux and will no doubt change. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 58
 P 3 – Percentage of Electronic Books to All Monographs Ø Unit of Measure – e-book item count; monograph item count. Ø Data Source – OPAC data & vendor data. Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – count all monograph items in the catalog or physically; exclude electronic reference books, etc. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 59
P 3 – Percentage of Electronic Books to All Monographs Ø Unit of Measure – e-book item count; monograph item count. Ø Data Source – OPAC data & vendor data. Ø Frequency – annually. Ø Process – count all monograph items in the catalog or physically; exclude electronic reference books, etc. Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 59
 Assessment of E-Metrics is DOABLE!! Ø This is a First Shot – Give it a Try ! Ø We Learn Only by Doing ! Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 60
Assessment of E-Metrics is DOABLE!! Ø This is a First Shot – Give it a Try ! Ø We Learn Only by Doing ! Association of Research Libraries www. arl. org 60


