5fca939b79aaeec17f52cc8aa959c10e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Area scaling from entanglement in flat space quantum field theory • Introduction • Area scaling of quantum fluctuations • Unruh radiation and Holography
Area scaling from entanglement in flat space quantum field theory • Introduction • Area scaling of quantum fluctuations • Unruh radiation and Holography
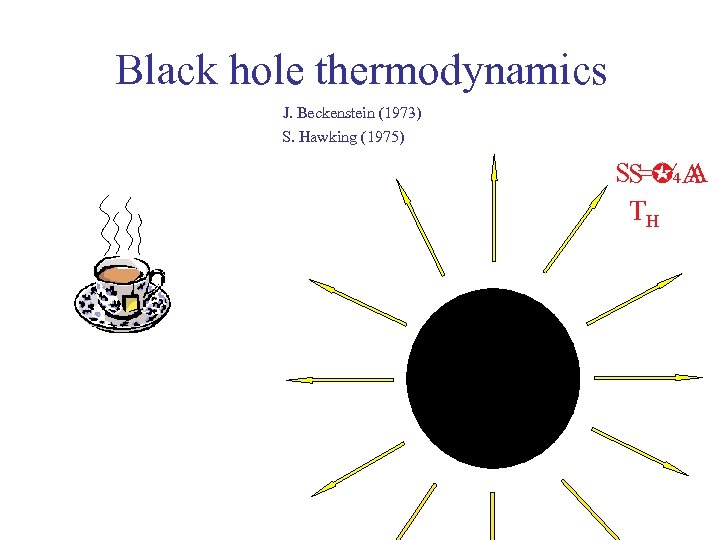 Black hole thermodynamics J. Beckenstein (1973) S. Hawking (1975) SS A =¼A TH
Black hole thermodynamics J. Beckenstein (1973) S. Hawking (1975) SS A =¼A TH
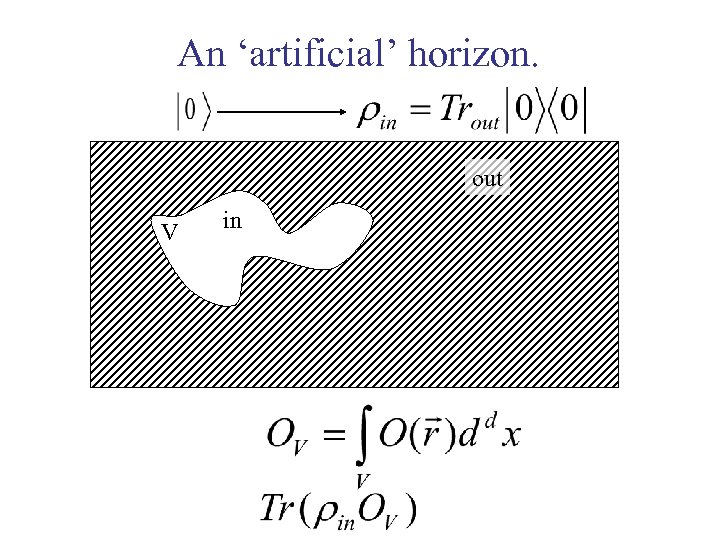 An ‘artificial’ horizon. out V in
An ‘artificial’ horizon. out V in
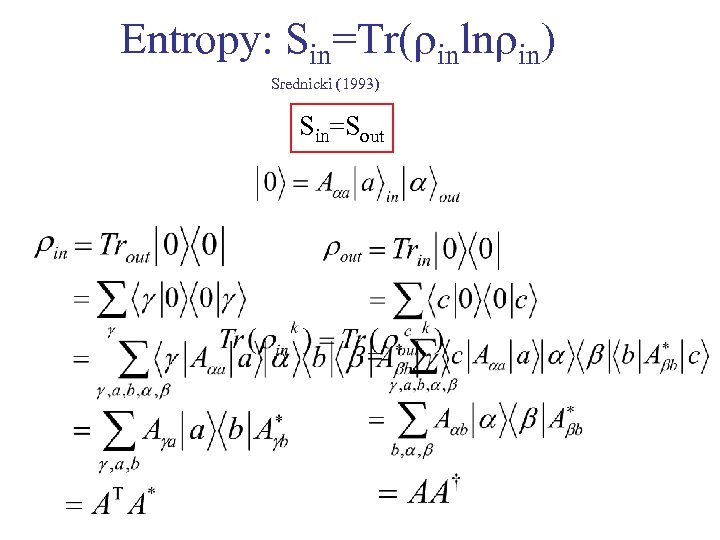 Entropy: Sin=Tr( inln in) Srednicki (1993) Sin=Sout
Entropy: Sin=Tr( inln in) Srednicki (1993) Sin=Sout
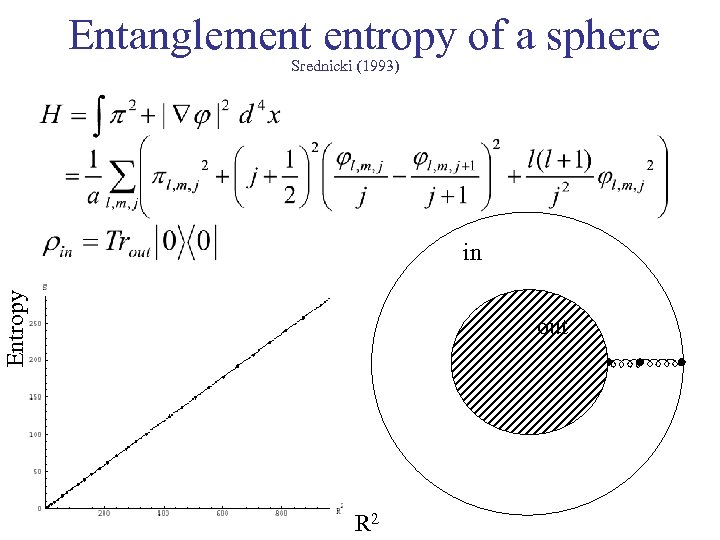 Entanglement entropy of a sphere Srednicki (1993) Entropy in out R 2
Entanglement entropy of a sphere Srednicki (1993) Entropy in out R 2
 Other Thermodynamic quantities Heat capacity: More generally: ? A
Other Thermodynamic quantities Heat capacity: More generally: ? A
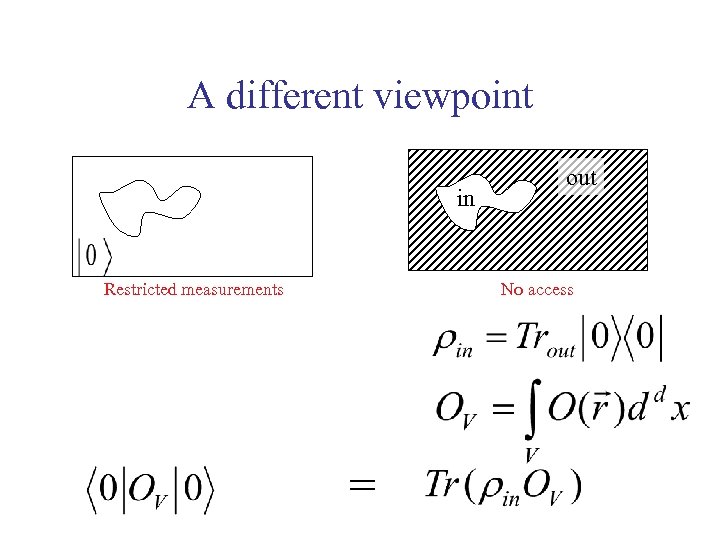 A different viewpoint in Restricted measurements out No access =
A different viewpoint in Restricted measurements out No access =
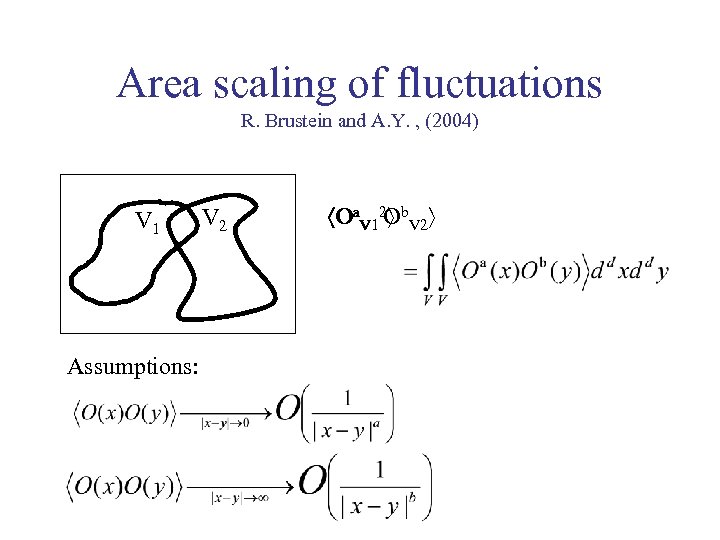 Area scaling of fluctuations R. Brustein and A. Y. , (2004) V 1 Assumptions: V 2 Oa. V 12 Ob. V 2
Area scaling of fluctuations R. Brustein and A. Y. , (2004) V 1 Assumptions: V 2 Oa. V 12 Ob. V 2
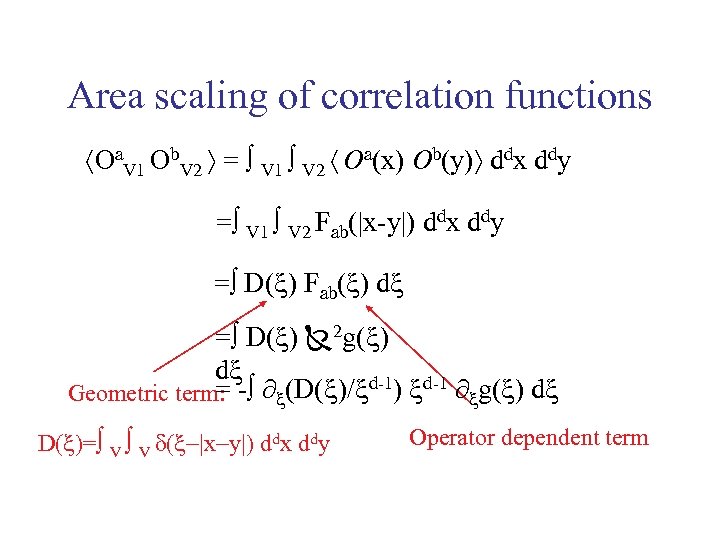 Area scaling of correlation functions Oa. V 1 Ob. V 2 = V 1 V 2 Oa(x) Ob(y) ddx ddy = V 1 V 2 Fab(|x-y|) ddx ddy = D( ) Fab( ) d = D( ) 2 g( ) d d-1 = Geometric term: - ∂ (D( )/ ) ∂ g( ) d D( )= V V d( x y ) ddx ddy Operator dependent term
Area scaling of correlation functions Oa. V 1 Ob. V 2 = V 1 V 2 Oa(x) Ob(y) ddx ddy = V 1 V 2 Fab(|x-y|) ddx ddy = D( ) Fab( ) d = D( ) 2 g( ) d d-1 = Geometric term: - ∂ (D( )/ ) ∂ g( ) d D( )= V V d( x y ) ddx ddy Operator dependent term
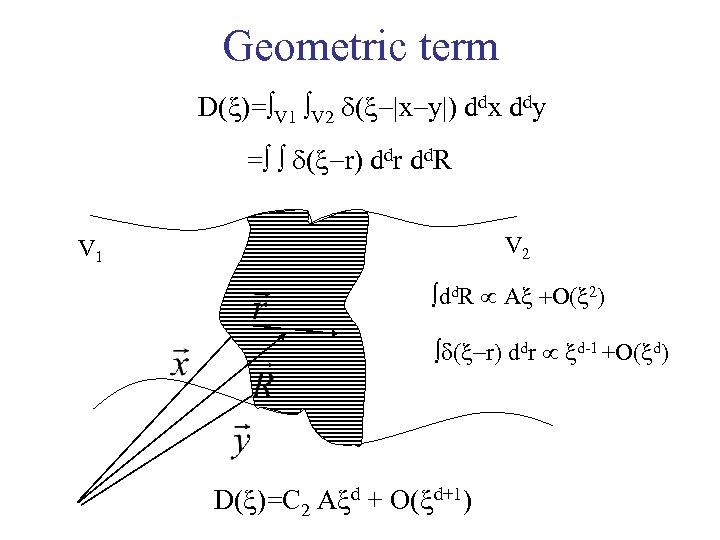 Geometric term D( )= V 1 V 2 d( x y ) ddx ddy = d( r) ddr dd. R V 2 V 1 dd. R A +O 2) d( r) ddr d-1 +O( d) D( )=C 2 A d + O( d+1)
Geometric term D( )= V 1 V 2 d( x y ) ddx ddy = d( r) ddr dd. R V 2 V 1 dd. R A +O 2) d( r) ddr d-1 +O( d) D( )=C 2 A d + O( d+1)
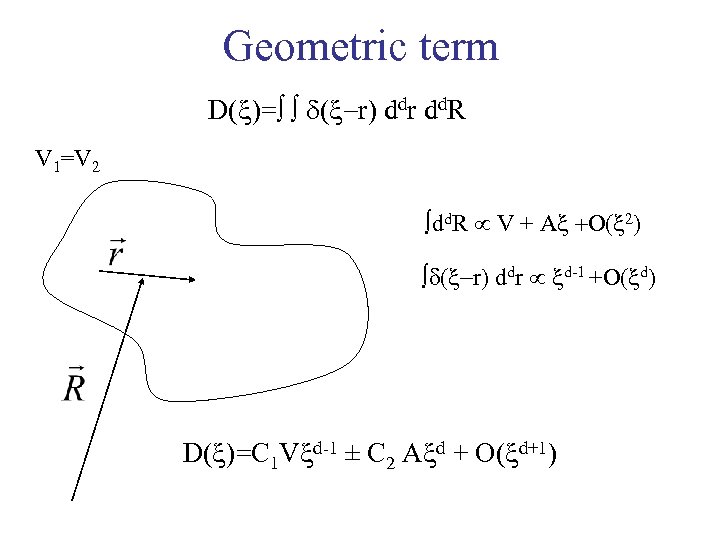 Geometric term D( )= d( r) ddr dd. R V 1=V 2 dd. R V + A +O 2) d( r) ddr d-1 +O( d) D( )=C 1 V d-1 ± C 2 A d + O( d+1)
Geometric term D( )= d( r) ddr dd. R V 1=V 2 dd. R V + A +O 2) d( r) ddr d-1 +O( d) D( )=C 1 V d-1 ± C 2 A d + O( d+1)
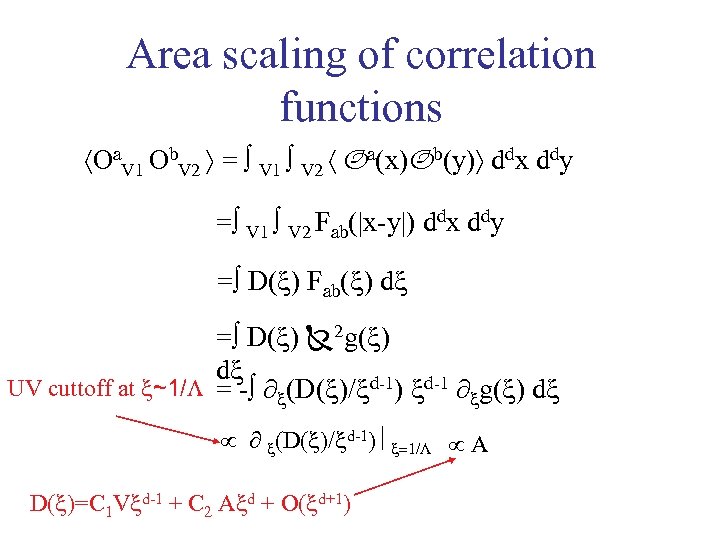 Area scaling of correlation functions Oa. V 1 Ob. V 2 = V 1 V 2 Oa(x)Ob(y) ddx ddy = V 1 V 2 Fab(|x-y|) ddx ddy = D( ) Fab( ) d = D( ) 2 g( ) d UV cuttoff at ~1/L = - ∂ (D( )/ d-1) d-1 ∂ g( ) d ∂ (D( )/ d-1) 1/L A D( )=C 1 V d-1 + C 2 A d + O( d+1)
Area scaling of correlation functions Oa. V 1 Ob. V 2 = V 1 V 2 Oa(x)Ob(y) ddx ddy = V 1 V 2 Fab(|x-y|) ddx ddy = D( ) Fab( ) d = D( ) 2 g( ) d UV cuttoff at ~1/L = - ∂ (D( )/ d-1) d-1 ∂ g( ) d ∂ (D( )/ d-1) 1/L A D( )=C 1 V d-1 + C 2 A d + O( d+1)
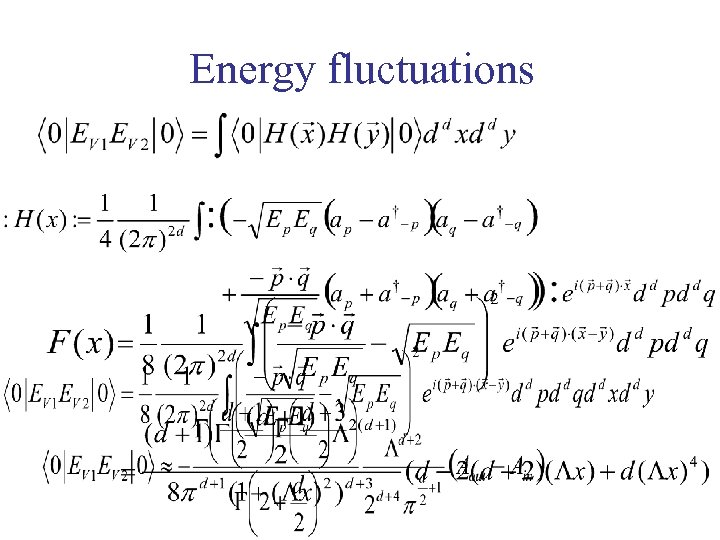 Energy fluctuations
Energy fluctuations
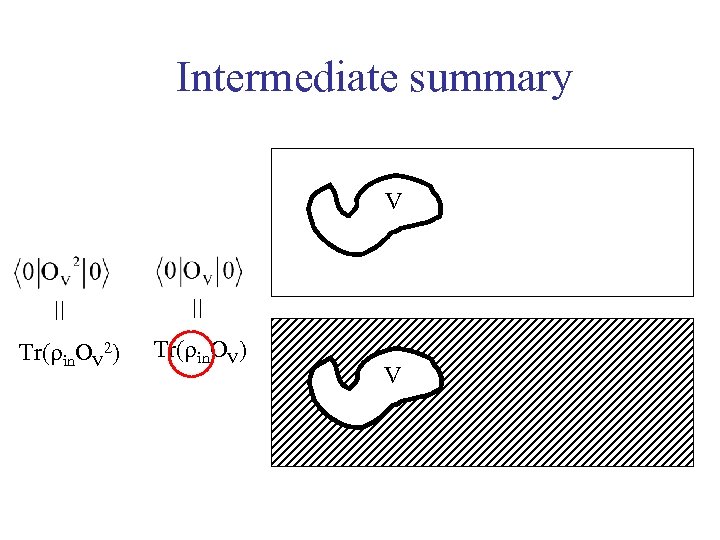 Intermediate summary V Tr( in. OV 2) Tr( in. OV) V
Intermediate summary V Tr( in. OV 2) Tr( in. OV) V
![Finding in in( ’in, ’’in) = Trout ( ’ ’’ Exp[-SE] Df D out Finding in in( ’in, ’’in) = Trout ( ’ ’’ Exp[-SE] Df D out](https://present5.com/presentation/5fca939b79aaeec17f52cc8aa959c10e/image-15.jpg) Finding in in( ’in, ’’in) = Trout ( ’ ’’ Exp[-SE] Df D out +)= ’(x) f(x, 0)= (x) t f(x, 0 -)= ’’(x) f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) out(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x) out(x) ’in(x) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df ’(x) ’’(x) x ’’in(x) f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x)
Finding in in( ’in, ’’in) = Trout ( ’ ’’ Exp[-SE] Df D out +)= ’(x) f(x, 0)= (x) t f(x, 0 -)= ’’(x) f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) out(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x) out(x) ’in(x) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df ’(x) ’’(x) x ’’in(x) f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x)
![Finding rho Kabbat & Strassler (1994) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df ’| e-b. K| ’’ Finding rho Kabbat & Strassler (1994) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df ’| e-b. K| ’’](https://present5.com/presentation/5fca939b79aaeec17f52cc8aa959c10e/image-16.jpg) Finding rho Kabbat & Strassler (1994) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df ’| e-b. K| ’’ f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x) t ’in(x) x ’’in(x)
Finding rho Kabbat & Strassler (1994) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df ’| e-b. K| ’’ f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x) t ’in(x) x ’’in(x)
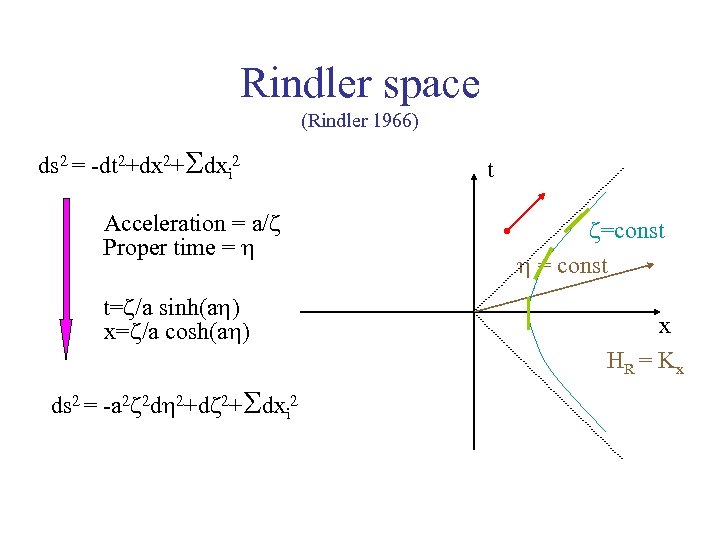 Rindler space (Rindler 1966) ds 2 = -dt 2+dx 2+Sdxi 2 Acceleration = a/ Proper time = t= /a sinh(a ) x= /a cosh(a ) ds 2 = -a 2 2 d 2+Sdxi 2 t =const = const x HR = Kx
Rindler space (Rindler 1966) ds 2 = -dt 2+dx 2+Sdxi 2 Acceleration = a/ Proper time = t= /a sinh(a ) x= /a cosh(a ) ds 2 = -a 2 2 d 2+Sdxi 2 t =const = const x HR = Kx
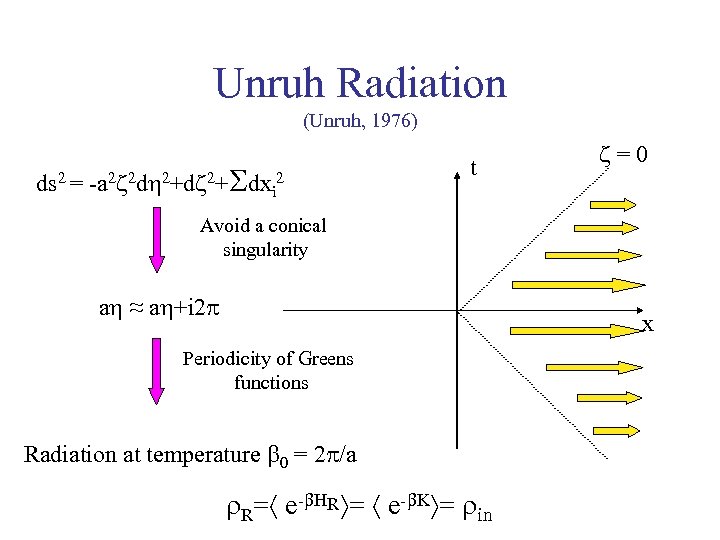 Unruh Radiation (Unruh, 1976) ds 2 = -a 2 2 d 2+Sdxi 2 t = 0 Avoid a conical singularity a ≈ a +i 2 p x Periodicity of Greens functions Radiation at temperature b 0 = 2 p/a R= e-b. HR = e-b. K = in
Unruh Radiation (Unruh, 1976) ds 2 = -a 2 2 d 2+Sdxi 2 t = 0 Avoid a conical singularity a ≈ a +i 2 p x Periodicity of Greens functions Radiation at temperature b 0 = 2 p/a R= e-b. HR = e-b. K = in
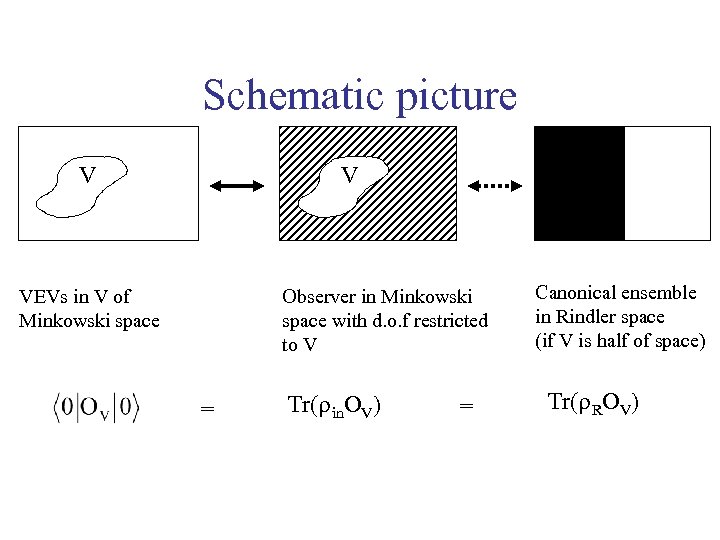 Schematic picture V V VEVs in V of Minkowski space Observer in Minkowski space with d. o. f restricted to V = Tr( in. OV) = Canonical ensemble in Rindler space (if V is half of space) Tr( ROV)
Schematic picture V V VEVs in V of Minkowski space Observer in Minkowski space with d. o. f restricted to V = Tr( in. OV) = Canonical ensemble in Rindler space (if V is half of space) Tr( ROV)
![Other shapes R. Brustein and A. Y. , (2003) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df b= Other shapes R. Brustein and A. Y. , (2003) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df b=](https://present5.com/presentation/5fca939b79aaeec17f52cc8aa959c10e/image-20.jpg) Other shapes R. Brustein and A. Y. , (2003) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df b= ’in|e-b. H 0| ’’out f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x) d/dt H 0 = 0 SE = 0 b. H 0 dt (x, t), +B. C. H 0=K, in={x|x>0} t ’in(x) x ’’in(x)
Other shapes R. Brustein and A. Y. , (2003) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df b= ’in|e-b. H 0| ’’out f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x) d/dt H 0 = 0 SE = 0 b. H 0 dt (x, t), +B. C. H 0=K, in={x|x>0} t ’in(x) x ’’in(x)
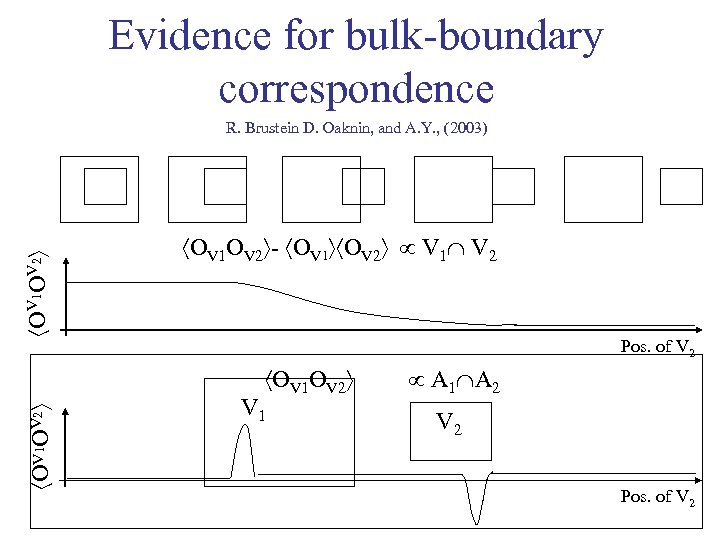 Evidence for bulk-boundary correspondence OV 1 OV 2 R. Brustein D. Oaknin, and A. Y. , (2003) OV 1 OV 2 - OV 1 OV 2 V 1 V 2 Pos. of V 2 OV 1 OV 2 V 1 A 1 A 2 V 2 Pos. of V 2
Evidence for bulk-boundary correspondence OV 1 OV 2 R. Brustein D. Oaknin, and A. Y. , (2003) OV 1 OV 2 - OV 1 OV 2 V 1 V 2 Pos. of V 2 OV 1 OV 2 V 1 A 1 A 2 V 2 Pos. of V 2
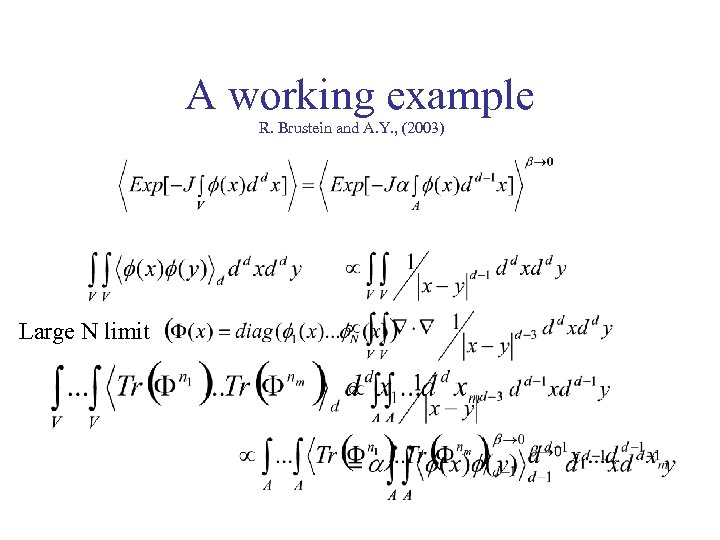 A working example R. Brustein and A. Y. , (2003) Large N limit
A working example R. Brustein and A. Y. , (2003) Large N limit
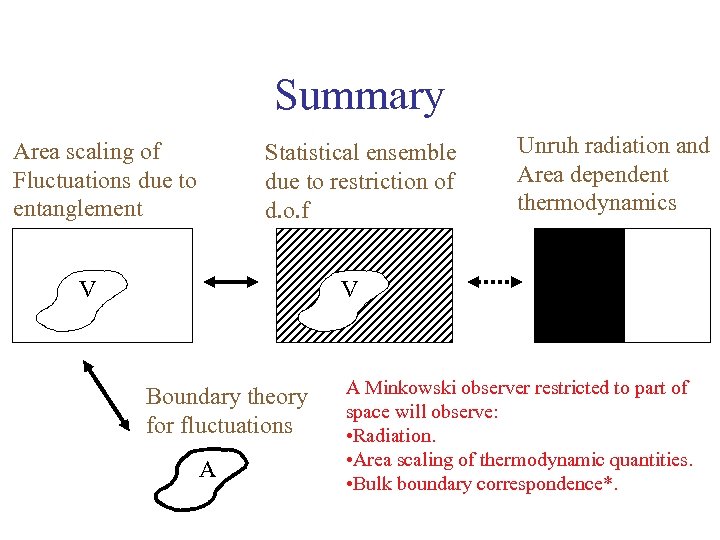 Summary Area scaling of Fluctuations due to entanglement Statistical ensemble due to restriction of d. o. f V Unruh radiation and Area dependent thermodynamics V Boundary theory for fluctuations A A Minkowski observer restricted to part of space will observe: • Radiation. • Area scaling of thermodynamic quantities. • Bulk boundary correspondence*.
Summary Area scaling of Fluctuations due to entanglement Statistical ensemble due to restriction of d. o. f V Unruh radiation and Area dependent thermodynamics V Boundary theory for fluctuations A A Minkowski observer restricted to part of space will observe: • Radiation. • Area scaling of thermodynamic quantities. • Bulk boundary correspondence*.
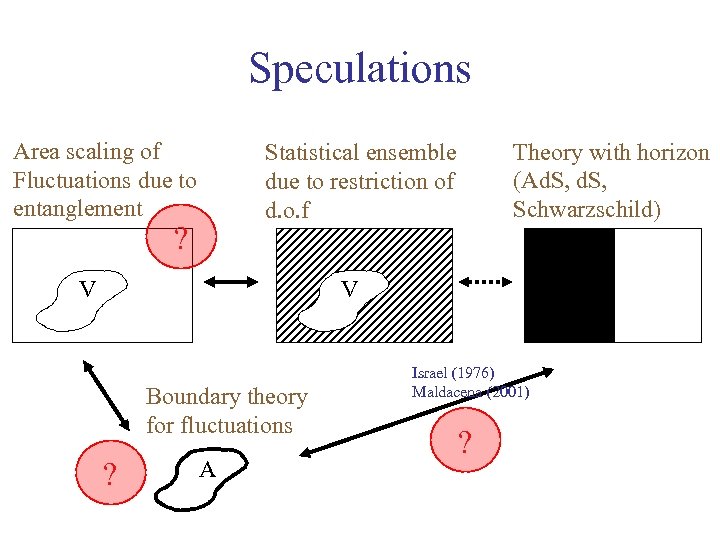 Speculations Area scaling of Fluctuations due to entanglement Theory with horizon (Ad. S, Schwarzschild) Statistical ensemble due to restriction of d. o. f ? V V Boundary theory for fluctuations ? A Israel (1976) Maldacena (2001) ?
Speculations Area scaling of Fluctuations due to entanglement Theory with horizon (Ad. S, Schwarzschild) Statistical ensemble due to restriction of d. o. f ? V V Boundary theory for fluctuations ? A Israel (1976) Maldacena (2001) ?
 Fin
Fin


