0c43449af014eb1a5eb041ec14bfc246.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Architecture Supported by: The sole responsibility for the content of this presentation lies with the authors. It does not necessarily reflect the opinion of the European Communities. The European Commission is not responsible for any use that may be made of the information contained therein. 1

Architecture Options for Intelligent Building c, green roof f, cooling at night a, good insulation g, controlled ventilation b, enough windows e, good sun protection d, building engineering 2

Architecture Shed Roof the sunny side of the shed roof collects solar energy the shaded side provides cool air for ventilation windows at shaded side provide even and natural illumination without direct sunlight 3
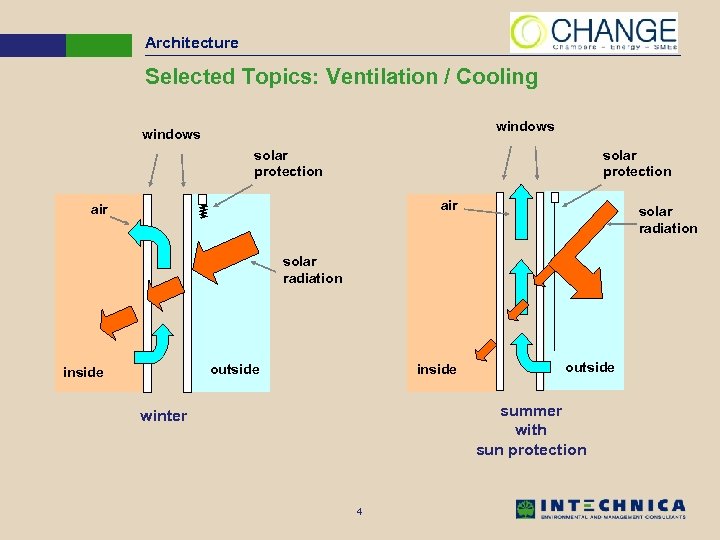
Architecture Selected Topics: Ventilation / Cooling windows solar protection air solar radiation inside outside summer with sun protection winter 4
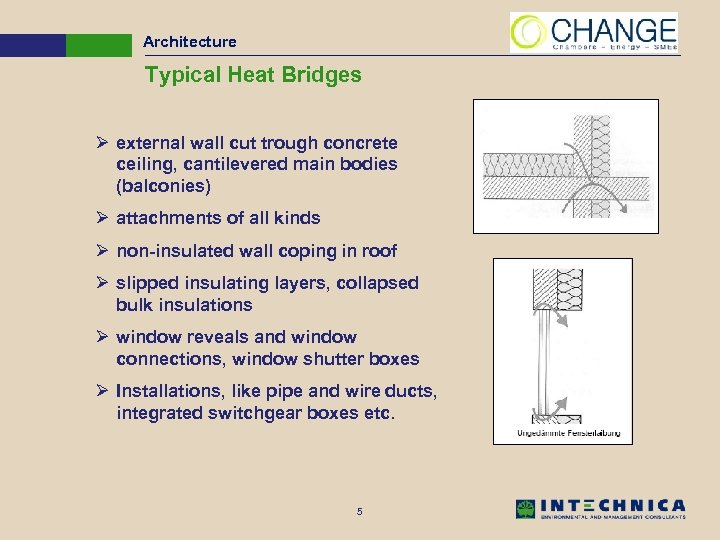
Architecture Typical Heat Bridges Ø external wall cut trough concrete ceiling, cantilevered main bodies (balconies) Ø attachments of all kinds Ø non-insulated wall coping in roof Ø slipped insulating layers, collapsed bulk insulations Ø window reveals and window connections, window shutter boxes Ø Installations, like pipe and wire ducts, integrated switchgear boxes etc. 5
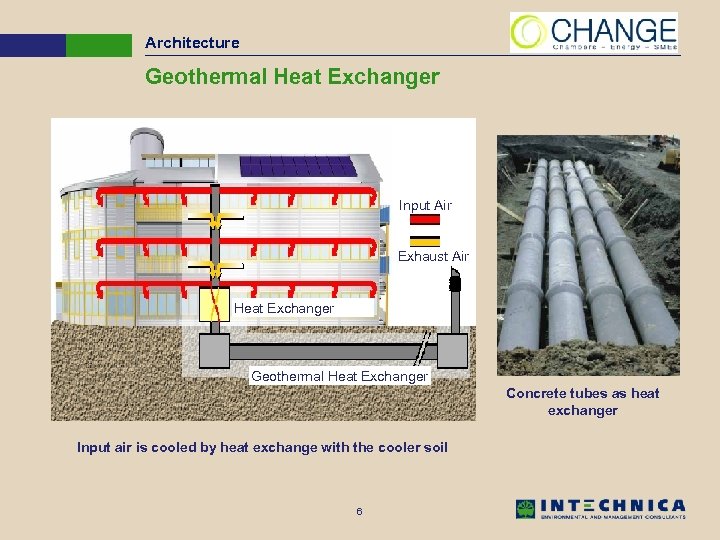
Architecture Geothermal Heat Exchanger Input Air Exhaust Air Heat Exchanger Geothermal Heat Exchanger Concrete tubes as heat exchanger Input air is cooled by heat exchange with the cooler soil 6
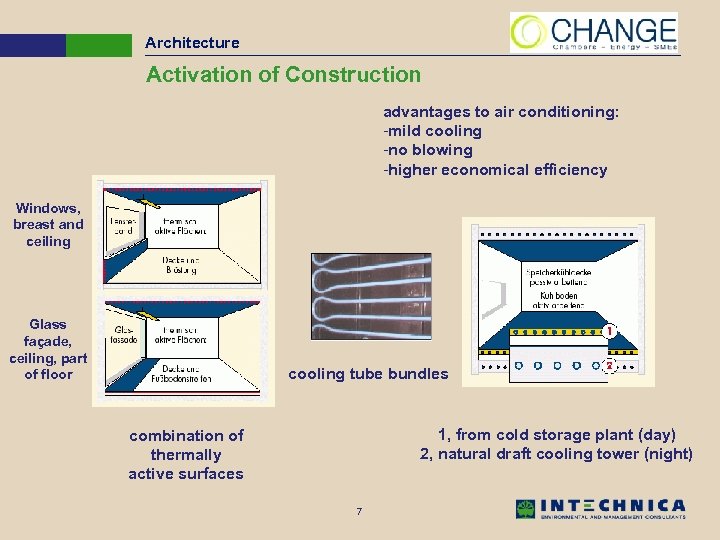
Architecture Activation of Construction advantages to air conditioning: -mild cooling -no blowing -higher economical efficiency Windows, breast and ceiling Glass façade, ceiling, part of floor cooling tube bundles 1, from cold storage plant (day) 2, natural draft cooling tower (night) combination of thermally active surfaces 7
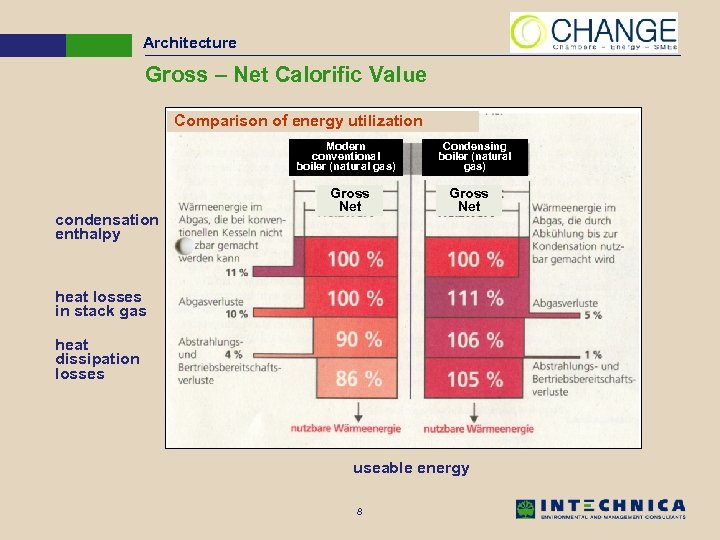
Architecture Gross – Net Calorific Value Comparison of energy utilization Modern conventional boiler (natural gas) condensation enthalpy Gross Net Condensing boiler (natural gas) Gross Net heat losses in stack gas heat dissipation losses useable energy 8
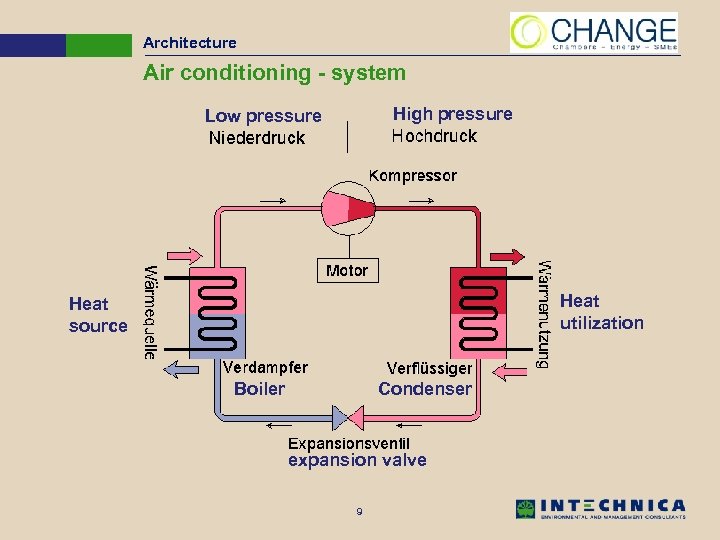
Architecture Air conditioning - system High pressure Low pressure Heat utilization Heat source Boiler Condenser expansion valve 9
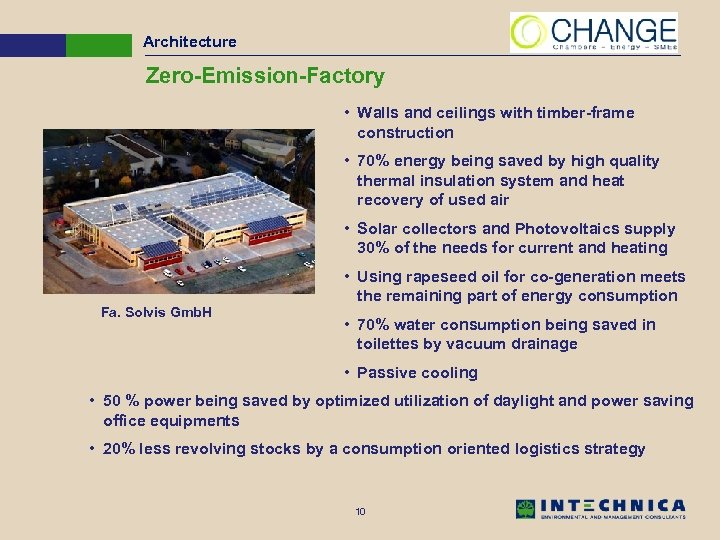
Architecture Zero-Emission-Factory • Walls and ceilings with timber-frame construction • 70% energy being saved by high quality thermal insulation system and heat recovery of used air • Solar collectors and Photovoltaics supply 30% of the needs for current and heating • Using rapeseed oil for co-generation meets the remaining part of energy consumption Fa. Solvis Gmb. H • 70% water consumption being saved in toilettes by vacuum drainage • Passive cooling • 50 % power being saved by optimized utilization of daylight and power saving office equipments • 20% less revolving stocks by a consumption oriented logistics strategy 10
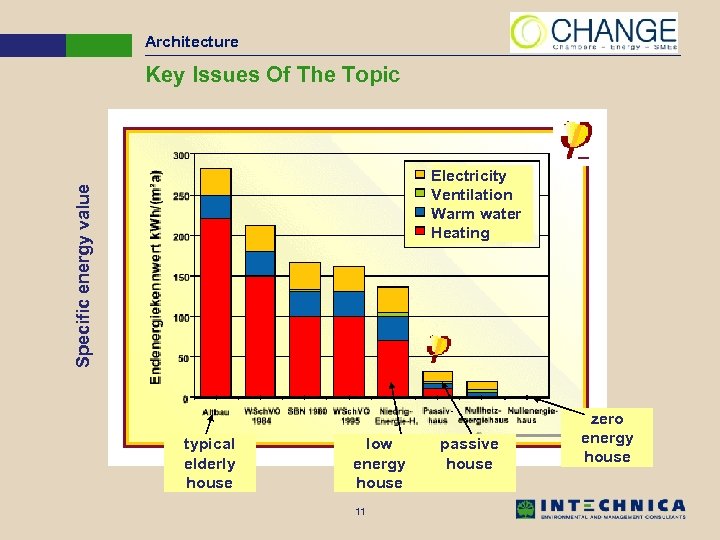
Architecture Key Issues Of The Topic Specific energy value Electricity Ventilation Warm water Heating typical elderly house low energy house 11 passive house zero energy house
Architecture Basics Of Energy Sensitive Construction Object-oriented and integral design Ø Definition of the energetic requirements and demand on energy key values in a user requirement specification Ø Engineers‘ participation in planning at an early stage Ø Optimization in the different phases of planning Ø Continuous check of the results in each planning phase Energetically optimized building concept Ø Compact parts of the building, i. e. smallest A / V- Ratio Ø Workspaces with big southward windows (external sun protection) Ø Reduce heat bridges = continuous insulation Ø Mostly hermetic building shell (Blower-Test) Ø Ventilation with heat recovery 12
0c43449af014eb1a5eb041ec14bfc246.ppt