5360923a5eeb154aa63762794bf840c8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Architecture of e. Health Solutions Connected Healthcare Framework A Stable Foundation for Agile Healthcare Dr Ilia Fortunov Senior Architect Microsoft EMEA Public Sector
Architecture of e. Health Solutions Connected Healthcare Framework A Stable Foundation for Agile Healthcare Dr Ilia Fortunov Senior Architect Microsoft EMEA Public Sector
 The Microsoft Vision for Healthcare Enable the transformation of healthcare delivery through innovative technology & partnerships that advance public health programs by enabling connected citizen care, improving quality of care & safety, and reducing the healthcare cost burden Connected Healthcare Framework 2
The Microsoft Vision for Healthcare Enable the transformation of healthcare delivery through innovative technology & partnerships that advance public health programs by enabling connected citizen care, improving quality of care & safety, and reducing the healthcare cost burden Connected Healthcare Framework 2
 Healthcare is a Complex System Healthcare differs from other large scale systems because: Healthcare business processes are highly varied They change constantly Multiple outcomes, often not predicable System usage is a function of user preference and practice Systems adapt to real-world conditions and a constantly changing environment The Connected Healthcare Framework recognises this by: Separating the dynamic part of the system (business processes and system usage) from the stable part (basic functionality and data structure). Connected Healthcare Framework 3
Healthcare is a Complex System Healthcare differs from other large scale systems because: Healthcare business processes are highly varied They change constantly Multiple outcomes, often not predicable System usage is a function of user preference and practice Systems adapt to real-world conditions and a constantly changing environment The Connected Healthcare Framework recognises this by: Separating the dynamic part of the system (business processes and system usage) from the stable part (basic functionality and data structure). Connected Healthcare Framework 3
 CHF – Guiding Principles Achieve Application Integration, through: A stable foundation and agile implementations Managed multiplicity of platform and location Flexible application configuration and process engineering Consistent, available, understandable Data Sources Legacy rejuvenation and reuse Expressed as: A Business Pattern for Healthcare Achieve Technical Interoperability, through: Open standards Best practice guidelines State of the art technical capabilities Secure, manageable, efficient infrastructures Expressed as: A Reference Architecture for Connected Healthcare Framework 4
CHF – Guiding Principles Achieve Application Integration, through: A stable foundation and agile implementations Managed multiplicity of platform and location Flexible application configuration and process engineering Consistent, available, understandable Data Sources Legacy rejuvenation and reuse Expressed as: A Business Pattern for Healthcare Achieve Technical Interoperability, through: Open standards Best practice guidelines State of the art technical capabilities Secure, manageable, efficient infrastructures Expressed as: A Reference Architecture for Connected Healthcare Framework 4
 Connected Healthcare Framework Focused on major issues specific to connected healthcare solutions Goes far beyond conventional white papers Provides: A Business Pattern for Healthcare A Reference Technical Architecture for Healthcare Based on real worldwide experience Created, reviewed and approved by Microsoft architects, engineering teams and consultants and Microsoft partners and customers Connected Healthcare Framework 5
Connected Healthcare Framework Focused on major issues specific to connected healthcare solutions Goes far beyond conventional white papers Provides: A Business Pattern for Healthcare A Reference Technical Architecture for Healthcare Based on real worldwide experience Created, reviewed and approved by Microsoft architects, engineering teams and consultants and Microsoft partners and customers Connected Healthcare Framework 5
 CHF – from Requirements to Solution Top 10 issues to address: How to create a Patient’s Health Record How to build a lifelong health history for a patient from information held in multiple, diverse systems How to mange Identity and Authorities How to identify a patient (or a healthcare professional) uniquely and reliably. How to “Join-up” different systems on different platforms How to interconnect diverse systems and how to make them interoperate How to communicate with remote systems How to reuse legacy systems How to achieve flexibility and agility How to achieve performance and scalability Connected Healthcare Framework 6
CHF – from Requirements to Solution Top 10 issues to address: How to create a Patient’s Health Record How to build a lifelong health history for a patient from information held in multiple, diverse systems How to mange Identity and Authorities How to identify a patient (or a healthcare professional) uniquely and reliably. How to “Join-up” different systems on different platforms How to interconnect diverse systems and how to make them interoperate How to communicate with remote systems How to reuse legacy systems How to achieve flexibility and agility How to achieve performance and scalability Connected Healthcare Framework 6
 CHF – Aims & Objectives (Demand side = What the Customer wants…. ) An Agile, Flexible Architecture Business-focused Processes, local procedures “Plug and Play” application integration Consistent, reliable standard processes with local implementation flexibility Workflow support Use of open, international standards Process orchestration Use of clinical messaging – HL 7 v 3, SNOMED - CT, IDC 10 Module reusability and replacability Privacy & Confidentiality Comprehensive functionality Consistent support for common tasks Speciality support on a common foundation Healthcare Business Intelligence Business Coverage Legacy Integration, including Integration of existing applications Integration with legacy messages Integration with terminology coding Role-based User Interfaces and Processes Across multi application, multi platform environments (medical error reduction) Preservation of context across apps Connected Healthcare Framework Patient Consent Security of data (encryption, sealed envelopes) Gatekeepers and guardians Data analysis Identification of best practise (role of coding) Forecasting future healthcare needs (could be based on Genomics based medicine) Decision support Knowledge tools Digital content Material on the web 7
CHF – Aims & Objectives (Demand side = What the Customer wants…. ) An Agile, Flexible Architecture Business-focused Processes, local procedures “Plug and Play” application integration Consistent, reliable standard processes with local implementation flexibility Workflow support Use of open, international standards Process orchestration Use of clinical messaging – HL 7 v 3, SNOMED - CT, IDC 10 Module reusability and replacability Privacy & Confidentiality Comprehensive functionality Consistent support for common tasks Speciality support on a common foundation Healthcare Business Intelligence Business Coverage Legacy Integration, including Integration of existing applications Integration with legacy messages Integration with terminology coding Role-based User Interfaces and Processes Across multi application, multi platform environments (medical error reduction) Preservation of context across apps Connected Healthcare Framework Patient Consent Security of data (encryption, sealed envelopes) Gatekeepers and guardians Data analysis Identification of best practise (role of coding) Forecasting future healthcare needs (could be based on Genomics based medicine) Decision support Knowledge tools Digital content Material on the web 7
 CHF – Needs (Supply side = What we must provide…. ) Agility and Flexibility Standards-based, modular, reusable, interoperable Scalability National, Regional, Local or Distributed application “Focusability” Patient-centric, Process-centric, Research-centric, Admin-centric, Speciality-centric Granularity From high-level summary to the deepest detail Implementation independent design Core Business and Data Services Business focused Processes, local procedures User focused, Role-based Presentation and working practice Thorough engineering and testing Connected Healthcare Framework 8
CHF – Needs (Supply side = What we must provide…. ) Agility and Flexibility Standards-based, modular, reusable, interoperable Scalability National, Regional, Local or Distributed application “Focusability” Patient-centric, Process-centric, Research-centric, Admin-centric, Speciality-centric Granularity From high-level summary to the deepest detail Implementation independent design Core Business and Data Services Business focused Processes, local procedures User focused, Role-based Presentation and working practice Thorough engineering and testing Connected Healthcare Framework 8
 CHF – Capabilities (Supply side = What we do provide……) Agility and Flexibility Flexible architectures Highly distributed to fully centralised Middleware Secure and Reliable Messaging Adapters and Connectors Buses and Hubs (e-Health Service Hub) Identity and Access Control Techniques Directory Services Single Sign On Federated identity and authentication Enterprise Application Integration Persistent to transient data stores and records Middleware Secure and Reliable Messaging Adapters and Connectors User Interface and Process Design Device sensitive interfaces and processes Local and user group specific processes Clinical speciality customisation Business Process Orchestration Reliable and secure message delivery, routing, transformation Connected Healthcare Framework Development Methods Component Based Development and Object Orientation Service Oriented Architecture and Web Services Technology Software Architecture. Net Framework Relational databases Data Management Clustering and failover Disaster recovery – data mirroring Scalability Scale-up and scale-out capability Performance Tuning services Dialogue Optimisation Security Authentication and Authorisation Mechanisms Encryption and secure messaging System Management System monitoring Software distribution 9
CHF – Capabilities (Supply side = What we do provide……) Agility and Flexibility Flexible architectures Highly distributed to fully centralised Middleware Secure and Reliable Messaging Adapters and Connectors Buses and Hubs (e-Health Service Hub) Identity and Access Control Techniques Directory Services Single Sign On Federated identity and authentication Enterprise Application Integration Persistent to transient data stores and records Middleware Secure and Reliable Messaging Adapters and Connectors User Interface and Process Design Device sensitive interfaces and processes Local and user group specific processes Clinical speciality customisation Business Process Orchestration Reliable and secure message delivery, routing, transformation Connected Healthcare Framework Development Methods Component Based Development and Object Orientation Service Oriented Architecture and Web Services Technology Software Architecture. Net Framework Relational databases Data Management Clustering and failover Disaster recovery – data mirroring Scalability Scale-up and scale-out capability Performance Tuning services Dialogue Optimisation Security Authentication and Authorisation Mechanisms Encryption and secure messaging System Management System monitoring Software distribution 9
 CHF Business Framework The CHF Business Framework addresses application integration and is based on a service oriented approach focused on defining a set of business components, each addressing a major subject area and offering a range of services that can be “orchestrated” to enable and support the wide range of healthcare business processes. Wherever possible, existing sources of functionality and data are used. It provides a Business Pattern for Healthcare Connected Healthcare Framework 10
CHF Business Framework The CHF Business Framework addresses application integration and is based on a service oriented approach focused on defining a set of business components, each addressing a major subject area and offering a range of services that can be “orchestrated” to enable and support the wide range of healthcare business processes. Wherever possible, existing sources of functionality and data are used. It provides a Business Pattern for Healthcare Connected Healthcare Framework 10
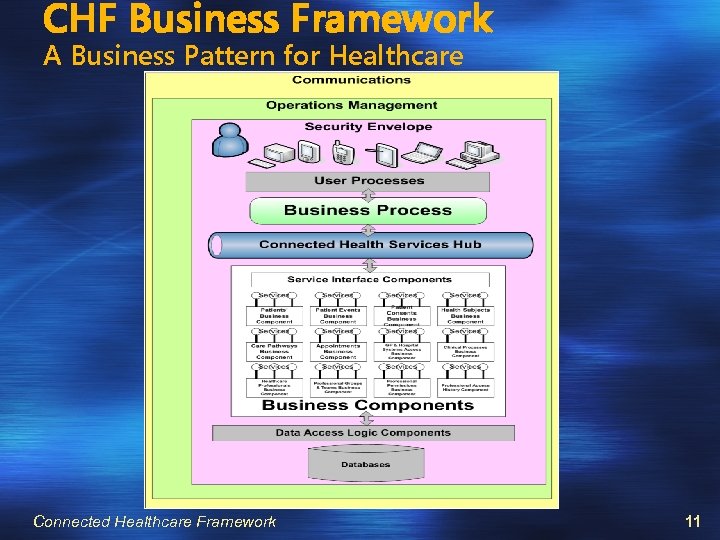 CHF Business Framework A Business Pattern for Healthcare Connected Healthcare Framework 11
CHF Business Framework A Business Pattern for Healthcare Connected Healthcare Framework 11
 CHF Technical Framework The CHF Technical Framework is concerned with interoperability and addresses the following key architectural challenges: Multiplicity Identity Management Integration Challenges Flexibility and Agility Securing the Solution Scalability, Performance and Availability Achieving the Common Hub It provides a Reference Architecture for e-Health Connected Healthcare Framework 12
CHF Technical Framework The CHF Technical Framework is concerned with interoperability and addresses the following key architectural challenges: Multiplicity Identity Management Integration Challenges Flexibility and Agility Securing the Solution Scalability, Performance and Availability Achieving the Common Hub It provides a Reference Architecture for e-Health Connected Healthcare Framework 12
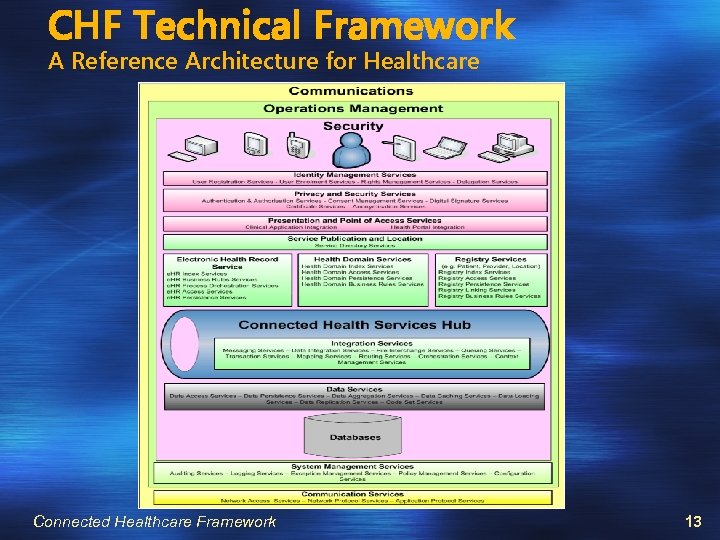 CHF Technical Framework A Reference Architecture for Healthcare Connected Healthcare Framework 13
CHF Technical Framework A Reference Architecture for Healthcare Connected Healthcare Framework 13
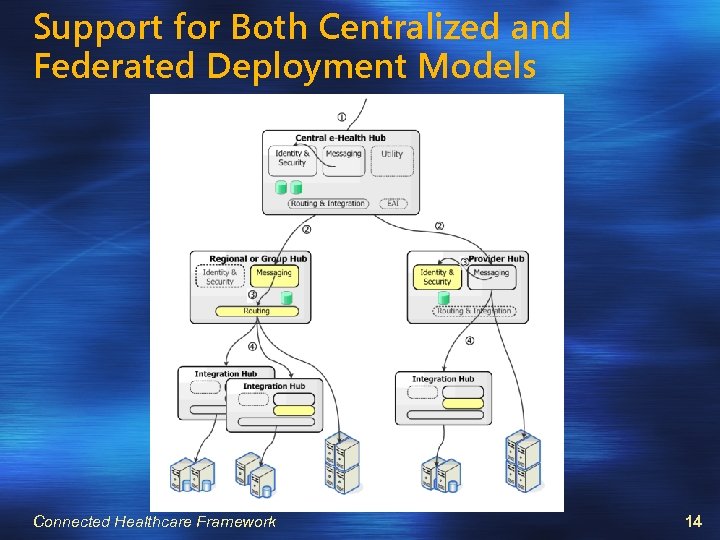 Support for Both Centralized and Federated Deployment Models Connected Healthcare Framework 14
Support for Both Centralized and Federated Deployment Models Connected Healthcare Framework 14
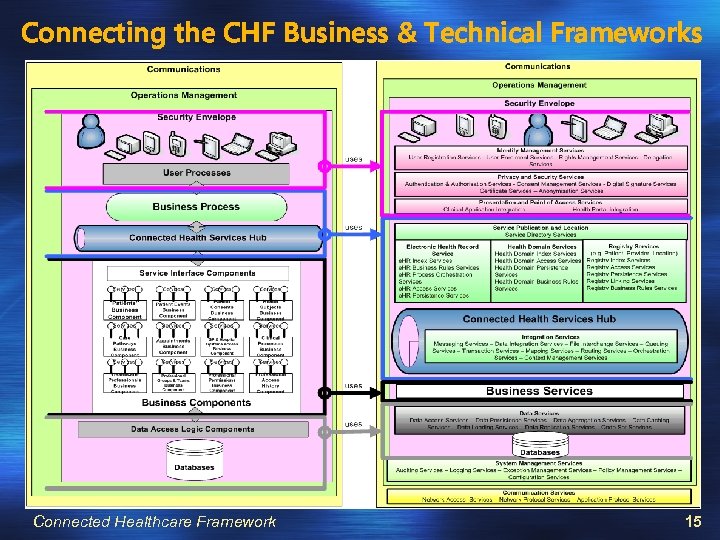 Connecting the CHF Business & Technical Frameworks Connected Healthcare Framework 15
Connecting the CHF Business & Technical Frameworks Connected Healthcare Framework 15
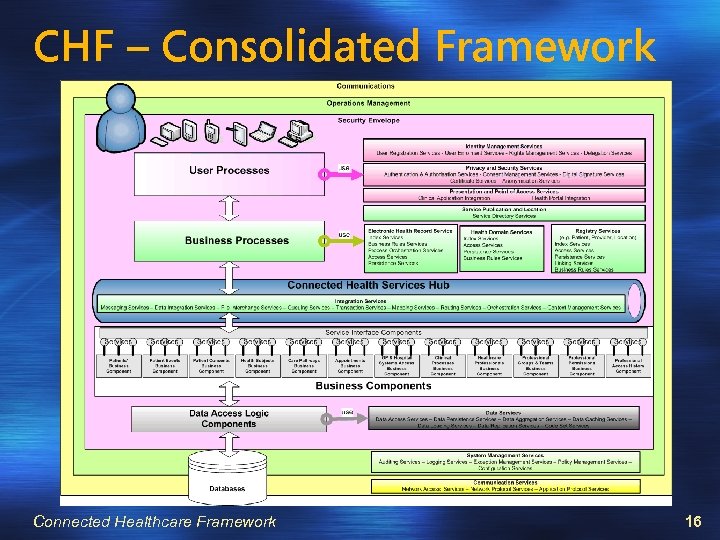 CHF – Consolidated Framework Connected Healthcare Framework 16
CHF – Consolidated Framework Connected Healthcare Framework 16
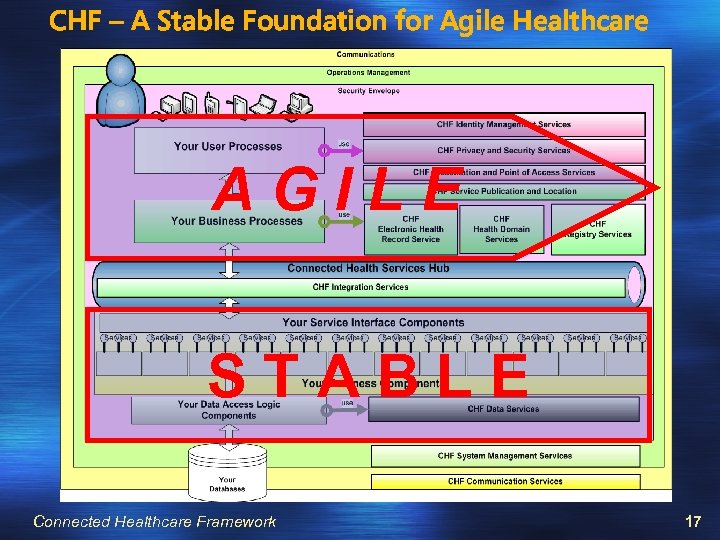 CHF – A Stable Foundation for Agile Healthcare AGILE STABLE Connected Healthcare Framework 17
CHF – A Stable Foundation for Agile Healthcare AGILE STABLE Connected Healthcare Framework 17
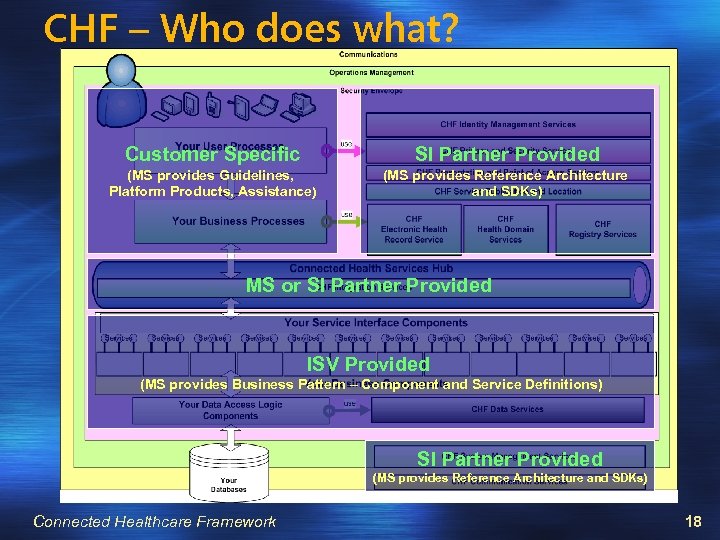 CHF – Who does what? Customer Specific SI Partner Provided (MS provides Guidelines, Platform Products, Assistance) (MS provides Reference Architecture and SDKs) MS or SI Partner Provided ISV Provided (MS provides Business Pattern – Component and Service Definitions) SI Partner Provided (MS provides Reference Architecture and SDKs) Connected Healthcare Framework 18
CHF – Who does what? Customer Specific SI Partner Provided (MS provides Guidelines, Platform Products, Assistance) (MS provides Reference Architecture and SDKs) MS or SI Partner Provided ISV Provided (MS provides Business Pattern – Component and Service Definitions) SI Partner Provided (MS provides Reference Architecture and SDKs) Connected Healthcare Framework 18
 Building Solutions using the CHF Key scenarios depending on the role: Customer - Formulating Requirements (RFP) Vendor/Systems Integrator - Meeting Requirements (Responding to an RFP) Software Vendor - Aligning an ISV Application with the CHF Infrastructure provider - Establishing the Environment CHF (Part 4) provides guidance for each, e. g. : Understanding Scope & Boundaries Understanding the Required Features Deriving the Architecture Defining the Solution Connected Healthcare Framework 19
Building Solutions using the CHF Key scenarios depending on the role: Customer - Formulating Requirements (RFP) Vendor/Systems Integrator - Meeting Requirements (Responding to an RFP) Software Vendor - Aligning an ISV Application with the CHF Infrastructure provider - Establishing the Environment CHF (Part 4) provides guidance for each, e. g. : Understanding Scope & Boundaries Understanding the Required Features Deriving the Architecture Defining the Solution Connected Healthcare Framework 19
 CHF – How To Engage ? Content is now being finalised Verification with selected customers and partners in several countries Will be published on a SSN (Solution Sharing Network) collaboration web site Workshops across the EMEA region and beyond to spread the knowledge Contact your local Microsoft subsidiary to engage Connected Healthcare Framework 20
CHF – How To Engage ? Content is now being finalised Verification with selected customers and partners in several countries Will be published on a SSN (Solution Sharing Network) collaboration web site Workshops across the EMEA region and beyond to spread the knowledge Contact your local Microsoft subsidiary to engage Connected Healthcare Framework 20
 © 2006 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. This presentation is for informational purposes only. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, in this summary. Connected Healthcare Framework 21
© 2006 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. This presentation is for informational purposes only. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, in this summary. Connected Healthcare Framework 21
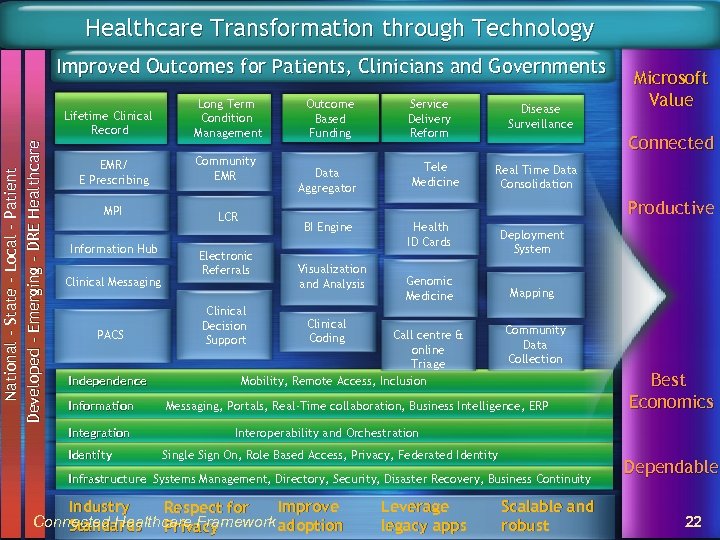 Healthcare Transformation through Technology Improved Outcomes for Patients, Clinicians and Governments National – State – Local - Patient Developed – Emerging – DRE Healthcare Lifetime Clinical Record Long Term Condition Management EMR/ E Prescribing Community EMR MPI LCR Information Hub Clinical Messaging PACS Independence Information Integration Identity Outcome Based Funding Data Aggregator Service Delivery Reform Tele Medicine Disease Surveillance Microsoft Value Connected Real Time Data Consolidation Productive BI Engine Electronic Referrals Clinical Decision Support Visualization and Analysis Health ID Cards Genomic Medicine Clinical Coding Call centre & online Triage Mobility, Remote Access, Inclusion Deployment System Mapping Community Data Collection Messaging, Portals, Real-Time collaboration, Business Intelligence, ERP Best Economics Interoperability and Orchestration Single Sign On, Role Based Access, Privacy, Federated Identity Infrastructure Systems Management, Directory, Security, Disaster Recovery, Business Continuity Improve Industry Respect for Connected Healthcare Framework adoption Standards Privacy Leverage legacy apps Scalable and robust Dependable 22
Healthcare Transformation through Technology Improved Outcomes for Patients, Clinicians and Governments National – State – Local - Patient Developed – Emerging – DRE Healthcare Lifetime Clinical Record Long Term Condition Management EMR/ E Prescribing Community EMR MPI LCR Information Hub Clinical Messaging PACS Independence Information Integration Identity Outcome Based Funding Data Aggregator Service Delivery Reform Tele Medicine Disease Surveillance Microsoft Value Connected Real Time Data Consolidation Productive BI Engine Electronic Referrals Clinical Decision Support Visualization and Analysis Health ID Cards Genomic Medicine Clinical Coding Call centre & online Triage Mobility, Remote Access, Inclusion Deployment System Mapping Community Data Collection Messaging, Portals, Real-Time collaboration, Business Intelligence, ERP Best Economics Interoperability and Orchestration Single Sign On, Role Based Access, Privacy, Federated Identity Infrastructure Systems Management, Directory, Security, Disaster Recovery, Business Continuity Improve Industry Respect for Connected Healthcare Framework adoption Standards Privacy Leverage legacy apps Scalable and robust Dependable 22
 Microsoft’s value proposition Connected – Interoperable by design Open architectures built on industry standards that facilitate the flow of patient information and clinical knowledge seamlessly through the healthcare continuum and across agencies Leverage legacy application and infrastructure investment Productive – Familiar tools to automate the way you work Let clinicians be clinicians: improve adoption Enable delivery of public health services in a standardized, replicable manner Best Economics – Driving down the cost of healthcare technology Create ROI faster than traditional investments An integrated platform that lowers TCO overall Local delivery model Scalable from single providers to county wide programs Dependable – Proven and Robust Applications that support 24 x 7 x 365 healthcare operations Financially stable Extensive partner ecosystem gives decision-makers choice Connected Healthcare Framework 23
Microsoft’s value proposition Connected – Interoperable by design Open architectures built on industry standards that facilitate the flow of patient information and clinical knowledge seamlessly through the healthcare continuum and across agencies Leverage legacy application and infrastructure investment Productive – Familiar tools to automate the way you work Let clinicians be clinicians: improve adoption Enable delivery of public health services in a standardized, replicable manner Best Economics – Driving down the cost of healthcare technology Create ROI faster than traditional investments An integrated platform that lowers TCO overall Local delivery model Scalable from single providers to county wide programs Dependable – Proven and Robust Applications that support 24 x 7 x 365 healthcare operations Financially stable Extensive partner ecosystem gives decision-makers choice Connected Healthcare Framework 23


