5c630212dcee028d777030a73d39b189.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Architecture and Techniques for Diagnosing Faults in IEEE 802. 11 Infrastructure Networks Atul Adya, Victor Bahl, Ranveer Chandra, Lili Qiu Microsoft Research 1
Architecture and Techniques for Diagnosing Faults in IEEE 802. 11 Infrastructure Networks Atul Adya, Victor Bahl, Ranveer Chandra, Lili Qiu Microsoft Research 1
 Wireless Network Woes • How many times have you heard users say: – “My machine says: wireless connection unavailable” – “Why can’t my machine authenticate? ” – “My performance on wireless really sucks” IT Dept: Several hundred complaints per month • You may have heard network admins say: – “I wonder if some one has sneakily installed an unauthorized access point” – “Do we have complete coverage in all the buildings? ” 2
Wireless Network Woes • How many times have you heard users say: – “My machine says: wireless connection unavailable” – “Why can’t my machine authenticate? ” – “My performance on wireless really sucks” IT Dept: Several hundred complaints per month • You may have heard network admins say: – “I wonder if some one has sneakily installed an unauthorized access point” – “Do we have complete coverage in all the buildings? ” 2
 Enterprise Wireless Problems Main problems observed by IT department: – Connectivity: RF Holes – Authentication: 802. 1 x protocol issues – Performance: Unexplained delays – Security: Rogue APs 3
Enterprise Wireless Problems Main problems observed by IT department: – Connectivity: RF Holes – Authentication: 802. 1 x protocol issues – Performance: Unexplained delays – Security: Rogue APs 3
 Existing Products • Provide management/diagnostic functions – E. g. , Air. Wave, CA’s NSM, Air Defense, Air Magnet • Insufficient functionality: – – No support for disconnected clients Weak root-cause analysis (raw data, mostly) Diagnosis only from the AP perspective Sometimes need expensive sensor deployment 4
Existing Products • Provide management/diagnostic functions – E. g. , Air. Wave, CA’s NSM, Air Defense, Air Magnet • Insufficient functionality: – – No support for disconnected clients Weak root-cause analysis (raw data, mostly) Diagnosis only from the AP perspective Sometimes need expensive sensor deployment 4
 Our Contributions • Flexible client-based framework for detection and diagnosis of wireless faults • Client Conduit: communication for disconnected clients via nearby connected clients • Diagnostic mechanisms – Approximate location of disconnected clients – Rogue AP detection – Performance problem analysis 5
Our Contributions • Flexible client-based framework for detection and diagnosis of wireless faults • Client Conduit: communication for disconnected clients via nearby connected clients • Diagnostic mechanisms – Approximate location of disconnected clients – Rogue AP detection – Performance problem analysis 5
 Talk Outline • Diagnostics architecture and implementation • Client Conduit: diagnosing disconnected clients • Diagnostic mechanisms – Locating disconnected clients – Detecting unauthorized APs – Analyzing performance problems • Summary and Future Work 6
Talk Outline • Diagnostics architecture and implementation • Client Conduit: diagnosing disconnected clients • Diagnostic mechanisms – Locating disconnected clients – Detecting unauthorized APs – Analyzing performance problems • Summary and Future Work 6
 Assumptions • Can install diagnostic software on clients – APs are typically closed platforms – Can provide improved diagnosis with modified APs • Nearby clients available for fault diagnosis – At least 13 active clients on our floor (approx. 2500 sq. feet) • Network admins maintain AP Location Database 7
Assumptions • Can install diagnostic software on clients – APs are typically closed platforms – Can provide improved diagnosis with modified APs • Nearby clients available for fault diagnosis – At least 13 active clients on our floor (approx. 2500 sq. feet) • Network admins maintain AP Location Database 7
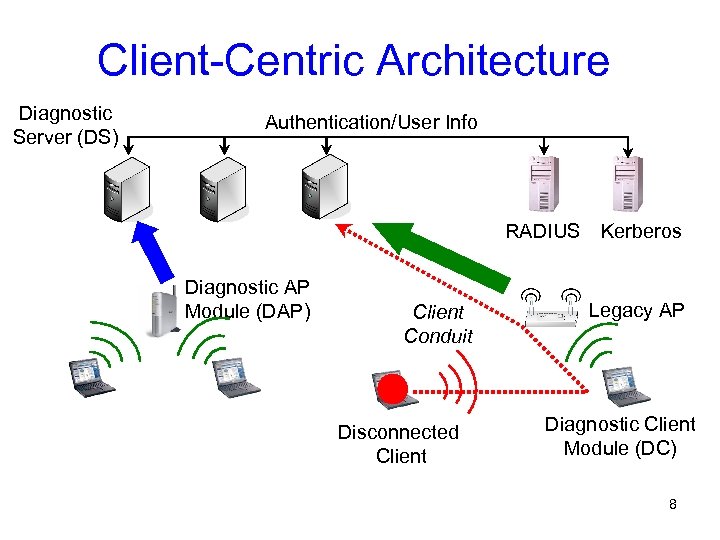 Client-Centric Architecture Diagnostic Server (DS) Authentication/User Info RADIUS Diagnostic AP Module (DAP) Client Conduit Disconnected Client Kerberos Legacy AP Diagnostic Client Module (DC) 8
Client-Centric Architecture Diagnostic Server (DS) Authentication/User Info RADIUS Diagnostic AP Module (DAP) Client Conduit Disconnected Client Kerberos Legacy AP Diagnostic Client Module (DC) 8
 Diagnostic Architecture Properties • Exploits client-view of network (not just APs) • Supports proactive and reactive mechanisms • Scalable • Secure 9
Diagnostic Architecture Properties • Exploits client-view of network (not just APs) • Supports proactive and reactive mechanisms • Scalable • Secure 9
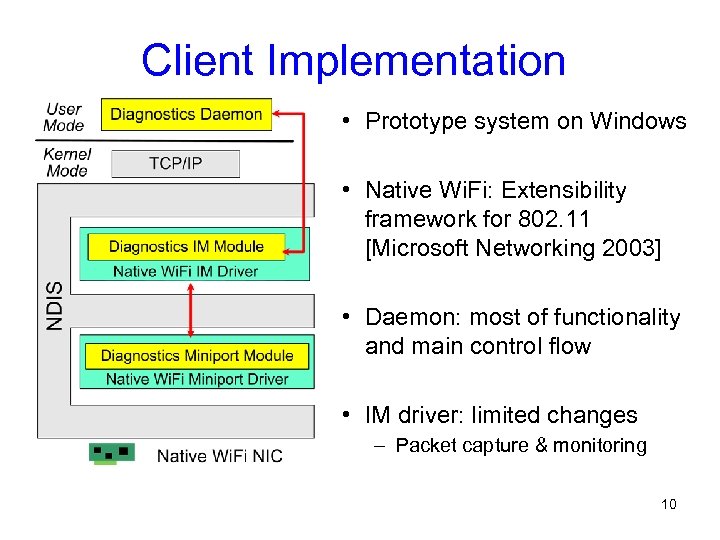 Client Implementation • Prototype system on Windows • Native Wi. Fi: Extensibility framework for 802. 11 [Microsoft Networking 2003] • Daemon: most of functionality and main control flow • IM driver: limited changes – Packet capture & monitoring 10
Client Implementation • Prototype system on Windows • Native Wi. Fi: Extensibility framework for 802. 11 [Microsoft Networking 2003] • Daemon: most of functionality and main control flow • IM driver: limited changes – Packet capture & monitoring 10
 Talk Outline • Diagnostics architecture and implementation • Client Conduit: diagnosing disconnected clients • Diagnostic mechanisms – Locating disconnected clients – Detecting unauthorized APs – Analyzing performance problems • Summary and Future Work 11
Talk Outline • Diagnostics architecture and implementation • Client Conduit: diagnosing disconnected clients • Diagnostic mechanisms – Locating disconnected clients – Detecting unauthorized APs – Analyzing performance problems • Summary and Future Work 11
 Cause of Disconnection • Lack of coverage – In an RF Hole – Just outside AP range • Authentication issues, e. g. , stale certificates • Protocol problems, e. g. , no DHCP address Can we communicate via nearby connected clients? 12
Cause of Disconnection • Lack of coverage – In an RF Hole – Just outside AP range • Authentication issues, e. g. , stale certificates • Protocol problems, e. g. , no DHCP address Can we communicate via nearby connected clients? 12
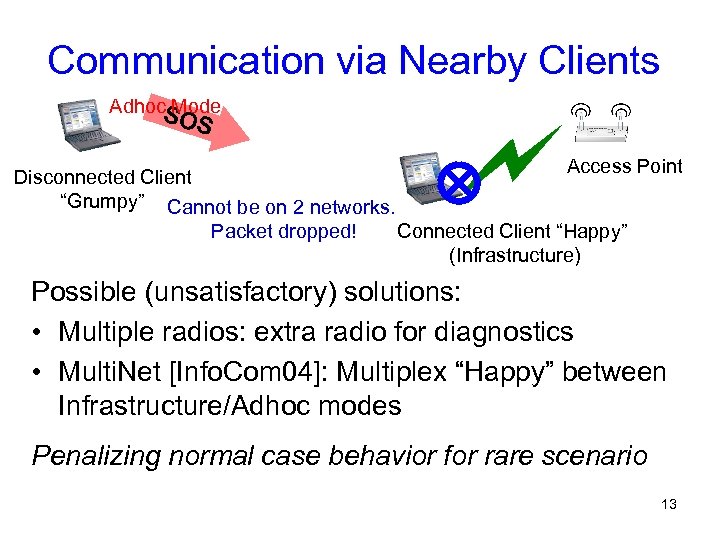 Communication via Nearby Clients Adhoc. S Mode OS Access Point Disconnected Client “Grumpy” Cannot be on 2 networks. Packet dropped! Connected Client “Happy” (Infrastructure) Possible (unsatisfactory) solutions: • Multiple radios: extra radio for diagnostics • Multi. Net [Info. Com 04]: Multiplex “Happy” between Infrastructure/Adhoc modes Penalizing normal case behavior for rare scenario 13
Communication via Nearby Clients Adhoc. S Mode OS Access Point Disconnected Client “Grumpy” Cannot be on 2 networks. Packet dropped! Connected Client “Happy” (Infrastructure) Possible (unsatisfactory) solutions: • Multiple radios: extra radio for diagnostics • Multi. Net [Info. Com 04]: Multiplex “Happy” between Infrastructure/Adhoc modes Penalizing normal case behavior for rare scenario 13
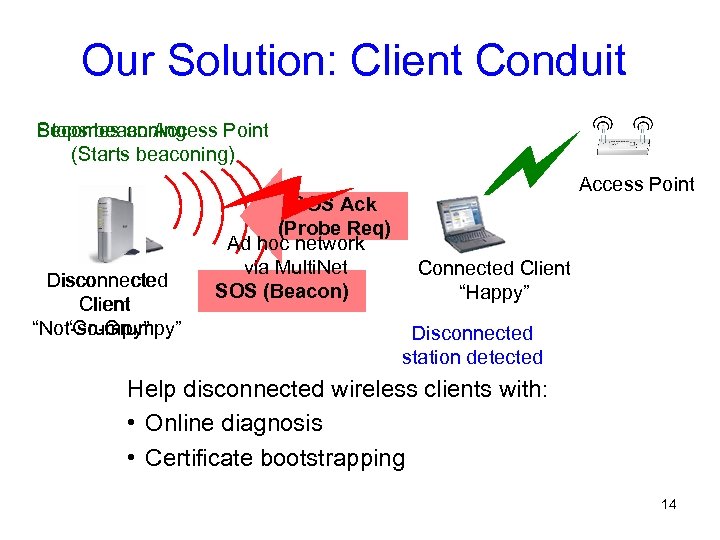 Our Solution: Client Conduit Becomes an Access Point Stops beaconing (Starts beaconing) Disconnected Client “Not-so-Grumpy” “Grumpy” SOS Ack (Probe Req) Ad hoc network via Multi. Net SOS (Beacon) Access Point Connected Client “Happy” Disconnected station detected Help disconnected wireless clients with: • Online diagnosis • Certificate bootstrapping 14
Our Solution: Client Conduit Becomes an Access Point Stops beaconing (Starts beaconing) Disconnected Client “Not-so-Grumpy” “Grumpy” SOS Ack (Probe Req) Ad hoc network via Multi. Net SOS (Beacon) Access Point Connected Client “Happy” Disconnected station detected Help disconnected wireless clients with: • Online diagnosis • Certificate bootstrapping 14
 Client Conduit Features • Incurs no extra overhead for connected clients – Use existing 802. 11 messages: beacons & probes • Works with legacy APs • Includes security mechanisms to avoid abuses 15
Client Conduit Features • Incurs no extra overhead for connected clients – Use existing 802. 11 messages: beacons & probes • Works with legacy APs • Includes security mechanisms to avoid abuses 15
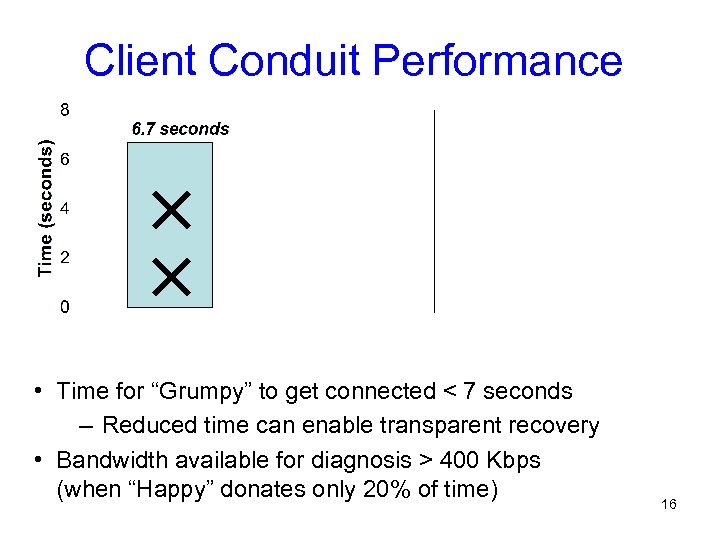 Client Conduit Performance • Time for “Grumpy” to get connected < 7 seconds – Reduced time can enable transparent recovery • Bandwidth available for diagnosis > 400 Kbps (when “Happy” donates only 20% of time) 16
Client Conduit Performance • Time for “Grumpy” to get connected < 7 seconds – Reduced time can enable transparent recovery • Bandwidth available for diagnosis > 400 Kbps (when “Happy” donates only 20% of time) 16
 Talk Outline • Diagnostics architecture and implementation • Client Conduit: diagnosing disconnected clients • Diagnostic mechanisms – Locating disconnected clients – Detecting unauthorized APs – Analyzing performance problems • Summary and Future Work 17
Talk Outline • Diagnostics architecture and implementation • Client Conduit: diagnosing disconnected clients • Diagnostic mechanisms – Locating disconnected clients – Detecting unauthorized APs – Analyzing performance problems • Summary and Future Work 17
 Locating Disconnected Clients Goal: Approximately locate to determine RF Holes Solution: Use nearby connected clients • “Grumpy” starts beaconing • Nearby clients report signal strength to server • Diagnostic server uses RADAR [Info. Com 00] twice – Locates connected clients – Locates “Grumpy” with clients as “anchor points” • Location error: 10 – 15 meters 18
Locating Disconnected Clients Goal: Approximately locate to determine RF Holes Solution: Use nearby connected clients • “Grumpy” starts beaconing • Nearby clients report signal strength to server • Diagnostic server uses RADAR [Info. Com 00] twice – Locates connected clients – Locates “Grumpy” with clients as “anchor points” • Location error: 10 – 15 meters 18
 Talk Outline • Diagnostics architecture and implementation • Client Conduit: diagnosing disconnected clients • Diagnostic mechanisms – Locating disconnected clients – Detecting unauthorized APs – Analyzing performance problems • Summary and Future Work 19
Talk Outline • Diagnostics architecture and implementation • Client Conduit: diagnosing disconnected clients • Diagnostic mechanisms – Locating disconnected clients – Detecting unauthorized APs – Analyzing performance problems • Summary and Future Work 19
 Rogue AP Problems Why problematic? • Allow network access to unauthorized users • Hurt performance: interfere with existing APs Detection goals: • Common case: mistakes by employees • Detect unauthorized IEEE 802. 11 APs – Not considering non-compliant APs Solution: Use clients for monitoring nearby APs 20
Rogue AP Problems Why problematic? • Allow network access to unauthorized users • Hurt performance: interfere with existing APs Detection goals: • Common case: mistakes by employees • Detect unauthorized IEEE 802. 11 APs – Not considering non-compliant APs Solution: Use clients for monitoring nearby APs 20
 Rogue AP Detection • Clients monitor nearby APs. Send to server: – MAC address, Channel, SSID, RSSI (for location) • Server checks 4 -tuple in AP Location Database • Obtaining AP Information at clients: – Same/overlapping channel as client: from Beacons – AP on non-overlapping channel: • Active Scan periodically • AP information from Probe Response 21
Rogue AP Detection • Clients monitor nearby APs. Send to server: – MAC address, Channel, SSID, RSSI (for location) • Server checks 4 -tuple in AP Location Database • Obtaining AP Information at clients: – Same/overlapping channel as client: from Beacons – AP on non-overlapping channel: • Active Scan periodically • AP information from Probe Response 21
 Rogue AP Detection Overheads • Bandwidth usage < 0. 2 Kbps per client • Can active scans be performed without disruption? – Sufficient idleness available (2½ – 3 min. ) – Simple threshold-based prediction: Active scan completed in idle period for 95% cases 22
Rogue AP Detection Overheads • Bandwidth usage < 0. 2 Kbps per client • Can active scans be performed without disruption? – Sufficient idleness available (2½ – 3 min. ) – Simple threshold-based prediction: Active scan completed in idle period for 95% cases 22
 Talk Outline • Diagnostics architecture and implementation • Client Conduit: diagnosing disconnected clients • Diagnostic mechanisms – Locating disconnected clients – Detecting unauthorized APs – Analyzing performance problems • Summary and Future Work 23
Talk Outline • Diagnostics architecture and implementation • Client Conduit: diagnosing disconnected clients • Diagnostic mechanisms – Locating disconnected clients – Detecting unauthorized APs – Analyzing performance problems • Summary and Future Work 23
 Summary • • Diagnostics critical for 802. 11 deployments Client-centric architecture Client Conduit Diagnosis using nearby clients – Locate disconnected clients – Detect rogue APs – Analyze performance problems • Prototype in Windows using Native Wi. Fi – Mechanisms are effective with low overheads 24
Summary • • Diagnostics critical for 802. 11 deployments Client-centric architecture Client Conduit Diagnosis using nearby clients – Locate disconnected clients – Detect rogue APs – Analyze performance problems • Prototype in Windows using Native Wi. Fi – Mechanisms are effective with low overheads 24
 Future Work • Detecting Rogue Ad Hoc networks • 802. 1 x protocol analyzer • Detailed wireless delay analyzer • Automated recovery after fault diagnosis 25
Future Work • Detecting Rogue Ad Hoc networks • 802. 1 x protocol analyzer • Detailed wireless delay analyzer • Automated recovery after fault diagnosis 25


