d878d9d5cc09d130f551c4939b749978.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Arab – Israeli Conflict Timeline to 2002

Basle Switzerland, 1897 1 st Zionist Congress convened to discuss “the Jewish problem” (The Basle Program)

1915 -1916 -1917 • Two of the most controversial and widely discussed documents concerning the beginnings of the Arab-Israeli conflict have been the Hussein-Mc. Mahon Letters and the Balfour Declaration. • The controversy centering around these two documents is due, in part, to the fact that they were the first concrete commitments made to the Arabs and the Jewish Zionists by the British government.

Attempts at Arab-Israeli Peace Photos courtesy of: Listverse. com January 3, 1919 Emir Faisal (son of the King of Hejaz) and Chaim Weizmann (later President of the World Zionist Organization) at the Paris Peace Conference, settling disputes stemming from World War I

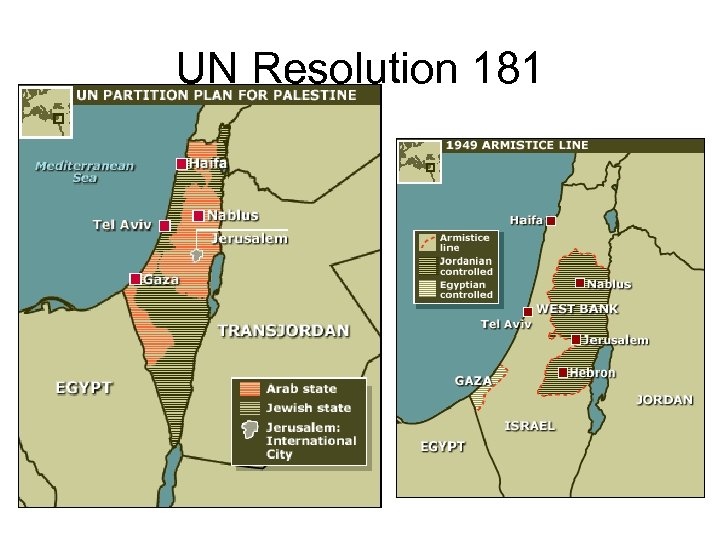
UN Resolution 181

Suez Crisis 1956

P. L. O. Est. 1964

British Political cartoon by Stan Mc. Murtry from the Daily Mail, 21 Nov 1977. Caption: “Meeting his enemies has been safe enough, - it's going back to his friends that takes guts. ” Text on sign reads: “TO THE ARAB WORLD. ”

“You don’t get an agreement between untrusting adversaries, even if they want it, without a broker. ”

Camp David (in Maryland)

Camp David Accords, 1978 The two agreements were signed at the White House and were witnessed by United States President Jimmy Carter. • The Camp David Accords were signed by Egyptian President Anwar El Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin on September 17, 1978, following twelve days of secret negotiations at Camp David.

Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty, 1979 • Signed on March 26, 1979, following the Camp David Accords. • Mutual recognition of each country by the other • Cessation of the state of war that had existed since the 1948 Arab-Israeli War • Complete withdrawal by Israel of its armed forces and civilians from the rest of the Sinai Peninsula • Free passage of Israeli ships through the Suez Canal and recognition of the Strait of Tiran and the Gulf of Aqaba as international waterways.


1987 -1993: 1 st Intifada Literal translation = “shaking off” or “uprising” violent and nonviolent protests

Madrid Conference, 1991 Hosted by the government of Spain and co-sponsored by the USA and the USSR. It convened on October 30, 1991 and lasted for three days. • In the aftermath of the 1991 Gulf War, US President George H. W. Bush and his Secretary of State James Baker formulated the framework of objectives, and together with the Soviet Union extended a letter of invitation, dated October 30, 1991 to Israel, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, and the Palestinians.

Oslo Accords, 1993 • The Declaration of Principles was a milestone in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. It was the first direct, face-to-face agreement between Israel and political representatives of Palestinians. • It was intended to be a framework for the future relations between Israel and the anticipated State of Palestine, when all outstanding final status issues between the two states would be addressed and resolved in one Package Agreement.
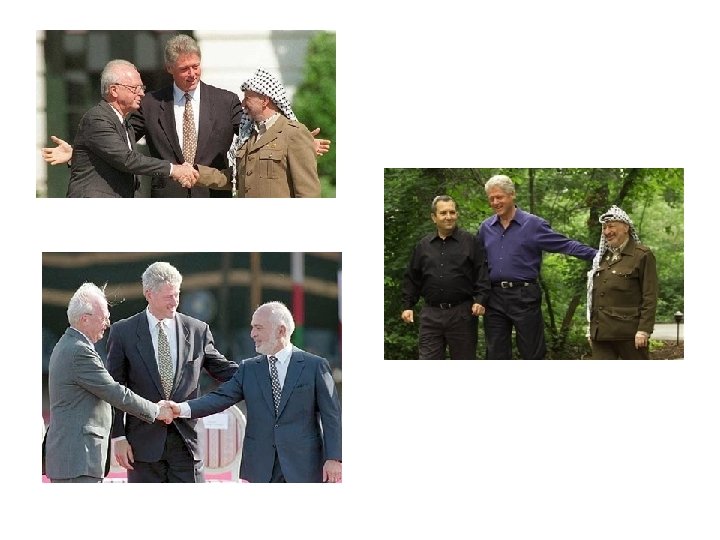


Israel - Jordan Treaty of Peace 1994 • Normalized relations between the two countries and resolved territorial disputes between them. • Closely linked with the efforts to create peace between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization. • Only the second Arab country to normalize relations with Israel.
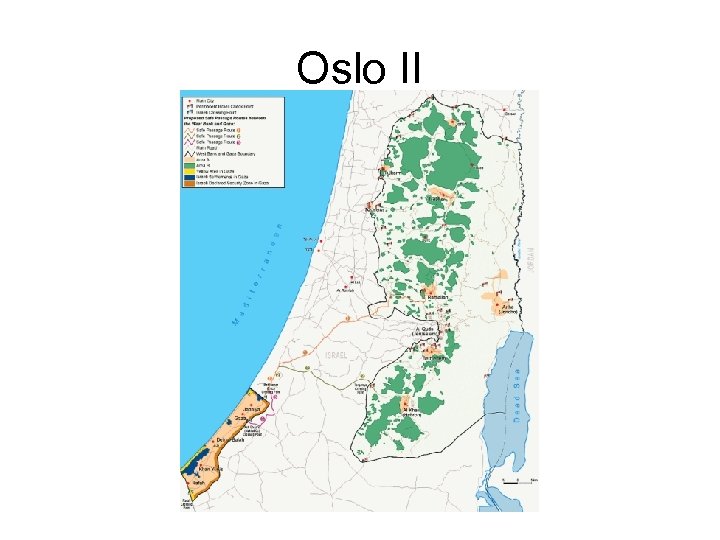
Oslo II

Middle East Peace Summit 2000 (Camp David II) • Again, held at Camp David • President Bill Clinton, Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Barak, and Palestinian Authority Chairman Yasser Arafat attended • An ultimately unsuccessful attempt to negotiate a “final status settlement” to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.

Three days before his term ended, the PA Chairman (Arafat) told Clinton that he was “a great man. ” “The hell I am, ” Clinton replied. “I’m a colossal failure, and you made me one. ”
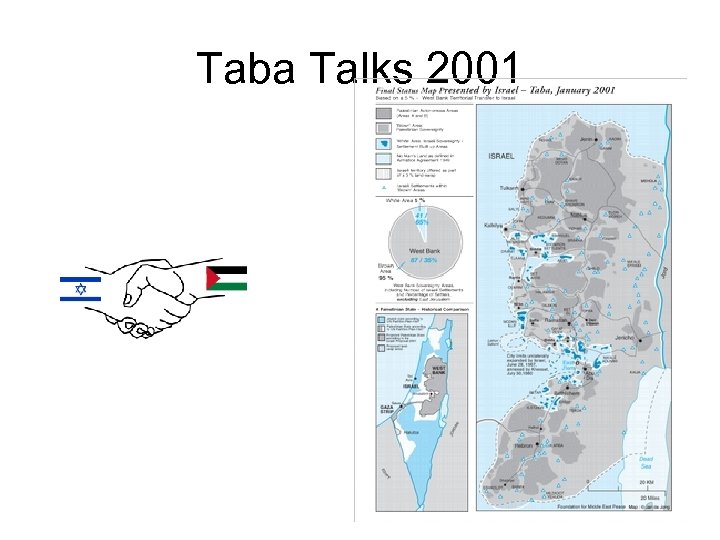
Taba Talks 2001

Beirut Summit 2002 • Jordan’s foreign minister said, “The Arab initiative put forth at the Beirut Summit in March offers comprehensive peace in the region based on the internationally recognized formulation of ‘land for peace’ — a return to 4 June 1967, borders in exchange for normal relations and a collective peace treaty. ”

Road Map for Peace, 2002 “The Roadmap represents a starting point toward achieving the vision of two states, a secure State of Israel and a viable, peaceful, democratic Palestine. It is the framework for progress towards lasting peace and security in the Middle East…” • Plan proposed by a “quartet” of international entities: the United States, the European Union, Russia, and the United Nations.

d878d9d5cc09d130f551c4939b749978.ppt