41de68596ca8439696393891837bc793.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 APUSH The shift from Authoritarianism to Individualism in the American colonies.
APUSH The shift from Authoritarianism to Individualism in the American colonies.
 African American Proverb “At first we had the land the white man had the Bible. Now we have the Bible and they have the land” Respond with references to the Native American - White relations. Make sure you have a clear, concise main Pick one § § § 1662 Powhatan uprising Roger Williams 1637 Pequot War 1675 King Phillips/Metacom War 1676 Bacon’s Rebellion Iroquois nation idea. Make sure you have Specific Factual Information to support your claim
African American Proverb “At first we had the land the white man had the Bible. Now we have the Bible and they have the land” Respond with references to the Native American - White relations. Make sure you have a clear, concise main Pick one § § § 1662 Powhatan uprising Roger Williams 1637 Pequot War 1675 King Phillips/Metacom War 1676 Bacon’s Rebellion Iroquois nation idea. Make sure you have Specific Factual Information to support your claim
 The shift from Authoritarianism to Individualism in the American colonies. Remember The Organizing Principal: Between 1607 and 1763, the British North American colonies developed experience in, and the expectation of self-government in the political, religious, economic, and social aspects of life.
The shift from Authoritarianism to Individualism in the American colonies. Remember The Organizing Principal: Between 1607 and 1763, the British North American colonies developed experience in, and the expectation of self-government in the political, religious, economic, and social aspects of life.
 Religion, Politics, Economics § Martin Luther 1517 Protestant Reformation § John Calvin - predestination Calvinism § Henry VIII of England - Anglican Church of England
Religion, Politics, Economics § Martin Luther 1517 Protestant Reformation § John Calvin - predestination Calvinism § Henry VIII of England - Anglican Church of England
 Beer and the Mayflower § The Mayflower is headed for Virginia…but ends up putting ashore at Plymouth rock. § One Pilgrim’s diary explains why: “We could not take time for further search or consideration, our victuals being much spent, especially our beer. ” § Once ashore, they promptly erected a brewhouse…. They needed to make a beer run!
Beer and the Mayflower § The Mayflower is headed for Virginia…but ends up putting ashore at Plymouth rock. § One Pilgrim’s diary explains why: “We could not take time for further search or consideration, our victuals being much spent, especially our beer. ” § Once ashore, they promptly erected a brewhouse…. They needed to make a beer run!
 Puritans/Separatists -Plymouth 1621 Va. Company - Mayflower Compact (squatters submitting to will of majority) Wm Bradford 1691 merge w/ Mass. Bay colony Keeps the rabble from rebelling
Puritans/Separatists -Plymouth 1621 Va. Company - Mayflower Compact (squatters submitting to will of majority) Wm Bradford 1691 merge w/ Mass. Bay colony Keeps the rabble from rebelling
 Covenant Theology “Covenant of Grace”: § between Puritan communities and God. “Social Covenant”: § Between members of Puritan communities with each other. § Required mutual watchfulness. § No toleration of deviance or disorder. § No privacy.
Covenant Theology “Covenant of Grace”: § between Puritan communities and God. “Social Covenant”: § Between members of Puritan communities with each other. § Required mutual watchfulness. § No toleration of deviance or disorder. § No privacy.
 Puritans - Mass. Bay Colony 1629 We shall be as a city on a hill. The eyes of all people are upon us. Successful. John Winthrop - City on a Hill - holy society Covenant w/ God - “freedmen” of congregation - Congregational Church. Larger voting pop. of males than in England. Still not a “democracy” “visible saints” only eligible for church membership and they = freedmen Purpose of gov’t was to enforce God’s laws to all ppl Everyone paid taxes to gov’t supported church BIBLE COMMONWEALTH John Cotton - defending duty of gov’t to enforce religious rules Power of preachers not absolute - hired/fired by congregation Can’t hold political office (historical fear) separation of church and state Protestant work ethic
Puritans - Mass. Bay Colony 1629 We shall be as a city on a hill. The eyes of all people are upon us. Successful. John Winthrop - City on a Hill - holy society Covenant w/ God - “freedmen” of congregation - Congregational Church. Larger voting pop. of males than in England. Still not a “democracy” “visible saints” only eligible for church membership and they = freedmen Purpose of gov’t was to enforce God’s laws to all ppl Everyone paid taxes to gov’t supported church BIBLE COMMONWEALTH John Cotton - defending duty of gov’t to enforce religious rules Power of preachers not absolute - hired/fired by congregation Can’t hold political office (historical fear) separation of church and state Protestant work ethic
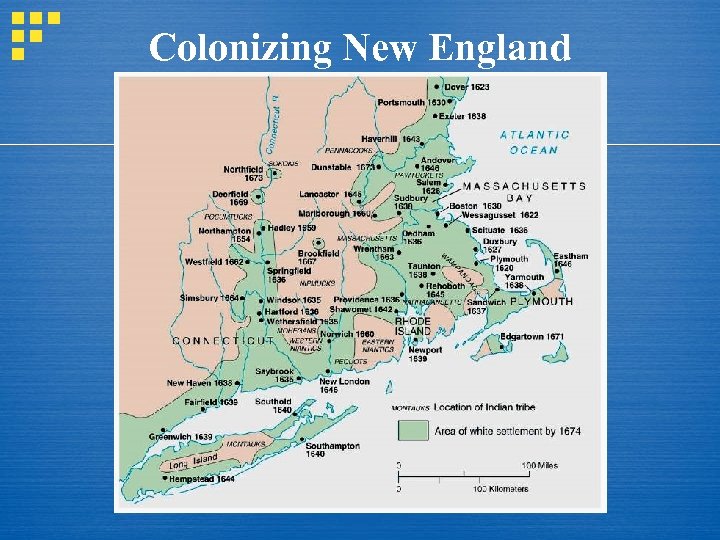 Colonizing New England
Colonizing New England
 Puritan “Rebels” & Rhode Island § Rhode Island - Religious toleration. civil gov’t has no authority to regulate religious behavior. Threatens patriararchal society If holy life no sure sign of salvation then truly saved shouldn’t even bother to obey law of God and man antinomianism - sewer. No religious compulsory oaths. No compulsory attendance at church, no taxes to support state church - manhood suffrage. - traditional home of the other wise minded. Royal Charter 1644.
Puritan “Rebels” & Rhode Island § Rhode Island - Religious toleration. civil gov’t has no authority to regulate religious behavior. Threatens patriararchal society If holy life no sure sign of salvation then truly saved shouldn’t even bother to obey law of God and man antinomianism - sewer. No religious compulsory oaths. No compulsory attendance at church, no taxes to support state church - manhood suffrage. - traditional home of the other wise minded. Royal Charter 1644.
 Connecticut 1630 § Dutch and English § Puritans led by Rev. Thomas Hooker § 1639 Fundamental Orders
Connecticut 1630 § Dutch and English § Puritans led by Rev. Thomas Hooker § 1639 Fundamental Orders
 Puritans vs. Indians § 1621 Plymouth befriended by Wampanoag Indians - Squanto & Massasoit § 1637 Pequot War English vs. Pequot tribe Connecticut River § Puritans criticized in Europe - conversion pushed § 1675 Metacom aka King Philip War - alliance among diff. tribes. Metacom captured - head displayed. He did slow the western march of settlers but natives no longer posed a threat
Puritans vs. Indians § 1621 Plymouth befriended by Wampanoag Indians - Squanto & Massasoit § 1637 Pequot War English vs. Pequot tribe Connecticut River § Puritans criticized in Europe - conversion pushed § 1675 Metacom aka King Philip War - alliance among diff. tribes. Metacom captured - head displayed. He did slow the western march of settlers but natives no longer posed a threat
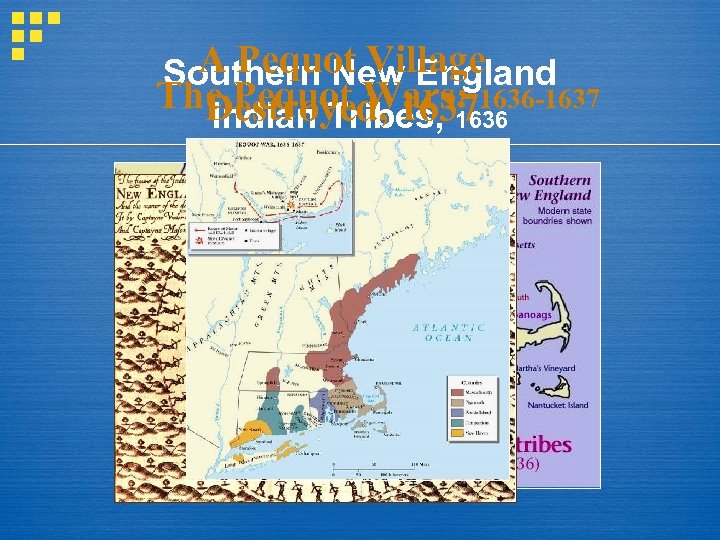 A Pequot Village Southern New England The Pequot Wars: 1636 -1637 Destroyed, 1637 Indian Tribes, 1636
A Pequot Village Southern New England The Pequot Wars: 1636 -1637 Destroyed, 1637 Indian Tribes, 1636

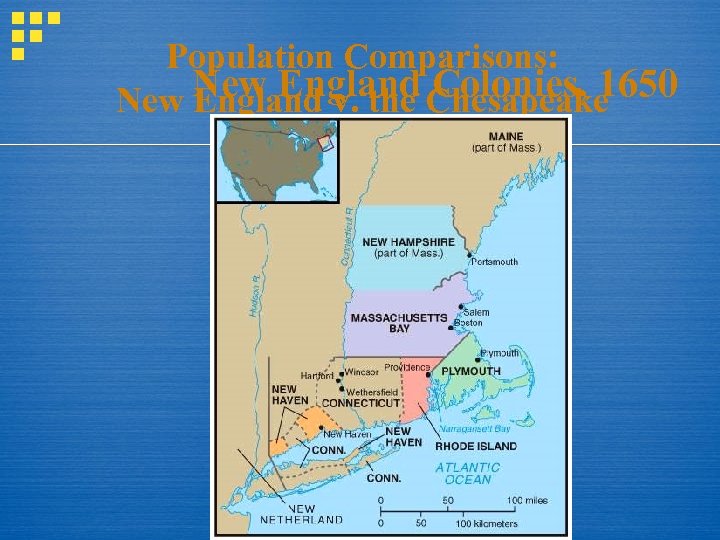 Population Comparisons: New England Chesapeake England v. the Colonies, 1650
Population Comparisons: New England Chesapeake England v. the Colonies, 1650
 Unity? § 1643 New England Confederation. England in civil war Purpose to band against natives, French, Dutch; also intercolonial runaways Each member (regardless of size) 2 votes (populous Mass. didn’t like this) Puritan club § § § Mass. Bay Plymouth Connecticut New Haven Connecticut valley settlements No Rhode Island No Maine settlements
Unity? § 1643 New England Confederation. England in civil war Purpose to band against natives, French, Dutch; also intercolonial runaways Each member (regardless of size) 2 votes (populous Mass. didn’t like this) Puritan club § § § Mass. Bay Plymouth Connecticut New Haven Connecticut valley settlements No Rhode Island No Maine settlements
 Unity Gone? § 1660 English crown restored under Charles II, James II, Wm and Mary § Colonial defiance § 1662 Charles II gave rival Connecticut sea-tosea charter § 1663 Rhode Island sanctioned § 1684 Mass Bay Colony’s charter revoked
Unity Gone? § 1660 English crown restored under Charles II, James II, Wm and Mary § Colonial defiance § 1662 Charles II gave rival Connecticut sea-tosea charter § 1663 Rhode Island sanctioned § 1684 Mass Bay Colony’s charter revoked
 First American Revolution? § 1686 Dominion of New England Not homegrown NE Confederation - this is royal All NE plus NY as well as E and W Jersey England did it to bolster defense ag. Indians England did it to make efficient administration of Navigation Laws § Colonial rivalries; stitch colonies to motherland; no trade with non-English countries § Smuggling becomes honorable Autocratic Sir Edmund Andros § Open affiliation with despised Church of England
First American Revolution? § 1686 Dominion of New England Not homegrown NE Confederation - this is royal All NE plus NY as well as E and W Jersey England did it to bolster defense ag. Indians England did it to make efficient administration of Navigation Laws § Colonial rivalries; stitch colonies to motherland; no trade with non-English countries § Smuggling becomes honorable Autocratic Sir Edmund Andros § Open affiliation with despised Church of England
 Dominion of New England Autocratic Sir Edmund Andros § § § Curbed town meetings Restricted court, press, schools Revoked land titles No popular assembly - tax w/out representation Surpress smuggling 1688 -1689 Glorious Revolution in England § Wm and Mary § Dominion of New England collapses
Dominion of New England Autocratic Sir Edmund Andros § § § Curbed town meetings Restricted court, press, schools Revoked land titles No popular assembly - tax w/out representation Surpress smuggling 1688 -1689 Glorious Revolution in England § Wm and Mary § Dominion of New England collapses
 New Mass. ? § Glorious Revolution didn’t mean much besides Andros leaving § 1691 new royal charter again - new permanent royal gov’t Loss ancient charter Now voting not just church members but all male property owners
New Mass. ? § Glorious Revolution didn’t mean much besides Andros leaving § 1691 new royal charter again - new permanent royal gov’t Loss ancient charter Now voting not just church members but all male property owners
 Glorious Revolution § Wm and Mary meant “salutory neglect” § But More English officials remain due to Charles II) They were often corrupt and loyal to England Not locally elected
Glorious Revolution § Wm and Mary meant “salutory neglect” § But More English officials remain due to Charles II) They were often corrupt and loyal to England Not locally elected
![Settling the Middle [or “Restoration”] Colonies Founded in the 1660 s by: § Friends Settling the Middle [or “Restoration”] Colonies Founded in the 1660 s by: § Friends](https://present5.com/presentation/41de68596ca8439696393891837bc793/image-22.jpg) Settling the Middle [or “Restoration”] Colonies Founded in the 1660 s by: § Friends of British King Charles II. § Land speculators. § Middle class farmers & craftsmen.
Settling the Middle [or “Restoration”] Colonies Founded in the 1660 s by: § Friends of British King Charles II. § Land speculators. § Middle class farmers & craftsmen.
 More Like Later America Than Other Regions! Economic diversity. Large cities à more cosmopolitan culture. Some slavery [6%-12% of the population]. Ethnic and religious diversity. Religious toleration. “Bread Colonies. ”
More Like Later America Than Other Regions! Economic diversity. Large cities à more cosmopolitan culture. Some slavery [6%-12% of the population]. Ethnic and religious diversity. Religious toleration. “Bread Colonies. ”
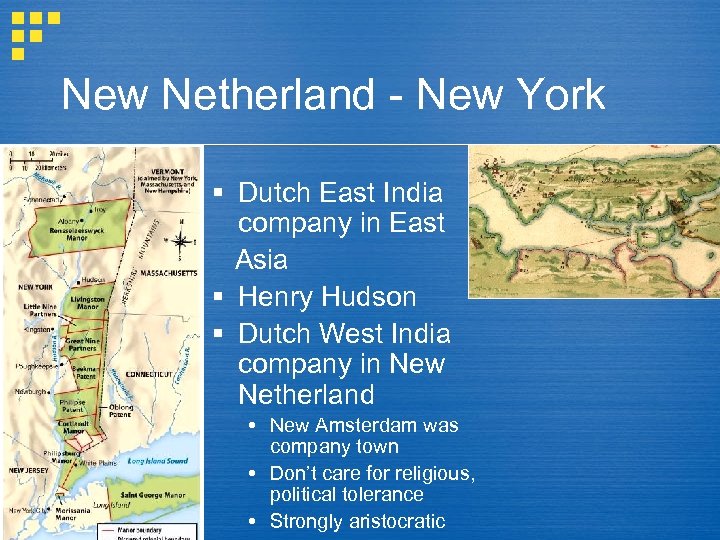 New Netherland - New York § Dutch East India company in East Asia § Henry Hudson § Dutch West India company in New Netherland New Amsterdam was company town Don’t care for religious, political tolerance Strongly aristocratic
New Netherland - New York § Dutch East India company in East Asia § Henry Hudson § Dutch West India company in New Netherland New Amsterdam was company town Don’t care for religious, political tolerance Strongly aristocratic
 New Netherland Neighbors § Hostile natives § Hostile New England esp Connecticut § New Sweden on Delaware River trespassed on New Netherland § 1655 Dutch wiped out New Sweden led by Peter Stuyvesant § 1664 Stuyvesant surrender to Duke of York § New Amsterdam becomes New York
New Netherland Neighbors § Hostile natives § Hostile New England esp Connecticut § New Sweden on Delaware River trespassed on New Netherland § 1655 Dutch wiped out New Sweden led by Peter Stuyvesant § 1664 Stuyvesant surrender to Duke of York § New Amsterdam becomes New York
 Pennsylvania § Dissenters - Quakers (Religious Society of Friends) - dissent against religious and civil authority Use “thees and thous” rather than titles All children of God Abhorred strife The “Holy Experiment”
Pennsylvania § Dissenters - Quakers (Religious Society of Friends) - dissent against religious and civil authority Use “thees and thous” rather than titles All children of God Abhorred strife The “Holy Experiment”
 Pennsylvania § 1681 William Penn granted immense territory by King § Best advertised colony § Liberal land policy § Traded and treated Indians fairly. § Liberal regime § Representative assembly elected by landowners § No tax supported state church drained coffers § Freedom of worship was guaranteed to all (except Jews/Catholics)
Pennsylvania § 1681 William Penn granted immense territory by King § Best advertised colony § Liberal land policy § Traded and treated Indians fairly. § Liberal regime § Representative assembly elected by landowners § No tax supported state church drained coffers § Freedom of worship was guaranteed to all (except Jews/Catholics)
 Pennsylvania § § § No provision for military defense No restrictions on immigrations Did have “blue laws” Rich ethnic mix Fast growing colony LEGACY: new commonwealth. Based on civil and religious liberty. Based on freedom fo conscience and worship
Pennsylvania § § § No provision for military defense No restrictions on immigrations Did have “blue laws” Rich ethnic mix Fast growing colony LEGACY: new commonwealth. Based on civil and religious liberty. Based on freedom fo conscience and worship
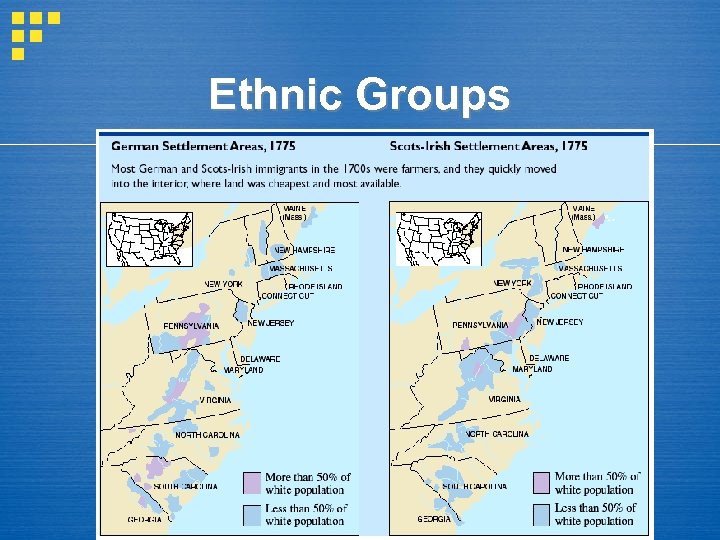 Ethnic Groups
Ethnic Groups
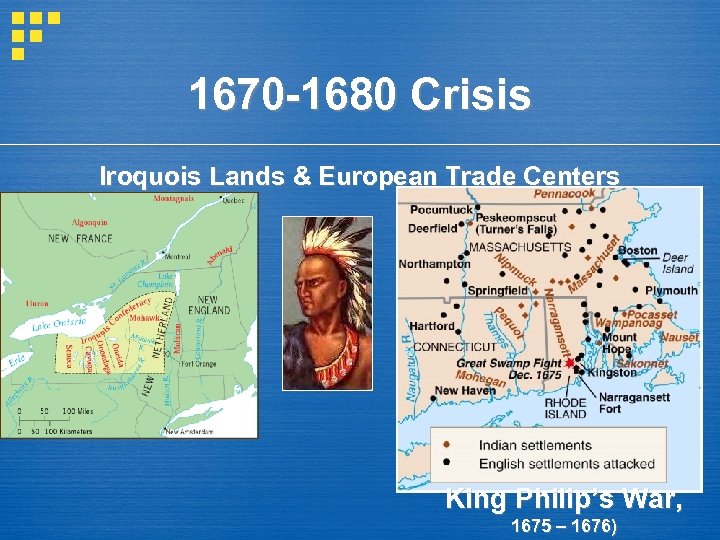 1670 -1680 Crisis Iroquois Lands & European Trade Centers King Philip’s War, 1675 – 1676)
1670 -1680 Crisis Iroquois Lands & European Trade Centers King Philip’s War, 1675 – 1676)
 From Authoritarianism to Individualism § Great Awakening § Enlightenment Powerpoint show
From Authoritarianism to Individualism § Great Awakening § Enlightenment Powerpoint show
 From Authoritarianism to Individualism § Puritan Farmer from Massachusetts in 1640 § Baptist seaman in Rhode Island in 1740 § Scholar of the Enlightenment at he College of William and Mary in Virginia in 1765. Compose paragraphs that characterize thinking of your character on each of the points listed below: His concept of God The individual’s reason for existence The individual’s relationship to God The need for education The individual’s role in government The individual’s responsibility for improving society
From Authoritarianism to Individualism § Puritan Farmer from Massachusetts in 1640 § Baptist seaman in Rhode Island in 1740 § Scholar of the Enlightenment at he College of William and Mary in Virginia in 1765. Compose paragraphs that characterize thinking of your character on each of the points listed below: His concept of God The individual’s reason for existence The individual’s relationship to God The need for education The individual’s role in government The individual’s responsibility for improving society
 Sequential Worksheet
Sequential Worksheet
 Homework § Carefully write out the question on the SFI worksheet provided. § Complete the SFI for Friday “To what extent did the 3 regions of colonial America develop separate societies in the years prior to the American Revolution? ”
Homework § Carefully write out the question on the SFI worksheet provided. § Complete the SFI for Friday “To what extent did the 3 regions of colonial America develop separate societies in the years prior to the American Revolution? ”


