72c4bb55eaad7b89f04d87dc3eae4553.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
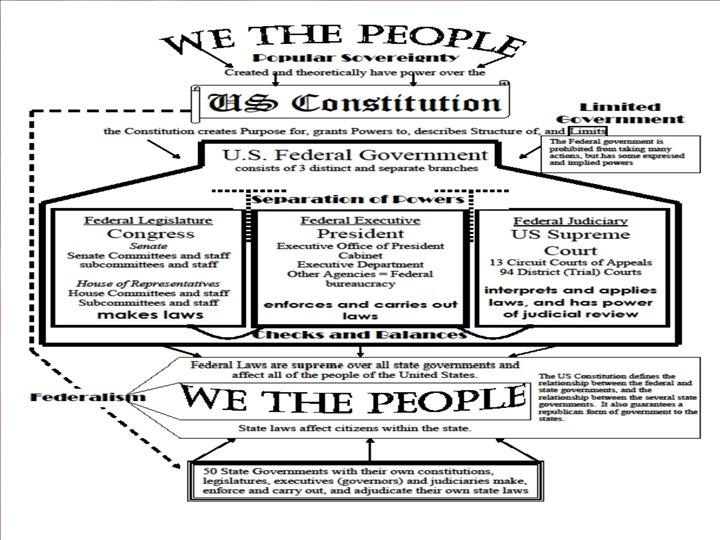
 APS Day 10 Agenda EU – The Constitution defines the structure and powers of a bicameral Congress. Legislation - the laws - are the written public policies. Intro to Congress – get (white) Unit 2 packet white 1. Structure of US Gov’t – review Kleinogram 2. Individually, complete assigned questions on Form of Congress p 3 -4 Constitutional description of Congress and its powers and limits 3. Group work to finish Form of Congress p 3 -4 4. Review key differences between Hof. R and Senate – take notes Legislation – laws that regulate public and private activity, distribute public resources, take private resources for public use or symbolically act. Bill Project – log on to http: //mrkleinsocstudy. pbworks. com/ With a partner, type this link in the URL box http: //www. thomas. gov/. 1. 2. 3. 4. Toggle "Bill Number" above the search box. In the "search" box type "HR 45. " When HR 45 comes up, click on "Text of Legislation, " then click on "Printer Friendly" link. Read through HR 45 and answer the following questions:
APS Day 10 Agenda EU – The Constitution defines the structure and powers of a bicameral Congress. Legislation - the laws - are the written public policies. Intro to Congress – get (white) Unit 2 packet white 1. Structure of US Gov’t – review Kleinogram 2. Individually, complete assigned questions on Form of Congress p 3 -4 Constitutional description of Congress and its powers and limits 3. Group work to finish Form of Congress p 3 -4 4. Review key differences between Hof. R and Senate – take notes Legislation – laws that regulate public and private activity, distribute public resources, take private resources for public use or symbolically act. Bill Project – log on to http: //mrkleinsocstudy. pbworks. com/ With a partner, type this link in the URL box http: //www. thomas. gov/. 1. 2. 3. 4. Toggle "Bill Number" above the search box. In the "search" box type "HR 45. " When HR 45 comes up, click on "Text of Legislation, " then click on "Printer Friendly" link. Read through HR 45 and answer the following questions:
 KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE HOUSE AND SENATE CONSTITUTIONAL DIFFERENCES HOUSE Two-year terms Comprises 435 members (apportioned by population) Must be 25 yrs old SENATE Six-year terms (1/3 up for reelection every two years) Comprises 100 members (2 from each state) Must be citizen for 7 years Must be 30 yrs old Must live in the state represented Must be citizen for 9 years Must live in the state represented Initiates all revenue bills Tries impeached officials Initiates impeachment procedures and passes articles of impeachment Offers "advice and consent" on many major presidential appointments Approves treaties
KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE HOUSE AND SENATE CONSTITUTIONAL DIFFERENCES HOUSE Two-year terms Comprises 435 members (apportioned by population) Must be 25 yrs old SENATE Six-year terms (1/3 up for reelection every two years) Comprises 100 members (2 from each state) Must be citizen for 7 years Must be 30 yrs old Must live in the state represented Must be citizen for 9 years Must live in the state represented Initiates all revenue bills Tries impeached officials Initiates impeachment procedures and passes articles of impeachment Offers "advice and consent" on many major presidential appointments Approves treaties
 DIFFERENCES IN OPERATION HOUSE SENATE More centralized, more formal, stronger leadership Less centralized, less formal, weaker leadership Rules Committee fairly powerful in controlling time and rules of debate (in conjunction with the majority leader) No Rules Committee; limits on debate come through unanimous consent or cloture vote of 60% to end a filibuster More impersonal More personal Members are highly specialized Members are generalist Emphasizes tax and revenue policy Emphasizes foreign policy Seniority important in determining power Seniority less important in determining power
DIFFERENCES IN OPERATION HOUSE SENATE More centralized, more formal, stronger leadership Less centralized, less formal, weaker leadership Rules Committee fairly powerful in controlling time and rules of debate (in conjunction with the majority leader) No Rules Committee; limits on debate come through unanimous consent or cloture vote of 60% to end a filibuster More impersonal More personal Members are highly specialized Members are generalist Emphasizes tax and revenue policy Emphasizes foreign policy Seniority important in determining power Seniority less important in determining power
 CHANGES IN THE INSTITUTION HOUSE Power formerly centralized in the hands of key committees and the leadership; breaking down House procedures are becoming more efficient, with less debate and fewer amendments SENATE Senate workload increasing and informality breaking down Members are becoming more specialized; debate and deliberations less frequent Both chambers are seeing increased partisanship and incivility – less compromise, less bipartisan activity, less friendliness
CHANGES IN THE INSTITUTION HOUSE Power formerly centralized in the hands of key committees and the leadership; breaking down House procedures are becoming more efficient, with less debate and fewer amendments SENATE Senate workload increasing and informality breaking down Members are becoming more specialized; debate and deliberations less frequent Both chambers are seeing increased partisanship and incivility – less compromise, less bipartisan activity, less friendliness
 House leadership Speaker – Nancy Pelosi (D-CA) Minority Leader Majority Leader John Boehner (R – OH) Steny Hoyer (D – MD) Minority Whip Majority Whip James E. Clyburn (D – SC) Eric Cantor (R -VA)
House leadership Speaker – Nancy Pelosi (D-CA) Minority Leader Majority Leader John Boehner (R – OH) Steny Hoyer (D – MD) Minority Whip Majority Whip James E. Clyburn (D – SC) Eric Cantor (R -VA)
 Senate Leadership President of the Senate Joe Biden U. S. Vice President Majority Leader Harry Reid Democrat, Nevada Minority Leader Mitch Mc. Connell Republican, Kentucky President Pro Tempore Robert C. Byrd Democrat, West Virginia Assistant Majority Leader (Democratic Whip) Richard Durbin Democrat, Illinois Assistant Minority Leader (Republican Whip) Jon Kyl Republican, Arizona
Senate Leadership President of the Senate Joe Biden U. S. Vice President Majority Leader Harry Reid Democrat, Nevada Minority Leader Mitch Mc. Connell Republican, Kentucky President Pro Tempore Robert C. Byrd Democrat, West Virginia Assistant Majority Leader (Democratic Whip) Richard Durbin Democrat, Illinois Assistant Minority Leader (Republican Whip) Jon Kyl Republican, Arizona
 Right click on this link to open in a new window : http: //www. thomas. gov/. Toggle "Bill Number" above the search box. In the "search" box type "HR 45. " When HR 45 comes up, click on "Text of Legislation, " then click on "Printer Friendly" link. Read through HR 45 and answer the following questions: 1. What is the purpose for this bill? 2. Who is the bill's sponsor? 3. Scroll through to the END of the table of contents and go to Sec. 2. What is the title of this section? 4. Section 2, Subsection (a) 3. can be connected to a very specific enumerated power of Congress listed in the US Constitution. Which enumerated power of Congress is referred to here? 5. Subsection (a) 6. explains why this bill's short title is named after Blair Holt. Why is the bill named after this person? 6. What key facts lead Congress to make this bill? 7. What rule is created by Sec. 101? 8. What is the title of Sec. 103? 9. According to Sec. 103, who is responsible for executing the rules set up by Sec. 101 10. What rule is created by Sec. 201? 11. According to Sec. 401, what are the penalties for violating the rules of Sec 101 of this bill? (Sec. 922 of Title 18 of US Code)
Right click on this link to open in a new window : http: //www. thomas. gov/. Toggle "Bill Number" above the search box. In the "search" box type "HR 45. " When HR 45 comes up, click on "Text of Legislation, " then click on "Printer Friendly" link. Read through HR 45 and answer the following questions: 1. What is the purpose for this bill? 2. Who is the bill's sponsor? 3. Scroll through to the END of the table of contents and go to Sec. 2. What is the title of this section? 4. Section 2, Subsection (a) 3. can be connected to a very specific enumerated power of Congress listed in the US Constitution. Which enumerated power of Congress is referred to here? 5. Subsection (a) 6. explains why this bill's short title is named after Blair Holt. Why is the bill named after this person? 6. What key facts lead Congress to make this bill? 7. What rule is created by Sec. 101? 8. What is the title of Sec. 103? 9. According to Sec. 103, who is responsible for executing the rules set up by Sec. 101 10. What rule is created by Sec. 201? 11. According to Sec. 401, what are the penalties for violating the rules of Sec 101 of this bill? (Sec. 922 of Title 18 of US Code)
 Read through HR 45 and answer the following questions: 1. What is the purpose for this bill? To provide for the implementation of a system of licensing for purchasers of certain firearms and for a record of sale system for those firearms, and for other purposes. 2. Who is the bill's sponsor? Mr. Bobby Rush (IL 1) 3. Scroll through to the END of the table of contents and go to Sec. 2. What is the title of this section? Findings 4. Section 2, Subsection (a) 3. can be connected to a very specific enumerated power of Congress listed in the US Constitution. Which enumerated power of Congress is referred to here? Interstate trade regulation power in commerce clause A 1, S 8, C 3 5. Section 2, Subsection (a) 6. explains why this bill's short title is named after Blair Holt. Why is the bill named after this person? A high school boy died from gunshot wounds after trying to protect a girl
Read through HR 45 and answer the following questions: 1. What is the purpose for this bill? To provide for the implementation of a system of licensing for purchasers of certain firearms and for a record of sale system for those firearms, and for other purposes. 2. Who is the bill's sponsor? Mr. Bobby Rush (IL 1) 3. Scroll through to the END of the table of contents and go to Sec. 2. What is the title of this section? Findings 4. Section 2, Subsection (a) 3. can be connected to a very specific enumerated power of Congress listed in the US Constitution. Which enumerated power of Congress is referred to here? Interstate trade regulation power in commerce clause A 1, S 8, C 3 5. Section 2, Subsection (a) 6. explains why this bill's short title is named after Blair Holt. Why is the bill named after this person? A high school boy died from gunshot wounds after trying to protect a girl
 6. What key facts lead Congress to make this bill? That lots of guns are sold across state lines and gun violence is associated with lots of homicides, suicides and non-fatal injuries and that it would be best if the rules were consistent throughout the country 7. What rule is created by Sec. 101? Need to get a license to own a handgun or clip-fed gun 8. What is the title of Sec. 103? Issuance of license 9. According to Sec. 103, who is responsible for executing the rules set up by Sec. 101 The Attorney General 10. What rule is created by Sec. 201? Can’t sell or trade a gun without a license 11. According to Sec. 401, what are the penalties for violating the rules of Sec 101 of this bill? (Sec. 922 of Title 18 of US Code) fine and/or imprisonment of 2, 5, or 10 years.
6. What key facts lead Congress to make this bill? That lots of guns are sold across state lines and gun violence is associated with lots of homicides, suicides and non-fatal injuries and that it would be best if the rules were consistent throughout the country 7. What rule is created by Sec. 101? Need to get a license to own a handgun or clip-fed gun 8. What is the title of Sec. 103? Issuance of license 9. According to Sec. 103, who is responsible for executing the rules set up by Sec. 101 The Attorney General 10. What rule is created by Sec. 201? Can’t sell or trade a gun without a license 11. According to Sec. 401, what are the penalties for violating the rules of Sec 101 of this bill? (Sec. 922 of Title 18 of US Code) fine and/or imprisonment of 2, 5, or 10 years.
 Standing committees • are permanent panels identified as such in chamber rules (House Rule X, Senate Rule XXV). Because they have legislative jurisdiction, standing committees consider bills and issues and recommend measures for consideration by their respective chambers. They also have oversight responsibility to monitor agencies, programs, and activities within their jurisdictions, and in some cases in areas that cut across committee jurisdictions. • Most of the work of each chamber is done by standing committees. Almost no laws are created without the hearings, debate, markup and approval of standing committees.
Standing committees • are permanent panels identified as such in chamber rules (House Rule X, Senate Rule XXV). Because they have legislative jurisdiction, standing committees consider bills and issues and recommend measures for consideration by their respective chambers. They also have oversight responsibility to monitor agencies, programs, and activities within their jurisdictions, and in some cases in areas that cut across committee jurisdictions. • Most of the work of each chamber is done by standing committees. Almost no laws are created without the hearings, debate, markup and approval of standing committees.
 Select or special committees • are established generally by a separate resolution of the chamber, sometimes to conduct investigations and studies, and, on other occasions, also to consider measures. Often, select committees examine emerging issues that don’t fit clearly within existing standing committee jurisdictions, or which cut across jurisdictional boundaries. A select committee may be permanent but is most often temporary. Instead of select, the Senate sometimes uses the term special committee (as in the Special Committee on Aging) or the current House Select Committee on Energy Independence and Global Warming.
Select or special committees • are established generally by a separate resolution of the chamber, sometimes to conduct investigations and studies, and, on other occasions, also to consider measures. Often, select committees examine emerging issues that don’t fit clearly within existing standing committee jurisdictions, or which cut across jurisdictional boundaries. A select committee may be permanent but is most often temporary. Instead of select, the Senate sometimes uses the term special committee (as in the Special Committee on Aging) or the current House Select Committee on Energy Independence and Global Warming.
 conference committee - A temporary, ad hoc panel composed of House and Senate conferees which is formed for the purpose of reconciling differences in legislation that has passed both chambers. Conference committees are usually convened to resolve bicameral differences on major and controversial legislation.
conference committee - A temporary, ad hoc panel composed of House and Senate conferees which is formed for the purpose of reconciling differences in legislation that has passed both chambers. Conference committees are usually convened to resolve bicameral differences on major and controversial legislation.
 Committees – who, what and why? For your committee, go to committee’s webpage found on the Senate. gov site: 1. Identify the Chair and minority ranking member 2. Identify the executive departments overseen 3. Identify the jurisdiction 4. Identify the key subcommittees.
Committees – who, what and why? For your committee, go to committee’s webpage found on the Senate. gov site: 1. Identify the Chair and minority ranking member 2. Identify the executive departments overseen 3. Identify the jurisdiction 4. Identify the key subcommittees.
 Democrats Oppose censorship Support organized labor Oppose wider searches w/o warrants Support expanding equality Support gun control Oppose new oil drilling Support social welfare spending Support wider health spending Support regulations on business Support tax increases Support barrier between church and state Support right to die Oppose capital punishment Support bilingualism Republicans Support censorship Oppose organized labor Support wider searches w/o warrants Oppose expanding equality through gov’t action Oppose gun control Support new oil drilling Oppose social welfare spending Oppose many regulations on business Oppose taxes Support religion working with state Oppose assisted suicide Support capital punishment Support English-only
Democrats Oppose censorship Support organized labor Oppose wider searches w/o warrants Support expanding equality Support gun control Oppose new oil drilling Support social welfare spending Support wider health spending Support regulations on business Support tax increases Support barrier between church and state Support right to die Oppose capital punishment Support bilingualism Republicans Support censorship Oppose organized labor Support wider searches w/o warrants Oppose expanding equality through gov’t action Oppose gun control Support new oil drilling Oppose social welfare spending Oppose many regulations on business Oppose taxes Support religion working with state Oppose assisted suicide Support capital punishment Support English-only


