398890b3aaada9ec50122ccd15a41081.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Appropriate Use of Constant Sum Data Joel Huber-Duke University Eric Bradlow-Wharton School Sawtooth Software Conference September 2001
Appropriate Use of Constant Sum Data • • What is Constant Sum Scale data? When will CSS data work? When will it fail? An analysis of Volumetric Data using both HBsum and HBreg

Single Choice Task Choose a potato chip snack given these options Lays Eagle Store brand Sour Cream Barbecue Regular Chips ½ oz bag ¾ oz bag 1 oz bag $. 50 $. 65 $. 75

Constant Sum Task In ten purchases indicate how many of each you would buy Lays Eagle Store brand Sour Cream Barbecue Regular Chips ½ oz bag ¾ oz bag 1 oz bag $. 50 $. 65 $. 75
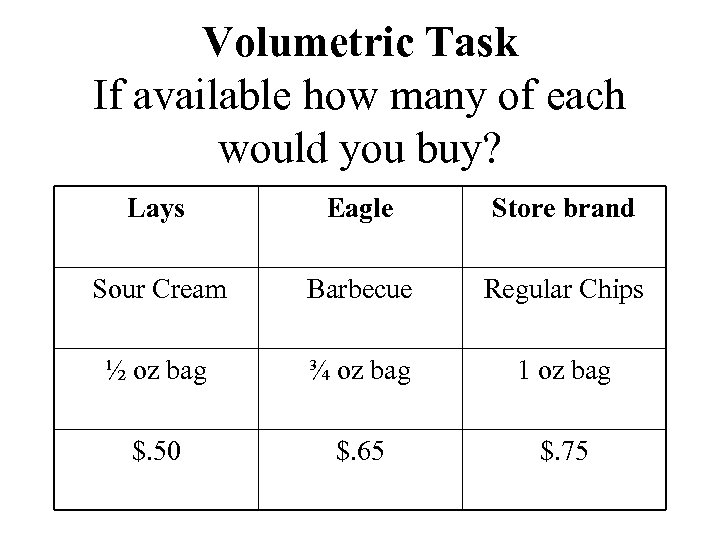
Volumetric Task If available how many of each would you buy? Lays Eagle Store brand Sour Cream Barbecue Regular Chips ½ oz bag ¾ oz bag 1 oz bag $. 50 $. 65 $. 75

Appropriate CSS usage • When people can estimate frequency of usage in a context—as examples: – Soft drink choice – Breakfast cereals – Prescriptions given diagnosis – Multiple supplier contracts

Inappropriate CSS usage • As a measure of preference strength – Allocate 10 points proportional to your preferences • As a measure of choice uncertainty – Indicate the probability of choosing each alternative • As a summary across different usage contexts – What proportion of beverage purchases will be Coke?

An example of conditional beverage choices • • • Drink Coke when tired Drink Sprite when thirsty Drink Heinekens with in-laws Drink Iron City with friends Drink Turning Leaf when romantic Drink Ripple when depressed
Alternative to constant sum • Condition choices on usage situation – Derive situation frequency from a separate direct question • Ask a single choice questions – Derive variability by conditioning on context, or error in choice model

Analysis of Volumetric Choice Data • Volume estimates among four frequently purchased non-durables • Each alternative defined by brand, type, size, incentive and price • 10 different randomized sets of alternatives • One fixed holdout set • Task: How many of each would you choose? (max=10)

People reacted differently to this task • • 22% of sets produced exactly one purchase 33% of the sets produced none 45% chose more than one purchase People differed in their likelihood to use these strategies.
Two-stage analysis process • Need to model both choice share and volume • First stage: Constant sum model with ‘none’ option • Second stage: Hierarchical Bayes regression with item utilities from the first stage

Constant Sum Stage • Sawtooth’s HBSUM estimates 13 parameters for each person. • Model: Sums are normalized as if generated from five independent probabilistic choices – Choice weight =5 – Ten tasks equivalent to 50 independent probabilistic choices • None is included as a fifth alternative

Holdout choice accuracy • 78% hit rate • Mean average error predicting choice share 2. 5 share points • Respondents differed strongly on their use of none
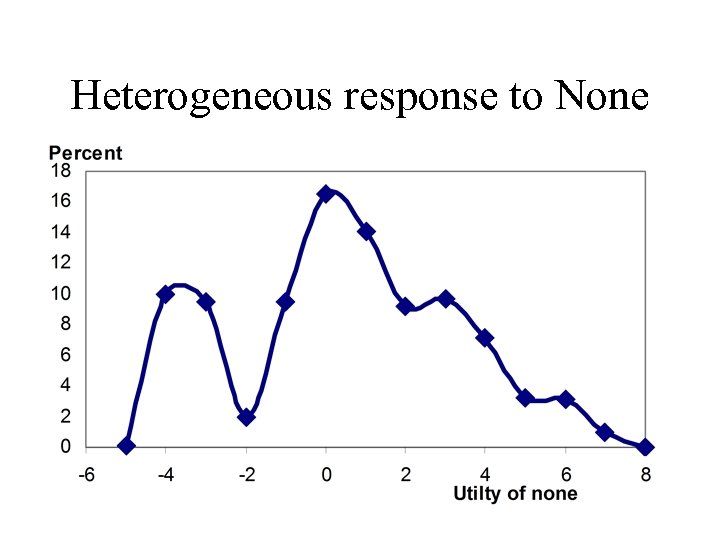
Heterogeneous response to None
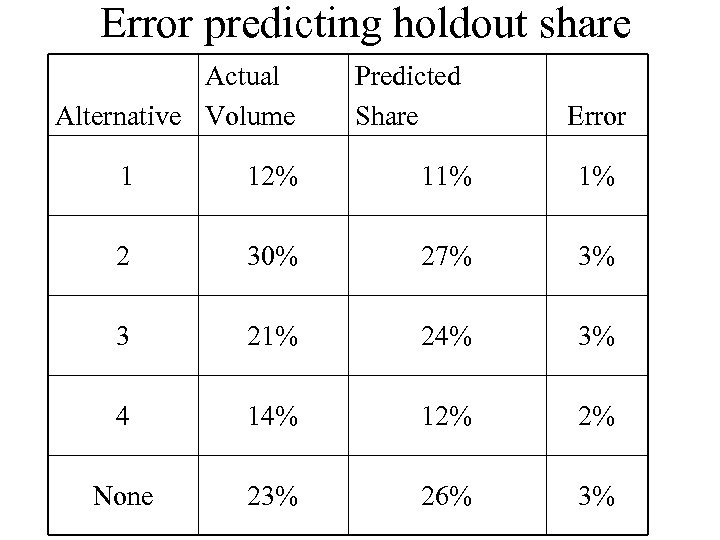
Error predicting holdout share Actual Alternative Volume Predicted Share Error 1 12% 11% 1% 2 30% 27% 3% 3 21% 24% 3% 4 14% 12% 2% None 23% 26% 3%

HBreg predicts volume as a function of: • A constant for each individual • The utility of each item (from HBsum) • Adjusting for the utility of the set – Coefficient will be negative to the extent that volumes are proportional to the relative value within a set
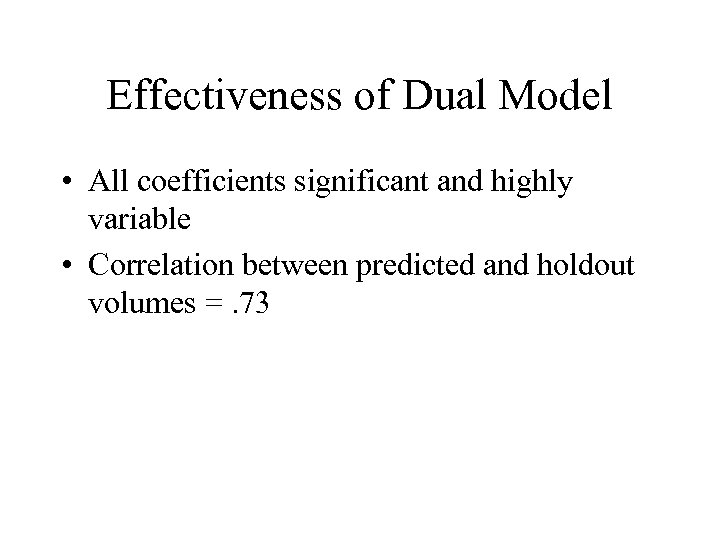
Effectiveness of Dual Model • All coefficients significant and highly variable • Correlation between predicted and holdout volumes =. 73
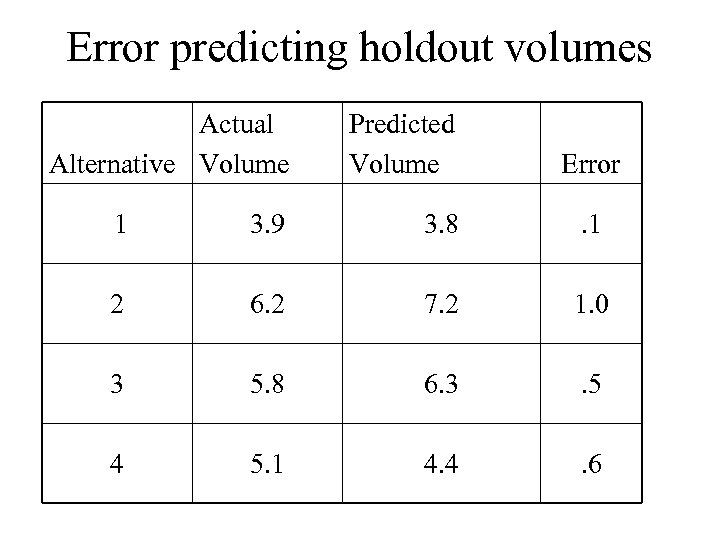
Error predicting holdout volumes Actual Alternative Volume Predicted Volume Error 1 3. 9 3. 8 . 1 2 6. 2 7. 2 1. 0 3 5. 8 6. 3 . 5 4 5. 1 4. 4 . 6

Conclusions • Constant sum scale measures are mainly appropriate when frequencies are easy to estimate given a set of alternatives • Volumetric estimates require even more of respondents, and thus are even more rare • Hierarchical Bayes methods are critical for correct modeling, because of the heterogeneity in the ways people respond to the task

Conclusions • We found heterogeneity with respect to – The use of None – The average volume – The partworths attached to the attributes – The degree to which alternatives are contrasted with others in the set • A two-stage HB allows people with idiosyncratic processes to be represented
398890b3aaada9ec50122ccd15a41081.ppt