 Approaches to the Pineal Region Jan M. Eckermann, MD Department of Neurosurgery
Approaches to the Pineal Region Jan M. Eckermann, MD Department of Neurosurgery
 Why go there? • Pineal cell tumors: pineocytomas, pineoblastomas • Germ cell tumors: teratomas, dermoid, epidermoid, endodermal sinus, embryonal cell, choriocarcinoma, germinoma, • Astrocytomas, meningioma, ependymoma, metastatic tumors
Why go there? • Pineal cell tumors: pineocytomas, pineoblastomas • Germ cell tumors: teratomas, dermoid, epidermoid, endodermal sinus, embryonal cell, choriocarcinoma, germinoma, • Astrocytomas, meningioma, ependymoma, metastatic tumors
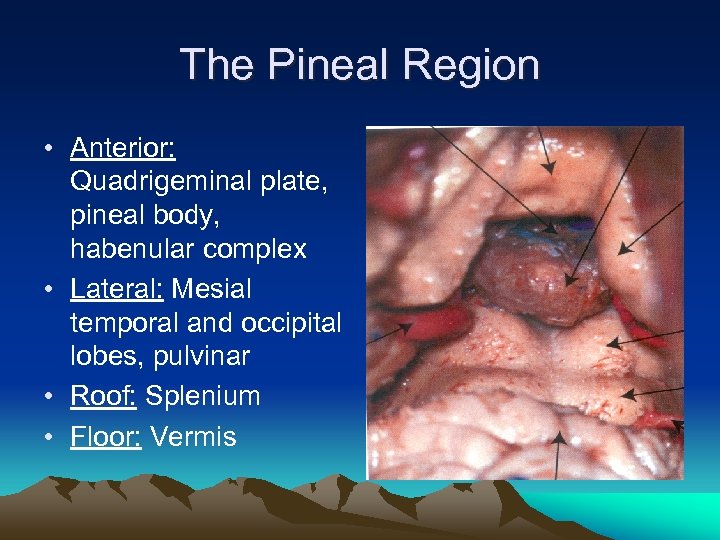 The Pineal Region • Anterior: Quadrigeminal plate, pineal body, habenular complex • Lateral: Mesial temporal and occipital lobes, pulvinar • Roof: Splenium • Floor: Vermis
The Pineal Region • Anterior: Quadrigeminal plate, pineal body, habenular complex • Lateral: Mesial temporal and occipital lobes, pulvinar • Roof: Splenium • Floor: Vermis
 The Quadrigeminal Cistern • Both supra- and infratentorial • Anterior: Superior medullary velum, quadrigeminal plate, pineal gland • Posterior: Thick arachnoid to tentorium • Lateral: Loose arachnoid separates from ambient cisterns
The Quadrigeminal Cistern • Both supra- and infratentorial • Anterior: Superior medullary velum, quadrigeminal plate, pineal gland • Posterior: Thick arachnoid to tentorium • Lateral: Loose arachnoid separates from ambient cisterns
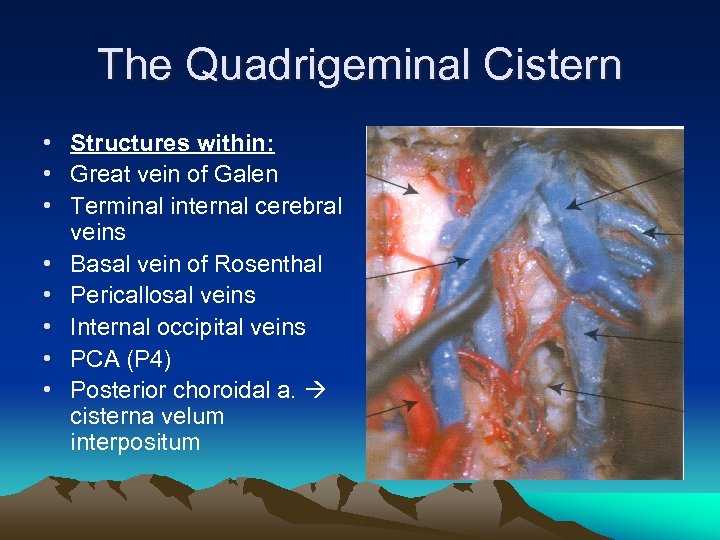 The Quadrigeminal Cistern • Structures within: • Great vein of Galen • Terminal internal cerebral veins • Basal vein of Rosenthal • Pericallosal veins • Internal occipital veins • PCA (P 4) • Posterior choroidal a. cisterna velum interpositum
The Quadrigeminal Cistern • Structures within: • Great vein of Galen • Terminal internal cerebral veins • Basal vein of Rosenthal • Pericallosal veins • Internal occipital veins • PCA (P 4) • Posterior choroidal a. cisterna velum interpositum
 Approaches • Supracerebellar – Infratentorial • Occiptial – Transtentorial • Combined Supratentorial – Infratentorial Transsinus
Approaches • Supracerebellar – Infratentorial • Occiptial – Transtentorial • Combined Supratentorial – Infratentorial Transsinus
 Supracerebellar – Infratentorial • Sitting or concord position • Midline or inverted Ushaped incision
Supracerebellar – Infratentorial • Sitting or concord position • Midline or inverted Ushaped incision
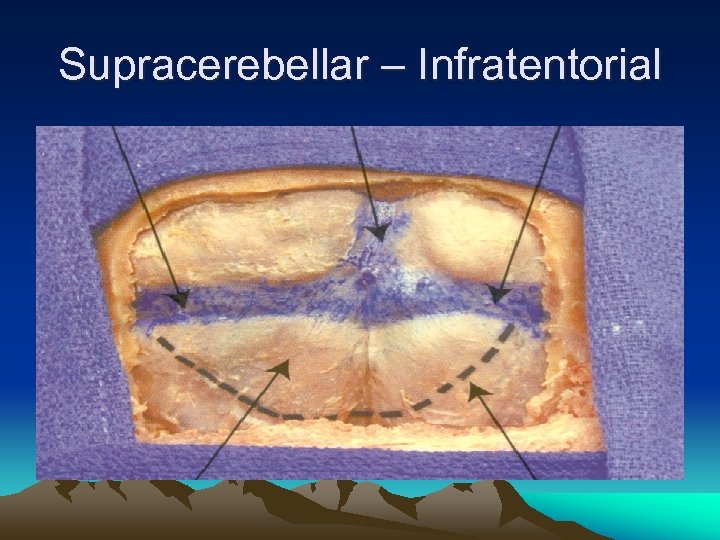 Supracerebellar – Infratentorial
Supracerebellar – Infratentorial
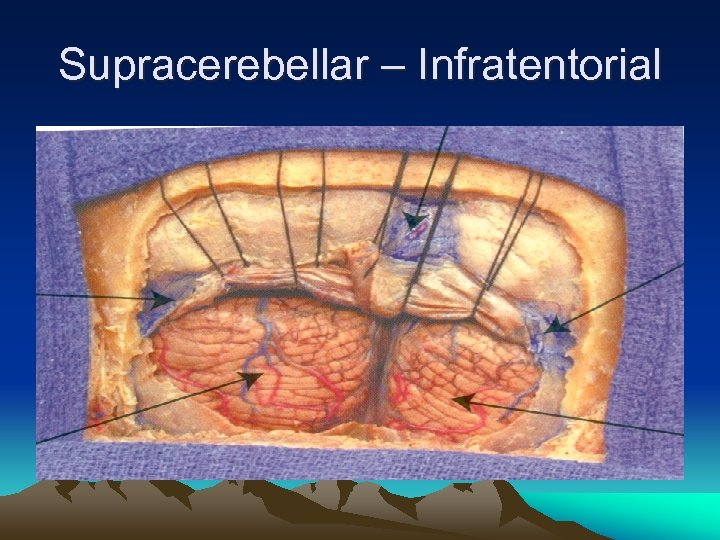 Supracerebellar – Infratentorial
Supracerebellar – Infratentorial
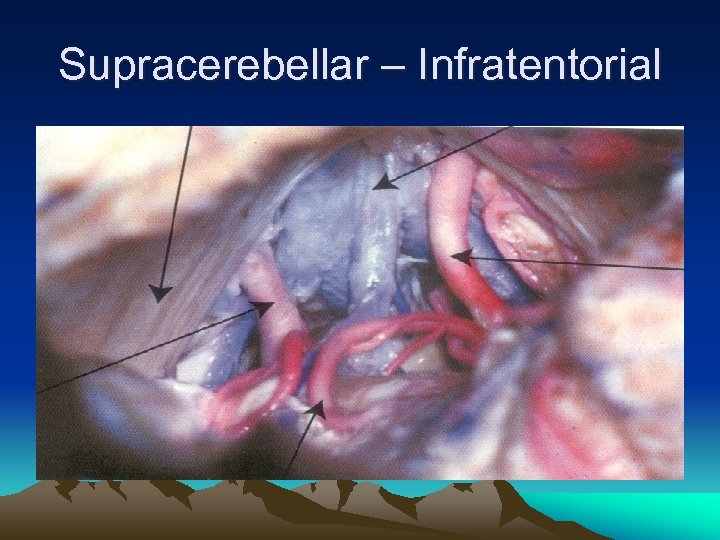 Supracerebellar – Infratentorial
Supracerebellar – Infratentorial
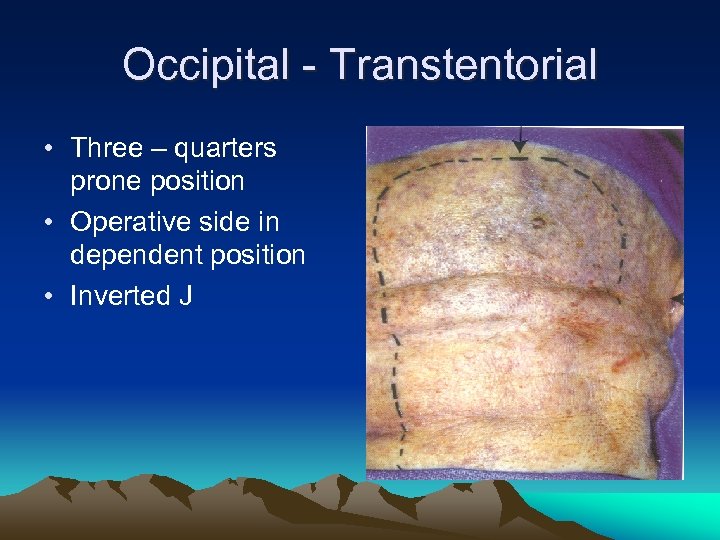 Occipital - Transtentorial • Three – quarters prone position • Operative side in dependent position • Inverted J
Occipital - Transtentorial • Three – quarters prone position • Operative side in dependent position • Inverted J
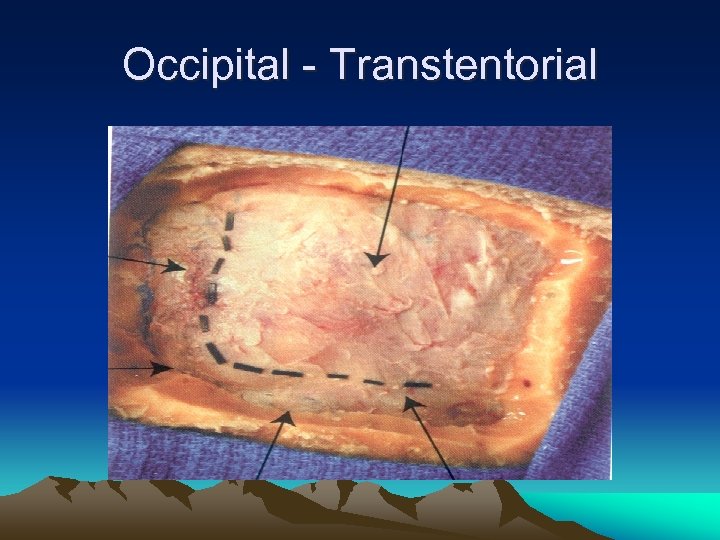 Occipital - Transtentorial
Occipital - Transtentorial
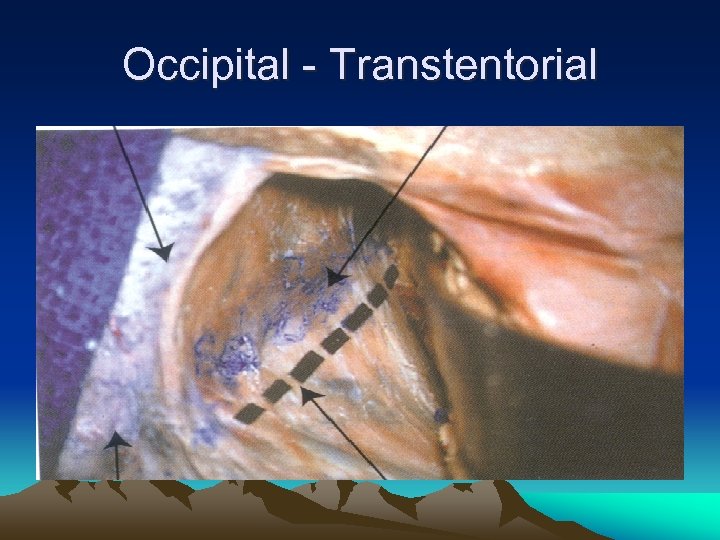 Occipital - Transtentorial
Occipital - Transtentorial
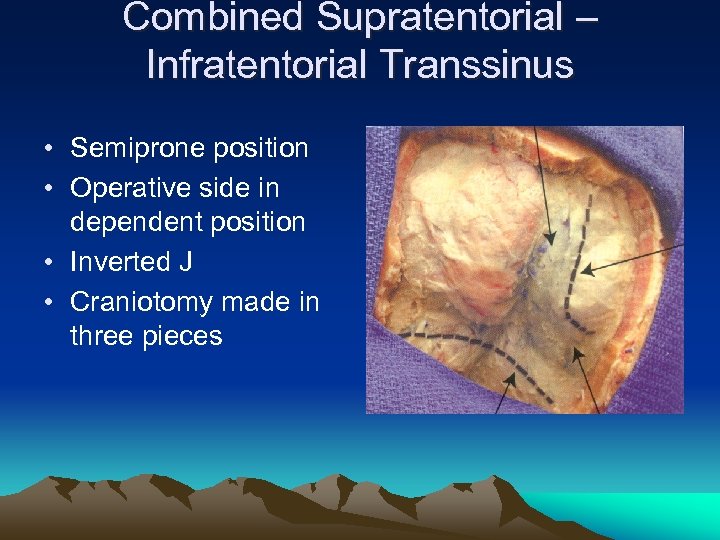 Combined Supratentorial – Infratentorial Transsinus • Semiprone position • Operative side in dependent position • Inverted J • Craniotomy made in three pieces
Combined Supratentorial – Infratentorial Transsinus • Semiprone position • Operative side in dependent position • Inverted J • Craniotomy made in three pieces
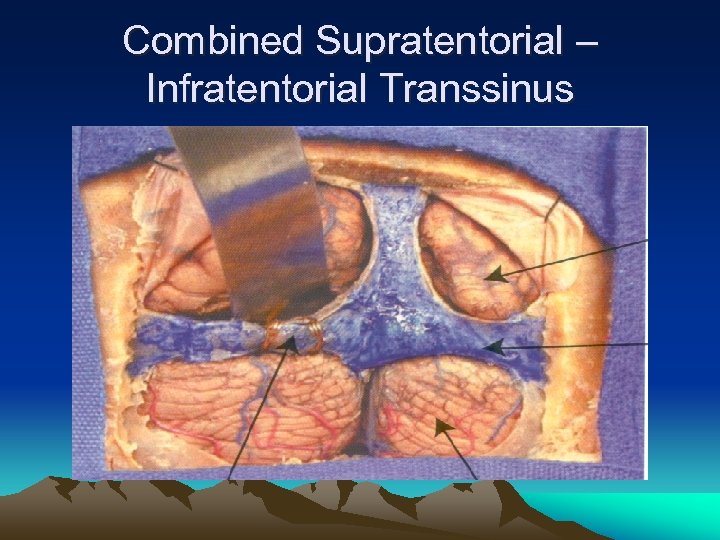 Combined Supratentorial – Infratentorial Transsinus
Combined Supratentorial – Infratentorial Transsinus
 Complications and Considerations • Supracerebellar – Infratentorial: • Air embolism • Ventricluar collapse SDH, pneumocephalus • Not suitable for superior extending lesions • Gravity retracting cerebellum
Complications and Considerations • Supracerebellar – Infratentorial: • Air embolism • Ventricluar collapse SDH, pneumocephalus • Not suitable for superior extending lesions • Gravity retracting cerebellum
 Complications and Considerations • Occiptial – Transtentorial: • Retraction of occipital lobes visual field defects • Disconnection syndrome • Limited exposure of contralateral side • Good view of quadrigeminal plate
Complications and Considerations • Occiptial – Transtentorial: • Retraction of occipital lobes visual field defects • Disconnection syndrome • Limited exposure of contralateral side • Good view of quadrigeminal plate
 Complications and Considerations • Combined Supratentorial – Infratentorial Transsinus: • Brain edema • Venous infarcts • Very wide exposure • Consider primary re-anastomosis or patch graft
Complications and Considerations • Combined Supratentorial – Infratentorial Transsinus: • Brain edema • Venous infarcts • Very wide exposure • Consider primary re-anastomosis or patch graft
 References • Fossett TF and Caputy JC. Operative Neurosurgical Anatomy. Thieme: New York 2002 • Haye AH and Laws ER. Brain Tumors. Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh 1995
References • Fossett TF and Caputy JC. Operative Neurosurgical Anatomy. Thieme: New York 2002 • Haye AH and Laws ER. Brain Tumors. Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh 1995