6dc2a8a63f946937cc97f53da733e690.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59
 Approaches in Maryland EMS Quality Improvement John New Director, MIEMSS Quality Management Prepared For: QA Officer Training Day 2, Session 3 – 9: 00 to 10: 30.
Approaches in Maryland EMS Quality Improvement John New Director, MIEMSS Quality Management Prepared For: QA Officer Training Day 2, Session 3 – 9: 00 to 10: 30.
 EMS Quality Approaches n n n n Quality Catalyst Overview Brief History of QM Essential Parts of Quality Organizations MIEMSS Experience Practical Example Assessing “Quality” Organizations Moving On Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
EMS Quality Approaches n n n n Quality Catalyst Overview Brief History of QM Essential Parts of Quality Organizations MIEMSS Experience Practical Example Assessing “Quality” Organizations Moving On Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Maryland’s EMS Quality Catalysts for Change A Leadership Guide To Quality Improvement A Leadership Guide to Quality Improvement for Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Systems. This publication is distributed by the US. . . www. nhtsa. dot. gov/people/injury/ems/Leaderguide/ - 101 k NHTSA (July 1997) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Maryland’s EMS Quality Catalysts for Change A Leadership Guide To Quality Improvement A Leadership Guide to Quality Improvement for Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Systems. This publication is distributed by the US. . . www. nhtsa. dot. gov/people/injury/ems/Leaderguide/ - 101 k NHTSA (July 1997) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
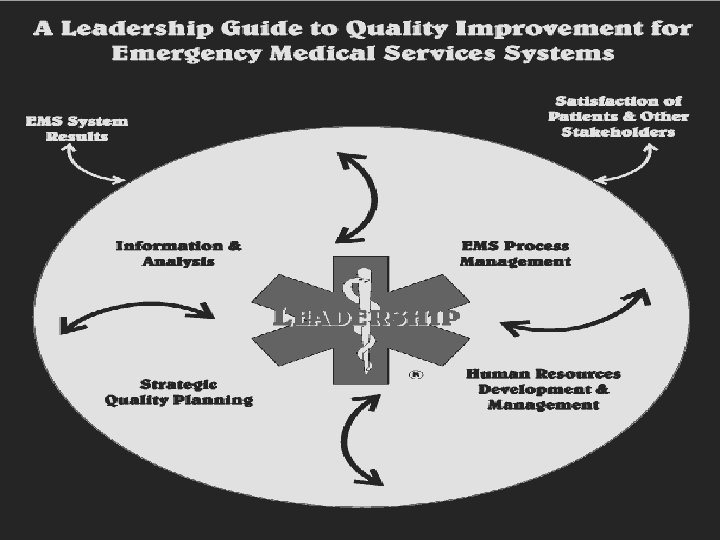 Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Maryland’s EMS Quality Catalysts for Change n “A Leadership Guide to Quality n Title 30 MIEMSS Regulations (Dec. 1999) Improvement for Emergency Medical Services Systems” – NHTSA (July 1997) n Subtitle 03 EMS Operations n n n Chapter 04 02 Quality Assurance Plan Chapter 04 03 Medical Review Committee Chapter 04 08 Quality Assurance Officer (Oct. 2007) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Maryland’s EMS Quality Catalysts for Change n “A Leadership Guide to Quality n Title 30 MIEMSS Regulations (Dec. 1999) Improvement for Emergency Medical Services Systems” – NHTSA (July 1997) n Subtitle 03 EMS Operations n n n Chapter 04 02 Quality Assurance Plan Chapter 04 03 Medical Review Committee Chapter 04 08 Quality Assurance Officer (Oct. 2007) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved

 Maryland’s EMS Quality Catalysts for Change n “A Leadership Guide to Quality n Title 30 MIEMSS Regulations (Dec. 1999) Improvement for Emergency Medical Services Systems” – NHTSA (July 1997) n Subtitle 03 EMS Operations n n Chapter 04 02 Quality Assurance Plan Chapter 04 03 Medical Review Committee Chapter 04 08 Quality Assurance Officer (Oct. 2007) Managing For Results (MFR) (June 1997) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Maryland’s EMS Quality Catalysts for Change n “A Leadership Guide to Quality n Title 30 MIEMSS Regulations (Dec. 1999) Improvement for Emergency Medical Services Systems” – NHTSA (July 1997) n Subtitle 03 EMS Operations n n Chapter 04 02 Quality Assurance Plan Chapter 04 03 Medical Review Committee Chapter 04 08 Quality Assurance Officer (Oct. 2007) Managing For Results (MFR) (June 1997) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved

 Catalyst Commonalities Leadership’s Role in defining EMS “Quality” n Accountability through Goal Setting and Measurement n A Need to be Proactive towards “Improvement” n Shift from Parochial Interests (silos) to Cooperative Excellence (system) n Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Catalyst Commonalities Leadership’s Role in defining EMS “Quality” n Accountability through Goal Setting and Measurement n A Need to be Proactive towards “Improvement” n Shift from Parochial Interests (silos) to Cooperative Excellence (system) n Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Evolutionary and Blended Focus A Series of Scientific and Humanistic Processes Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Evolutionary and Blended Focus A Series of Scientific and Humanistic Processes Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Quality Management (QM) Defined n A Process That Integrates: n n n Strategic Planning and Leadership Commitment An Empowered Work Force Recognition of Customers, Stakeholders, Processors Data Utilization and Analysis Results Based Management n n Quality Control Quality Improvement Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Quality Management (QM) Defined n A Process That Integrates: n n n Strategic Planning and Leadership Commitment An Empowered Work Force Recognition of Customers, Stakeholders, Processors Data Utilization and Analysis Results Based Management n n Quality Control Quality Improvement Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
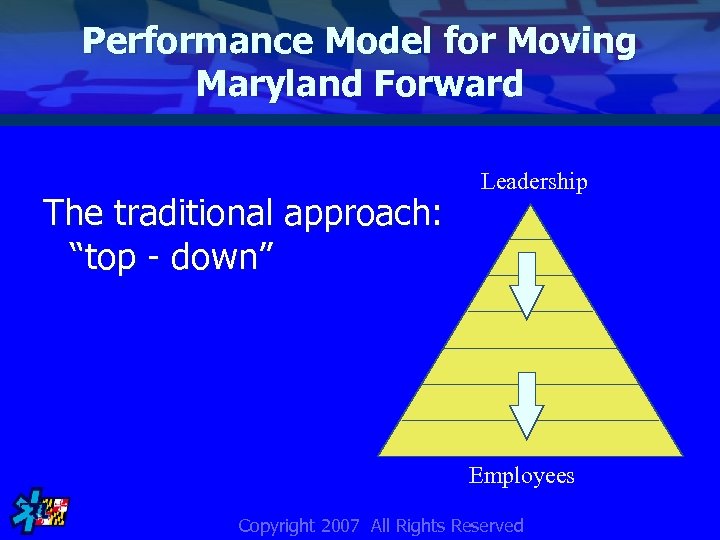 Performance Model for Moving Maryland Forward The traditional approach: “top - down” Leadership Employees Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Performance Model for Moving Maryland Forward The traditional approach: “top - down” Leadership Employees Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
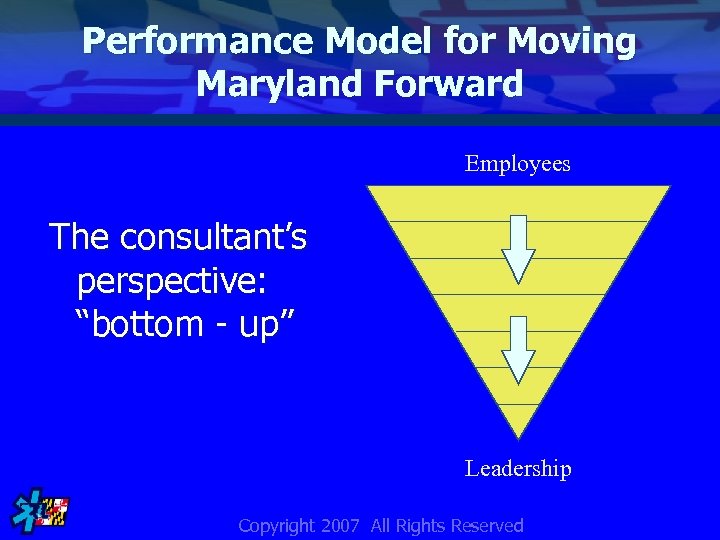 Performance Model for Moving Maryland Forward Employees The consultant’s perspective: “bottom - up” Leadership Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Performance Model for Moving Maryland Forward Employees The consultant’s perspective: “bottom - up” Leadership Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
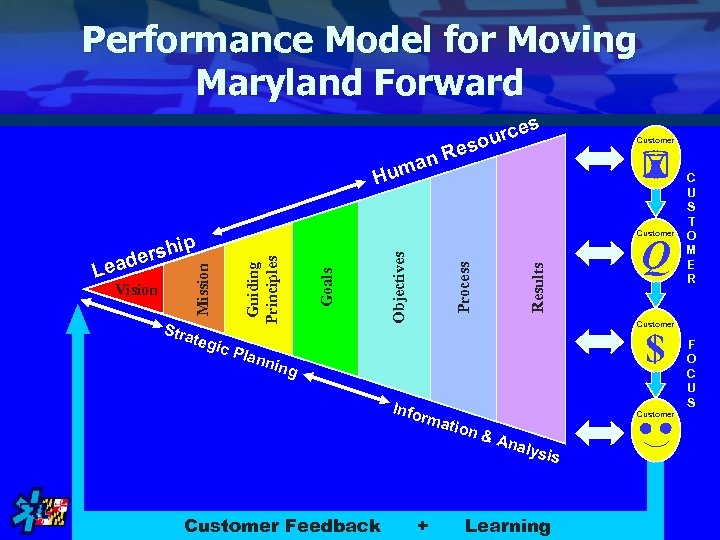 Performance Model for Moving Maryland Forward man Hu tegi c Pl Results Process Goals Objectives Stra Guiding Principles Vision Mission Lea Customer p rshi de rces u eso R Q Customer $ ann ing Info C U S T O M E R rma t ion Customer &A naly sis Copyright 2007 All + Customer Feedback Rights Reserved Learning F O C U S
Performance Model for Moving Maryland Forward man Hu tegi c Pl Results Process Goals Objectives Stra Guiding Principles Vision Mission Lea Customer p rshi de rces u eso R Q Customer $ ann ing Info C U S T O M E R rma t ion Customer &A naly sis Copyright 2007 All + Customer Feedback Rights Reserved Learning F O C U S
 What’s In A Name? CQI - Continuous Quality Improvement n TQM - Total Quality Management n TQS - Total Quality Systems n QSI - Quality Systems Improvement n TQ - Total Quality n QI - Quality Improvement n Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
What’s In A Name? CQI - Continuous Quality Improvement n TQM - Total Quality Management n TQS - Total Quality Systems n QSI - Quality Systems Improvement n TQ - Total Quality n QI - Quality Improvement n Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Quality Management Is Not Traditional Quality Assurance n Tasked Focused n One Right Way n Tough On People n Control/Micro Management n Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Quality Management Is Not Traditional Quality Assurance n Tasked Focused n One Right Way n Tough On People n Control/Micro Management n Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Why Change Management Philosophy n Internal Reasons for Change n Improve Planning Process Budget (Show direct/indirect savings) n Resources Assessment (Identify justifiable items) n n Meet Greater Needs of Organization n Increase Productivity n Increase Employee Morale, Recruitment, Retention Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Why Change Management Philosophy n Internal Reasons for Change n Improve Planning Process Budget (Show direct/indirect savings) n Resources Assessment (Identify justifiable items) n n Meet Greater Needs of Organization n Increase Productivity n Increase Employee Morale, Recruitment, Retention Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Why Change Management Philosophy n External Reasons for Change n Tighter Fiscal Allotments n n Improve Accountability of Given Resources n n Expectation of Tax Cuts not Tax Increases What’s expected is met Market Forces n Competition form Other EMS Services Potential and Actual Patient Expectation Changes n Demographics and Technology n Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Why Change Management Philosophy n External Reasons for Change n Tighter Fiscal Allotments n n Improve Accountability of Given Resources n n Expectation of Tax Cuts not Tax Increases What’s expected is met Market Forces n Competition form Other EMS Services Potential and Actual Patient Expectation Changes n Demographics and Technology n Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Cost of Poor Quality Iceberg Arguments “OBVIOUS” Unsatisfied Complaints Overtime Inspection “LESS OBVIOUS” Job Burn-out Customer Dissatisfaction Doing a Lot, Finishing Little 5, 35 Day Forms Poor Communication Unnecessary Field Service Rush Development Costs Wasted Effort Workplace Hassles Job-hopping More Meetings Departmental and Other Agency Turf Battles Validation Errors Grievances Absenteeism 11 th Hour Jobs Duplication of Effort Low Morale Retraining Lost Time Equipment Failure Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Cost of Poor Quality Iceberg Arguments “OBVIOUS” Unsatisfied Complaints Overtime Inspection “LESS OBVIOUS” Job Burn-out Customer Dissatisfaction Doing a Lot, Finishing Little 5, 35 Day Forms Poor Communication Unnecessary Field Service Rush Development Costs Wasted Effort Workplace Hassles Job-hopping More Meetings Departmental and Other Agency Turf Battles Validation Errors Grievances Absenteeism 11 th Hour Jobs Duplication of Effort Low Morale Retraining Lost Time Equipment Failure Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Historical “Quality” Mind Sets n Capitalistic n n If It’s Not Broke, Don't’ Fix It n n n Assumes Quality is a Given (Slow to React to Change) Sign of Stability (or Sign of Stagnation) Monopoly n n Caveat Emptor (Customer is Responsible for Quality) We’re the Only Supplier Around (Is Usually Short Lived) Quality Imperative n Customer’s Expectations (Meet and Exceed) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Historical “Quality” Mind Sets n Capitalistic n n If It’s Not Broke, Don't’ Fix It n n n Assumes Quality is a Given (Slow to React to Change) Sign of Stability (or Sign of Stagnation) Monopoly n n Caveat Emptor (Customer is Responsible for Quality) We’re the Only Supplier Around (Is Usually Short Lived) Quality Imperative n Customer’s Expectations (Meet and Exceed) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Quality Management In Industry n Walter Shewart (1930’s) - Statistical Quality Control n n Developed Plan, Do, Check and Act cycle (PDCA) W. Edwards Deming (1950’s) - Humanism n Production Flaws are rooted in system design, not in the commitment of the work force. Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Quality Management In Industry n Walter Shewart (1930’s) - Statistical Quality Control n n Developed Plan, Do, Check and Act cycle (PDCA) W. Edwards Deming (1950’s) - Humanism n Production Flaws are rooted in system design, not in the commitment of the work force. Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Quality Management In Industry n Joseph Juran (1950’s) - Total Integrating n Stressed inter-dependency of entire production process. n Philip Crosby (1970’s) - Quality Is Free n Associated quality with cost or no quality=lost $ Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Quality Management In Industry n Joseph Juran (1950’s) - Total Integrating n Stressed inter-dependency of entire production process. n Philip Crosby (1970’s) - Quality Is Free n Associated quality with cost or no quality=lost $ Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Industrial Quality Management Distilled “Eventually I was able to distill into a simple set of precepts the philosophy Dad had followed in managing the business for 40 years: n Give full consideration to the individual employee. n Spend a lot of time making customers happy. n Go the last mile to do every thing right. ” Thomas J. Watson, Jr. President and son of the founder of IBM Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Industrial Quality Management Distilled “Eventually I was able to distill into a simple set of precepts the philosophy Dad had followed in managing the business for 40 years: n Give full consideration to the individual employee. n Spend a lot of time making customers happy. n Go the last mile to do every thing right. ” Thomas J. Watson, Jr. President and son of the founder of IBM Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 QM - Scientific Side n Scientific Side (Analytical Approach) • Objective Data vs. Anecdotal Decision Basis • Understanding of Complex Processes • Quality Control (Determine process gauges) • Quality Improvement (Move beyond existing limits) • AKA - Statistical Quality Control Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
QM - Scientific Side n Scientific Side (Analytical Approach) • Objective Data vs. Anecdotal Decision Basis • Understanding of Complex Processes • Quality Control (Determine process gauges) • Quality Improvement (Move beyond existing limits) • AKA - Statistical Quality Control Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 QM - Humanistic Side n Customer Focus • Who Are They? • Did We Meet Their Requirements? • Can We Exceed Their Expectations? • Internal / External Customer Focus • AKA - Participative Management Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
QM - Humanistic Side n Customer Focus • Who Are They? • Did We Meet Their Requirements? • Can We Exceed Their Expectations? • Internal / External Customer Focus • AKA - Participative Management Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 QM - Humanistic Side n Hawthorne Experiment • 1924 - 1932 • Western Electric Plant, Chicago • Relay Assemblers • Controlled Experiment Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
QM - Humanistic Side n Hawthorne Experiment • 1924 - 1932 • Western Electric Plant, Chicago • Relay Assemblers • Controlled Experiment Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 QM - Humanistic Side n Hawthorne Experiment Results • Output Increases When: • Improvement in resources • Have trust / cooperation among supervisor and worker • Fear in the workplace is eliminated • Monotony is reduced Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
QM - Humanistic Side n Hawthorne Experiment Results • Output Increases When: • Improvement in resources • Have trust / cooperation among supervisor and worker • Fear in the workplace is eliminated • Monotony is reduced Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Characteristics of Quality Organizations EMS System Results Continual Improvement Process Management Measurement Total Involvement Customer Focus & Satisfaction Leadership Total Quality Organizational Mission, Vision, & Principles Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Characteristics of Quality Organizations EMS System Results Continual Improvement Process Management Measurement Total Involvement Customer Focus & Satisfaction Leadership Total Quality Organizational Mission, Vision, & Principles Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 QM - Leadership n Leadership Role • • Establishing Organization’s Quality Plan at All Program Levels Encourage a System of Participative Management Utilize Tools and Methods in Reaching Goals Walk the Walk, Talk the Talk Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
QM - Leadership n Leadership Role • • Establishing Organization’s Quality Plan at All Program Levels Encourage a System of Participative Management Utilize Tools and Methods in Reaching Goals Walk the Walk, Talk the Talk Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 QM - Leadership n Leadership By Example Imperial Trans -Antarctic Expedition n 1914, • • Cpt. Ernest Shackleton & crew of the Endurance leave for Antarctica 300 miles from land, trapped in ice pack 28 men spend 20 months on ice pack Move or Stay Plan “Gold Watch” Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
QM - Leadership n Leadership By Example Imperial Trans -Antarctic Expedition n 1914, • • Cpt. Ernest Shackleton & crew of the Endurance leave for Antarctica 300 miles from land, trapped in ice pack 28 men spend 20 months on ice pack Move or Stay Plan “Gold Watch” Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Environmental Assessment S trengths - internal system pluses W eaknesses - internal system negatives O pportunities - external to system pluses T hreats - external to system negatives n Used to establish original Maryland EMS Plan (1998) and subsequent updates (2000, 2004, 2006) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Environmental Assessment S trengths - internal system pluses W eaknesses - internal system negatives O pportunities - external to system pluses T hreats - external to system negatives n Used to establish original Maryland EMS Plan (1998) and subsequent updates (2000, 2004, 2006) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Maryland EMS Environment (2004) n Strengths n n Comprehensive Statewide System - Designated trauma and specialty centers Human Resources - Well-trained and committed prehospital care providers operating under uniform protocols Communications - Statewide system integrated with local personnel trained to EMD standards Med-Evac System - Operated under Maryland State Police with full state coverage Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Maryland EMS Environment (2004) n Strengths n n Comprehensive Statewide System - Designated trauma and specialty centers Human Resources - Well-trained and committed prehospital care providers operating under uniform protocols Communications - Statewide system integrated with local personnel trained to EMD standards Med-Evac System - Operated under Maryland State Police with full state coverage Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Maryland EMS Environment (2004) n Strengths (continued) n Support - Strong legislative and executive support of EMS n Lead Agency - Effective state agency that has established a broad network of communications among provider groups n Quality Assurance/Quality Improvement Established program with access to data Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved -
Maryland EMS Environment (2004) n Strengths (continued) n Support - Strong legislative and executive support of EMS n Lead Agency - Effective state agency that has established a broad network of communications among provider groups n Quality Assurance/Quality Improvement Established program with access to data Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved -
 Maryland EMS Environment (2004) n Weaknesses n Resource Capacity - Insufficient hospital response to n Med-Evac System- Reliance on weather dependent n n surges and overused resource Funding - Unresolved financial issues Disaster Training - Insufficient inter-agency training Communication Resources - No statewide EMRC Inter-Agency Communications - Poor communications among fire, police, & EMS in the event of an emergency Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Maryland EMS Environment (2004) n Weaknesses n Resource Capacity - Insufficient hospital response to n Med-Evac System- Reliance on weather dependent n n surges and overused resource Funding - Unresolved financial issues Disaster Training - Insufficient inter-agency training Communication Resources - No statewide EMRC Inter-Agency Communications - Poor communications among fire, police, & EMS in the event of an emergency Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Maryland EMS Environment (2004) n Weaknesses (continued) n Public Awareness - Lack of sufficient EMS public n Quality Assurance/ Quality Improvement - n n awareness and prevention measures Insufficient use of data and incomplete post care knowledge Human Resources - Insufficient ALS providers in rural areas Skills Retention - Challenge in maintaining skills within all EMS services (prehospital/clinical) Specialty Patients - More attention to pediatric/geriatric needs Uncompensated Care - High levels Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Maryland EMS Environment (2004) n Weaknesses (continued) n Public Awareness - Lack of sufficient EMS public n Quality Assurance/ Quality Improvement - n n awareness and prevention measures Insufficient use of data and incomplete post care knowledge Human Resources - Insufficient ALS providers in rural areas Skills Retention - Challenge in maintaining skills within all EMS services (prehospital/clinical) Specialty Patients - More attention to pediatric/geriatric needs Uncompensated Care - High levels Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Maryland EMS Environment (2004) n Opportunities Funding - In response to terrorism n Research - Comprehensive system with unique n characteristics Public Perception - Positive image of EMS services n Successful Models - Use trauma system template to n n n improve other health care delivery components Technology - Combine telemedicine methods with existing communications system to improve prehospital triage Interagency Collaboration - Build upon strong specialty ctr. relationships to develop/improve other collaborative efforts Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Maryland EMS Environment (2004) n Opportunities Funding - In response to terrorism n Research - Comprehensive system with unique n characteristics Public Perception - Positive image of EMS services n Successful Models - Use trauma system template to n n n improve other health care delivery components Technology - Combine telemedicine methods with existing communications system to improve prehospital triage Interagency Collaboration - Build upon strong specialty ctr. relationships to develop/improve other collaborative efforts Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Maryland EMS Environment (2004) n Threats n Fiscal - Increased uninsured population / uncompensated care n Human Resources - Recruitment and retention of all n Patient Care - Increase in barriers to definitive patient n Special Interest - Needs prioritized based upon n Trauma System - Financial issues concerning regional healthcare provider types care parochial or territorial interests and state trauma system Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Maryland EMS Environment (2004) n Threats n Fiscal - Increased uninsured population / uncompensated care n Human Resources - Recruitment and retention of all n Patient Care - Increase in barriers to definitive patient n Special Interest - Needs prioritized based upon n Trauma System - Financial issues concerning regional healthcare provider types care parochial or territorial interests and state trauma system Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 QM - At MIEMSS Mission n Philosophy n Structure n Trivialized Summary n Tools Overview n Results n Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
QM - At MIEMSS Mission n Philosophy n Structure n Trivialized Summary n Tools Overview n Results n Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 MIEMSS Mission Statement As the lead emergency medical services (EMS) agency, MIEMSS will provide the leadership, direction, expertise, and coordination of resources to continuously improve the efficient and effective provision of EMS throughout the state of Maryland. This includes all phases of emergency care: prevention, out of hospital, hospital and rehabilitation. n n n Resource rather than a regulator Embrace the QM philosophy Comprehensive - statewide and continuum of care Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
MIEMSS Mission Statement As the lead emergency medical services (EMS) agency, MIEMSS will provide the leadership, direction, expertise, and coordination of resources to continuously improve the efficient and effective provision of EMS throughout the state of Maryland. This includes all phases of emergency care: prevention, out of hospital, hospital and rehabilitation. n n n Resource rather than a regulator Embrace the QM philosophy Comprehensive - statewide and continuum of care Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Philosophy Implementation Question 1. What’s the difference between QM and other management types? Others can stress “Bad Apples” for poor performances n QM attempts to understand failure from a system point of view. n n n Document the process Measure the system feature (timeliness, access, etc. ) Make improvement recommendation(s) Implement best improvement(s) Measure it again Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Philosophy Implementation Question 1. What’s the difference between QM and other management types? Others can stress “Bad Apples” for poor performances n QM attempts to understand failure from a system point of view. n n n Document the process Measure the system feature (timeliness, access, etc. ) Make improvement recommendation(s) Implement best improvement(s) Measure it again Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Philosophy Implementation Question 2. So, I’m not responsible for my mistakes now - right? This is not unconditional surrender to the work force n All employees accept responsibility for: n n n Quality training (Leadership first, real time application) Quality methods understanding and use (Apply the science) Support one and other (Feelings of uneasiness/fear of failure) Leave your ego’s at the door (This is not a lynching) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Philosophy Implementation Question 2. So, I’m not responsible for my mistakes now - right? This is not unconditional surrender to the work force n All employees accept responsibility for: n n n Quality training (Leadership first, real time application) Quality methods understanding and use (Apply the science) Support one and other (Feelings of uneasiness/fear of failure) Leave your ego’s at the door (This is not a lynching) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Philosophy Implementation Question 3. Isn’t this really Quality Assurance we’re talking about? Traditional QA is based on reaction to failure and can tend to focus on punitive results. n Quality Control gets us a “stable process” n Quality Improvement moves us beyond stable and provides gains along key features. n n Effectiveness Efficiency Timeliness Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Philosophy Implementation Question 3. Isn’t this really Quality Assurance we’re talking about? Traditional QA is based on reaction to failure and can tend to focus on punitive results. n Quality Control gets us a “stable process” n Quality Improvement moves us beyond stable and provides gains along key features. n n Effectiveness Efficiency Timeliness Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Maryland EMS Quality Leadership Council § Link MIEMSS Programs with EMS Community § Established Confidentiality Agreements/Data Inventory § Initiate QI Teams – Establish System “Gauges” for: § § § § MIEMSS Administration Medical Aeromedical Pediatric Trauma Prehospital Education & Training Regional/Jurisdictional Councils Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Maryland EMS Quality Leadership Council § Link MIEMSS Programs with EMS Community § Established Confidentiality Agreements/Data Inventory § Initiate QI Teams – Establish System “Gauges” for: § § § § MIEMSS Administration Medical Aeromedical Pediatric Trauma Prehospital Education & Training Regional/Jurisdictional Councils Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
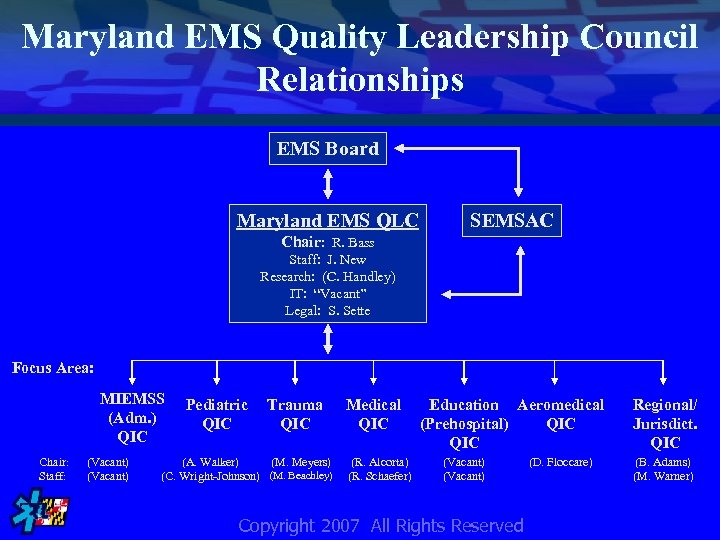 Maryland EMS Quality Leadership Council Relationships EMS Board Maryland EMS QLC SEMSAC Chair: R. Bass Staff: J. New Research: (C. Handley) IT: “Vacant” Legal: S. Sette Focus Area: MIEMSS (Adm. ) QIC Chair: Staff: (Vacant) Pediatric QIC Trauma QIC (A. Walker) (M. Meyers) (M. Beachley) (C. Wright-Johnson) Medical QIC (R. Alcorta) (R. Schaefer) Education Aeromedical (Prehospital) QIC (Vacant) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved (D. Floccare) Regional/ Jurisdict. QIC (B. Adams) (M. Warner)
Maryland EMS Quality Leadership Council Relationships EMS Board Maryland EMS QLC SEMSAC Chair: R. Bass Staff: J. New Research: (C. Handley) IT: “Vacant” Legal: S. Sette Focus Area: MIEMSS (Adm. ) QIC Chair: Staff: (Vacant) Pediatric QIC Trauma QIC (A. Walker) (M. Meyers) (M. Beachley) (C. Wright-Johnson) Medical QIC (R. Alcorta) (R. Schaefer) Education Aeromedical (Prehospital) QIC (Vacant) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved (D. Floccare) Regional/ Jurisdict. QIC (B. Adams) (M. Warner)
 MIEMSS QM View (trivialized) 1% 1% 1% 94% Plan (Structure for Getting There) Knowledge (Teams, Tools and Methods) Commitment (Leadership and Employee Buy In) Communication (Intra and Inter Agency) Recognition (Mission, Customers, Consumers) Respect (For job, for co-workers) Common Sense (How would you like to be serviced? ) 100% Customer, Employee, and Manager Satisfaction Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
MIEMSS QM View (trivialized) 1% 1% 1% 94% Plan (Structure for Getting There) Knowledge (Teams, Tools and Methods) Commitment (Leadership and Employee Buy In) Communication (Intra and Inter Agency) Recognition (Mission, Customers, Consumers) Respect (For job, for co-workers) Common Sense (How would you like to be serviced? ) 100% Customer, Employee, and Manager Satisfaction Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Quality Improvement Tools n n n n QI Teams (Group of process knowledge experts) Team Leader, Facilitator, Timer, Recorder Team Charter and By-Laws (What you do/how you do it) Brainstorm (Get Ideas/Problems Out Into The Open) Process Flow Diagrams (Document Process Complexity) Fishbone Diagrams (Identify Cause) Histograms (Measure Impact of Cause/Results) Run Charts (Measure Feature Over Time) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Quality Improvement Tools n n n n QI Teams (Group of process knowledge experts) Team Leader, Facilitator, Timer, Recorder Team Charter and By-Laws (What you do/how you do it) Brainstorm (Get Ideas/Problems Out Into The Open) Process Flow Diagrams (Document Process Complexity) Fishbone Diagrams (Identify Cause) Histograms (Measure Impact of Cause/Results) Run Charts (Measure Feature Over Time) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
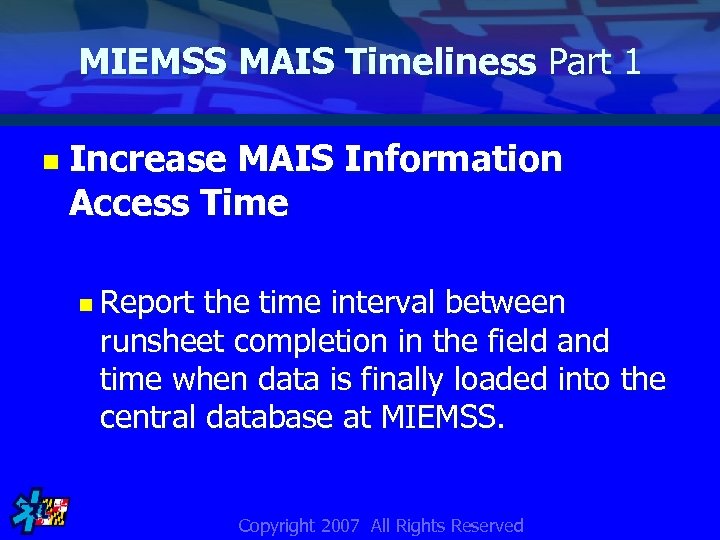 MIEMSS MAIS Timeliness Part 1 n Increase MAIS Information Access Time n Report the time interval between runsheet completion in the field and time when data is finally loaded into the central database at MIEMSS. Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
MIEMSS MAIS Timeliness Part 1 n Increase MAIS Information Access Time n Report the time interval between runsheet completion in the field and time when data is finally loaded into the central database at MIEMSS. Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved

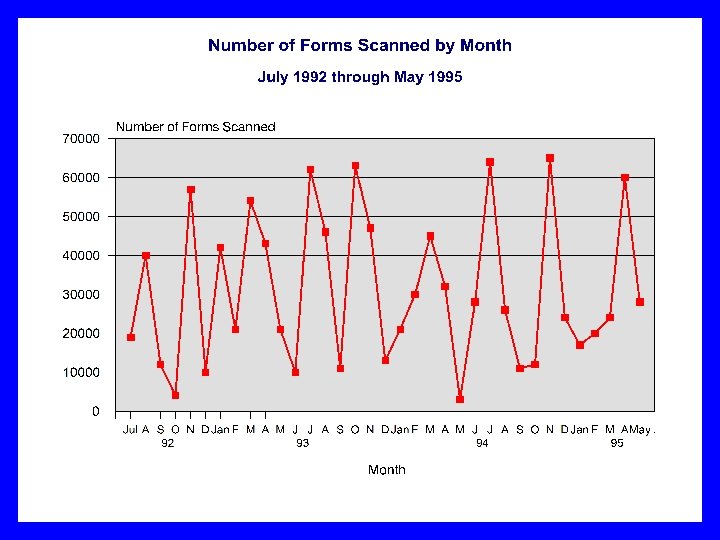
 MIEMSS MAIS Timeliness Part 2 n Measure the number of forms scanned per month by MIEMSS MIS Department. n Report the volume of forms submitted by month. Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
MIEMSS MAIS Timeliness Part 2 n Measure the number of forms scanned per month by MIEMSS MIS Department. n Report the volume of forms submitted by month. Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 MIEMSS MAIS Timeliness Part 3 n n Examine variation by Jurisdiction Brainstorm cause(s) for delays and make recommendations for improvement. Standardize forms submission regionally n Inform Non MIEMSS processors of delays. n Eliminate pre-sorting by MIEMSS staff through Optical Scanning and archiving n n Measure again Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
MIEMSS MAIS Timeliness Part 3 n n Examine variation by Jurisdiction Brainstorm cause(s) for delays and make recommendations for improvement. Standardize forms submission regionally n Inform Non MIEMSS processors of delays. n Eliminate pre-sorting by MIEMSS staff through Optical Scanning and archiving n n Measure again Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
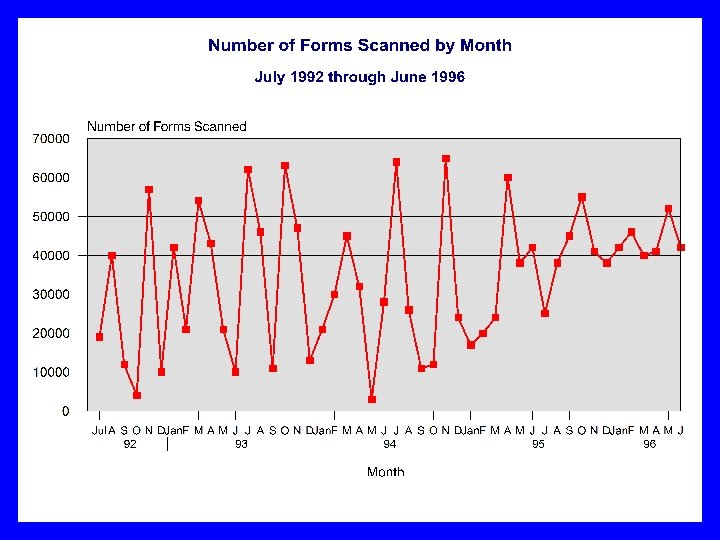
 MIEMSS MAIS Timeliness Part 4 n Check Your Results n Maintain a Run Chart of Process Measure. Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
MIEMSS MAIS Timeliness Part 4 n Check Your Results n Maintain a Run Chart of Process Measure. Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved

 Crucial Steps to Success (Baldrige Model) n Get Leadership to Buy-In n n Not just approval, but to be trained, to use QM Develop Strategic Quality Plan Long/Short term organizational objectives n Identify ways to achieve those objectives n Measure effectiveness n n Ensure Customer and Stakeholder Satisfaction n External and internal organizational satisfaction Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Crucial Steps to Success (Baldrige Model) n Get Leadership to Buy-In n n Not just approval, but to be trained, to use QM Develop Strategic Quality Plan Long/Short term organizational objectives n Identify ways to achieve those objectives n Measure effectiveness n n Ensure Customer and Stakeholder Satisfaction n External and internal organizational satisfaction Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Crucial Steps to Success (Baldrige Model) n Utilize Information and Analyses n n Provide Human Resource Development n n Develop full potential of work force Understand Improve Processes n n Use valid data to “manage by fact” Ensure good relationships across all process owners Focus on System Results n Assess quality results and the organization’s success at achieving quality improvement Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
Crucial Steps to Success (Baldrige Model) n Utilize Information and Analyses n n Provide Human Resource Development n n Develop full potential of work force Understand Improve Processes n n Use valid data to “manage by fact” Ensure good relationships across all process owners Focus on System Results n Assess quality results and the organization’s success at achieving quality improvement Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Implementation Steps To Consider n n n Initiate Quality Council (charter, rules) Identify key process(es), key indicator(s). Plan quality improvement strategies Measure Initiate improvements Measure again Customer Q Customer $ Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved Customer
Implementation Steps To Consider n n n Initiate Quality Council (charter, rules) Identify key process(es), key indicator(s). Plan quality improvement strategies Measure Initiate improvements Measure again Customer Q Customer $ Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved Customer
 When Are We There? “The Race For Quality Has No Finish Line” David T. Kearns – Former Chairman of XEROX (Winner of the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
When Are We There? “The Race For Quality Has No Finish Line” David T. Kearns – Former Chairman of XEROX (Winner of the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award) Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved
 Conclusion n Questions n Comments Department of Quality Management n Thank Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved You!
Conclusion n Questions n Comments Department of Quality Management n Thank Copyright 2007 All Rights Reserved You!


