6bc7d602ec709ed0ea2fcf7d0aa60979.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Applying MESE processes to Improve Online E-Voting Prototype System with PTC Web Services Master Project Defense Hakan Evecek 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 1
Applying MESE processes to Improve Online E-Voting Prototype System with PTC Web Services Master Project Defense Hakan Evecek 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 1
 Outline of the Talk Introduction Document overview prepared for this project. Related Work Paillier Threshold Cryptography (PTC) PTC Web Services Suggested Improvement ◦ Encryption/Decryption Optimization ◦ User Interface Online E-Voting System Future Directions Conclusion 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 2
Outline of the Talk Introduction Document overview prepared for this project. Related Work Paillier Threshold Cryptography (PTC) PTC Web Services Suggested Improvement ◦ Encryption/Decryption Optimization ◦ User Interface Online E-Voting System Future Directions Conclusion 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 2
 Introduction General idea behind Electronic Voting: ◦ Similar to the manual voting - only much faster and cheaper, however Is the voter confident with the process? Can Administrators monitoring verify that one vote is recorded for each voter? How trustable the tally process? Is it socially acceptable? Many countries are looking for E-Voting solutions. In other words, what are the e-voting requirements: 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 3
Introduction General idea behind Electronic Voting: ◦ Similar to the manual voting - only much faster and cheaper, however Is the voter confident with the process? Can Administrators monitoring verify that one vote is recorded for each voter? How trustable the tally process? Is it socially acceptable? Many countries are looking for E-Voting solutions. In other words, what are the e-voting requirements: 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 3
 E-Voting Requirements • Basic requirements for electronic voting • Privacy – All votes should be kept secret • • • Completeness – All valid votes should be counted correctly Soundness – Any invalid vote should not be counted Unreusability – No voter can vote twice Eligibility – Only authorized voters can cast a vote Fairness – Nothing can affect the voting 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 4
E-Voting Requirements • Basic requirements for electronic voting • Privacy – All votes should be kept secret • • • Completeness – All valid votes should be counted correctly Soundness – Any invalid vote should not be counted Unreusability – No voter can vote twice Eligibility – Only authorized voters can cast a vote Fairness – Nothing can affect the voting 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 4
 E-Voting Requirements • Extended Requirements for electronic voting • Robustness – faulty behavior of any reasonably sized coalition of participants can be tolerated. In other words, the system must be able to tolerate to certain faulty conditions and must be able to manage these situations. • Universal Verifiability – any party can verify the result of the voting • Receipt-freeness – Voters are unable to prove the content of his/her vote • Incoercibility – Voter cannot be coerced into casting a particular vote by a coercer. 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 5
E-Voting Requirements • Extended Requirements for electronic voting • Robustness – faulty behavior of any reasonably sized coalition of participants can be tolerated. In other words, the system must be able to tolerate to certain faulty conditions and must be able to manage these situations. • Universal Verifiability – any party can verify the result of the voting • Receipt-freeness – Voters are unable to prove the content of his/her vote • Incoercibility – Voter cannot be coerced into casting a particular vote by a coercer. 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 5
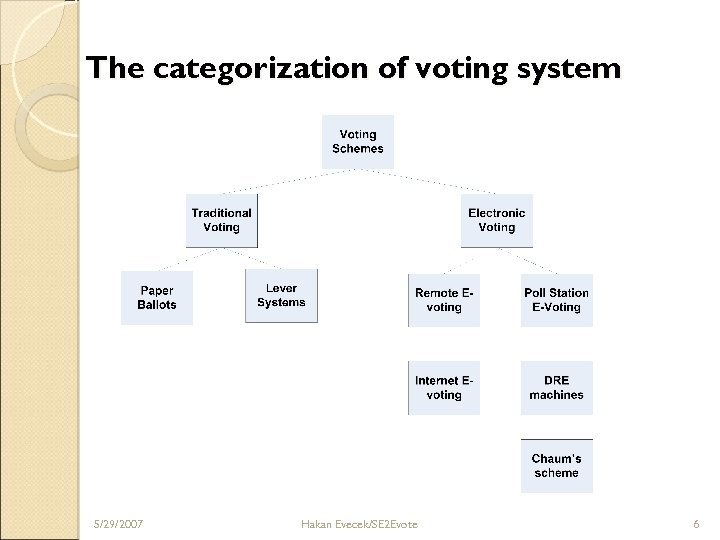 The categorization of voting system 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 6
The categorization of voting system 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 6
 MESE Processes Applied for Online EVoting System Project Proposal and Plan Software Requirements Document (SRS) Software Design Specification (SDS) Testing Document Defects List Project Report 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 7
MESE Processes Applied for Online EVoting System Project Proposal and Plan Software Requirements Document (SRS) Software Design Specification (SDS) Testing Document Defects List Project Report 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 7
 Related Work Other Techniques Used In E-voting Protocols ◦ A Secure and Optimally Efficient Multi-Authority Election Scheme (Cramer, Gennaro, Schoenmakers) Receipt-free: protocols where vote-buying or coercing is not possible because voters cannot prove to others how they voted. ◦ Non-Interactive Zero Knowledge Proofs Proof does not require interaction Proof does not reveal any other information Prove vote is valid without revealing content of vote Prove two encryptions encrypt the same message without revealing message 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 8
Related Work Other Techniques Used In E-voting Protocols ◦ A Secure and Optimally Efficient Multi-Authority Election Scheme (Cramer, Gennaro, Schoenmakers) Receipt-free: protocols where vote-buying or coercing is not possible because voters cannot prove to others how they voted. ◦ Non-Interactive Zero Knowledge Proofs Proof does not require interaction Proof does not reveal any other information Prove vote is valid without revealing content of vote Prove two encryptions encrypt the same message without revealing message 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 8
![Cryptographic Techniques Implemented by Bret Wilson Paillier Crypto. System [15] ◦ Trapdoor Discrete Logarithm Cryptographic Techniques Implemented by Bret Wilson Paillier Crypto. System [15] ◦ Trapdoor Discrete Logarithm](https://present5.com/presentation/6bc7d602ec709ed0ea2fcf7d0aa60979/image-9.jpg) Cryptographic Techniques Implemented by Bret Wilson Paillier Crypto. System [15] ◦ Trapdoor Discrete Logarithm Scheme ◦ c = g. Mrn mod n 2 n is an RSA modulus (modulus of 2 safe primes) Safe prime - p = 2 q + 1 where q is also prime g is an integer of order nα mod n 2 r is a random number in Z * n ◦ M = L(cλ(n) mod n 2)/L(gλ(n) mod n 2) mod n ◦ L(u) = (u-1)/n, λ(n)=lcm((p-1)(q-1)) ◦ Important Properties Probabilistic (randomness of E(M)) Homomorphic E(M 1 + M 2) = E(M 1) x E(M 2), E(k x M) = E(M)k Self-blinding D(E(M) rn mod n 2 ) = m 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 9
Cryptographic Techniques Implemented by Bret Wilson Paillier Crypto. System [15] ◦ Trapdoor Discrete Logarithm Scheme ◦ c = g. Mrn mod n 2 n is an RSA modulus (modulus of 2 safe primes) Safe prime - p = 2 q + 1 where q is also prime g is an integer of order nα mod n 2 r is a random number in Z * n ◦ M = L(cλ(n) mod n 2)/L(gλ(n) mod n 2) mod n ◦ L(u) = (u-1)/n, λ(n)=lcm((p-1)(q-1)) ◦ Important Properties Probabilistic (randomness of E(M)) Homomorphic E(M 1 + M 2) = E(M 1) x E(M 2), E(k x M) = E(M)k Self-blinding D(E(M) rn mod n 2 ) = m 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 9
![Cryptographic Techniques Implemented Threshold Encryption [15] ◦ Public key encryption as usual ◦ Distribute Cryptographic Techniques Implemented Threshold Encryption [15] ◦ Public key encryption as usual ◦ Distribute](https://present5.com/presentation/6bc7d602ec709ed0ea2fcf7d0aa60979/image-10.jpg) Cryptographic Techniques Implemented Threshold Encryption [15] ◦ Public key encryption as usual ◦ Distribute secret key “shares” among i participants ◦ Decryption can only be accomplished if a threshold number t of the i participants cooperate No information about m can be obtained with less than t participants cooperating Shamir Secret Sharing ◦ Lagrange Interpolation formula ◦ f(X) = Σti=0 ai. Xi ◦ a 0 is secret, ai are random, f(X) are “secret shares” X is share index (1 to number of servers) ◦ If enough f(X) available it is possible to recover a 0 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 10
Cryptographic Techniques Implemented Threshold Encryption [15] ◦ Public key encryption as usual ◦ Distribute secret key “shares” among i participants ◦ Decryption can only be accomplished if a threshold number t of the i participants cooperate No information about m can be obtained with less than t participants cooperating Shamir Secret Sharing ◦ Lagrange Interpolation formula ◦ f(X) = Σti=0 ai. Xi ◦ a 0 is secret, ai are random, f(X) are “secret shares” X is share index (1 to number of servers) ◦ If enough f(X) available it is possible to recover a 0 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 10
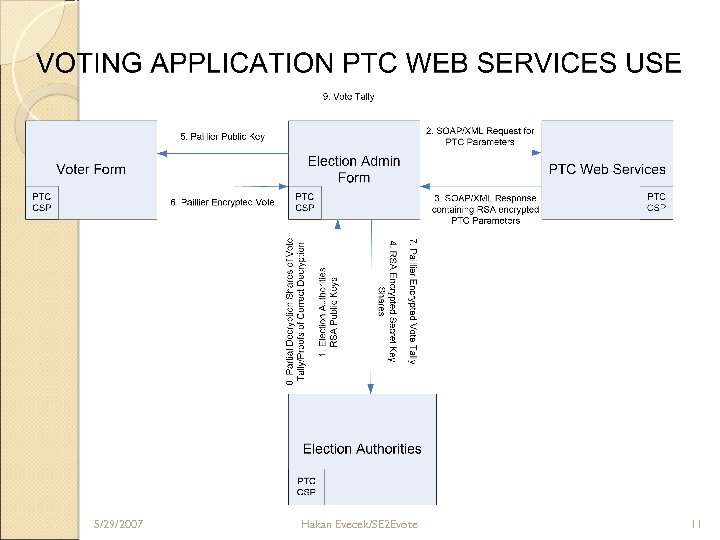 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 11
5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 11
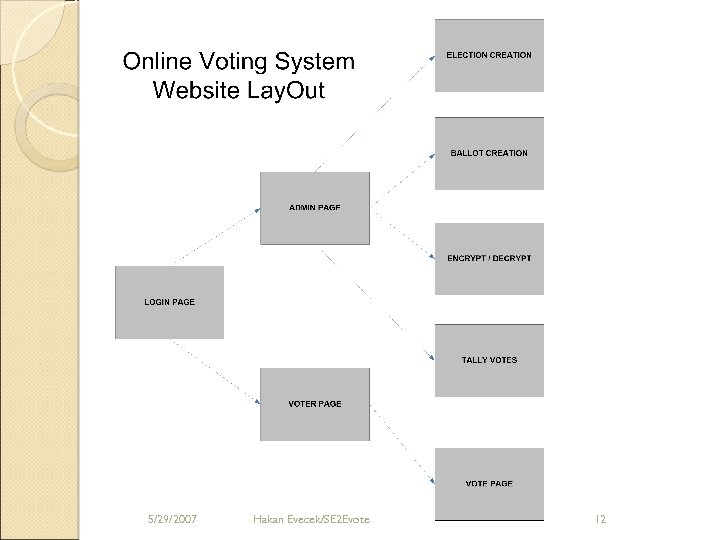 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 12
5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 12
 User Login Page Assumed that users has registered previously and has secure login credentials provided. Admin Users Voters Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart (CAPTCHA) 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 13
User Login Page Assumed that users has registered previously and has secure login credentials provided. Admin Users Voters Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart (CAPTCHA) 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 13
 Admin Page Election Creation Encryption/Decryption Tally Vote Generate Safe Prime Numbers Ballot Creation 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 14
Admin Page Election Creation Encryption/Decryption Tally Vote Generate Safe Prime Numbers Ballot Creation 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 14
 Voter Page Voter can access to the elections and complete the voting process. Automatically loads the voting page. ◦ Allows vote, then doesn’t allow user to vote again 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 15
Voter Page Voter can access to the elections and complete the voting process. Automatically loads the voting page. ◦ Allows vote, then doesn’t allow user to vote again 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 15
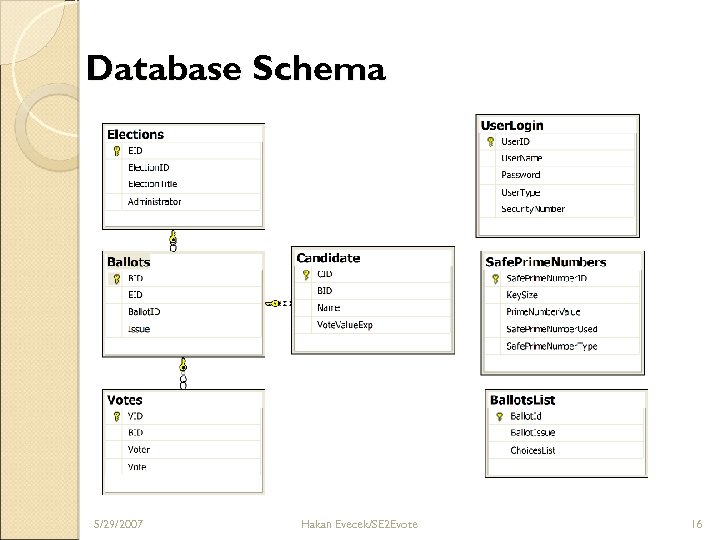 Database Schema 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 16
Database Schema 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 16
 Suggested Key Generation, Encryption/Decryption Optimization Safe Prime Numbers Pre-Computation Process. Chinese Remainder Theorem to calculate p, q separately and then multiply for n. • Paillier Scheme Pre-Computation for decryption. • • 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 17
Suggested Key Generation, Encryption/Decryption Optimization Safe Prime Numbers Pre-Computation Process. Chinese Remainder Theorem to calculate p, q separately and then multiply for n. • Paillier Scheme Pre-Computation for decryption. • • 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 17
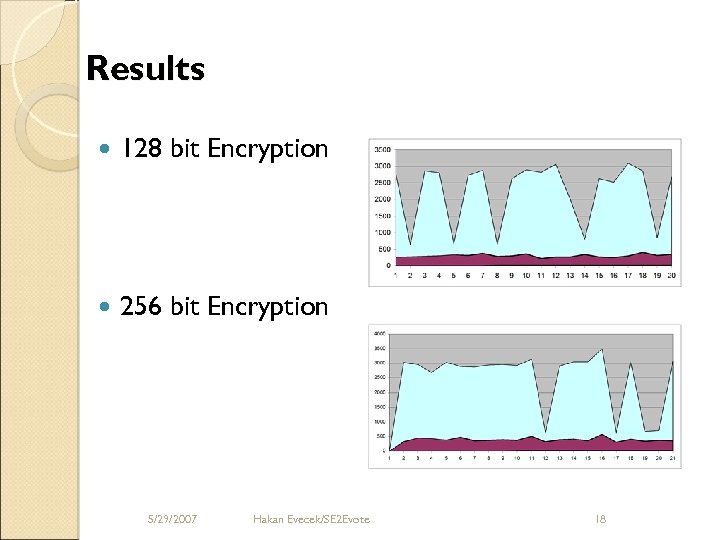 Results 128 bit Encryption 256 bit Encryption 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 18
Results 128 bit Encryption 256 bit Encryption 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 18
 Lessons Learned Add problems encountered and how you solve them. Mistakes made and how you discovered them. Tell story. 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 19
Lessons Learned Add problems encountered and how you solve them. Mistakes made and how you discovered them. Tell story. 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 19
 Future Direction Implement the suggested CRT improvement into the code. Implement constant value pre-computation for decryption process. Fix XML solution in the code. Add more web application security protocols and processes. Implement registration and voter identity verification process. ◦ Authenticity of election parameters/ballots not currently guaranteed Implement signing of election parameters/ballots by admin 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 20
Future Direction Implement the suggested CRT improvement into the code. Implement constant value pre-computation for decryption process. Fix XML solution in the code. Add more web application security protocols and processes. Implement registration and voter identity verification process. ◦ Authenticity of election parameters/ballots not currently guaranteed Implement signing of election parameters/ballots by admin 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 20
 Conclusion Summarize/itemize what you have achieved. 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 21
Conclusion Summarize/itemize what you have achieved. 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 21
![References [1] http: //cris. joongbu. ac. kr/publication/evoting_implementation-APIEMS 2004. pdf Implementation issues in a secure References [1] http: //cris. joongbu. ac. kr/publication/evoting_implementation-APIEMS 2004. pdf Implementation issues in a secure](https://present5.com/presentation/6bc7d602ec709ed0ea2fcf7d0aa60979/image-22.jpg) References [1] http: //cris. joongbu. ac. kr/publication/evoting_implementation-APIEMS 2004. pdf Implementation issues in a secure e-voting schemes, Riza Aditya, Byoungcheon Lee, Colin Boyd and Ed Dawson. schemes, [3] http: //www. cs. virginia. edu/~pev 5 b/writing/academic/thesis. html Vote Early, Vote Often, and Vote. Here: A Security Analysis of Vote. Here , Philip E. Varner, May 11, 2001. [5] http: //www. trustycom. fr/pdf/Fo. Po. St 00. pdf P. Fouque, G. Poupard, J. Stern, Sharing Decryption in the Context of Voting or Lotteries, Financial Cryptography 2000 Proceedings. Lotteries, [6] http: //www. captcha. net/ , the Official CAPTCHA web site. [7] http: //www. vote. caltech. edu/reports/alv-nag_loyola. pdf R. Michael Alvarez, Jonathan Nagler, The Likely consequences of Internet Voting for Political Representations. [10] I. Damgard, M. Jurik, J. Nielson, A Generalization of Paillier’s Public-Key System with Applications to Electronic Voting , Aarhus University, Dept. of Computer Science. [15] B. Wilson, C. E. Chow, Paillier Threshold Cryptography Web Service User’s Guide, University of Colorado – Colorado Guide, Springs Master’s Project, 2006. [16]http: //www. cs. rit. edu: 8080/ms/static/spr/2005/4/kar 1141/report. pdf , Progress on Probabilistic Encryption Schemes, Kert [16]http: //www. cs. rit. edu: 8080/ms/static/spr/2005/4/kar 1141/report. pdf Richardson, July 2006. [17] http: //www. cs. umd. edu/~jkatz/THESES/staub. pdf. gz An Analysis of Chaum’s voter-verifiable election scheme, Julie Ann Staub, 2005 [18] http: //www. brics. dk/RS/00/45/BRICS-RS-00 -45. pdf Ivan Damgard and Mads J. Jurik, A Generalization, a Simplification and Some Applications of Paillier’s Probabilistic Public-Key System, PKC 2001. [19] http: //www. cryptovirology. com/cryptovfiles/newbook/Chapter 4. pdf Implementing Perfect Questionable Encryptions, Adam L. Young and Moti M. Yung. [20] http: //www. rsa. com/rsalabs/cryptobytes/Crypto. Bytes_January_2002_final. pdf Crypto. Bytes, Dan Boneh, Hovav Shacham, Spring 2002. [21] http: //www. gemplus. com/smart/rd/publications/pdf/Pai 99 pai. pdf Public-Key Crypto. Systems Based on Composite Degree Residuosity Classes, Pascal Paillier, 1999 [22] http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Paillier_cryptosystem , Paillier Crytosystem from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 22
References [1] http: //cris. joongbu. ac. kr/publication/evoting_implementation-APIEMS 2004. pdf Implementation issues in a secure e-voting schemes, Riza Aditya, Byoungcheon Lee, Colin Boyd and Ed Dawson. schemes, [3] http: //www. cs. virginia. edu/~pev 5 b/writing/academic/thesis. html Vote Early, Vote Often, and Vote. Here: A Security Analysis of Vote. Here , Philip E. Varner, May 11, 2001. [5] http: //www. trustycom. fr/pdf/Fo. Po. St 00. pdf P. Fouque, G. Poupard, J. Stern, Sharing Decryption in the Context of Voting or Lotteries, Financial Cryptography 2000 Proceedings. Lotteries, [6] http: //www. captcha. net/ , the Official CAPTCHA web site. [7] http: //www. vote. caltech. edu/reports/alv-nag_loyola. pdf R. Michael Alvarez, Jonathan Nagler, The Likely consequences of Internet Voting for Political Representations. [10] I. Damgard, M. Jurik, J. Nielson, A Generalization of Paillier’s Public-Key System with Applications to Electronic Voting , Aarhus University, Dept. of Computer Science. [15] B. Wilson, C. E. Chow, Paillier Threshold Cryptography Web Service User’s Guide, University of Colorado – Colorado Guide, Springs Master’s Project, 2006. [16]http: //www. cs. rit. edu: 8080/ms/static/spr/2005/4/kar 1141/report. pdf , Progress on Probabilistic Encryption Schemes, Kert [16]http: //www. cs. rit. edu: 8080/ms/static/spr/2005/4/kar 1141/report. pdf Richardson, July 2006. [17] http: //www. cs. umd. edu/~jkatz/THESES/staub. pdf. gz An Analysis of Chaum’s voter-verifiable election scheme, Julie Ann Staub, 2005 [18] http: //www. brics. dk/RS/00/45/BRICS-RS-00 -45. pdf Ivan Damgard and Mads J. Jurik, A Generalization, a Simplification and Some Applications of Paillier’s Probabilistic Public-Key System, PKC 2001. [19] http: //www. cryptovirology. com/cryptovfiles/newbook/Chapter 4. pdf Implementing Perfect Questionable Encryptions, Adam L. Young and Moti M. Yung. [20] http: //www. rsa. com/rsalabs/cryptobytes/Crypto. Bytes_January_2002_final. pdf Crypto. Bytes, Dan Boneh, Hovav Shacham, Spring 2002. [21] http: //www. gemplus. com/smart/rd/publications/pdf/Pai 99 pai. pdf Public-Key Crypto. Systems Based on Composite Degree Residuosity Classes, Pascal Paillier, 1999 [22] http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Paillier_cryptosystem , Paillier Crytosystem from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. 5/29/2007 Hakan Evecek/SE 2 Evote 22


