ABS3 - Complex Business Organisations OK.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 11

APPLIED BUSINESS STUDIES ABS 3 – Complex Business Organisations Regional Economics and Management, Vyat. GU

Content • Multinational companies • Central Power versus Remote locations • Networks: owned and operated, owned and non-operated, non-owned and non-operated • Joint-ventures: Operated, Co-operated, Nonoperated businesses • Case: Classifying organisations and knowing how to work with them (continued, 2/2)

Case – Classifying organisations and knowing to work with them The different stakeholders in the oil industry What is their mission? To whom are they dutiable? How are they integrated vertically and extended geographically? How do these actors structure their businesses? • • • Governments (departments of energy, ministries of petroleum, . . . ) NOC = national oil companies (Sonatrach) IOC = international oil companies (Exxon, TOTAL) Oilfield services companies (Schlumberger) Niche players (PUMA Energy) Energy giants (GDF SUEZ).
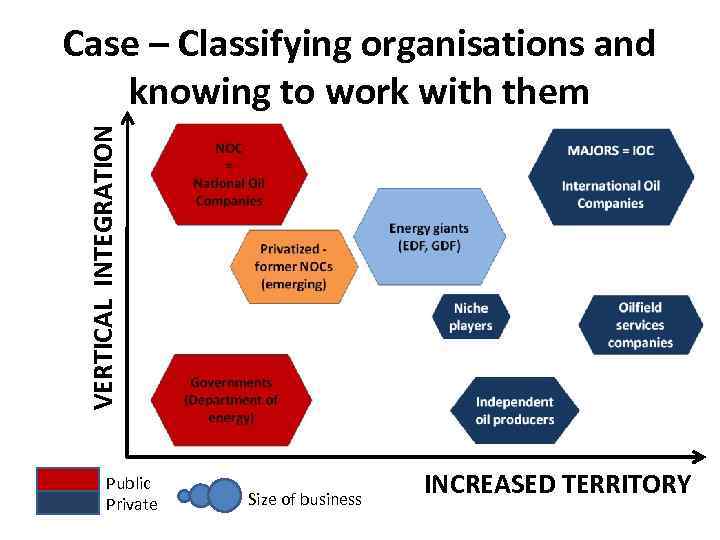
VERTICAL INTEGRATION Case – Classifying organisations and knowing to work with them Public Private Size of business INCREASED TERRITORY

Multinational companies Specificities of multinational companies • The organisation structure does not support only the company’s mission, it must also comply with local regulations and policies (laws) Impact on organisational structure regarding taxation of revenue, labour / employment laws. Legal entities are created to comply with local regulations in countries where needed: to record revenues or hire employees for example. Usually a multinational company adopts either a fully geographical structure, either a matrix organisation Impact on management is how to balance autonomy and dependency of various locations.

Central Power versus Remote locations Where to have the decision centre? Remember: • The closer you are, the most control you have. • The decision are taken where the resource is allocated. Local resources (benefits) = local power How to enforce compliance? Centralizing resources. Internal control and validation with Corporate decision making and support. Cultural diversity and communications • In multinational complex environments, ensure that people understand each other. Promote Corporate mission so that each employee shares same objectives. Make them clear. Make cultural diversity a strength.
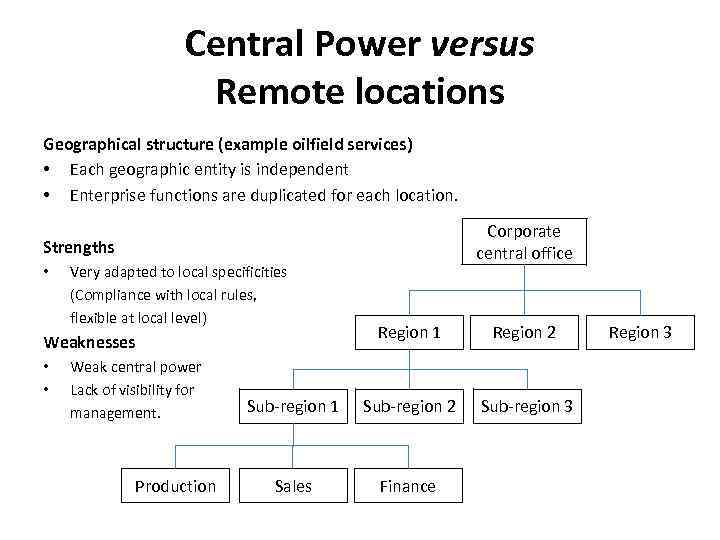
Central Power versus Remote locations Geographical structure (example oilfield services) • Each geographic entity is independent • Enterprise functions are duplicated for each location. Corporate central office Strengths • Very adapted to local specificities (Compliance with local rules, flexible at local level) Region 1 Region 2 Sub-region 1 Sub-region 2 Sub-region 3 Sales Finance Weaknesses • • Weak central power Lack of visibility for management. Production Region 3
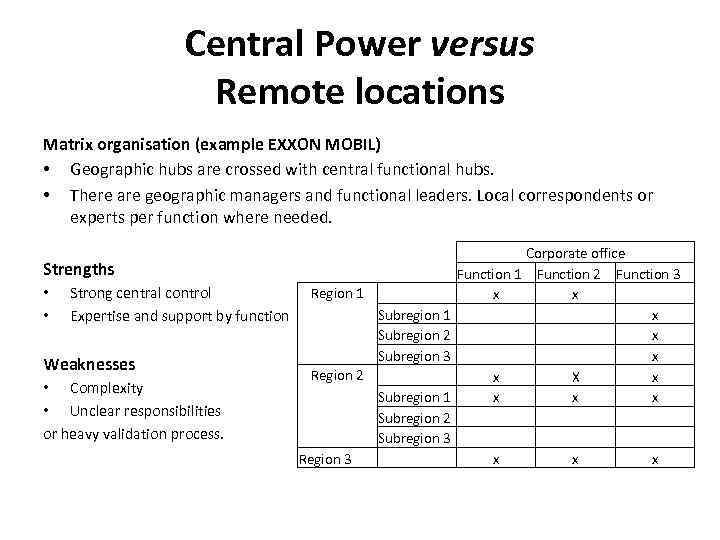
Central Power versus Remote locations Matrix organisation (example EXXON MOBIL) • Geographic hubs are crossed with central functional hubs. • There are geographic managers and functional leaders. Local correspondents or experts per function where needed. Strengths • • Strong central control Expertise and support by function Weaknesses • Complexity • Unclear responsibilities or heavy validation process. Region 1 Subregion 1 Subregion 2 Subregion 3 Region 2 Subregion 1 Subregion 2 Subregion 3 Region 3 Corporate office Function 1 Function 2 Function 3 x x x x X x x x
Networks What are distribution networks? • Chain of distribution points to reach your final customer. Types of distribution networks • COCO: Company owned, company operated (employee) • CODO: Company owned, distributor operated (franchisee) • DODO: Distributor owned, distributor operated (licensee). Benefits and specificities • For the company: Extended territory/scalability, combining resources when • • owned, benchmarking, branding, single decision making process if operated For the distributor: Brand, service support, feedback on experience, limited risk (price volatility, shortage of stock) Example: gas stations.

Joint-ventures When? • Sharing an investment risk (common) • Local governmental policy, law (common) • Sharing experience, combining strengths (rare) Where is the decision taken? • Operated, co-operated, non-operated. Examples • Exploiting an oilfield.
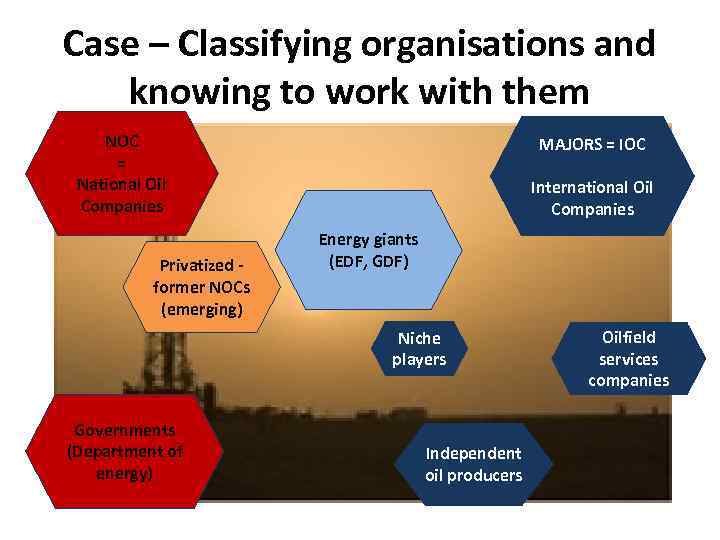
Case – Classifying organisations and knowing to work with them NOC = National Oil Companies Privatized former NOCs (emerging) MAJORS = IOC International Oil Companies Energy giants (EDF, GDF) Niche players Governments (Department of energy) Independent oil producers Oilfield services companies
ABS3 - Complex Business Organisations OK.pptx