c73e7326d83bbddc3c740eacf289f688.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Application of Geospatial technology in MGNREGS

Objectives Use of GIS and RS for planning and monitoring of MGNREGS works for generation of social capital and employment. Mapping the area and understanding the demographic profile, economic status of the stakeholders Usage of the model as a platform for capacity building of the local community, Village/Taluka Panchayat and Project Implementing Agencies (PIA). Capturing the existing assets, current coverage of the area and generation of future action plan. Use of various tools including RS Imagery for monitoring & evaluation.
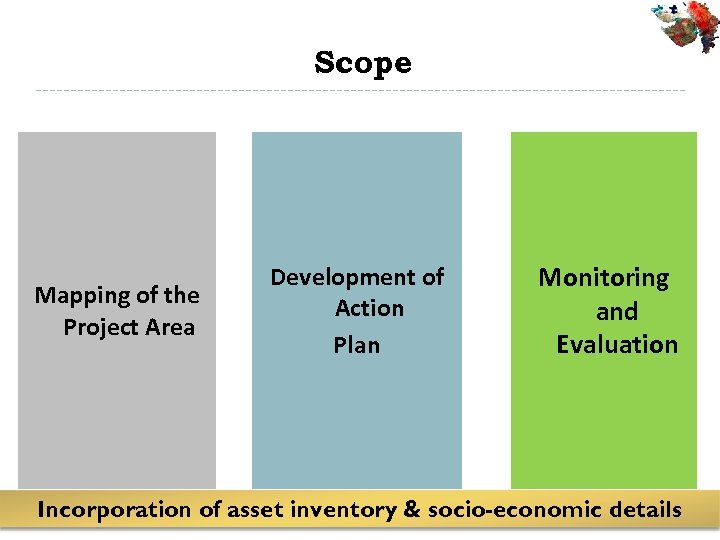
Scope Mapping of the Project Area Development of Action Plan Monitoring and Evaluation Incorporation of asset inventory & socio-economic details
Convergence of Geospatial Technologies GIS RS ICT GPS e-Gram Total Turnkey Solutions Courtesy: NRSA/ISRO

Tools to be used Geographic Information System (GIS) Global Positioning System (GPS) instruments Remote Sensing (RS) Imagery Management Information System (MIS) [NREGASoft] Participatory Rural Appraisal(PRA) & Focus Group Discussions (FGD) Social Audit
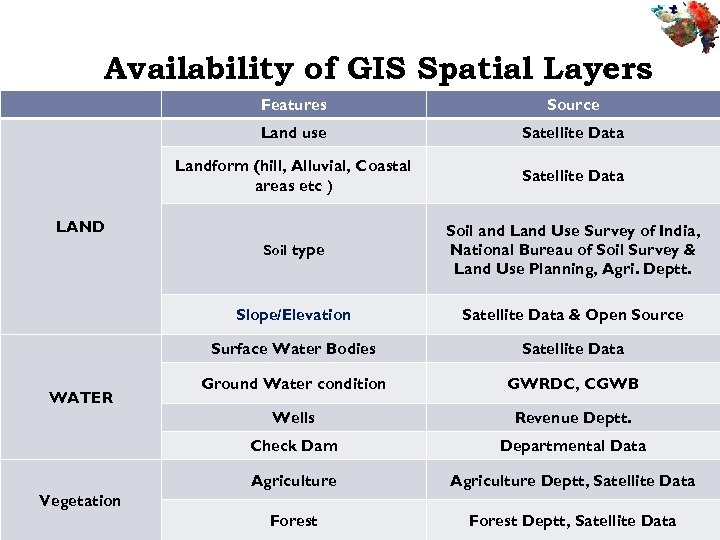
Availability of GIS Spatial Layers Features Source Land use Satellite Data Landform (hill, Alluvial, Coastal areas etc ) Satellite Data Soil type Soil and Land Use Survey of India, National Bureau of Soil Survey & Land Use Planning, Agri. Deptt. Slope/Elevation Satellite Data & Open Source Surface Water Bodies Satellite Data Ground Water condition GWRDC, CGWB Wells Revenue Deptt. Check Dam Departmental Data Agriculture Deptt, Satellite Data Forest Deptt, Satellite Data LAND WATER Vegetation
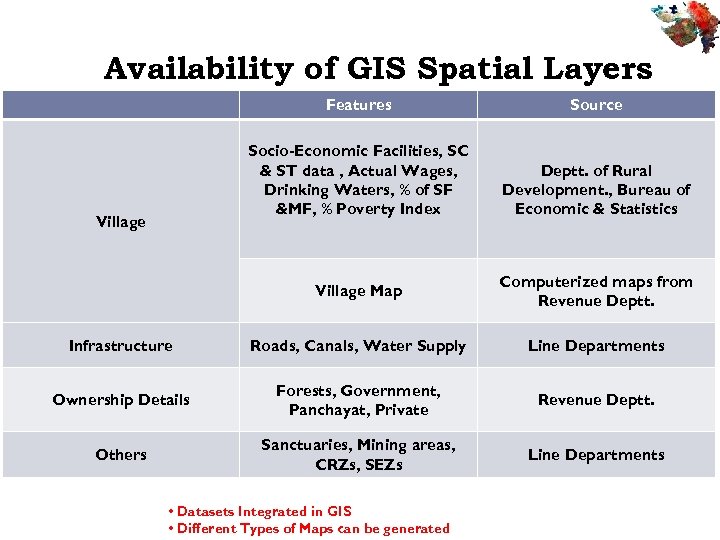
Availability of GIS Spatial Layers Features Socio-Economic Facilities, SC & ST data , Actual Wages, Drinking Waters, % of SF &MF, % Poverty Index Village Source Deptt. of Rural Development. , Bureau of Economic & Statistics Village Map Computerized maps from Revenue Deptt. Infrastructure Roads, Canals, Water Supply Line Departments Ownership Details Forests, Government, Panchayat, Private Revenue Deptt. Others Sanctuaries, Mining areas, CRZs, SEZs Line Departments • Datasets Integrated in GIS • Different Types of Maps can be generated
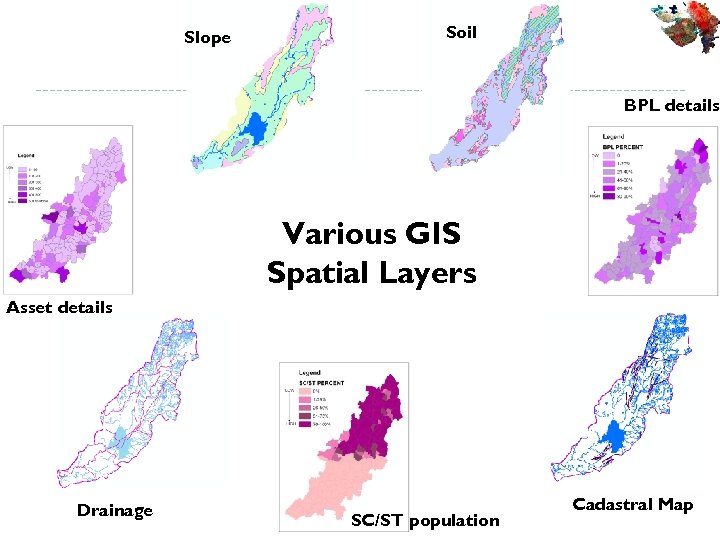
Slope Soil BPL details Various GIS Spatial Layers Asset details Drainage SC/ST population Cadastral Map

Why Plan at Micro watershed level 80% of the MGNREGS works are based on Drought proofing, Flood control & protection works, Land development, Micro & macro irrigation works, Natural Resource Management (NRM), Renovation of traditional water bodies (Desilting) Absence of holistic & integrated approach leads to inadequate returns on investment Effective planning at Micro-watershed Level (500 -1000 Ha. ) would result in the creation of sustainable assets and concrete measurable outcomes at village level.
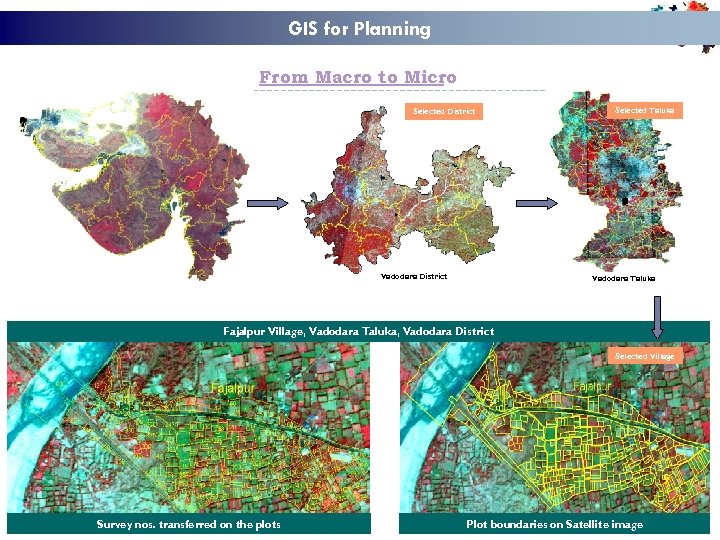
GIS for Planning From Macro to Micro Selected District Vadodara District Selected Taluka Vadodara Taluka Fajalpur Village, Vadodara Taluka, Vadodara District Selected Village Survey nos. transferred on the plots Plot boundaries on Satellite image
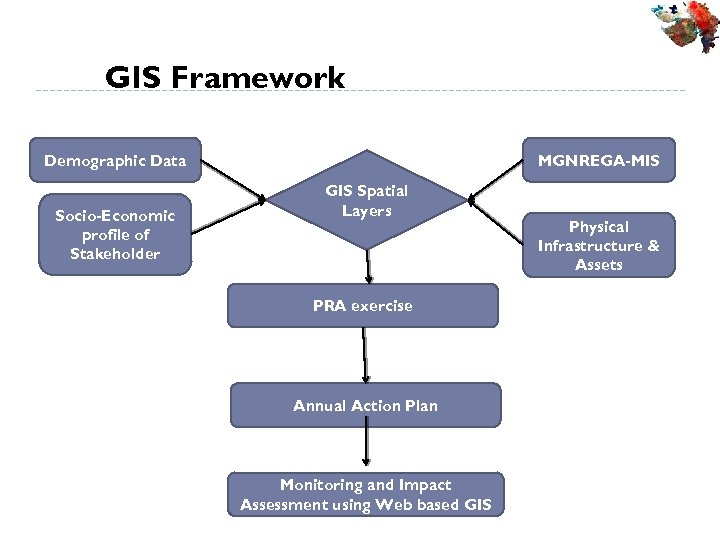
GIS Framework Demographic Data Socio-Economic profile of Stakeholder MGNREGA-MIS GIS Spatial Layers PRA exercise Annual Action Plan Monitoring and Impact Assessment using Web based GIS Physical Infrastructure & Assets

GIS based planning & monitoring for MGNREGS A CASE STUDY
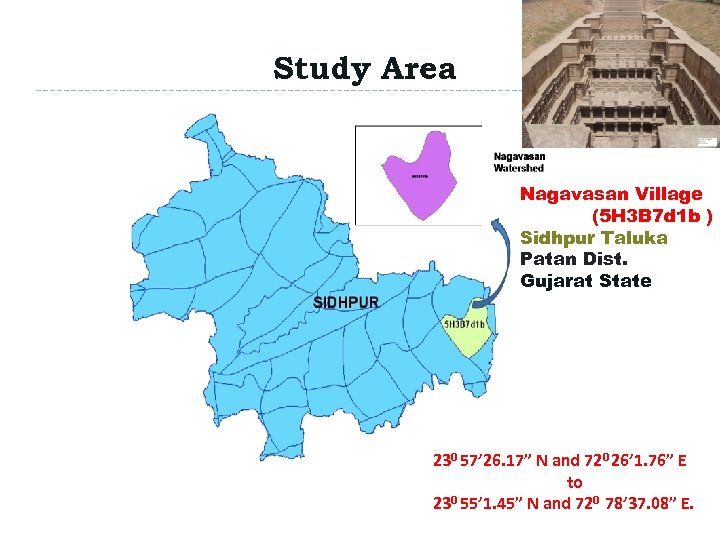
Study Area Patan Dist. Nagavasan Village Sidhpur Taluka (5 H 3 B 7 d 1 b ) Sidhpur Taluka Patan Dist. Gujarat State 230 57’ 26. 17” N and 720 26’ 1. 76” E to 230 55’ 1. 45” N and 720 78’ 37. 08” E.

About Study area Low rainfall area (700 mm) Prone to excessive soil erosion due to ravines and sparse vegetative cover leads to inadequate recharge of ground water and siltation of water harvesting structures. Low agriculture & milk productivity Biotic pressure on Gauchar and community land because of non-production of fodder on private land

Land Parcel Map with Survey Numbers
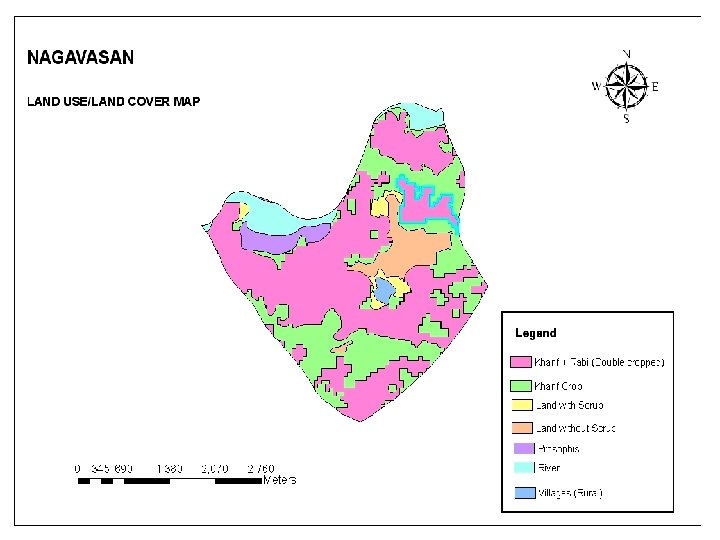
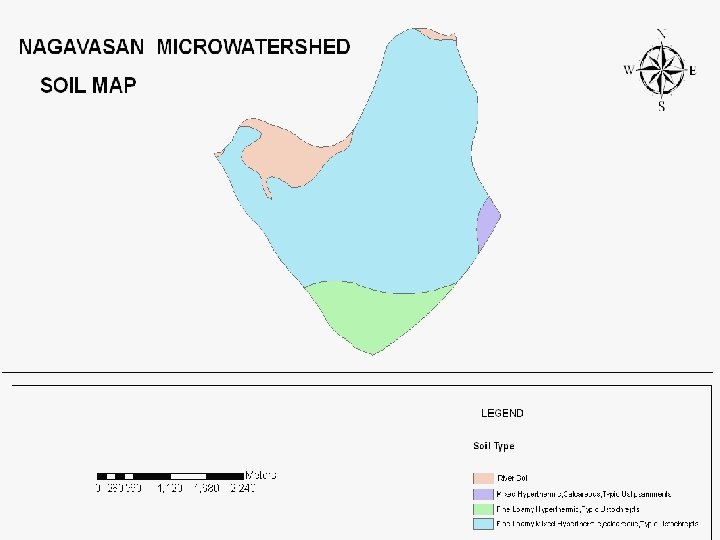

Action Plan Parameters • • Socio-economic parameters • BPL population • SC/ST population • Small/Marginal farmers • Landless Bio-Physical parameters • Ground water status • Vegetative cover status • Geomorphology of the area • Soil erodability status • Cropping pattern etc

Action Plan Parameters (Contd. ) • Asset inventory • Existing water harvesting structures • Community land • Gauchar land • Land holdings by SC/ST • Land holdings by Marginal Farmers • Road connectivity • Gram Panchayat office • Irrigation structures (wells, field channels etc. ) • Previous works under NREGS & other schemes
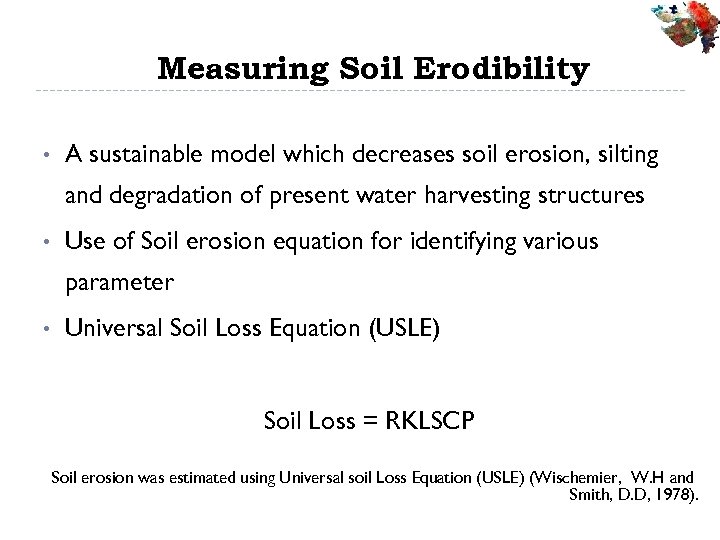
Measuring Soil Erodibility • A sustainable model which decreases soil erosion, silting and degradation of present water harvesting structures • Use of Soil erosion equation for identifying various parameter • Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) Soil Loss = RKLSCP Soil erosion was estimated using Universal soil Loss Equation (USLE) (Wischemier, W. H and Smith, D. D, 1978).

Measuring Soil Erodibility • ‘K’ is the erodibility factor - depends on soil characteristics (percent of sand, silt, organic matter content. K- Factor map for soil is prepared accordingly. • ‘LS’ is calculated from slope map - mainly dependent on percent slope and slope-length for each category of slope • ‘C’ factor is dependent on crop and the local vegetation. This is mapped from the land use and land cover map • ‘P’ factor is dependent on conservation practices applied or ought to be applied in watershed under NREGA.
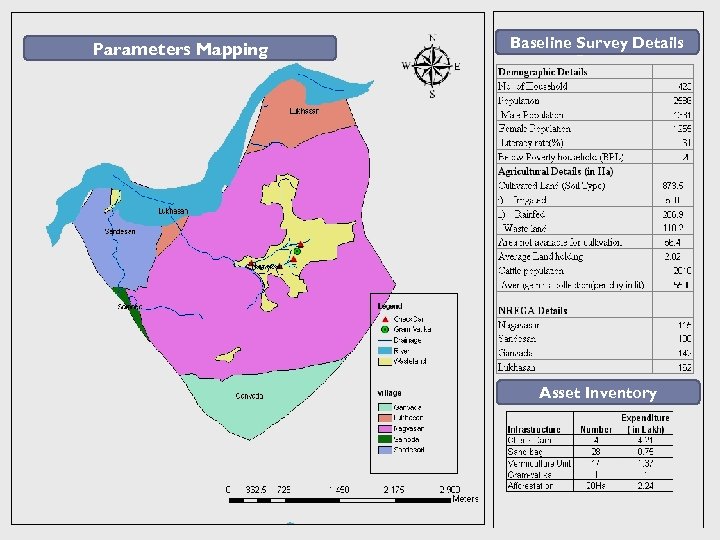
Parameters Mapping Baseline Survey Details Village Profile Asset Inventory
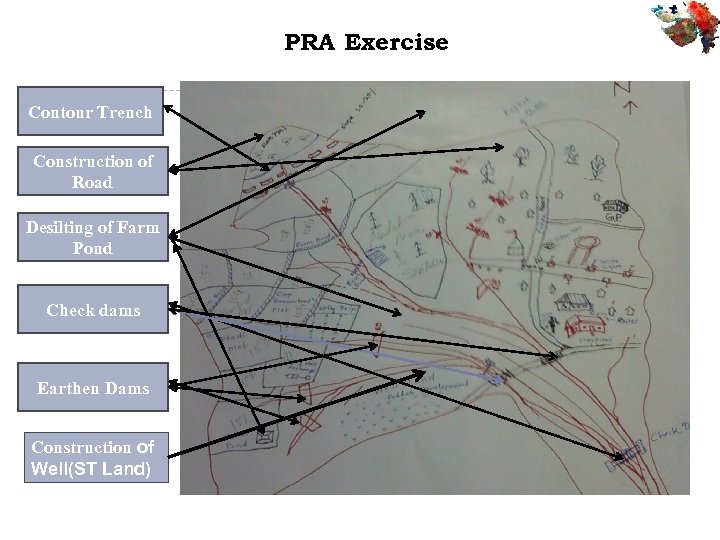
PRA Exercise Contour Trench Construction of Road Desilting of Farm Pond Check dams Earthen Dams Construction of Well(ST Land)
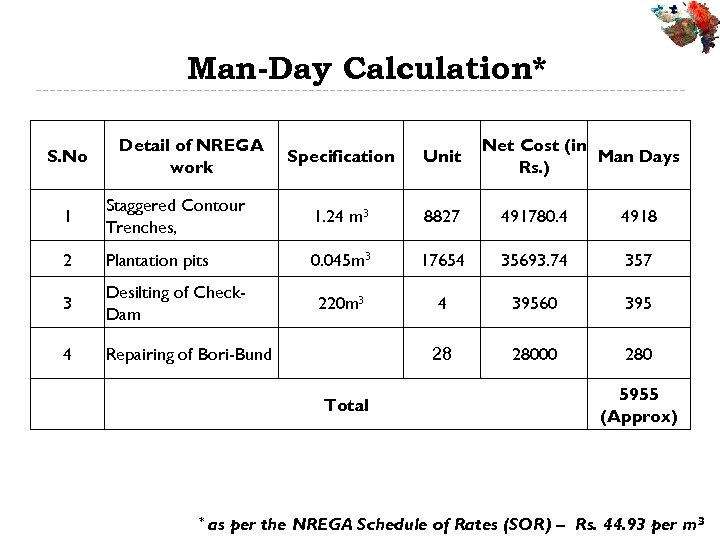
Man-Day Calculation* S. No Detail of NREGA work Specification Unit Net Cost (in Man Days Rs. ) 1 Staggered Contour Trenches, 1. 24 m 3 8827 491780. 4 4918 2 Plantation pits 0. 045 m 3 17654 35693. 74 357 3 Desilting of Check. Dam 220 m 3 4 39560 395 4 Repairing of Bori-Bund 28 28000 280 Total * as 5955 (Approx) per the NREGA Schedule of Rates (SOR) – Rs. 44. 93 per m 3
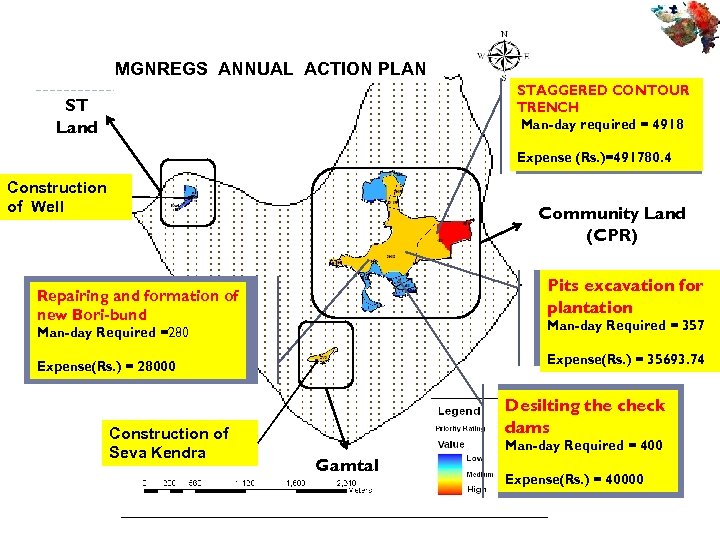
MGNREGS ANNUAL ACTION PLAN STAGGERED CONTOUR TRENCH Man-day required = 4918 ST Land Expense (Rs. )=491780. 4 Construction of Well Community Land (CPR) Pits excavation for plantation Repairing and formation of new Bori-bund Man-day Required = 357 Man-day Required =280 Expense(Rs. ) = 35693. 74 Expense(Rs. ) = 28000 Construction of Seva Kendra Desilting the check dams Man-day Required = 400 Gamtal Expense(Rs. ) = 40000
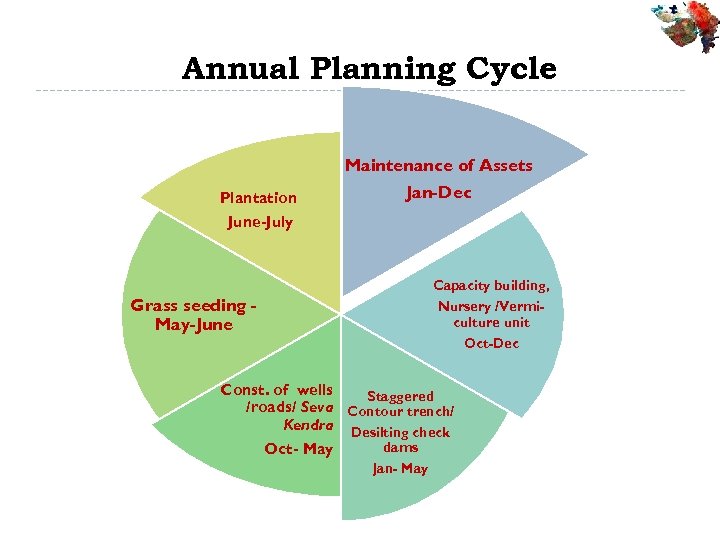
Annual Planning Cycle Maintenance of Assets Plantation Jan-Dec June-July Capacity building, Grass seeding May-June Nursery /Vermiculture unit Oct-Dec Const. of wells Staggered /roads/ Seva Contour trench/ Kendra Desilting check dams Oct- May Jan- May
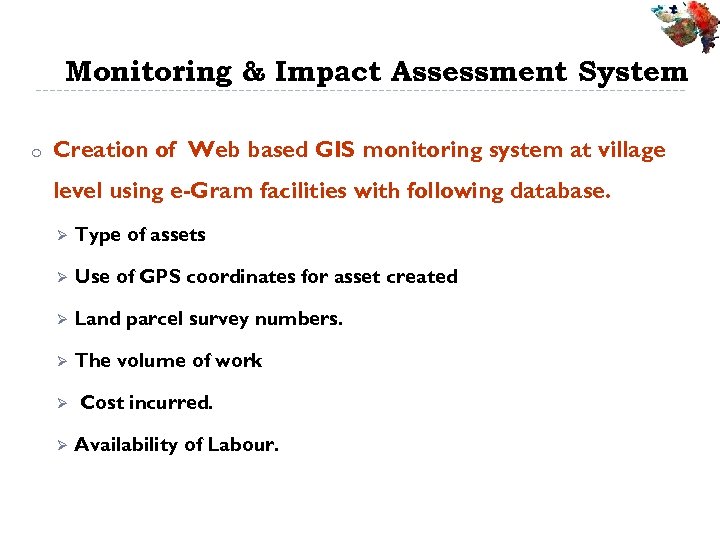
Monitoring & Impact Assessment System o Creation of Web based GIS monitoring system at village level using e-Gram facilities with following database. Ø Type of assets Ø Use of GPS coordinates for asset created Ø Land parcel survey numbers. Ø The volume of work Ø Ø Cost incurred. Availability of Labour.
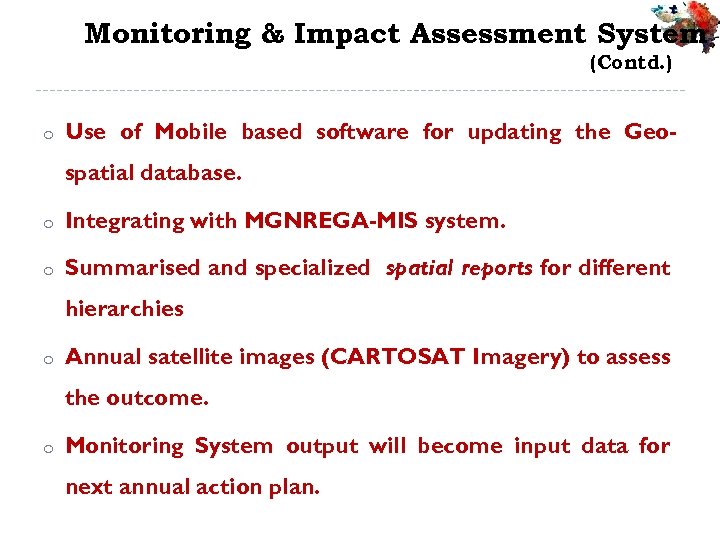
Monitoring & Impact Assessment System (Contd. ) o Use of Mobile based software for updating the Geospatial database. o Integrating with MGNREGA-MIS system. o Summarised and specialized spatial reports for different hierarchies o Annual satellite images (CARTOSAT Imagery) to assess the outcome. o Monitoring System output will become input data for next annual action plan.
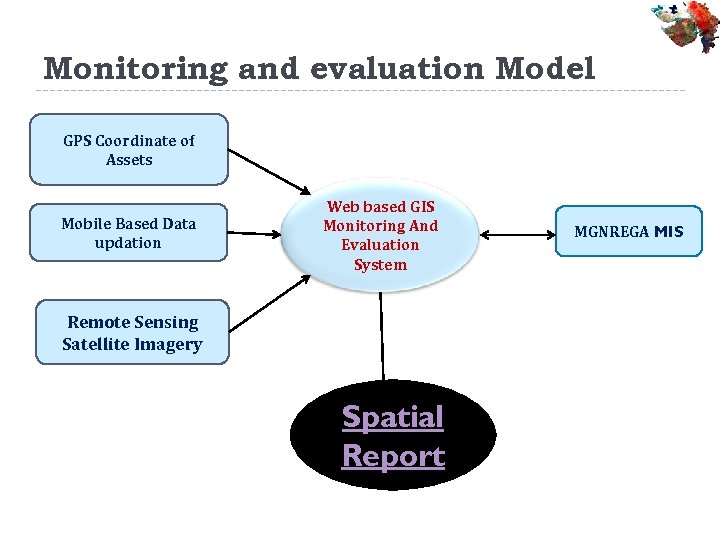
Monitoring and evaluation Model GPS Coordinate of Assets Mobile Based Data updation Web based GIS Monitoring And Evaluation System Remote Sensing Satellite Imagery Spatial Report MGNREGA MIS
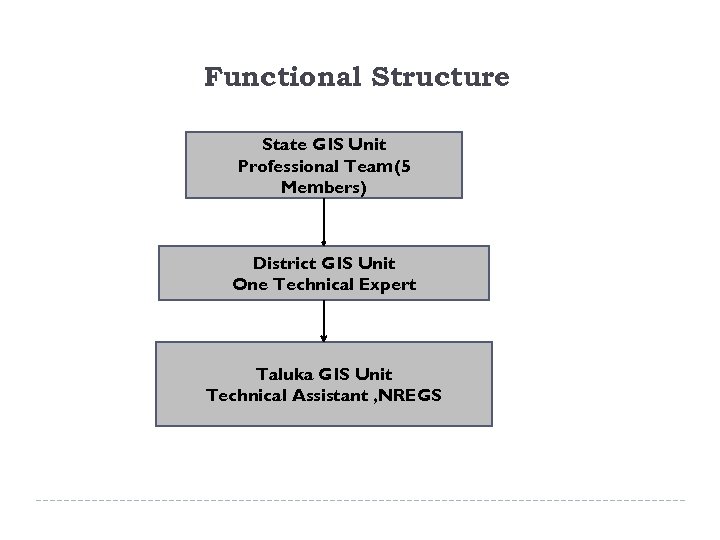
Functional Structure State GIS Unit Professional Team(5 Members) District GIS Unit One Technical Expert Taluka GIS Unit Technical Assistant , NREGS

Technical Resources Computer and Printer(At District and Taluka level) GIS Software GPS Instrument Scanner Digital Camera

Financial Implications State Level GIS Unit – Rs. 5 crore (Initial) and Rs. 1 Crore Recurring Cost Per annum. District Level GIS Unit – Rs. 25 Lakh (Intial) and Rs. 5 Lakh Recurring Cost Per annum Taluka Level GIS Unit - Rs. 5 Lakh and Rs. 1 Lakh Recurring Cost Per annum

Capacity Building at village level Capacity building of Village & Taluka level panchayat employees regarding the use of various GIS map and GPS instruments. Technical assistance to field engineers/Talati-cum. Mantri for better data collection. Exposure visit of different stakeholders to best managed projects

Conclusion Geographic Information system (GIS) has a vital role as a Decision Support System. Decentralization of MGNREGS activities and creation & management of asset inventory requires a proper scientific tool. The scope of GIS as an Information System acts as a solution for reliable, real-time and authentic information.

Thank You
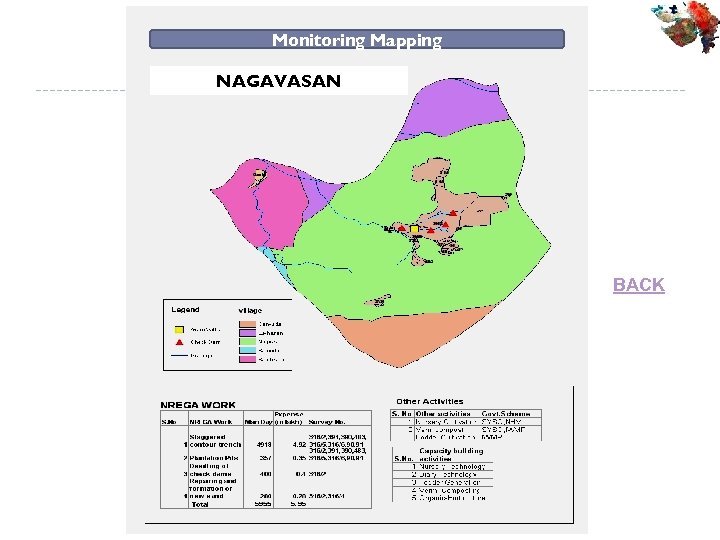
Monitoring Mapping NAGAVASAN BACK
c73e7326d83bbddc3c740eacf289f688.ppt