e3f13976b70fc55a1323aa9be1aeedad.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Application Architectures for Interactive Web Applications: Java JSP and Model/View/Controller Techniques Jeff Schmitt November 16, 2001

ABSTRACT This talk is the report of my sabbatical leave during Spring 2001 in which I explored some new techniques in using the Java language to develop interactive web applications. Java Server Pages technology (JSP) facilitates the development of interactive websites with dynamically generated content. JSP programs contain ordinary HTML tags mixed with Java code. Custom tag libraries and Template processing are techniques which allow the Java code to be isolated from the HTML. This application architecture is based on the principles of Model/View/Controller.
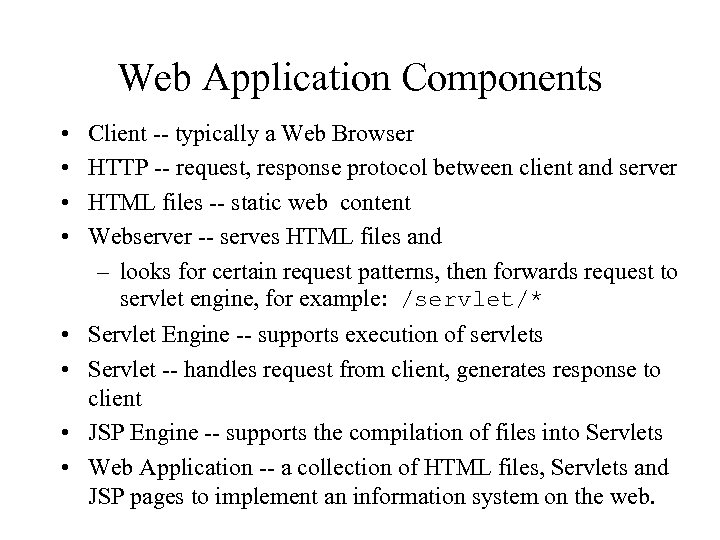
Web Application Components • • Client -- typically a Web Browser HTTP -- request, response protocol between client and server HTML files -- static web content Webserver -- serves HTML files and – looks for certain request patterns, then forwards request to servlet engine, for example: /servlet/* • Servlet Engine -- supports execution of servlets • Servlet -- handles request from client, generates response to client • JSP Engine -- supports the compilation of files into Servlets • Web Application -- a collection of HTML files, Servlets and JSP pages to implement an information system on the web.
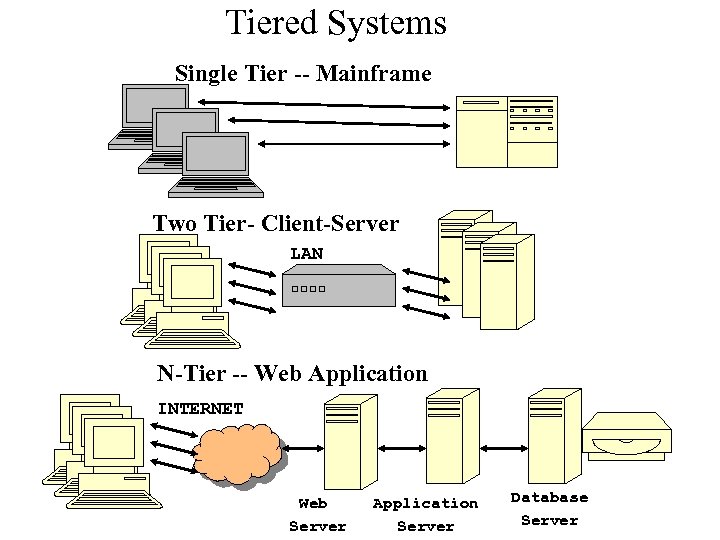
Tiered Systems Single Tier -- Mainframe Two Tier- Client-Server LAN N-Tier -- Web Application INTERNET Web Server Application Server Database Server
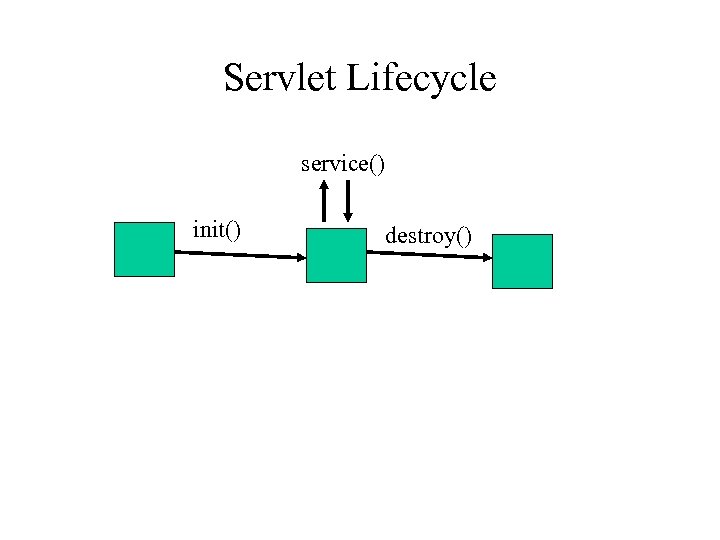
Servlet Lifecycle service() init() destroy()
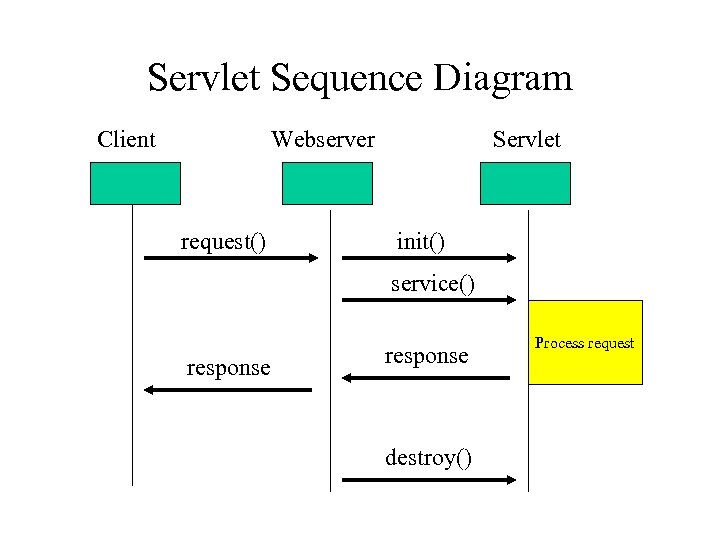
Servlet Sequence Diagram Client Webserver request() Servlet init() service() response destroy() Process request
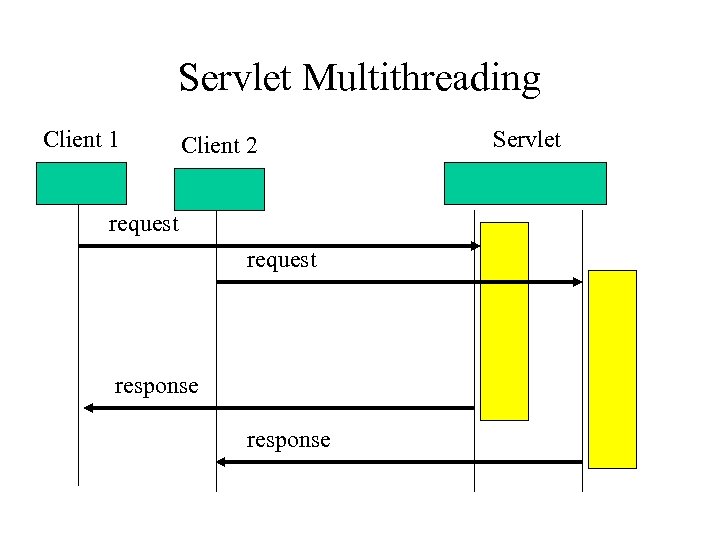
Servlet Multithreading Client 1 Client 2 request response Servlet
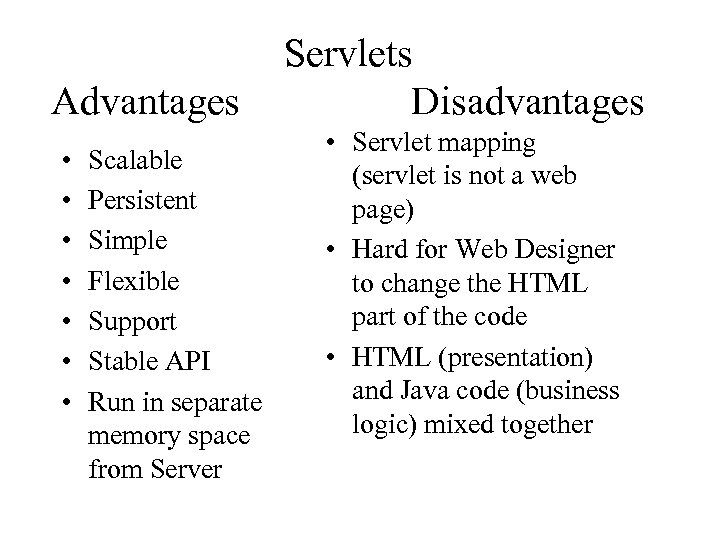
Advantages • • Scalable Persistent Simple Flexible Support Stable API Run in separate memory space from Server Servlets Disadvantages • Servlet mapping (servlet is not a web page) • Hard for Web Designer to change the HTML part of the code • HTML (presentation) and Java code (business logic) mixed together

XML Notation • Begin and end within same tag: <something/> • Begin and end as two separate tags: <something> … </something> • Document Type Definition <? xml version="1. 0" encoding="ISO-8859 -1"? > <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc. //DTD Web Application 2. 2//EN" "http: //java. sun. com/j 2 ee/dtds/web-app_2_2. dtd">
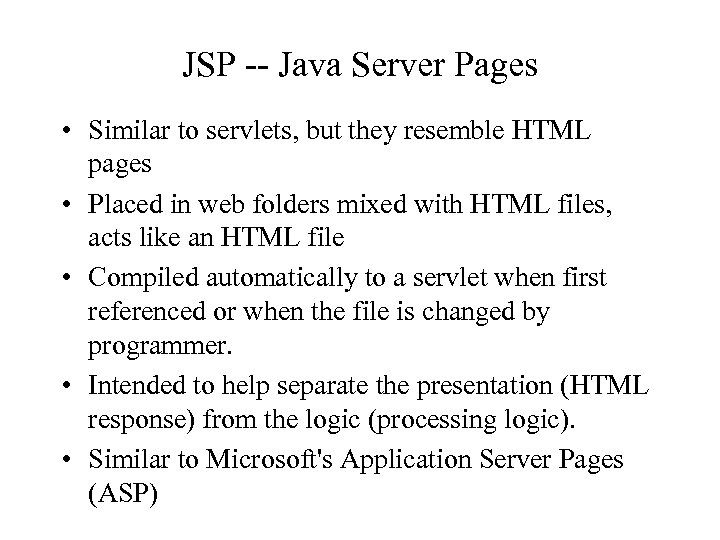
JSP -- Java Server Pages • Similar to servlets, but they resemble HTML pages • Placed in web folders mixed with HTML files, acts like an HTML file • Compiled automatically to a servlet when first referenced or when the file is changed by programmer. • Intended to help separate the presentation (HTML response) from the logic (processing logic). • Similar to Microsoft's Application Server Pages (ASP)
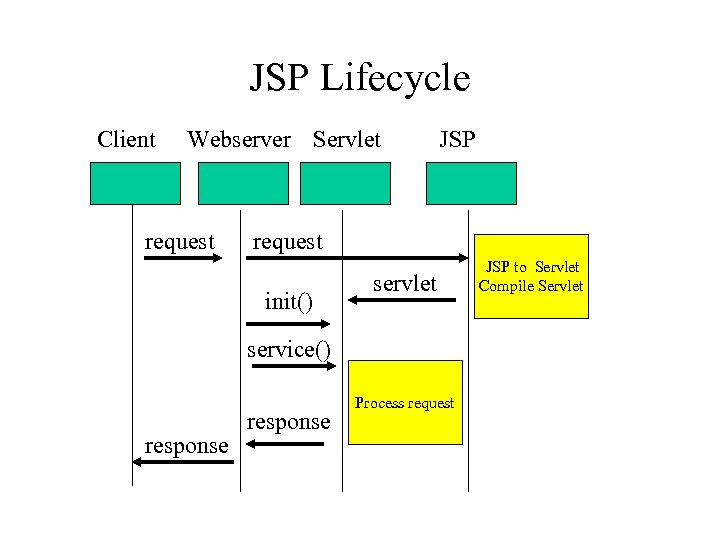
JSP Lifecycle Client Webserver Servlet request JSP request init() servlet service() response Process request JSP to Servlet Compile Servlet

JSP scripting elements • JSP Comments <%-- jsp comment --%> • Declarations: placed in static part of servlet <%! String file. Path="/users"; %> • Expressions: evaluate to a string <%= request. get. Parameter("NAME")%> • Scriptlets: any Java statements <% (java statements) %> • Template Text: inserted into response <TABLE BORDER=1> <TR><TH>Name: <TD><INPUT NAME="NAME" size=50 MAXLENGTH=50>
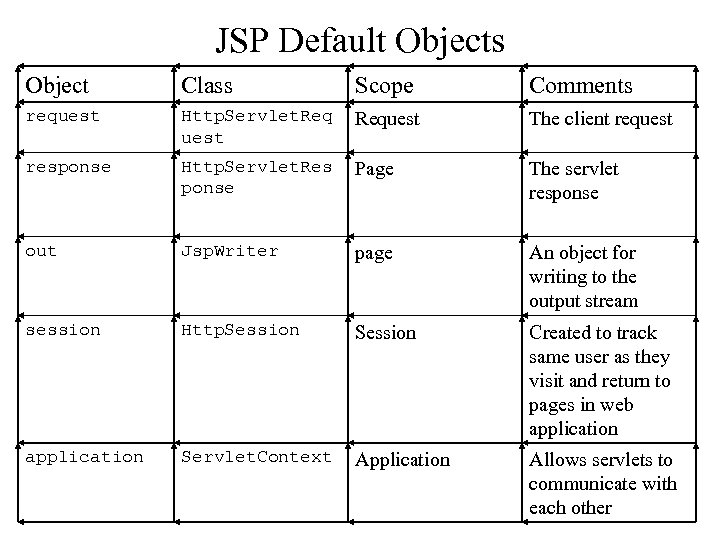
JSP Default Objects Object Class Scope Comments request Http. Servlet. Req uest Request The client request response Http. Servlet. Res ponse Page The servlet response out Jsp. Writer page An object for writing to the output stream session Http. Session Created to track same user as they visit and return to pages in web application Servlet. Context Application Allows servlets to communicate with each other
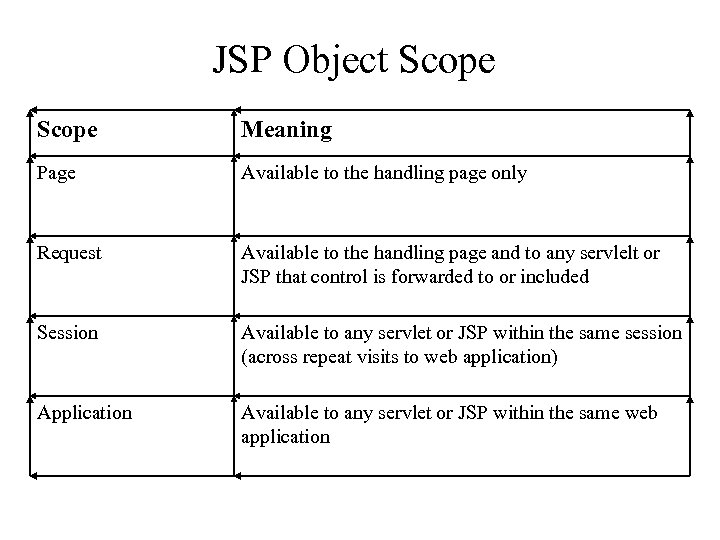
JSP Object Scope Meaning Page Available to the handling page only Request Available to the handling page and to any servlelt or JSP that control is forwarded to or included Session Available to any servlet or JSP within the same session (across repeat visits to web application) Application Available to any servlet or JSP within the same web application

Custom JSP tags • Assemble reusable JSP code for easy use • An XML-like front end to access Java programming • Designed to bridge the intersection between java programmers and web designers • Tag library holds definitions of custom tags <%@ taglib uri="jakarta-taglib/dbtags" prefix="sql" %> • Custom tags save in Tag Library File. tld • Many useful Tag Libraries exist for the common tasks such as database access, email, file access

DBTags • • From Apache Jakarta project Allow use of JDBC with Java details hidden Easy to use Invisible exception handling

<sql: connection> • establish connection to server <%-- open a database connection --%> <sql: connection id="conn 1"> <%-- required --%> <sql: url>jdbc: mysql: //localhost/test</sql: url> <%-- optional --%> <sql: driver>org. gjt. mm. mysql. Driver</sql: driver> <%-- optional --%> <sql: user. Id>root</sql: user. Id> <%-- optional --%> <sql: password>not. Very. Secure</sql: password> </sql: connection>

Statement and Query • The "escape. Sql" tag can be used inside a SQL query to SQL-escape your input values if they contain single quotes. <%-- insert a row into the database --%> <sql: statement id="stmt 1" conn="conn 1"> <%-- set the SQL query --%> <sql: query> insert into test_books (id, name) values (3, '<sql: escape. Sql> <%=request. get. Parameter("book_title")%></sql: escape. Sql>') </sql: query> <%-- execute the query --%> <sql: execute/> </sql: statement>

<sql: resultset> <table> <sql: statement id="stmt 1" conn="conn 1"> <sql: query> select id, name, description from test_books order by 1 </sql: query> <%-- loop through the rows of your query --%> <sql: result. Set id="rset 2"> <tr> <td><sql: get. Column position="1"/></td> <td><sql: get. Column position="2"/></td> <td><sql: get. Column position="3"/> <%-- print out a comment if the book has no description --%> <sql: was. Null>[no description]</sql: was. Null></td> </tr> </sql: result. Set> </sql: statement> </table>
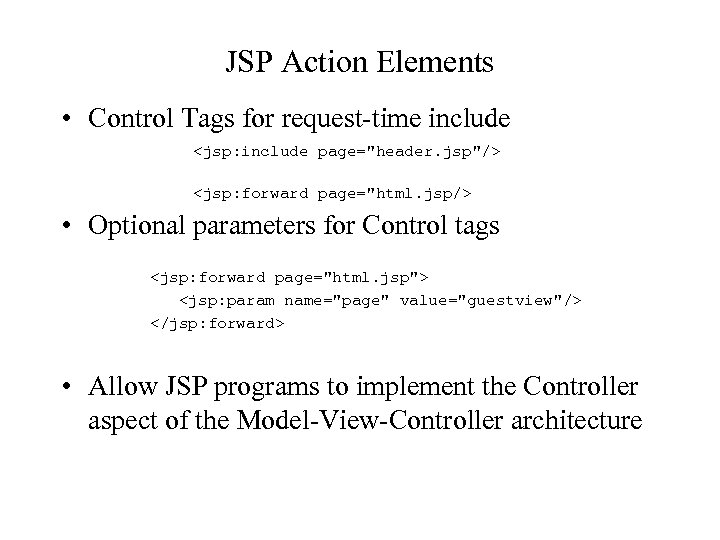
JSP Action Elements • Control Tags for request-time include <jsp: include page="header. jsp"/> <jsp: forward page="html. jsp/> • Optional parameters for Control tags <jsp: forward page="html. jsp"> <jsp: param name="page" value="guestview"/> </jsp: forward> • Allow JSP programs to implement the Controller aspect of the Model-View-Controller architecture
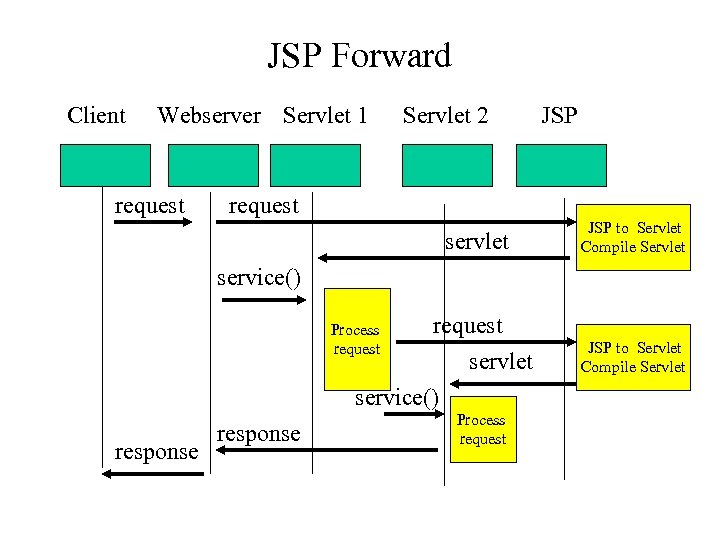
JSP Forward Client Webserver Servlet 1 request Servlet 2 JSP request servlet JSP to Servlet Compile Servlet service() request servlet service() Process request response Process request JSP to Servlet Compile Servlet
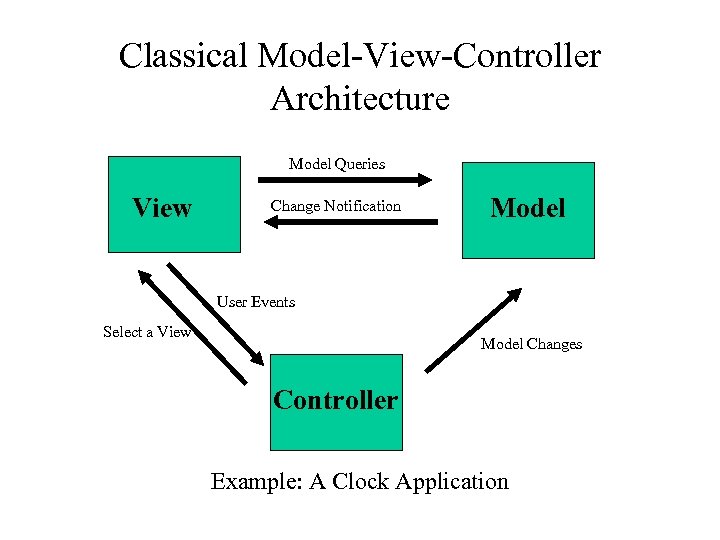
Classical Model-View-Controller Architecture Model Queries View Change Notification Model User Events Select a View Model Changes Controller Example: A Clock Application

Problems with JSP • Although intended to help separate the presentation logic (VIEW) from the business logic (MODEL), JSP does not go far enough • JSP programs are often a mix of HTML and business logic, which creates a problem if the design of the page (VIEW) needs to be changed • HTML changes need to be made by web designers who are not necessarily programmers • Solutions to this problem include Web. Macro, Struts, Free. Marker, Velocity
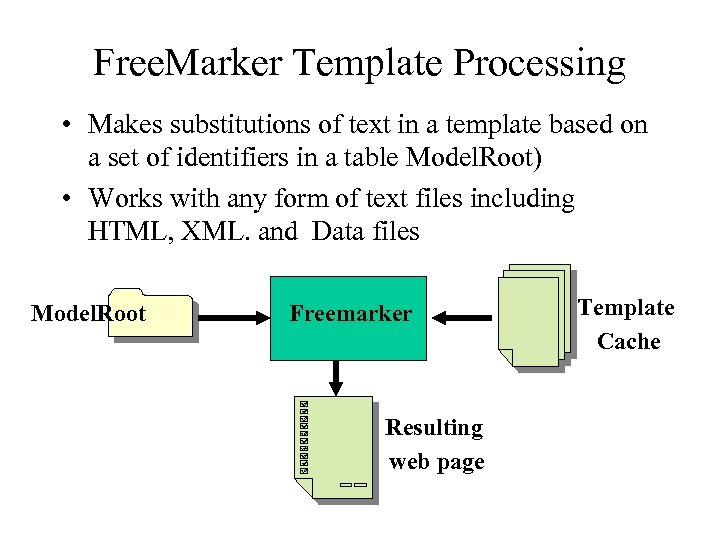
Free. Marker Template Processing • Makes substitutions of text in a template based on a set of identifiers in a table Model. Root) • Works with any form of text files including HTML, XML. and Data files Model. Root Freemarker Resulting web page Template Cache

Free. Marker Data Structures • Simple. Hash -- a random access table of words. Each word is associated with a value which can be any of the three Freemarker structures • Simple. List -- a sequential access list of any of the three Freemarker structures • Simple. Scalar -- a String of text Model. Root -- the root of the structure must be a Simple. Hash
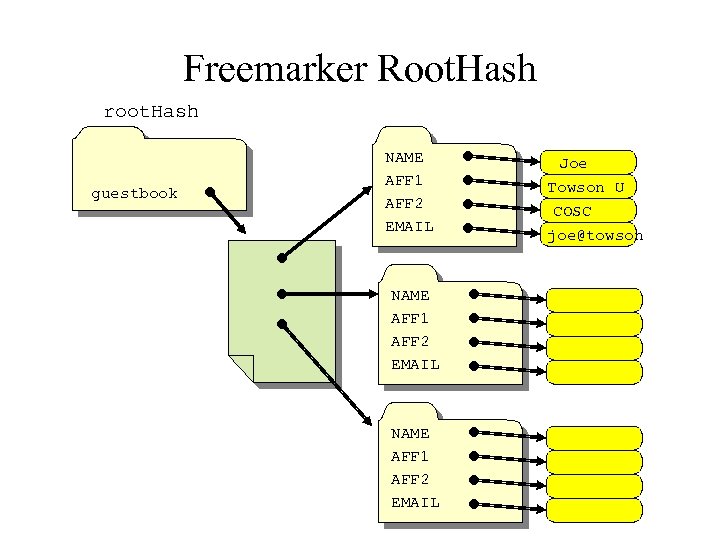
Freemarker Root. Hash root. Hash guestbook NAME AFF 1 AFF 2 EMAIL Joe Towson U COSC joe@towson
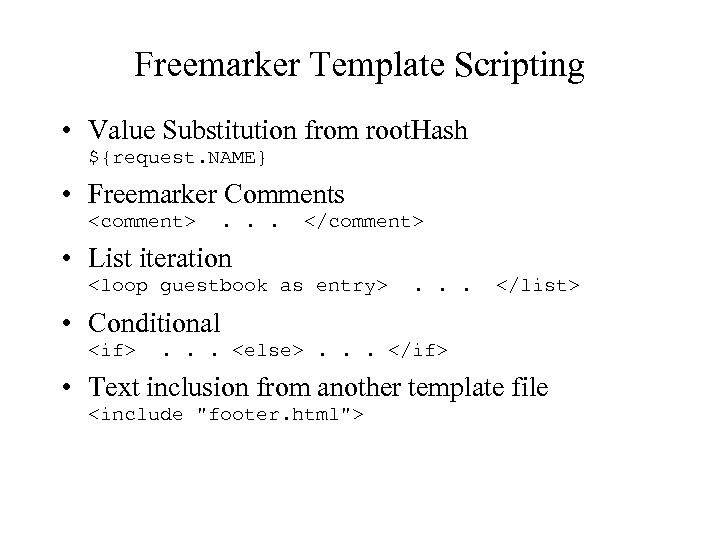
Freemarker Template Scripting • Value Substitution from root. Hash ${request. NAME} • Freemarker Comments <comment> . . . </comment> • List iteration <loop guestbook as entry> . . . </list> • Conditional <if> . . . <else>. . . </if> • Text inclusion from another template file <include "footer. html">

Free. Marker Template Cache • Manages the folder where templates are stored • Loads and compiles templates into tokenized form for efficiency • Recognizes changes to templates while application is running
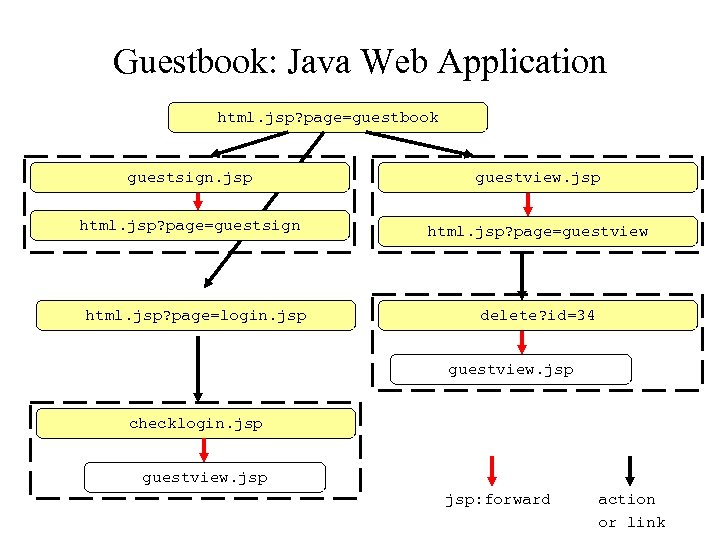
Guestbook: Java Web Application html. jsp? page=guestbook guestsign. jsp guestview. jsp html. jsp? page=guestsign html. jsp? page=guestview html. jsp? page=login. jsp delete? id=34 guestview. jsp checklogin. jsp guestview. jsp: forward action or link

Guestbook Demo http: //www. mycgiserver. com/~fontanini/intro fm/html. jsp? page=guestbook

I 18 N • • • Internationalization Language and Cultural differences Dates Times Browser sends header: Accept-language: en-us First two characters choose template file: – guestbook_en. html – guestbook_it. html • Example: http: //www. mycgiserver. com/~fontanini/fm/guestbook. jsp

Conclusion • JSP is Java that looks like HTML • Custom Tags make programming “easy” • Separation of business logic and presentation is desirable for larger “Enterprise” projects • JSP alone does not achieve this separation • EJB, and other technologies are complicated • Template processing provides the desired separation, rather easily and elegantly. • Thank you for attending. Any questions?
e3f13976b70fc55a1323aa9be1aeedad.ppt