ce9a42aab855c239a231fc515bf069c0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 100

APHG REVIEW BOOK IN A NUTSHELL BY ALEX COLEMAN

CENTRAL PLACE THEORY Developed by Walter Christaller Saw the economic world as a spatial model City location and the level of economic exchange could be analyzed using central places within hexagons which overlapped

ARITHMETIC DENSITY Number of things per square unit of distance.

AGRICULTURAL DENSITY Number of people per square unit of land actively under cultivation.
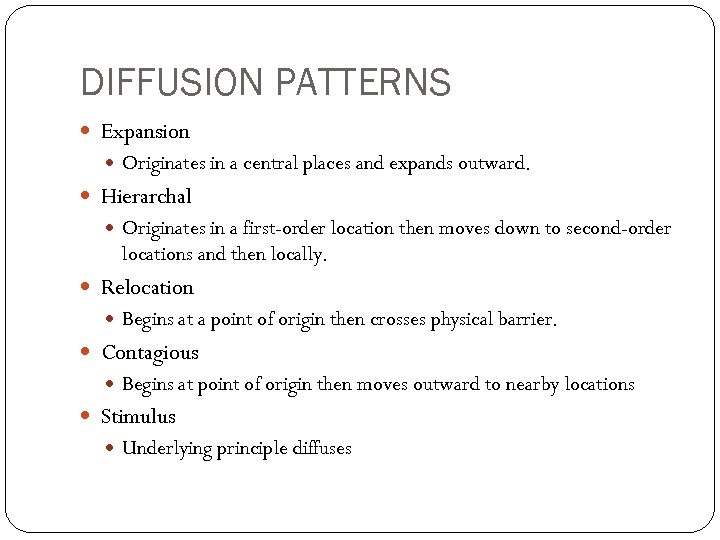
DIFFUSION PATTERNS Expansion Originates in a central places and expands outward. Hierarchal Originates in a first-order location then moves down to second-order locations and then locally. Relocation Begins at a point of origin then crosses physical barrier. Contagious Begins at point of origin then moves outward to nearby locations Stimulus Underlying principle diffuses
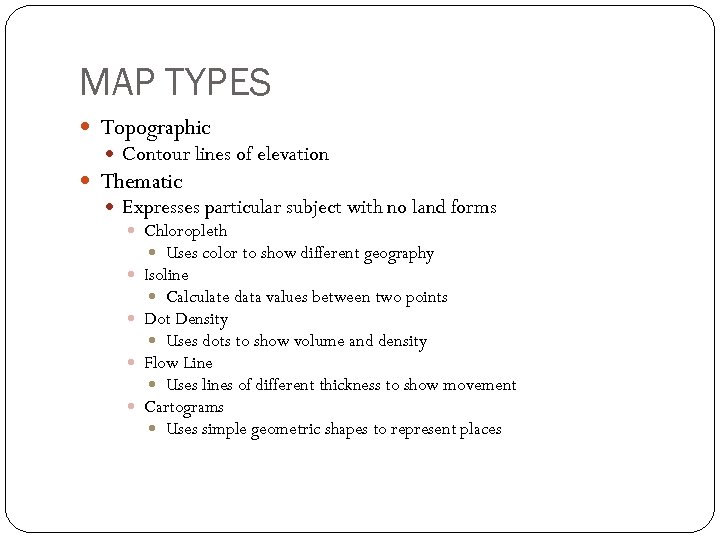
MAP TYPES Topographic Contour lines of elevation Thematic Expresses particular subject with no land forms Chloropleth Uses color to show different geography Isoline Calculate data values between two points Dot Density Uses dots to show volume and density Flow Line Uses lines of different thickness to show movement Cartograms Uses simple geometric shapes to represent places
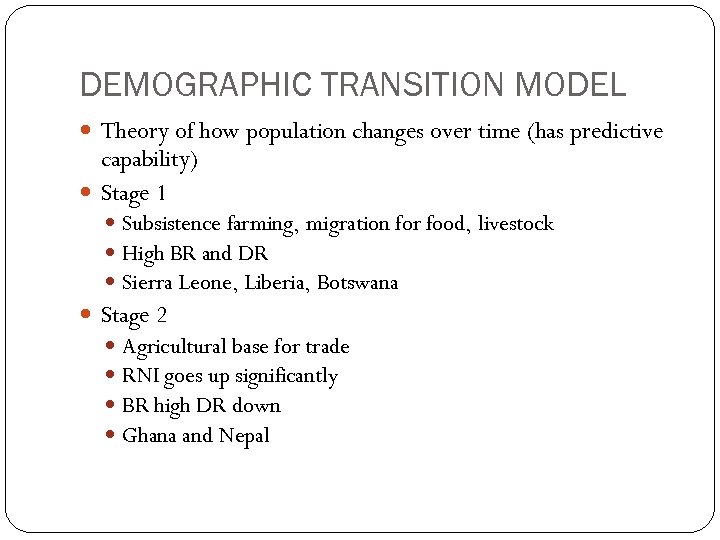
DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION MODEL Theory of how population changes over time (has predictive capability) Stage 1 Subsistence farming, migration for food, livestock High BR and DR Sierra Leone, Liberia, Botswana Stage 2 Agricultural base for trade RNI goes up significantly BR high DR down Ghana and Nepal
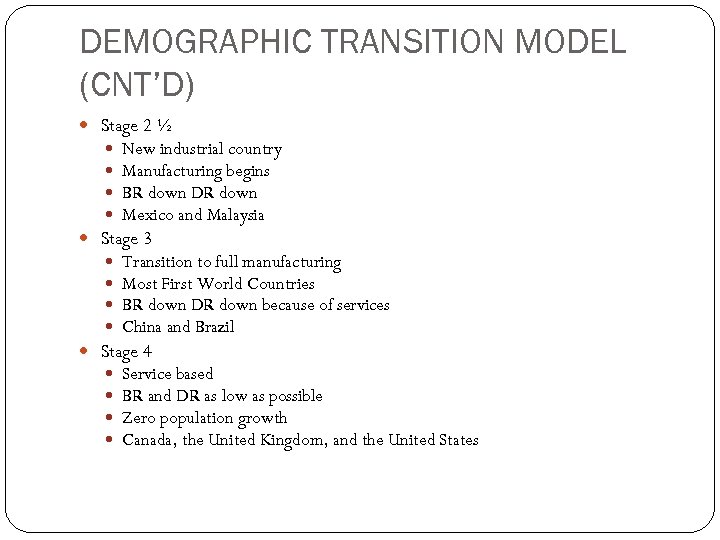
DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION MODEL (CNT’D) Stage 2 ½ New industrial country Manufacturing begins BR down DR down Mexico and Malaysia Stage 3 Transition to full manufacturing Most First World Countries BR down DR down because of services China and Brazil Stage 4 Service based BR and DR as low as possible Zero population growth Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States

MALTHUSIAN THEORY Global population would exceed food production Didn’t happen because of agricultural revolutions Neo- Malthusians Sustainability: may be problems keeping up in the long-run Increasing per capita demand: the amount of food person has gone of greatly Natural resource depletion: nonrenewables will run out like wood, minerals, and energy

POPULATION PYRAMIDS Population structures based on ages Shapes Triangle Fast growing Extended Triangle Moderate growth Column Slow growth Reduced pentagon Shrinking Gaps War Older on top
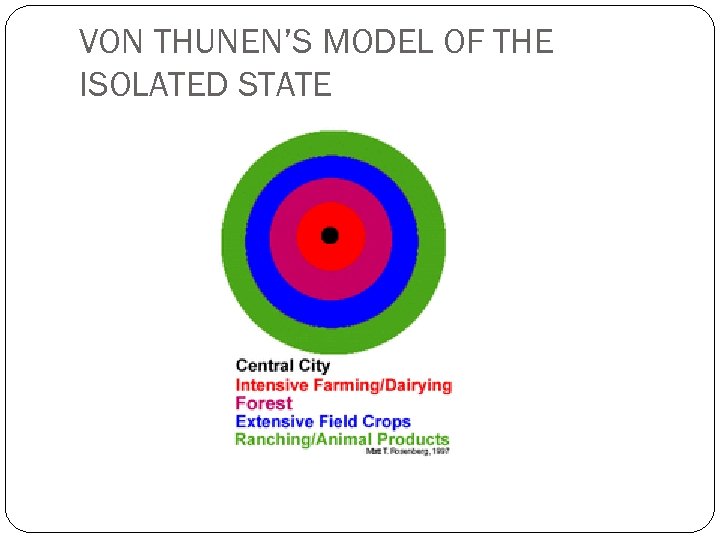
VON THUNEN’S MODEL OF THE ISOLATED STATE
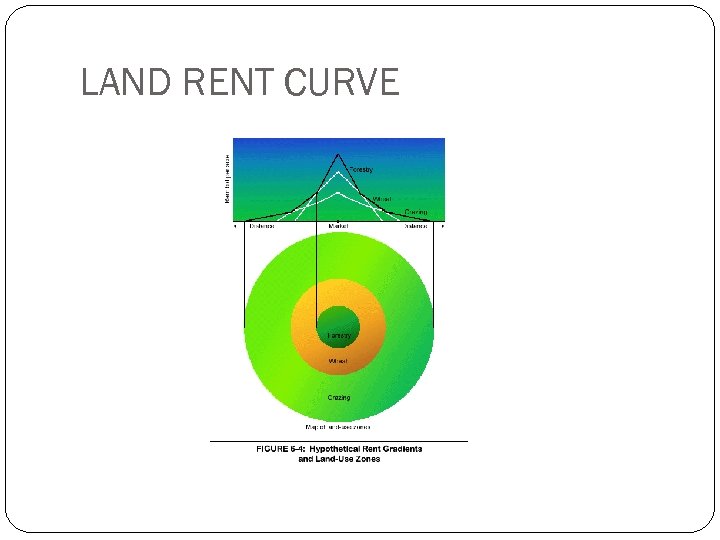
LAND RENT CURVE
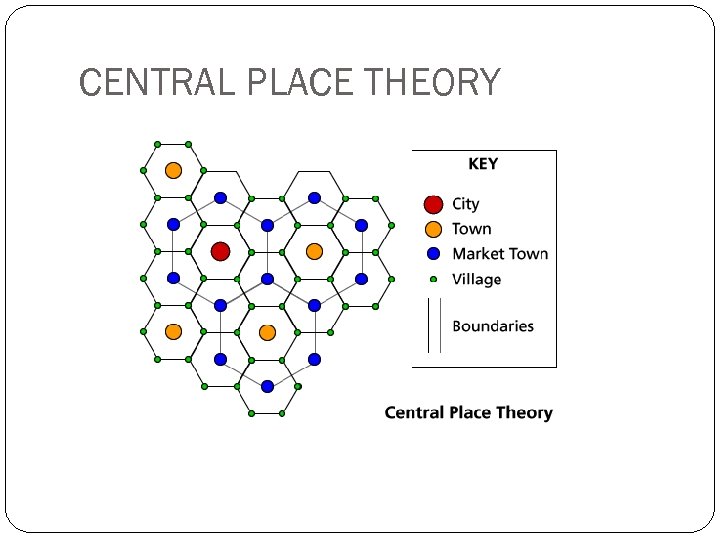
CENTRAL PLACE THEORY
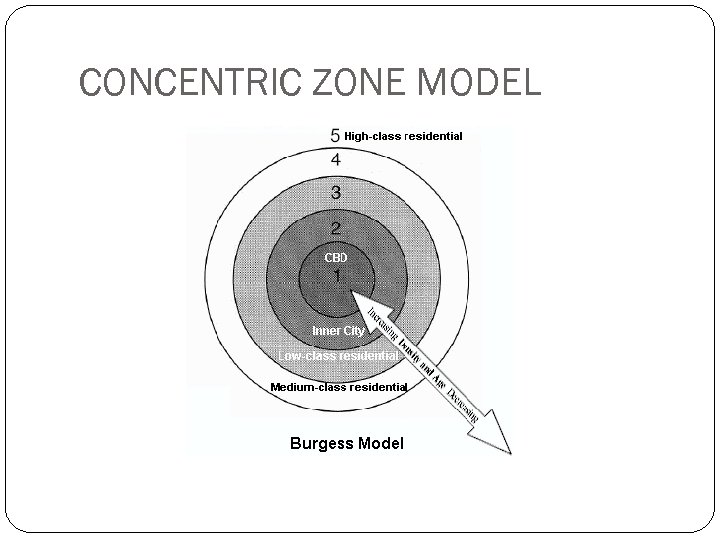
CONCENTRIC ZONE MODEL
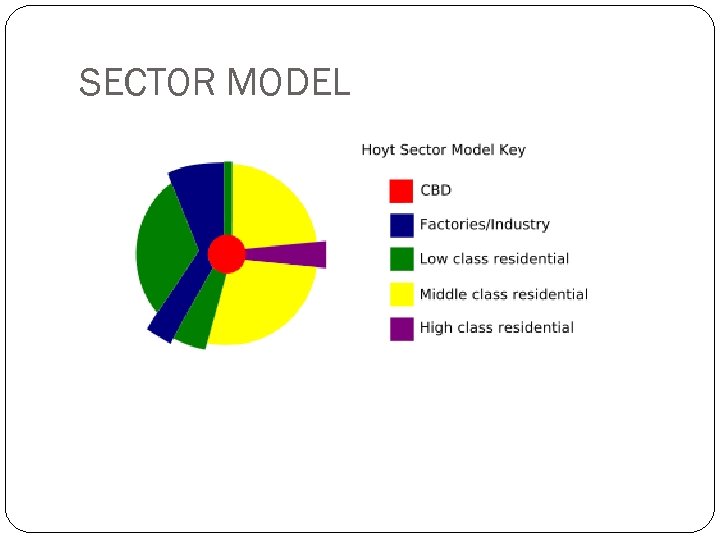
SECTOR MODEL
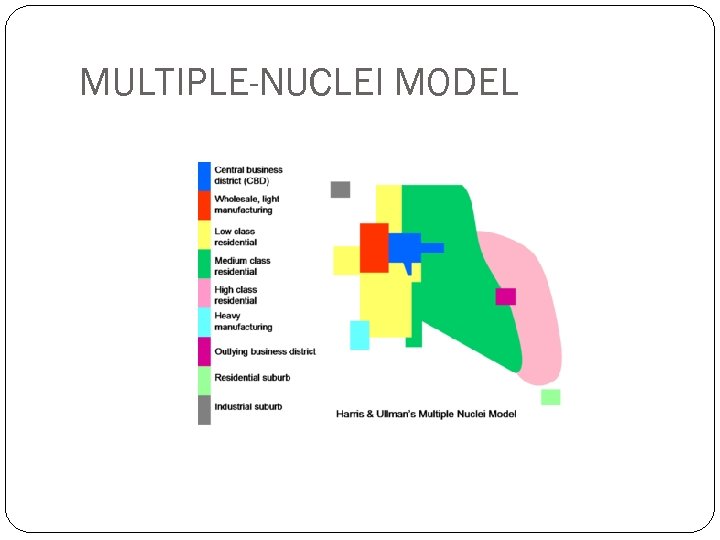
MULTIPLE-NUCLEI MODEL

GALATIC CITY MODEL
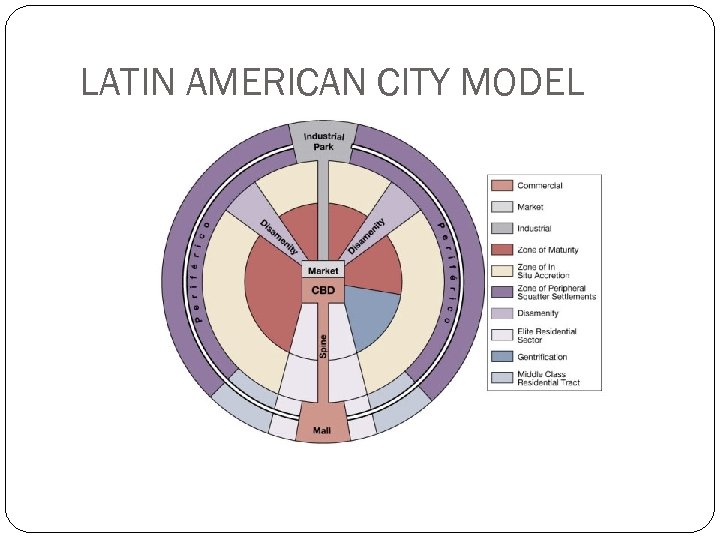
LATIN AMERICAN CITY MODEL
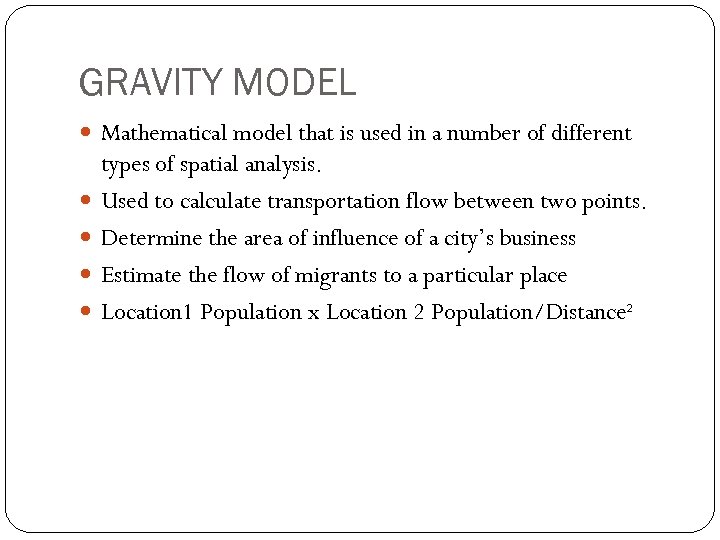
GRAVITY MODEL Mathematical model that is used in a number of different types of spatial analysis. Used to calculate transportation flow between two points. Determine the area of influence of a city’s business Estimate the flow of migrants to a particular place Location 1 Population x Location 2 Population/Distance²

GIS, GPS, AND REMOTE SENSING GIS Data layers that show different geographic features GPS Uses satellites to show your position on Earth Remote Sensing Arial photography used for GIS.

BIRTH RATE Total number of infants born living counted in a year Live births/ (Population/1000) Higher birth rates in LDCs Lower birth rates in MDCs

DEATH RATE The number of deaths per year divided by 1000. Deaths/(Population/1000) High death rates in LDCs Low death rates in MDCs Advances in technology have increased life expectancy
RATE OF NATURAL INCREASE (RNI) Difference in the amount of population change BR-DR/10 Possible to be negative

DOUBLING TIME How long it would take for a country to double in size 70/RNI

NET MIGRATION RATE Total migration (Number of Immigrants/(Population/1000))-(Number of Emigrants/(Population/1000)) Can be negative

THE DEMOGRAPHIC EQUATION ((BR-DR)+NMR)/10= Percentage Rate

TOTAL FERTILITY RATE Average number of children born to each woman age 15 to 45 Number of children/Number of women

CENTROID Geographic center of a country

MIGRATION Inter-regional or internal One region of a country to another Transnational One country to another Step migration People move up in hierarchy of location for work or other reasons Chain migration Pioneers establish a new place which is a foothold for more migration Periodic movement Annual or seasonal movement Push factors War Environmental hazards High cost of land Pull factors Employment Services

LANGUAGE Linguistic region A place where a language is spoken Can have different dialects within the region Lingua franca Bridge language like English or French

ANATOLIAN VS. KURGAN THEORY Anatolian Group of Indians migrated from India to Turkey and brought their language and then to Europe Kurgan Group of Indians went from India to Central Asia then across the Eurasian steppe to Western Europe.

RELIGION Universalizing religions accept Accept followers from everywhere Ethnic religions Only from specific ethnic groups Animist Voodoo, Native American Worship nature Migration Hindu-Buddhist Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism Reincarnation Hindus: caste system, Buddhists: oppose the caste Abrahamic Judaism, Christianity, and Islam Believe in God to a certain degree Common ancestors of Abraham Jesus Christ was a figurehead Islam: Five Pillars got them to Heaven

NATION AND ETHNICITY Nation Population represented by a single characteristic Culture group is another name Ethnicity Genetic heritage and political allegiance Race Genetic heritage and physical characteristics

ENVIRONMENTAL DETERMINISM Friedrich Ratzel The physical geography shapes the culture

POSSIBILISM Carl Saur Cultures were partially shaped by the environment
INTERNAL VS. EXTERNAL INDENTITY Internal Expressing cultural heritage within the area it originated External Expressing culture where they do not share the common culture or geographic background

CULTURAL REGIONS Homogeneous characteristics of culture in an area

CULTURAL HEARTHS Origin of a given culture Nile River Mesopotamia The Indus Valley Mesoamerica The Andean Highland Northeast Chile West Africa

SEQUENT OCCUPANCE Replacing dominant cultures over time Lagos, Nigeria going from British control to Nigerian

ACCULTURATION Fully adopting the culture of the dominant population

CULTURAL GLOBALIZATION Media has combined cultures so much that the cultures have lost their connection to their heritage and to nature

ETHNIC AND RELIGIOUS CONFLICTS Ethnic cleansing People of one ethnic group are eliminated by another Yugoslavian Croats and Serbs Genocide Large scale systematic killing of people of one ethnic group Holocaust Darfur Rwanda

UNITS OF POLITICAL ORGANIZATION Country An identifiable land area Nation A population with a single culture State A population under a single government Nation-state Single culture under a single government Japan, Iceland, Ireland

NATIONALISM Existing culture group that desires political representation or independence

STATELESS NATION Culture group is not included or allowed to share in the state political process Kurds in Iraq, Iran, and Syria Basques in northern Spain Hmong in Laos, Vietnam, Thailand, and southern China

CONFEDERATION Several smaller states make up a federal government US, Australia, Brazil, Russia

MICROSTATES Sovereign states that are smaller but hold the same position of larger states Dominica, Luxembourg, Malta, Singapore

MULTI-STATE NATIONS Supernationalism Two or more states align together for a common purpose UN, WTO, WHO, EU, NATO, OPEC, NAFTA

THE EUROPEAN UNION Free trade union Open borders Uniform currency One court for international issues One parliament World’s largest economy Constitution is not yet ratified

ENCLAVES AND EXCLAVES Enclave The minority group concentrated inside another country Ethnic neighborhood in Quebec Exclave Fragmented piece of sovereign territory separated by land from the main part of the country Alaska

WATER BORDERS AT SEA Territorial sea: 12 nautical-mile limit to sovereignty Exclusive Economic Zone: Given country only allowed to exploit economically within 200 miles High Seas Outside of 12 mile limit

BORDER TYPES Physical Natural borders like rivers or mountains Cultural Estimated boundaries between people groups Geometric Surveyed along lines of latitude and longitude

BORDER CONFLICTS Frontier Open and undefined territory Peaceful Resolutions 1846 Oregon Treaty, Louisiana Purchase 1804 Post-colonial boundary conflicts Conference of Berlin 1884 making international borders for Africa Created the “Tyranny of the Map” because they did not consider cultural boundaries genocides in Rwanda were because of these issues

TERRITORIAL MORPHOLOGY Compact Shape without irregularity Nigeria Fragmented Broken into pieces Philippines Elongated Stretched out, long Chile Prorupt Panhandle Italy Perforated Has a country inside of it South Africa Landlocked Has no oceans or seas Switzerland

ANNEXATION Territory is added as a result of the land purchase or when it is claimed through incorporation
GERRYMANDERING Attempt to try to stack votes to guarantee congressional support for one particular party and “fix” elections

ABSOLUTE MONARCHY Supreme ruler runs the country Present day Saudi Arabia, Brunei, UAE

CONSTITUTIONAL MONARCHY Monarch can dismiss parliament, appoints judges, is commander in chief, holds the monarchal estates. Great Britain, Belgium, Japan

COMMONWEALTH COUNTRIES Retain the British monarch as their head of state Canada, Jamaica, Australia

FREE-MARKET DEMOCRACY VS. SOCIALISM Free-market does not try to put barriers on the economy (US and UK) Republics Free of aristocratic or monarchal control Need separation of powers and flexible constitution Socialism tries to distribute everything and centrally run the economy (USSR) Lacked incentive to produce and surplus of goods

GEOPOLITICS Global-scale relationships between sovereign states. Exam likes to ask about Cold War and relationships between democracies and Communist countries

CENTRIPETAL AND CENTRIFUGAL FORCES Centripetal Factors that hold together social and political fabric of the state Nationalism, well-liked leader, productive economy, effective social welfare programs Centrifugal forces Factors that tear apart the social and political fabric of the state Cultural differences or conflicts, political corruption, failing economy, natural disasters Yugoslavia had a good leader who identfied with everyone and he died and left a power vacuum

BALKANIZATION AND IRREDENTISM Balkanization When the political landscape goes from a larger state to several smaller states Yugoslavia, Czechoslovakia, Austro- Hungarian Empire, USSR Irredentism When a minority group desires to break away from a multi- ethnic state Or align itself with another state Chechnya, Timor, Ossetia

REUNIFICATION When nations were torn apart, but then come back together East and West Germany, return of the canal zone to Panama, Yemen

HEARTLAND-RIMLAND MODEL Halford Mackinder Effort to define the global geopolitical landscape and determine areas of potential future conflict Largest was Eastern European steppe in Russia at the time this was called the Heartland Rimland was rest of the continents of Europe and Asia and parts of Northern Africa Landwolves Eager to grab the area from the land (France) Seawolves Eager to grab the area from the sea (UK and Japan)

SHATTERBELT THEORY Saul Cohen Changed the Heartland to “Pivot Area” Changed the Rimland into the “Inner Crescent” Rest of the world was the “Outer Crescent” (US)

CONTAINMENT THEORY George Kennan Soviet Union would try to capture buffer states US would try to build a containment wall Worked out well at first Communism died in Greece and Iran US feared domino effect that if one state fell then many would follow

FARMING PRACTICES Intensive Lots of labor or small plot of land Extensive Limited labor or large plot of land Pastoralism Agriculture based on the seasonal movement of animals (nomadic herding) Plant domestication Plant cultivatars used plants for food and used it to make clothing Subsistence farming Feeding only the producer’s household Extensive subsistence Low amounts of labor in less populated areas (South America)

FARMING PRACTICES (CNT’D) Non subsistence agriculture Cash-cropping to sell goods at markets Plantation Domestic consumption and exporting crops Bananas in Brazil, Sugar in Florida, Coffee in Ethiopia Communism and agriculture Communes resulted made of several families

HUMAN ECOLOGY How humans interact with nature

TYPES OF CROPPING Crop rotation One crop is planted on a plot of land then switched to another plot later Multi-cropping Planting one or more than one crop on the same land Sustainable yield Amount of crops or animals that can be raised without endangering environment or too many expenses Non-food crops Textiles, animal feed, ethanol, biodiesel Shifting cultivation Slash and burn in rainforests

NEGATIVES OF CROPPING Extensive pastoralism Shifting animal herds between grazing pastures Overgrazing Too much grazing has led to dry grassland being eaten away Desertification Any human process that turns a vegetated environment into a desert-like landscape Soil salinization Evaporation of water trapping salt on the surface

AGRICULTURAL REVOLUTIONS First Vegetative planting Plants grown together Seed agriculture Fertilized seeds were planted together Animal domestication Breeding of animals for specific purposes Size of farms Small, mainly subsistence Columbian Exchange (popular on AP exams) Maize, peppers, potatoes, tomatoes, yucca, tobacco, rubber, peanuts, chocolate, and turkeys to Old World Wheat, rice, coffee, apples, citrus, horses, cattle, hogs, chickens, sheep, goats, and diseases to the New World

AGRICULTURAL REVOLUTIONS Second Mid- 1800 s to early 1900 s Developed Hybrid plants Fertilizers Pesticides Machines such as trucks, tractors, pumps, and trailers
AGRICULTURAL REVOLUTIONS Third Improvements Genetic engineering Development of vaccines, antibiotics, and growth hormones Factory farming Agribusiness Corporate agriculture Large scale extensive farms controlled by one company Seeing the end of the family farm in America

SPECIALIZED AGRICULTURE Natural foods emerging Non genetically modified foods (GMOs) Organics Hormone-free Grass-fed beef Alternative livestock Lamb, bison, llamas, goose, and duck Fish Farming Wineries

SECTORS OF PRODUCTION Primary Agriculture, mining, energy, forestry, fisheries Secondary Processing of raw materials (manufacturing) Tertiary (services) Transportation, wholesaling, retailing of the finished goods Quaternary Wholesaling, finance, banking, insurance, real estate, advertising, and marketing Quinary production Retailing, tourism, entertainment, and communication, government, or education, and utilities

LEVELS OF DEVELOPMENT First World Industrialized and service based Free markets High level of productivity High quality of life Second World Communist countries Centrally planned economies Third World Mainly agricultural Low levels of productivity Low quality of life Fourth World Third World with economic crisis Fifth World Third World with no government

NEWLY INDUSTRIALIZED COUNTRIES Third world states that have made a shift from agriculture to manufacturing Mexico, Brazil, Dominican Republic, Nigeria, China, Vietnam, India

COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE Country has the ability to produce a good or service at less cost than other states

ASIAN TIGERS Old Asian Tigers Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore Developed because of foreign aid during the 50 s, 60 s, and 70 s New Asian Tigers China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam Developed because of foreign direct investment during the 80 s and 90 s Growth possible because of cheap land, labor, and resources; and a lack of environmental regulations

ECONOMIC MEASURES OF DEVELOPMENT GDP: total volume of a country’s economy Good+ Services GNI: dollar value of all goods and services produced in a country plus the value of exports minus imports Goods+ Services+(Exports-Imports) Trade surplus Exports>Imports Trade deficit Exports<Imports GDP per capita GDP/Population GNI per capita GNI/Population

HUMAN DEVELOPMENT INDEX Designed by the UN to measure the level of development of states based on GDP per capita, the adult literacy rate, average level of education, and total life expectancy Score is indexed from. 0 -1. 0 Intent is to provide a more balanced measure of development

OTHER MEASUREMENTS The Gini coefficient Measures the difference between the rich and the poor population groups on a scale of 0 -100 The Gender-Related Development Index Compares men and women much of the way that HDI is calculated

ROSTOW’S STAGES OF GROWTH Walter Rostow 5 stages of growth Traditional society: focused on primary production Preconditions for takeoff: leadership invests in infrastructure more technology is used Takeoff: begins to shift focus to industry Drive to maturity: technology advances, industry grows rapidly, workers become skilled Age of mass consumption: highly specialized production like cars or energy, technology knowledge high, education levels are high, agriculture mechanized

DEPENDENCY THEORY Most LDCs are dependent on MDCs to provide employment Prebisch Thesis Detailed the dependency of the Third World economy on First World loans and investments to pay for their infrastructure Claimed that LDCs could never break the bonds of their dependence because they could never manufacture for themselves or make any extra money

BREAKING THE CYCLE OF DEPENDENCY LDC programs that try to break free from MDC control Internalization of economic capital Requires companies to deposit profits from the factories in LDC banks and reinvest locally Import substitution Instead of buying First World produced consumer-products, they would buy from LDC factories Nationalization of natural resource-based industries Instead of allowing foreign companies to own resources, local governments would Profit-sharing agreements Foreign companies agree to share part of the profits they get with the governments Technology development programs Use limited funds to invest in technological advances and worker training

OTHER DEVELOPMENT APPROACHES Tourism Brings in a good deal of money from foreigners Ecotourism has become very popular through rain forests, reefs, and savannahs Free trade agreements Improve international trade and boost economies Free-market reforms Allowing people to trade freely from a country, abolishing Communism

THEORY OF LOCATION Alfred Weber Determines the optimal factory locations Bulk-reducing manufacturing: close to the inputs (limestone, coal, and water) Bulk-gaining manufacturing: close to the consumers (cars)
FORDIST VS. POST-FORDIST PRODUCTION Fordist Relied on a single company owning all the aspects of production Post-Fordist Companies now dependent on many different manufacturers to build parts of cars

RETAIL LOCATION THEORY Threshold Minimum number of people required to support a business Range Maximum distance people are willing to travel to gain access to the service Spatial margin of profitability Area where local demand for the service maximizes profit
AGGLOMERATION AND DEGLOMERATION Agglomeration Concentration of human activities in a cluster or around a central place Agglomeration economies Find firms with related or similar products together and share in the advantages of skilled labor, specialized suppliers, and service providers Deglomeration When a location is overloaded with similar firms or services

SUBURBAN SPRAWL Sprawl Expansion of housing, transportation, and commercial development to undeveloped land on the urban periphery Anti-growth movements Push land laws to limit the growth in suburban areas Growth boundaries Set minimums for lot sizes of homes so they do not become packed in by the growth

EDGE CITIES CBDs that have grown in the suburbs

CITY TYPES Colonial cities Originated in colonial trade retained their European-style archetecture Fall-line cities Ports that were upstream to the point where ocan ships could no longer navigate (break-in-bulk point): Boston, Albany, Baltamore Medieval Cities Urban centers that date back to the Renaissance: Rome, Paris, London, Kyoto, Beijing Gateway cities Places where immigrants have made their way into a country: New York, Miami, Toronto Entrepot Port city in which goods are shipped in at one price and shipped out for another Megacities More than 10 million people: Tokyo, New York, Mexico City Megalopolis Urbanized area of two or more cities that merge together: Northeastern US

CITY TYPES (CNT’D) World City Global center of finance First-order: New York, London, Tokyo Second-order: Los Angeles, Washington DC, Chicago, Frankfort, Paris Third-order: San Francisco, Miami, Sydney Primate city Largest city is more than twice the size of the second largest

RANK SIZE RULE The nth largest city is 1/n the size of the country’s largest city

UBRAN SOCIETY Segregation Ethnic neighborhoods have sprung up: Chinatown Redlining Designing homes so that African Americans cannot buy in that area Restrictive covenants Putting “whites only” clauses in home agreements Racial steering Real estate agents encouraging African Americans to only buy in certain areas

GENTRIFICATION The economic reinvestment in existing real estate Historical renovation Has had the negative effect of driving lower-class citizens out because of higher prices

URBAN SUSTAINABILITY Many problems to address Balancing taxes and maintaining municipal services Expensive schools Traffic congestion Pollution Mass transit can fix some of these problems New downtown housing Mixed-use buildings Both hosing and commercial space (New Urbanization)
ce9a42aab855c239a231fc515bf069c0.ppt