75fb883f97bc248afbd325430f4aa5e3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY CH. 6 REVIEW Migration
AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY CH. 6 REVIEW Migration
 UNIT 2 ESSENTIAL Q • What does Population tell us about the world, its countries, & their relationships to one another?
UNIT 2 ESSENTIAL Q • What does Population tell us about the world, its countries, & their relationships to one another?
 CH. 6 Guiding Q • What are the factors that stimulate migration, & are all factors / migrations equal?
CH. 6 Guiding Q • What are the factors that stimulate migration, & are all factors / migrations equal?
 Migration? ? ? • Why do people move? ? ? – Emigration – leaving from – Immigration – going to
Migration? ? ? • Why do people move? ? ? – Emigration – leaving from – Immigration – going to
 Factors that Stimulate Migration (Why Migrate? ? ? ) ► Conflict (Civil War) § 1990 s Yugoslavia: drove 3 million from homes § Rwanda: 2 million fled to Zaire & Tanzania § Sudan (Darfur) Genocide 2004 ► Economic Conditions § Poverty § Chance for work & better life ► Political Strife § Oppressive regimes (Cuba, Zimbabwe, Uganda, Myanmar, North Korea)
Factors that Stimulate Migration (Why Migrate? ? ? ) ► Conflict (Civil War) § 1990 s Yugoslavia: drove 3 million from homes § Rwanda: 2 million fled to Zaire & Tanzania § Sudan (Darfur) Genocide 2004 ► Economic Conditions § Poverty § Chance for work & better life ► Political Strife § Oppressive regimes (Cuba, Zimbabwe, Uganda, Myanmar, North Korea)
 Factors (con. ) ► Cultural Circumstances § Jews to Israel ► Environmental Change § Irish Potato Famine § CA earthquake = emigrations § Carrying Capacity (matrix scene) ► Technological Advances § Easier to travel & move § Info availability ► USA is most mobile (moving) country in the world
Factors (con. ) ► Cultural Circumstances § Jews to Israel ► Environmental Change § Irish Potato Famine § CA earthquake = emigrations § Carrying Capacity (matrix scene) ► Technological Advances § Easier to travel & move § Info availability ► USA is most mobile (moving) country in the world
 Voluntary vs. Forced Migrations • Voluntary Migration • Forced Migration • COUNTER MIGRATION: Gov’t sending back caught Illegal immigrants
Voluntary vs. Forced Migrations • Voluntary Migration • Forced Migration • COUNTER MIGRATION: Gov’t sending back caught Illegal immigrants
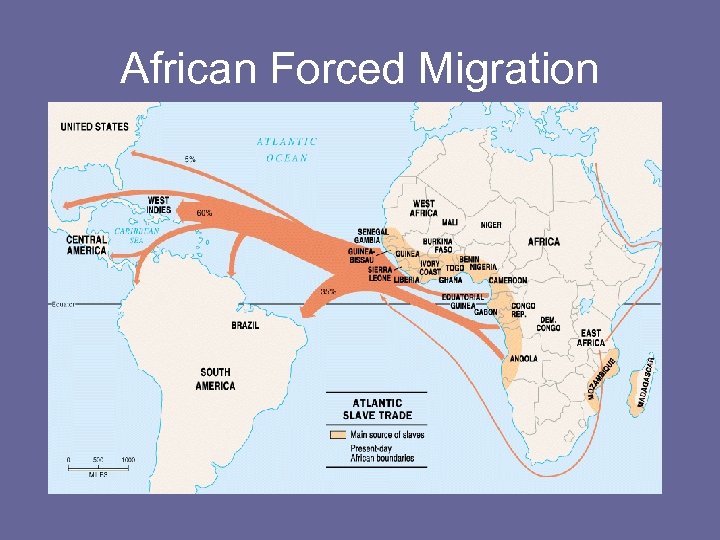 African Forced Migration
African Forced Migration
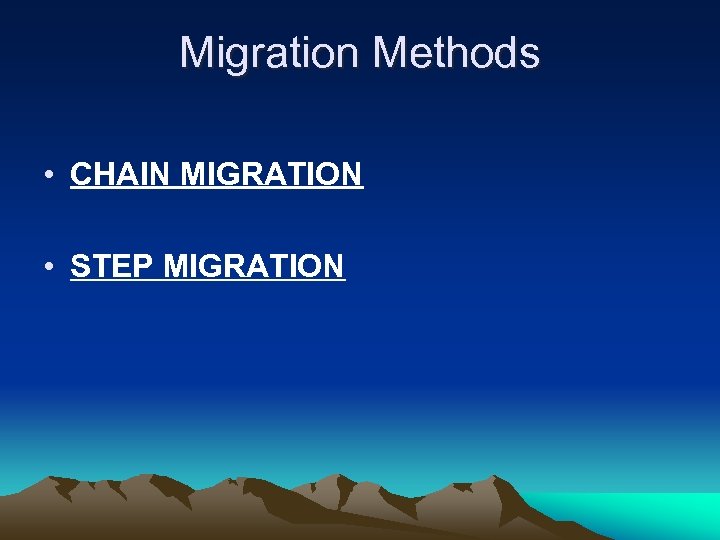 Migration Methods • CHAIN MIGRATION • STEP MIGRATION
Migration Methods • CHAIN MIGRATION • STEP MIGRATION
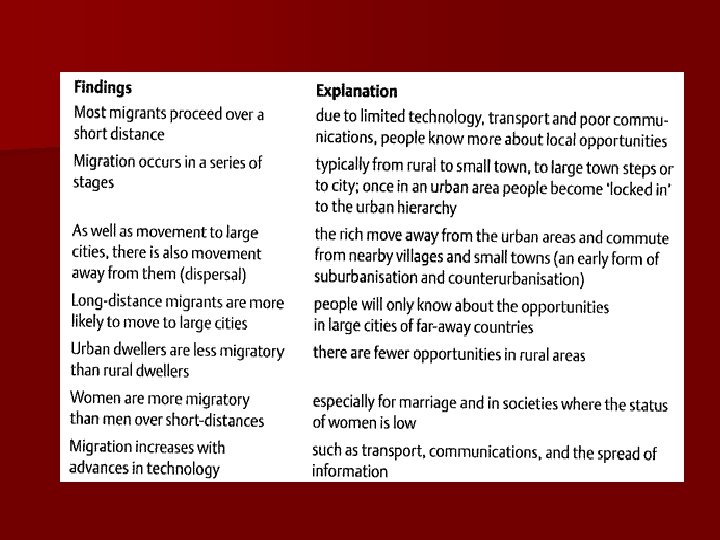
 Ernst Ravenstein British Demographer n 5 Laws of Migration – (look up Note Sheet & (Book Notes)) n Gravity Model: A measure (mathematical prediction) of the interaction of places – # of migrants declines as distance they must travel increases
Ernst Ravenstein British Demographer n 5 Laws of Migration – (look up Note Sheet & (Book Notes)) n Gravity Model: A measure (mathematical prediction) of the interaction of places – # of migrants declines as distance they must travel increases

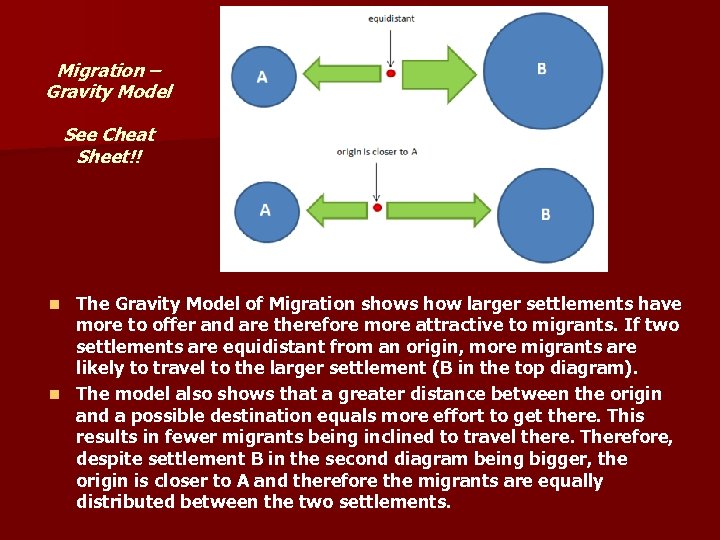 Migration – Gravity Model See Cheat Sheet!! The Gravity Model of Migration shows how larger settlements have more to offer and are therefore more attractive to migrants. If two settlements are equidistant from an origin, more migrants are likely to travel to the larger settlement (B in the top diagram). n The model also shows that a greater distance between the origin and a possible destination equals more effort to get there. This results in fewer migrants being inclined to travel there. Therefore, despite settlement B in the second diagram being bigger, the origin is closer to A and therefore the migrants are equally distributed between the two settlements. n
Migration – Gravity Model See Cheat Sheet!! The Gravity Model of Migration shows how larger settlements have more to offer and are therefore more attractive to migrants. If two settlements are equidistant from an origin, more migrants are likely to travel to the larger settlement (B in the top diagram). n The model also shows that a greater distance between the origin and a possible destination equals more effort to get there. This results in fewer migrants being inclined to travel there. Therefore, despite settlement B in the second diagram being bigger, the origin is closer to A and therefore the migrants are equally distributed between the two settlements. n
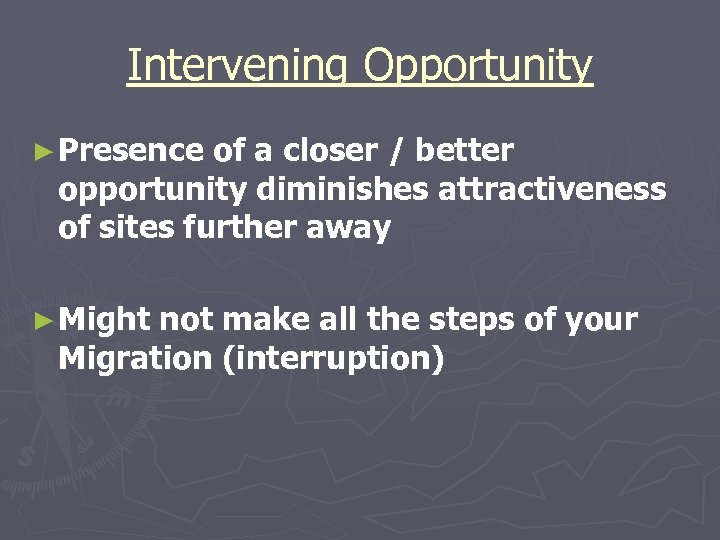 Intervening Opportunity ► Presence of a closer / better opportunity diminishes attractiveness of sites further away ► Might not make all the steps of your Migration (interruption)
Intervening Opportunity ► Presence of a closer / better opportunity diminishes attractiveness of sites further away ► Might not make all the steps of your Migration (interruption)
 Location vs. Distance n n Absolute & Relative Location (remember? !) Absolute Distance Relative Distance Why is People’s perception of distance often distorted? ? ?
Location vs. Distance n n Absolute & Relative Location (remember? !) Absolute Distance Relative Distance Why is People’s perception of distance often distorted? ? ?
 n n Distance Decay ? ? ? As distance increases, your perception of a place declines n Human activity declines as distance from the source increases (gravity model!!!)
n n Distance Decay ? ? ? As distance increases, your perception of a place declines n Human activity declines as distance from the source increases (gravity model!!!)
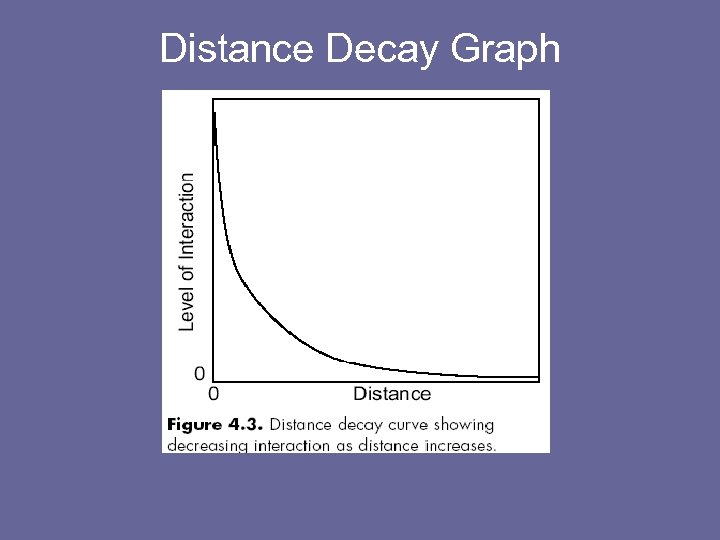 Distance Decay Graph
Distance Decay Graph
 The Dearborn Garden Homes 27 th and State St.
The Dearborn Garden Homes 27 th and State St.



 Types of Human Movement n Activity (Action) Space – ? ? ? n Cyclic movement – ? ? ? n Seasonal Movement - ? ? ? n Nomadism - ? ? ?
Types of Human Movement n Activity (Action) Space – ? ? ? n Cyclic movement – ? ? ? n Seasonal Movement - ? ? ? n Nomadism - ? ? ?
 Types of Human Movement n Periodic Movement – ? ? ? n Transhumance – ? ? ?
Types of Human Movement n Periodic Movement – ? ? ? n Transhumance – ? ? ?
 DISLOCATION • Sudden and Forced Migrations yield… • Refugees: ? ? ? • Dislocated involuntarily from original place of settlement & unable to return • Difference between Refugee & Migrant?
DISLOCATION • Sudden and Forced Migrations yield… • Refugees: ? ? ? • Dislocated involuntarily from original place of settlement & unable to return • Difference between Refugee & Migrant?
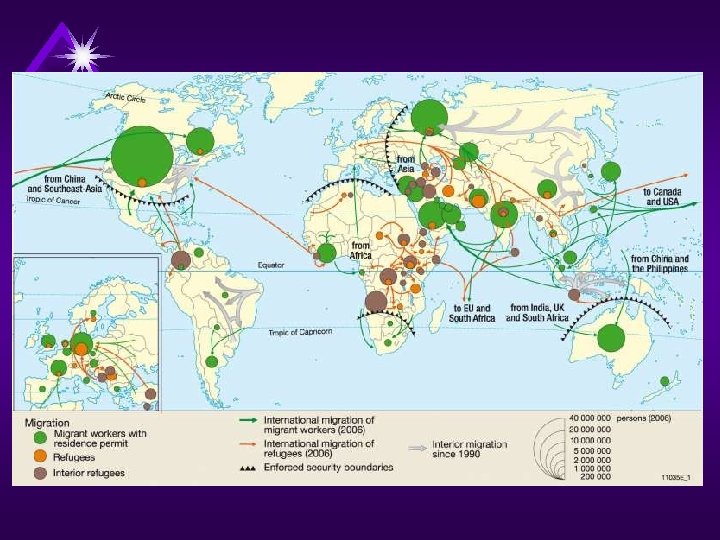
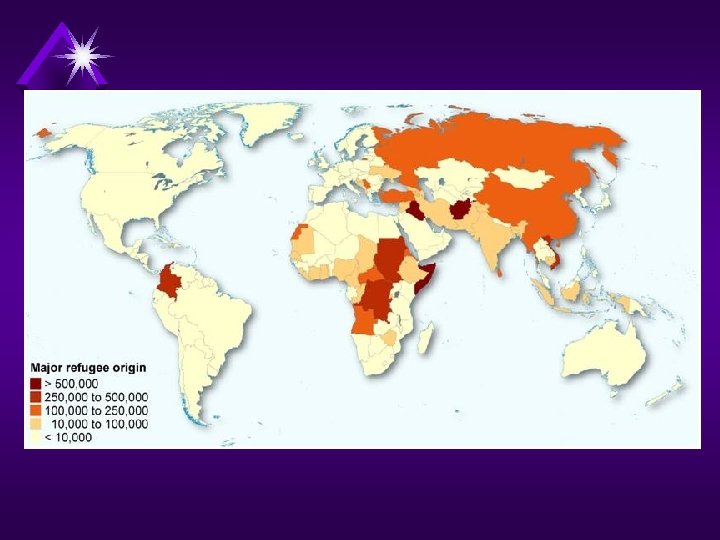
 Regions of Dislocation • Subsaharan Africa (Sudan, Rwanda, Congo) • Middle East (Israel & Palestine, Iraq, SYRIA) • Europe (Former Yugoslavia) • South Asia (Sri Lanka, Afghanistan) • South East Asia (Cambodia 1975, Myanmar (Burma)
Regions of Dislocation • Subsaharan Africa (Sudan, Rwanda, Congo) • Middle East (Israel & Palestine, Iraq, SYRIA) • Europe (Former Yugoslavia) • South Asia (Sri Lanka, Afghanistan) • South East Asia (Cambodia 1975, Myanmar (Burma)
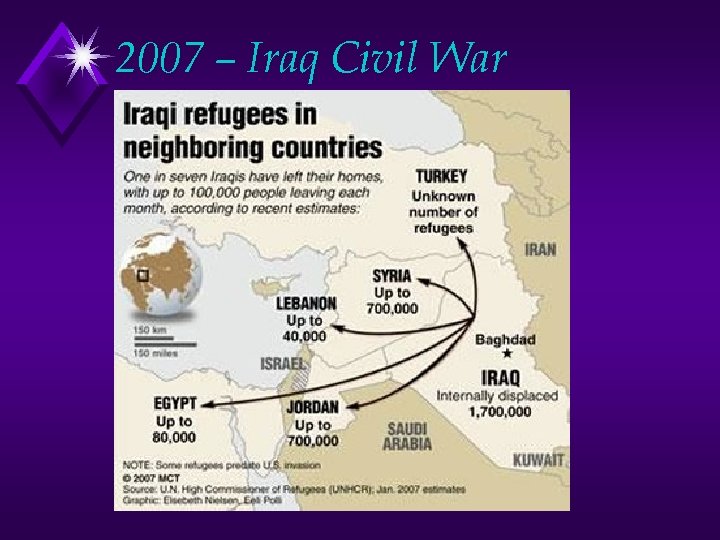 2007 – Iraq Civil War
2007 – Iraq Civil War
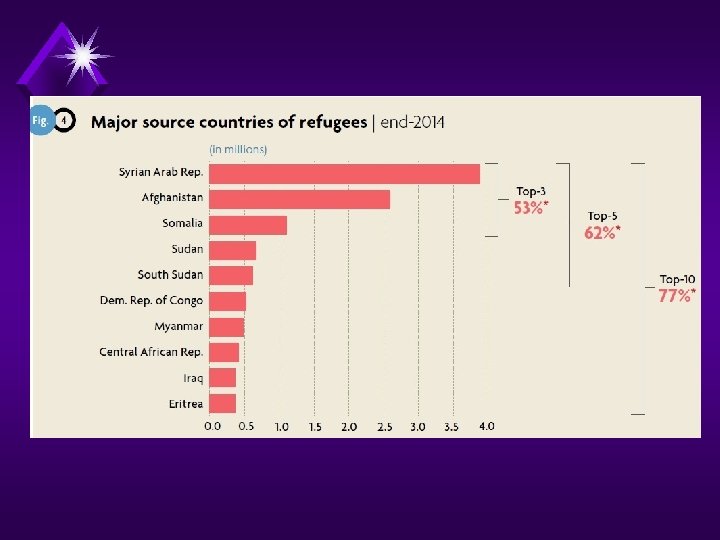
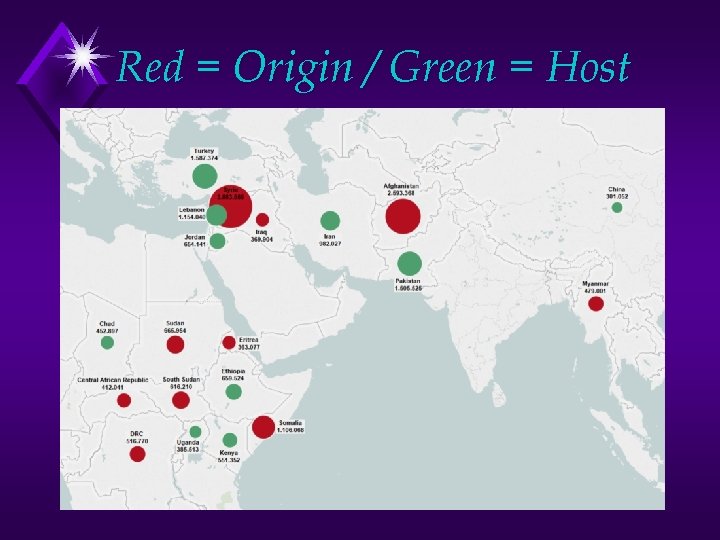 Red = Origin / Green = Host
Red = Origin / Green = Host
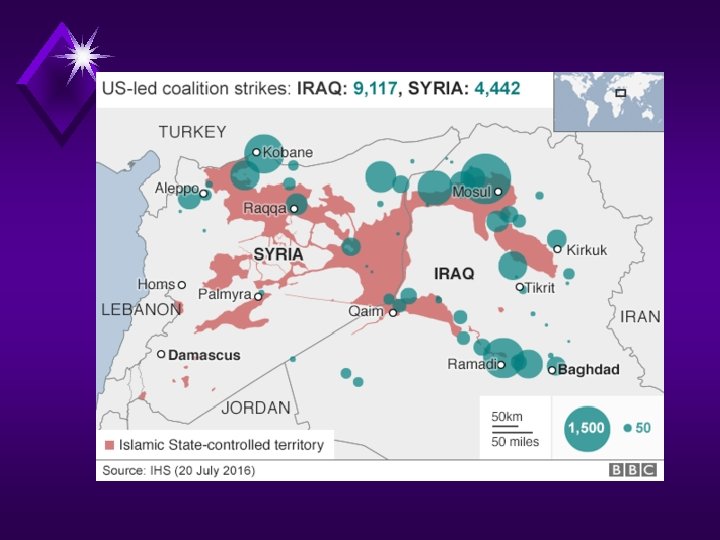
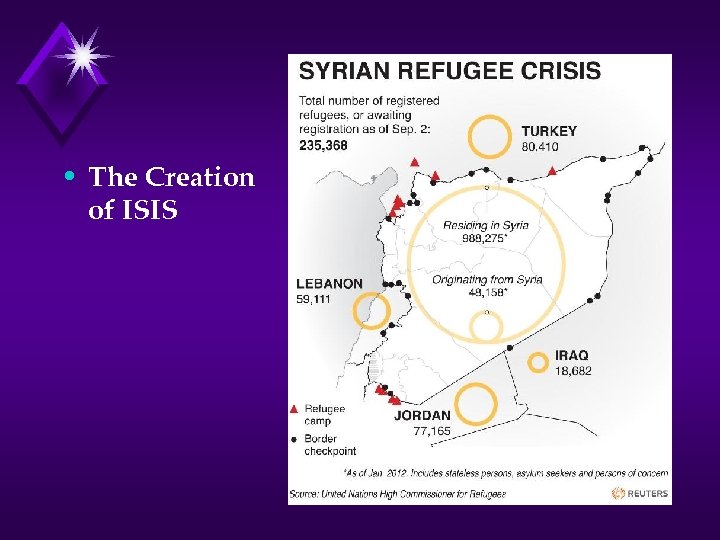 • The Creation of ISIS
• The Creation of ISIS
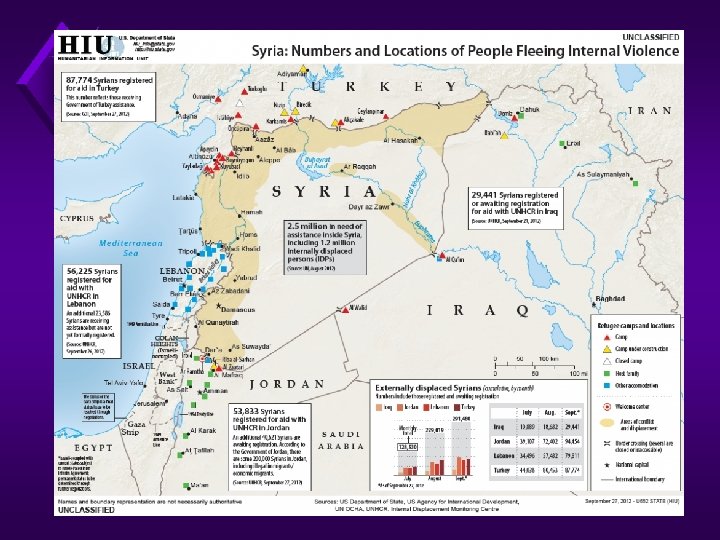
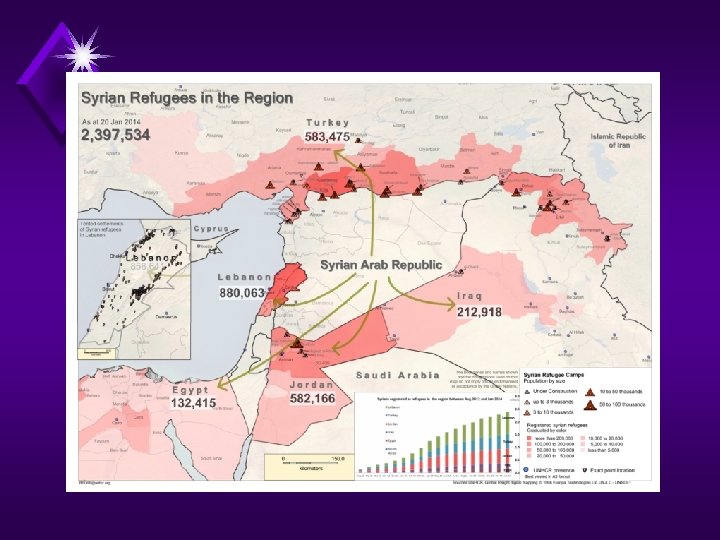
 Aerial view shows the Al-Zaatari (Syria > Jordan) refugee camp
Aerial view shows the Al-Zaatari (Syria > Jordan) refugee camp
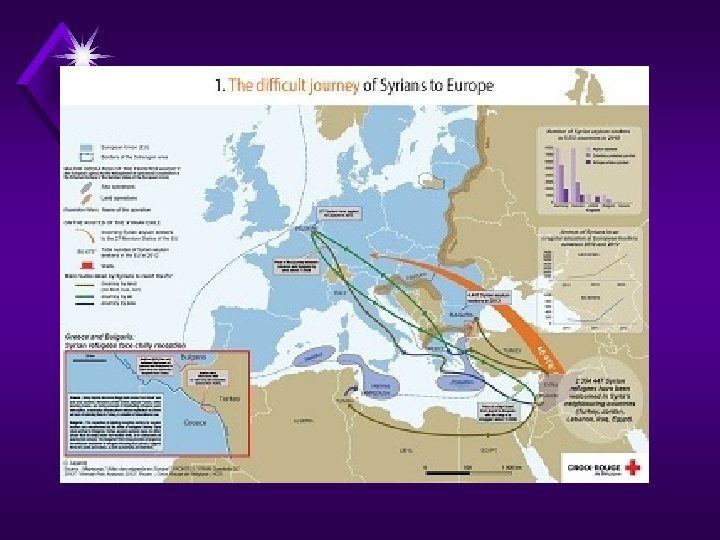
 Refugee / Migrant Crisis
Refugee / Migrant Crisis
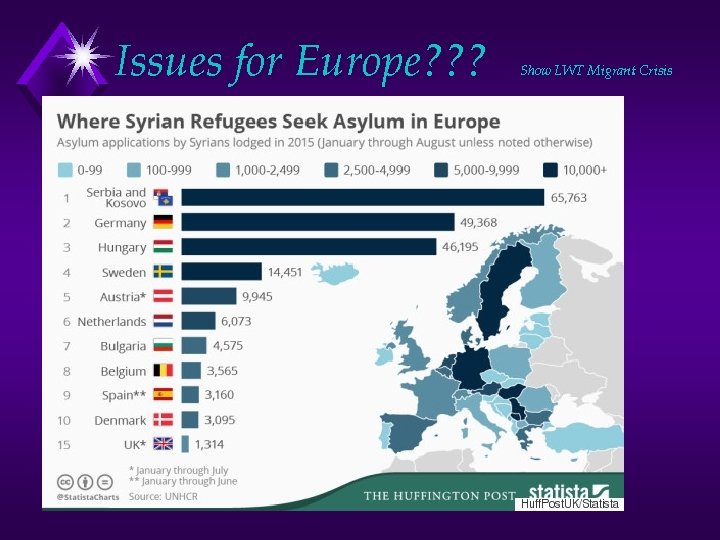 Issues for Europe? ? ? Show LWT Migrant Crisis
Issues for Europe? ? ? Show LWT Migrant Crisis
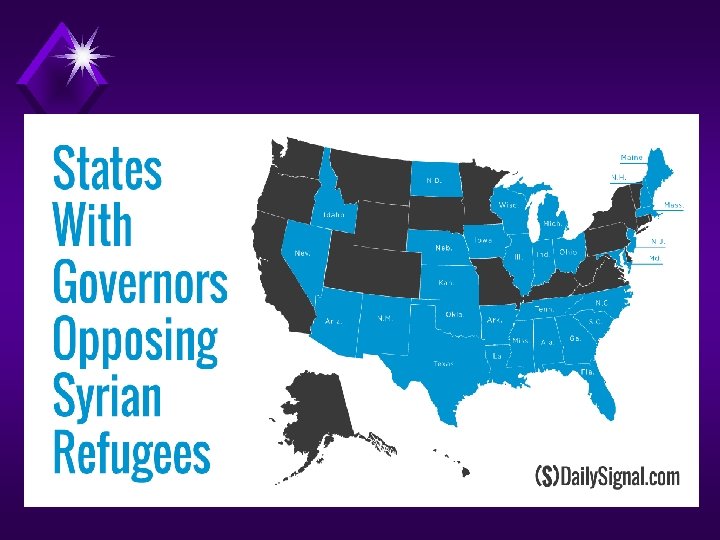
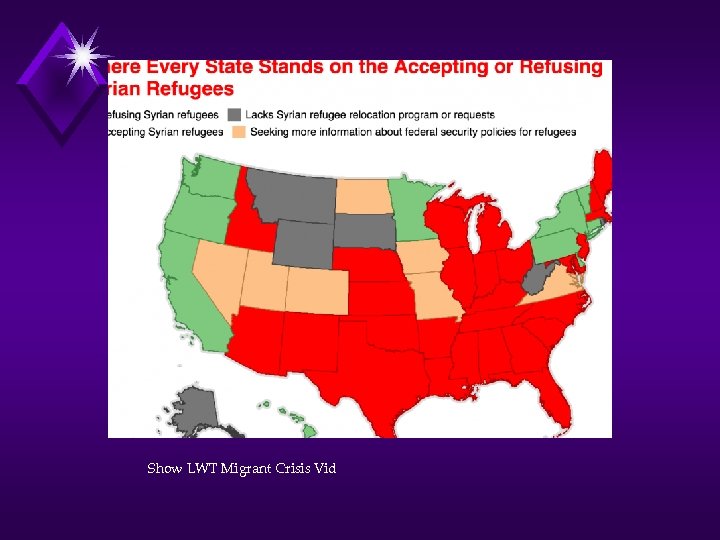 Show LWT Migrant Crisis Vid
Show LWT Migrant Crisis Vid
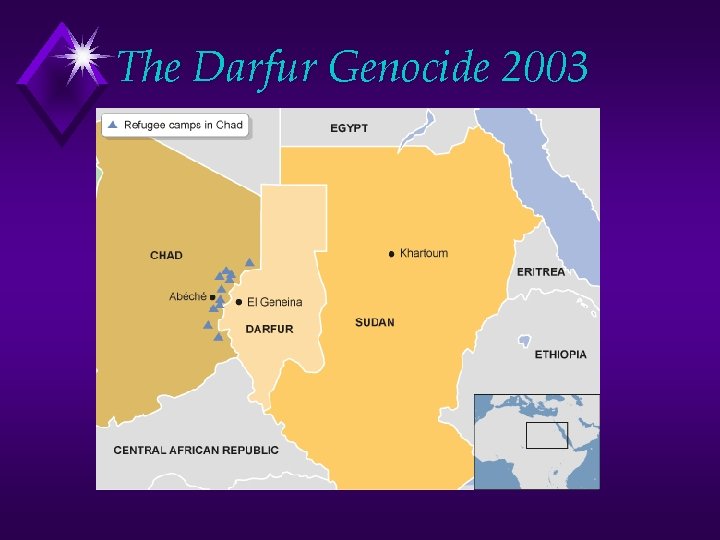 The Darfur Genocide 2003
The Darfur Genocide 2003
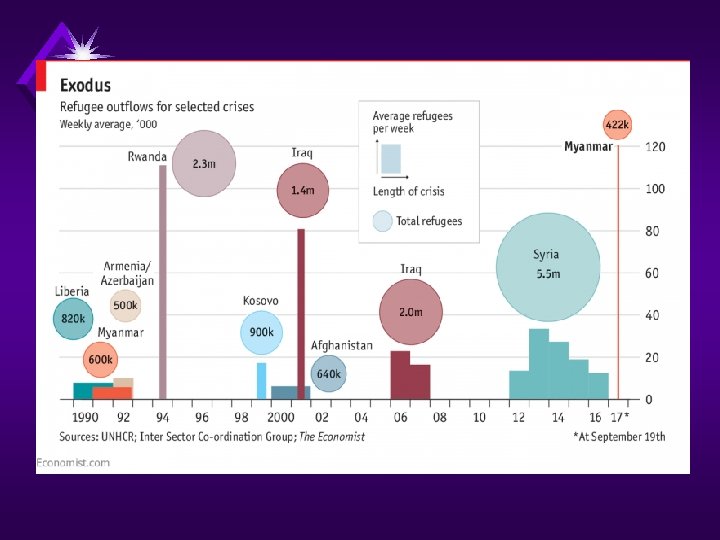
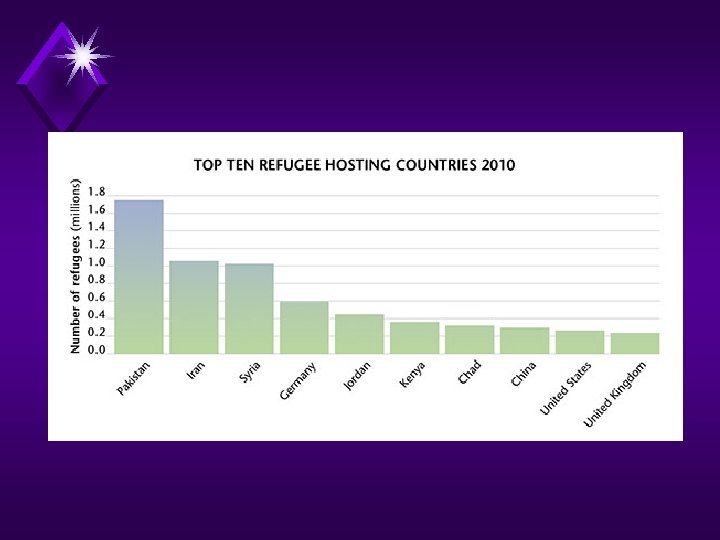
 • UN Refugee estimates: • 1980 – 8 million • 2000 – 18 million • 2015 – 50 million!!! • Why Difficult to know exact totals? ?
• UN Refugee estimates: • 1980 – 8 million • 2000 – 18 million • 2015 – 50 million!!! • Why Difficult to know exact totals? ?
 Types of Refugees • INTER-national Refugee: ? ? ? • (external) crossed international borders • EX? ? ? • INTRA-national Refugee: ? ? ? • (internal) remained in original country • EX? ? ?
Types of Refugees • INTER-national Refugee: ? ? ? • (external) crossed international borders • EX? ? ? • INTRA-national Refugee: ? ? ? • (internal) remained in original country • EX? ? ?
 Refugee Status • Temporary Refugee • Permanent Refugee
Refugee Status • Temporary Refugee • Permanent Refugee
 How to Tell if a Refugee (& not a Migrant) • 1. Move only with what they can carry on their backs • 2. Make 1 st step on foot (bicycle, wagon) • 3. Move without official documents
How to Tell if a Refugee (& not a Migrant) • 1. Move only with what they can carry on their backs • 2. Make 1 st step on foot (bicycle, wagon) • 3. Move without official documents
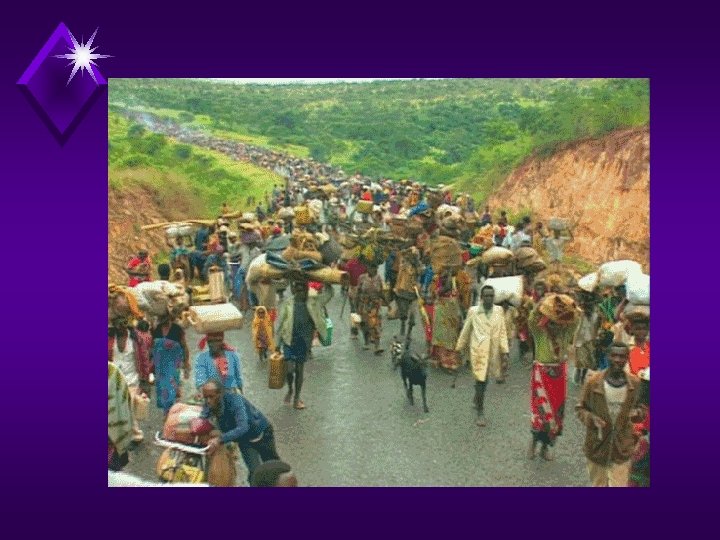

 Rwandan Refugee Camp in Zaire
Rwandan Refugee Camp in Zaire
 CH. 6 Guiding Q • What are the factors that stimulate migration, & are all factors / migrations equal?
CH. 6 Guiding Q • What are the factors that stimulate migration, & are all factors / migrations equal?


