b2d85d02322708706eae97a12fa4994d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 7

AP Economics September 6, 2016 1. Review HW: Comparative Advantage 2. Lesson 1 -4: Demand 3. HW: Activity 1 -4 (ONLY PARTS A AND B) and Comparative Advantage Practice 4. Current Event Due Friday

Demand • Demand: Amount of a good or service consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price. • Data is displayed as a Schedule or Curve • Law of Demand: All other factors equal, as the price of a commodity increases, the quantity demanded for the commodity will decrease, and vice versa. • P↑ Qd↓ • P↓ Qd↑
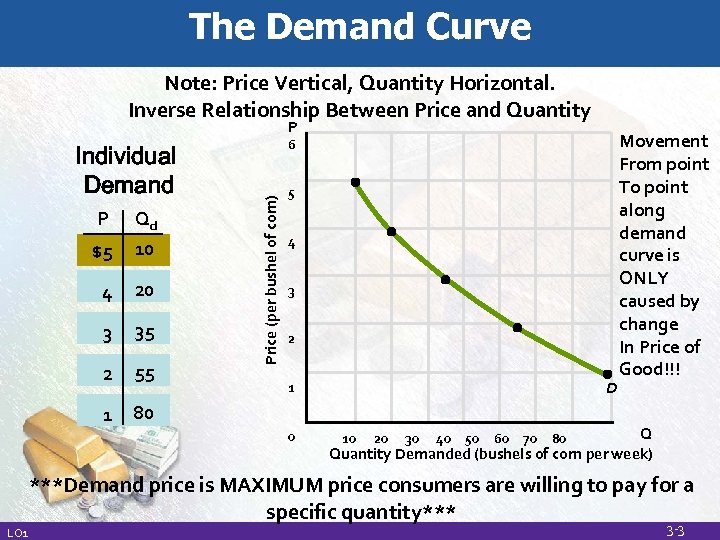
The Demand Curve Note: Price Vertical, Quantity Horizontal. Inverse Relationship Between Price and Quantity P P $5 Qd 10 4 20 3 35 2 55 1 Price (per bushel of corn) Individual Demand 6 5 80 4 3 2 D 1 0 Movement From point To point along demand curve is ONLY caused by change In Price of Good!!! Q Quantity Demanded (bushels of corn per week) 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 ***Demand price is MAXIMUM price consumers are willing to pay for a specific quantity*** LO 1 3 -3

Determinants of Demand (Demand Curve Shifters) If the entire curve shifts right (INCREASE IN DEMAND), people are willing and able to buy more AT EACH PRICE! If the entire curve shifts left (DECREASE IN DEMAND), people are willing and able to buy less AT EACH PRICE! What are the Demand Curve Shifters (What if “all-other-thingsequal changes? ”) 1. Change in Consumer Tastes 2. Change in Number of Buyers 3. Change in Consumer Incomes 4. Change in Prices of Complementary and/or Substitute Goods 5. Change in Consumer Expectations Complementary Goods: Goods used in conjunction (hot dogs and hot dog buns) Substitute Goods: Similar Goods that can be substituted for (Coke and Pepsi)

AP Economics September 10, 2015 1. Finish Demand: Consumer Surplus 2. HW: Finish Activities 1 -4 and 1 -5 3. Current Event Due Tomorrow

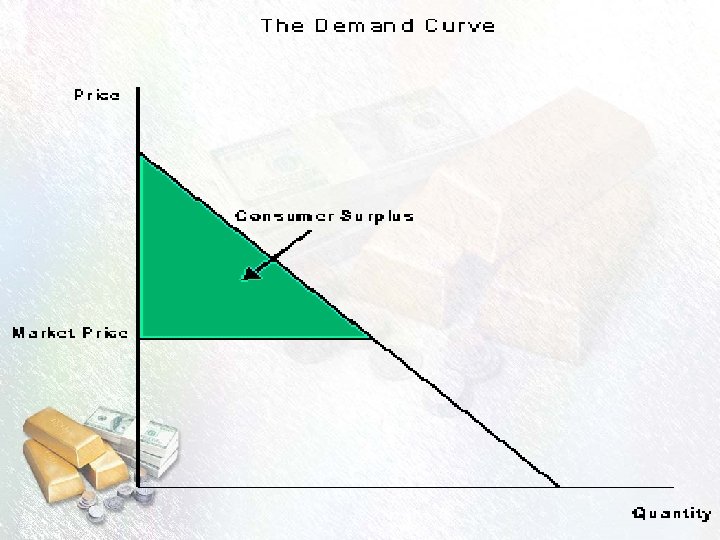
Consumer Surplus • The Demand Price is the maximum price consumers are willing and able to pay. • Of course consumers would be willing to pay lower than this maximum price! • Consumer Surplus: The difference between the amount a person is willing and able to pay for a unit of a commodity and the actual price paid for it.
b2d85d02322708706eae97a12fa4994d.ppt