Aortic Valve Disease Normal Aortic Valve









- Размер: 26.3 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 68
Описание презентации Aortic Valve Disease Normal Aortic Valve по слайдам
 Aortic Valve Disease
Aortic Valve Disease
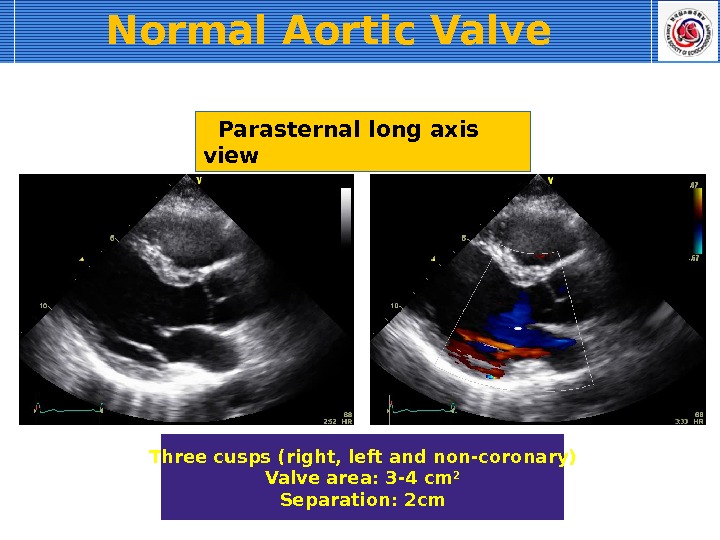
 Normal Aortic Valve Parasternal long axis view Three cusps (right, left and non-coronary) Valve area: 3 -4 cm 2 Separation: 2 cm
Normal Aortic Valve Parasternal long axis view Three cusps (right, left and non-coronary) Valve area: 3 -4 cm 2 Separation: 2 cm
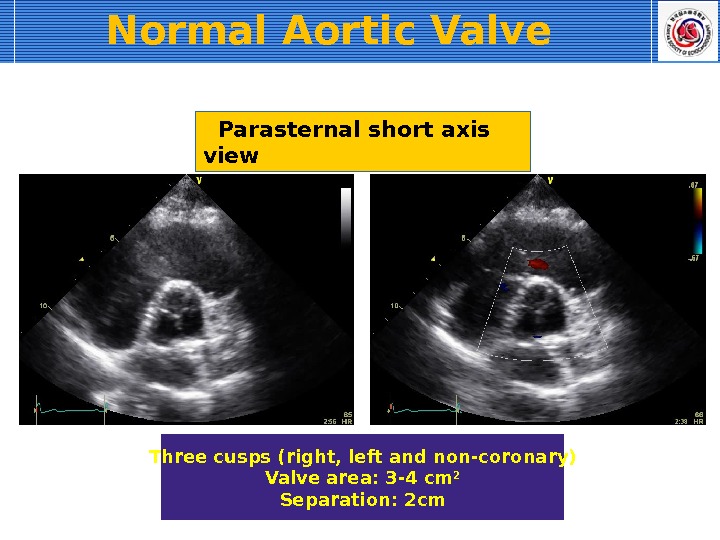
 Parasternal short axis view Three cusps (right, left and non-coronary) Valve area: 3 -4 cm 2 Separation: 2 cm. Normal Aortic Valve
Parasternal short axis view Three cusps (right, left and non-coronary) Valve area: 3 -4 cm 2 Separation: 2 cm. Normal Aortic Valve
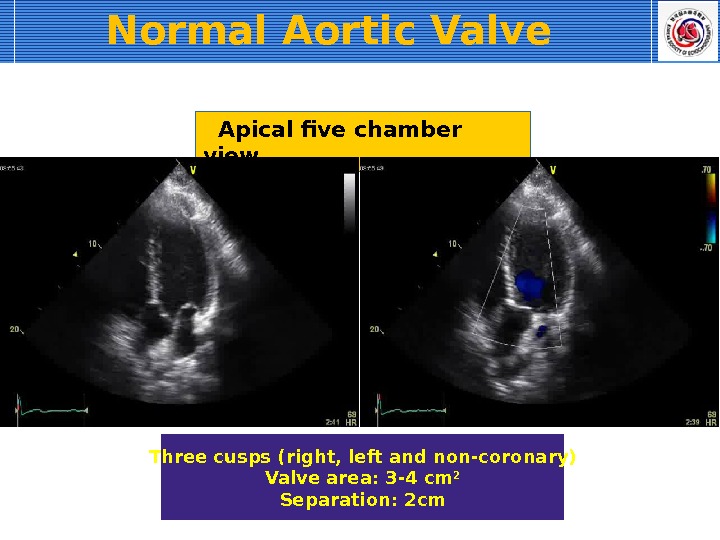
 Apical five chamber view Three cusps (right, left and non-coronary) Valve area: 3 -4 cm 2 Separation: 2 cm. Normal Aortic Valve
Apical five chamber view Three cusps (right, left and non-coronary) Valve area: 3 -4 cm 2 Separation: 2 cm. Normal Aortic Valve
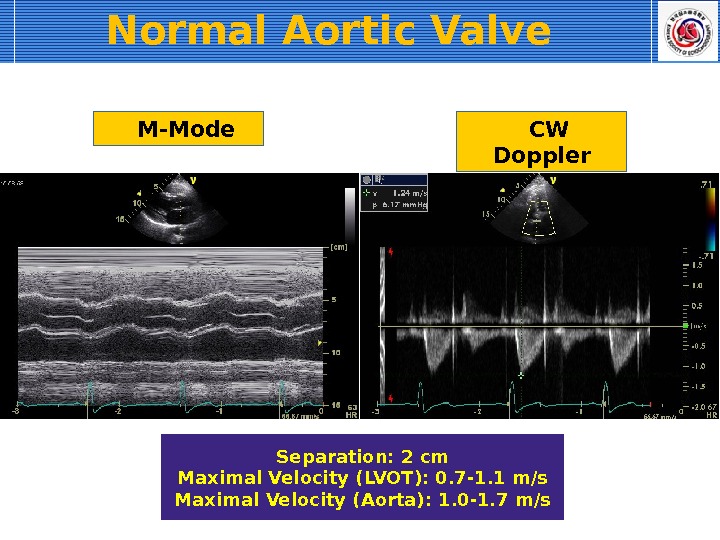
 M-Mode Separation: 2 cm Maximal Velocity (LVOT): 0. 7 -1. 1 m/s Maximal Velocity (Aorta): 1. 0 -1. 7 m/s CW Doppler. Normal Aortic Valve
M-Mode Separation: 2 cm Maximal Velocity (LVOT): 0. 7 -1. 1 m/s Maximal Velocity (Aorta): 1. 0 -1. 7 m/s CW Doppler. Normal Aortic Valve
 Congenital Anomaly Unicuspid valve Bicuspid valve Quadricuspid valve
Congenital Anomaly Unicuspid valve Bicuspid valve Quadricuspid valve
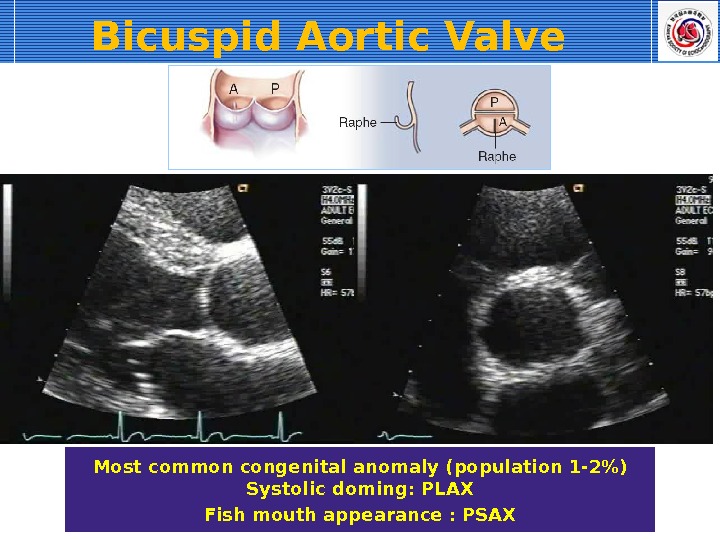
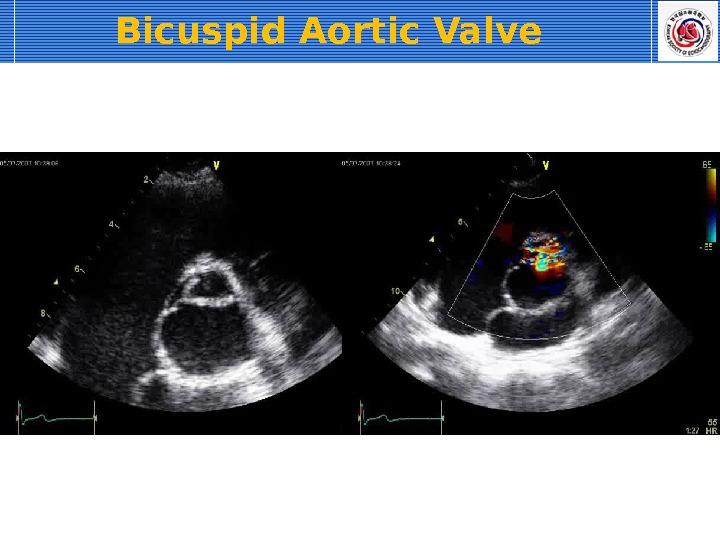
 Bicuspid Aortic Valve Most common congenital anomaly (population 1 -2%) Systolic doming: PLAX Fish mouth appearance : PSAX
Bicuspid Aortic Valve Most common congenital anomaly (population 1 -2%) Systolic doming: PLAX Fish mouth appearance : PSAX
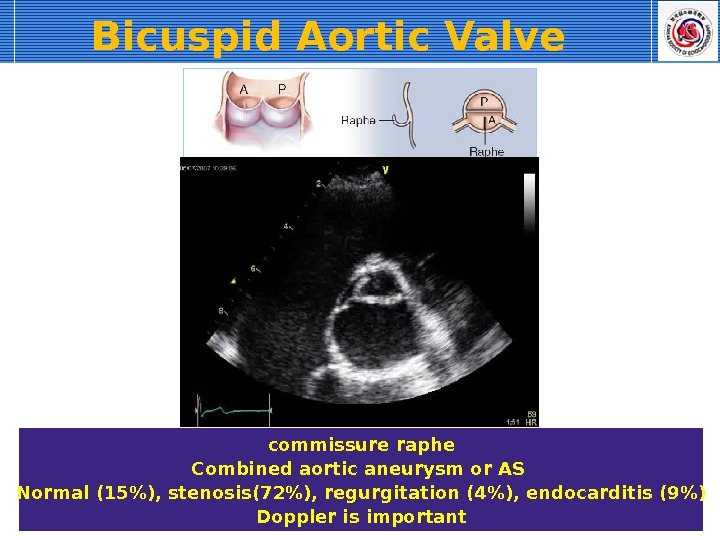
 commissure raphe Combined aortic aneurysm or AS Normal (15%), stenosis(72%), regurgitation (4%), endocarditis (9%) Doppler is important. Bicuspid Aortic Valve
commissure raphe Combined aortic aneurysm or AS Normal (15%), stenosis(72%), regurgitation (4%), endocarditis (9%) Doppler is important. Bicuspid Aortic Valve
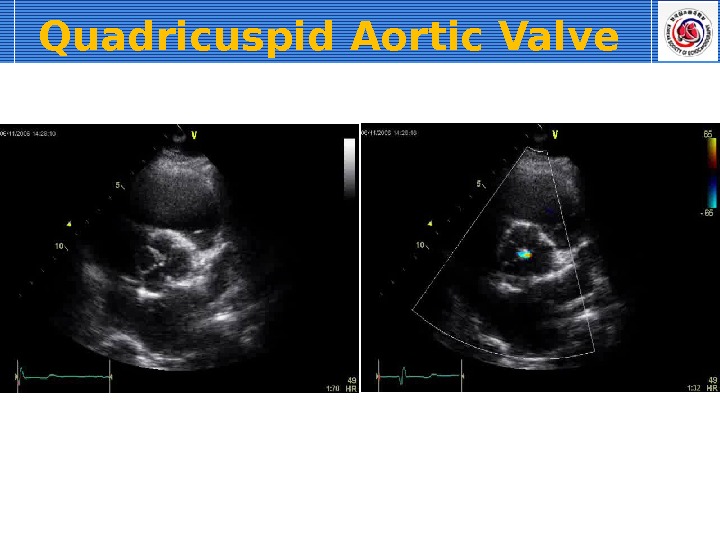
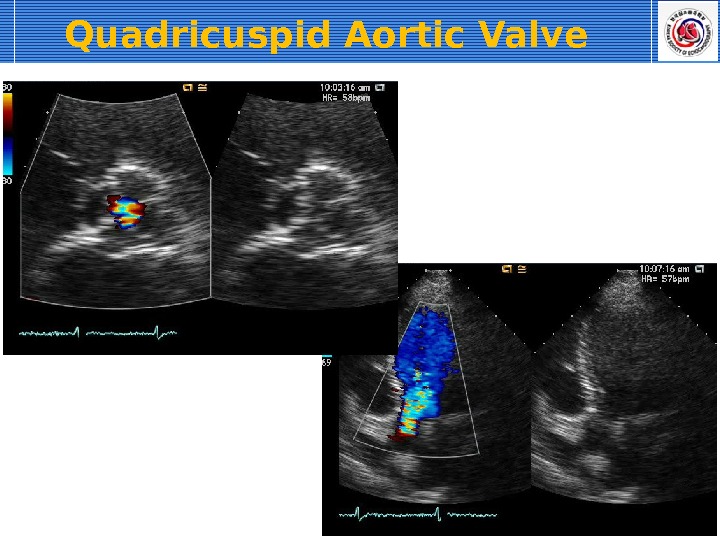
 Quadricuspid Aortic Valve
Quadricuspid Aortic Valve
 Aortic Stenosis
Aortic Stenosis
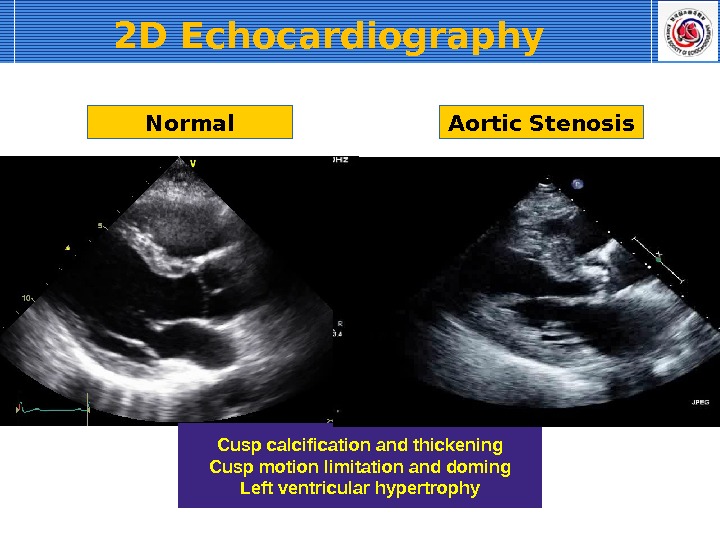
 2 D Echocardiography Normal Aortic Stenosis Cusp calcification and thickening Cusp motion limitation and doming Left ventricular hypertrophy
2 D Echocardiography Normal Aortic Stenosis Cusp calcification and thickening Cusp motion limitation and doming Left ventricular hypertrophy
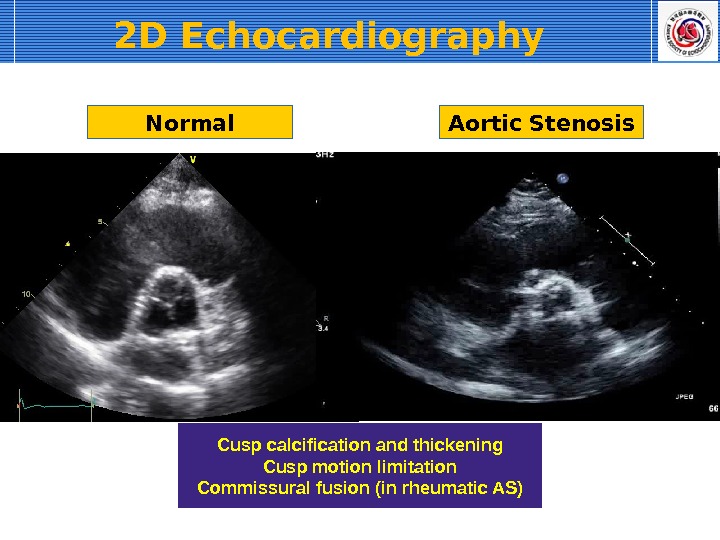
 Normal Aortic Stenosis Cusp calcification and thickening Cusp motion limitation Commissural fusion (in rheumatic AS)2 D Echocardiography
Normal Aortic Stenosis Cusp calcification and thickening Cusp motion limitation Commissural fusion (in rheumatic AS)2 D Echocardiography
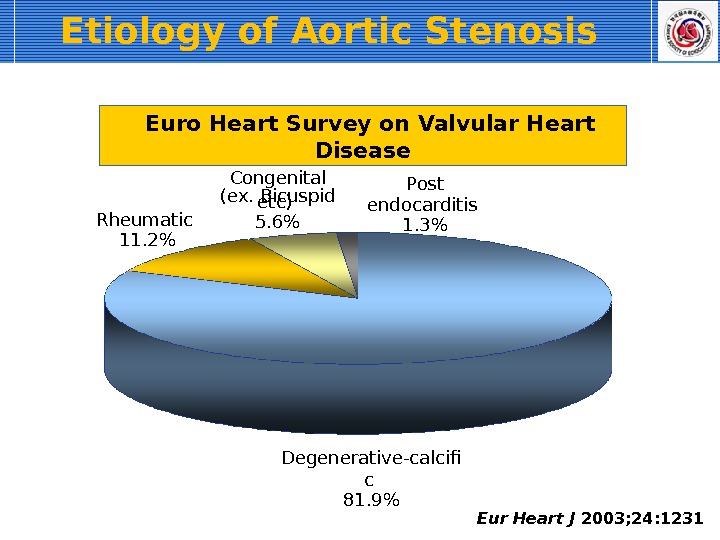
 Etiology of Aortic Stenosis Eur Heart J 2003; 24: 1231 Degenerative-calcif c 81. 9%Rheumatic 11. 2% Congenital (ex. Bicuspid etc) 5. 6% Post endocarditis 1. 3% Euro Heart Survey on Valvular Heart Disease
Etiology of Aortic Stenosis Eur Heart J 2003; 24: 1231 Degenerative-calcif c 81. 9%Rheumatic 11. 2% Congenital (ex. Bicuspid etc) 5. 6% Post endocarditis 1. 3% Euro Heart Survey on Valvular Heart Disease
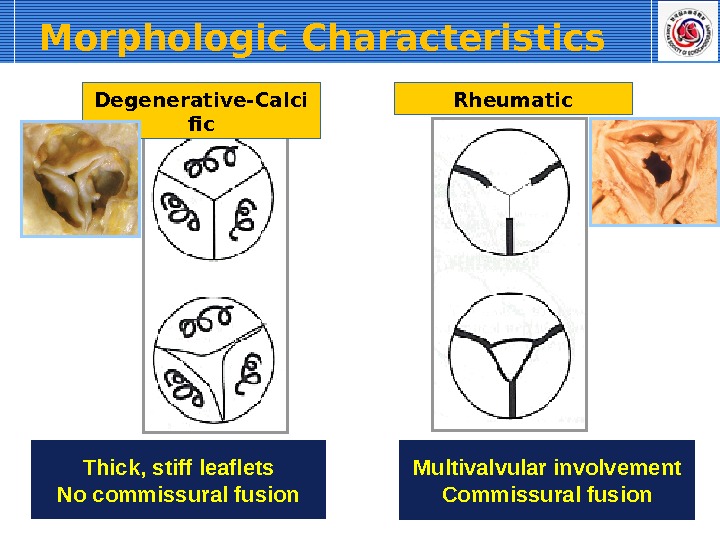
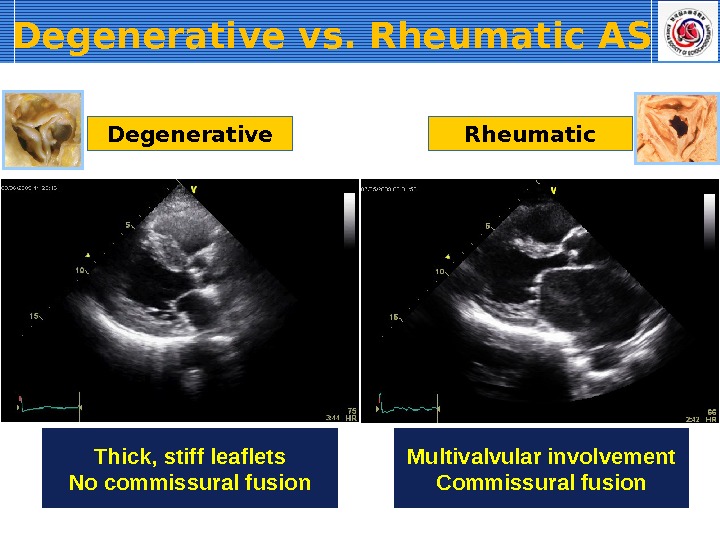
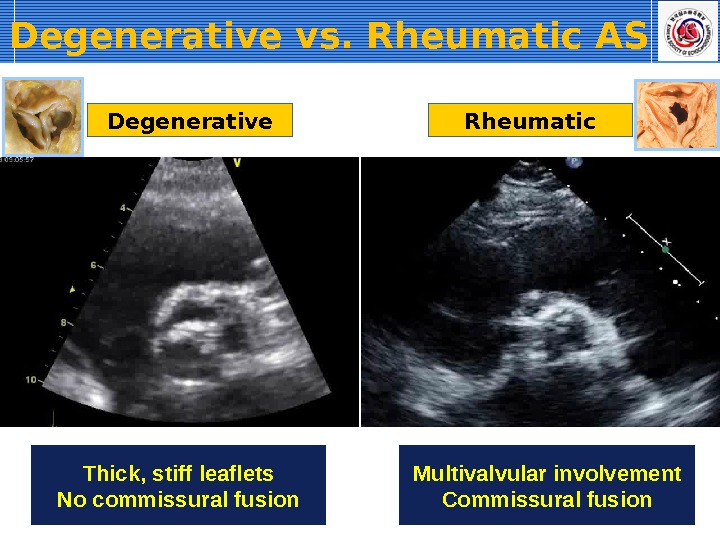
 Morphologic Characteristics Degenerative-Calci fic Rheumatic Thick, stiff leaflets No commissural fusion Multivalvular involvement Commissural fusion
Morphologic Characteristics Degenerative-Calci fic Rheumatic Thick, stiff leaflets No commissural fusion Multivalvular involvement Commissural fusion
 Degenerative vs. Rheumatic AS Thick, stiff leaflets No commissural fusion Degenerative Rheumatic Multivalvular involvement Commissural fusion
Degenerative vs. Rheumatic AS Thick, stiff leaflets No commissural fusion Degenerative Rheumatic Multivalvular involvement Commissural fusion
 Thick, stiff leaflets No commissural fusion Multivalvular involvement Commissural fusion. Degenerative Rheumatic. Degenerative vs. Rheumatic AS
Thick, stiff leaflets No commissural fusion Multivalvular involvement Commissural fusion. Degenerative Rheumatic. Degenerative vs. Rheumatic AS
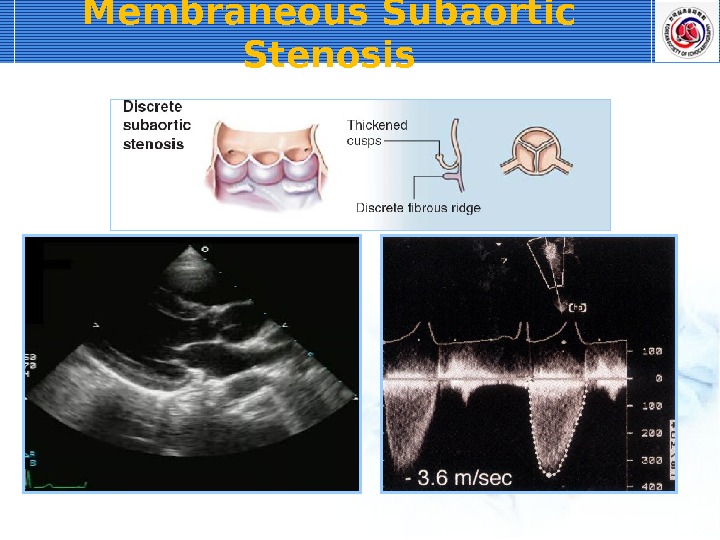
 Membraneous Subaortic Stenosis
Membraneous Subaortic Stenosis
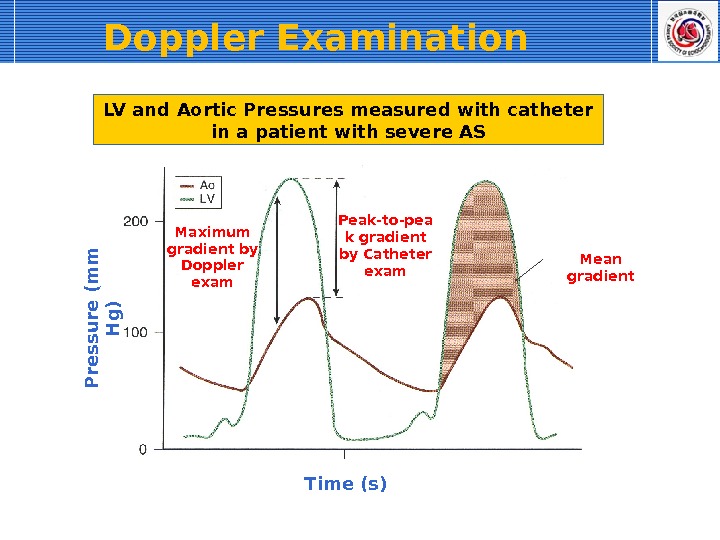
 Doppler Examination Time (s)P re s s u re (m m H g )Maximum gradient by Doppler exam Peak-to-pea k gradient by Catheter exam Mean gradient. LV and Aortic Pressures measured with catheter in a patient with severe AS
Doppler Examination Time (s)P re s s u re (m m H g )Maximum gradient by Doppler exam Peak-to-pea k gradient by Catheter exam Mean gradient. LV and Aortic Pressures measured with catheter in a patient with severe AS
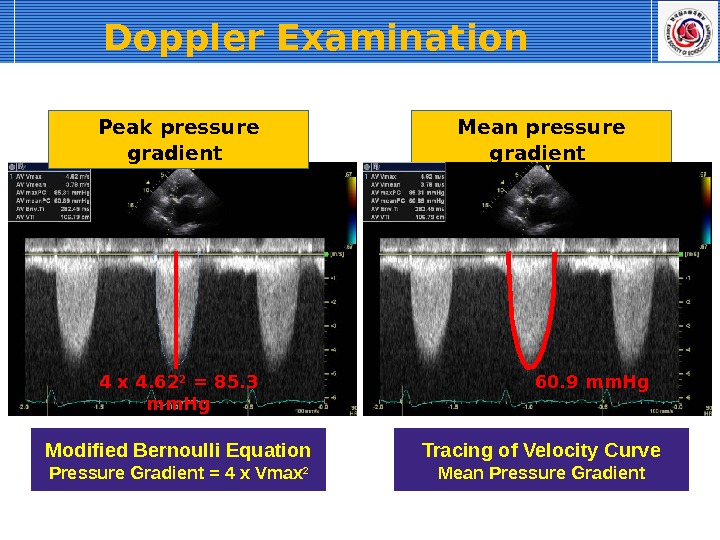
 Peak pressure gradient Mean pressure gradient Modified Bernoulli Equation Pressure Gradient = 4 x Vmax 24 x 4. 62 2 = 85. 3 mm. Hg Tracing of Velocity Curve Mean Pressure Gradient 60. 9 mm. Hg. Doppler Examination
Peak pressure gradient Mean pressure gradient Modified Bernoulli Equation Pressure Gradient = 4 x Vmax 24 x 4. 62 2 = 85. 3 mm. Hg Tracing of Velocity Curve Mean Pressure Gradient 60. 9 mm. Hg. Doppler Examination
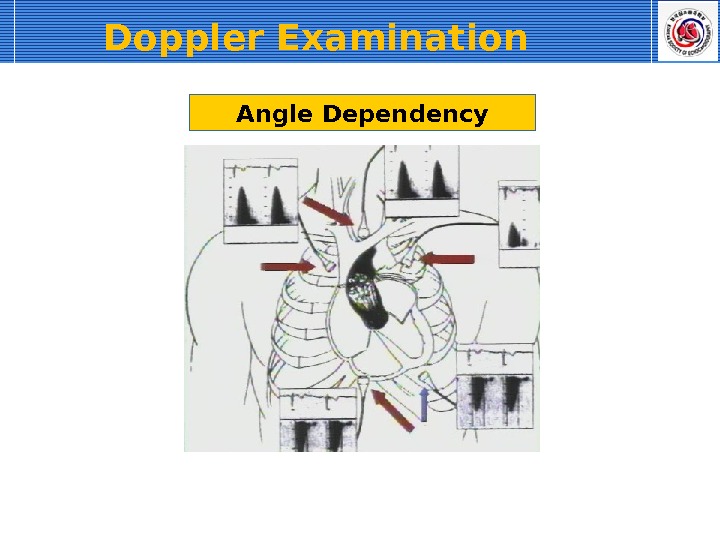
 Angle Dependency. Doppler Examination
Angle Dependency. Doppler Examination
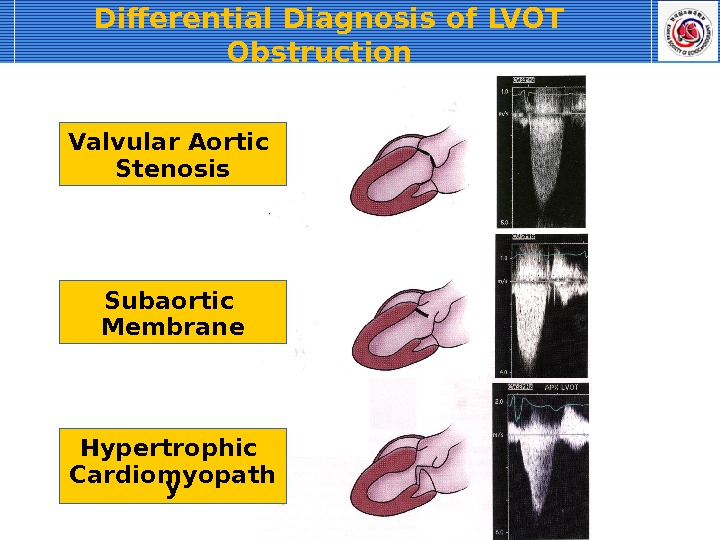
 Differential Diagnosis of LVOT Obstruction Valvular Aortic Stenosis Subaortic Membrane Hypertrophic Cardiomyopath y
Differential Diagnosis of LVOT Obstruction Valvular Aortic Stenosis Subaortic Membrane Hypertrophic Cardiomyopath y
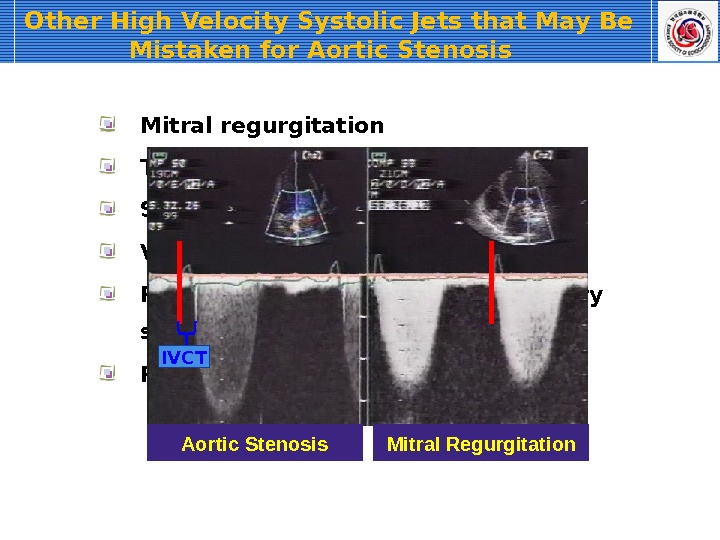
 Other High Velocity Systolic Jets that May Be Mistaken for Aortic Stenosis Mitral regurgitation Tricuspid regurgitation Supravalvular stenosis Ventricular septal defect Pulmonic or branch pulmonary artery stenosis Peripheral vascular stenosis (e. q. , subclavian artery) IVCT Aortic Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation
Other High Velocity Systolic Jets that May Be Mistaken for Aortic Stenosis Mitral regurgitation Tricuspid regurgitation Supravalvular stenosis Ventricular septal defect Pulmonic or branch pulmonary artery stenosis Peripheral vascular stenosis (e. q. , subclavian artery) IVCT Aortic Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation
 Calculation of Valve Area 2 D Planimetry Continuity equation
Calculation of Valve Area 2 D Planimetry Continuity equation
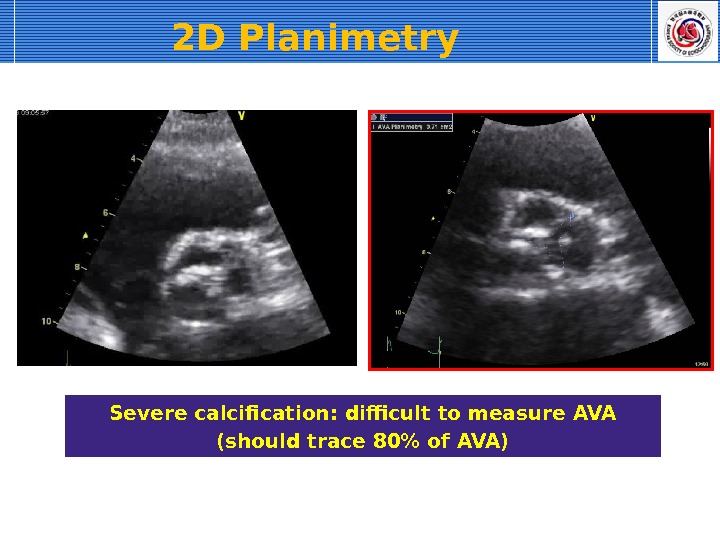
 2 D Planimetry Severe calcification: difficult to measure AVA (should trace 80% of AVA)
2 D Planimetry Severe calcification: difficult to measure AVA (should trace 80% of AVA)
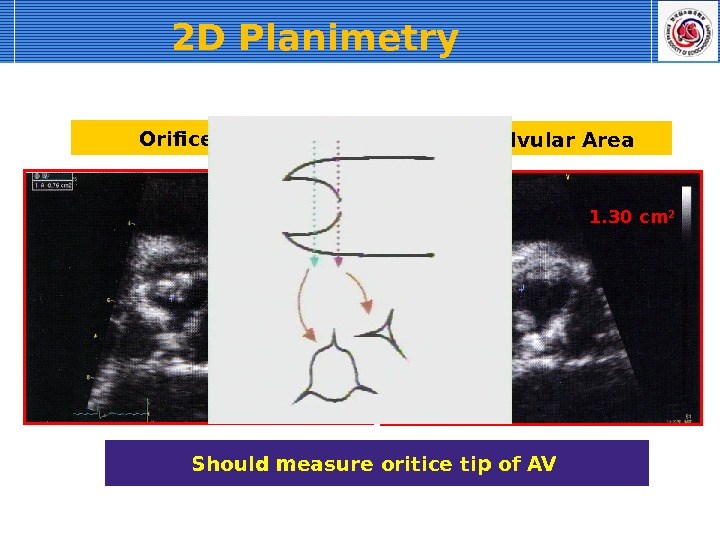
 Should measure oritice tip of AV Subvalvular Area 1. 30 cm 2 Orifice Tip 0. 76 cm 22 D Planimetry
Should measure oritice tip of AV Subvalvular Area 1. 30 cm 2 Orifice Tip 0. 76 cm 22 D Planimetry
 Continuity Equation LVOT Stroke Volume = AS-Jet Stroke Volume LVOT CSA x LVOT TVI = AVA x AS-Jet TVI AVA = (LVOT CSA x LVOT TVI) / AS-Jet TVI CSA LVO TTVI LVO T TVI AVCSA AVA = X
Continuity Equation LVOT Stroke Volume = AS-Jet Stroke Volume LVOT CSA x LVOT TVI = AVA x AS-Jet TVI AVA = (LVOT CSA x LVOT TVI) / AS-Jet TVI CSA LVO TTVI LVO T TVI AVCSA AVA = X
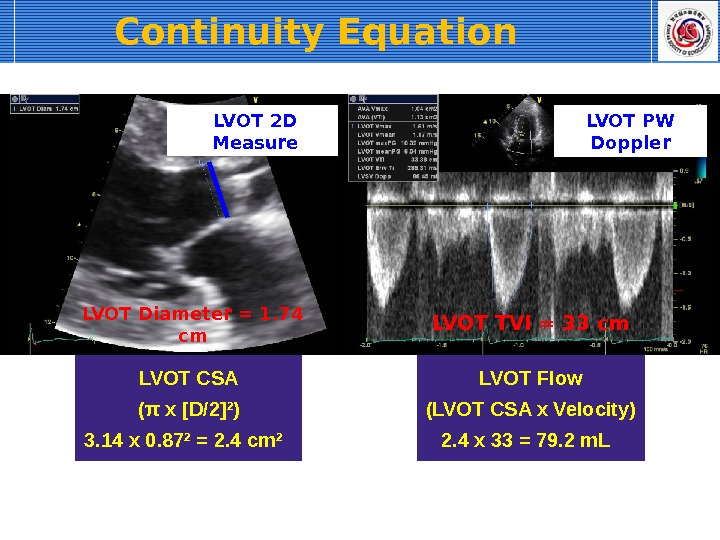
![LVOT Diameter = 1. 74 cm LVOT CSA ( π x [D/2] 2 ) 3. 14 LVOT Diameter = 1. 74 cm LVOT CSA ( π x [D/2] 2 ) 3. 14](/docs//5-2_aortic_valve_disease_images/5-2_aortic_valve_disease_26.jpg) LVOT Diameter = 1. 74 cm LVOT CSA ( π x [D/2] 2 ) 3. 14 x 0. 87 2 = 2. 4 cm 2 LVOT 2 D Measure LVOT TVI = 33 cm LVOT Flow (LVOT CSA x Velocity) 2. 4 x 33 = 79. 2 m. L LVOT PW Doppler. Continuity Equation
LVOT Diameter = 1. 74 cm LVOT CSA ( π x [D/2] 2 ) 3. 14 x 0. 87 2 = 2. 4 cm 2 LVOT 2 D Measure LVOT TVI = 33 cm LVOT Flow (LVOT CSA x Velocity) 2. 4 x 33 = 79. 2 m. L LVOT PW Doppler. Continuity Equation
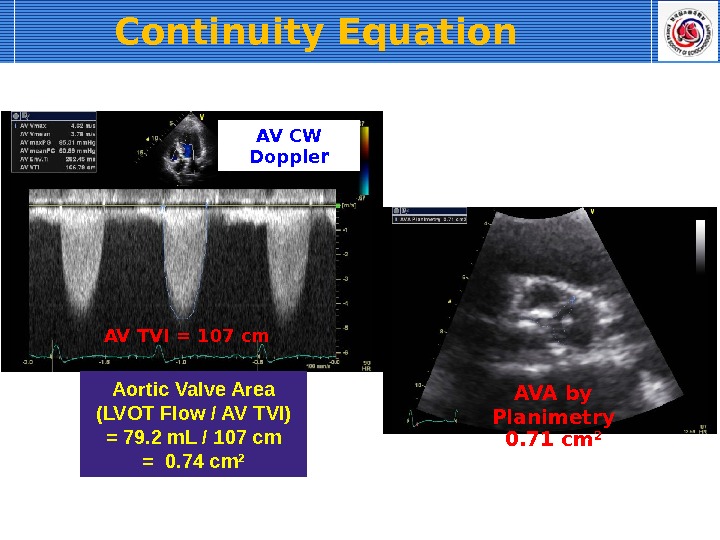
 AV TVI = 107 cm Aortic Valve Area (LVOT Flow / AV TVI) = 79. 2 m. L / 107 cm = 0. 74 cm 2 AV CW Doppler AVA by Planimetry 0. 71 cm 2 Continuity Equation
AV TVI = 107 cm Aortic Valve Area (LVOT Flow / AV TVI) = 79. 2 m. L / 107 cm = 0. 74 cm 2 AV CW Doppler AVA by Planimetry 0. 71 cm 2 Continuity Equation
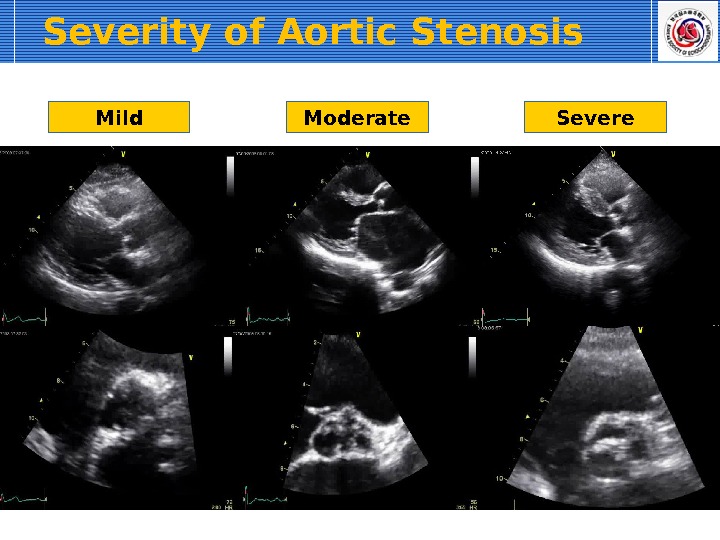
 Severity of Aortic Stenosis Mild Moderate Severe
Severity of Aortic Stenosis Mild Moderate Severe
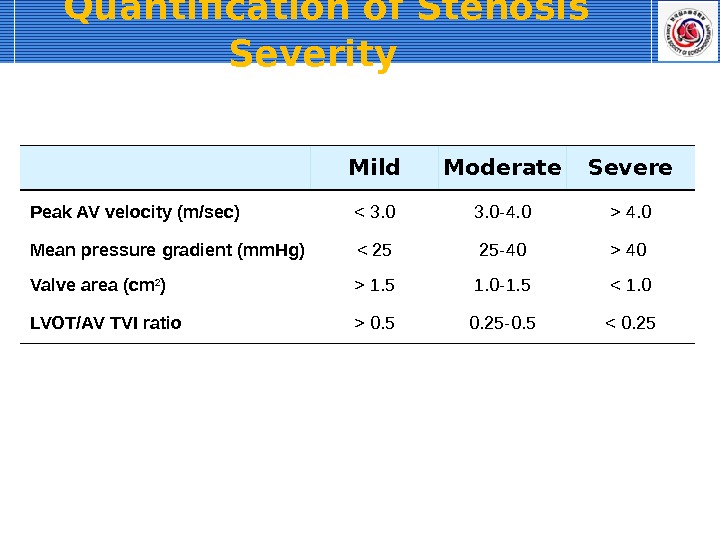
 Quantification of Stenosis Severity Mild Moderate Severe Peak AV velocity (m/sec) 4. 0 Mean pressure gradient (mm. Hg) 40 Valve area (cm 2 ) > 1. 5 1. 0 -1. 5 0. 5 0. 25 -0. 5 < 0.
Quantification of Stenosis Severity Mild Moderate Severe Peak AV velocity (m/sec) 4. 0 Mean pressure gradient (mm. Hg) 40 Valve area (cm 2 ) > 1. 5 1. 0 -1. 5 0. 5 0. 25 -0. 5 < 0.
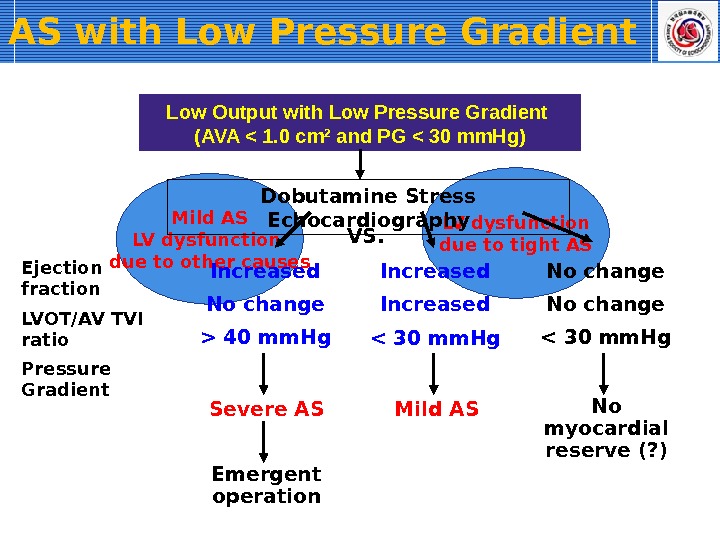
 Mild AS LV dysfunction due to other causes LV dysfunction due to tight ASVS. AS with Low Pressure Gradient Low Output with Low Pressure Gradient (AVA < 1. 0 cm 2 and PG < 30 mm. Hg) Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography Ejection fraction LVOT/AV TVI ratio Pressure Gradient < 30 mm. Hg Increased Mild AS 40 mm. Hg No change Increased Severe AS Emergent operation
Mild AS LV dysfunction due to other causes LV dysfunction due to tight ASVS. AS with Low Pressure Gradient Low Output with Low Pressure Gradient (AVA < 1. 0 cm 2 and PG < 30 mm. Hg) Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography Ejection fraction LVOT/AV TVI ratio Pressure Gradient < 30 mm. Hg Increased Mild AS 40 mm. Hg No change Increased Severe AS Emergent operation
 Aortic Regurgitation
Aortic Regurgitation
 Etiology of Aortic Regurgitation Cusp pathology Aortic wall pathology including aortitis Congenital
Etiology of Aortic Regurgitation Cusp pathology Aortic wall pathology including aortitis Congenital
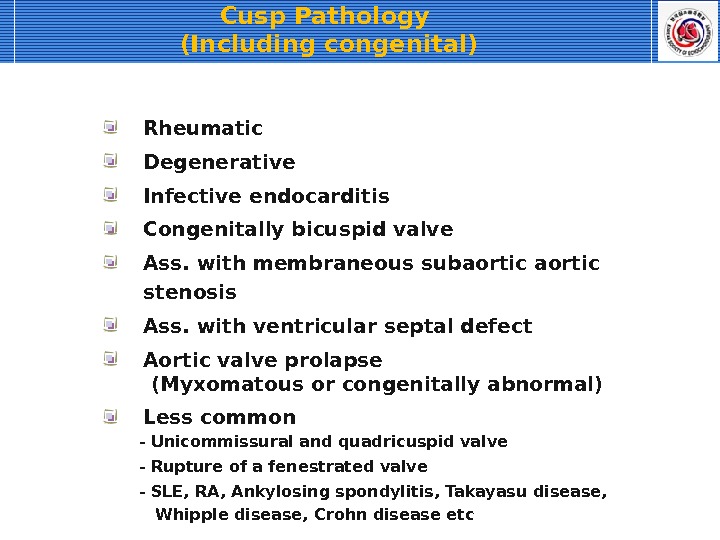
 Cusp Pathology (Including congenital) Rheumatic Degenerative Infective endocarditis Congenitally bicuspid valve Ass. with membraneous subaortic stenosis Ass. with ventricular septal defect Aortic valve prolapse (Myxomatous or congenitally abnormal) Less common — Unicommissural and quadricuspid valve — Rupture of a fenestrated valve — SLE, RA, Ankylosing spondylitis, Takayasu disease, Whipple disease, Crohn disease etc
Cusp Pathology (Including congenital) Rheumatic Degenerative Infective endocarditis Congenitally bicuspid valve Ass. with membraneous subaortic stenosis Ass. with ventricular septal defect Aortic valve prolapse (Myxomatous or congenitally abnormal) Less common — Unicommissural and quadricuspid valve — Rupture of a fenestrated valve — SLE, RA, Ankylosing spondylitis, Takayasu disease, Whipple disease, Crohn disease etc
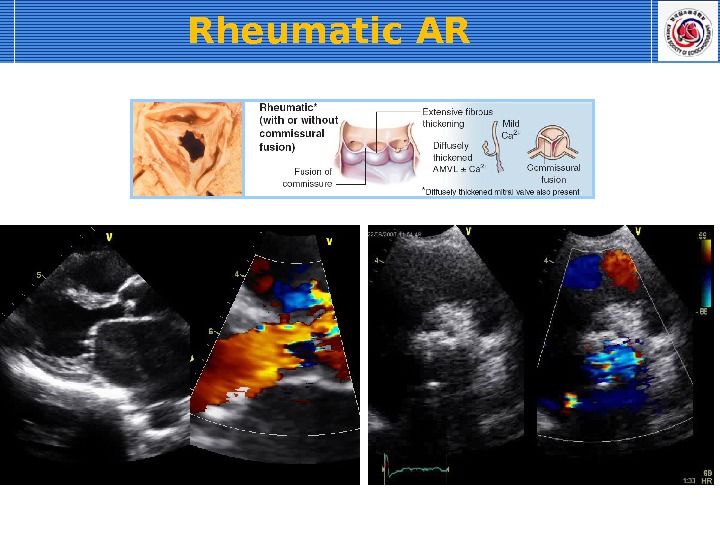
 Rheumatic AR
Rheumatic AR
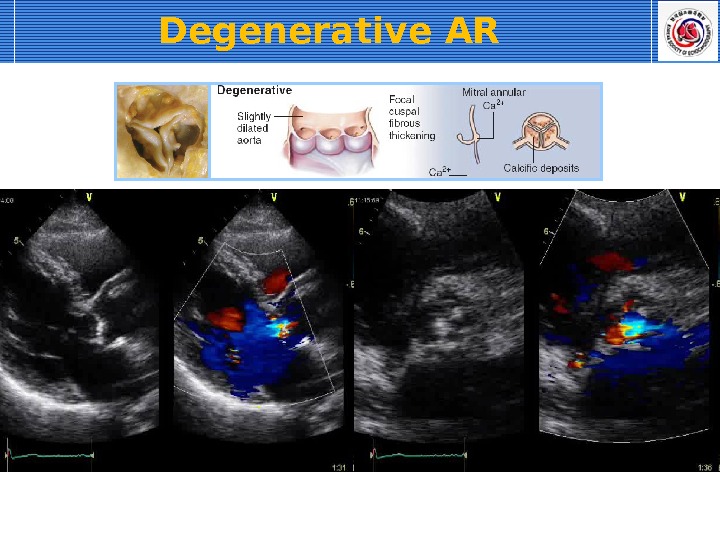
 Degenerative AR
Degenerative AR
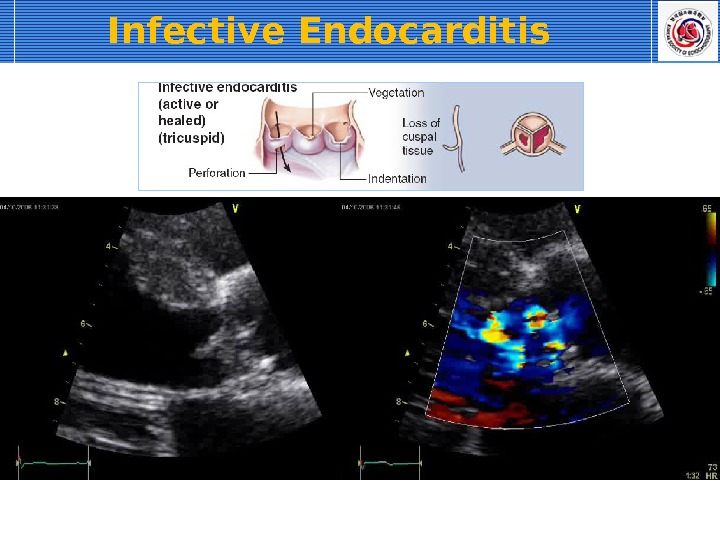
 Infective Endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis
 Bicuspid Aortic Valve
Bicuspid Aortic Valve
 Quadricuspid Aortic Valve
Quadricuspid Aortic Valve
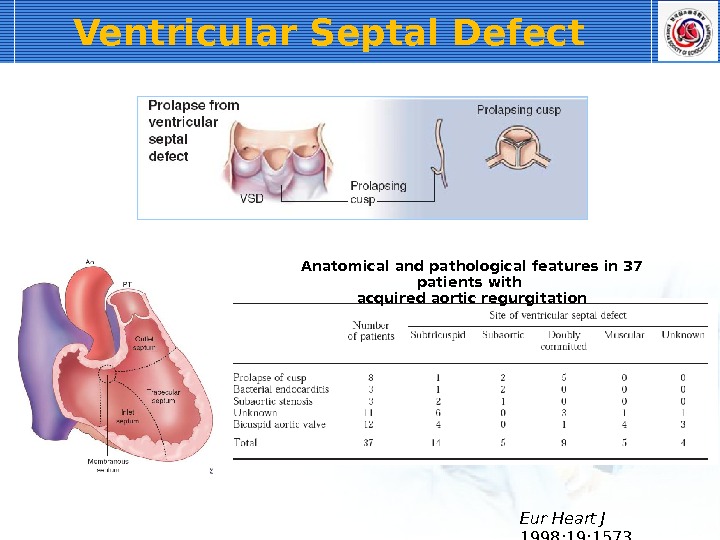
 Ventricular Septal Defect Eur Heart J 1998; 19: 1573 Anatomical and pathological features in 37 patients with acquired aortic regurgitation
Ventricular Septal Defect Eur Heart J 1998; 19: 1573 Anatomical and pathological features in 37 patients with acquired aortic regurgitation
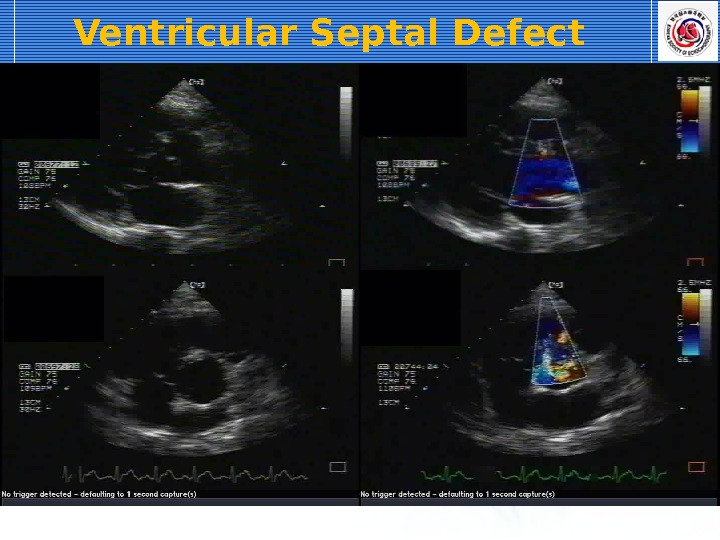
 Ventricular Septal Defect
Ventricular Septal Defect
 Aortic Valve Prolapse Best seen in parasternal long axis view Disruption of commissural support — Dissection — Dilatation — Ass. with VSD — Myxomatous or congenitally abnormality
Aortic Valve Prolapse Best seen in parasternal long axis view Disruption of commissural support — Dissection — Dilatation — Ass. with VSD — Myxomatous or congenitally abnormality
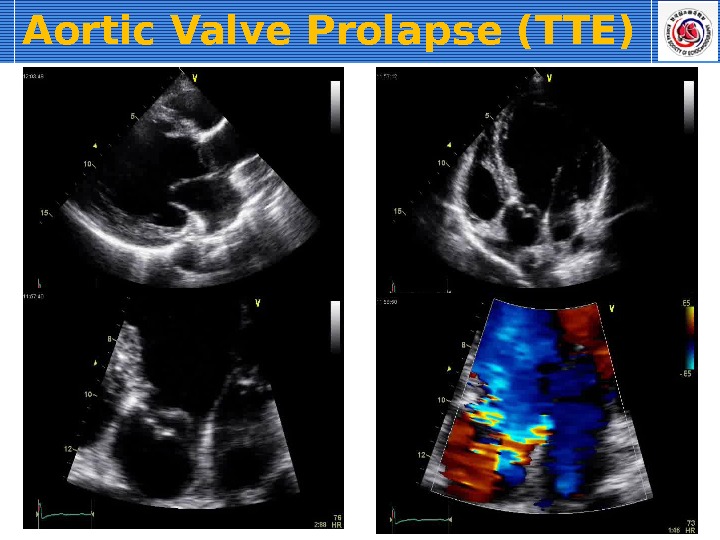
 Aortic Valve Prolapse (TTE)
Aortic Valve Prolapse (TTE)
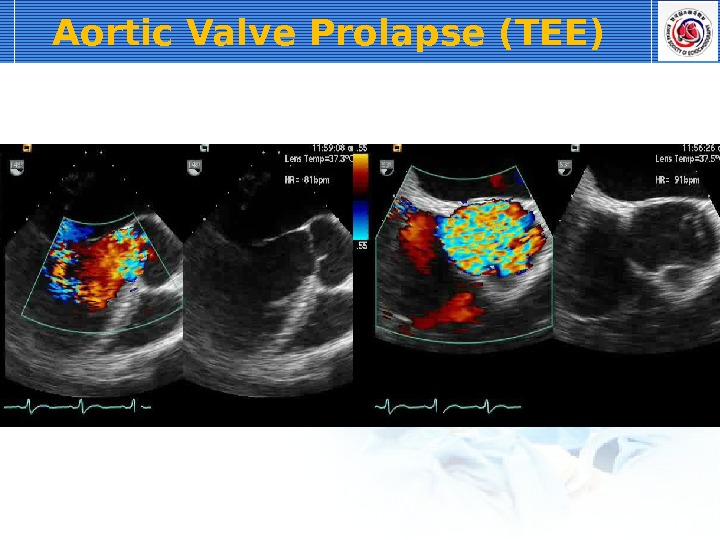
 Aortic Valve Prolapse (TEE)
Aortic Valve Prolapse (TEE)
 Aortic Root Disease Aortic dilatation related with — Hypertension — Age-related (degenerative) — Bicuspid AV Aortic dissection Cystic medial necrosis (Marfan syndrome) Takayasu arteritis Behcet’s disease Ankylosing spondylitis Less common — Syphilitic aortitis, psoriatic arthritis, UC, giant cell arteritis — relapsing polychondritis, Reiter syndrome
Aortic Root Disease Aortic dilatation related with — Hypertension — Age-related (degenerative) — Bicuspid AV Aortic dissection Cystic medial necrosis (Marfan syndrome) Takayasu arteritis Behcet’s disease Ankylosing spondylitis Less common — Syphilitic aortitis, psoriatic arthritis, UC, giant cell arteritis — relapsing polychondritis, Reiter syndrome
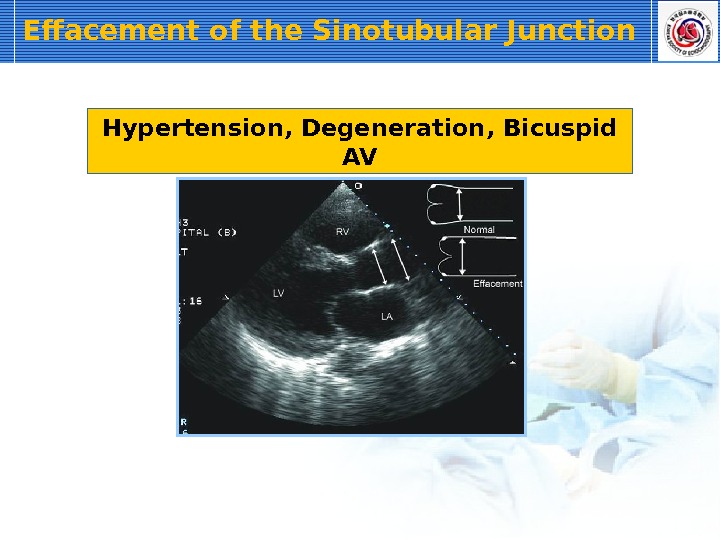
 Effacement of the Sinotubular Junction Hypertension, Degeneration, Bicuspid AV
Effacement of the Sinotubular Junction Hypertension, Degeneration, Bicuspid AV
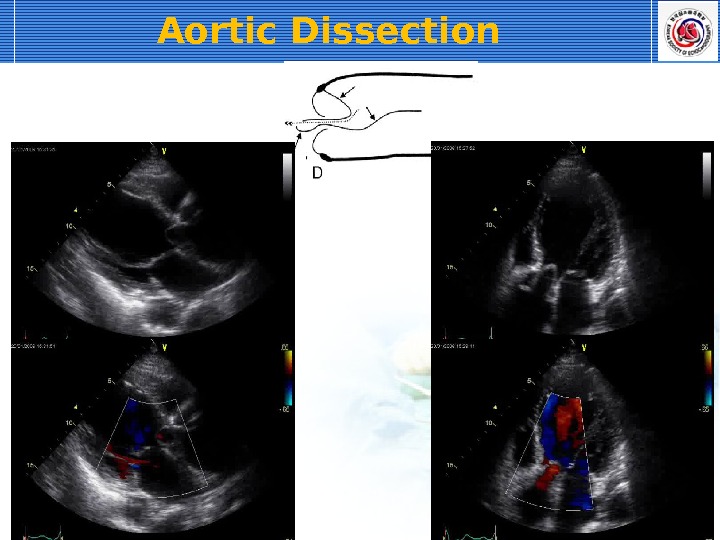
 Aortic Dissection
Aortic Dissection
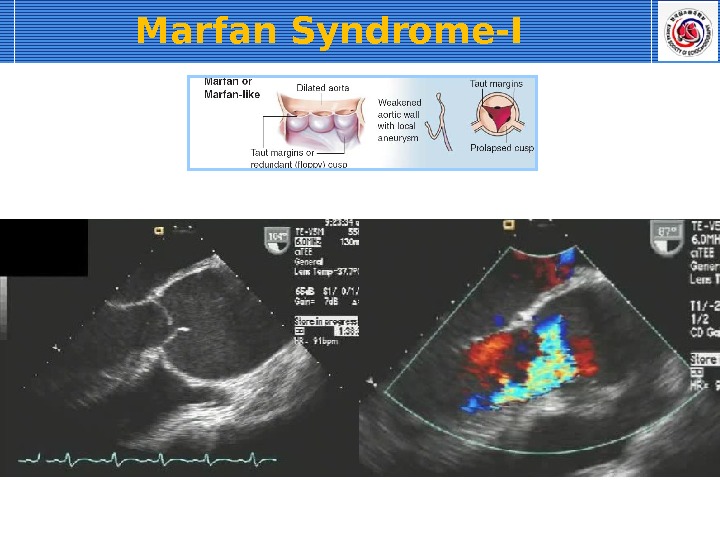
 Marfan Syndrome-I
Marfan Syndrome-I
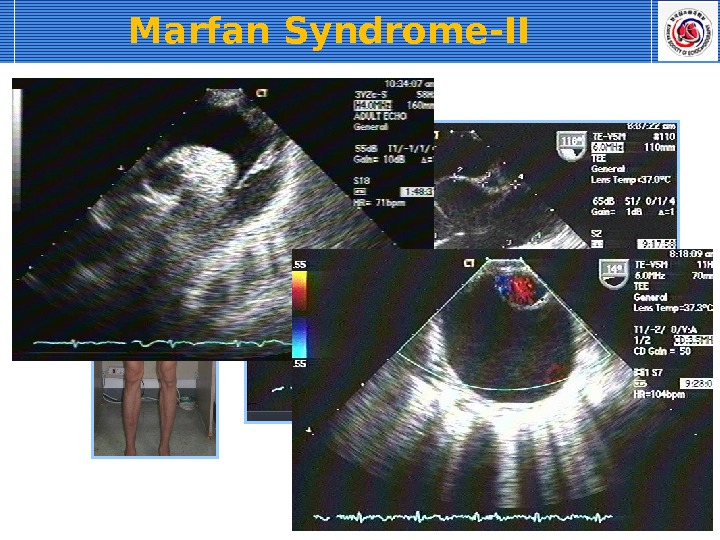
 Marfan Syndrome-II
Marfan Syndrome-II
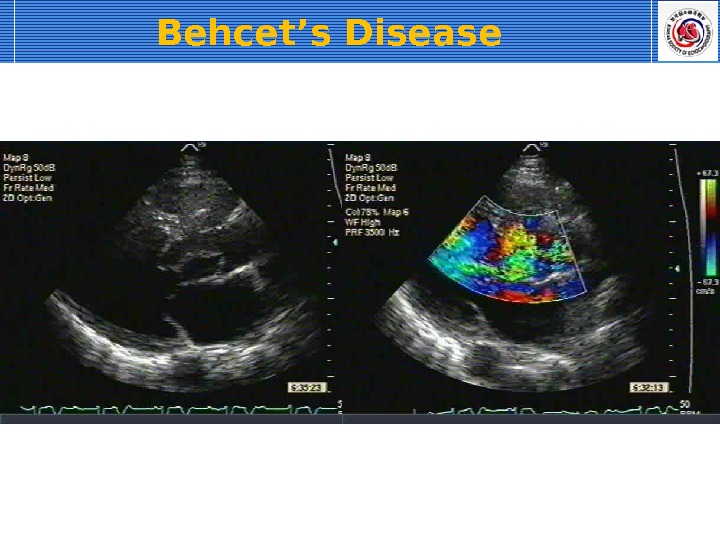
 Behcet’s Disease
Behcet’s Disease
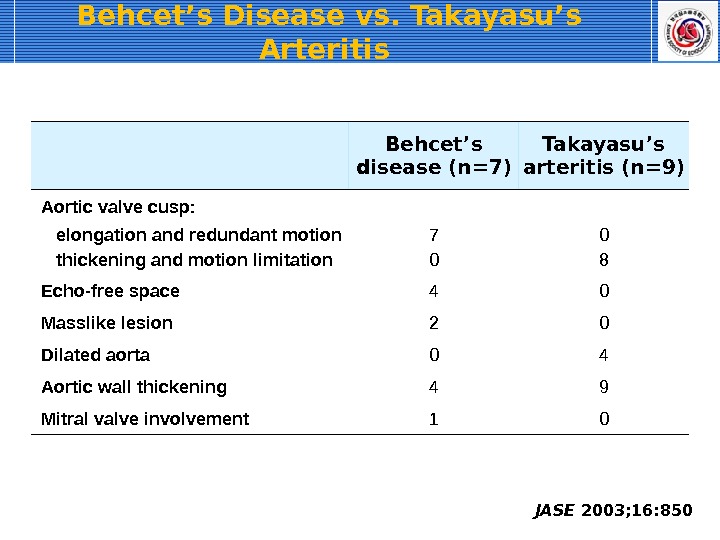
 Behcet’s Disease vs. Takayasu’s Arteritis JASE 2003; 16: 850 Behcet’s disease (n=7) Takayasu’s arteritis (n=9) Aortic valve cusp: elongation and redundant motion 7 0 thickening and motion limitation 0 8 Echo-free space 4 0 Masslike lesion 2 0 Dilated aorta 0 4 Aortic wall thickening 4 9 Mitral valve involvement
Behcet’s Disease vs. Takayasu’s Arteritis JASE 2003; 16: 850 Behcet’s disease (n=7) Takayasu’s arteritis (n=9) Aortic valve cusp: elongation and redundant motion 7 0 thickening and motion limitation 0 8 Echo-free space 4 0 Masslike lesion 2 0 Dilated aorta 0 4 Aortic wall thickening 4 9 Mitral valve involvement
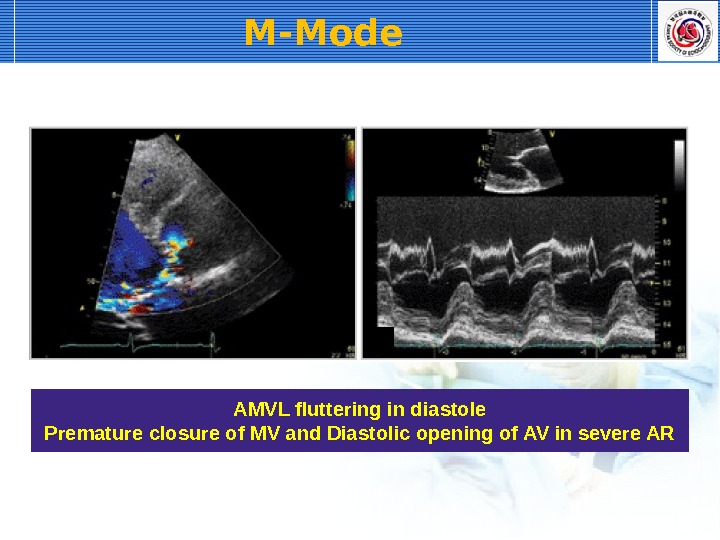
 M-Mode AMVL fluttering in diastole Premature closure of MV and Diastolic opening of AV in severe AR
M-Mode AMVL fluttering in diastole Premature closure of MV and Diastolic opening of AV in severe AR
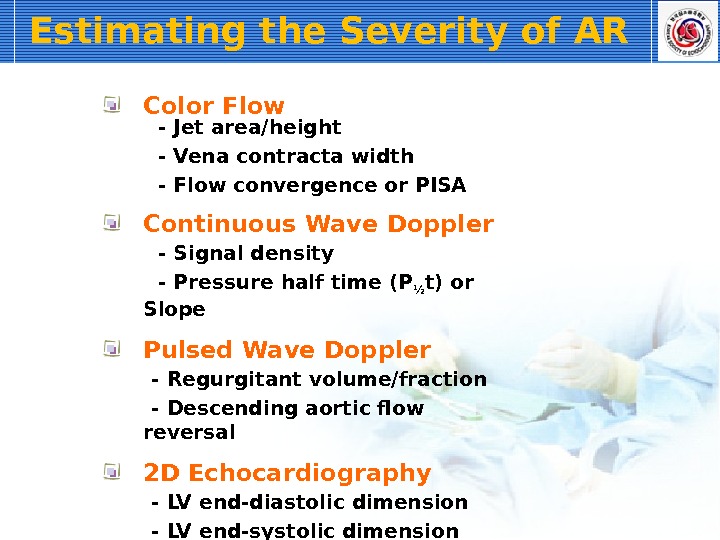
 Estimating the Severity of AR Color Flow — Jet area/height — Vena contracta width — Flow convergence or PISA Continuous Wave Doppler — Signal density — Pressure half time (P ½ t) or Slope Pulsed Wave Doppler — Regurgitant volume/fraction — Descending aortic flow reversal 2 D Echocardiography — LV end-diastolic dimension — LV end-systolic dimension
Estimating the Severity of AR Color Flow — Jet area/height — Vena contracta width — Flow convergence or PISA Continuous Wave Doppler — Signal density — Pressure half time (P ½ t) or Slope Pulsed Wave Doppler — Regurgitant volume/fraction — Descending aortic flow reversal 2 D Echocardiography — LV end-diastolic dimension — LV end-systolic dimension
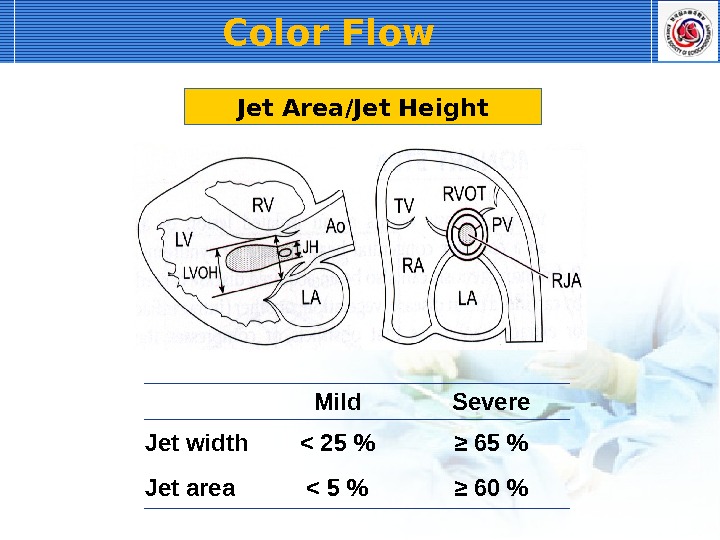
 Color Flow Jet Area/Jet Height Mild Severe Jet width < 25 % ≥ 65 % Jet area < 5 % ≥ 60 %
Color Flow Jet Area/Jet Height Mild Severe Jet width < 25 % ≥ 65 % Jet area < 5 % ≥ 60 %
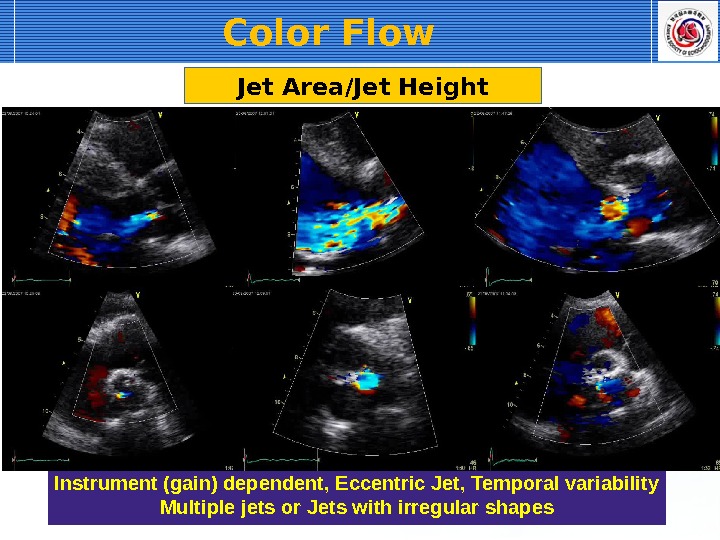
 Jet Area/Jet Height Instrument (gain) dependent, Eccentric Jet, Temporal variability Multiple jets or Jets with irregular shapes Color Flow
Jet Area/Jet Height Instrument (gain) dependent, Eccentric Jet, Temporal variability Multiple jets or Jets with irregular shapes Color Flow
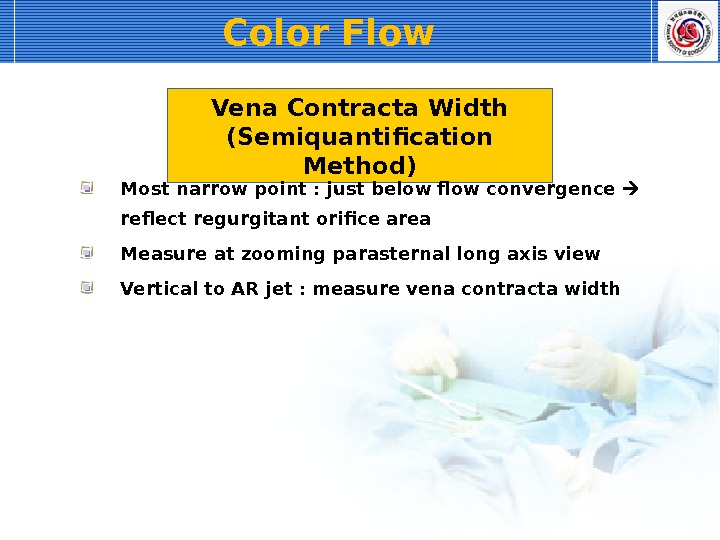
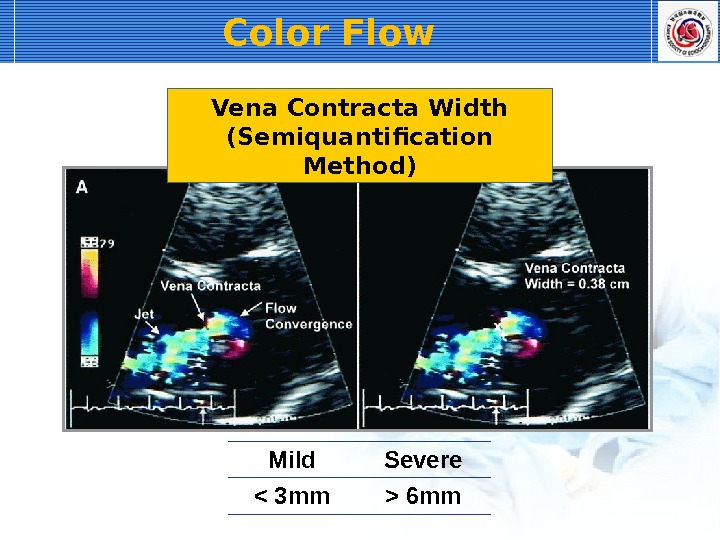
 Vena Contracta Width (Semiquantification Method) Most narrow point : just below flow convergence reflect regurgitant orifice area Measure at zooming parasternal long axis view Vertical to AR jet : measure vena contracta width Color Flow
Vena Contracta Width (Semiquantification Method) Most narrow point : just below flow convergence reflect regurgitant orifice area Measure at zooming parasternal long axis view Vertical to AR jet : measure vena contracta width Color Flow
 Mild Severe 6 mm. Vena Contracta Width (Semiquantification Method)Color Flow
Mild Severe 6 mm. Vena Contracta Width (Semiquantification Method)Color Flow
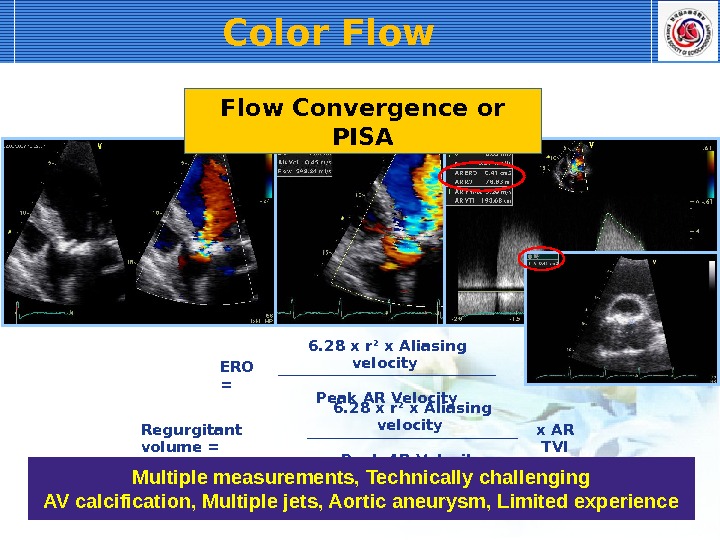
 Color Flow ERO = 6. 28 x r 2 x Aliasing velocity Peak AR Velocity Regurgitant volume = 6. 28 x r 2 x Aliasing velocity x AR TVI Peak AR Velocity. Flow Convergence or PISA Multiple measurements, Technically challenging AV calcification, Multiple jets, Aortic aneurysm, Limited experience
Color Flow ERO = 6. 28 x r 2 x Aliasing velocity Peak AR Velocity Regurgitant volume = 6. 28 x r 2 x Aliasing velocity x AR TVI Peak AR Velocity. Flow Convergence or PISA Multiple measurements, Technically challenging AV calcification, Multiple jets, Aortic aneurysm, Limited experience
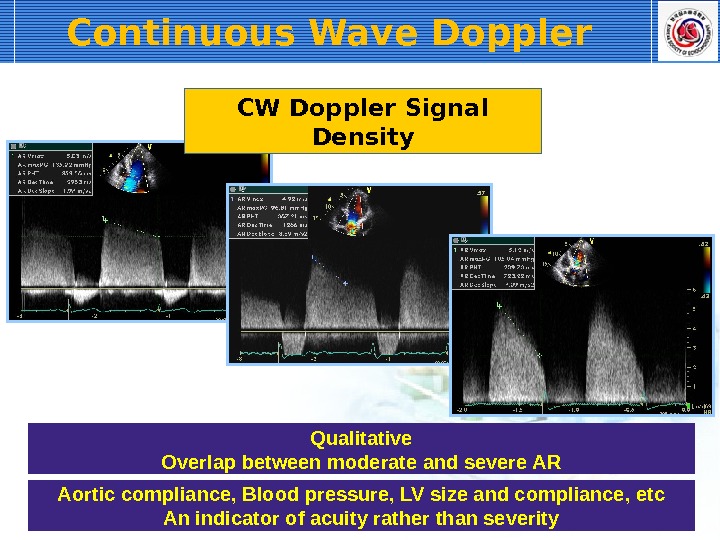
 Continuous Wave Doppler CW Doppler Signal Density Qualitative Overlap between moderate and severe AR Aortic compliance, Blood pressure, LV size and compliance, etc An indicator of acuity rather than severity
Continuous Wave Doppler CW Doppler Signal Density Qualitative Overlap between moderate and severe AR Aortic compliance, Blood pressure, LV size and compliance, etc An indicator of acuity rather than severity
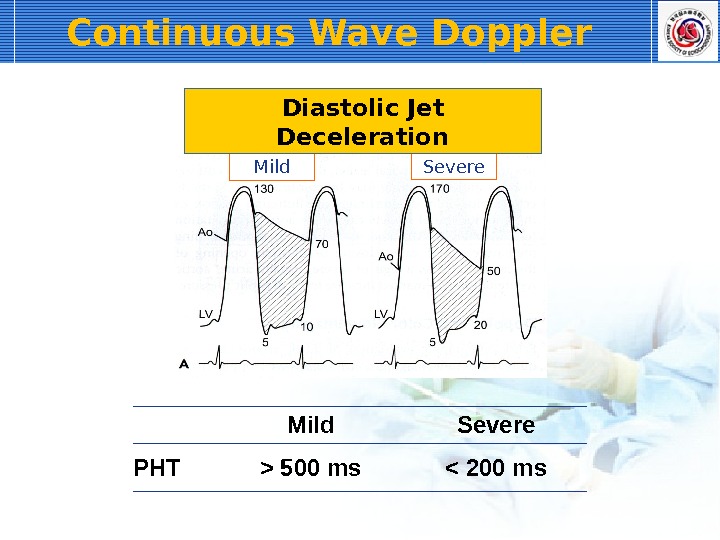
 Continuous Wave Doppler Mild Severe PHT > 500 ms < 200 ms. Diastolic Jet Deceleration
Continuous Wave Doppler Mild Severe PHT > 500 ms < 200 ms. Diastolic Jet Deceleration
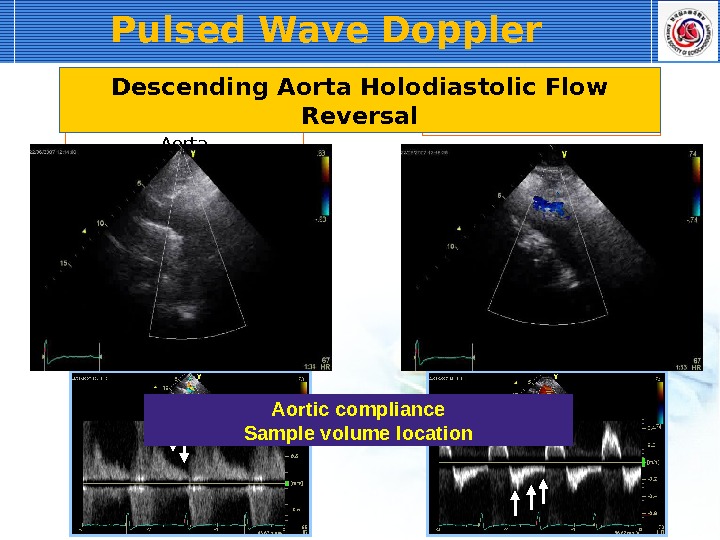
 Pulsed Wave Doppler Descending Thoracic Aorta Abdominal Aorta. Descending Aorta Holodiastolic Flow Reversal Aortic compliance Sample volume location
Pulsed Wave Doppler Descending Thoracic Aorta Abdominal Aorta. Descending Aorta Holodiastolic Flow Reversal Aortic compliance Sample volume location
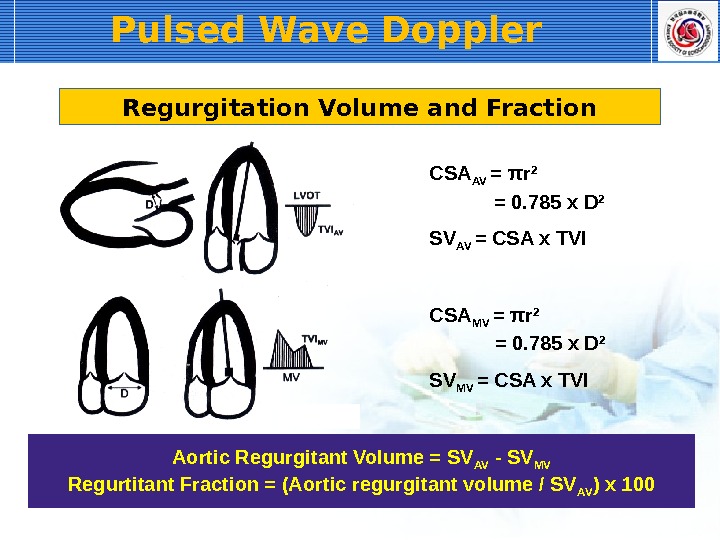
 Pulsed Wave Doppler SV AV = CSA x TVICSA AV = π r 2 = 0. 785 x D 2 SV MV = CSA x TVICSA MV = π r 2 = 0. 785 x D 2 Regurgitation Volume and Fraction Aortic Regurgitant Volume = SV AV — SV MV Regurtitant Fraction = (Aortic regurgitant volume / SV AV ) x
Pulsed Wave Doppler SV AV = CSA x TVICSA AV = π r 2 = 0. 785 x D 2 SV MV = CSA x TVICSA MV = π r 2 = 0. 785 x D 2 Regurgitation Volume and Fraction Aortic Regurgitant Volume = SV AV — SV MV Regurtitant Fraction = (Aortic regurgitant volume / SV AV ) x
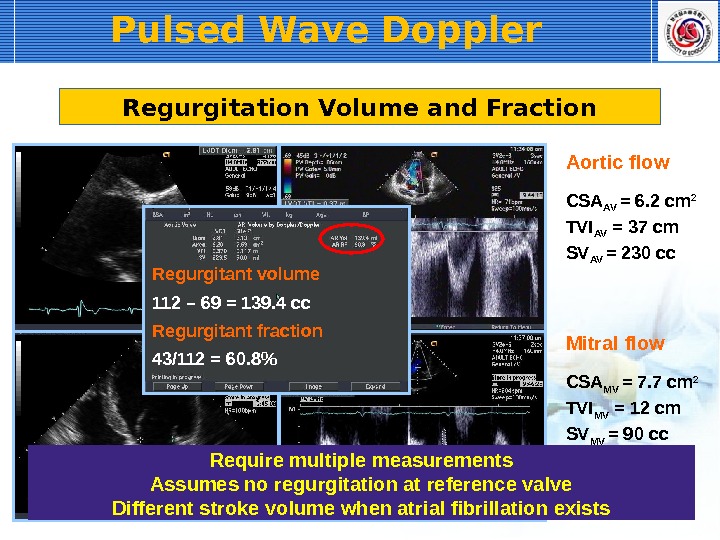
 Pulsed Wave Doppler CSA AV = 6. 2 cm 2 TVI AV = 37 cm SV AV = 230 cc. Aortic flow CSA MV = 7. 7 cm 2 TVI MV = 12 cm SV MV = 90 cc. Mitral flow. Regurgitation Volume and Fraction 112 – 69 = 139. 4 cc. Regurgitant volume 43/112 = 60. 8%Regurgitant fraction Require multiple measurements Assumes no regurgitation at reference valve Different stroke volume when atrial fibrillation exists
Pulsed Wave Doppler CSA AV = 6. 2 cm 2 TVI AV = 37 cm SV AV = 230 cc. Aortic flow CSA MV = 7. 7 cm 2 TVI MV = 12 cm SV MV = 90 cc. Mitral flow. Regurgitation Volume and Fraction 112 – 69 = 139. 4 cc. Regurgitant volume 43/112 = 60. 8%Regurgitant fraction Require multiple measurements Assumes no regurgitation at reference valve Different stroke volume when atrial fibrillation exists
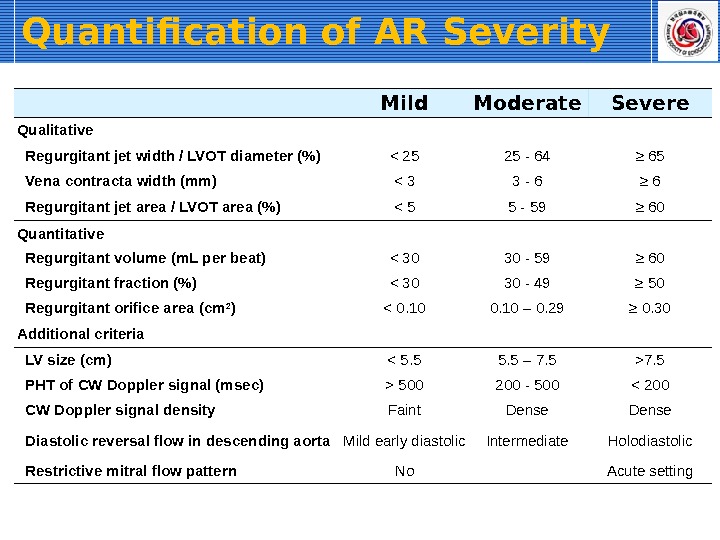
 Quantification of AR Severity Mild Moderate Severe Qualitative Regurgitant jet width / LVOT diameter (%) < 25 25 — 64 ≥ 65 Vena contracta width (mm) < 3 3 — 6 ≥ 6 Regurgitant jet area / LVOT area (%) < 5 5 — 59 ≥ 60 Quantitative Regurgitant volume (m. L per beat) < 30 30 — 59 ≥ 60 Regurgitant fraction (%) < 30 30 — 49 ≥ 50 Regurgitant orifice area (cm 2 ) < 0. 10 – 0. 29 ≥ 0. 30 Additional criteria LV size (cm) 7. 5 PHT of CW Doppler signal (msec) > 500 200 — 500 < 200 CW Doppler signal density Faint Dense Diastolic reversal flow in descending aorta Mild early diastolic Intermediate Holodiastolic Restrictive mitral flow pattern No Acute setting
Quantification of AR Severity Mild Moderate Severe Qualitative Regurgitant jet width / LVOT diameter (%) < 25 25 — 64 ≥ 65 Vena contracta width (mm) < 3 3 — 6 ≥ 6 Regurgitant jet area / LVOT area (%) < 5 5 — 59 ≥ 60 Quantitative Regurgitant volume (m. L per beat) < 30 30 — 59 ≥ 60 Regurgitant fraction (%) < 30 30 — 49 ≥ 50 Regurgitant orifice area (cm 2 ) < 0. 10 – 0. 29 ≥ 0. 30 Additional criteria LV size (cm) 7. 5 PHT of CW Doppler signal (msec) > 500 200 — 500 < 200 CW Doppler signal density Faint Dense Diastolic reversal flow in descending aorta Mild early diastolic Intermediate Holodiastolic Restrictive mitral flow pattern No Acute setting
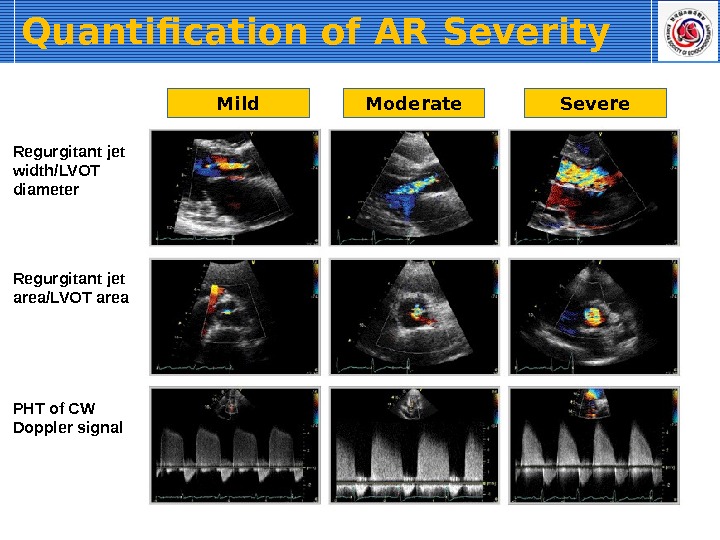
 Mild Moderate Severe Regurgitant jet width/LVOT diameter Regurgitant jet area/LVOT area PHT of CW Doppler signal Quantification of AR Severity
Mild Moderate Severe Regurgitant jet width/LVOT diameter Regurgitant jet area/LVOT area PHT of CW Doppler signal Quantification of AR Severity
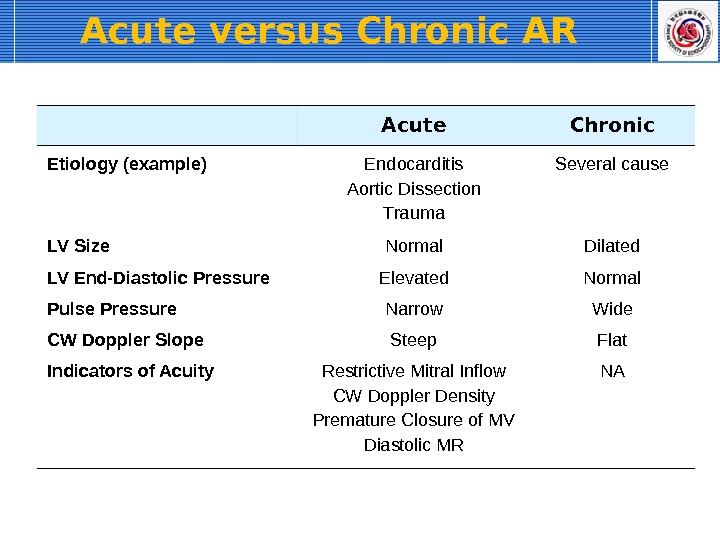
 Acute versus Chronic AR Acute Chronic Etiology (example) Endocarditis Aortic Dissection Trauma Several cause LV Size Normal Dilated LV End-Diastolic Pressure Elevated Normal Pulse Pressure Narrow Wide CW Doppler Slope Steep Flat Indicators of Acuity Restrictive Mitral Inflow CW Doppler Density Premature Closure of MV Diastolic MR N
Acute versus Chronic AR Acute Chronic Etiology (example) Endocarditis Aortic Dissection Trauma Several cause LV Size Normal Dilated LV End-Diastolic Pressure Elevated Normal Pulse Pressure Narrow Wide CW Doppler Slope Steep Flat Indicators of Acuity Restrictive Mitral Inflow CW Doppler Density Premature Closure of MV Diastolic MR N
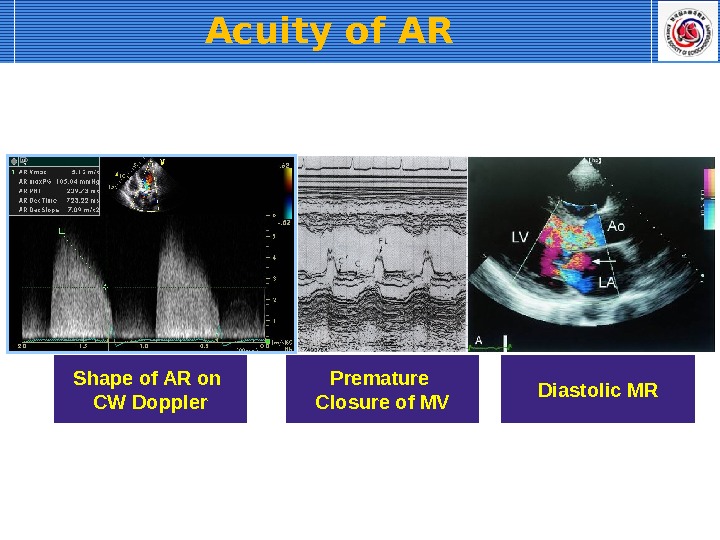
 Acuity of AR Shape of AR on CW Doppler Premature Closure of MV Diastolic MR
Acuity of AR Shape of AR on CW Doppler Premature Closure of MV Diastolic MR


