8c47dc6f7da461291c7e1fa2e82233ff.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Antoni Cieśla, Zbigniew Hanzelka, Jacek Nalepa, Tadeusz Orzechowski, Jan Rusek Master-degree specialization in Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems, carried in English at the AGH-UST International Conference on Engineering Education ICEE 2005, The Silesian University of Technology, Gliwice, Poland, July 25 - 29, 2005. http: //icee 2005. polsl. pl The AGH University of Science and Technology (AGH-UST), Krakow, Poland, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Automatics, Computer Science and Electronics (EAIE), launches the master-degree studies in the area of Electrical Engineering, carried entirely in the English language. For this end a new, as if inter-modular, specialization has been proposed, called Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems (CEES). The specialization is a new one, though very close to one of the specializations carried in the Polish language, within the "modulus C" of the unified, master-degree studies. The duration of the studies within the specialization is four semesters, whereby the fourth semester is devoted for preparation of the diploma work. The project starts in the autumn-to-winter semester of the academic year 2005 -to-2006. The project has been successfully put into the whole acceptance procedures, both at the EAIE Faculty and AGH-UST senate levels. After gathering of all the indispensable acceptances, it was possible to arrange a meeting with potential candidates for the studies within the proposed specialization, to be carried in the English language. The meeting (held on February 25 th, 2005) has gathered about 18 students. First they have been exposed to short presentation of objectives, courses and regulations. Thereafter the questions of the audience have been answered by prof. Antoni Cieśla (lecturer and pro-dean catering for Electrical Engineering), prof. Zbigniew Hanzelka (lecturer) and prof. Jan Rusek (lecturer). From the atmosphere of the one and half hour lasting meeting, it can justifiably be concluded that about 12 students will volunteer for the proposed specialization. Those involved in preparation of the project are deeply convinced, that the existence of a group with English as an exclusive language of lectures and tutorials will prepare the EAIE Faculty to meet the growing challenge of being able to propose studies not only for the Polish but also for the foreign candidates. At the same time, carrying lectures and tutorials in the English language will promote the knowledge of the technical vocabulary among the whole academic community of the AGH-UST. _______________ An article would present some details of the new venture, including objectives, methods and regulations, all prepared for the new specialization to be carried in the English language.

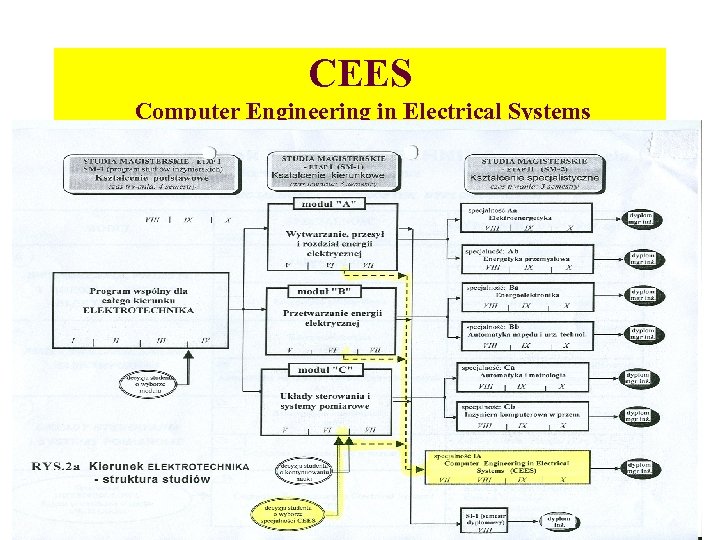
CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems • Objectives and methods: • The student will be exposed to advanced knowledge of computer science within softwer and hardware, to the knowledge of modern methods of control, electrical circuits analysis and modelling, signal aquisition and processing, etc. • The student will also gain the knowledge about basic electric and electronic equipment (machines, drives, power electronics) as well as about technological processes such as thermal processes, generation, transmission and distribution of electrical energy, control systems, etc. • Based on the above targets, the graduate of the CEES specuialization will be an engineer of broad knowledge of proctical informatics, which he will be able to apply to control the know-to-him objects, systems and electrical processes.
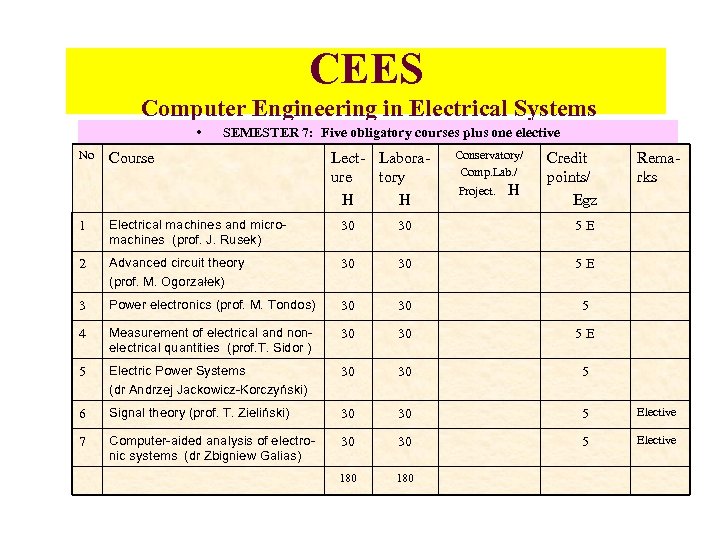
CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems • No SEMESTER 7: Five obligatory courses plus one elective Course Lect- Laboraure tory H H Conservatory/ Comp. Lab. / Project. H Credit points/ Egz Remarks 1 Electrical machines and micromachines (prof. J. Rusek) 30 30 5 E 2 Advanced circuit theory (prof. M. Ogorzałek) 30 30 5 E 3 Power electronics (prof. M. Tondos) 30 30 5 4 Measurement of electrical and nonelectrical quantities (prof. T. Sidor ) 30 30 5 Electric Power Systems (dr Andrzej Jackowicz-Korczyński) 30 30 5 6 Signal theory (prof. T. Zieliński) 30 30 5 Elective 7 Computer-aided analysis of electronic systems (dr Zbigniew Galias) 30 30 5 Elective 180
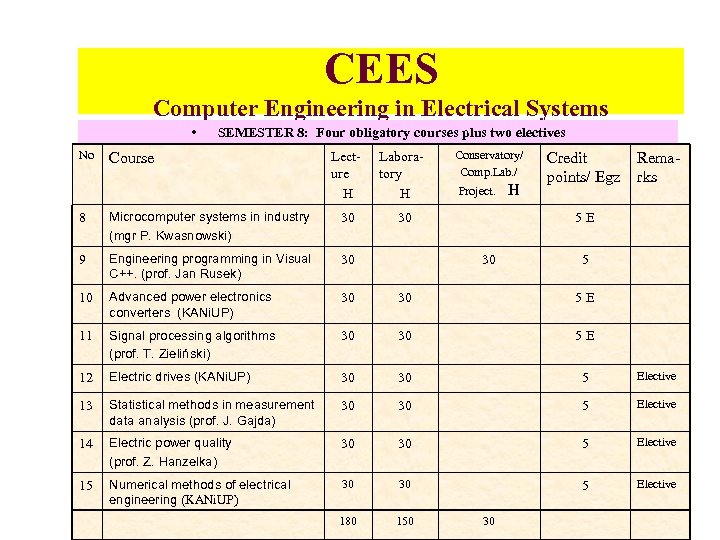
CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems • No SEMESTER 8: Four obligatory courses plus two electives Course Lecture H Laboratory H Conservatory/ Comp. Lab. / 30 Project. H Credit points/ Egz Remarks 8 Microcomputer systems in industry (mgr P. Kwasnowski) 30 9 Engineering programming in Visual C++. (prof. Jan Rusek) 30 10 Advanced power electronics converters (KANi. UP) 30 30 5 E 11 Signal processing algorithms (prof. T. Zieliński) 30 30 5 E 12 Electric drives (KANi. UP) 30 30 5 Elective 13 Statistical methods in measurement data analysis (prof. J. Gajda) 30 30 5 Elective 14 Electric power quality (prof. Z. Hanzelka) 30 30 5 Elective 15 Numerical methods of electrical engineering (KANi. UP) 30 30 5 Elective 180 150 5 E 30 30 5
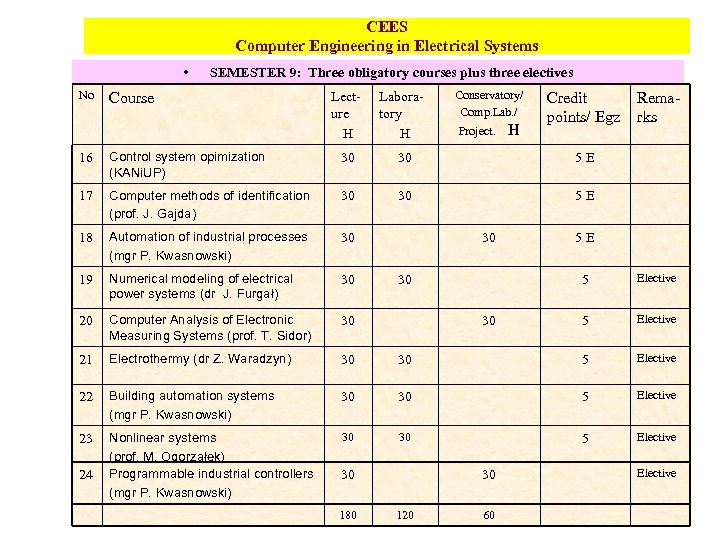
CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems • No SEMESTER 9: Three obligatory courses plus three electives Course Lecture H Laboratory H Conservatory/ Comp. Lab. / Project. H Credit points/ Egz 16 Control system opimization (KANi. UP) 30 30 5 E 17 Computer methods of identification (prof. J. Gajda) 30 30 5 E 18 Automation of industrial processes (mgr P. Kwasnowski) 30 19 Numerical modeling of electrical power systems (dr J. Furgał) 30 20 Computer Analysis of Electronic Measuring Systems (prof. T. Sidor) 30 21 Electrothermy (dr Z. Waradzyn) 30 22 Building automation systems (mgr P. Kwasnowski) 23 Nonlinear systems (prof. M. Ogorzałek) Programmable industrial controllers (mgr P. Kwasnowski) Remarks 24 30 5 E 5 Elective 5 Elective 30 30 30 180 30 120 60 Elective
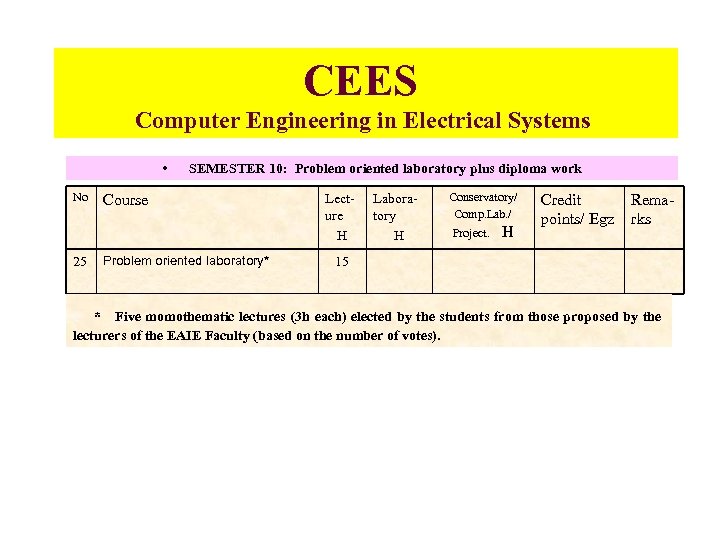
CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems • No 25 SEMESTER 10: Problem oriented laboratory plus diploma work Course Problem oriented laboratory* Lecture H Laboratory H Conservatory/ Comp. Lab. / Project. H Credit points/ Egz Remarks 15 * Five momothematic lectures (3 h each) elected by the students from those proposed by the lecturers of the EAIE Faculty (based on the number of votes).

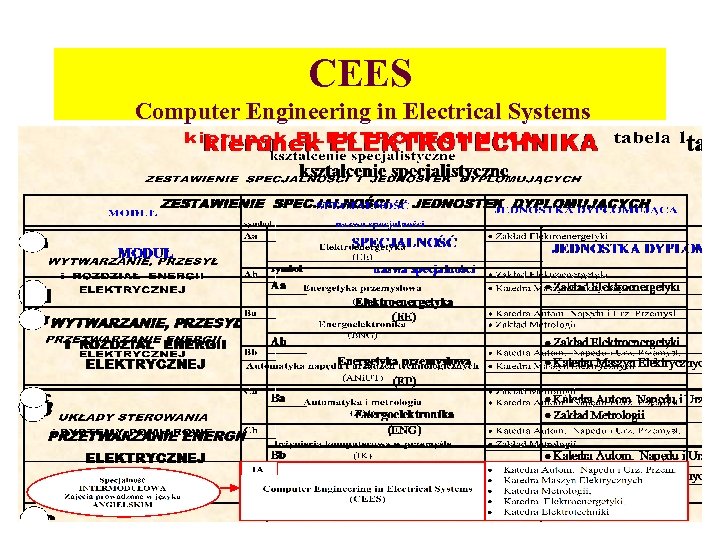
CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems • • • AGH University of Science and Technology (AGH-UST), Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Automatics, Computer Science and Electronics (EAIE), Al. Mickiewicza 30, 30 -059 Krakow, Poland • Regulations for the foreign language specialization of Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems (CEES) • General information • • The studies in the English language within the specialization of CEES last 4 semesters and are carried: • 1. Within the unified studies (SJ) of Electrical Engineering, in successive 7 th , 8 th, 9 th and 10 th semesters. • 2. Within the master-degree complementary studies (SUM), in successive 1 st , 2 nd , 3 rd and 4 th semesters. • • Remark: the CEES specialization within the SJ and SUM studies are carried along the same plane and program of the studies, whereby semester 7 th within the SJ studies coincide with the semester 1 st of the SUM studies.

CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems • 3. For the CEES specialization, carried within the SJ studies mentioned in paragraph 1, the following candidates can be qualified: • a. Polish nationals who have completed the engineering (i. e. bachelor-degree) studies of Electrical Engineering and are in possession of the diploma testifying completion of these studies, b. Polish nationals who have completed the engineering (i. e. bachelor-degree) studies of other specialization or line of studies, close to Electrical Engineering, what can be concluded from the diploma and relevant certificate e. g. in the form of diploma supplement (see also paragraph 8). c. students studding Electrical Engineering, at the EAIE Faculty of the AGH University of Science and Technology, after completion of the 6 th semester, d. students of other lines of studies, carried in the form of unified studies SJ at the EAIE Faculty of AGH-UST (see also paragraph 8), e. foreigners, being in possession of appropriate diploma of completion of the 1 st-degree (bachelor-degree) studies of Electrical Engineering, • foreigners, who are studying Electrical Engineering and wish to continue their studies at the AGH-UST, and have thus far gathered at least 180 ETCS points of basic and specializing courses defined in the educational standards for Electrical Engineering.

CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems • • Language requirements 4. The candidate for the studies within the CEES specialization should be in possession of advanced command of the English language, both in writing and speaking, so as to be able to understand lectures, actively take part in tutorial, laboratory and seminar exercises, prepare writing reports of exercises, pass writing exams as well as answer questions both during exercises and examination procedure. The application form of the candidate should be attached by the declaration of the language knowledge of the following form: I declare that my command of the English language fulfills the demands defined in the Regulations for the CEES specialization. All the consequences of not fulfilling the above criteria, up to excluding from the CEES specialization, fall exclusively on the student.

CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems • • • Particular requirements 5. Application form for the specialization of CEES should be handed in to the pro-dean catering for Electrical Engineering, not later than on 15 th May of each calendar year. 6. Students of Electrical Engineering and other lines of studies carried as unified studies at the EAIE Faculty of the AGH-UST, hand in the application form during the 6 th semester, not later than on 15 th May of each calendar year. 7. The decision about qualification of the student is taken by the pro-dean catering for Electrical Engineering, not later than on 15 th June of each calendar year. 8. With respect to the candidates mentioned in paragraphs 3 b and 3 d, the prodean catering for Electrical Engineering may find some program differences and may specify the making up conditions.

CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems • • • Diploma work, completion of studies 9. The diploma work should be prepared in the English language. Presentation of the work, its defense and diploma examination are carried in the English language. Completion of the CEES specialization is certified by the diploma of receiving the title (grade) of master engineer in Electrical Engineering. The fact of studying in the English language as well as the subject scope of completed studies remains notified in the diploma supplement.

CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems • • • Finansing 10. The level of gratifying the employees for teaching in the English language is determined by the dean in compliance with the rules issued by the ministry of National Education. 11. The costs of attending the courses resulting from program differences are covered by the student. The level of the payment contributed by the student is defined by the pro-dean catering for Electrical Engineering, in compliance with the quotas established by the rector.

CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems • • • Others
CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems
CEES Computer Engineering in Electrical Systems
Electrical Machines and Micromachines • • • • · Single phase and three phase transformers: equivalent circuits, steady-state equations, phasor diagrams. · Three phase synchronous machines: Park’s transform and equivalent circuits, steady-state equations, phasor diagrams, synchronization, reactive power control. · Induction machines: squirrel cage and slip ring rotor, torque-speed characteristics, starting up, speed control, · Two-phase servo induction motors. · Single-phase capacitor motors. · Commutator machines: shunt-connected DC machines, series-connected DC machines, ac-commutator machines, dc-brushless micromachines. · Stepper motors: permanent-magnet, variable-reluctance and hybrid steppers, unipolar and bipolar supply, damping of commutation overvoltages, full-step and half-step operation, · DC and AC tachometers. · Resolvers. · Selsyns, including transformer link. · Static converters for driving systems: power electronics elements, controlled rectifiers, inverters, cycloconverters. Laboratory: · Calculations of transformers’ parameters and characteristics. · Calculations of torque, currents power and reactive power of synchronous machines. · Calculations of torque and currents of induction machines. · Calculations of torque and currents of dc and ac commutator machines.

Engineering programming in Visual C++ • • • • • • • · Visual C++ environment: App. Wizard, App. Studio, Class. Wizard. Creating applications. · Functions, strings, pointers, references, tables, function name overloading. · Memory allocation: operators new and delete. · Classes: member variables and functions. Constructor and destructor. · Loops: for, do and do-while. Condition instruction if and the switch. · Inheritance. Public, private and protected variables. Directive #include. · Logical and bit-wise “and” and “or’. Defining single-argument operators. · Creating SDI applications: classes Cmy. App, CMain. Frame, Cmy. Doc and Cmy. View. · Adding own classes and communication between various classes. · Function On. Drawing rectangles ellipses and inscriptions. Color adjustment. · Initializing of classes in On. Initial. Update. · Buttons and Create function. Creating bitmap resources and covering buttons. · Use of class CPtr. Array for storing data in Cmy. Doc. · Use of CFile. Dialog and CFile to read from or write to external files. · Adding and editing icons for Toolbar. Writing to title bar. · Serving COMMAND and UPDATE_COMAND_UI commands. · Massage maps. Class CArchive and serialization. · Serving keyboard and mouse. Functions Capture, Release. Capture and Clip. Cursor. · Printing and Print. Preview. Print engine. Logical and device coordinates. · Resizing, mapping and translating window’s and viewport’s origins. · Device Context, compatible Device. Context and compatible Bitmap. · Use of functions Bit. Blt and Stretch. Blt. · Adding new menu and new menu items. Serving notification messages. · Dialog boxes, Tab controls. Selecting graphical objects. · Passing text and bitmaps to clipboard. Reading text or bitmap form clipboard. · Registering with Windows user’s clipboard format. · Storing graphics in enhanced metafile format. · Application SDI with two views in split window: drawing pane and edit pane.
8c47dc6f7da461291c7e1fa2e82233ff.ppt