ANTITRUST POLICY & REGULATION Instructor: Zhanar Dessyupova, MPA


















22852-week_2_antitrust.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 ANTITRUST POLICY & REGULATION Instructor: Zhanar Dessyupova, MPA
ANTITRUST POLICY & REGULATION Instructor: Zhanar Dessyupova, MPA
 Major topics Antitrust defined The history of Antitrust laws Examples of antitrust cases Exemptions from antitrust regulation
Major topics Antitrust defined The history of Antitrust laws Examples of antitrust cases Exemptions from antitrust regulation
 Questions? What is Competition? What is Trust? What is Monopoly? What is Oligopoly? What is Antitrust laws?
Questions? What is Competition? What is Trust? What is Monopoly? What is Oligopoly? What is Antitrust laws?
 Industrial organization Economic analysis of the market is based on 3 key concepts: 1) Structure (concentration, product differentiation, entry barriers) 2) Conduct (or behavior) 3) Performance
Industrial organization Economic analysis of the market is based on 3 key concepts: 1) Structure (concentration, product differentiation, entry barriers) 2) Conduct (or behavior) 3) Performance
 Structure Concentration – number of firms in the market and how sales are distributed among them Product differentiation – a strategy in which one firm product is distinguished from competing products by means of its design, services, quality, location, etc Entry barriers – describe the ease with which a new firm can enter an industry
Structure Concentration – number of firms in the market and how sales are distributed among them Product differentiation – a strategy in which one firm product is distinguished from competing products by means of its design, services, quality, location, etc Entry barriers – describe the ease with which a new firm can enter an industry
 Conduct Conduct refers to decisions made by firms in regard of price, quantity, advertising, research and development, etc 2 states of conduct: competition and collusion Explicit collusion – when firm form a cartel Tacit collusion – achievement of mutual understanding without open communication
Conduct Conduct refers to decisions made by firms in regard of price, quantity, advertising, research and development, etc 2 states of conduct: competition and collusion Explicit collusion – when firm form a cartel Tacit collusion – achievement of mutual understanding without open communication
 Performance Efficiency – allocation of resources within given state of technology Technical progress – an efficiency with which an industry develop new and better production methods and products
Performance Efficiency – allocation of resources within given state of technology Technical progress – an efficiency with which an industry develop new and better production methods and products
 ANTITRUST POLICY AND REGULATION Antitrust Policy – laws and government actions to promote competition and prevent monopoly Competition should be primary mechanism to produce good economic results
ANTITRUST POLICY AND REGULATION Antitrust Policy – laws and government actions to promote competition and prevent monopoly Competition should be primary mechanism to produce good economic results
 THE ANTITRUST LAWS Historical Background Trusts – dominant firms during the 1870-80s formed several industries controlled by a single decision group (Monopoly) Monopoly Pricing seeks to maximize revenue by producing less output at higher prices Regulatory Agencies created to control: Natural Monopolies
THE ANTITRUST LAWS Historical Background Trusts – dominant firms during the 1870-80s formed several industries controlled by a single decision group (Monopoly) Monopoly Pricing seeks to maximize revenue by producing less output at higher prices Regulatory Agencies created to control: Natural Monopolies
 THE ANTITRUST LAWS Sherman Act of 1890 Section 1 - Restraint of Trade illegal Section 2 – Monopolization is a Felony Treble Damages – 3x damage award
THE ANTITRUST LAWS Sherman Act of 1890 Section 1 - Restraint of Trade illegal Section 2 – Monopolization is a Felony Treble Damages – 3x damage award
 THE ANTITRUST LAWS Clayton Act of 1914 Section 2 - Price Discrimination illegal if not justified on costs differences and when it reduces competition Section 3 - Tying Contracts illegal when one needs to buy another product as a condition of obtaining desired products
THE ANTITRUST LAWS Clayton Act of 1914 Section 2 - Price Discrimination illegal if not justified on costs differences and when it reduces competition Section 3 - Tying Contracts illegal when one needs to buy another product as a condition of obtaining desired products
 THE ANTITRUST LAWS Clayton Act of 1914 Section 7 – Stock Ownership of other firms illegal if it results in less competition Section 8 – Interlocking Directorates, situations where a director of one firms is also a board member of a competing firm – in large corporations where the effect would be a reduction of competition
THE ANTITRUST LAWS Clayton Act of 1914 Section 7 – Stock Ownership of other firms illegal if it results in less competition Section 8 – Interlocking Directorates, situations where a director of one firms is also a board member of a competing firm – in large corporations where the effect would be a reduction of competition
 THE ANTITRUST LAWS Federal Trade Commission Act of 1914 Established FTC Holds Hearings on Complaints
THE ANTITRUST LAWS Federal Trade Commission Act of 1914 Established FTC Holds Hearings on Complaints
 Celler-Kefauver Act of 1950 Strengthened Clayton Act Regarding Asset Ownership in Competing Firms Anticompetitive Mergers Illegal No Matter How Accomplished THE ANTITRUST LAWS
Celler-Kefauver Act of 1950 Strengthened Clayton Act Regarding Asset Ownership in Competing Firms Anticompetitive Mergers Illegal No Matter How Accomplished THE ANTITRUST LAWS
 THE ANTITRUST LAWS Issues of Interpretation Monopoly Behavior vs. Structure Standard Oil Case - 1911 U.S. Steel Case – 1920 Rule of Reason Alcoa Case - 1945 The Relevant Market Du Pont Cellophane Case (innocent – flexible packaging materials)
THE ANTITRUST LAWS Issues of Interpretation Monopoly Behavior vs. Structure Standard Oil Case - 1911 U.S. Steel Case – 1920 Rule of Reason Alcoa Case - 1945 The Relevant Market Du Pont Cellophane Case (innocent – flexible packaging materials)
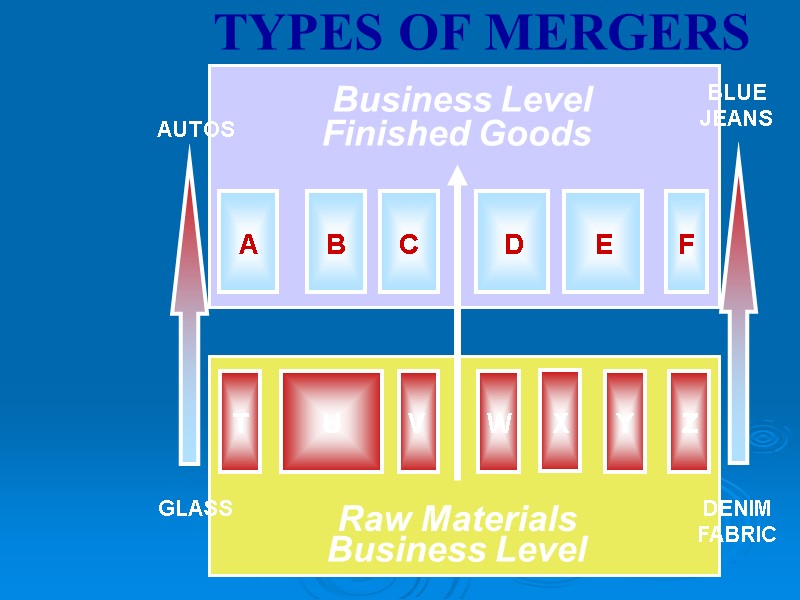
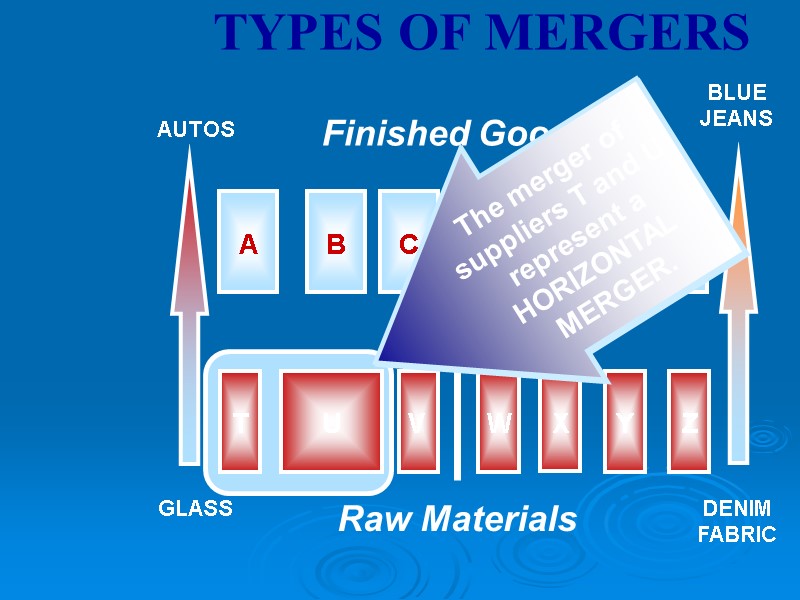
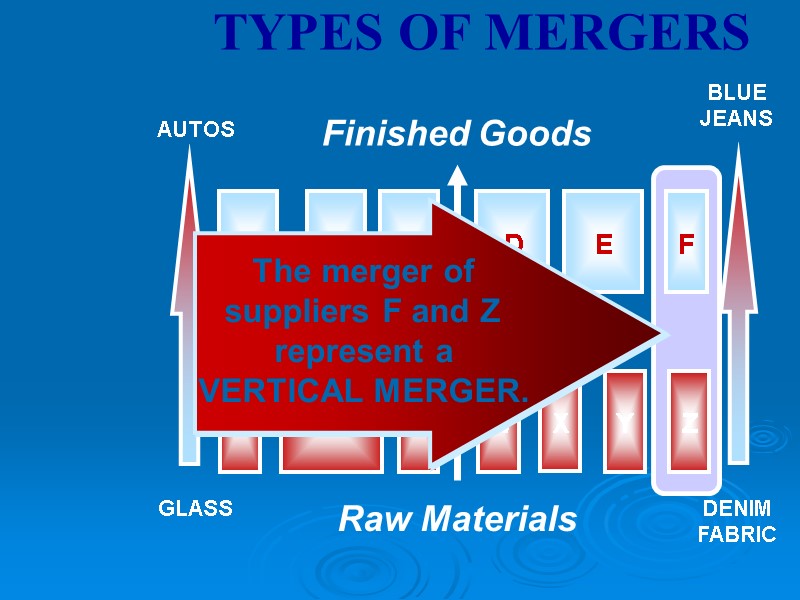
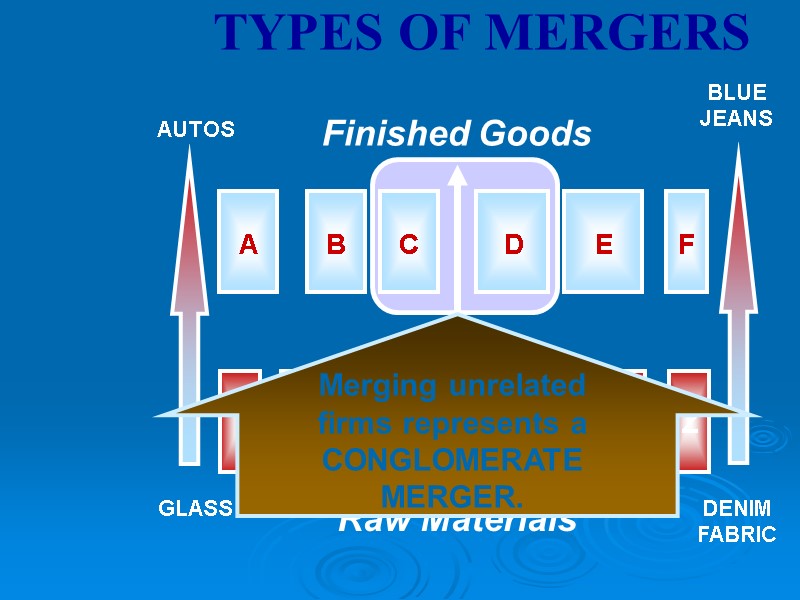
 THE ANTITRUST LAWS Effectiveness of Antitrust Monopoly – Microsoft Case Mergers Merger Types Horizontal Merger Vertical Merger Conglomerate Merger Price Fixing Tying Contracts
THE ANTITRUST LAWS Effectiveness of Antitrust Monopoly – Microsoft Case Mergers Merger Types Horizontal Merger Vertical Merger Conglomerate Merger Price Fixing Tying Contracts
 Raw Materials Finished Goods TYPES OF MERGERS AUTOS GLASS BLUE JEANS DENIM FABRIC
Raw Materials Finished Goods TYPES OF MERGERS AUTOS GLASS BLUE JEANS DENIM FABRIC
 Raw Materials Finished Goods TYPES OF MERGERS AUTOS GLASS BLUE JEANS DENIM FABRIC
Raw Materials Finished Goods TYPES OF MERGERS AUTOS GLASS BLUE JEANS DENIM FABRIC
 Raw Materials Finished Goods TYPES OF MERGERS AUTOS GLASS BLUE JEANS DENIM FABRIC
Raw Materials Finished Goods TYPES OF MERGERS AUTOS GLASS BLUE JEANS DENIM FABRIC
 Raw Materials Finished Goods TYPES OF MERGERS AUTOS GLASS BLUE JEANS DENIM FABRIC
Raw Materials Finished Goods TYPES OF MERGERS AUTOS GLASS BLUE JEANS DENIM FABRIC
 Exemptions from Antitrust Congress has granted certain industries and business activities exemptions: Labor unions Export associations Agricultural cooperatives Regulated industries Professional sport teams Joint research and development ventures
Exemptions from Antitrust Congress has granted certain industries and business activities exemptions: Labor unions Export associations Agricultural cooperatives Regulated industries Professional sport teams Joint research and development ventures

