ad2483ee6969831fbc1aad377f6e388f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Anode + Cathode = Electrolysis Finished : 8 a-class students Kazakh-Turkish schools Amanzhan Alikhan and Bagyt Bekzat Teacher: Physics teacher Enes bey
Anode + Cathode = Electrolysis Finished : 8 a-class students Kazakh-Turkish schools Amanzhan Alikhan and Bagyt Bekzat Teacher: Physics teacher Enes bey
 Цель работы: Explore the essence of the electrolysis process and find the area of its application.
Цель работы: Explore the essence of the electrolysis process and find the area of its application.
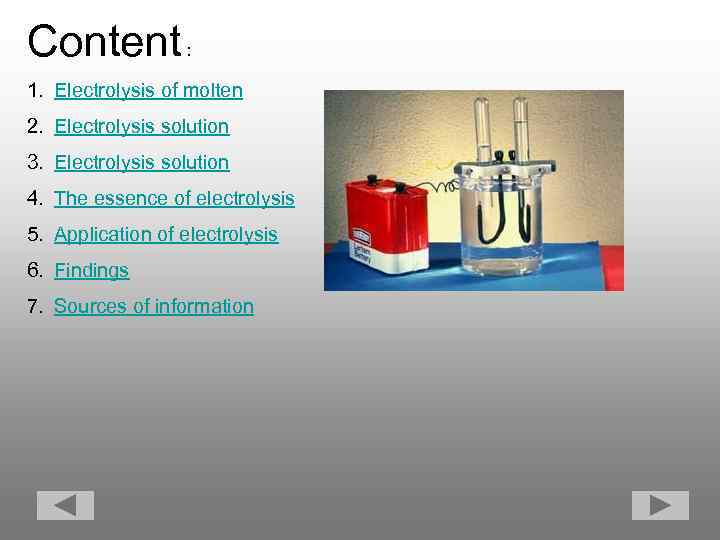 Content : 1. Electrolysis of molten 2. Electrolysis solution 3. Electrolysis solution 4. The essence of electrolysis 5. Application of electrolysis 6. Findings 7. Sources of information
Content : 1. Electrolysis of molten 2. Electrolysis solution 3. Electrolysis solution 4. The essence of electrolysis 5. Application of electrolysis 6. Findings 7. Sources of information
 Electrolysis of molten If table salt to melt , it will split into ions of the crystal lattice. In this form the sodium cations and anions of chlorine Na. CI -> Na + + CI Omit the melt electrodes constant electric current. Heading toward the cathode , the sodium cation with a receiving one electron , i. e. is restored : Na + + ē -> Na 0 Cathode , where there is a constant excess of electrons , is a reducing agent. By the anode is directed chlorine anion. Since the anode constant lack of electrons , chlorine ion donates an electron , becoming a neutral atom , oxidized : Cl-- ē -> Cl 0 Anode , where permanent lack of electrons , is an oxidant. 2 Na. Cl -> 2 Na + Cl 2 ELECTROLYSIS - redox process occurring under the influence of an electric current.
Electrolysis of molten If table salt to melt , it will split into ions of the crystal lattice. In this form the sodium cations and anions of chlorine Na. CI -> Na + + CI Omit the melt electrodes constant electric current. Heading toward the cathode , the sodium cation with a receiving one electron , i. e. is restored : Na + + ē -> Na 0 Cathode , where there is a constant excess of electrons , is a reducing agent. By the anode is directed chlorine anion. Since the anode constant lack of electrons , chlorine ion donates an electron , becoming a neutral atom , oxidized : Cl-- ē -> Cl 0 Anode , where permanent lack of electrons , is an oxidant. 2 Na. Cl -> 2 Na + Cl 2 ELECTROLYSIS - redox process occurring under the influence of an electric current.
 Electrolysis-redox process that occurs at the electrodes during the passage of electric current through the electrolyte solution or melt. At the cathode (-)-reconstitution At the anode (+)-oxidation Examples electrolysis melts: For inactive metal salts and acids anoxic (Cu. Cl 2) electrolysis solution and salt melt the same. Li+, K+, Ca 2+, Na+, Mg 2+, Al 3+, Zn 2+, Cr 3+, Fe 2+, Ni 2+, Sn 2+, Pb 2+, H+, Cu 2+, Hg 2+, Ag+, Pt 4+, Au 3+. Increased oxidative activity of ions F-, NO 3 -, SO 42 -, OH-, Cl-, Br-, I-, S 2 Увеличение восстановительной активности ионов
Electrolysis-redox process that occurs at the electrodes during the passage of electric current through the electrolyte solution or melt. At the cathode (-)-reconstitution At the anode (+)-oxidation Examples electrolysis melts: For inactive metal salts and acids anoxic (Cu. Cl 2) electrolysis solution and salt melt the same. Li+, K+, Ca 2+, Na+, Mg 2+, Al 3+, Zn 2+, Cr 3+, Fe 2+, Ni 2+, Sn 2+, Pb 2+, H+, Cu 2+, Hg 2+, Ag+, Pt 4+, Au 3+. Increased oxidative activity of ions F-, NO 3 -, SO 42 -, OH-, Cl-, Br-, I-, S 2 Увеличение восстановительной активности ионов
 Electrolysis solution In aqueous solutions , the process acquires a number of features , as it involves water. In solution , addition salt dissociation occurs very weak dissociation of water. Na. CI -> Na + + CI H 2 O -> H + + OH Thus, the solution formed two kinds of cations (Na + and H +) and two kinds of anions (CI- and OH-). In the series of metals sodium hydrogen is worth much more to the left. Therefore, regenerative properties of the sodium atom is stronger than a hydrogen atom. But oxidative properties of Na + ion exhibits much weaker than the ion H +, therefore at the cathode will not recover sodium metal and hydrogen; 2 H 2 O + 2ē -> H 2 + 2 OH The sodium ions in the solution will be so long as to discharge completely by hydrogen ions. Be directed towards the anode and anions are CI- OH-, restorative properties which also vary (see anions number arranged in order of increasing the ability to oxidation ). CI- anions are oxidized more easily than OH-, therefore, the anode process will take place : CI-- ē → CI 0
Electrolysis solution In aqueous solutions , the process acquires a number of features , as it involves water. In solution , addition salt dissociation occurs very weak dissociation of water. Na. CI -> Na + + CI H 2 O -> H + + OH Thus, the solution formed two kinds of cations (Na + and H +) and two kinds of anions (CI- and OH-). In the series of metals sodium hydrogen is worth much more to the left. Therefore, regenerative properties of the sodium atom is stronger than a hydrogen atom. But oxidative properties of Na + ion exhibits much weaker than the ion H +, therefore at the cathode will not recover sodium metal and hydrogen; 2 H 2 O + 2ē -> H 2 + 2 OH The sodium ions in the solution will be so long as to discharge completely by hydrogen ions. Be directed towards the anode and anions are CI- OH-, restorative properties which also vary (see anions number arranged in order of increasing the ability to oxidation ). CI- anions are oxidized more easily than OH-, therefore, the anode process will take place : CI-- ē → CI 0
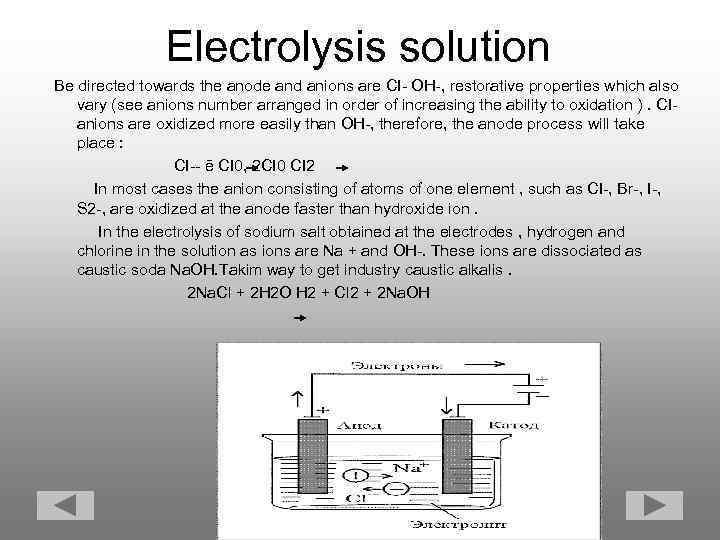 Electrolysis solution Be directed towards the anode and anions are CI- OH-, restorative properties which also vary (see anions number arranged in order of increasing the ability to oxidation ). CI- anions are oxidized more easily than OH-, therefore, the anode process will take place : CI-- ē CI 0, 2 CI 0 CI 2 In most cases the anion consisting of atoms of one element , such as CI-, Br-, I-, S 2 -, are oxidized at the anode faster than hydroxide ion. In the electrolysis of sodium salt obtained at the electrodes , hydrogen and chlorine in the solution as ions are Na + and OH-. These ions are dissociated as caustic soda Na. OH. Takim way to get industry caustic alkalis. 2 Na. Cl + 2 H 2 O H 2 + Cl 2 + 2 Na. OH
Electrolysis solution Be directed towards the anode and anions are CI- OH-, restorative properties which also vary (see anions number arranged in order of increasing the ability to oxidation ). CI- anions are oxidized more easily than OH-, therefore, the anode process will take place : CI-- ē CI 0, 2 CI 0 CI 2 In most cases the anion consisting of atoms of one element , such as CI-, Br-, I-, S 2 -, are oxidized at the anode faster than hydroxide ion. In the electrolysis of sodium salt obtained at the electrodes , hydrogen and chlorine in the solution as ions are Na + and OH-. These ions are dissociated as caustic soda Na. OH. Takim way to get industry caustic alkalis. 2 Na. Cl + 2 H 2 O H 2 + Cl 2 + 2 Na. OH
 Electrolysis of water is always performed in the presence of an inert electrolyte (to increase the conductivity of the electrolyte is very weak - water) Depending inert electrolyte electrolysis is carried out in a neutral, acidic or alkaline environment. When choosing an inert electrolyte, be aware that never reduced at the cathode in an aqueous solution with metal cations, which are typical reducing agents (eg Li +, Cs +, K +, Ca 2 +, Na +, Mg 2 +, Al 3 +) and never oxidized at the anode oxygen O-II anion oxo acid element with the highest degree of oxidation (eg Cl. O 4 -, SO 42 -, NO 3 -, PO 43 -, CO 32 -, Si. O 44 -, Mn. O 4 -), instead oxidized water
Electrolysis of water is always performed in the presence of an inert electrolyte (to increase the conductivity of the electrolyte is very weak - water) Depending inert electrolyte electrolysis is carried out in a neutral, acidic or alkaline environment. When choosing an inert electrolyte, be aware that never reduced at the cathode in an aqueous solution with metal cations, which are typical reducing agents (eg Li +, Cs +, K +, Ca 2 +, Na +, Mg 2 +, Al 3 +) and never oxidized at the anode oxygen O-II anion oxo acid element with the highest degree of oxidation (eg Cl. O 4 -, SO 42 -, NO 3 -, PO 43 -, CO 32 -, Si. O 44 -, Mn. O 4 -), instead oxidized water
 Examples of electrolysis of salt solutions: anions are oxidized at the anode, Cl, O oxygen instead of water molecules as the electronegativity of the chlorine is less than the oxygen and, consequently, chloro donates electrons more easily than oxygen cations on the cathode recovered Cu, rather than the water molecules, hydrogen H, as copper is the right to hydrogen in the electrochemical series, i. e. receives electrons easier than H in water
Examples of electrolysis of salt solutions: anions are oxidized at the anode, Cl, O oxygen instead of water molecules as the electronegativity of the chlorine is less than the oxygen and, consequently, chloro donates electrons more easily than oxygen cations on the cathode recovered Cu, rather than the water molecules, hydrogen H, as copper is the right to hydrogen in the electrochemical series, i. e. receives electrons easier than H in water
 The essence of electrolysis To carry out the electrolysis to the negative pole of the external DC source is coupled cathode to the positive terminal and - an anode and then immerse them in an electrolytic cell with an electrolyte solution or melt As a result of the electrolysis at the electrodes (cathode and anode) are allocated corresponding to the oxidation and reduction products, in which, depending on the conditions may react with the solvent material of the electrode, etc. , so-called secondary processes
The essence of electrolysis To carry out the electrolysis to the negative pole of the external DC source is coupled cathode to the positive terminal and - an anode and then immerse them in an electrolytic cell with an electrolyte solution or melt As a result of the electrolysis at the electrodes (cathode and anode) are allocated corresponding to the oxidation and reduction products, in which, depending on the conditions may react with the solvent material of the electrode, etc. , so-called secondary processes
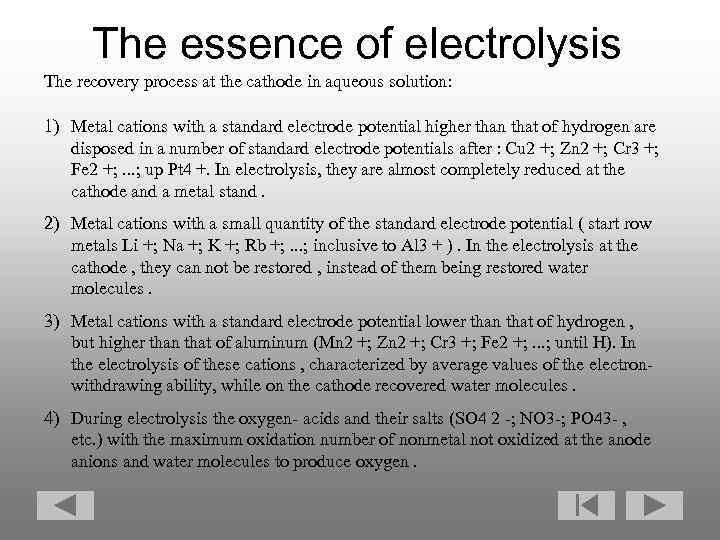 The essence of electrolysis The recovery process at the cathode in aqueous solution: 1) Metal cations with a standard electrode potential higher than that of hydrogen are disposed in a number of standard electrode potentials after : Cu 2 +; Zn 2 +; Cr 3 +; Fe 2 +; . . . ; up Pt 4 +. In electrolysis, they are almost completely reduced at the cathode and a metal stand. 2) Metal cations with a small quantity of the standard electrode potential ( start row metals Li +; Na +; K +; Rb +; . . . ; inclusive to Al 3 + ). In the electrolysis at the cathode , they can not be restored , instead of them being restored water molecules. 3) Metal cations with a standard electrode potential lower than that of hydrogen , but higher than that of aluminum (Mn 2 +; Zn 2 +; Cr 3 +; Fe 2 +; . . . ; until H). In the electrolysis of these cations , characterized by average values of the electronwithdrawing ability, while on the cathode recovered water molecules. 4) During electrolysis the oxygen- acids and their salts (SO 4 2 -; NO 3 -; PO 43 - , etc. ) with the maximum oxidation number of nonmetal not oxidized at the anode anions and water molecules to produce oxygen.
The essence of electrolysis The recovery process at the cathode in aqueous solution: 1) Metal cations with a standard electrode potential higher than that of hydrogen are disposed in a number of standard electrode potentials after : Cu 2 +; Zn 2 +; Cr 3 +; Fe 2 +; . . . ; up Pt 4 +. In electrolysis, they are almost completely reduced at the cathode and a metal stand. 2) Metal cations with a small quantity of the standard electrode potential ( start row metals Li +; Na +; K +; Rb +; . . . ; inclusive to Al 3 + ). In the electrolysis at the cathode , they can not be restored , instead of them being restored water molecules. 3) Metal cations with a standard electrode potential lower than that of hydrogen , but higher than that of aluminum (Mn 2 +; Zn 2 +; Cr 3 +; Fe 2 +; . . . ; until H). In the electrolysis of these cations , characterized by average values of the electronwithdrawing ability, while on the cathode recovered water molecules. 4) During electrolysis the oxygen- acids and their salts (SO 4 2 -; NO 3 -; PO 43 - , etc. ) with the maximum oxidation number of nonmetal not oxidized at the anode anions and water molecules to produce oxygen.
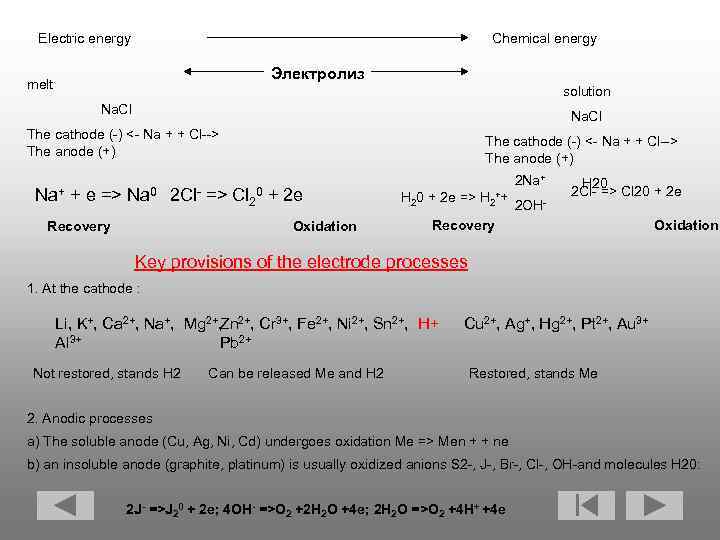 Electric energy Chemical energy Электролиз melt solution Na. Cl The cathode (-) <- Na + + Cl--> The anode (+) Na+ + e => Na 0 The cathode (-) <- Na + + Cl--> The anode (+) 2 Cl- => Cl 20 + 2 e Recovery Oxidation 2 Na+ H 20 2 Cl- => Cl 20 + 2 e H 20 + 2 e => H 2++ 2 OHRecovery Oxidation Key provisions of the electrode processes 1. At the cathode : Li, K+, Ca 2+, Na+, Mg 2+, Cr 3+, Fe 2+, Ni 2+, Sn 2+, H+ Zn 3+ Al Pb 2+ Not restored, stands H 2 Can be released Me and H 2 Cu 2+, Ag+, Hg 2+, Pt 2+, Au 3+ Restored, stands Me 2. Anodic processes a) The soluble anode (Cu, Ag, Ni, Cd) undergoes oxidation Me => Men + + ne b) an insoluble anode (graphite, platinum) is usually oxidized anions S 2 -, J-, Br-, Cl-, OH-and molecules H 20: 2 J- =>J 20 + 2 e; 4 OH- =>O 2 +2 H 2 O +4 e; 2 H 2 O =>O 2 +4 H+ +4 e
Electric energy Chemical energy Электролиз melt solution Na. Cl The cathode (-) <- Na + + Cl--> The anode (+) Na+ + e => Na 0 The cathode (-) <- Na + + Cl--> The anode (+) 2 Cl- => Cl 20 + 2 e Recovery Oxidation 2 Na+ H 20 2 Cl- => Cl 20 + 2 e H 20 + 2 e => H 2++ 2 OHRecovery Oxidation Key provisions of the electrode processes 1. At the cathode : Li, K+, Ca 2+, Na+, Mg 2+, Cr 3+, Fe 2+, Ni 2+, Sn 2+, H+ Zn 3+ Al Pb 2+ Not restored, stands H 2 Can be released Me and H 2 Cu 2+, Ag+, Hg 2+, Pt 2+, Au 3+ Restored, stands Me 2. Anodic processes a) The soluble anode (Cu, Ag, Ni, Cd) undergoes oxidation Me => Men + + ne b) an insoluble anode (graphite, platinum) is usually oxidized anions S 2 -, J-, Br-, Cl-, OH-and molecules H 20: 2 J- =>J 20 + 2 e; 4 OH- =>O 2 +2 H 2 O +4 e; 2 H 2 O =>O 2 +4 H+ +4 e
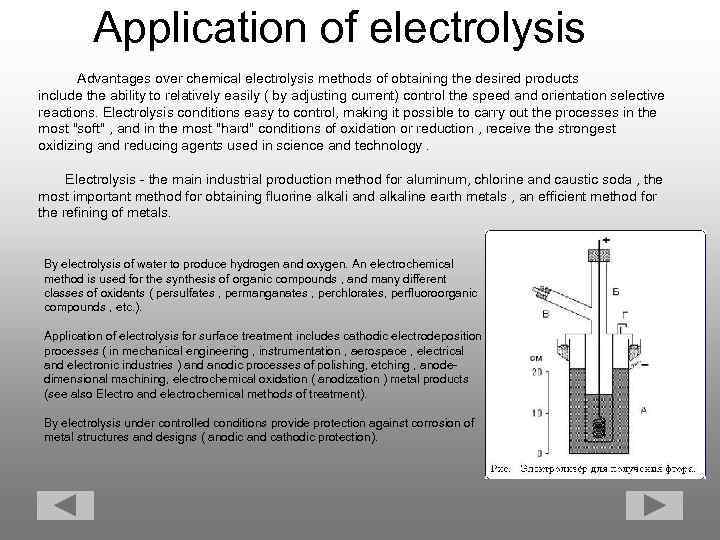 Application of electrolysis Advantages over chemical electrolysis methods of obtaining the desired products include the ability to relatively easily ( by adjusting current) control the speed and orientation selective reactions. Electrolysis conditions easy to control, making it possible to carry out the processes in the most "soft" , and in the most "hard" conditions of oxidation or reduction , receive the strongest oxidizing and reducing agents used in science and technology. Electrolysis - the main industrial production method for aluminum, chlorine and caustic soda , the most important method for obtaining fluorine alkali and alkaline earth metals , an efficient method for the refining of metals. By electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen and oxygen. An electrochemical method is used for the synthesis of organic compounds , and many different classes of oxidants ( persulfates , permanganates , perchlorates, perfluoroorganic compounds , etc. ). Application of electrolysis for surface treatment includes cathodic electrodeposition processes ( in mechanical engineering , instrumentation , aerospace , electrical and electronic industries ) and anodic processes of polishing, etching , anode- dimensional machining, electrochemical oxidation ( anodization ) metal products (see also Electro and electrochemical methods of treatment). By electrolysis under controlled conditions provide protection against corrosion of metal structures and designs ( anodic and cathodic protection).
Application of electrolysis Advantages over chemical electrolysis methods of obtaining the desired products include the ability to relatively easily ( by adjusting current) control the speed and orientation selective reactions. Electrolysis conditions easy to control, making it possible to carry out the processes in the most "soft" , and in the most "hard" conditions of oxidation or reduction , receive the strongest oxidizing and reducing agents used in science and technology. Electrolysis - the main industrial production method for aluminum, chlorine and caustic soda , the most important method for obtaining fluorine alkali and alkaline earth metals , an efficient method for the refining of metals. By electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen and oxygen. An electrochemical method is used for the synthesis of organic compounds , and many different classes of oxidants ( persulfates , permanganates , perchlorates, perfluoroorganic compounds , etc. ). Application of electrolysis for surface treatment includes cathodic electrodeposition processes ( in mechanical engineering , instrumentation , aerospace , electrical and electronic industries ) and anodic processes of polishing, etching , anode- dimensional machining, electrochemical oxidation ( anodization ) metal products (see also Electro and electrochemical methods of treatment). By electrolysis under controlled conditions provide protection against corrosion of metal structures and designs ( anodic and cathodic protection).
 Electrochemical processes are widely used in various fields of modern technology, analytical chemistry, biochemistry, etc. In the chemical industry is prepared by electrolysis of chlorine and fluorine, an alkali, chlorates and perchlorates, persulfates, and persulfuric acid, is chemically pure hydrogen and oxygen, etc. While some substances obtained by reduction at the cathode (aldehydes, aminophenols, etc. ), other electrooxidation at the anode (chlorates, perchlorates, potassium permanganate, etc. ) Electroplating - a field of applied electrochemistry, the process has metal plating on the surface of both metallic and non-metallic products by passing a direct electric current through solutions of their salts. Electroplating is subdivided into the electroplating and electroforming. Electroplating- electrodepositing a metal onto the surface of another metal, which is firmly bound (adhered) to the metal covers (subject) serving as the cathode of the cell. Electroplating-production by electrolysis of accurate, easily detachable metal copies relatively considerable thickness as various non-metallic and metallic objects called matrices. The electroforming is used for applying a relatively thick metal plating of other metals (e. g. , formation of "surface-layer of nickel, silver, gold, etc. ).
Electrochemical processes are widely used in various fields of modern technology, analytical chemistry, biochemistry, etc. In the chemical industry is prepared by electrolysis of chlorine and fluorine, an alkali, chlorates and perchlorates, persulfates, and persulfuric acid, is chemically pure hydrogen and oxygen, etc. While some substances obtained by reduction at the cathode (aldehydes, aminophenols, etc. ), other electrooxidation at the anode (chlorates, perchlorates, potassium permanganate, etc. ) Electroplating - a field of applied electrochemistry, the process has metal plating on the surface of both metallic and non-metallic products by passing a direct electric current through solutions of their salts. Electroplating is subdivided into the electroplating and electroforming. Electroplating- electrodepositing a metal onto the surface of another metal, which is firmly bound (adhered) to the metal covers (subject) serving as the cathode of the cell. Electroplating-production by electrolysis of accurate, easily detachable metal copies relatively considerable thickness as various non-metallic and metallic objects called matrices. The electroforming is used for applying a relatively thick metal plating of other metals (e. g. , formation of "surface-layer of nickel, silver, gold, etc. ).
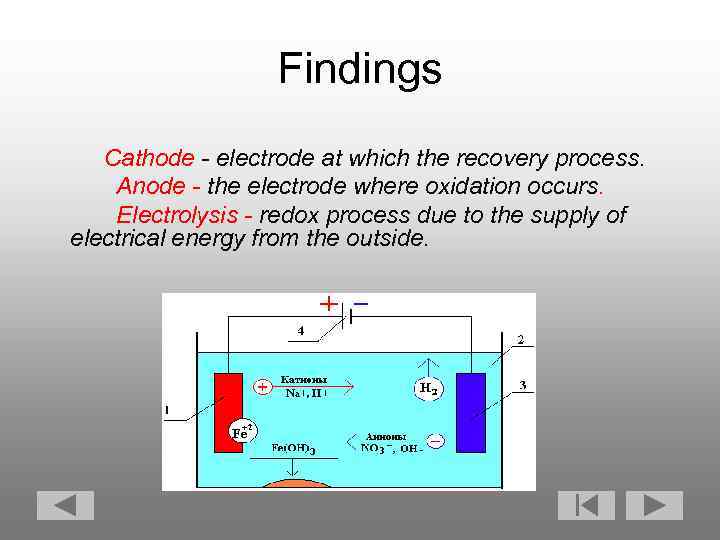 Findings Cathode - electrode at which the recovery process. Anode - the electrode where oxidation occurs. Electrolysis - redox process due to the supply of electrical energy from the outside.
Findings Cathode - electrode at which the recovery process. Anode - the electrode where oxidation occurs. Electrolysis - redox process due to the supply of electrical energy from the outside.


