d56d2bd9a6e00596d442bcb78ce19e8b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Announcements • Dr. Gerald Urquhart • Developed LBS 126

Internet and World Wide Web • Which came first - Internet or WWW?

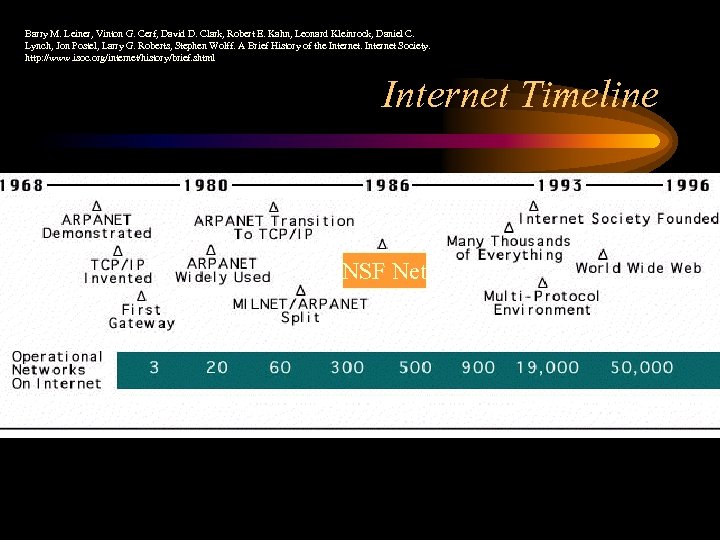
The Internet • Internet is a network of interconnected computers that is now global • Internet born in 1969 - called ARPANET • 1969 ARPANET was connection of computers at UCLA, Stanford, UCSB, Univ. of Utah

State of computers? • What was the state of computers in the late 1960 s and early 1970 s?

Computers late 60 s & 70 s • No Personal Computers – all large mainframe computers in la • Mid 1970 s – initial personal computers – Altair: Box with blinking lights • Late 1970 s – Apple 2, first usable PC

Personal Computing? • Just a box with blinking lights • Not where Networking/ Internet was being developed

Internet - 1970 s • 1972 - Telnet developed as a way to connect to remote computer • 1972 – Email introduced – 1977 - U. Wisconsin has first “large” Email system 100 users • 1973 - ARPANET goes international • 1973 - File Transfer Protocol (FTP) established

State of computers? • What was the state of computers in the early 1980 s?

Computers 1980 s • 1981 – IBM PC • 1984 – Apple Macintosh • 1986 – Modem becomes option on PCs

Internet - 1980 s • 1984 - Domain Name Server introduced – allows naming of hosts, no longer numeric • 1986 - NSFNET created – in 1990, becomes backbone of modern Internet when ARPANET is decommissioned – Completely privatized by 1995 – 56 K interconnection initially, increased rapidly
Barry M. Leiner, Vinton G. Cerf, David D. Clark, Robert E. Kahn, Leonard Kleinrock, Daniel C. Lynch, Jon Postel, Larry G. Roberts, Stephen Wolff. A Brief History of the Internet Society. http: //www. isoc. org/internet/history/brief. shtml Internet Timeline NSF Net

Internet 1990 s • 1991 - Tim Berners-Lee releases World Wide Web! – TBL is computer programmer at CERN, a physics lab in Europe (new book Weaving the Web by TBL) • 1993 - Mosaic (becomes Netscape) designed by graduate students at University of Illinois – first point-and-click browser – later developed into Netscape Navigator • These are the two most significant events in the formation of the WWW

Internet 1990 s • 1991 - Tim Berners-Lee releases World Wide Web! – TBL is computer programmer at CERN, a physics lab in Europe (book Weaving the Web by TBL) • 1993 - Mosaic (becomes Netscape) designed by graduate students at University of Illinois – first point-and-click browser – later developed into Netscape Navigator • These are the two most significant events in the formation of the WWW

World Wide Web • Via Internet, computers can contact each other • Public files on computers can be read by remote user – usually Hyper. Text Markup Language (. html) • URL - Universal Resource Locator - is name of file on a remote computer • http: //www. msu. edu/~urquhar 5/tour/active. html

HTTP • World Wide Web uses HTTP Servers, better known as web server • Receive HTTP type request and send requested file in packets

Web Browsers • Mosaic (1993) was first point-and-click browser • Web browsers are the software we use to view web pages • Netscape Navigator and Internet Explorer are most popular • Netscape Navigator was original, but Microsoft leveraged IE on market

State of computers? • What was the state of computers in the early to mid 1990 s?

Computer History – 1990 s • Windows 95 GUI made computing easier for PC-bound masses • Windows 95 + Internet (AOL, others) Huge increase in number of home PCs • Computer on every desk in workplace

Universal Resource Locator http: //www. msu. edu/~urquhar 5/tour/active. html http: // /~urquhar 5/tour/active. html identifies type of transfer File Location on Remote Computer www. msu. edu Domain Name name of remote computer

21 st Century – File Sharing • Internet allowed sharing of simple information • FTP was initial file sharing system, but a bit hard to use • WWW advanced type of info allowed, but not designed for file-sharing • Napster, Ka. Za. A, Morpheus and Lime. Wire are file-sharing.

Napster • Napster was a music sharing community • Used a central server to catalog who had what • This central server violated music industry’s copyrights • Napster now screens transfers to see if they are copyrighted material

Peer to Peer • • • Peer to Peer (P 2 P) file sharing Lime. Wire is good one Ka. Za. A is faster and more advanced Kazaa Lite is preferred by many Morpheus is modified Ka. Za. A for Music City Network – really messed up these days • Each person has a “node” that advertises his or her files • Supernodes – compile lists of what nodes have

Collapse of the Information Economy • Huge economic growth in late 1990 s was due to “prospecting” on up-and-coming Internet companies • Most were never profitable – Amazon. com just posted its first Annual Profit (2003) since going public in 1997! • Major Internet Backbone Providers (Worldcom, Global Crossing) are struggling

What is WWW? • Via Internet, computers can contact each other • Public files on computers can be read by remote user – usually Hyper. Text Markup Language (. html) • HTTP - Hyper. Text Transfer Protocol • URL - Universal Resource Locator - is name of file on a remote computer • http: //www. msu. edu/~urquhar 5/tour/active. html

How to make a web page • Define the two basic steps required in making a web page.

Two Basic Steps • Create an HTML File • Upload file to server – Saving to P: drive eliminates this step

. html • Web documents are text files with. html extension • These text files have HTML “tags” in them

HTML Tags • Each opening HTML tag has a closing HTML tag that matches it. – <P> for begin paragraph is followed by </P> for end paragraph – <P> goes at beginning of paragraph – </P> goes at end of paragraph

Example of Tags • <P>Here is the paragraph about something</P><P>Here is the second paragraph</P> What it will look like: Here is the paragraph about something. Here is the second paragraph.

Essential HTML Tags • • • <HTML> begins HTML document <BODY> begins body of document <H 1>Here’s a header in big type</H 1> <P>Here’s a paragraph</P> </BODY> ends body </HTML> ends HTML document

Browser Output of Page If you opened that page in Netscape Navigator, it would look like this: http: //www. msu. edu/course/lbs/126/lectures/viewsource. html Here’s a header in big type Here’s a paragraph

View Page Source • Using “View Page Source” allows you to see the HTML behind a page • When we get into advanced HTML pages, this can be really important for learning how someone did something • http: //puffin. bird. audubon. org/

File Transfer Protocol • FTP Program (also called FTP client) used to transfer files from your computer to your public web directory housed on the MSU computers • WS_FTP LE is a good, free FTP program • In MSU Labs, can directly save stuff in your AFS space, on the P: drive, in the web directory

Your personal web space • Http: //www. msu. edu/~pilotname/index. html • Three steps: – Make your pilot web space public (in advanced features) – Create a file named index. html – Use FTP to transfer a file named index. html into your web directory

Netscape Composer • Netscape Composer allows WYSIWYG (what-you-see-is-what-you-get) editing of web pages • Controls similar to Microsoft word – font formatting, colors, etc.

Macromedia Dreamweaver • Excellent Site Building Tool • Allows organization of files, ftp, and WYSIWYG editing all-in-one

Microsoft Front Page • All-in-One program like Dreamweaver • Uses “proprietary tags” that can’t be read by some browsers (Netscape) • Uses non-standard HTML, style sheets, etc
d56d2bd9a6e00596d442bcb78ce19e8b.ppt