animal_gene_eng_Sk2017_full_version.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 79
 Animal gene engineering Practical course Skoltech– RAS Gene Biology Alexei Deikin, Evgeniia Zotova Spring 2017
Animal gene engineering Practical course Skoltech– RAS Gene Biology Alexei Deikin, Evgeniia Zotova Spring 2017
 Why do we need to modify animal genomes? • Fundamental research • Biotechnology • Food industry
Why do we need to modify animal genomes? • Fundamental research • Biotechnology • Food industry
 Which animals are modified and for what purpose?
Which animals are modified and for what purpose?
 Which modifications can be introduced into a genome? • Insertion of gene (knock-in) • Deletion of gene (knock-out) • ? ? ?
Which modifications can be introduced into a genome? • Insertion of gene (knock-in) • Deletion of gene (knock-out) • ? ? ?
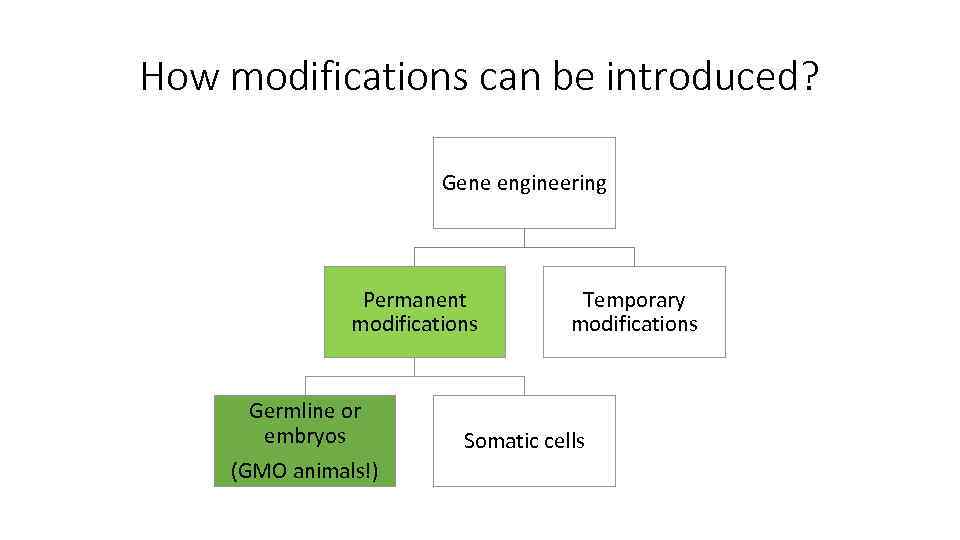 How modifications can be introduced? Gene engineering Permanent modifications Germline or embryos (GMO animals!) Temporary modifications Somatic cells
How modifications can be introduced? Gene engineering Permanent modifications Germline or embryos (GMO animals!) Temporary modifications Somatic cells
 We create GMO animals: Microinjections What and where?
We create GMO animals: Microinjections What and where?
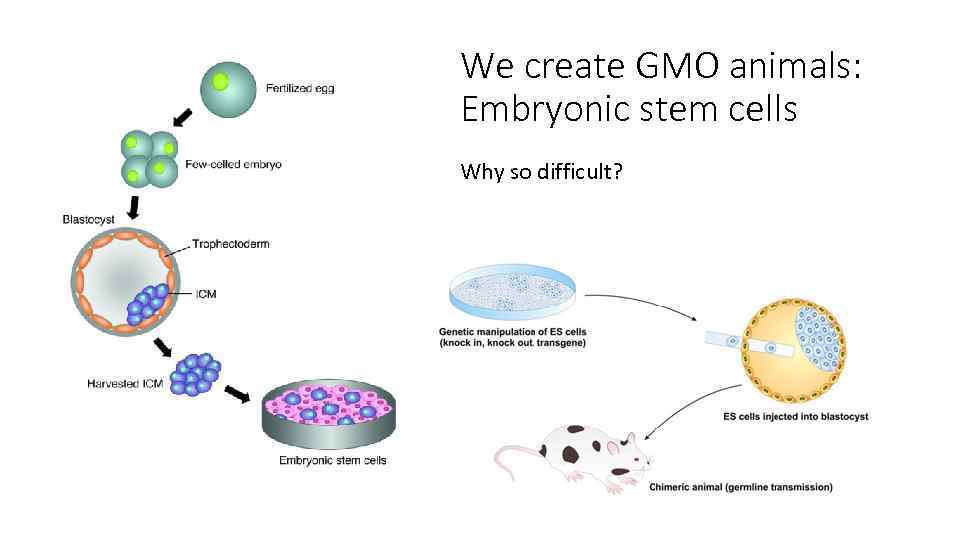 We create GMO animals: Embryonic stem cells Why so difficult?
We create GMO animals: Embryonic stem cells Why so difficult?
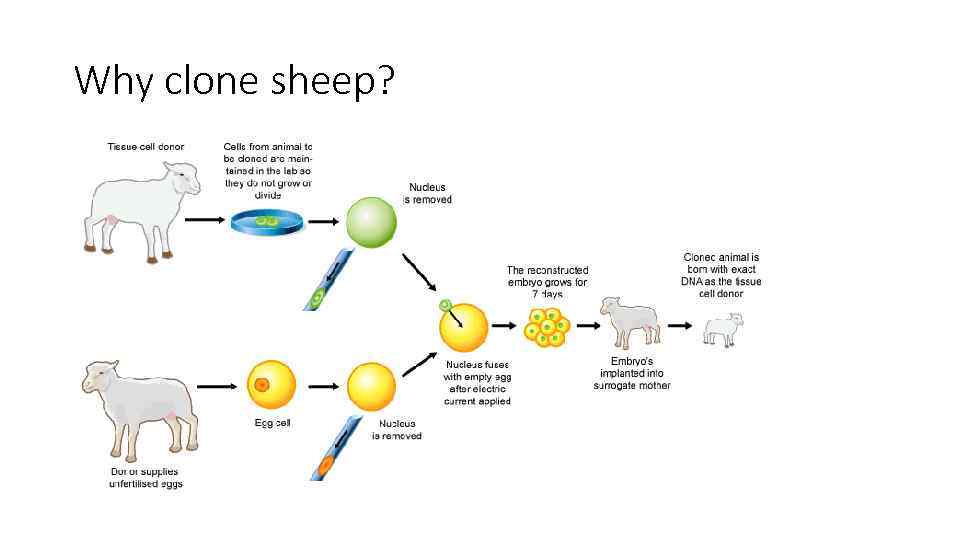 Why clone sheep?
Why clone sheep?
 Difficulties with mammals • Harvest embryos • Put them back in a pseudopregnant female
Difficulties with mammals • Harvest embryos • Put them back in a pseudopregnant female
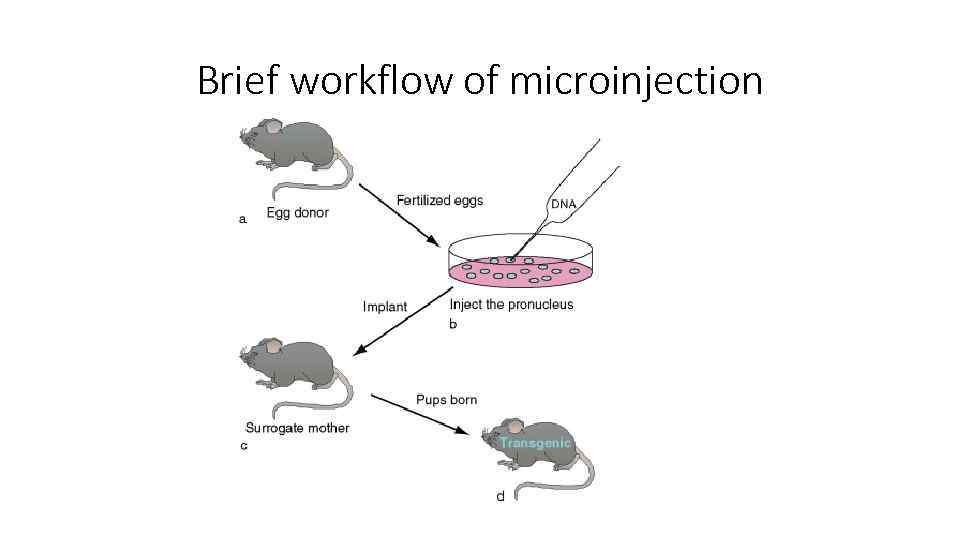 Brief workflow of microinjection
Brief workflow of microinjection
 Practical course • Animal handling • Determine stage of mouse estrous cycle • Harvesting of embryos • Microinjections • Cultivation of embryos • Embryo transfer
Practical course • Animal handling • Determine stage of mouse estrous cycle • Harvesting of embryos • Microinjections • Cultivation of embryos • Embryo transfer
 Practice: Animal handling • Housing • Methods of drug administration • Surgery with anesthesia
Practice: Animal handling • Housing • Methods of drug administration • Surgery with anesthesia
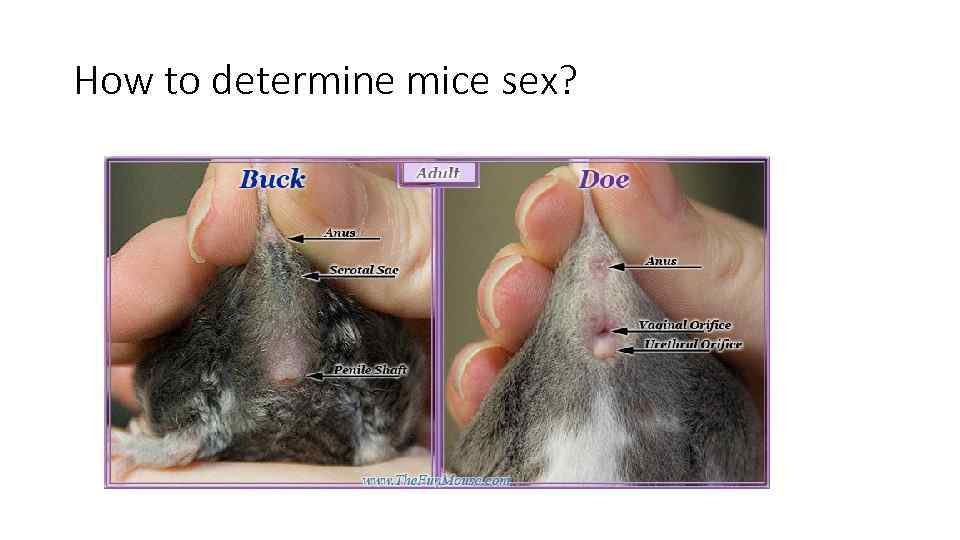 How to determine mice sex?
How to determine mice sex?
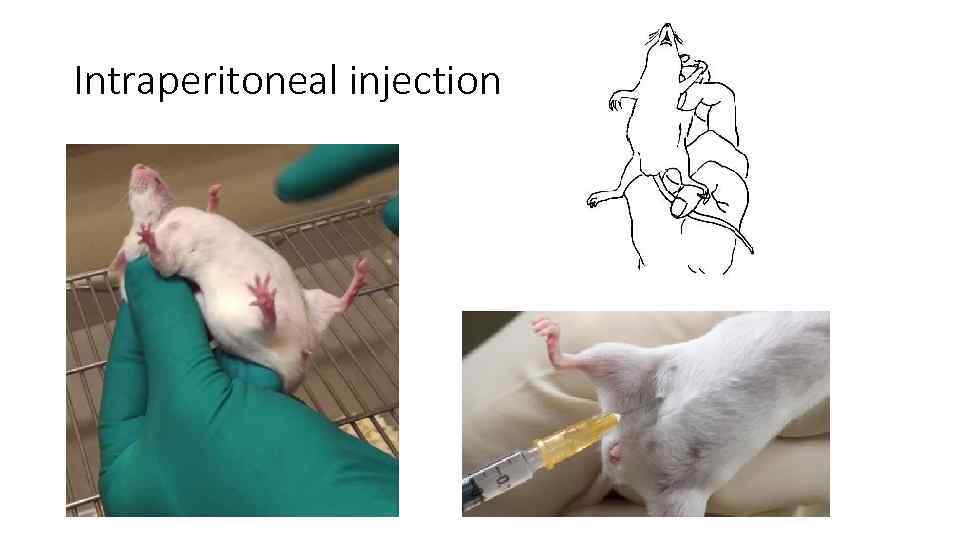 Intraperitoneal injection
Intraperitoneal injection
 Syringe scales are variable • Volume – 1 ml (is written down on syringe) • Scale can be 30, 40, 100 units • Scale interval = 1000 ul / n units
Syringe scales are variable • Volume – 1 ml (is written down on syringe) • Scale can be 30, 40, 100 units • Scale interval = 1000 ul / n units
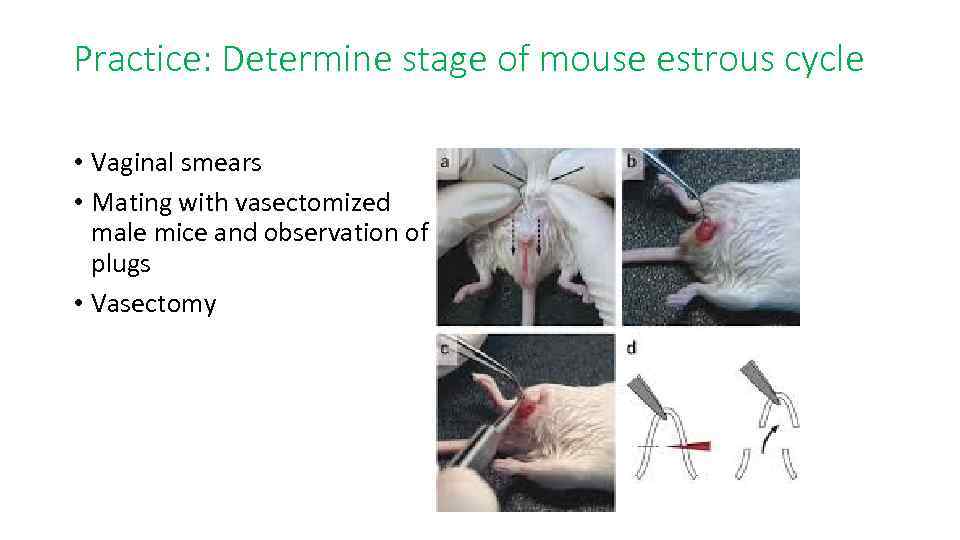 Practice: Determine stage of mouse estrous cycle • Vaginal smears • Mating with vasectomized male mice and observation of plugs • Vasectomy
Practice: Determine stage of mouse estrous cycle • Vaginal smears • Mating with vasectomized male mice and observation of plugs • Vasectomy
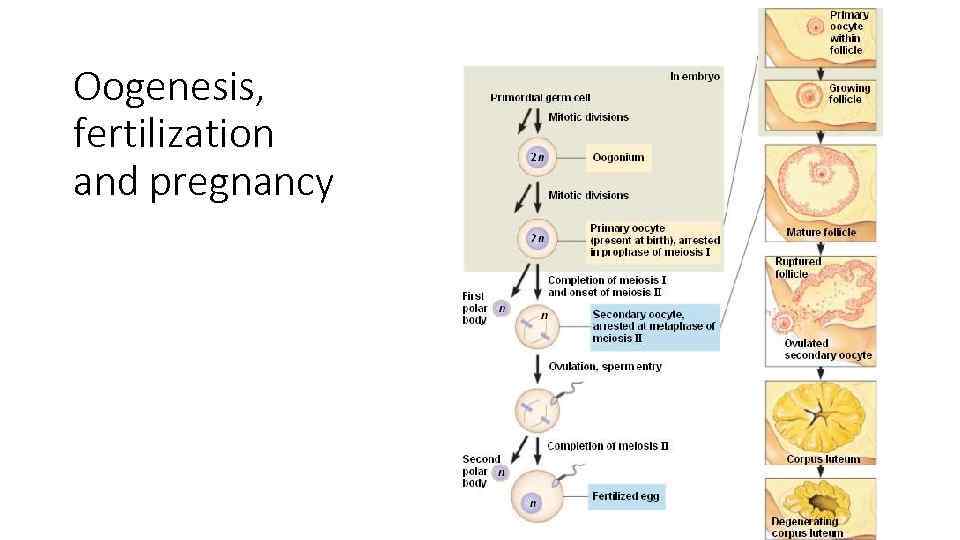 Oogenesis, fertilization and pregnancy
Oogenesis, fertilization and pregnancy
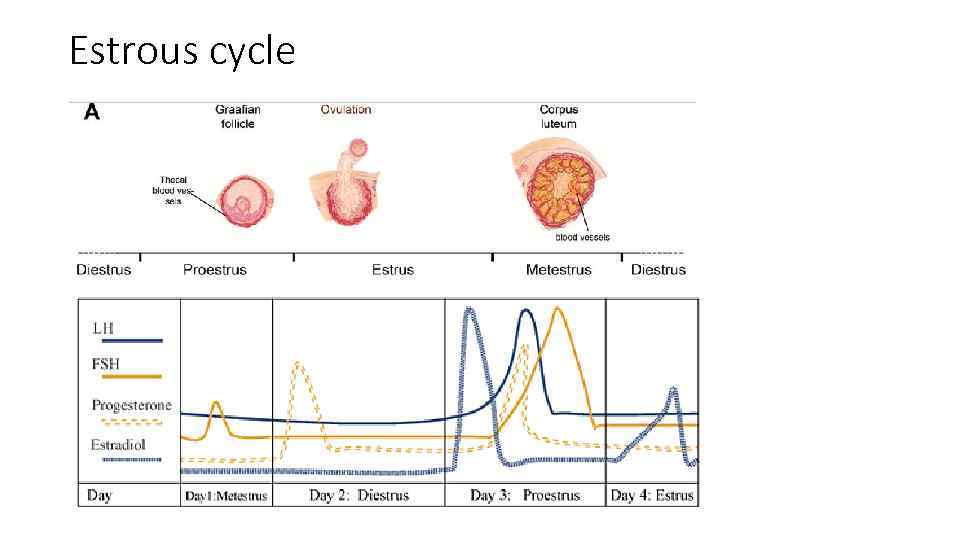 Estrous cycle
Estrous cycle
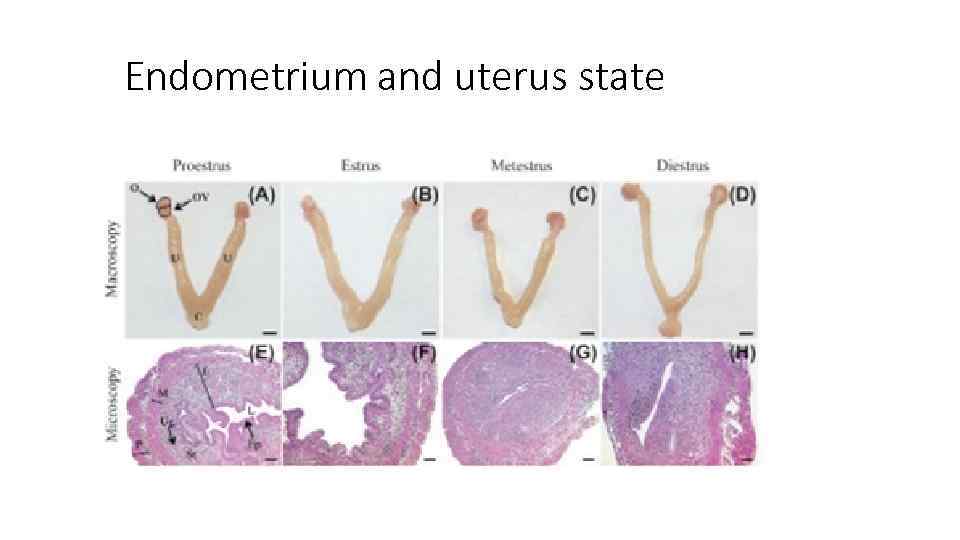 Endometrium and uterus state
Endometrium and uterus state
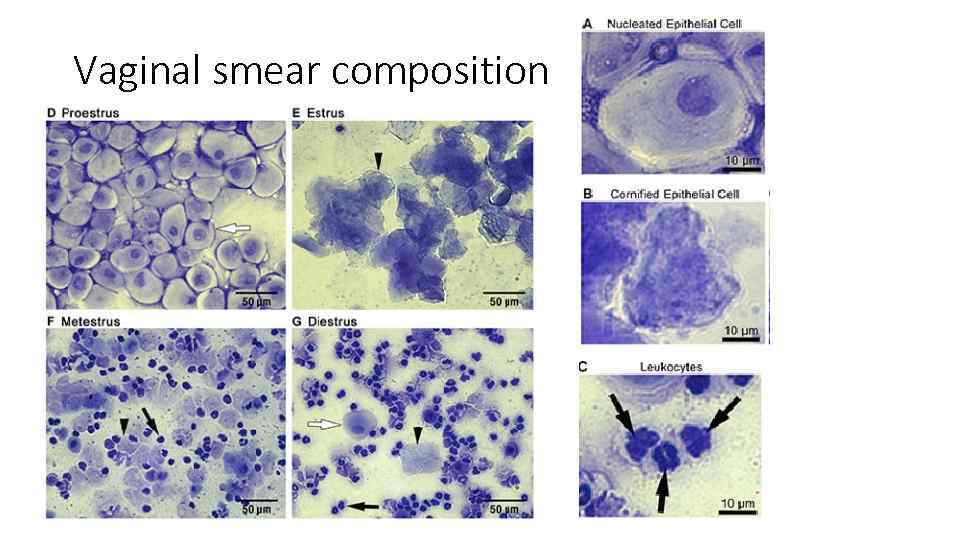 Vaginal smear composition
Vaginal smear composition
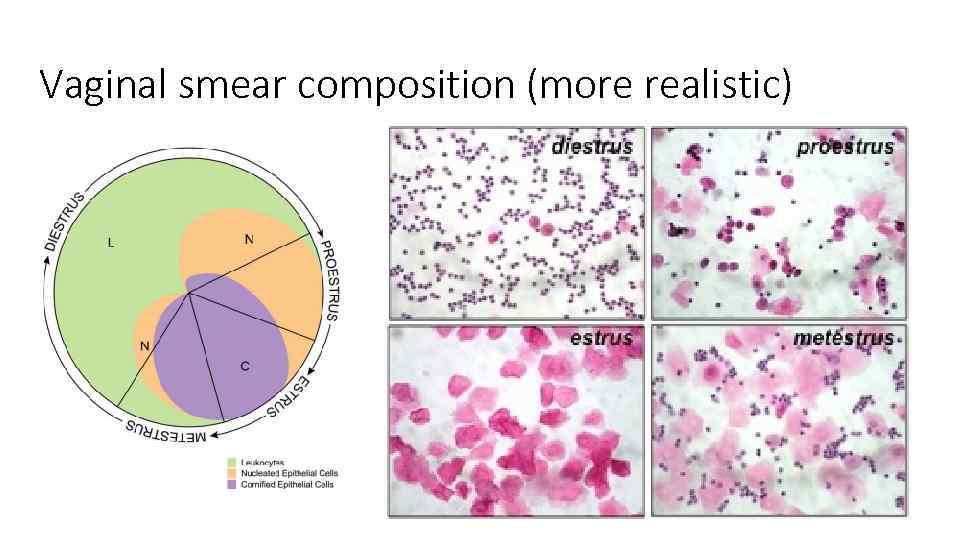 Vaginal smear composition (more realistic)
Vaginal smear composition (more realistic)
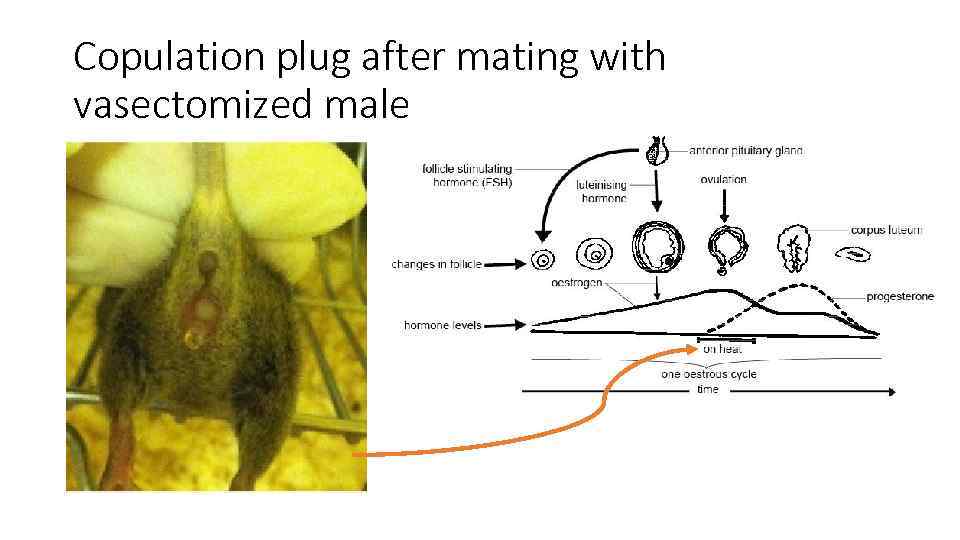 Copulation plug after mating with vasectomized male
Copulation plug after mating with vasectomized male
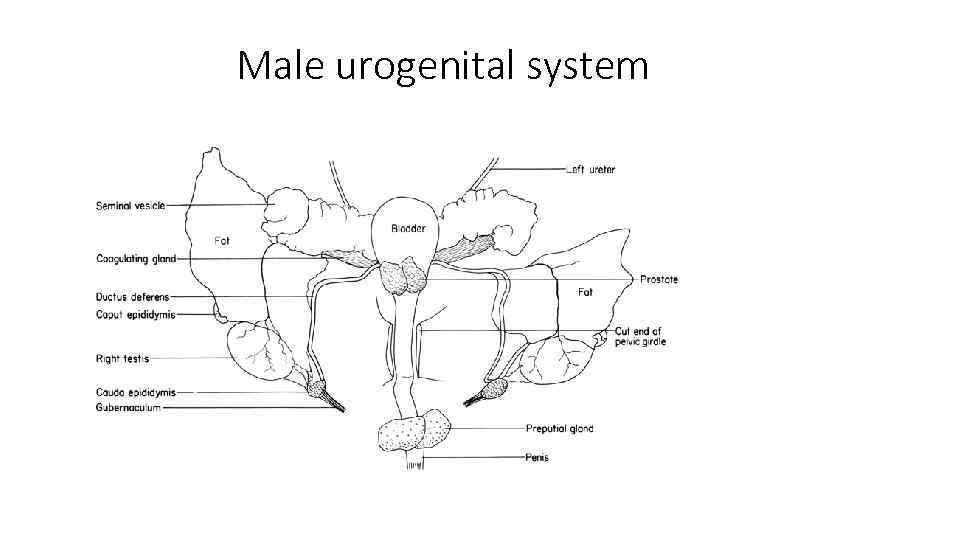 Male urogenital system
Male urogenital system
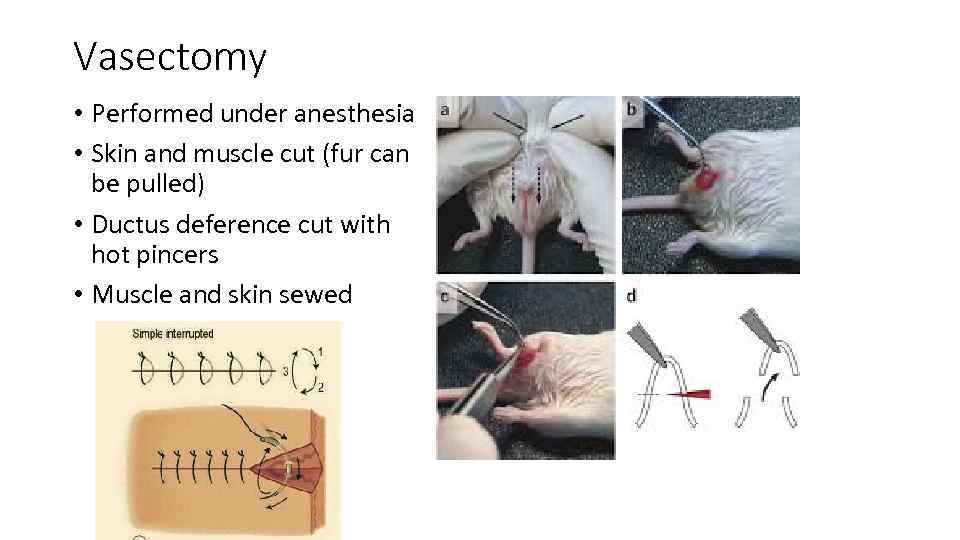 Vasectomy • Performed under anesthesia • Skin and muscle cut (fur can be pulled) • Ductus deference cut with hot pincers • Muscle and skin sewed
Vasectomy • Performed under anesthesia • Skin and muscle cut (fur can be pulled) • Ductus deference cut with hot pincers • Muscle and skin sewed
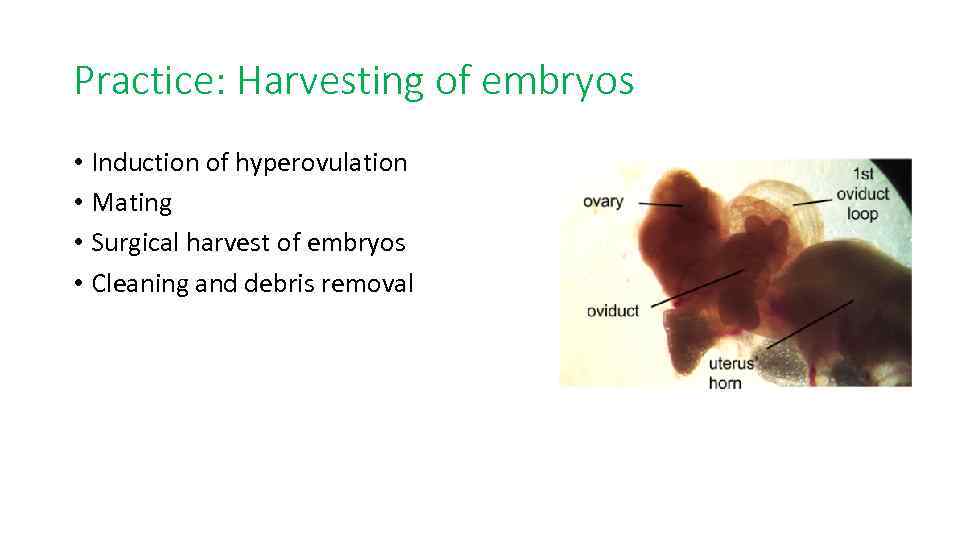 Practice: Harvesting of embryos • Induction of hyperovulation • Mating • Surgical harvest of embryos • Cleaning and debris removal
Practice: Harvesting of embryos • Induction of hyperovulation • Mating • Surgical harvest of embryos • Cleaning and debris removal
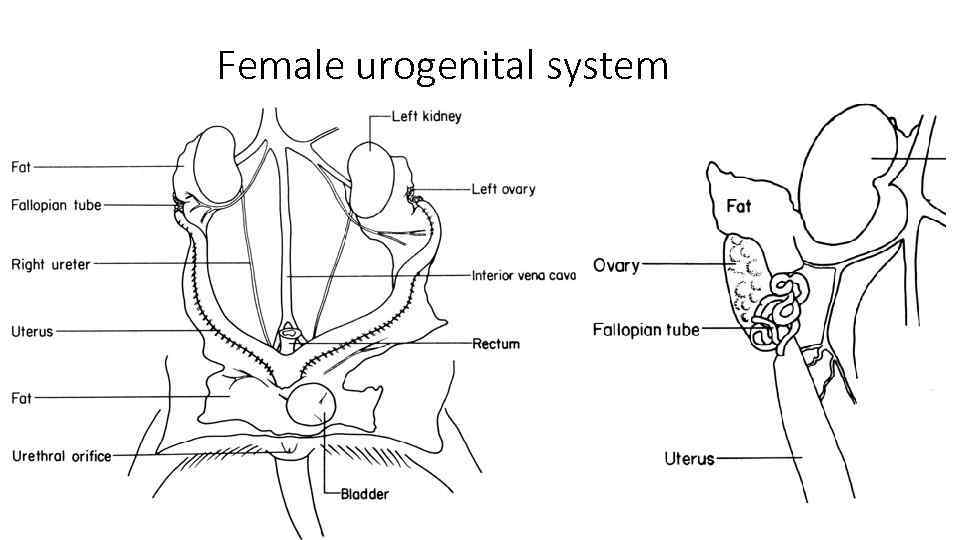 Female urogenital system
Female urogenital system
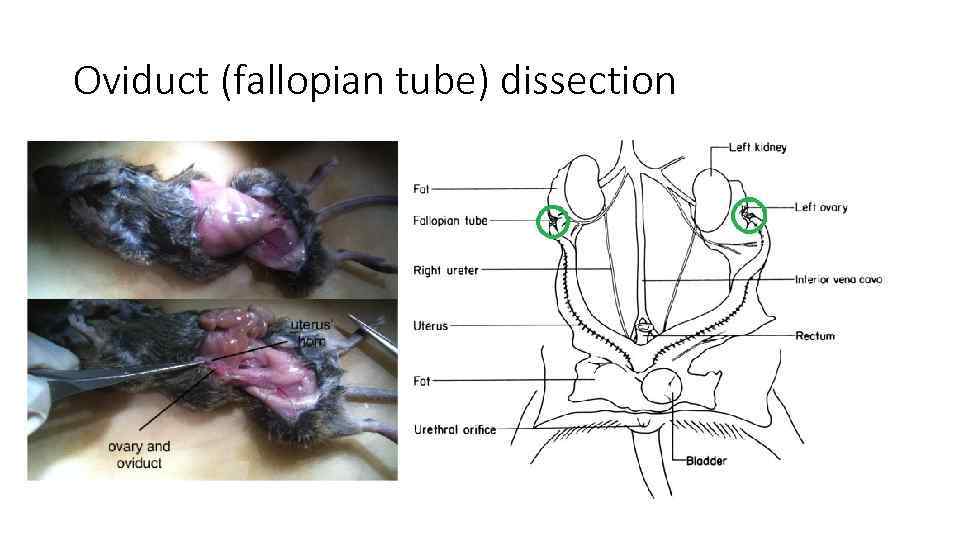 Oviduct (fallopian tube) dissection
Oviduct (fallopian tube) dissection
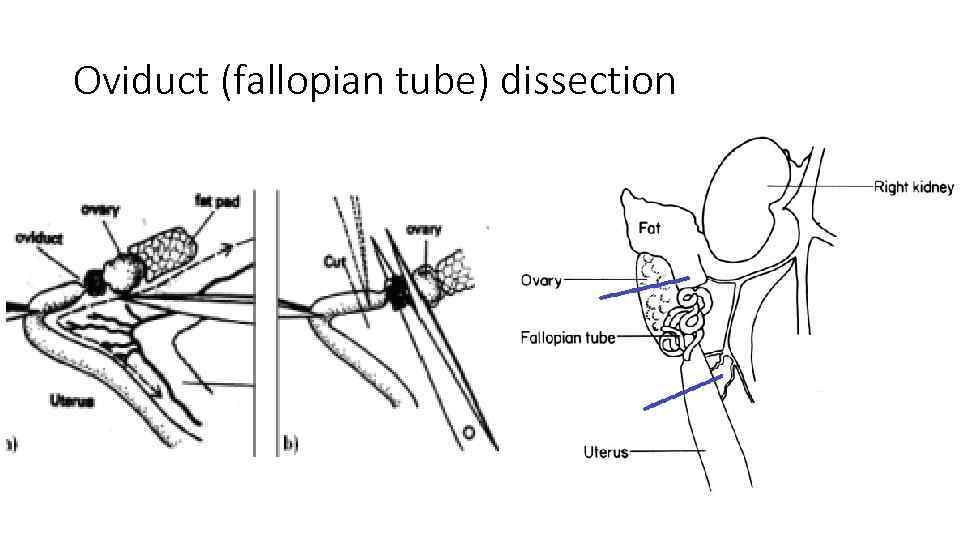 Oviduct (fallopian tube) dissection
Oviduct (fallopian tube) dissection
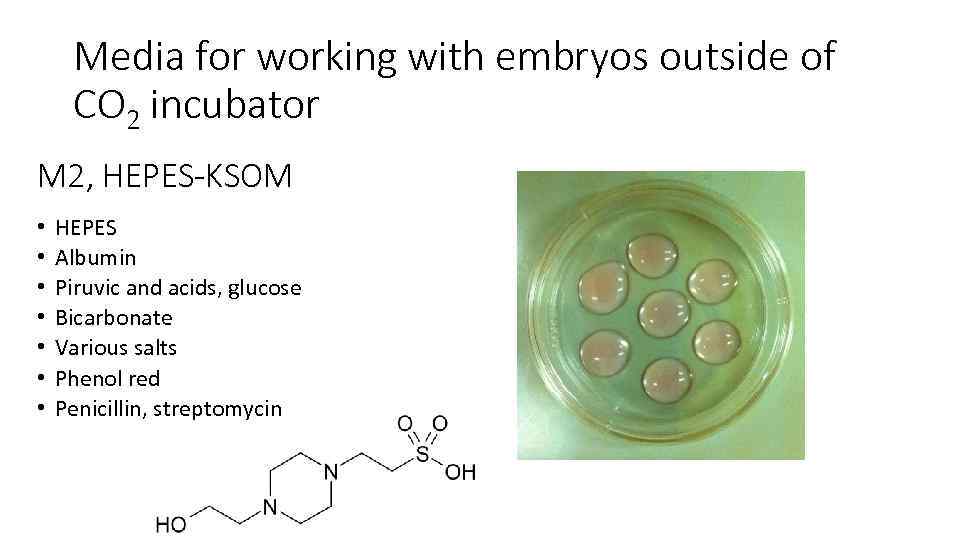 Media for working with embryos outside of CO 2 incubator М 2, HEPES-KSOM • • HEPES Albumin Piruvic and acids, glucose Bicarbonate Various salts Phenol red Penicillin, streptomycin
Media for working with embryos outside of CO 2 incubator М 2, HEPES-KSOM • • HEPES Albumin Piruvic and acids, glucose Bicarbonate Various salts Phenol red Penicillin, streptomycin
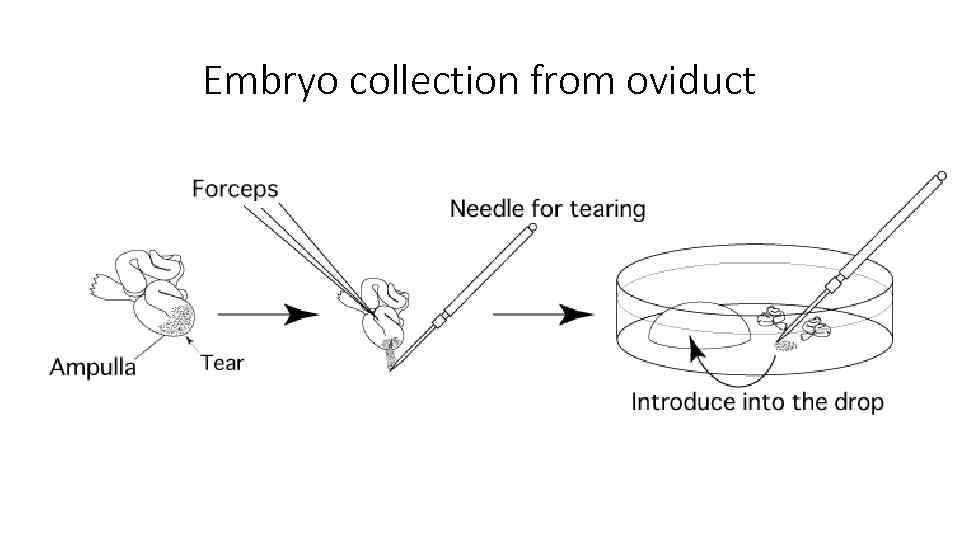 Embryo collection from oviduct
Embryo collection from oviduct
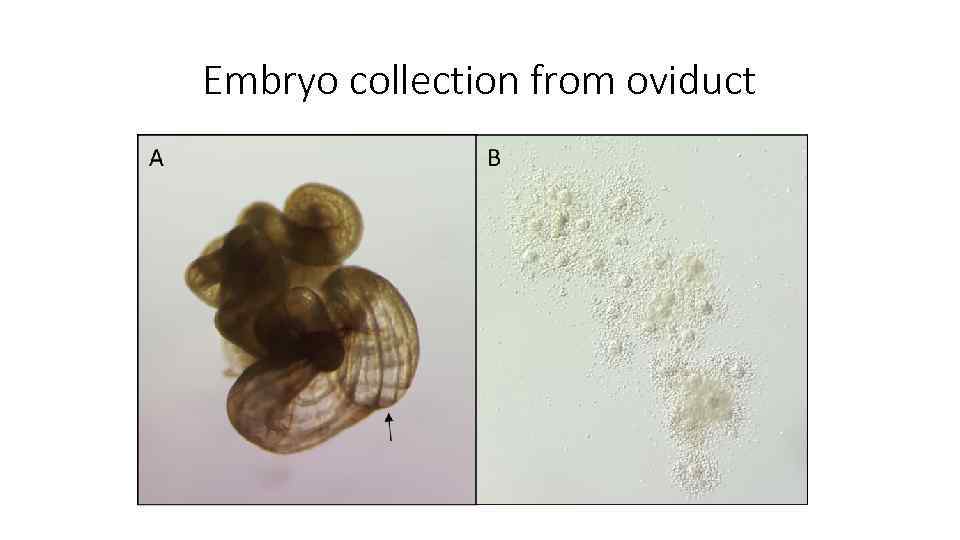 Embryo collection from oviduct
Embryo collection from oviduct
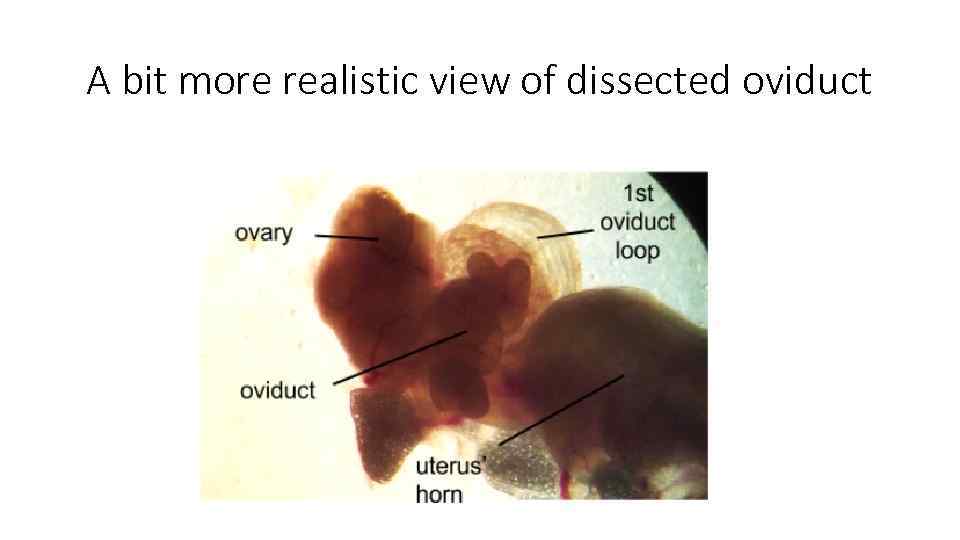 A bit more realistic view of dissected oviduct
A bit more realistic view of dissected oviduct
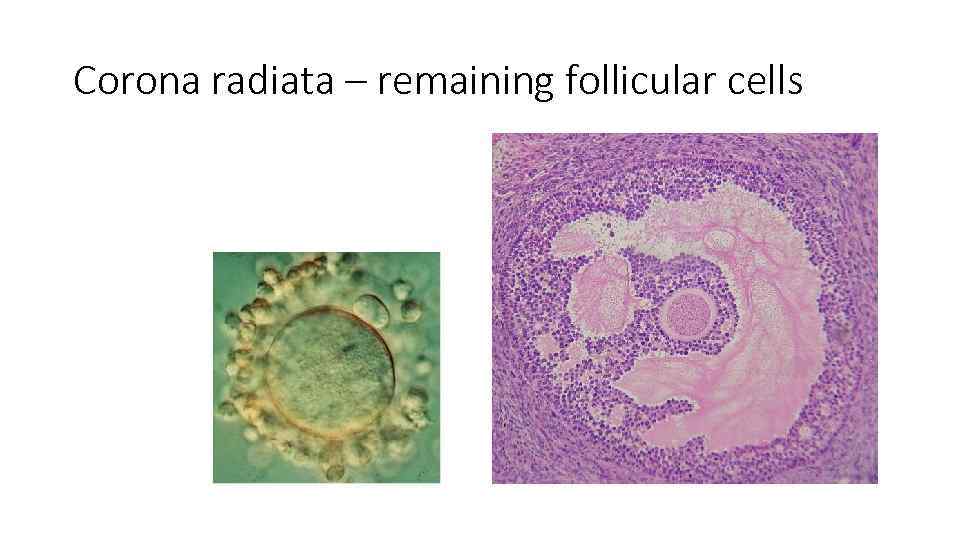 Corona radiata – remaining follicular cells
Corona radiata – remaining follicular cells
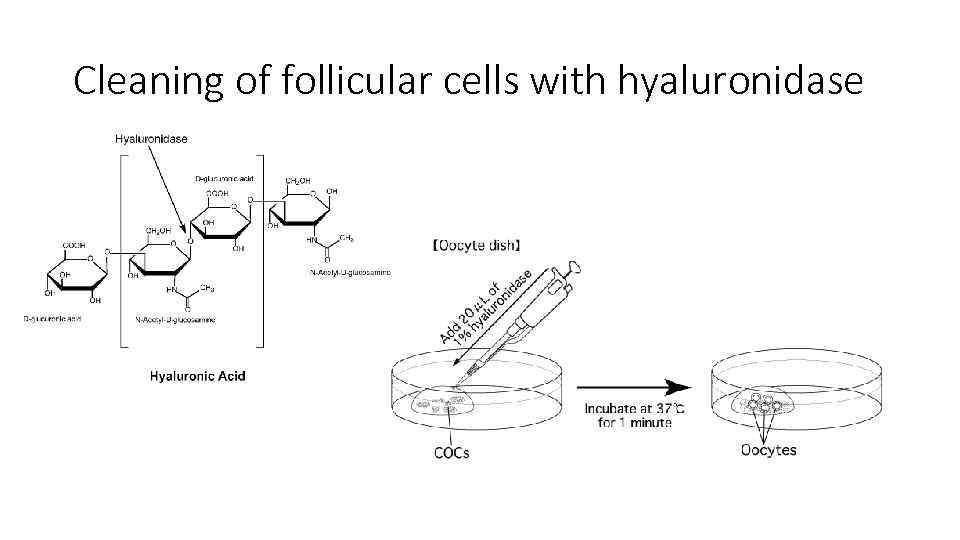 Cleaning of follicular cells with hyaluronidase
Cleaning of follicular cells with hyaluronidase
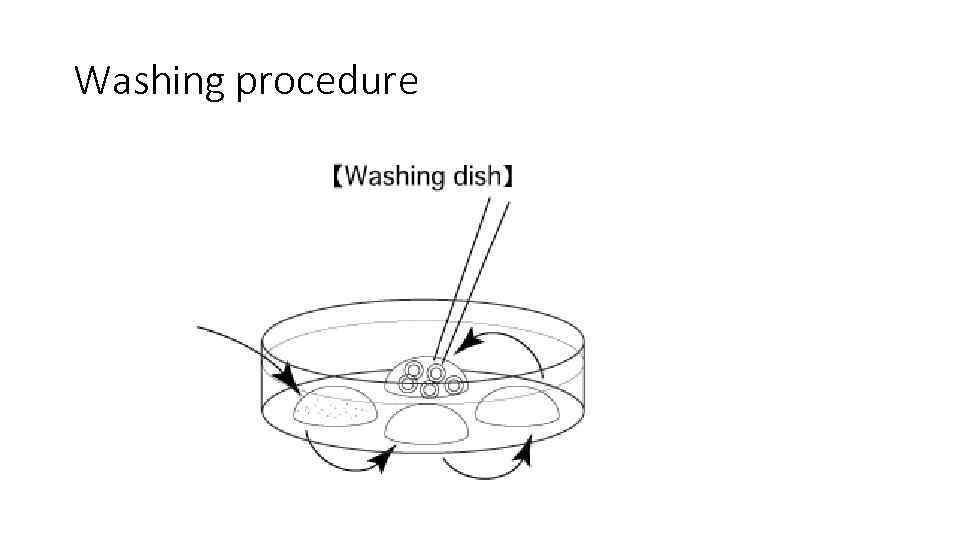 Washing procedure
Washing procedure
 Capillary preparation • Capillary (outer diameter 1 mm) • Pulling • Microforge (allows to chose diameter and mill the tip) • Best inner diameter > 100 um
Capillary preparation • Capillary (outer diameter 1 mm) • Pulling • Microforge (allows to chose diameter and mill the tip) • Best inner diameter > 100 um
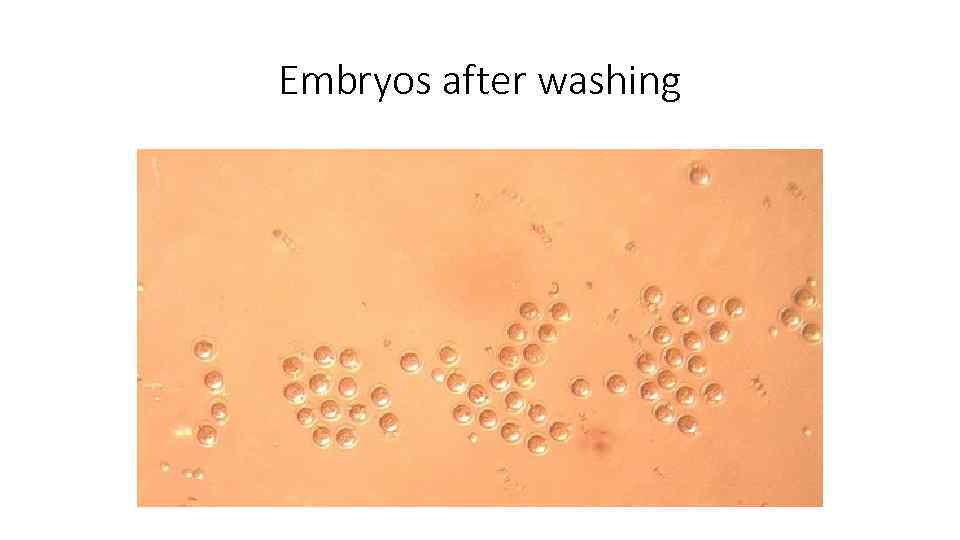 Embryos after washing
Embryos after washing
 Practice: Microinjections • Injection solution preparation • Microinstruments: transfer capillary, microneedle and sucker capillary • Handling pullers and microforge • Assembly of microinjection camera • Microinjections
Practice: Microinjections • Injection solution preparation • Microinstruments: transfer capillary, microneedle and sucker capillary • Handling pullers and microforge • Assembly of microinjection camera • Microinjections
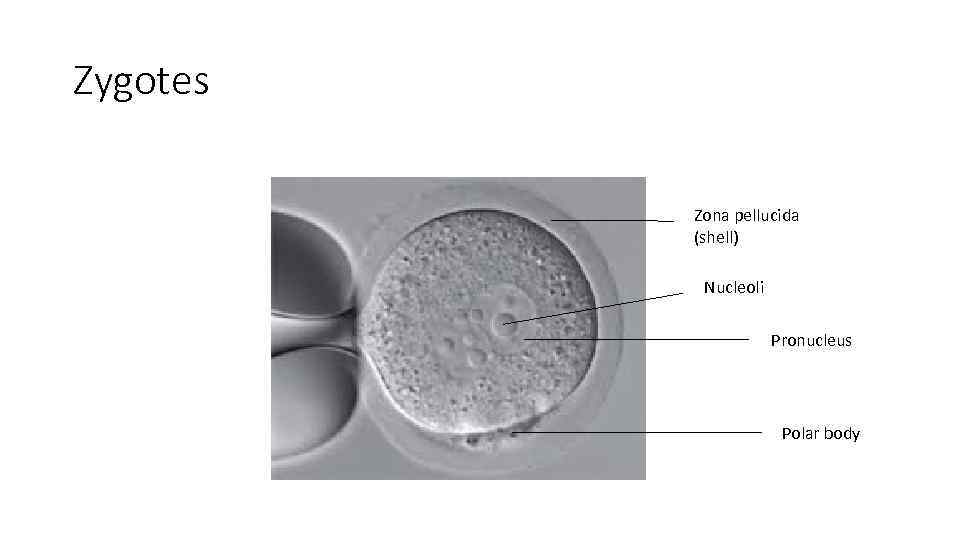 Zygotes Zona pellucida (shell) Nucleoli Pronucleus Polar body
Zygotes Zona pellucida (shell) Nucleoli Pronucleus Polar body
 Microinjection camera • 2 halves of coverslip • Drop of M 2 medium • Paraffin oil
Microinjection camera • 2 halves of coverslip • Drop of M 2 medium • Paraffin oil
 Microscope for microinjections • Inverted • Contrasting optic • 5 x + 40 x objectives • Microneedle and holder pipette manipulators • Pressure regulation device • CO 2 gas cylinder
Microscope for microinjections • Inverted • Contrasting optic • 5 x + 40 x objectives • Microneedle and holder pipette manipulators • Pressure regulation device • CO 2 gas cylinder
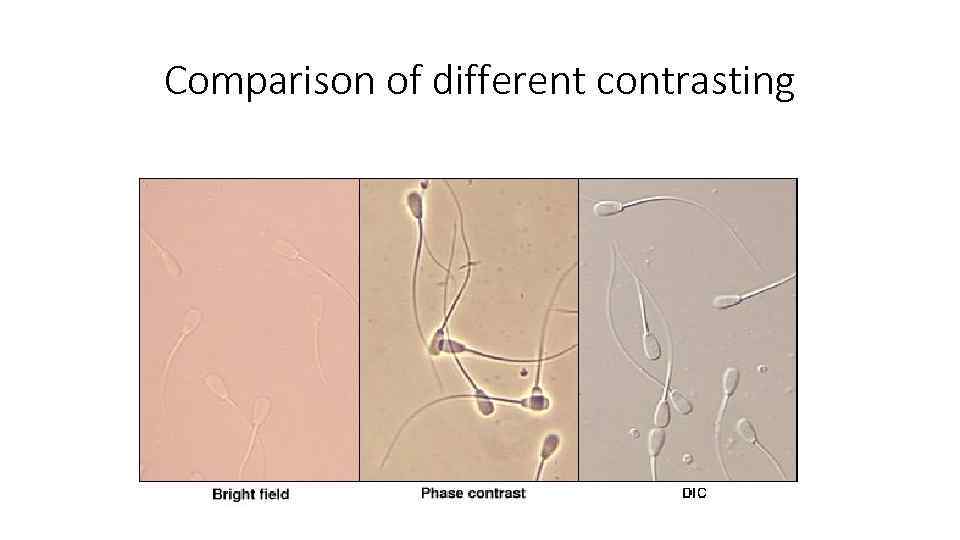 Comparison of different contrasting
Comparison of different contrasting
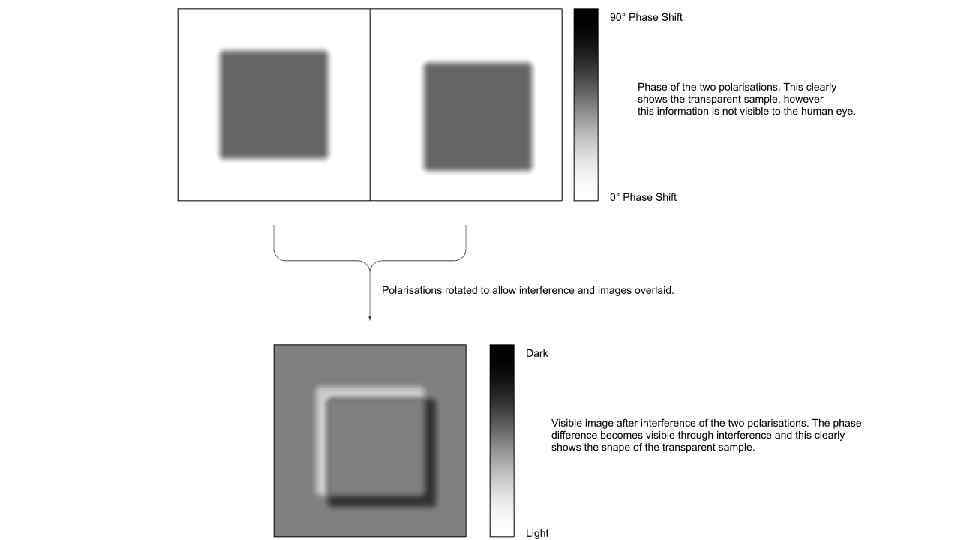
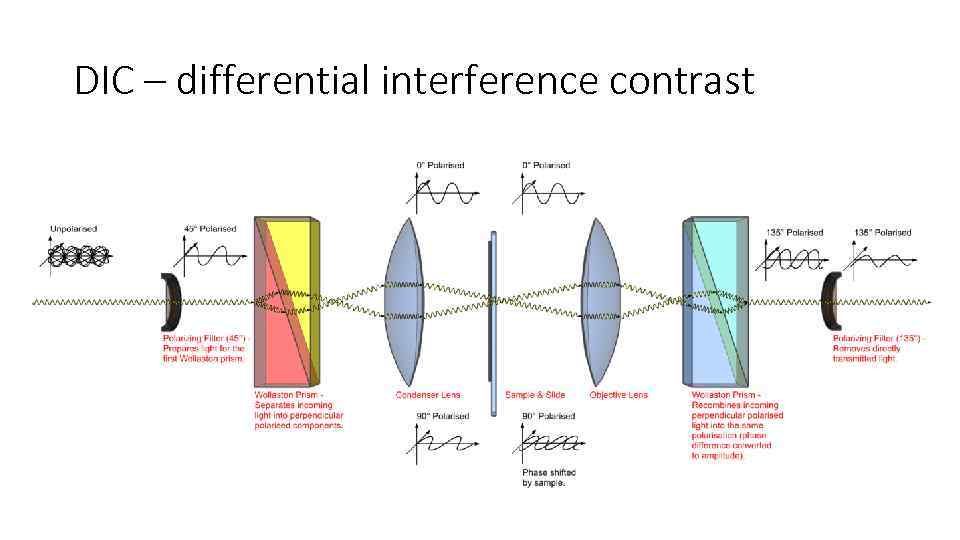 DIC – differential interference contrast
DIC – differential interference contrast
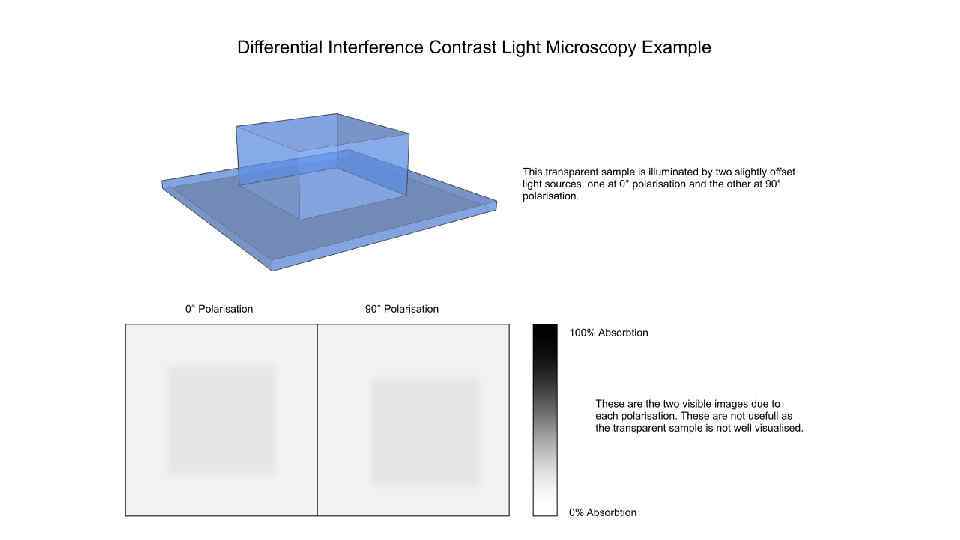
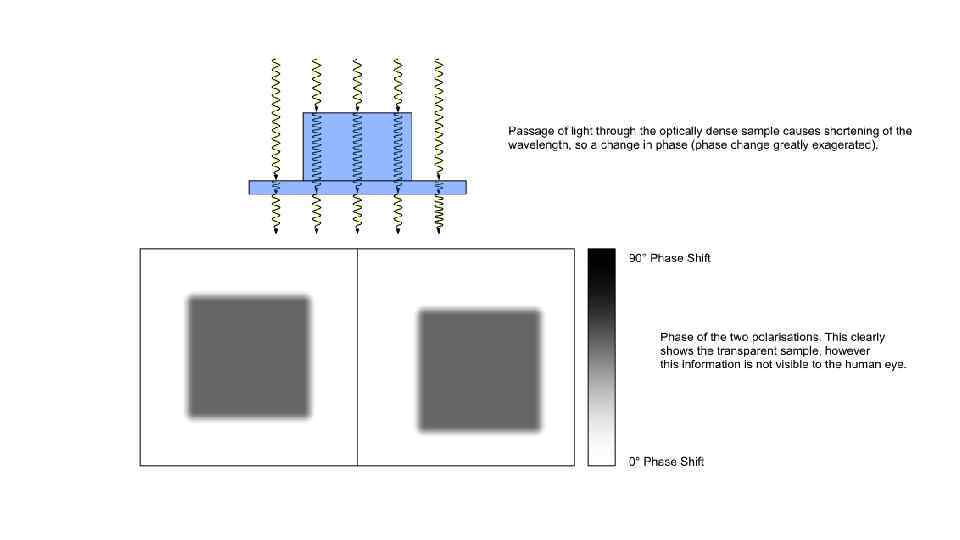
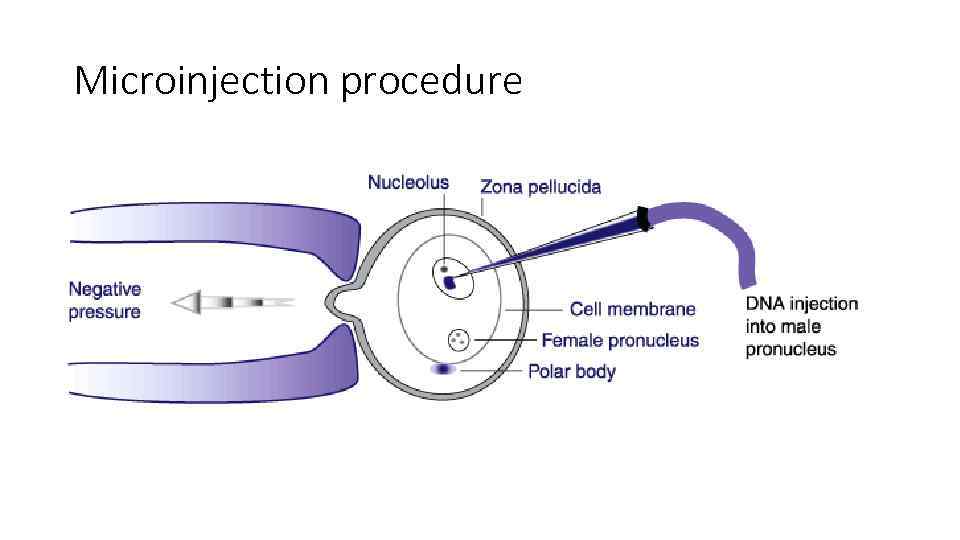 Microinjection procedure
Microinjection procedure
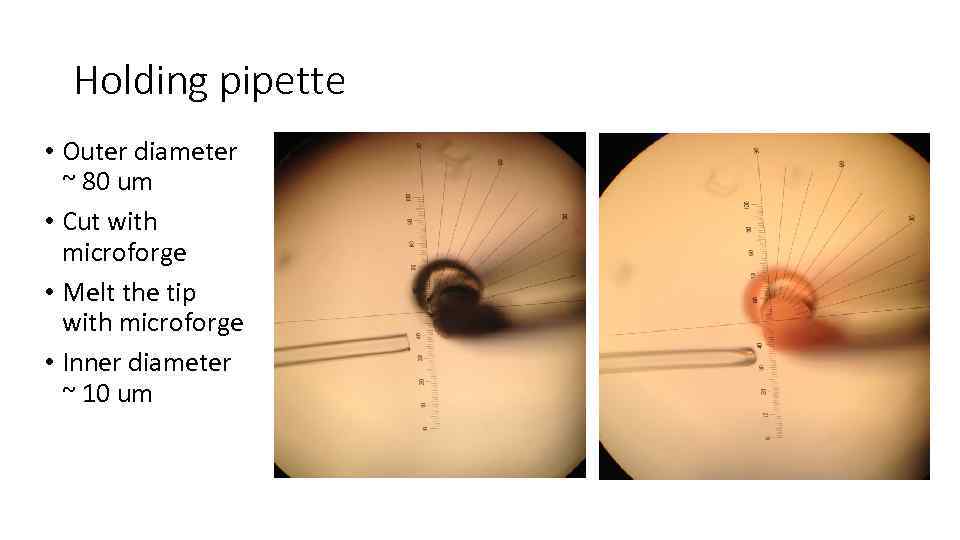 Holding pipette • Outer diameter ~ 80 um • Cut with microforge • Melt the tip with microforge • Inner diameter ~ 10 um
Holding pipette • Outer diameter ~ 80 um • Cut with microforge • Melt the tip with microforge • Inner diameter ~ 10 um
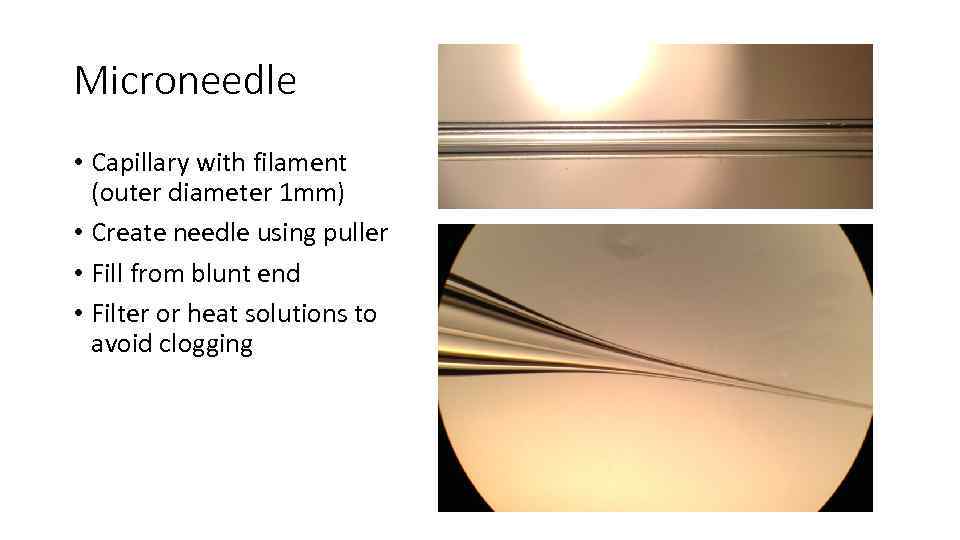 Microneedle • Capillary with filament (outer diameter 1 mm) • Create needle using puller • Fill from blunt end • Filter or heat solutions to avoid clogging
Microneedle • Capillary with filament (outer diameter 1 mm) • Create needle using puller • Fill from blunt end • Filter or heat solutions to avoid clogging
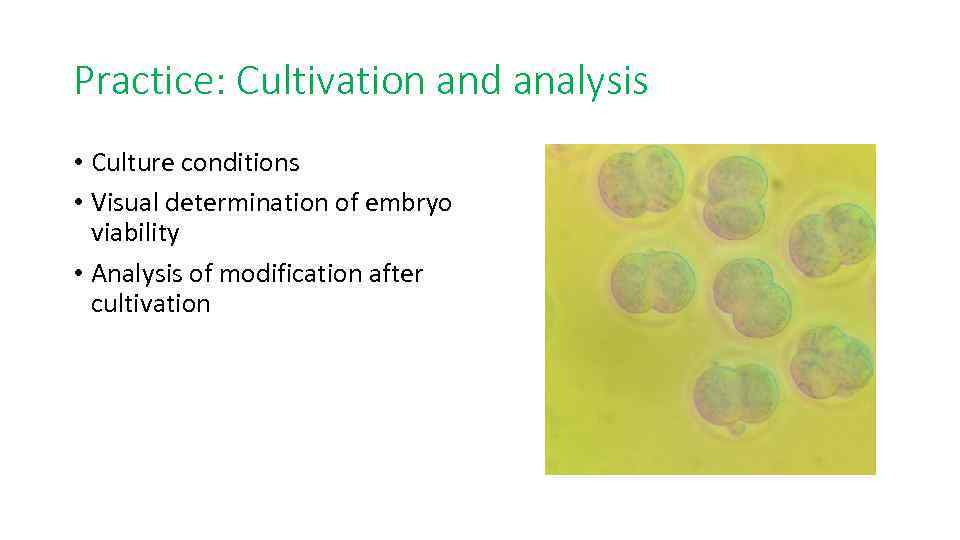 Practice: Cultivation and analysis • Culture conditions • Visual determination of embryo viability • Analysis of modification after cultivation
Practice: Cultivation and analysis • Culture conditions • Visual determination of embryo viability • Analysis of modification after cultivation
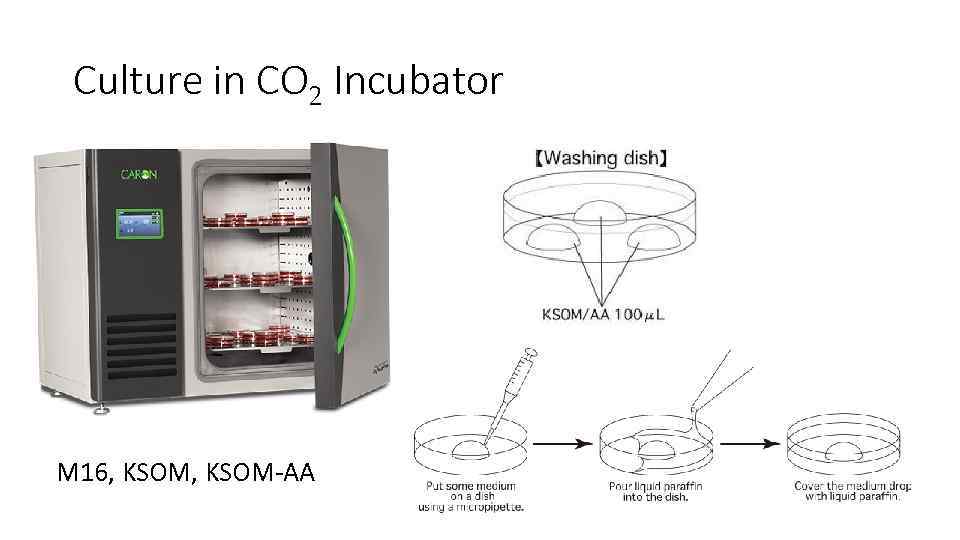 Culture in CO 2 Incubator M 16, KSOM-AA
Culture in CO 2 Incubator M 16, KSOM-AA
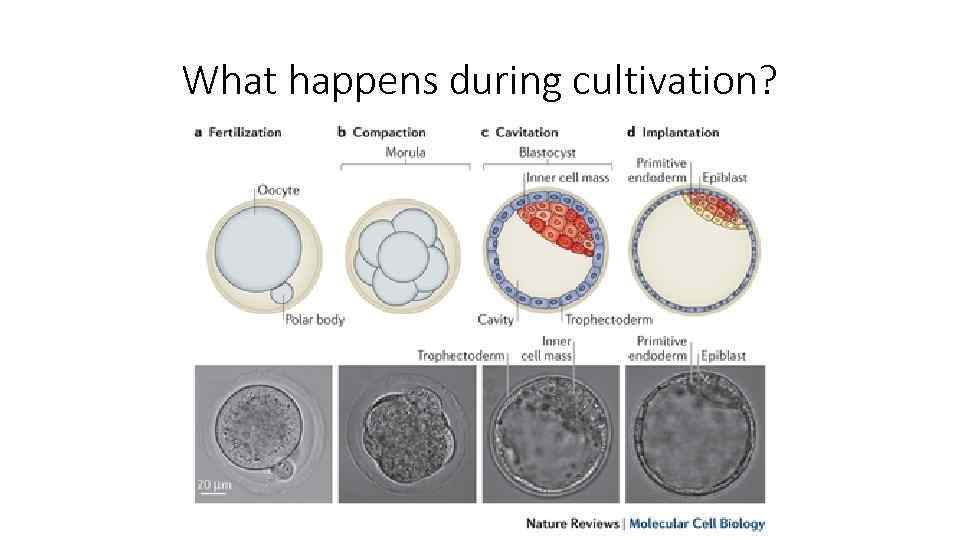 What happens during cultivation?
What happens during cultivation?
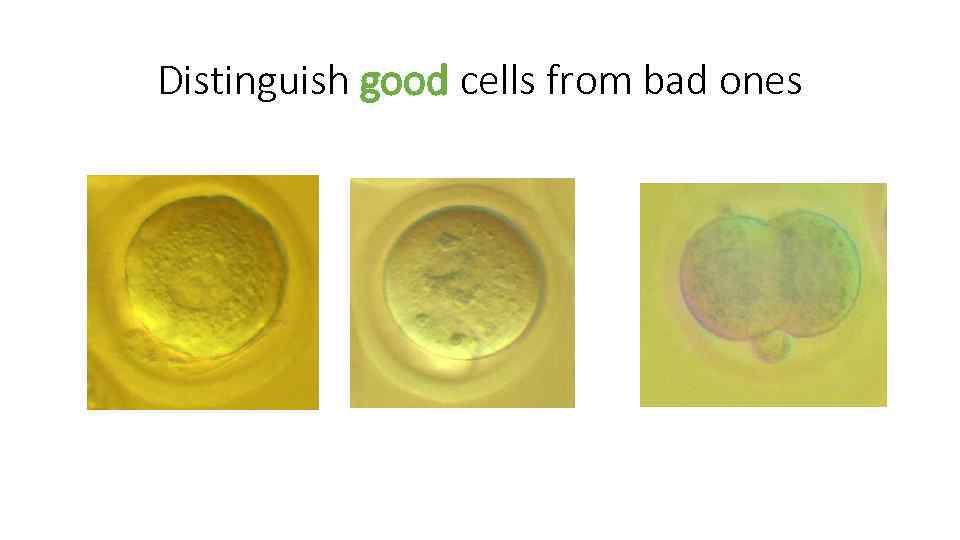 Distinguish good cells from bad ones
Distinguish good cells from bad ones
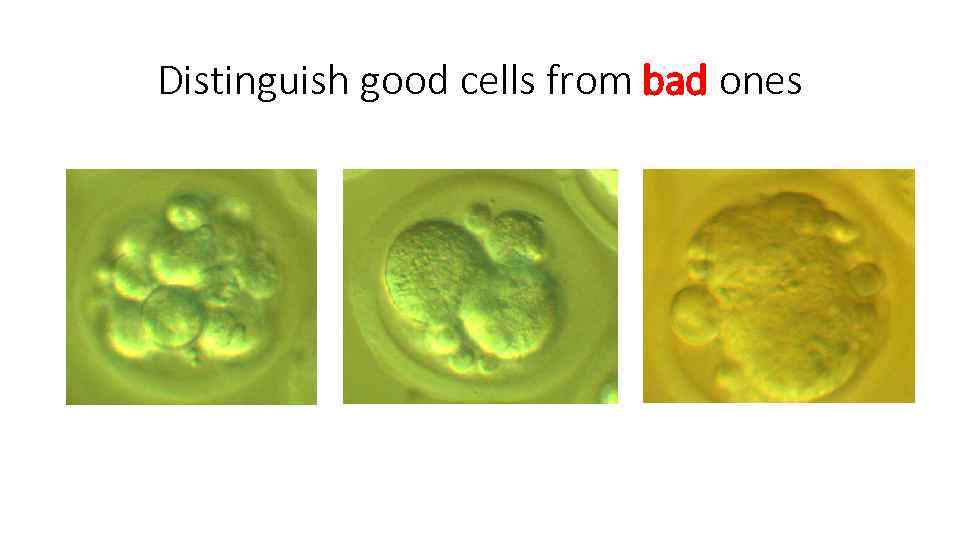 Distinguish good cells from bad ones
Distinguish good cells from bad ones
 Distinguish good cells from dead ones
Distinguish good cells from dead ones
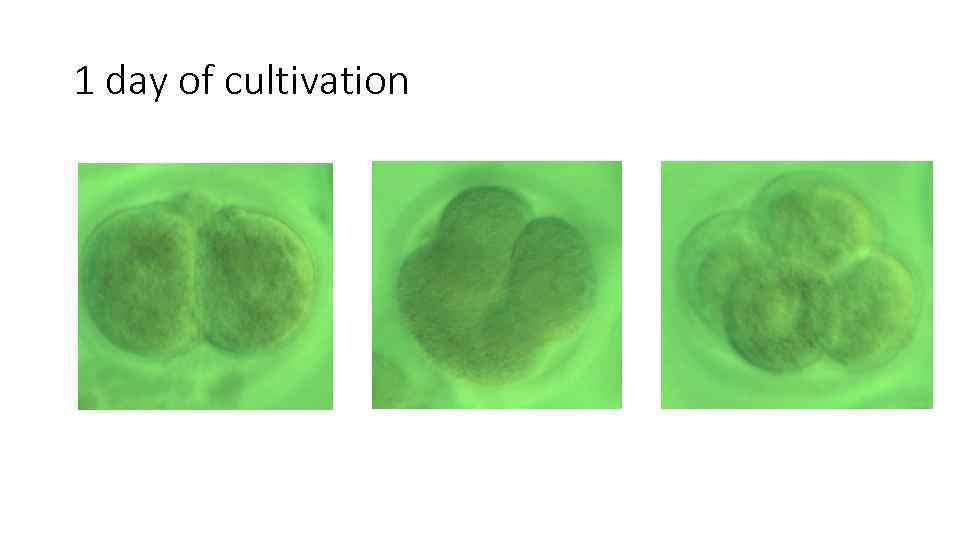 1 day of cultivation
1 day of cultivation
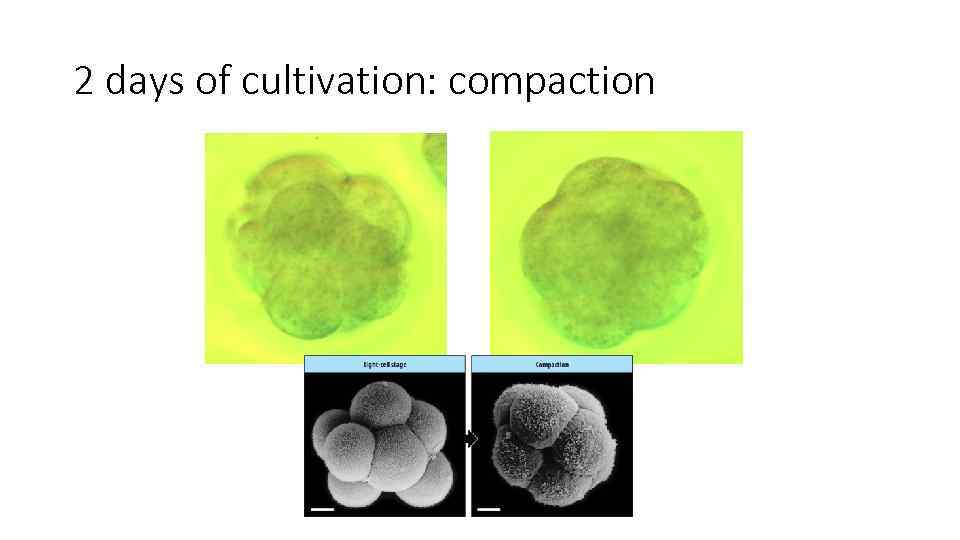 2 days of cultivation: compaction
2 days of cultivation: compaction
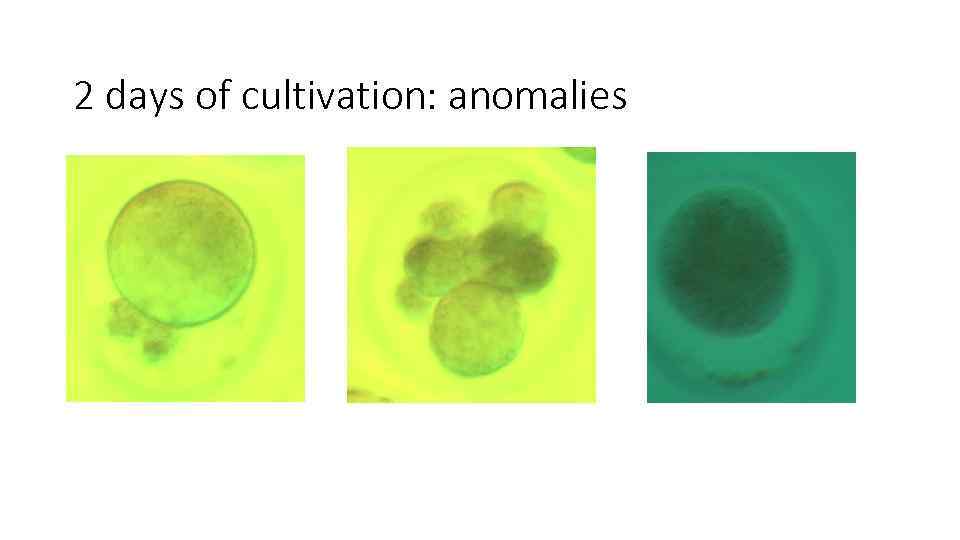 2 days of cultivation: anomalies
2 days of cultivation: anomalies
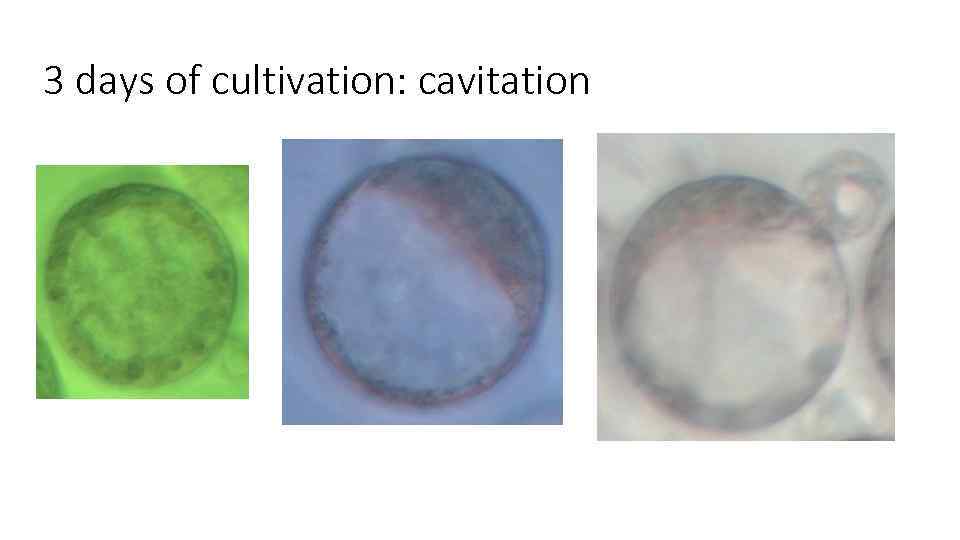 3 days of cultivation: cavitation
3 days of cultivation: cavitation
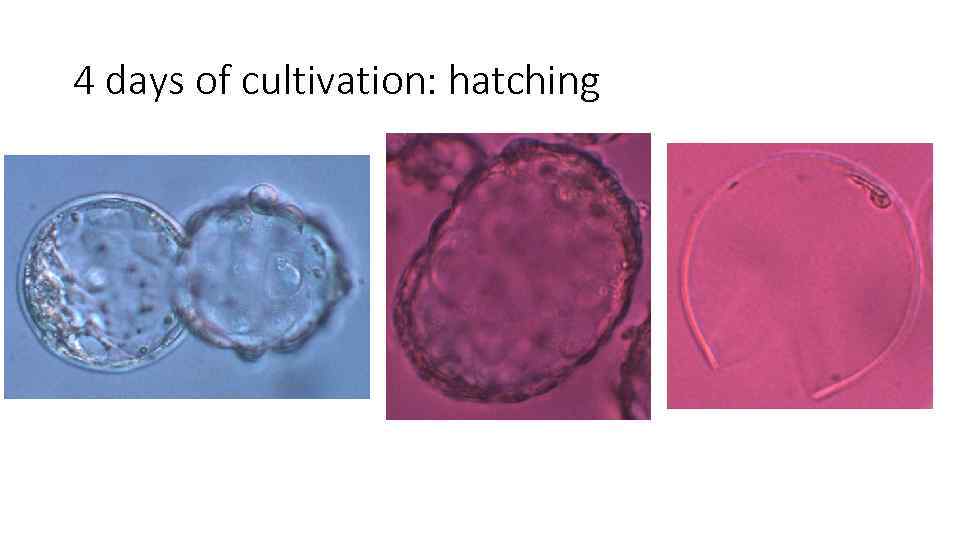 4 days of cultivation: hatching
4 days of cultivation: hatching
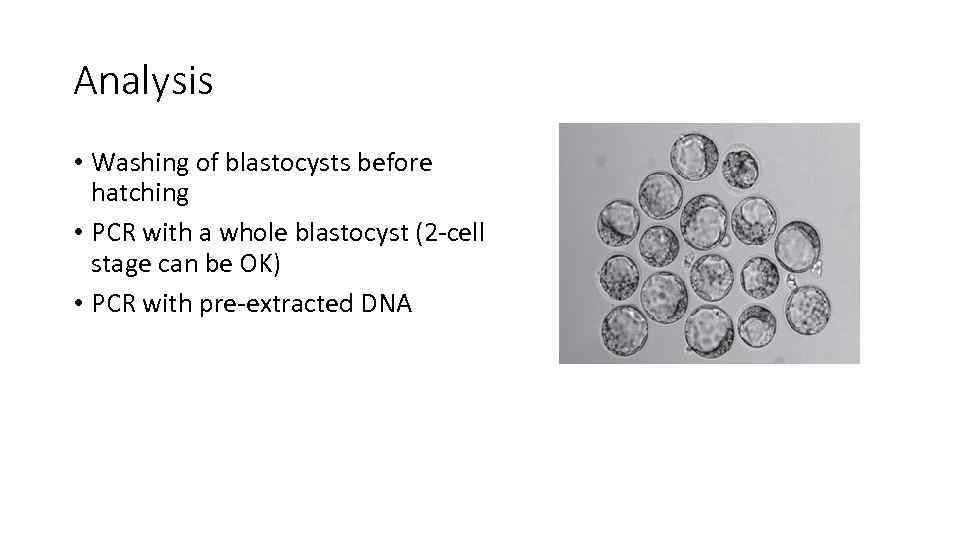 Analysis • Washing of blastocysts before hatching • PCR with a whole blastocyst (2 -cell stage can be OK) • PCR with pre-extracted DNA
Analysis • Washing of blastocysts before hatching • PCR with a whole blastocyst (2 -cell stage can be OK) • PCR with pre-extracted DNA
 Blastocyst DNA extraction protocol • Add to the each tube 10 ul of BLB • Incubate 10 min at 56 o. C and 10 min at 95 o. C • Freeze and store at -20 before use • Use 5 ul of solution in PCR BLB • 100 ul of 1 M Tris-HCl p. H 8, 3 • 100 ul of 1 M KCl • 100 ul of 0, 2% gelatin • 4, 5 ul of Tween-20 • 6, 25 ul of Proteinase K 20 mg/ml solution • bring final volume to 1 m. L
Blastocyst DNA extraction protocol • Add to the each tube 10 ul of BLB • Incubate 10 min at 56 o. C and 10 min at 95 o. C • Freeze and store at -20 before use • Use 5 ul of solution in PCR BLB • 100 ul of 1 M Tris-HCl p. H 8, 3 • 100 ul of 1 M KCl • 100 ul of 0, 2% gelatin • 4, 5 ul of Tween-20 • 6, 25 ul of Proteinase K 20 mg/ml solution • bring final volume to 1 m. L
 Practice: Embryo transfer • Pseudopregnancy • Embryo transfer in the fallopian tubes • Embryo transfer into uterine horns • Pregnancy
Practice: Embryo transfer • Pseudopregnancy • Embryo transfer in the fallopian tubes • Embryo transfer into uterine horns • Pregnancy
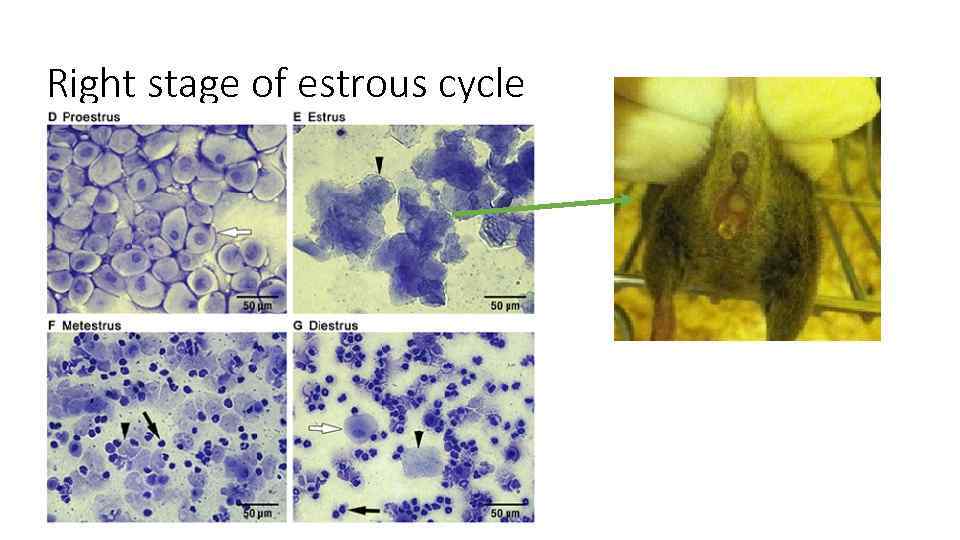 Right stage of estrous cycle
Right stage of estrous cycle
 Embryo transfer into oviducts • Single cell stage, 2 cell stage • Recipient in estrus
Embryo transfer into oviducts • Single cell stage, 2 cell stage • Recipient in estrus
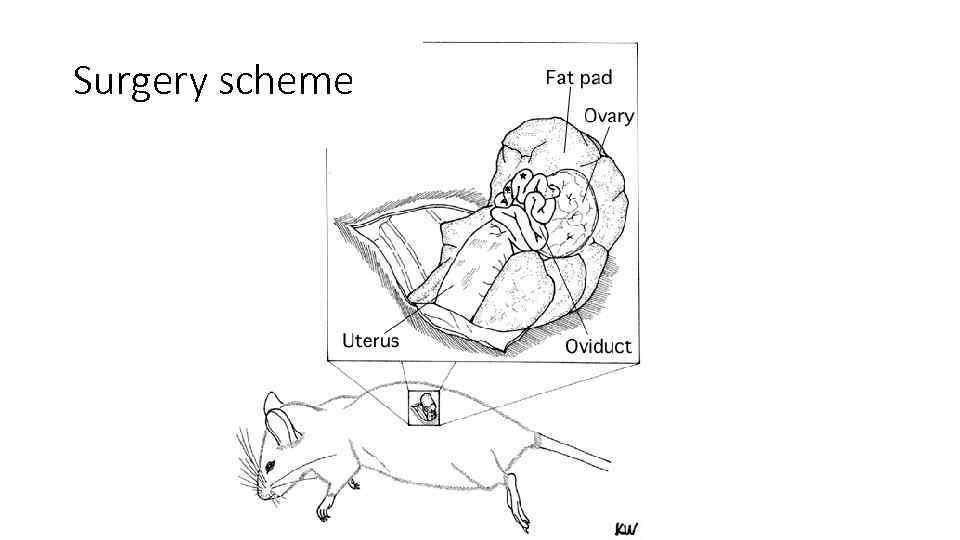 Surgery scheme
Surgery scheme
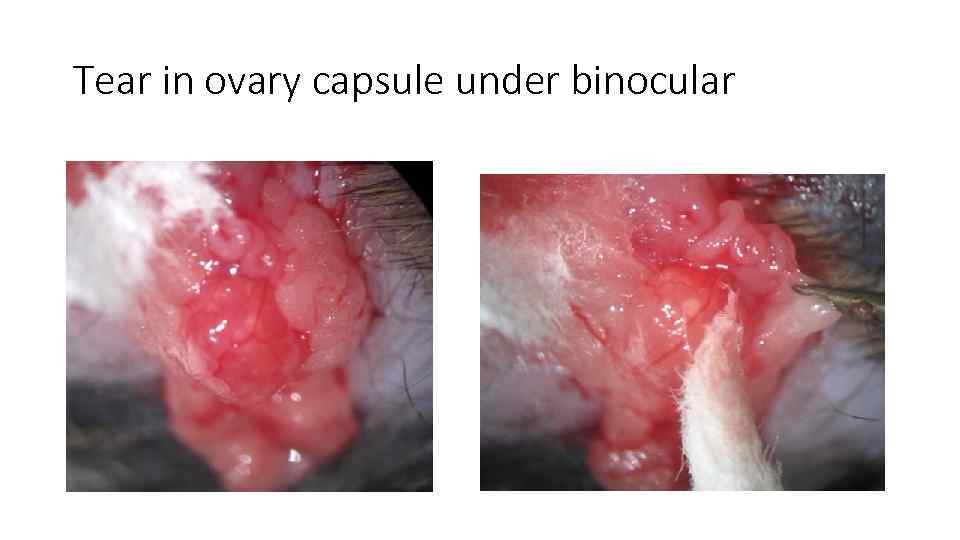 Tear in ovary capsule under binocular
Tear in ovary capsule under binocular
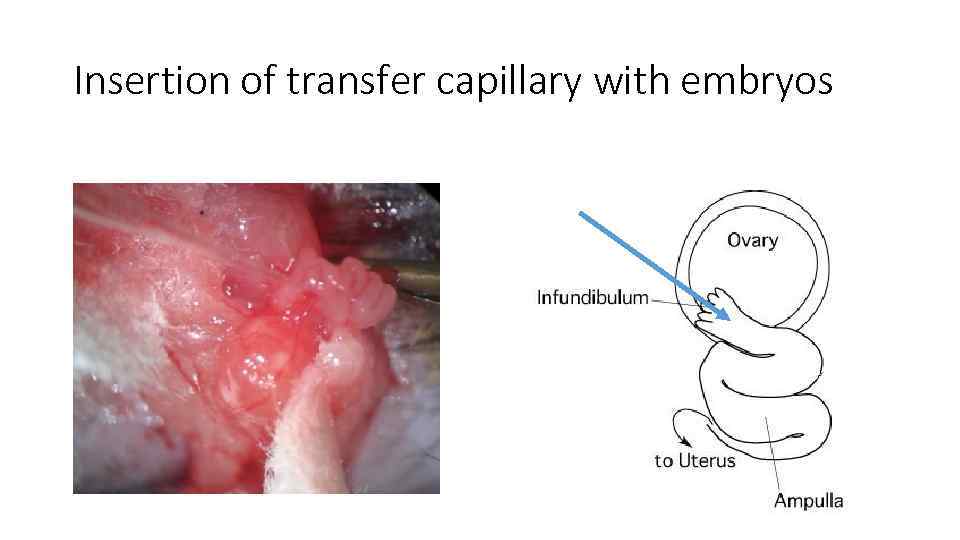 Insertion of transfer capillary with embryos
Insertion of transfer capillary with embryos
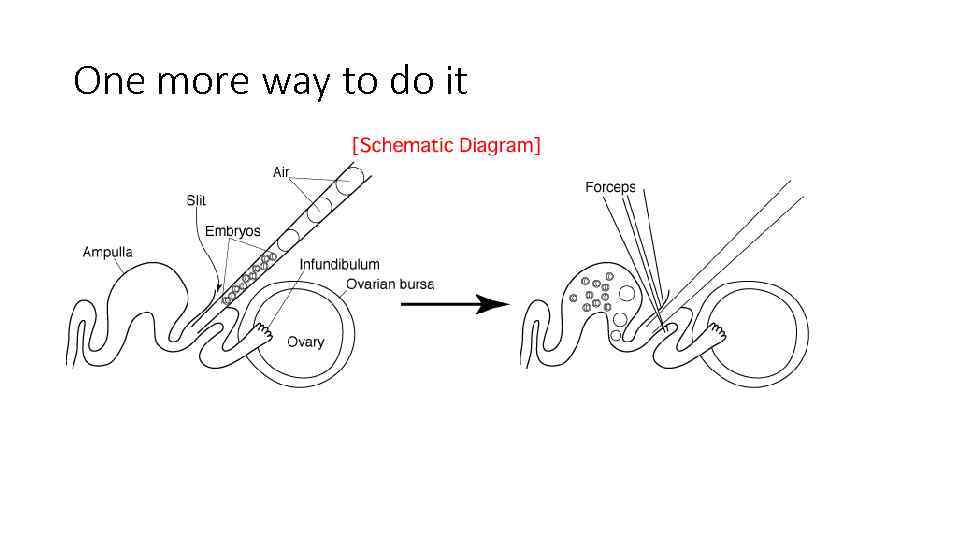 One more way to do it
One more way to do it
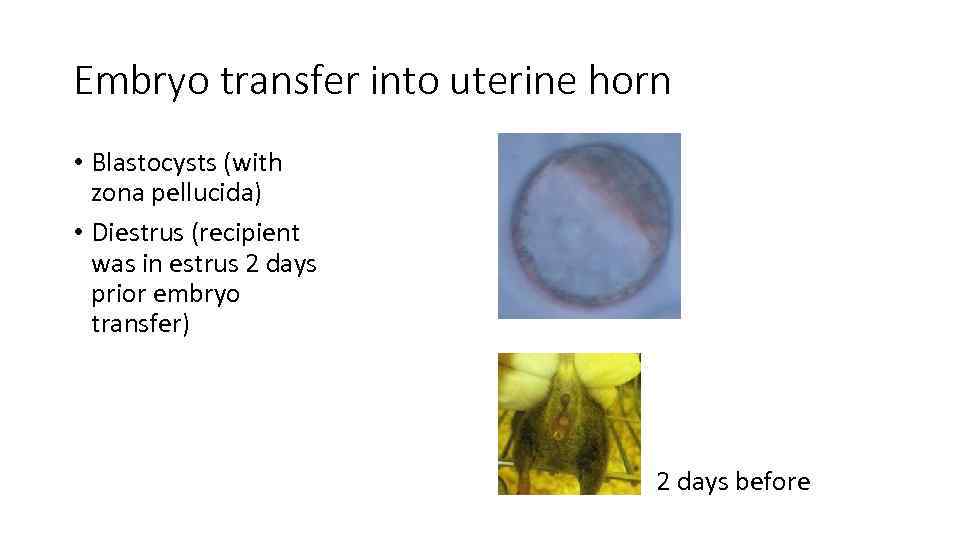 Embryo transfer into uterine horn • Blastocysts (with zona pellucida) • Diestrus (recipient was in estrus 2 days prior embryo transfer) 2 days before
Embryo transfer into uterine horn • Blastocysts (with zona pellucida) • Diestrus (recipient was in estrus 2 days prior embryo transfer) 2 days before
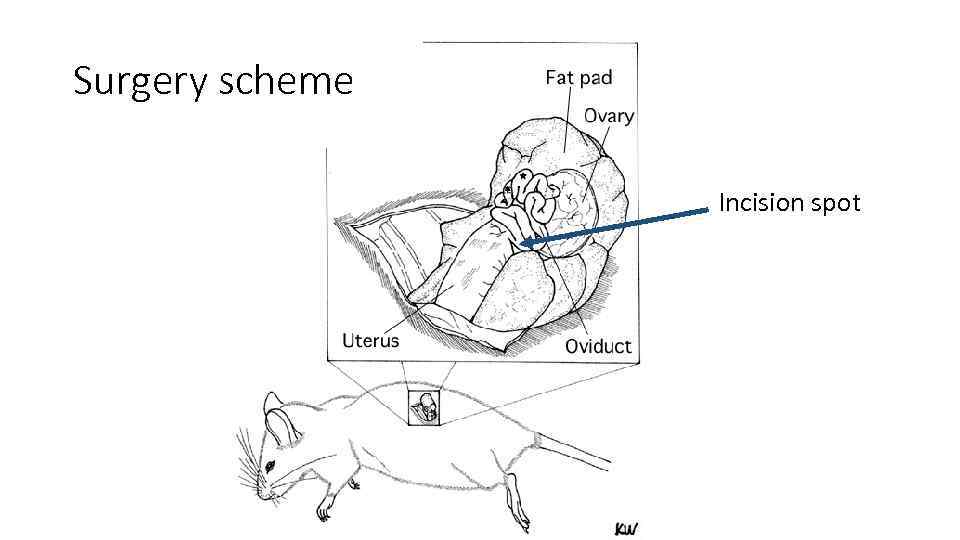 Surgery scheme Incision spot
Surgery scheme Incision spot
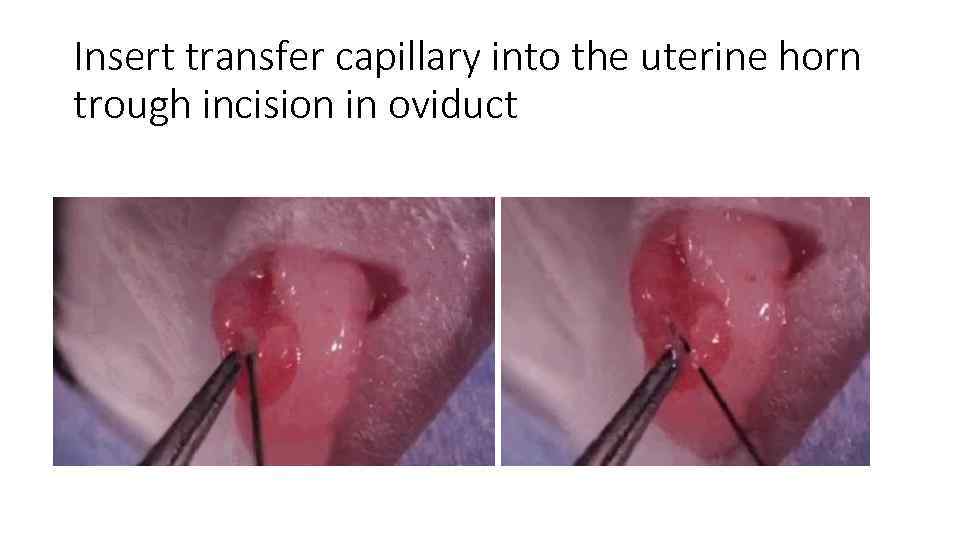 Insert transfer capillary into the uterine horn trough incision in oviduct
Insert transfer capillary into the uterine horn trough incision in oviduct
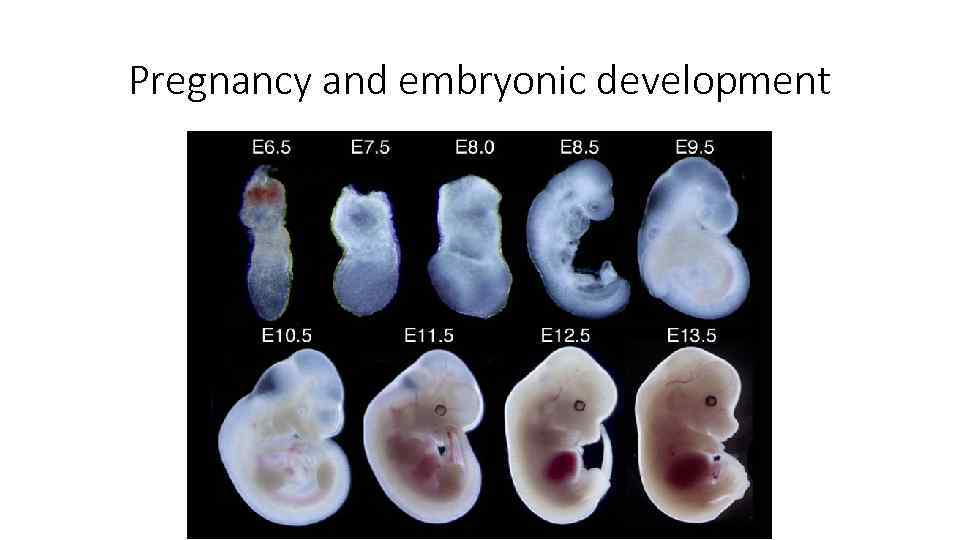 Pregnancy and embryonic development
Pregnancy and embryonic development
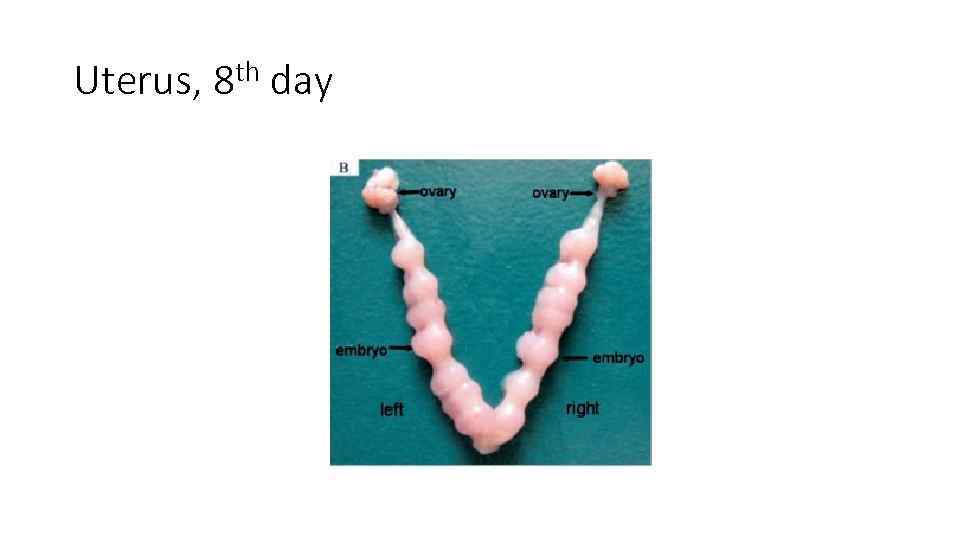 Uterus, 8 th day
Uterus, 8 th day
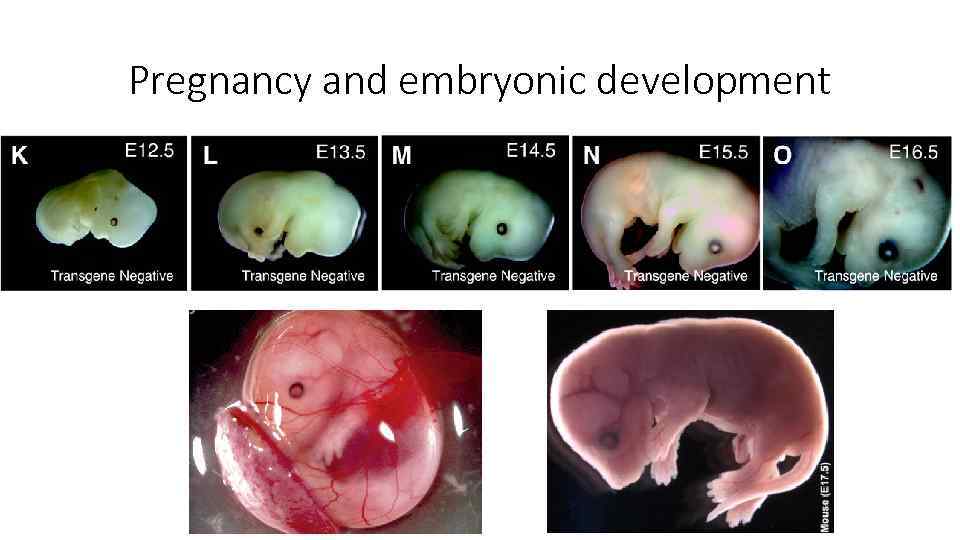 Pregnancy and embryonic development
Pregnancy and embryonic development
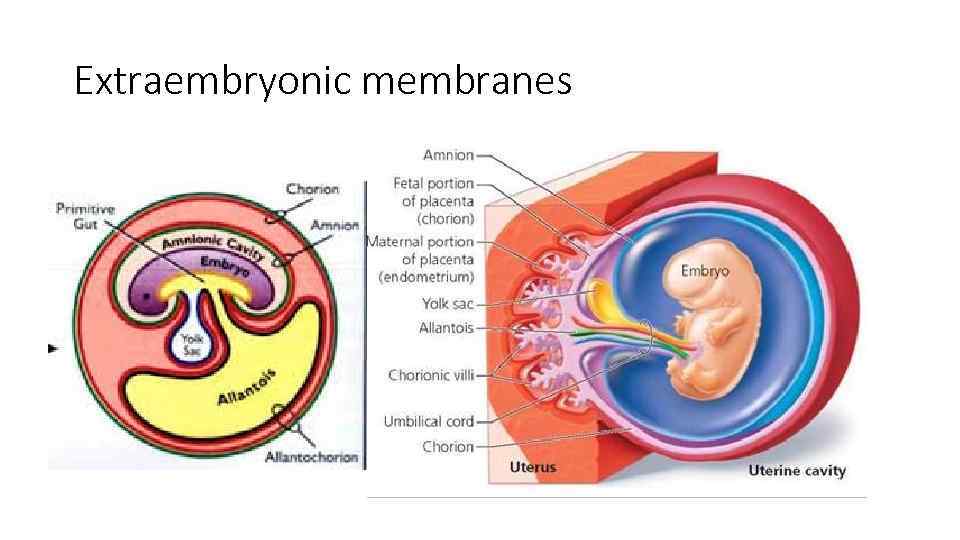 Extraembryonic membranes
Extraembryonic membranes
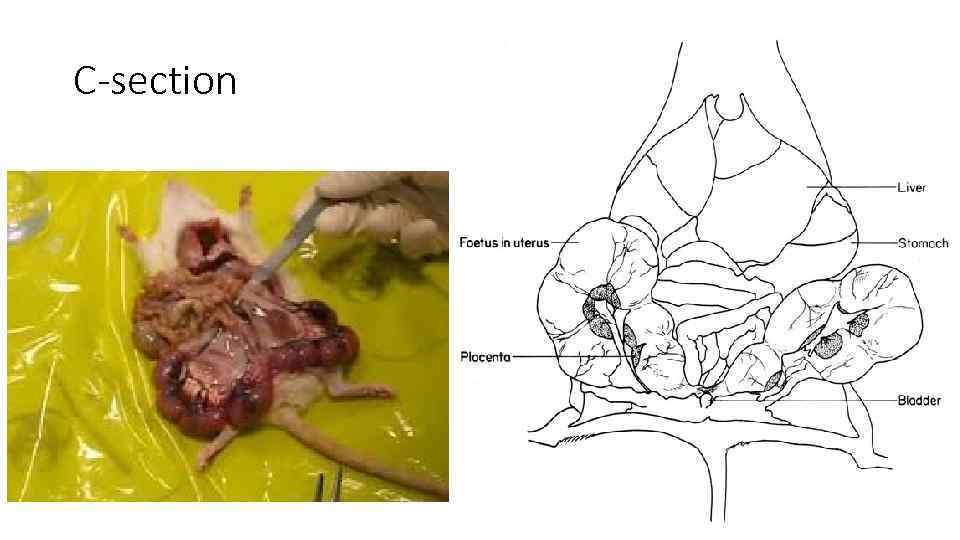 C-section
C-section
 Newborn mouse pups
Newborn mouse pups
 Feeding (~21 day)
Feeding (~21 day)


