fb70c77bb5c4212e2a009b4971e09552.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Angola Workshop on Oil Revenue Management Appropriate Fiscal Responses to the Rapid Accumulation of Oil Revenues By Francisco G. Carneiro May - 2006 The World Bank - Angola
Angola Workshop on Oil Revenue Management Appropriate Fiscal Responses to the Rapid Accumulation of Oil Revenues By Francisco G. Carneiro May - 2006 The World Bank - Angola
 Structure of the Presentation • Background and main challenges • Government actions to relaunch the economy • Administration of oil revenues • Appropriate fiscal responses • Summary of recommendations
Structure of the Presentation • Background and main challenges • Government actions to relaunch the economy • Administration of oil revenues • Appropriate fiscal responses • Summary of recommendations
 Background: The Most Challenging Issues Facing Angola in the Near Future
Background: The Most Challenging Issues Facing Angola in the Near Future
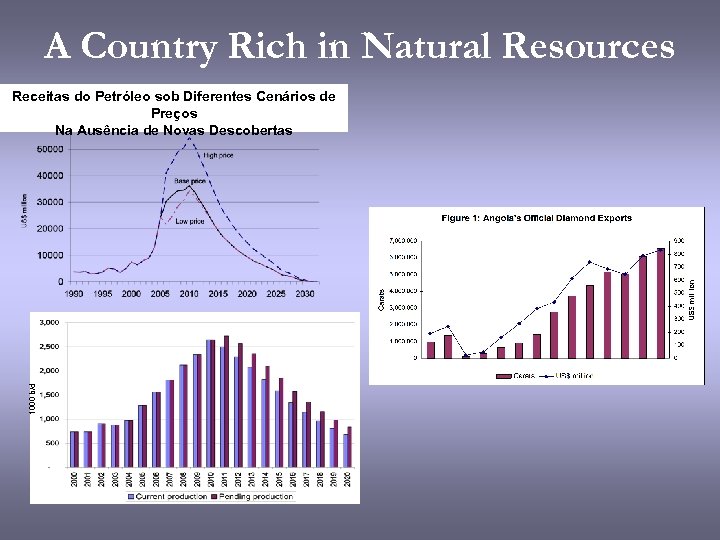 A Country Rich in Natural Resources 1000 b/d Receitas do Petróleo sob Diferentes Cenários de Preços Na Ausência de Novas Descobertas
A Country Rich in Natural Resources 1000 b/d Receitas do Petróleo sob Diferentes Cenários de Preços Na Ausência de Novas Descobertas
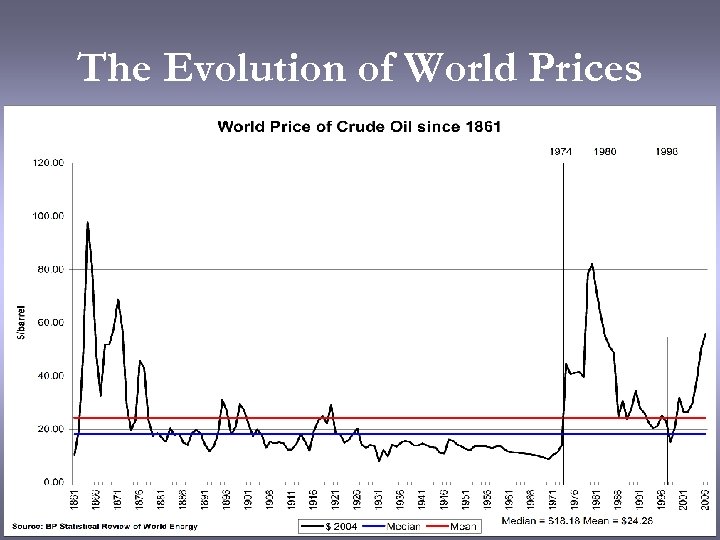 The Evolution of World Prices
The Evolution of World Prices
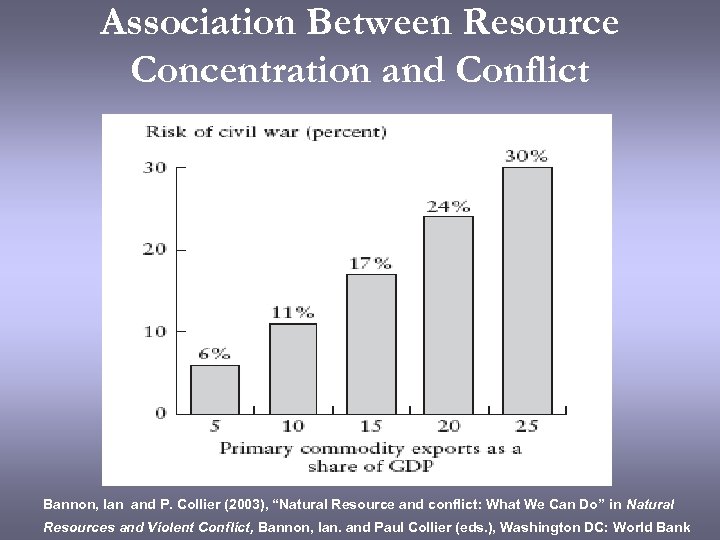 Association Between Resource Concentration and Conflict Bannon, Ian and P. Collier (2003), “Natural Resource and conflict: What We Can Do” in Natural Resources and Violent Conflict, Bannon, Ian. and Paul Collier (eds. ), Washington DC: World Bank
Association Between Resource Concentration and Conflict Bannon, Ian and P. Collier (2003), “Natural Resource and conflict: What We Can Do” in Natural Resources and Violent Conflict, Bannon, Ian. and Paul Collier (eds. ), Washington DC: World Bank
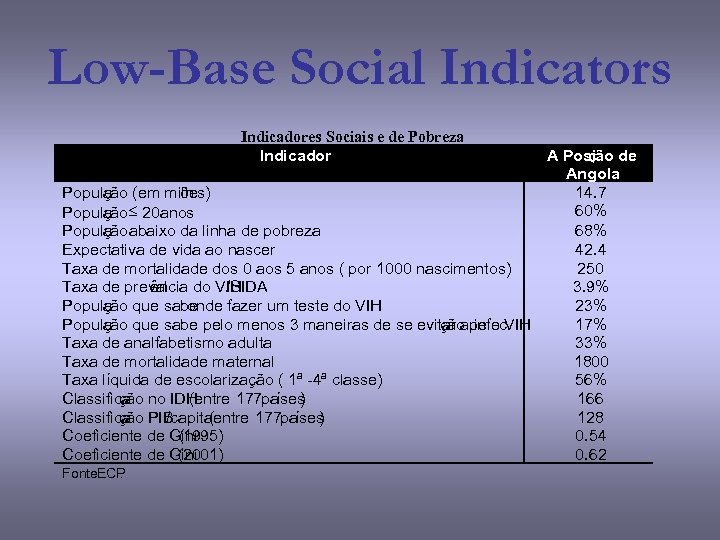 Low-Base Social Indicators Indicadores Sociais e de Pobreza Indicador Populaão (em milh ç ões) Populaão £ 20 anos ç Populaão abaixo da linha de pobreza ç Expectativa de vida ao nascer Taxa de mortalidade dos 0 aos 5 anos ( por 1000 nascimentos) Taxa de preval ência do VIH /SIDA Populaão que sabe ç onde fazer um teste do VIH Populaão que sabe pelo menos 3 maneiras de se evitar apelo VIH ç ção infec Taxa de analfabetismo adulta Taxa de mortalidade maternal Taxa líquida de escolarização ( 1ª -4ª classe) Classifica no IDH ção (entre 177 países ) Classifica PIB ção /capita (entre 177 países ) Coeficiente de Gini (1995) Coeficiente de Gini (2001) Fonte. ECP : . A Posi de ção Angola 14. 7 60% 68% 42. 4 250 3. 9% 23% 17% 33% 1800 56% 166 128 0. 54 0. 62
Low-Base Social Indicators Indicadores Sociais e de Pobreza Indicador Populaão (em milh ç ões) Populaão £ 20 anos ç Populaão abaixo da linha de pobreza ç Expectativa de vida ao nascer Taxa de mortalidade dos 0 aos 5 anos ( por 1000 nascimentos) Taxa de preval ência do VIH /SIDA Populaão que sabe ç onde fazer um teste do VIH Populaão que sabe pelo menos 3 maneiras de se evitar apelo VIH ç ção infec Taxa de analfabetismo adulta Taxa de mortalidade maternal Taxa líquida de escolarização ( 1ª -4ª classe) Classifica no IDH ção (entre 177 países ) Classifica PIB ção /capita (entre 177 países ) Coeficiente de Gini (1995) Coeficiente de Gini (2001) Fonte. ECP : . A Posi de ção Angola 14. 7 60% 68% 42. 4 250 3. 9% 23% 17% 33% 1800 56% 166 128 0. 54 0. 62
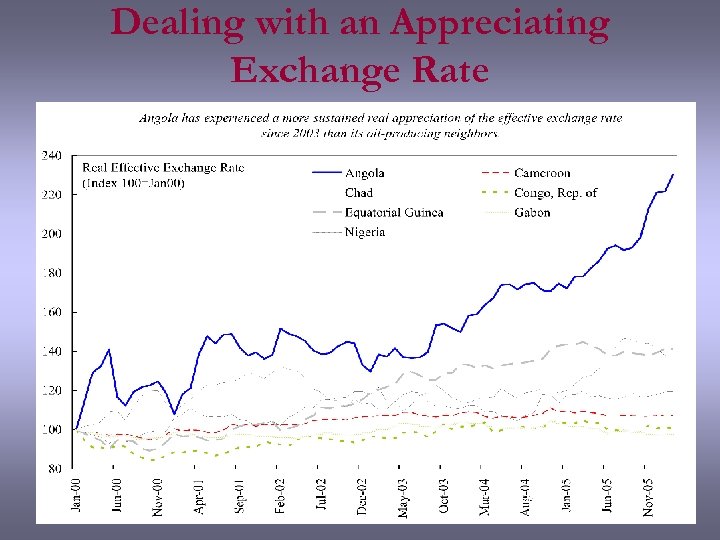 Dealing with an Appreciating Exchange Rate
Dealing with an Appreciating Exchange Rate
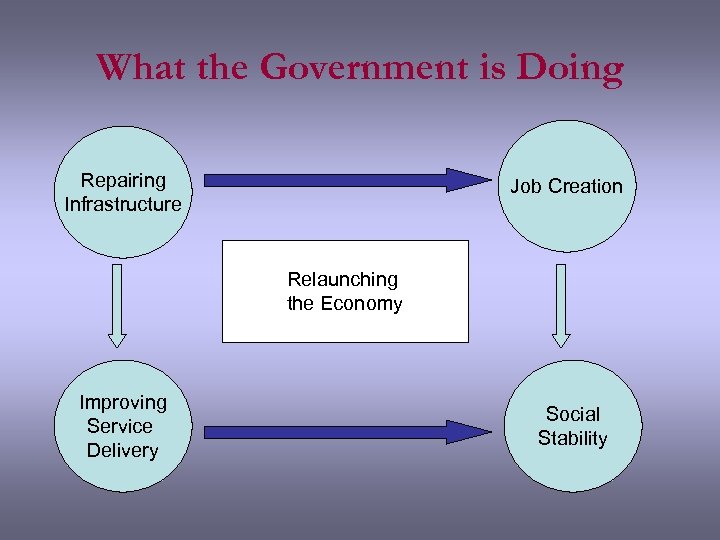 What the Government is Doing Repairing Infrastructure Job Creation Relaunching the Economy Improving Service Delivery Social Stability
What the Government is Doing Repairing Infrastructure Job Creation Relaunching the Economy Improving Service Delivery Social Stability
 Causal Factors • Technical Factors: – “Paradox of Plenty” – Volatility of revenues • Political Factors: – Diminished governance – Under-investment in capacity
Causal Factors • Technical Factors: – “Paradox of Plenty” – Volatility of revenues • Political Factors: – Diminished governance – Under-investment in capacity
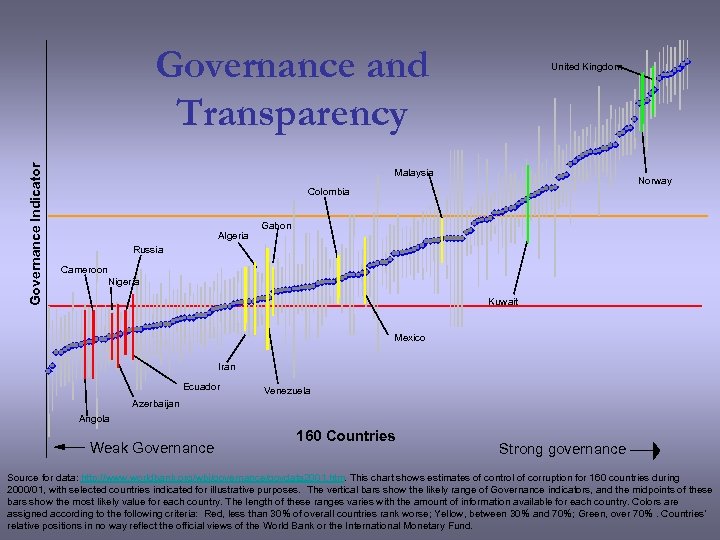 Governance Indicator Governance and Transparency United Kingdom Malaysia Norway Colombia Algeria Gabon Russia Cameroon Nigeria Kuwait Mexico Iran Ecuador Venezuela Azerbaijan Angola Weak Governance 160 Countries Strong governance Source for data: http: //www. worldbank. org/wbi/governance/govdata 2001. htm. This chart shows estimates of control of corruption for 160 countries during 2000/01, with selected countries indicated for illustrative purposes. The vertical bars show the likely range of Governance indicators, and the midpoints of these bars show the most likely value for each country. The length of these ranges varies with the amount of information available for each country. Colors are assigned according to the following criteria: Red, less than 30% of overall countries rank worse; Yellow, between 30% and 70%; Green, over 70%. Countries’ relative positions in no way reflect the official views of the World Bank or the International Monetary Fund.
Governance Indicator Governance and Transparency United Kingdom Malaysia Norway Colombia Algeria Gabon Russia Cameroon Nigeria Kuwait Mexico Iran Ecuador Venezuela Azerbaijan Angola Weak Governance 160 Countries Strong governance Source for data: http: //www. worldbank. org/wbi/governance/govdata 2001. htm. This chart shows estimates of control of corruption for 160 countries during 2000/01, with selected countries indicated for illustrative purposes. The vertical bars show the likely range of Governance indicators, and the midpoints of these bars show the most likely value for each country. The length of these ranges varies with the amount of information available for each country. Colors are assigned according to the following criteria: Red, less than 30% of overall countries rank worse; Yellow, between 30% and 70%; Green, over 70%. Countries’ relative positions in no way reflect the official views of the World Bank or the International Monetary Fund.
 Weak Institutional Capacity • National Tax Department (DNI) – USD $10 billion in revenues (2004) – > 30 companies – > 60 contracts – 6 professional staff
Weak Institutional Capacity • National Tax Department (DNI) – USD $10 billion in revenues (2004) – > 30 companies – > 60 contracts – 6 professional staff
 Sector Management Assessment • World class reserves with robust pre-tax economics • Up-to-date legal and contractual regime • Acceptable post-tax returns • Very significant production build-up, but with significant mid-term peaking….
Sector Management Assessment • World class reserves with robust pre-tax economics • Up-to-date legal and contractual regime • Acceptable post-tax returns • Very significant production build-up, but with significant mid-term peaking….
 The Way Forward The way forward requires: 1. Better capacity to forecast revenues 2. Appropriate fiscal policies 3. Some form of a stabilization fund (conta de reserva do Tesouro)
The Way Forward The way forward requires: 1. Better capacity to forecast revenues 2. Appropriate fiscal policies 3. Some form of a stabilization fund (conta de reserva do Tesouro)
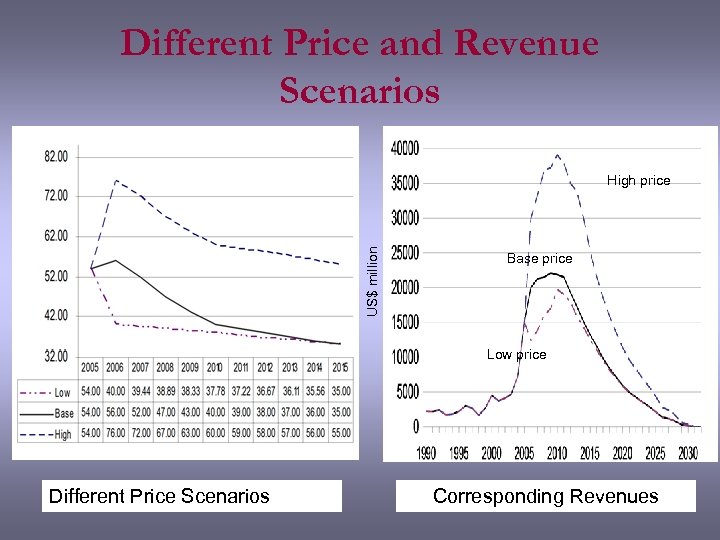 Different Price and Revenue Scenarios US$ million High price Base price Low price Different Price Scenarios Corresponding Revenues
Different Price and Revenue Scenarios US$ million High price Base price Low price Different Price Scenarios Corresponding Revenues
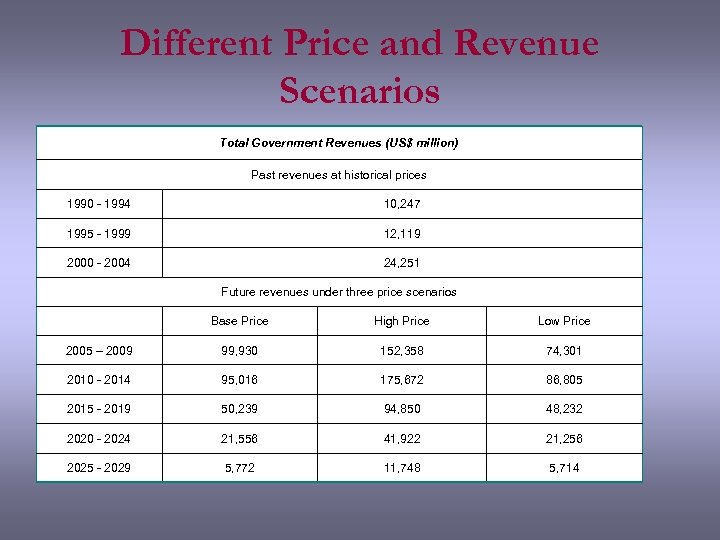 Different Price and Revenue Scenarios Total Government Revenues (US$ million) Past revenues at historical prices 1990 - 1994 10, 247 1995 - 1999 12, 119 2000 - 2004 24, 251 Future revenues under three price scenarios Base Price High Price Low Price 2005 – 2009 99, 930 152, 358 74, 301 2010 - 2014 95, 016 175, 672 86, 805 2015 - 2019 50, 239 94, 850 48, 232 2020 - 2024 21, 556 41, 922 21, 256 2025 - 2029 5, 772 11, 748 5, 714
Different Price and Revenue Scenarios Total Government Revenues (US$ million) Past revenues at historical prices 1990 - 1994 10, 247 1995 - 1999 12, 119 2000 - 2004 24, 251 Future revenues under three price scenarios Base Price High Price Low Price 2005 – 2009 99, 930 152, 358 74, 301 2010 - 2014 95, 016 175, 672 86, 805 2015 - 2019 50, 239 94, 850 48, 232 2020 - 2024 21, 556 41, 922 21, 256 2025 - 2029 5, 772 11, 748 5, 714
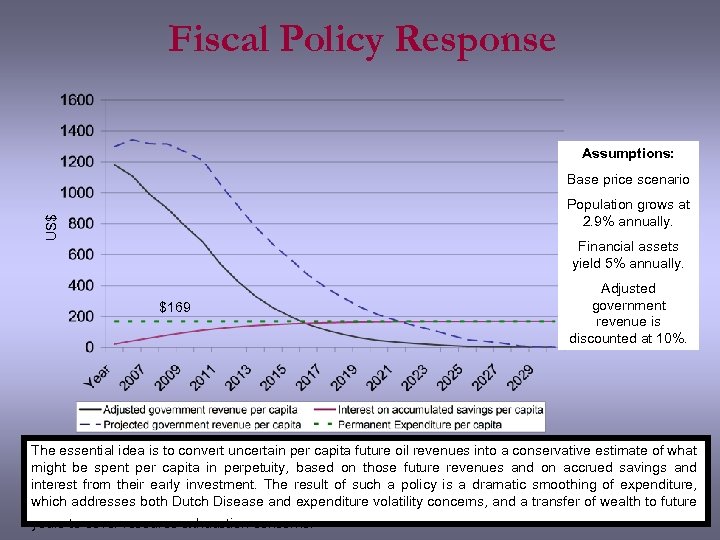 Fiscal Policy Response Assumptions: Base price scenario US$ Population grows at 2. 9% annually. Financial assets yield 5% annually. $169 Adjusted government revenue is discounted at 10%. The essential idea is to convert uncertain per capita future oil revenues into a conservative estimate of what might be spent per capita in perpetuity, based on those future revenues and on accrued savings and interest from their early investment. The result of such a policy is a dramatic smoothing of expenditure, which addresses both Dutch Disease and expenditure volatility concerns, and a transfer of wealth to future years to cover resource exhaustion concerns.
Fiscal Policy Response Assumptions: Base price scenario US$ Population grows at 2. 9% annually. Financial assets yield 5% annually. $169 Adjusted government revenue is discounted at 10%. The essential idea is to convert uncertain per capita future oil revenues into a conservative estimate of what might be spent per capita in perpetuity, based on those future revenues and on accrued savings and interest from their early investment. The result of such a policy is a dramatic smoothing of expenditure, which addresses both Dutch Disease and expenditure volatility concerns, and a transfer of wealth to future years to cover resource exhaustion concerns.
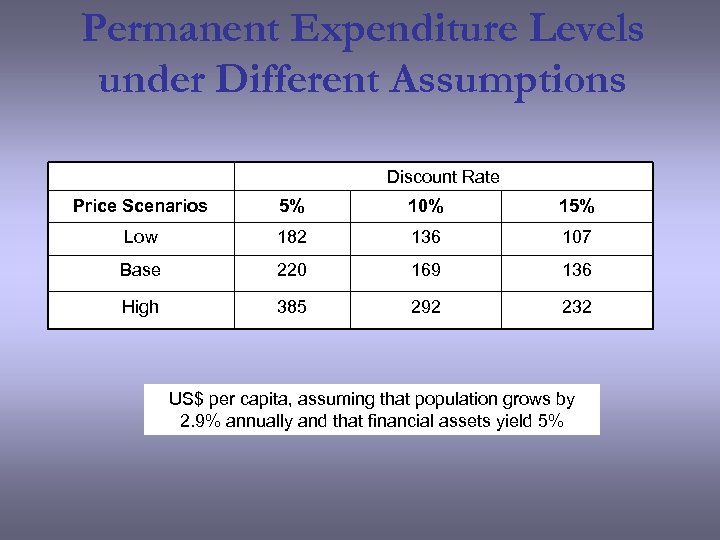 Permanent Expenditure Levels under Different Assumptions Discount Rate Price Scenarios 5% 10% 15% Low 182 136 107 Base 220 169 136 High 385 292 232 US$ per capita, assuming that population grows by 2. 9% annually and that financial assets yield 5%
Permanent Expenditure Levels under Different Assumptions Discount Rate Price Scenarios 5% 10% 15% Low 182 136 107 Base 220 169 136 High 385 292 232 US$ per capita, assuming that population grows by 2. 9% annually and that financial assets yield 5%
 Practical and Political Considerations • Need for agreement on assumptions • Institutional capacity requirements • Popular opposition current savings/deferred expenditures
Practical and Political Considerations • Need for agreement on assumptions • Institutional capacity requirements • Popular opposition current savings/deferred expenditures
 Economic Policy Objectives • Manage the impact of an appreciating real exchange rate • Agree on a strategy to absorb oil windfall with a view to move to an MTEF • Build international reserves/the oil reserve account as buffers against the foreign exchange/fiscal impact of revenue volatility • Promote rapid and bold improvements in procurement practices
Economic Policy Objectives • Manage the impact of an appreciating real exchange rate • Agree on a strategy to absorb oil windfall with a view to move to an MTEF • Build international reserves/the oil reserve account as buffers against the foreign exchange/fiscal impact of revenue volatility • Promote rapid and bold improvements in procurement practices
 Options to Deal with the Effects of Appreciation of the Currency Reduce Costs • Detailed analysis of the structure of production costs is essential • Use of oil revenues for productive investment (e. g. , infrastructure) can lower domestic costs for the entire economy • Do not try to fight against the appreciating trend
Options to Deal with the Effects of Appreciation of the Currency Reduce Costs • Detailed analysis of the structure of production costs is essential • Use of oil revenues for productive investment (e. g. , infrastructure) can lower domestic costs for the entire economy • Do not try to fight against the appreciating trend
 Institutional Options to Manage the Windfall
Institutional Options to Manage the Windfall
 Summary of the Recommendations Improve Governance • Adopt best practice policies to manage natural resources • Invest in institutional capacity • Improve transparency • Consolidate macroeconomic stability Strong political commitment to guarantee the success of the reforms
Summary of the Recommendations Improve Governance • Adopt best practice policies to manage natural resources • Invest in institutional capacity • Improve transparency • Consolidate macroeconomic stability Strong political commitment to guarantee the success of the reforms


