 Angina pectoris Ana Gašparović Mentor: A. Žmegač Horvat
Angina pectoris Ana Gašparović Mentor: A. Žmegač Horvat
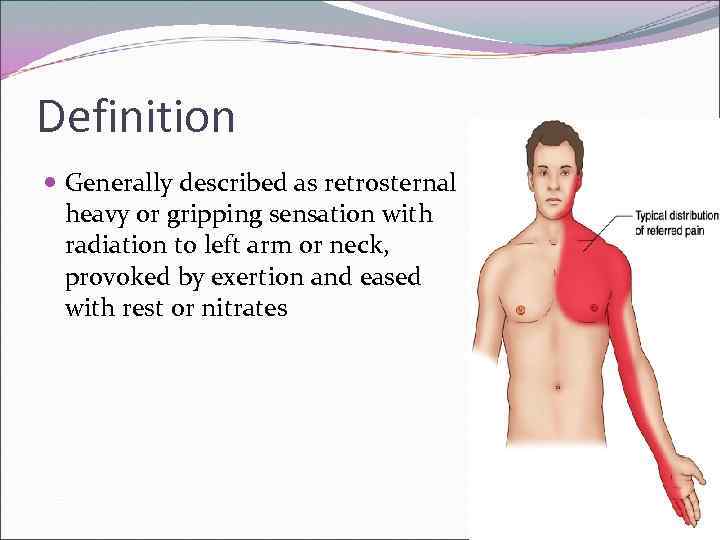 Definition Generally described as retrosternal heavy or gripping sensation with radiation to left arm or neck, provoked by exertion and eased with rest or nitrates
Definition Generally described as retrosternal heavy or gripping sensation with radiation to left arm or neck, provoked by exertion and eased with rest or nitrates
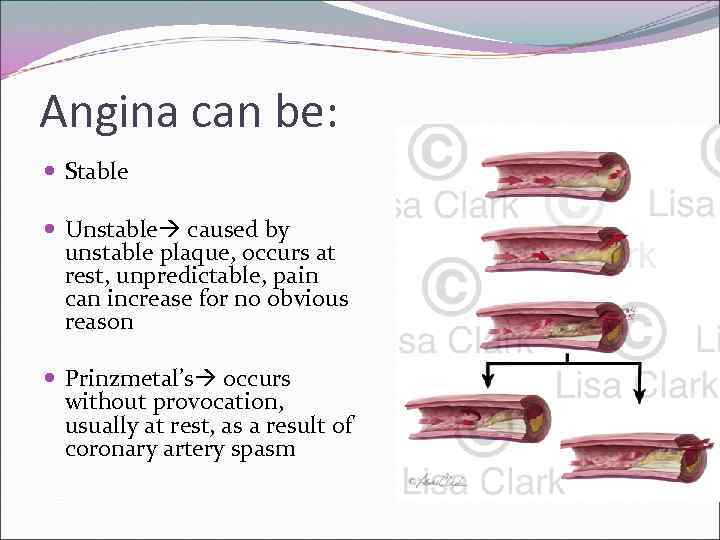 Angina can be: Stable Unstable caused by unstable plaque, occurs at rest, unpredictable, pain can increase for no obvious reason Prinzmetal’s occurs without provocation, usually at rest, as a result of coronary artery spasm
Angina can be: Stable Unstable caused by unstable plaque, occurs at rest, unpredictable, pain can increase for no obvious reason Prinzmetal’s occurs without provocation, usually at rest, as a result of coronary artery spasm
 Stable angina pectoris Provoked by physical exertion, especially in cold weather, after meals and commonly aggravated by anger or excitement The pain fades quickly with rest In some patients pain occurs predictably at a certain level of exertion
Stable angina pectoris Provoked by physical exertion, especially in cold weather, after meals and commonly aggravated by anger or excitement The pain fades quickly with rest In some patients pain occurs predictably at a certain level of exertion
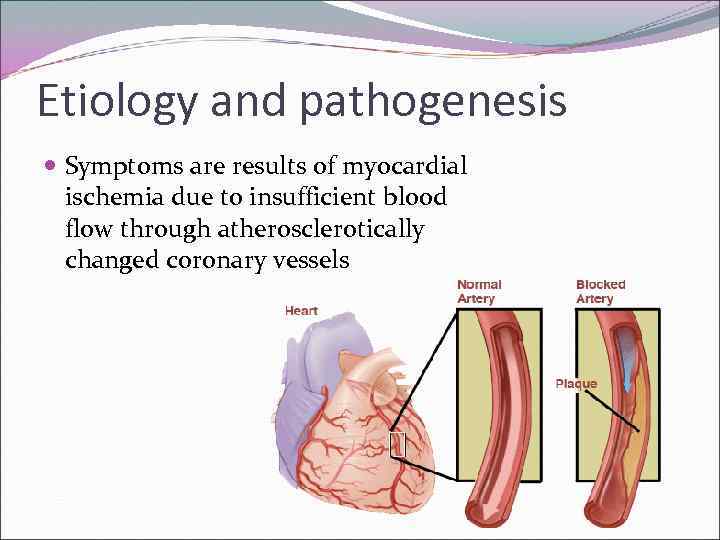 Etiology and pathogenesis Symptoms are results of myocardial ischemia due to insufficient blood flow through atherosclerotically changed coronary vessels
Etiology and pathogenesis Symptoms are results of myocardial ischemia due to insufficient blood flow through atherosclerotically changed coronary vessels
 Clinical symptoms Patient history is a˝golden standard˝ Retrosternal pain Dyspnea Nausea Arrhythmia Restlessness Levine sign Pain eased after taking nitrates
Clinical symptoms Patient history is a˝golden standard˝ Retrosternal pain Dyspnea Nausea Arrhythmia Restlessness Levine sign Pain eased after taking nitrates
 Physical examination Hypertension Obesity Hyperglycemia Hyperlipidemia Auscultation
Physical examination Hypertension Obesity Hyperglycemia Hyperlipidemia Auscultation
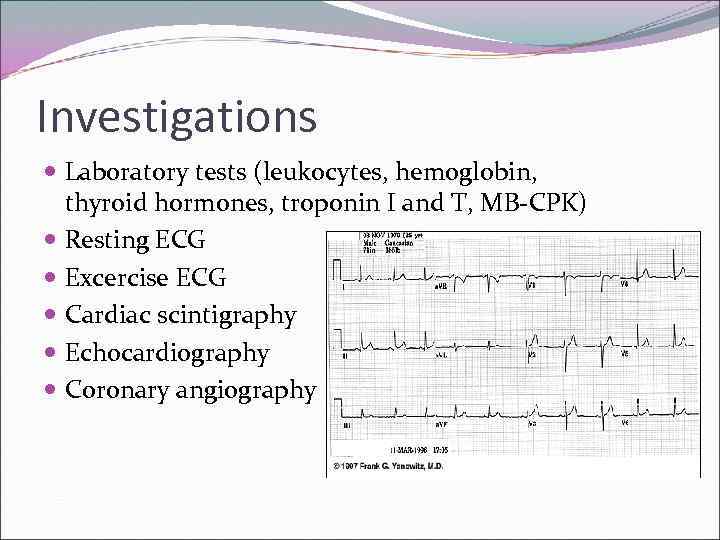 Investigations Laboratory tests (leukocytes, hemoglobin, thyroid hormones, troponin I and T, MB-CPK) Resting ECG Excercise ECG Cardiac scintigraphy Echocardiography Coronary angiography
Investigations Laboratory tests (leukocytes, hemoglobin, thyroid hormones, troponin I and T, MB-CPK) Resting ECG Excercise ECG Cardiac scintigraphy Echocardiography Coronary angiography
 Treatment Prognostic therapy: Aspirin, lipid-lowering therapy Symptomatic treatment: GTN, beta-blockers, long-acting nitrates, calcium-channel blockers, ACEI Percutaneous coronary intervention, coronary artery bypass grafting
Treatment Prognostic therapy: Aspirin, lipid-lowering therapy Symptomatic treatment: GTN, beta-blockers, long-acting nitrates, calcium-channel blockers, ACEI Percutaneous coronary intervention, coronary artery bypass grafting
 Literature : P. Kumar and M. Clark: Kumar & Clark’s Clinical Medicine Božidar Vrhovac and associates: Interna Medicina Damjanov, Jukić, Nola : Patologija
Literature : P. Kumar and M. Clark: Kumar & Clark’s Clinical Medicine Božidar Vrhovac and associates: Interna Medicina Damjanov, Jukić, Nola : Patologija