82264277e6c8a9bd68a052d52703292a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 Andrew Jackson: Who was he? Crazy guy who had A political mastermind Champion of the “Common Man”? No Idea what he Was Doing A Ruthless Tyrant who abused his power
Andrew Jackson: Who was he? Crazy guy who had A political mastermind Champion of the “Common Man”? No Idea what he Was Doing A Ruthless Tyrant who abused his power
 Awesome Andrew? A War Hero Boogey Man Checks under his bed for Jackson Defender of the People Loves America Has no Filter Says what He wants
Awesome Andrew? A War Hero Boogey Man Checks under his bed for Jackson Defender of the People Loves America Has no Filter Says what He wants

 JACKSON’S FIRST PRESIDENTIAL RUN THE ELECTION OF 1824
JACKSON’S FIRST PRESIDENTIAL RUN THE ELECTION OF 1824
 Voting Requirements n n n Jackson and his supporters created a new political party that became the Democratic Party. Adams and his supporters became the National Republicans. Many thought Adams was out of touch with the people. Jackson was a popular war hero—“a man of the people. ” In the 1820 s voting restrictions in many states—such as the requirement for property ownership—were being lifted, allowing poor people to become voters.
Voting Requirements n n n Jackson and his supporters created a new political party that became the Democratic Party. Adams and his supporters became the National Republicans. Many thought Adams was out of touch with the people. Jackson was a popular war hero—“a man of the people. ” In the 1820 s voting restrictions in many states—such as the requirement for property ownership—were being lifted, allowing poor people to become voters.
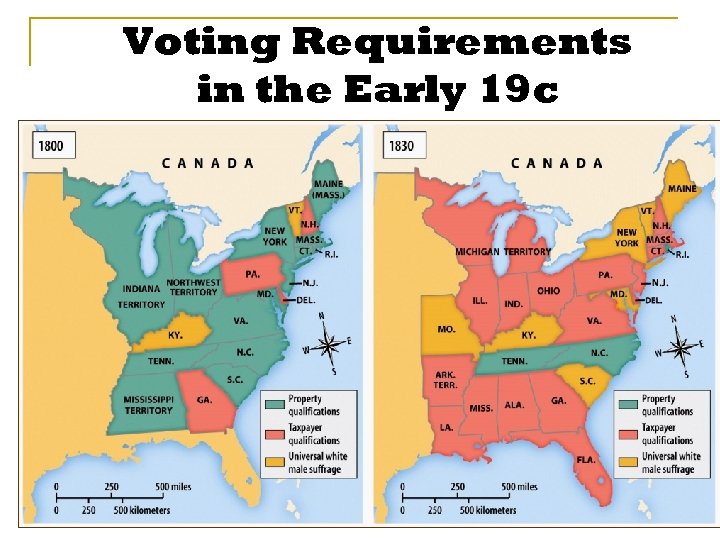 Voting Requirements in the Early 19 c
Voting Requirements in the Early 19 c
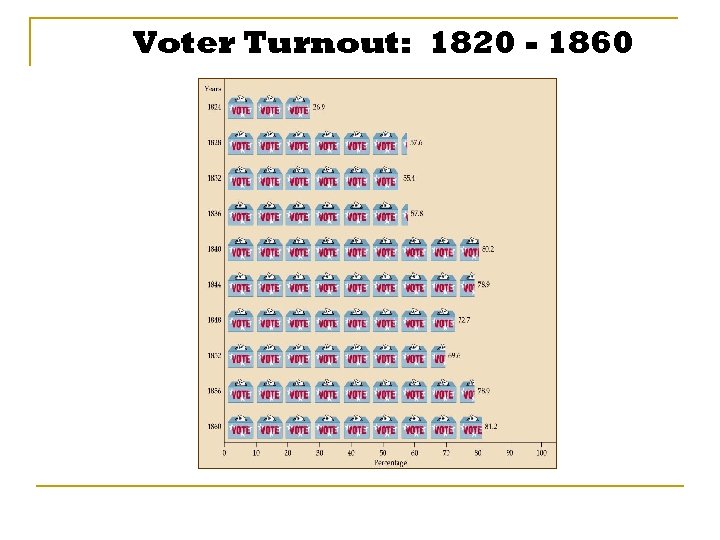 Voter Turnout: 1820 - 1860
Voter Turnout: 1820 - 1860
![Jackson’s Opponents in 1824 Henry Clay [KY] John Quincy Adams [MA] William H. Crawford Jackson’s Opponents in 1824 Henry Clay [KY] John Quincy Adams [MA] William H. Crawford](https://present5.com/presentation/82264277e6c8a9bd68a052d52703292a/image-8.jpg) Jackson’s Opponents in 1824 Henry Clay [KY] John Quincy Adams [MA] William H. Crawford [GA] John C. Calhoun [SC]
Jackson’s Opponents in 1824 Henry Clay [KY] John Quincy Adams [MA] William H. Crawford [GA] John C. Calhoun [SC]
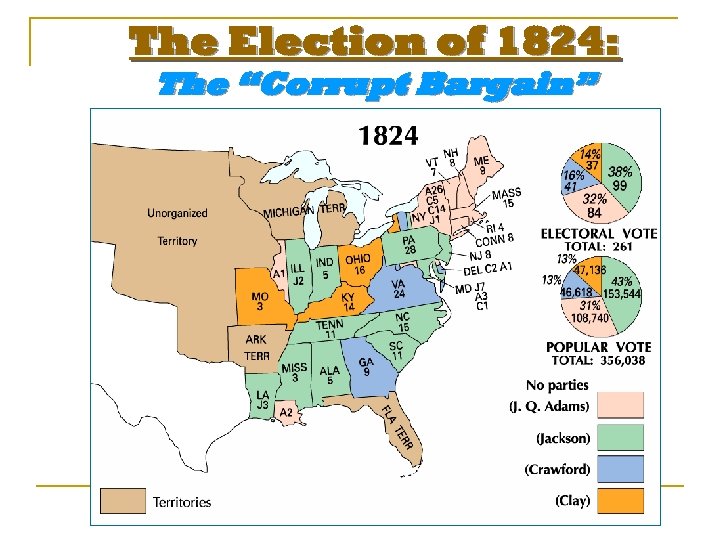 The Election of 1824: The “Corrupt Bargain”
The Election of 1824: The “Corrupt Bargain”
 Compare the Election of 1824 to today’s campaigns
Compare the Election of 1824 to today’s campaigns
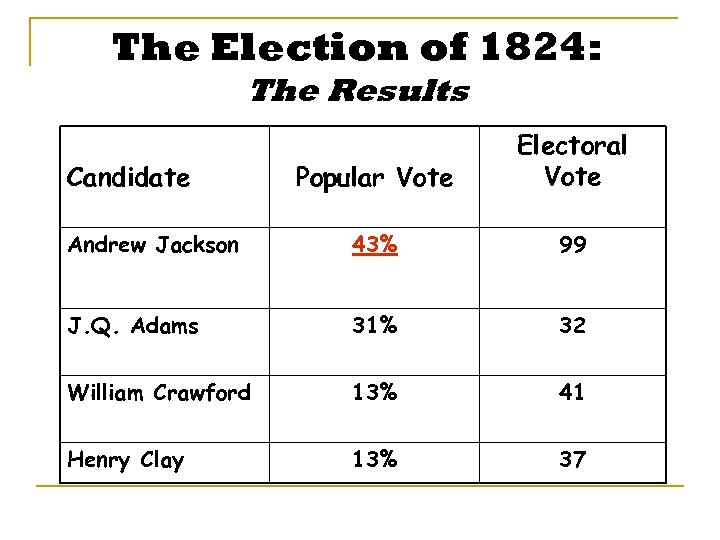 The Election of 1824: The Results Popular Vote Electoral Vote Andrew Jackson 43% 99 J. Q. Adams 31% 32 William Crawford 13% 41 Henry Clay 13% 37 Candidate
The Election of 1824: The Results Popular Vote Electoral Vote Andrew Jackson 43% 99 J. Q. Adams 31% 32 William Crawford 13% 41 Henry Clay 13% 37 Candidate
 The New Political Parties NATIONAL REPUBLICANS 1. JQA, Clay, Webster 2. Strong national govt. 3. Favored the BUS, tariffs, internal improvements, and industry 4. Best/privileged run the govt. DEMOCRATS 1. Jackson and Calhoun 2. Believed in state’s rights and federal restraint 3. Favored the liberty of the individual 4. Protected the common man.
The New Political Parties NATIONAL REPUBLICANS 1. JQA, Clay, Webster 2. Strong national govt. 3. Favored the BUS, tariffs, internal improvements, and industry 4. Best/privileged run the govt. DEMOCRATS 1. Jackson and Calhoun 2. Believed in state’s rights and federal restraint 3. Favored the liberty of the individual 4. Protected the common man.
 John Quincy Adams as President Successful as Sec. of State Not popular; failed to relate the common man. Supported protective tariff, BUS and internal improvements Minority president, last of the Federalists and connection with the Founding Fathers…. Citizens believed that Jackson was robbed – sabotaged JQA
John Quincy Adams as President Successful as Sec. of State Not popular; failed to relate the common man. Supported protective tariff, BUS and internal improvements Minority president, last of the Federalists and connection with the Founding Fathers…. Citizens believed that Jackson was robbed – sabotaged JQA
 The “King Mob” – Jackson’s Inauguration
The “King Mob” – Jackson’s Inauguration
 How should guests behave at the White House? Andrew Jackson won the presidency in 1828 as the candidate of the common man. Rough-hewn voters in the West and South, especially, thought of him as one of their own. So when the new president threw open the doors of the White House to anyone who wanted to attend his inaugural reception in 1829, thousands showed up to get a glimpse of their hero—and of the White House. An estimated 20, 000 well-wishers pushed and shoved their way into the White House staterooms. They trampled the carpets with muddy boots and climbed on the upholstered sofas and chairs. They broke china, smashed glassware, and bloodied more than a few noses. Finally, harried servants brought tubs of punch, ice cream, and lemonade outside, as people climbed through open windows to escape the riotous scene. The new president himself fled to the safety of a hotel. Jackson’s opponents denounced the day as “the reign of King Mob. ” One of Jackson’s colleagues, however, was more forgiving. He called it “a proud day for the people. ”
How should guests behave at the White House? Andrew Jackson won the presidency in 1828 as the candidate of the common man. Rough-hewn voters in the West and South, especially, thought of him as one of their own. So when the new president threw open the doors of the White House to anyone who wanted to attend his inaugural reception in 1829, thousands showed up to get a glimpse of their hero—and of the White House. An estimated 20, 000 well-wishers pushed and shoved their way into the White House staterooms. They trampled the carpets with muddy boots and climbed on the upholstered sofas and chairs. They broke china, smashed glassware, and bloodied more than a few noses. Finally, harried servants brought tubs of punch, ice cream, and lemonade outside, as people climbed through open windows to escape the riotous scene. The new president himself fled to the safety of a hotel. Jackson’s opponents denounced the day as “the reign of King Mob. ” One of Jackson’s colleagues, however, was more forgiving. He called it “a proud day for the people. ”
 Jackson’s Top Ten 10. Andrew Jackson was the first President from west of the Appalachian Mountains. 9. Andrew Jackson was the first Tennessean to serve in the U. S. House of Representatives. 8. Andrew Jackson was the first territorial Governor of Florida. 7. Andrew Jackson was the first person to serve as a U. S. Representative, Senator, and President. 6. Andrew Jackson exercised his veto power 12 times as President, more than all of his predecessors combined.
Jackson’s Top Ten 10. Andrew Jackson was the first President from west of the Appalachian Mountains. 9. Andrew Jackson was the first Tennessean to serve in the U. S. House of Representatives. 8. Andrew Jackson was the first territorial Governor of Florida. 7. Andrew Jackson was the first person to serve as a U. S. Representative, Senator, and President. 6. Andrew Jackson exercised his veto power 12 times as President, more than all of his predecessors combined.
 5. Andrew Jackson was the first President to articulate that as President he represented all the people and the will of the majority must govern. 4. Andrew Jackson helped found and was the first U. S. President to represent the Democratic Party. 3. Andrew Jackson is the only U. S. President to be censured by the U. S. Senate. The censure (official criticism) was cancelled in the last year of his presidency.
5. Andrew Jackson was the first President to articulate that as President he represented all the people and the will of the majority must govern. 4. Andrew Jackson helped found and was the first U. S. President to represent the Democratic Party. 3. Andrew Jackson is the only U. S. President to be censured by the U. S. Senate. The censure (official criticism) was cancelled in the last year of his presidency.
 2. The first assassination attempt on a sitting U. S. President occurred on January 30, 1835, when Robert Lawrence failed to slay Andrew Jackson. 1. Andrew Jackson was the only President in American History to pay off the national debt and leave office with the country in the black.
2. The first assassination attempt on a sitting U. S. President occurred on January 30, 1835, when Robert Lawrence failed to slay Andrew Jackson. 1. Andrew Jackson was the only President in American History to pay off the national debt and leave office with the country in the black.
 Jackson’s Beliefs n n Only hold power for a brief period of time Spoils System q “To the victor belongs the spoils of the enemy” “Kitchen Cabinet” – made up of his friends Believed that the “Common Man” was capable of great things
Jackson’s Beliefs n n Only hold power for a brief period of time Spoils System q “To the victor belongs the spoils of the enemy” “Kitchen Cabinet” – made up of his friends Believed that the “Common Man” was capable of great things
 Jackson’s Goals as President: CRAZY? !? ! Or good ideas? n n Government for the “Common Man” Abolish the Electoral College Relocate Native Americans Get rid of the National Debt q n n “Live within your means” Get rid of the National Bank Do away with Paper Money
Jackson’s Goals as President: CRAZY? !? ! Or good ideas? n n Government for the “Common Man” Abolish the Electoral College Relocate Native Americans Get rid of the National Debt q n n “Live within your means” Get rid of the National Bank Do away with Paper Money
 Major Issues of Jackson’s Presidency n n “Tariff of Abominations” Nullification Crisis – South Carolina Fighting the Bank of the United States Indian Removal
Major Issues of Jackson’s Presidency n n “Tariff of Abominations” Nullification Crisis – South Carolina Fighting the Bank of the United States Indian Removal
 Tariff of Abominations n n n 1824 Tariff Increased q Protected North – Hurt South q North is getting rich off of us q Discriminated against the South q Violated State’s Rights Calhoun (VP) says that states can nullify laws and secede q Hit too close to home Jackson: “OUR FEDERAL UNION – IT MUST BE PRESERVED”
Tariff of Abominations n n n 1824 Tariff Increased q Protected North – Hurt South q North is getting rich off of us q Discriminated against the South q Violated State’s Rights Calhoun (VP) says that states can nullify laws and secede q Hit too close to home Jackson: “OUR FEDERAL UNION – IT MUST BE PRESERVED”
 What does the Tariff do? Protects the Northern Manufacturing Destiny lay in cotton
What does the Tariff do? Protects the Northern Manufacturing Destiny lay in cotton
 1832 Tariff Conflict 3 1832 --> new tariff 3 South Carolina’s reaction 3 3 Threatens to secede Jackson’s response 3 3 3 “I will hang Calhoun” Force Bill – Can attack S. Carolina Clay’s “Compromise” Tariff 3 Tariff will be lowered over 10 years
1832 Tariff Conflict 3 1832 --> new tariff 3 South Carolina’s reaction 3 3 Threatens to secede Jackson’s response 3 3 3 “I will hang Calhoun” Force Bill – Can attack S. Carolina Clay’s “Compromise” Tariff 3 Tariff will be lowered over 10 years
 Hamilton, your bank stinks!!!
Hamilton, your bank stinks!!!
 Jackson vs. The Bank
Jackson vs. The Bank
 Why hate the Bank n n Unconstitutional Too much power q q n Controls the Gold and Silver q n Small group of Eastern Bankers Doesn’t protect “Common Man” Decides how much money is worth Corrupt q q q Make up Interest Rates Choose banks to lend to (or not) Print as much money as they want.
Why hate the Bank n n Unconstitutional Too much power q q n Controls the Gold and Silver q n Small group of Eastern Bankers Doesn’t protect “Common Man” Decides how much money is worth Corrupt q q q Make up Interest Rates Choose banks to lend to (or not) Print as much money as they want.
![Clay/Biddle vs. Jackson VS Nicholas Biddle [Corrupt Head of the Bank] Henry Clay [Jackson’s Clay/Biddle vs. Jackson VS Nicholas Biddle [Corrupt Head of the Bank] Henry Clay [Jackson’s](https://present5.com/presentation/82264277e6c8a9bd68a052d52703292a/image-28.jpg) Clay/Biddle vs. Jackson VS Nicholas Biddle [Corrupt Head of the Bank] Henry Clay [Jackson’s Rival] President Jackson
Clay/Biddle vs. Jackson VS Nicholas Biddle [Corrupt Head of the Bank] Henry Clay [Jackson’s Rival] President Jackson
 Clay and Biddle’s Trap n Petition to renew the BUS early q n Dare Jackson to Veto it q n Right before Election of 1832 Believed that the Bank was too important Clay ran against him in 1832
Clay and Biddle’s Trap n Petition to renew the BUS early q n Dare Jackson to Veto it q n Right before Election of 1832 Believed that the Bank was too important Clay ran against him in 1832
 The Bank & the 1832 Election § Jackson refused to sign the bill to re-charter. Ø The Bank is trying to destroy me, but I will destroy it! § Jackson drops Calhoun and runs with Martin Van Buren.
The Bank & the 1832 Election § Jackson refused to sign the bill to re-charter. Ø The Bank is trying to destroy me, but I will destroy it! § Jackson drops Calhoun and runs with Martin Van Buren.
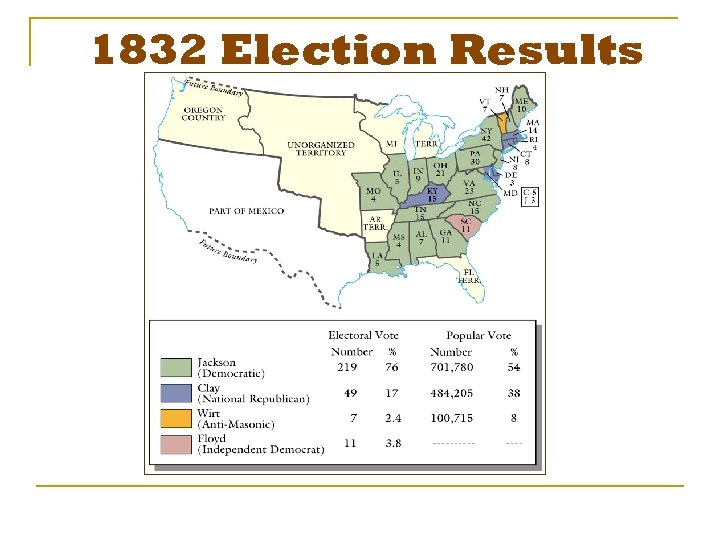 1832 Election Results
1832 Election Results
 Biddle’s Response n n Controls the Money = Unstoppable Tries to get the people to turn against Jackson q q q n Raises Interest Rates Doesn’t give out loans Foreclosed on Small Businesses Jackson’s Response: “Go to Biddle – HE IS THE MAN THAT CONTROLS THE MONEY”
Biddle’s Response n n Controls the Money = Unstoppable Tries to get the people to turn against Jackson q q q n Raises Interest Rates Doesn’t give out loans Foreclosed on Small Businesses Jackson’s Response: “Go to Biddle – HE IS THE MAN THAT CONTROLS THE MONEY”
 Killing the Bank 3 Pet Banks 3 Moves Gold and Silver into State Banks 3 Kills the BUS by taking away its money (power) 3 1832 Jackson vetoed the extension of the 2 nd National Bank of the United States. 3 1836 the charter expired. 3 1841 the bank went bankrupt!
Killing the Bank 3 Pet Banks 3 Moves Gold and Silver into State Banks 3 Kills the BUS by taking away its money (power) 3 1832 Jackson vetoed the extension of the 2 nd National Bank of the United States. 3 1836 the charter expired. 3 1841 the bank went bankrupt!
 Jackson vs. The Native Americans
Jackson vs. The Native Americans
 5 Tribes n n n Five major Native American groups lived in the southeastern United States q Cherokee, Choctaw, Chickasaw, Seminole, and Creek. White Americans called them the “five civilized tribes” because many of them had adopted aspects of European and American culture. q Many white Americans viewed them as inferior. Farmland was becoming scarce in the East, and white settlers coveted the Indians’ lands.
5 Tribes n n n Five major Native American groups lived in the southeastern United States q Cherokee, Choctaw, Chickasaw, Seminole, and Creek. White Americans called them the “five civilized tribes” because many of them had adopted aspects of European and American culture. q Many white Americans viewed them as inferior. Farmland was becoming scarce in the East, and white settlers coveted the Indians’ lands.

 Indian Removal Act (1830) n n n Called for the relocation of the five nations to an area west of the Mississippi River called Indian Territory, now present-day Oklahoma. The U. S. Army marched the Choctaw, the Creek, and the Chickasaw west, hundreds of miles, to Indian Territory. Many died on the long trek due to exposure, malnutrition, and disease.
Indian Removal Act (1830) n n n Called for the relocation of the five nations to an area west of the Mississippi River called Indian Territory, now present-day Oklahoma. The U. S. Army marched the Choctaw, the Creek, and the Chickasaw west, hundreds of miles, to Indian Territory. Many died on the long trek due to exposure, malnutrition, and disease.
 Indian Removal 3 Why did Jackson do this? 3 1. New Land 3 2. Safer for Settlers 3 3. Cannot Exist with N. A’s 3 1830 Indian Removal Act – Nullifies Treaties 3 Cherokee Nation v. GA (1831), Worcester v. GA (1832) 3 3 Johan Marshall Sides with Native Americans Jackson: 3 John Marshall has made his decision, now let him enforce it!
Indian Removal 3 Why did Jackson do this? 3 1. New Land 3 2. Safer for Settlers 3 3. Cannot Exist with N. A’s 3 1830 Indian Removal Act – Nullifies Treaties 3 Cherokee Nation v. GA (1831), Worcester v. GA (1832) 3 3 Johan Marshall Sides with Native Americans Jackson: 3 John Marshall has made his decision, now let him enforce it!
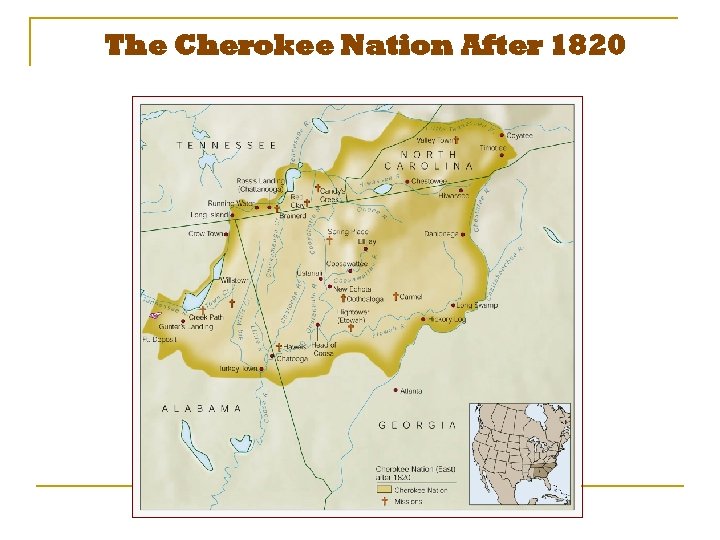 The Cherokee Nation After 1820
The Cherokee Nation After 1820
 Cherokee Fight Back n n n The Cherokee fought their removal in the American court system. They sued the federal government, claiming that they had the right to be respected as a foreign country. The Supreme Court in 1831 ruled against the Cherokee.
Cherokee Fight Back n n n The Cherokee fought their removal in the American court system. They sued the federal government, claiming that they had the right to be respected as a foreign country. The Supreme Court in 1831 ruled against the Cherokee.
 Worcester v. Georgia (1832) n n The state of Georgia, carrying out the Indian Removal Act, ordered Samuel Austin Worcester, a white man and a friend to the Cherokee, to leave Cherokee land. Worcester brought suit on behalf of himself and the Cherokee. The Supreme Court ruled against Georgia, denying it the right to take Cherokee lands. To get around the Court’s ruling, government officials signed a treaty with Cherokee leaders who favored relocation.
Worcester v. Georgia (1832) n n The state of Georgia, carrying out the Indian Removal Act, ordered Samuel Austin Worcester, a white man and a friend to the Cherokee, to leave Cherokee land. Worcester brought suit on behalf of himself and the Cherokee. The Supreme Court ruled against Georgia, denying it the right to take Cherokee lands. To get around the Court’s ruling, government officials signed a treaty with Cherokee leaders who favored relocation.
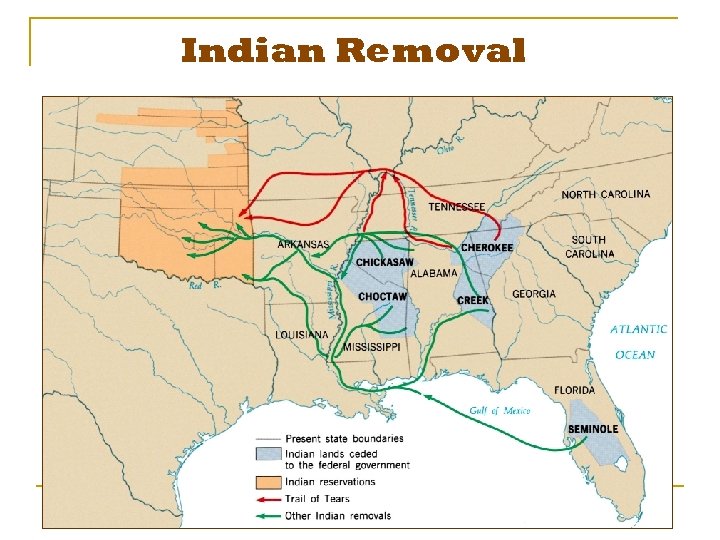 Indian Removal
Indian Removal
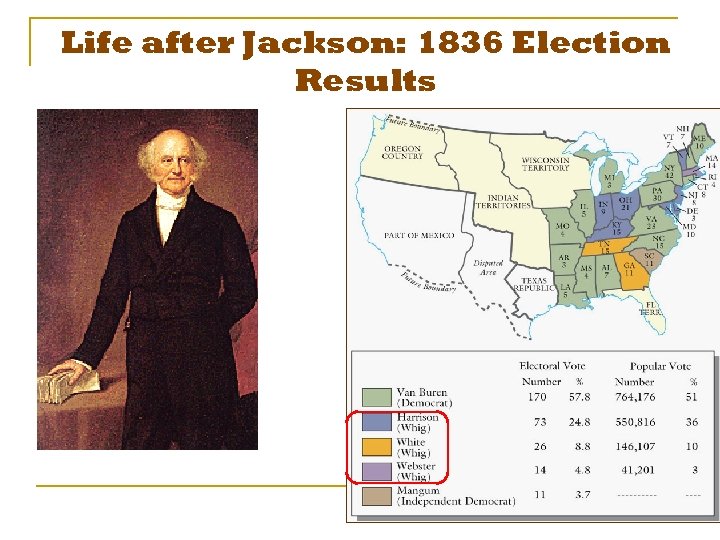 Life after Jackson: 1836 Election Results
Life after Jackson: 1836 Election Results
 “Soft” (paper) $ 3 Allows Banks to issues notes easily 3 Supported rapid economic growth & speculation. “Hard” (specie) $ VS. 3 Felt that coin was the only safe currency. 3 Suspicious of expansion & speculation.
“Soft” (paper) $ 3 Allows Banks to issues notes easily 3 Supported rapid economic growth & speculation. “Hard” (specie) $ VS. 3 Felt that coin was the only safe currency. 3 Suspicious of expansion & speculation.
 The Panic of 1837 – Jackson’s Fault? $ “Wildcat” Bank issues too much money $ Banknotes loose their value. $ Only pay for land with Hard money (Gold and Silver) $ Credit not available. $ Bank Rushes to trade in paper $ Banks/Businesses began to fail. $ Unemployment rose.
The Panic of 1837 – Jackson’s Fault? $ “Wildcat” Bank issues too much money $ Banknotes loose their value. $ Only pay for land with Hard money (Gold and Silver) $ Credit not available. $ Bank Rushes to trade in paper $ Banks/Businesses began to fail. $ Unemployment rose.
 The Panic of 1837 Hits Everyone!
The Panic of 1837 Hits Everyone!
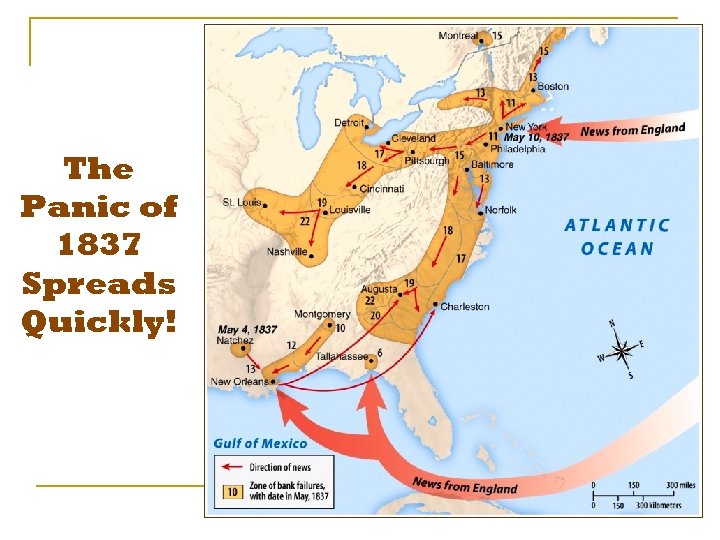 The Panic of 1837 Spreads Quickly!
The Panic of 1837 Spreads Quickly!
 Lasting Impact of Jackson n Is Jacksonian Democracy Dead today? Do people control politics today? Is this still a government by the people for the people?
Lasting Impact of Jackson n Is Jacksonian Democracy Dead today? Do people control politics today? Is this still a government by the people for the people?


